Mupirocin by BIOMES PHARMACEUTICALS LLC MUPIROCIN cream
Mupirocin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Mupirocin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by BIOMES PHARMACEUTICALS LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MUPIROCIN Cream safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MUPIROCIN Cream.
MUPIROCIN cream USP, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1987INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Mupirocin cream is an RNA synthetase inhibitor antibacterial indicated for the treatment of secondarily infected traumatic skin lesions (up to 10 cm in length or 100 cm2 in area) due to susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Cream: 2.15% w/w mupirocin calcium USP (equivalent to 2% mupirocin free acid) in 15-gram and 30-gram tubes. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity to mupirocin or any of the excipients of mupirocin cream. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, urticaria, angioedema, and generalized rash have been reported in patients treated with formulations of mupirocin, including mupirocin cream. (5.1)
- Eye Irritation: Avoid contact with eyes. (5.2)
- Local Irritation: Discontinue in the event of sensitization or severe local irritation. (5.3)
- Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): If diarrhea occurs, evaluate patients for CDAD. (5.4)
- Potential for Microbial Overgrowth: Prolonged use may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms, including fungi. (5.5)
- Risk Associated with Mucosal Use: Mupirocin cream is not formulated for use on mucosal surfaces. A separate formulation, †Bactroban nasal ointment, is available for intranasal use. (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most frequent adverse reactions (at least 1%) were headache, rash, and nausea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Biomes Pharmaceuticals LLC., USA at 1-517-507-5222 or
FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Severe Allergic Reactions
5.2 Eye Irritation
5.3 Local Irritation
5.4 Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
5.5 Potential for Microbial Overgrowth
5.6 Risk Associated with Mucosal Use
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For Topical Use Only.
- Apply a small amount of mupirocin cream, with a cotton swab or gauze pad, to the affected area 3 times daily for 10 days.
- Cover the treated area with gauze dressing if desired.
- Re-evaluate patients not showing a clinical response within 3 to 5 days.
- Mupirocin cream is not for intranasal, ophthalmic, or other mucosal use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6)].
- Do not apply mupirocin cream concurrently with any other lotions, creams or ointments [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Click here to enter Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Allergic Reactions
Systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, urticaria, angioedema, and generalized rash, have been reported in patients treated with formulations of mupirocin, including mupirocin cream [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Eye Irritation
Avoid contact with the eyes. In case of accidental contact, rinse well with water.
5.3 Local Irritation
In the event of a sensitization or severe local irritation from mupirocin cream, usage should be discontinued, and appropriate alternative therapy for the infection instituted.
5.4 Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.5 Potential for Microbial Overgrowth
As with other antibacterial products, prolonged use of mupirocin cream may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms, including fungi [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Eye Irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Local Irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In 2 randomized, double-blind, double-dummy trials, 339 subjects were treated with topical mupirocin cream plus oral placebo. Adverse reactions occurred in 28 (8.3%) subjects. The following adverse reactions were reported by at least 1% of subjects in connection with the use of mupirocin cream in clinical trials: headache (1.7%), rash (1.1%), and nausea (1.1%).
Other adverse reactions which occurred in less than 1% of subjects were: abdominal pain, burning at application site, cellulitis, dermatitis, dizziness, pruritus, secondary wound infection, and ulcerative stomatitis.
In a supportive trial in the treatment of secondarily infected eczema, 82 subjects were treated with mupirocin cream. The incidence of adverse reactions was as follows: nausea (4.9%), headache and burning at application site (3.6% each), pruritus (2.4%), and 1 report each of abdominal pain, bleeding secondary to eczema, pain secondary to eczema, hives, dry skin, and rash.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of mupirocin cream. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These reactions have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal relationship to mupirocin cream.
Immune System Disorders
Systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, urticaria, angioedema, and generalized rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Click here to enter Use in Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of mupirocin cream (contains equivalent of 2% mupirocin free acid) in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Developmental toxicity studies have been performed with mupirocin administered subcutaneously to rats and rabbits at doses up to 160 mg per kg per day in both species. This dose is 22 and 43 times, respectively, the human topical dose (approximately 60 mg mupirocin per day) based on body surface area. There was no evidence of fetal harm due to mupirocin.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when mupirocin cream is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of mupirocin cream have been established in the age-groups 3 months to 16 years. Use of mupirocin cream in these age-groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials of mupirocin cream in adults with additional data from 93 pediatric subjects studied as part of the pivotal trials in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Mupirocin cream USP, 2% contains the dihydrate crystalline calcium hemi-salt of the RNA synthetase inhibitor antibacterial, mupirocin. Chemically, it is (αE,2S,3R,4R,5S)-5-[(2S,3S,4S,5S)-2,3-epoxy-5-hydroxy-4-methylhexyl]tetrahydro-3,4-dihydroxy-β-methyl-2H-pyran-2-crotonic acid, ester with 9-hydroxynonanoic acid, calcium salt (2:1), dihydrate.
