GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT- follitropin injection, solution
Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by EMD Serono, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject® (follitropin alfa injection) for subcutaneous use
*revised formulation female
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is a prefilled gonadotropin-containing auto-injection device indicated for:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ovulation Induction (2.2)
- Initial starting dose of the first cycle - 75 International Units of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® per day for 14 days, administered subcutaneously
- Individualization doses after 14 days
- Doses larger than 300 International Units of FSH per day are not recommended
Assisted Reproductive Technology (2.3)
- Initial starting dose of the first cycle - 150 International Units per day, administered subcutaneously
- Dosage adjustments after 3-5 days and by 75-150 International Units at each adjustment
- Do not administer doses greater than 450 International Units per day
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 300 International Units per 0.5 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system (3)
- Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 450 International Units per 0.75 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system (3)
- Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 900 International Units per 1.5 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is contraindicated in women who exhibit (4):
- Hypersensitivity to recombinant FSH preparations or one of their excipients
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- Pregnancy
- Uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organ.
- Tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis (5.1)
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement (5.2)
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (5.3)
- Pulmonary and Vascular Complications (5.4)
- Ovarian Torsion (5.5)
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Births (5.6)
- Congenital Malformation (5.7)
- Ectopic Pregnancy (5.8)
- Spontaneous Abortion (5.9)
- Ovarian Neoplasms (5.10)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in ovulation induction include: headache, abdominal pain, ovarian hyperstimulation (6.1)
- The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in ART include: abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal enlargement, headache, injection site bruising (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact EMD Serono at 1-800-283-8088, Ext 5563 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Do not use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® in pregnant women (4, 8.1),
- Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. (8.3)
- Pediatric Use: Safety and efficacy not established. (8.4)
- Renal and Hepatic Insufficiency: Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® in women with renal or hepatic insufficiency have not been established. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Induction of Ovulation and Pregnancy in Oligo-Anovulatory Women in whom the Cause of Infertility is Functional and Not Due to Primary Ovarian Failure.
1.2 Development of Multiple Follicles in Ovulatory Women as Part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Cycle.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dosing for Ovulation Induction
2.3 Recommended Dosing for Assisted Reproductive Technology
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis
5.2 Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
5.3 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
5.4 Pulmonary and Vascular Complications
5.5 Ovarian Torsion
5.6 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
5.7 Congenital Malformations
5.8 Ectopic Pregnancy
5.9 Spontaneous Abortion
5.10 Ovarian Neoplasms
5.11 Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Insufficiency
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Ovulation Induction (OI)
14.2 Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Dosing and Use of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
17.2 Duration and Necessary Monitoring in Women Undergoing Therapy with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
17.3 Instructions Regarding a Missed Dose
17.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
17.5 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Induction of Ovulation and Pregnancy in Oligo-Anovulatory Women in whom the Cause of Infertility is Functional and Not Due to Primary Ovarian Failure.
Prior to initiation of treatment with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®:
- Perform a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation
- Exclude primary ovarian failure
- Exclude the possibility of pregnancy
- Demonstrate tubal patency
- Evaluate the fertility status of the male partner
1.2 Development of Multiple Follicles in Ovulatory Women as Part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Cycle.
Prior to initiation of treatment with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®:
- Perform a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation, and diagnose the cause of infertility
- Exclude the possibility of pregnancy
- Evaluate the fertility status of the male partner
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is a pre-filled disposable auto-injection device intended for multiple dose use.
- Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® can be set in 12.5 International Units increments.
- Administer Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® subcutaneously in the abdomen as described in Instructions for Use
- Do not attempt to mix any other medications inside of the device with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
- Instruct women to remove the Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® from the refrigerator at least 30 minutes prior to use in order to allow Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® to warm to room temperature and avoid the discomfort of a cold injection.
2.2 Recommended Dosing for Ovulation Induction
The dosing scheme is stepwise and is individualized for each woman [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Starting doses less than 37.5 International Units have not been studied in clinical trials and are not recommended.
- A starting daily dose of 75 International Units of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is administered subcutaneously daily for 14 days in the first cycle of use.
In subsequent cycles of treatment, the starting dose (and dosage adjustments) of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® should be determined based on the history of the ovarian response to Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
- The following should be considered when planning the woman's individualized dose:
- Appropriate Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® dose adjustment(s) should be used to prevent multiple follicular growth and cycle cancellation.
- The maximum, individualized, daily dose of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is 300 International Units per day.
- In general, do not exceed 35 days of treatment.
- If indicated by the ovarian response after the initial 14 days, make an incremental adjustment in dose, up to 37.5 International Units.
- If indicated by the ovarian response, make additional incremental adjustments in dose, up to 37.5 International Units, every 7 days.
- Treatment should continue until follicular growth and/or serum estradiol levels indicate an adequate ovarian response.
- When pre-ovulatory conditions are reached, administer human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to induce final oocyte maturation and ovulation.
Withhold hCG in cases where the ovarian monitoring suggests an increased risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) on the last day of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.11)].
- Encourage the woman and her partner to have intercourse daily, beginning on the day prior to the administration of hCG and until ovulation becomes apparent.
Discourage intercourse when the risk for OHSS is increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
2.3 Recommended Dosing for Assisted Reproductive Technology
The dosing scheme follows a stepwise approach and is individualized for each woman.
- Beginning on cycle day 2 or 3, a starting dose of 150 International Units of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is administered subcutaneously daily until sufficient follicular development, as determined by ultrasound in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels, is attained. In most cases, therapy should not exceed 10 days.
In women under 35 years of age whose endogenous gonadotropin levels are suppressed, initiate Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® administration at a dose of 150 International Units per day.
