TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE paste
Triamcinolone Acetonide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Triamcinolone Acetonide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Triamcinolone Acetonide Dental Paste USP, 0.1%, contains the corticosteroid triamcinolone acetonide in an adhesive vehicle suitable for application to oral tissues. Triamcinolone acetonide is designated chemically as 9-fluoro-11β, 16α, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with acetone. The structural formula of triamcinolone acetonide is as follows:
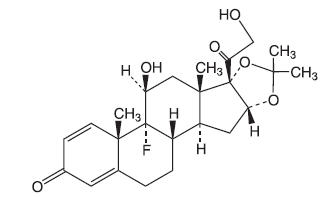
C24H31FO6 MW 434.50
Each gram of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste contains 1 mg triamcinolone acetonide in an emollient dental paste containing carboxymethylcellulose sodium, gelatin, and pectin in a plasticized hydrocarbon gel (a polyethylene and mineral oil gel base).
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Like other topical corticosteroids, triamcinolone acetonide has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of the topical steroids, in general, is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor, arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Pharmacokinetics
The extent of absorption through the oral mucosa is determined by multiple factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the mucosal barrier, the duration of therapy, and the presence of inflammation and/or other disease processes. Once absorbed through the mucous membranes, the disposition of corticosteroids is similar to that of systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to the plasma proteins in varying degrees. Corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys; some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Triamcinolone acetonide dental paste may cause local adverse reactions. If irritation develops, triamcinolone acetonide dental paste should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact sensitization with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant mucosal infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
If significant regeneration or repair of oral tissues has not occurred in seven days, additional investigation into the etiology of the oral lesion is advised.
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, glucosuria, and other adverse effects known to occur with parenterally-administered steroid preparations; therefore, it may be advisable to periodically evaluate patients on prolonged therapy with corticosteroid-containing dental pastes for evidence of HPA axis suppression (see PRECAUTIONS, Laboratory Tests). If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug or to reduce the frequency of application. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of therapy.
Information for the Patient
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician or dentist. It is for oral use only; it is not intended for ophthalmic or dermatological use.
- Patients should be advised not to use this medication for any disorder other than for which it was prescribed.
- Patients should report any signs of adverse reactions.
- As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, contact the physician or dentist.
Laboratory Tests
A urinary free cortisol test and ACTH stimulation test may be helpful in evaluating HPA axis suppression.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been performed to evaluate triamcinolone acetonide for potential to induce carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy Category C
Teratogenic effects
Triamcinolone acetonide has been shown to induce teratogenic effects in several species. In mice and rabbits, triamcinolone acetonide induced an increased incidence of cleft palate at dosages of approximately 120 µg/kg/day and 24 µg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 12 times and 10 times the amount in a typical daily human dose of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste when compared following normalization of the data on the basis of body surface area estimates, respectively). In monkeys, triamcinolone acetonide induced cranial skeletal malformations at the lowest dosage studied (500 µg/kg/day), which was approximately 200 times the amount in a typical daily human dose of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste when compared following normalization of the data on the basis of body surface area estimates. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. However, a retrospective analysis of birth defects among children born to mothers that used drugs of the same class as triamcinolone acetonide dental paste (corticosteroids) during pregnancy found an approximately 3 times increased incidence of cleft palate. Triamcinolone acetonide dental paste should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether oral application of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Caution should be exercised when corticosteroid-containing dental pastes are prescribed for a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste in children is unknown. Pediatric patients may demonstrate greater susceptibility to topical corticosteroid-induced HPA axis suppression and Cushing's Syndrome than mature patients because of a larger skin surface area to body weight ratio. Administration of corticosteroid-containing dental pastes to children should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of triamcinolone acetonide dental paste did not include sufficient numbers of subjects age 65 and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following local adverse reactions may occur with corticosteroid-containing dental pastes: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, blistering or peeling not present prior to therapy, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the oral mucosa, secondary infection, and atrophy of the oral mucosa.
Also, see PRECAUTIONS for potential effects of systemic absorption.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Press a small dab (about 1/4 inch) to the lesion until a thin film develops. A larger quantity may be required for coverage of some lesions. For optimal results use only enough to coat the lesion with a thin film. Do not rub in. Attempting to spread this preparation may result in granular, gritty sensation and cause it to crumble. After application, however, a smooth, slippery film develops.
The preparation should be applied at bedtime to permit steroid contact with the lesion throughout the night. Depending on the severity of symptoms, it may be necessary to apply the preparation two or three times a day, preferably after meals. If significant repair or regeneration has not occurred in seven days, further investigation is advisable.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Triamcinolone Acetonide Dental Paste USP, 0.1% is supplied in tubes containing 5 g of dental paste (NDC 51672–1267-5) and 7.5 g of dental paste (NDC: 51672-1267-8).
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 7.5 g Tube Carton
NDC: 51672-1267-8
7.5 g
Triamcinolone Acetonide
Dental Paste USP, 0.1%FOR TOPICAL USE IN ADJUNCTIVE TREATMENT OF ORAL LESIONS
Rx only
TARO
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE
triamcinolone acetonide pasteProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51672-1267 Route of Administration DENTAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Triamcinolone Acetonide (UNII: F446C597KA) (Triamcinolone Acetonide - UNII:F446C597KA) Triamcinolone Acetonide 1 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) pectin (UNII: 89NA02M4RX) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: K679OBS311) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) mineral oil (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (light beige) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51672-1267-5 1 in 1 CARTON 10/01/1986 1 5 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51672-1267-8 1 in 1 CARTON 10/01/1986 2 7.5 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA070730 10/01/1986 Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceuticals Inc. 206263295 MANUFACTURE(51672-1267)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.