The molecular formula of mupirocin calcium USP is (C26H43O9)2Ca2H2O, and the molecular weight is 1075.3. The molecular weight of mupirocin free acid is 500.6. The structural formula of mupirocin calcium USP is:
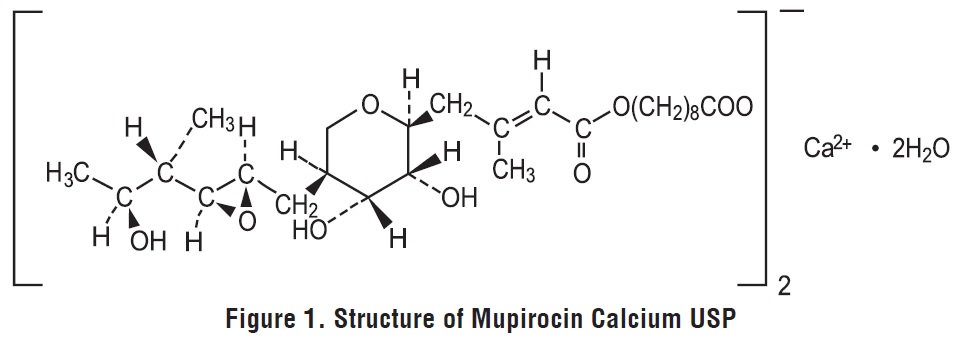
Mupirocin cream USP is a white cream that contains 2.15% w/w mupirocin calcium USP (equivalent to 2% mupirocin free acid) in an oil- and water-based emulsion. The inactive ingredients are benzyl alcohol, glycerol monostearate, mineral oil, phenoxyethanol, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, purified water and xanthan gum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Click here to enter Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mupirocin is an RNA synthetase inhibitor antibacterial [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Systemic absorption of mupirocin through intact human skin is minimal. The systemic absorption of mupirocin was studied following application of mupirocin cream 3 times daily for 5 days to various skin lesions greater than 10 cm in length or 100 cm2 in area in 16 adults (aged 29 to 60 years) and 10 children (aged 3 to 12 years). Some systemic absorption was observed as evidenced by the detection of the metabolite, monic acid, in urine. Data from this trial indicated more frequent occurrence of percutaneous absorption in children (90% of subjects) compared with adults (44% of subjects); however, the observed urinary concentrations in children (0.07 to 1.3 mcg per mL [1 pediatric subject had no detectable level]) are within the observed range (0.08 to 10.03 mcg per mL [9 adults had no detectable level]) in the adult population. In general, the degree of percutaneous absorption following multiple dosing appears to be minimal in adults and children.
The effect of the concurrent application of mupirocin cream with other topical products has not been studied [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Elimination
In a trial conducted in 7 healthy adult male subjects, the elimination half-life after intravenous administration of mupirocin was 20 to 40 minutes for mupirocin and 30 to 80 minutes for monic acid.
Metabolism: Following intravenous or oral administration, mupirocin is rapidly metabolized. The principal metabolite, monic acid, demonstrates no antibacterial activity.
Excretion: Monic acid is predominantly eliminated by renal excretion.
Special Populations
Renal Impairment: The pharmacokinetics of mupirocin have not been studied in individuals with renal insufficiency.
12.4 Microbiology
Mupirocin is an RNA synthetase inhibitor antibacterial produced by fermentation using the organism Pseudomonas fluorescens.
Mechanism of Action
Mupirocin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by reversibly and specifically binding to bacterial isoleucyltransfer RNA (tRNA) synthetase.
Mupirocin is bactericidal at concentrations achieved by topical administration. Mupirocin is highly protein bound (greater than 97%) and the effect of wound secretions on the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of mupirocin has not been determined.