In women 35 years of age and older whose endogenous gonadotropin levels are suppressed, initiate Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® administration at a dose of 225 International Units per day. - Adjust the dose after 5 days based on the woman's ovarian response, as determined by ultrasound evaluation of follicular growth and serum estradiol levels.
- Do not make additional dosage adjustments more frequently than every 3-5 days or by more than 75-150 International Units at each adjustment.
- Continue treatment until adequate follicular development is evident, and then administer hCG.
The administration of hCG should be withheld in cases where the ovarian monitoring suggests an increased risk of OHSS on the last day of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.11)]. - Doses greater than 450 International Units per day are not recommended.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 300 International Units per 0.5 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 450 International Units per 0.75 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system Injection: Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® 900 International Units per 1.5 mL in prefilled, multiple dose disposable delivery system -
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is contraindicated in women who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant FSH products
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- Pregnancy
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is contraindicated in women who are pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the woman becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the woman should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus. - Presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, or pituitary disorders) [see Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2)]
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- Tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® should only be used by physicians who are experienced in infertility treatment. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains a gonadotropic substance capable of causing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in women with or without pulmonary or vascular complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5)] and multiple births [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Gonadotropin therapy requires the availability of appropriate monitoring facilities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. The lowest effective dose should be used.
Careful attention should be given to the diagnosis of infertility and the selection of candidates for Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® therapy [see Indications and Usage (1.1, 1.2) and Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis
Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing experience with Gonal-f® and Gonal-f® RFF. Symptoms have included dyspnea, facial edema, pruritis, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy including supportive measures if cardiovascular instability and/or respiratory compromise occur, and discontinue further use.
5.2 Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
In order to minimize the hazards associated with abnormal ovarian enlargement that may occur with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® therapy, treatment should be individualized and the lowest effective dose should be used [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)]. Use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels is important to minimize the risk of ovarian stimulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® therapy, hCG should not be administered in order to reduce the chance of developing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Intercourse should be prohibited in women with significant ovarian enlargement after ovulation because of the danger of hemoperitoneum resulting from rupture of ovarian cysts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5.3 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS is a medical entity distinct from uncomplicated ovarian enlargement and may progress rapidly to become a serious medical event. OHSS is characterized by a dramatic increase in vascular permeability, which can result in a rapid accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, thorax, and potentially, the pericardium. The early warning signs of development of OHSS are severe pelvic pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. Abdominal pain, abdominal distension, gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, severe ovarian enlargement, weight gain, dyspnea, and oliguria have been reported with OHSS. Clinical evaluation may reveal hypovolemia, hemoconcentration, electrolyte imbalances, ascites, hemoperitoneum, pleural effusions, hydrothorax, acute pulmonary distress, and thromboembolic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Transient liver function test abnormalities suggestive of hepatic dysfunction with or without morphologic changes on liver biopsy, have been reported in association with OHSS.
OHSS occurs after gonadotropin treatment has been discontinued and it can develop rapidly, reaching its maximum about seven to ten days following treatment. Usually, OHSS resolves spontaneously with the onset of menses. If there is evidence that OHSS may be developing prior to hCG administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], the hCG must be withheld. Cases of OHSS are more common, more severe, and more protracted if pregnancy occurs; therefore, women should be assessed for the development of OHSS for at least two weeks after hCG administration.
If serious OHSS occurs, gonadotropins, including hCG, should be stopped and consideration should be given as to whether the woman needs to be hospitalized. Treatment is primarily symptomatic and overall should consist of bed rest, fluid and electrolyte management, and analgesics (if needed). Because the use of diuretics can accentuate the diminished intravascular volume, diuretics should be avoided except in the late phase of resolution as described below. The management of OHSS may be divided into three phases as follows:
-
Acute Phase:
Management should be directed at preventing hemoconcentration due to loss of intravascular volume to the third space and minimizing the risk of thromboembolic phenomena and kidney damage. Fluid intake and output, weight, hematocrit, serum and urinary electrolytes, urine specific gravity, BUN and creatinine, total proteins with albumin: globulin ratio, coagulation studies, electrocardiogram to monitor for hyperkalemia, and abdominal girth should be thoroughly assessed daily or more often based on the clinical need. Treatment, consisting of limited intravenous fluids, electrolytes, human serum albumin, is intended to normalize electrolytes while maintaining an acceptable but somewhat reduced intravascular volume. Full correction of the intravascular volume deficit may lead to an unacceptable increase in the amount of third space fluid accumulation. -
Chronic Phase:
After the acute phase is successfully managed as above, excessive fluid accumulation in the third space should be limited by instituting severe potassium, sodium, and fluid restriction. -
Resolution Phase:
As third space fluid returns to the intravascular compartment, a fall in hematocrit and increasing urinary output are observed in the absence of any increase in intake. Peripheral and/or pulmonary edema may result if the kidneys are unable to excrete third space fluid as rapidly as it is mobilized. Diuretics may be indicated during the resolution phase, if necessary, to combat pulmonary edema.
Ascitic, pleural, and pericardial fluid should not be removed unless there is the necessity to relieve symptoms such as pulmonary distress or cardiac tamponade.
OHSS increases the risk of injury to the ovary. Pelvic examination or intercourse may cause rupture of an ovarian cyst, which may result in hemoperitoneum, and should therefore be avoided.
If bleeding occurs and requires surgical intervention, the clinical objective should be to control the bleeding and retain as much ovarian tissue as possible. A physician experienced in the management of this syndrome, or who is experienced in the management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances should be consulted.
During clinical trials with Gonal-f® RFF, OHSS occurred in 7.2% of 83 women and 4.6% of 237 women treated with Gonal-f® RFF for ovulation induction and during Assisted Reproductive Technology, respectively.
5.4 Pulmonary and Vascular Complications
Serious pulmonary conditions (e.g., atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins. In addition, thromboembolic events both in association with, and separate from OHSS have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins including Gonal-f® RFF. Intravascular thrombosis and embolism, which may originate in venous or arterial vessels, can result in reduced blood flow to critical organs or the extremities. Women with generally recognized risk factors for thrombosis, such as personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarctions. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of ovulation induction and assisted reproductive technology need to be weighed against the risks. It should be noted that pregnancy also carries an increased risk of thrombosis.
5.5 Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins. This may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cyst and polycystic ovaries. Damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply can be limited by early diagnosis and immediate detorsion.
5.6 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
Multi-fetal gestation and births have been reported with all gonadotropin therapy including therapy with Gonal-f® RFF.
During clinical trials with Gonal-f® RFF, multiple births occurred in 20% of live births in women receiving therapy for ovulation induction and 35.1 % of live births in women undergoing ART.
The woman and her partner should be advised of the potential risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth before beginning therapy with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
5.7 Congenital Malformations
The incidence of congenital malformations after some ART [specifically in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, maternal and paternal genetic background, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI. There are no indications that the use of gonadotropins during IVF or ICSI is associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations.
5.8 Ectopic Pregnancy
Since infertile women undergoing ART often have tubal abnormalities, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy may be increased. Early confirmation of intrauterine pregnancy should be determined by β-hCG testing and transvaginal ultrasound.
5.9 Spontaneous Abortion
The risk of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) is increased with gonadotropin products. However, causality has not been established. The increased risk may be a factor of the underlying infertility.
5.10 Ovarian Neoplasms
There have been infrequent reports of ovarian neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in women who have had multiple drug therapy for controlled ovarian stimulation, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
5.11 Laboratory Tests
In most instances, treatment of women with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® will result only in follicular growth and maturation. In the absence of an endogenous LH surge, hCG is given when monitoring of the woman indicates that sufficient follicular development has occurred. This may be estimated by ultrasound alone or in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels. The combination of both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement are useful for monitoring follicular growth and maturation, timing of the ovulatory trigger, detecting ovarian enlargement and minimizing the risk of the OHSS and multiple gestation.
The clinical confirmation of ovulation is obtained by direct or indirect indices of progesterone production as well as sonographic evidence of ovulation.
Direct or indirect indices of progesterone production:
- Urinary or serum luteinizing hormone (LH) rise
- A rise in basal body temperature
- Increase in serum progesterone
- Menstruation following a shift in basal body temperature
Sonographic evidence of ovulation:
- Collapsed follicle
- Fluid in the cul-de-sac
- Features consistent with corpus luteum formation
- Secretory endometrium
-
Acute Phase:
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Ovarian Torsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Congenital Malformations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Ectopic Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Spontaneous Abortion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Ovarian Neoplasms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of Gonal-f® RFF was examined in two clinical studies (one ovulation induction study and one ART study).
Ovulation Induction
In a multiple cycle (3), assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active comparator study vs. a recombinant FSH comparator, a total of 83 oligo-anovulatory infertile women were randomized and underwent ovulation induction with Gonal-f® RFF. Adverse reactions occurring in at least 2.0% of women receiving Gonal-f® RFF are listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Common Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥ 2% in an Ovulation Induction Study System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions Gonal-f® RFF
N=83*(176 treatment cycles†)
n‡ (%)- * total number of women treated with Gonal-f® RFF
- † up to 3 treatment cycles per woman
- ‡ number of women with the adverse reaction
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Headache 22 (26.5%) Gastrointestinal System Abdominal Pain 10 (12.0%) Nausea 3 (3.6%) Flatulence 3 (3.6%) Diarrhea 3 (3.6%) Neoplasm Ovarian Cyst 3 (3.6%) Reproductive, Female Ovarian Hyperstimulation 6 (7.2%) Application Site Injection Site Pain 4 (4.8%) Injection Site Inflammation 2 (2.4%) Assisted Reproductive Technology
In a single cycle, assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active comparator study vs. a recombinant FSH comparator, a total of 237 normal ovulatory infertile women were randomized and received Gonal-f® RFF as part of an ART [in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycle (ICSI)] cycle. All women received pituitary down-regulation with gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist before stimulation. Adverse Reactions occurring in at least 2.0% of women are listed in Table 2.
Table 2: Common Adverse Reactions Reported at a Frequency of ≥ 2% in an Assisted Reproductive Technologies Study System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions Gonal-f® RFF
N=237*
n† (%)- * total number of women treated with Gonal-f® RFF
- † number of women with the adverse reaction
Gastrointestinal System Abdominal Pain 55 (23.2%) Nausea 19 (8.0%) Body as a Whole- General Abdomen Enlarged 33 (13.9%) Central and Peripheral Nervous System Headache 44 (18.6%) Application Site Disorders Injection Site Bruising 23 (9.7%) Injection Site Pain 13 (5.5%) Injection Site Inflammation 10 (4.2%) Injection Site Reaction 10 (4.2%) Application Site Edema 6 (2.5%) Reproductive, Female Ovarian Hyperstimulation 11 (4.6%) 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during postmarketing use of Gonal-f® RFF. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, the frequency or a causal relationship to Gonal-f® RFF cannot be reliably determined.
Body as a Whole - General: hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactoid reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Respiratory System: asthma
Vascular disorders: thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects
[see Contraindications (4)].