Mechanism of Resistance
When mupirocin resistance occurs, it results from the production of a modified isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase, or the acquisition of, by genetic transfer, a plasmid mediating a new isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. High-level plasmid-mediated resistance (MIC ≥512 mcg/mL) has been reported in increasing numbers of isolates of S. aureus and with higher frequency in coagulase-negative staphylococci. Mupirocin resistance occurs with greater frequency in methicillin-resistant than methicillin-susceptible staphylococci.
Cross Resistance
Due to its mode of action, mupirocin does not demonstrate cross resistance with other classes of antimicrobial agents.
Antimicrobial Activity
Mupirocin has been shown to be active against susceptible isolates of S. aureus and S. pyogenes, both in vitro and in clinical trials [see Indications and Usage (1)]. The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. Mupirocin is active against most isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Susceptibility Testing
High-level mupirocin resistance (≥512 mcg/mL) may be determined using standard disk diffusion or broth microdilution tests.1,2 Because of the occurrence of mupirocin resistance in methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), it is appropriate to test MRSA populations for mupirocin susceptibility prior to the use of mupirocin using a standardized method.3,4,5
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Click here to enter Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential of mupirocin calcium have not been conducted.
Results of the following studies performed with mupirocin calcium or mupirocin sodium in vitro and in vivo did not indicate a potential for genotoxicity: rat primary hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis, sediment analysis for DNA strand breaks, Salmonella reversion test (Ames), Escherichia coli mutation assay, metaphase analysis of human lymphocytes, mouse lymphoma assay, and bone marrow micronuclei assay in mice.
Reproduction studies were performed with mupirocin administered subcutaneously to male and female rats at doses up to 100 mg per kg per day which is 14 times the human topical dose (approximately 60 mg mupirocin per day) based on body surface area. Neither evidence of impaired fertility nor impaired reproductive performance attributable to mupirocin was observed.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of topical mupirocin cream for the treatment of secondarily infected traumatic skin lesions (e.g., lacerations, sutured wounds, and abrasions not more than 10 cm in length or 100 cm2 in total area) was compared with that of oral cephalexin in 2 randomized, double-blind, double-dummy clinical trials. Clinical efficacy rates at follow-up in the per-protocol populations (adults and pediatric subjects included) were 96.1% for mupirocin cream (n = 231) and 93.1% for oral cephalexin (n = 219). Pathogen eradication rates at follow-up in the per-protocol populations were 100% for both mupirocin cream and oral cephalexin.
Pediatrics
There were 93 pediatric subjects aged 2 weeks to 16 years enrolled per protocol in the secondarily infected skin lesion trials, although only 3 were younger than 2 years of age in the population treated with mupirocin cream. Subjects were randomized to either 10 days of topical mupirocin cream 3 times daily or 10 days of oral cephalexin (250 mg 4 times daily for subjects greater than 40 kg or 25 mg per kg per day oral suspension in 4 divided doses for subjects less than or equal to 40 kg). Clinical efficacy at follow-up (7 to 12 days post-therapy) in the per-protocol populations was 97.7% (43 of 44) for mupirocin cream and 93.9% (46 of 49) for cephalexin.
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-fifth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S25. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Rd., Suite 2500, Wayne, PA 19087, USA, 2015.
- 2. Patel J, Gorwitz RJ, et al. Mupirocin Resistance. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2009; 49(6): 935-41.
- 3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard – Tenth Edition. CLSI document M07-A10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087, USA, 2015.
- 4. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard – Twelfth Edition. CLSI document M02-A12. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087, USA, 2015.
- 5. Finlay JE, Miller LA, Poupard JA. Interpretive criteria for testing susceptibility of staphylococci to mupirocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997;41(5):1137-1139.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Mupirocin cream USP, 2% is supplied in 15-gram and 30-gram tubes.
Mupirocin cream USP is a white cream that contains 2.15% w/w mupirocin calcium USP (equivalent to 2% mupirocin free acid) in an oil- and water-based emulsion.
NDC: 69150-225-01 15-gram tube (1 tube per carton)
NDC: 69150-225-03 30-gram tube (1 tube per carton)
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Advise the patient to administer mupirocin cream as follows:
- Use mupirocin cream only as directed by the healthcare provider. It is for external use only. Avoid contact of mupirocin cream with the eyes. If mupirocin cream gets in the eyes, rinse thoroughly with water.
- Do not use mupirocin cream in the nose.
- Wash your hands before and after applying mupirocin cream.
- Use a gauze pad or cotton swab to apply a small amount of mupirocin cream to the affected area. The treated area may be covered by gauze dressing if desired.