Animal Data
Embryofetal development studies with recombinant human FSH in rats, where dosing occurred during organogenesis, showed a dose dependent increase in difficult and prolonged parturition in dams, and dose dependent increases in resorptions, pre- and post-implantation losses, and stillborn pups at doses representing 5 and 41 times the lowest clinical dose of 75 IU based on body surface area. Pre-/post-natal development studies with recombinant human FSH in rats, where dosing occurred from mid-gestation through lactation, showed difficult and prolonged parturition in all dams dosed at 41 times the lowest clinical dose of 75 IU based on body surface area, along with maternal death and stillborn pups associated with the difficult and prolonged parturition. This toxicity was not observed in dams and offspring dosed at a level 5 times the lowest clinical dose of 75 IU based on body surface area.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the nursing infant from Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Aside from possible OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and multiple gestations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)], there is no additional information on the consequences of acute overdosage with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains human follicle stimulating hormone (hFSH), a glycoprotein hormone manufactured by recombinant DNA technology. The active drug substance, follitropin alfa, has a dimeric structure consisting of two non-covalently linked, non-identical glycoproteins designated as the α-and β-subunits. The α-and β-subunits have 92 and 111 amino acids, respectively, and their primary and tertiary structures are indistinguishable from those of human follicle stimulating hormone.
Recombinant human FSH production occurs in genetically modified Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells cultured in bioreactors. Purification by immunochromatography using an antibody specifically binding FSH results in a highly purified preparation with a consistent FSH isoform profile, and a high specific activity. The protein content is assessed by size exclusion high pressure liquid chromatography. The biological activity of follitropin alfa is determined by measuring the increase in ovary weight in female rats. The in vivo biological activity of follitropin alfa has been calibrated against the first International Standard for recombinant human follicle stimulating hormone established in 1995 by the Expert Committee on Biological Standards of the World Health Organization. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains no luteinizing hormone (LH) activity. Based on available data derived from physico-chemical tests and bioassays, follitropin alfa and follitropin beta, another recombinant follicle stimulating hormone product, are indistinguishable.
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is a disposable, prefilled drug delivery system intended for the subcutaneous injection of multiple and variable doses of a liquid formulation of follitropin alfa.
Each Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is filled with 415 International Units (30 mcg), 568 International Units (41 mcg), or 1026 International Units (75 mcg) follitropin alfa to deliver at least 300 International Units (22 mcg) in 0.5 mL, 450 International Units (33 mcg) in 0.75 mL, or 900 International Units (66 mcg) in 1.5 mL, respectively. Each Redi-ject® also contains 60 mg/mL sucrose, 3.0 mg/mL m-cresol, 1.1 mg/mL di-sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 0.45 mg/mL sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, 0.1 mg/mL methionine, 0.1 mg/mL Poloxamer 188. O-phosphoric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be used for pH adjustment.
Under current storage conditions, Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may contain up to 10% of oxidized follitropin alfa.
Therapeutic Class: Infertility
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), the active component in Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®, is required for normal follicular growth, follicular maturation, and gonadal steroid production. The level of FSH is critical for the onset and duration of follicular development, and consequently for the timing and number of follicles reaching maturity.
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® stimulates ovarian follicular growth in women who do not have primary ovarian failure. In order to effect the final phase of follicle maturation, resumption of meiosis, and rupture of the follicle in the absence of an endogenous LH surge, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) must be given following treatment with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® when monitoring of the woman indicates that appropriate follicular development parameters have been achieved. There is inter-woman variability in response to FSH administration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Single-dose pharmacokinetics of follitropin alfa were determined following subcutaneous administration of 300 International Units of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® to 21 pre-menopausal healthy female volunteers who were pituitary down-regulated with a GnRH agonist.
The descriptive statistics for the pharmacokinetic parameters are presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Pharmacokinetic parameters of FSH following administration of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® (300 International Units subcutaneously in a single dose) Parameter Healthy Volunteers (N=21) Mean % CV Abbreviations are:
Cmax: peak concentration (above baseline)
tmax: time of Cmax
t1/2: elimination half lifeAUClast (IU hr/L) 884 20% Cmax (IU/L) 9.83 23% tmax (hr) 15.5 43% t1/2 (hr) 53 52% Absorption
The absorption rate of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® following subcutaneous administration is slower than the elimination rate. Hence, the pharmacokinetics of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® are absorption rate-limited.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®. However, follitropin alfa showed no mutagenic activity in a series of tests performed to evaluate its potential genetic toxicity including, bacterial and mammalian cell mutation tests, a chromosomal aberration test and a micronucleus test.
Impaired fertility has been reported in rats, exposed to pharmacological doses of follitropin alfa (greater than or equal to 40 International Units per kg per day, greater than or equal to 5 times the lowest clinical dose of 75 International Units) for extended periods, through reduced fecundity.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of Gonal-f® RFF were examined in two clinical studies (one ovulation induction study and one ART study).
14.1 Ovulation Induction (OI)
Ovulation induction was evaluated in a randomized, assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active-controlled, study in oligo-anovulatory infertile women. Women were randomized to either Gonal-f® RFF (n=83), administered subcutaneously, or a comparator recombinant human FSH. The use of insulin-sensitizing agents was allowed during the study. The study was designed to evaluate and compare mean ovulation rates in the first cycle of treatment. Results for Gonal-f® RFF are presented in Table 4. Also presented in this table are secondary outcome results from cycle 1 through cycle 3. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in any of the secondary outcomes.
Table 4: Cumulative Ovulation and Clinical Pregnancy Rates in Ovulation Induction Gonal-f® RFF (n=83) Cycle Cumulative* Percent Ovulation Cumulative* Clinical Pregnancy† Rate - * Cumulative rates were determined per woman over cycles 1, 2, and 3.
- † Clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy for which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
- ‡ Non-inferior to comparator recombinant human FSH based on a two-sided 95% confidence interval, intent-to-treat analysis.
- § Secondary efficacy outcomes. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
Cycle 1 72%‡ 28%§ Cycle 2 89%§ 41%§ Cycle 3 92%§ 45%§ 14.2 Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
The efficacy of Gonal-f® RFF was evaluated in a randomized, assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active controlled study in healthy normal ovulatory, infertile women treated for one cycle with controlled ovarian stimulation, as part of an ART [in vitro fertilization (IVF), or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] cycle. Women were randomized to either Gonal-f® RFF (n=237), administered subcutaneously, or a comparator recombinant human FSH. Randomization was stratified by insemination technique, (IVF vs. ICSI). All women received pituitary down-regulation with a GnRH agonist before stimulation with recombinant FSH. Efficacy was assessed using the mean number of fertilized oocytes the day after insemination. The initial doses of Gonal-f® RFF were 150 International Units per day for women less than 35 years of age and 225 International Units per day for women 35 years of age and older. The maximum dose given for both age groups was 450 International Units per day. Treatment outcomes for Gonal-f® RFF are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5: Treatment Outcomes in ART Study Outcome value (n) - * Non-inferior to comparator recombinant human FSH based on a two-sided 95% confidence interval, intent-to-treat analysis.
- † Subgroup analyses. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in subgroups.
- ‡ A clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 35-42 after hCG administration.
- § Secondary efficacy outcomes. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
Mean number of 2PN oocytes per woman 6.3 (237)* Mean number of 2PN oocytes per subject receiving IVF 6.1 (88)† Mean number of 2PN oocytes per subject receiving ICSI 6.5 (132)† Clinical pregnancy‡ rate per attempt 33.5% (218)§ Clinical pregnancy‡ rate per embryo transfer 35.8% (204)§ Mean treatment duration in days (range) 9.7 [3-21] (230)§ -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is a disposable, prefilled multiple-dose delivery system containing a sterile, ready-to-use liquid formulation of follitropin alfa. Each Redi-ject® is supplied in a carton containing 29G × 1/2 inch disposable needles to be used for administration.
The following package presentations are available:
NDC: 44087-1115-1 - One Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains 415 International Units of follitropin alfa to deliver 300 International Units per 0.5 mL and 5 single-use disposable 29G × ½" needles
NDC: 44087-1116-1 - One Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains 568 International Units of follitropin alfa to deliver 450 International Units per 0.75 mL and 7 single-use disposable 29G × ½" needles
NDC: 44087-1117-1 - One Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains 1026 International Units of follitropin alfa to deliver 900 International Units per 1.5 mL and 14 single-use disposable 29G × ½" needles
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store the Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) until dispensed. Upon dispensing, store Redi-ject® refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) until the expiration date, or at room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) for up to three months or until the expiration date, whichever occurs first. After the first injection, store refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 28 days. Protect from light. Do not freeze. Discard unused material after 28 days.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
17.1 Dosing and Use of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
Instruct women on the correct usage and dosing of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)]. Instruct women to view the dose display in bright light and to adjust the position of the Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® to minimize dose window glare. Caution women not to change the dosage or the schedule of administration unless she is told to do so by her healthcare provider. Instruct women to remove the Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® from the refrigerator at least 30 minutes prior to use in order to allow Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® to warm to room temperature and avoid the discomfort of a cold injection.
17.2 Duration and Necessary Monitoring in Women Undergoing Therapy with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
Prior to beginning therapy with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®, inform women about the time commitment and monitoring procedures necessary for treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
17.3 Instructions Regarding a Missed Dose
Inform the woman that if she misses or forgets to take a dose of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®, the next dose should not be doubled and she should call her healthcare provider for further dosing instructions.
17.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Inform women regarding the risks of OHSS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] and OHSS-associated symptoms including lung and blood vessel problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] and ovarian torsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] with the use of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
17.5 Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
Inform women regarding the risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth with the use of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Patient Information
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® (gon-AL-eff ar-eff-eff REH dee-jekt)
(follitropin alfa injection)
for subcutaneous useGonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject® (follitropin alfa injection) for subcutaneous use
*revised formulation female
Read this Patient Information before you start using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is an injection Pen that delivers a prescription medicine containing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) used in infertile women to:
- help healthy ovaries develop (mature) and release an egg
- cause your ovaries to make multiple (more than 1) eggs as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) program
Who should not use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
Do not use the Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® if you:
- are allergic to recombinant human FSH or any of the ingredients in Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
- have ovaries that no longer make eggs (primary ovarian failure)
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- have uncontrolled thyroid or adrenal problems
- have a tumor in your female organs, including your ovaries, breast, or uterus that may get worse with high levels of estrogen
- have a tumor in your brain, such as a tumor in your pituitary or hypothalamus
- have abnormal bleeding from your uterus or vagina
- have ovarian cysts or large ovaries, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
Before you use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or have had asthma
- have been told by a healthcare provider that you have an increased risk for blood clots (thrombosis)
- have ever had a blood clot (thrombosis), or anyone in your family has ever had a blood clot (thrombosis)
- have had stomach (abdominal) surgery
- have had twisting of your ovary (ovarian torsion)
- had or have a cyst on your ovary
- have polycystic ovarian disease
- have any other medical conditions
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
- Read the "Instructions for Use" that comes with Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® for information about the right way to use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
- Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® is given by injection under your skin. Do not inject Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® until your healthcare provider has taught you the correct way to use it.
- Change your injection site as your healthcare provider showed you.