- Report to the healthcare provider any signs of local adverse reactions. Mupirocin cream should be stopped and the healthcare provider contacted if irritation, severe itching, or rash occurs.
- Report to the healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room if severe allergic reactions, such as swelling of the lips, face, or tongue, or wheezing occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- If no improvement is seen in 3 to 5 days, contact the healthcare provider.
†Bactroban is a registered trademark of the GSK group of companies.
Manufactured for:
Biomes Pharmaceuticals LLC., USA
Lansing, MI 48906Questions? 1 (517) 507-5222
www.biomesglobal.comMarch 2016
-
Patient Information
Mupirocin (mue-PIR-oh-sin)
Cream USPWhat is mupirocin cream?
Mupirocin cream is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical use) to treat certain skin infections caused by bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. It is not known if mupirocin cream is safe and effective in children under 3 months of age.
Who should not use mupirocin cream?
Do not use mupirocin cream if:
- you are allergic to mupirocin or any of the ingredients in mupirocin cream. See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of the ingredients in mupirocin cream.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using mupirocin cream?
Before using mupirocin cream, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if mupirocin cream will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if mupirocin cream passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you can use mupirocin cream while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Do not mix mupirocin cream with other lotions, creams, or ointments.
How should I use mupirocin cream?
- Mupirocin cream is for use on the skin (topical). Do not get mupirocin cream in your eyes, nose, mouth, or vagina (mucosal surfaces).
- Use mupirocin cream exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Apply a small amount of mupirocin cream, with a cotton swab or gauze pad, to the affected area 3 times each day. Apply mupirocin cream for 10 days.
- It is important that you take the full course of mupirocin cream. Do not stop early because your symptoms may disappear before the infection is fully cleared.
- Wash your hands before and afterapplying mupirocin cream.
- After applying mupirocin cream, you may cover the treated area with a clean gauze pad, unless your healthcare provider has told you to leave it uncovered.
- Talk to your healthcare provider if your skin does not improve after 3 to 5 days of treatment with mupirocin cream.
What are the possible side effects of mupirocin cream?
Mupirocin cream may cause serious side effects, including:
- severe allergic reactions. Stop using mupirocin cream and call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms of a severe allergic reaction:
- o hives
- o trouble breathing or wheezing
- o swelling of your face, lips, mouth, or tongue
- o dizziness, fast heartbeat, or pounding in your chest
- o a rash over your whole body
- eye irritation. Do not get mupirocin cream in your eyes. If mupirocin cream gets in your eyes, rinse your eyes well with water.
- irritation in the area mupirocin cream is used. A rash may occur after using mupirocin cream and can be severe. Stop using mupirocin cream and call your healthcare provider if you develop an irritation, severe itching, or a rash while using mupirocin cream.
- a type of diarrhea called clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). CDAD may happen in people who use or have used medicine to treat bacterial infections. The severity of CDAD can range from mild diarrhea to severe diarrhea that may cause death (fatal colitis). Call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room right away if you have diarrhea while using or after you stop using mupirocin cream.
The most common side effects of mupirocin cream include:
- headache
- rash
- nausea
These are not all the possible side effects of mupirocin cream. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store mupirocin cream?
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- Do not freeze mupirocin cream.
- Keep mupirocin cream and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of mupirocin cream
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use mupirocin cream for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give mupirocin cream to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about mupirocin cream that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in mupirocin cream?
Active Ingredient: mupirocin calcium USP
Inactive Ingredients: benzyl alcohol, glycerol monostearate, mineral oil, phenoxyethanol, polyoxyl 20 cetostearyl ether, purified water and xanthan gum.
Manufactured by:
Biomes Pharmaceuticals LLC.,
Lansing, MI 48906Questions? 1(517)507-5222
www.biomesglobal.comMarch 2016
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MUPIROCIN
mupirocin creamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69150-225 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MUPIROCIN CALCIUM (UNII: RG38I2P540) (MUPIROCIN - UNII:D0GX863OA5) MUPIROCIN 2 g in 100 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MINERAL OIL (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) PHENOXYETHANOL (UNII: HIE492ZZ3T) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) BENZYL ALCOHOL (UNII: LKG8494WBH) POLYOXYL 20 CETOSTEARYL ETHER (UNII: YRC528SWUY) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69150-225-01 15 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 03/22/2016 2 NDC: 69150-225-03 30 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/27/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA201587 03/22/2016 Labeler - BIOMES PHARMACEUTICALS LLC (078644310)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