- Use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Do not change your dose of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Call your healthcare provider if you have any questions about your dose or how to use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
What are the possible side effects of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may cause serious side effects, including:
-
severe allergic reactions. Women who have used Gonal-f®, Gonal-f® RFF, or Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® in the past may have a severe allergic reaction right away when they use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® again. This severe allergic reaction may lead to death. If you have any of the following symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, stop using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® and go to the hospital right away:
- shortness of breath
- swelling of your face
- itchy, red bumps or rash on your skin (hives)
- ovaries that are too large. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may cause your ovaries to be abnormally large. Symptoms of large ovaries include bloating or pain in your lower stomach (pelvic) area.
-
ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may cause OHSS. OHSS is a serious medical condition that can happen when your ovaries produce too many eggs (overstimulated). OHSS can cause fluid to suddenly build up in the area of your stomach, chest, and heart, and can cause blood clots to form. In rare cases OHSS has caused death. OHSS may also happen after you stop using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®. Stop using Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® and call your healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms of OHSS, including:
- trouble breathing
- severe lower stomach (pelvic) area pain
- decreased urine output
- nausea
- vomiting
- weight gain
- diarrhea
- lung problems. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may cause serious lung problems including fluid in your lungs (atelectasis), trouble breathing (acute respiratory distress syndrome), and worsening of asthma.
-
blood clots. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may increase your chance of having blood clots in your blood vessels. Blood clots can cause:
- blood vessel problems (thrombophlebitis)
- stroke
- loss of your arm or leg
- blood clot in your lung (pulmonary embolus)
- twisting (torsion) of your ovary. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may increase the chance of your ovary twisting if you already have certain conditions such as OHSS, pregnancy and previous abdominal surgery. Twisting of your ovary may lead to blood flow being cut off to your ovary.
- pregnancy with and birth of multiple babies. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may increase your chance of having a pregnancy with more than 1 baby. Having a pregnancy and giving birth to more than 1 baby at a time increases the health risk for you and your babies. Your healthcare provider should tell you about your chances of multiple births.
-
birth defects. A baby born after an ART cycle may have an increased chance of having birth defects. Your chances of having a baby with birth defects may increase depending on:
- your age
- certain sperm problems
- your genetic background and that of your partner
- a pregnancy with more than 1 baby at a time
- ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside your womb). Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® may increase your chance of having a pregnancy that is abnormally outside of your womb. Your chance of having a pregnancy outside of your womb is increased if you also have fallopian tube problems.
- miscarriage. Your chance of loss of an early pregnancy may be increased if you had difficulty becoming pregnant.
- tumors of the ovary. If you have used medicines like Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® more than 1 time to get pregnant, you may have an increased chance of having tumors in your ovary(ies) (including cancer).
The most common side effects of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® include:
- headache
- stomach pain
- stomach bloating
- bruising at the injection site
- nausea
These are not all the possible side effects of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®. For more information, call your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
-
Before you use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® for the first time, store your Pen:
- in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until the expiration date, or
- store your Pen at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for up to 3 months or until the expiration date, whichever comes first
- After you use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® and there is still medicine left, store your Pen in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) or at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) up to 28 days. Throw away any unused Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® after 28 days.
- Store your Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® with the Pen cap on in a safe place.
- Store Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® away from light.
- Do not freeze Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
Keep Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important patient information about Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.fertilitylifelines.com, or call 1-866-538-7879.
What are the ingredients in Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®?
Active ingredient: follitropin alfa (r-hFSH)
Inactive ingredients: sucrose, meta-cresol, di-sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, methionine, Poloxamer 188, O-phosphoric acid, sodium hydroxide
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
EMD Serono
GONAL-f® RFF Redi-ject®
(follitropin alfa injection)
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
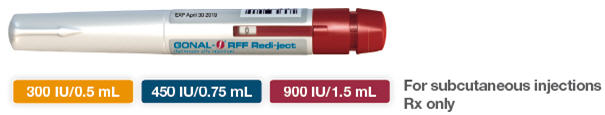
GONAL-f® RFF Redi-ject®
(follitropin alfa injection)
Important
- Read these instructions completely before you begin.
- Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject (follitropin alfa injection) is for use under the skin only (subcutaneous).
- Only use Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject if your healthcare provider trains you on how to use it correctly.
Warning: Do not reuse needles.
Warning: Do not share the pen and needles with another person, because doing so can cause an infection.
- The pen comes in 3 different IU amounts

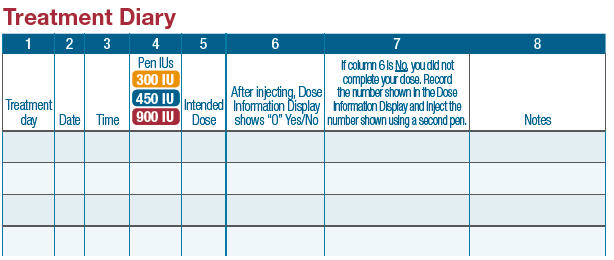
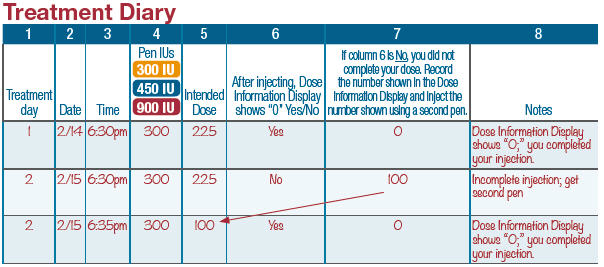
- Use the attached treatment diary to make sure you take the correct dose. Consult your healthcare provider on proper use of your treatment diary.
- You might need to use more than one pen to give today's intended dose. Contact your healthcare provider with any questions.
- The Dose Information Display is used for setting your dose, to confirm a completed dose, and to display the amount remaining to complete your intended dose.
Gather your supplies
- ▯
Take the carton out of the refrigerator at least 30 minutes before you inject to let it warm to room temperature.

Caution: Do not use a microwave or other heating element to warm up the pen.
- ▯ Prepare a clean, flat surface, such as a table or countertop, in a well-lit area.
- ▯ Identify a firm, vertical surface, such as the side of your Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject carton or a wall.
- ▯ Fill in the first 5 columns of the treatment diary. Refer to the treatment diary for sample entries.
- ▯ You will also need a sharps container, alcohol pads, and a writing utensil (not included).

Get familiar with the parts of your pen and needle
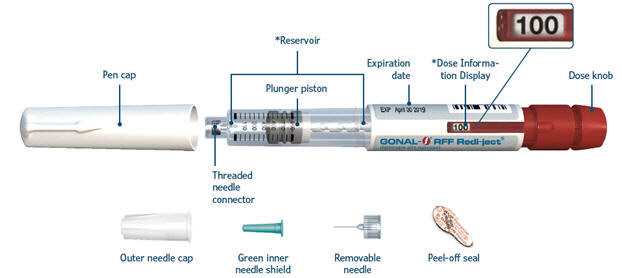
*The numbers on the Dose Information Display and reservoir represent the number of International Units (IU) of medicine.
Step 1 Get Ready
- ▯ Wash your hands with soap and water and dry them well.

Caution: Do not shake the pen. If you shake the pen, air bubbles may appear in the medicine.
- ▯ Remove the pen and a new needle from the carton.
- ▯ Check the expiration date on the pen label. Warning: Do not use an expired pen. Get a new pen from your healthcare provider or pharmacist.

Step 2 Choose and prepare your injection site
Note: Your healthcare provider should show you the injection sites to use around your stomach area.
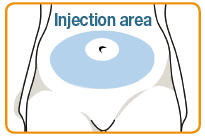
- ▯ Select your injection site and wipe the skin with an alcohol pad to clean the site.
- ▯ Choose a different injection site each time you give your injection to reduce redness, irritation, or other skin problems.
Step 3 Attach your needle
- ▯ Pull off the pen cap.

- ▯ Make sure the plastic reservoir that holds the medicine is not cracked. Confirm the medicine is clear, colorless, and does not contain particles. If the plastic is cracked or if the liquid is discolored or cloudy, get a new pen from your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- ▯ Check that the needle's peel-off seal is not broken. If it is, get a new needle.
- ▯ Peel off the needle seal.

- ▯ Push the needle on the clear, plastic end of the pen, and twist the needle until you cannot twist is anymore.
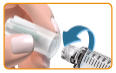
Caution: Do not attach the needle too tightly, the needle could be difficult to remove after the injection.
- ▯ Pull off the outer needle cap and save it for removing the needle after the injection.
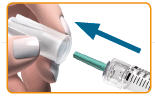
- ▯ Keeping the needle pointing up, carefully pull off the green inner needle shield and throw it away.

Warning: Do not recap the needle with the green inner needle shield you could get a needle stick injury.
Important If Then Using a new pen Check for a droplet of liquid at the tip of the needle. 
If you see a droplet go to Step 4 Dial your Dose If no droplet is seen, or you are unsure, follow the instructions in Appendix B. Re-using a pen You do not have to check for droplets of liquid at the tip of the needle. Go to Step 4 Dial your Dose Step 4 Dial your dose
Note: Call your healthcare provider if you are unsure of today's intended dose.
Caution: Do not push or pull the dose knob while you turn it to avoid damaging it.
- ▯
Turn the dose knob until your intended dose shows in the Dose Information Display.
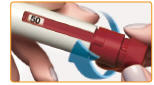
Note: You can turn the dose knob backward if you turn it past your intended dose.
Step 5 Inject your dose
Important
- ▯ Make sure the Dose Information Display matches the intended dose recorded in Column 5 in your treatment diary.
Example: If your intended dose is 150IU, confirm that the Dose Information Display reads 150.

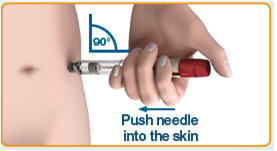
Caution: You might bend the needle if you do not insert the needle straight in at a 90° angle.
- ▯ Hold the pen at a 90° angle to the injection site, and push the needle into your skin.
- ▯ Use your thumb to press the dose knob straight down as far as it will go.
Caution: Do not release the dose knob until you remove the needle from your skin. Hold the dose knob down for a slow count of 5 before you remove the needle from your skin. Then release the knob after removal of the needle from your skin.

- ▯ Remove the needle from your skin, release the dose knob, and put the pen on the table.
- ▯ After injecting, fill in "Yes" or "No" in Column 6 of the treatment diary to record if the Dose Information Display shows "0".
Warning: If the Dose Information Display does not show "0", you did not complete your dose.
- ▯ Fill in Column 7 of the treatment diary with the number in the Dose Information Display.
- ▯ You will need to use a second pen to inject the number shown in the Dose Information Display to complete your dose.
Step 6 Remove and throw away your needle
Warning: You must remove the needle from the pen and throw away after each injection to avoid risk of infection.
- ▯ Lay the outer needle cap on its side on a flat surface.
- ▯
Hold the pen with the needle attached in one hand, and slip the needle into the outer needle cap without using your other hand.
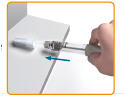
- ▯
Push the capped needle against a firm, vertical surface, such as a Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject carton or a wall, until you hear a "click".

- ▯
Twist off the capped needle and throw it away in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. See Appendix C for proper disposal information.
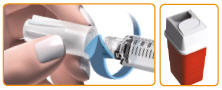
- ▯
After removing the needle, recap the pen.

- ▯ If the pen is empty after your injection, throw it away in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. See Appendix C for proper disposal information.
Step 7 Record your injection
Important
- ▯ After injecting, fill in Column 7 of the treatment diary by recording the number you see in the Dose Information Display.
- ▯ If the Dose Information Display shows "0", you have completed your dose.
- ▯
If the Dose Information Display does not show "0", you did not complete your dose. You need to inject the number shown in the Dose Information Display using a second pen.
- – Follow the instructions in Appendix A: Completing an Incomplete dose.
- – The amount you need to inject using the second pen might be less than expected because of the extra medicine (see note below). Always inject the amount you wrote in Column 7 of the treatment diary to complete your dose.
- – Refer to the treatment diary for sample entries.
Note: The pen contains extra medicine to ensure that you receive the full amount indicated on the pen (300 IU, 450 IU, or 900 IU).
Appendix A: Completing an incomplete dose
- ▯ The number recorded in Column 7 in the treatment diary indicates the number you need to dial with the second pen to complete today's intended dose. To complete the dose with a second pen, repeat Steps 1 through 7.
Appendix B: How to create a droplet of liquid
- ▯
If you do not see a droplet of liquid on the tip of the needle when using a pen for the first time, turn the dose knob until the Dose Information Display reads "25".

- ▯
With the needle pointing up, gently tap the reservoir so that any air bubbles rise to the top.
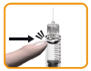
- ▯
Hold the pen with the needle pointing up. Slowly press the dose knob in all the way. One or more tiny drops of liquid will appear at the tip of the needle. Release the dose knob. Make sure that the Dose Information Display reads "0".
- ▯ Go to Step 4 Dial your dose.
Appendix C: How to throw away used needles and empty pens
- ▯ Put used needles and empty pens in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container immediately after use.

Warning: Do not throw away loose needles and pens in your household trash.
- ▯
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- Made of heavy-duty plastic,
- Can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- Upright and stable during use,
- Leak resistant, and
- Properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- ▯
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/consumer-products/safely-using-sharps-needles-and-syringes-home-work-and-travel
- Do not reuse the needles
- Do not throw way (dispose of) your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.
- Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Appendix D: How to store your pen
- ▯ Store all pens with the cap attached and away from light.
- ▯ Store new pens in the refrigerator between 36° F and 46° F (2°C and 8° C) until the expiration date, or at room temperature between 68° F and 77° F (20°C and 25°C) for up to 3 months or until the expiration date, whichever comes first.
- ▯ Do not freeze the pen.
- ▯ Keep the pen out of reach of children.
- ▯ If you have medicine left in a pen after injecting, store it in the refrigerator or at room temperature for up to 28 day. After 28 days, you must throw away (discard) your pen in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. See Appendix C for proper disposal information.
For more information, call 1-866-538-7879.
To view the Instructions for Use video, please visit www.Rediject.com
EMD Serono, Inc
Rockland, MA 02370
EMD Serono, Inc. is an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
©2017 EMD Serono, Inc.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: February 2020
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 44087-1115-1
GONAL-f ® RFF Redi-ject®
300 IU / 0.5 mL
(follitropin alfa injection)
For subcutaneous injection
Do not shakeRx only
1 Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
5 needles for injection (29 gauge)
* revised formulation femaleEMD
SERONO
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 450 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 44087-1116-1
GONAL-f ® RFF Redi-ject®
450 IU / 0.75 mL
(follitropin alfa injection)
For subcutaneous injection
Do not shakeRx only
1 Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
7 needles for injection (29 gauge)
* revised formulation femaleEMD
SERONO
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 900 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 44087-1117-1
GONAL-f ® RFF Redi-ject®
900 IU / 1.5 mL
(follitropin alfa injection)
For subcutaneous injection
Do not shakeRx only
1 Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
14 needles for injection (29 gauge)
* revised formulation femaleEMD
SERONO
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 IU Kit Carton
NDC: 44087-1118-1
GONAL-f ® RFF Redi-ject®
150 IU / 0.25 mL
(follitropin alfa injection)
For subcutaneous injection
Do not shakeRx only
1 Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject®
4 needles for injection (29 gauge)
* revised formulation femaleEMD
SERONO
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-1115 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 300 [iU] in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-1115-1 1 in 1 CARTON 10/16/2013 1 0.5 mL in 1 PACKAGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021684 10/16/2013 GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-1116 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 450 [iU] in 0.75 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-1116-1 1 in 1 CARTON 10/16/2013 1 0.75 mL in 1 PACKAGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021684 10/16/2013 GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-1117 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 900 [iU] in 1.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-1117-1 1 in 1 CARTON 10/16/2013 1 1.5 mL in 1 PACKAGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021684 10/16/2013 GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT
follitropin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 44087-1118 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FOLLITROPIN (UNII: 076WHW89TW) (FOLLITROPIN - UNII:076WHW89TW) FOLLITROPIN 150 [iU] in 0.25 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) METACRESOL (UNII: GGO4Y809LO) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC, MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 593YOG76RN) METHIONINE (UNII: AE28F7PNPL) POLOXAMER 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 44087-1118-1 1 in 1 CARTON 11/25/2019 11/25/2019 1 0.25 mL in 1 PACKAGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021684 11/25/2019 11/25/2019 Labeler - EMD Serono, Inc. (088514898)
Trademark Results [Gonal-f RFF Redi-ject]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 GONAL-F RFF REDI-JECT 86110018 4689651 Live/Registered |
Merck KGaA 2013-11-04 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.