ACTOS- pioglitazone hydrochloride tablet
Actos by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Actos by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dispensing Solutions, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ACTOS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ACTOS.
ACTOS (pioglitazone hydrochloride) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1999WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Thiazolidinediones, including ACTOS, cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure in some patients. (5.1)
- After initiation of ACTOS, and after dose increases, monitor patients carefully for signs and symptoms of heart failure (e.g., excessive, rapid weight gain, dyspnea, and/or edema). If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOS must be considered. (5.1)
- ACTOS is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure.
- Initiation of ACTOS in patients with established New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure is contraindicated. (4, 5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ACTOS is a thiazolidinedione and an agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in multiple clinical settings. (1.1, 14)
Important Limitation of Use:
- Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. (1.2)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Initiate ACTOS at 15 mg or 30 mg once daily. Limit initial dose to 15 mg once daily in patients with NYHA Class I or II heart failure. (2.1)
- If there is inadequate glycemic control, the dose can be increased in 15 mg increments up to a maximum of 45 mg once daily. (2.1)
- The maximum recommended dose of ACTOS is 15 mg once daily in patients taking strong CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., gemfibrozil). (2.3, 7.1)
- Obtain liver tests before starting ACTOS. If abnormal, use caution when treating with ACTOS, investigate the probable cause, treat (if possible) and follow appropriately. Monitoring liver tests while on ACTOS is not recommended in patients without liver disease. (5.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Congestive heart failure: Fluid retention may occur and can exacerbate or lead to congestive heart failure. Combination use with insulin and use in congestive heart failure NYHA Class I and II may increase risk. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms. (5.1)
- Edema: Dose-related edema may occur. (5.2)
- Hepatic effects: Postmarketing reports of hepatic failure, sometimes fatal. Causality cannot be excluded. If liver injury is detected, promptly interrupt ACTOS and assess patient for probable cause, then treat cause if possible, to resolution or stabilization. Do not restart ACTOS if liver injury is confirmed and no alternate etiology can be found. (5.3)
- Fractures: Increased incidence in female patients. Apply current standards of care for assessing and maintaining bone health. (5.4)
- Bladder cancer: Preclinical and clinical trial data, and results from an observational study suggest an increased risk of bladder cancer in pioglitazone users. The observational data further suggest that the risk increases with duration of use. Do not use in patients with active bladder cancer. Use caution when using in patients with a prior history of bladder cancer (5.5)
- Hypoglycemia: When used with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, a lower dose of the insulin or insulin secretagogue may be needed to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. (5.6)
- Macular edema: Postmarketing reports. Recommend regular eye exams in all patients with diabetes according to current standards of care with prompt evaluation for acute visual changes. (5.7)
- Macrovascular outcomes: There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with ACTOS or any other anti-diabetic drug. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5% and at a rate higher than with placebo) include upper respiratory tract infection, headache, sinusitis, myalgia, and pharyngitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-825-3327 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2011
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy
1.2 Important Limitation of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations for all patients
2.2 Concomitant use with an insulin secretagogue or insulin
2.3 Coadministration with strong CYP2C8 inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Congestive Heart Failure
5.2 Edema
5.3 Hepatic Effects
5.4 Fractures
5.5 Urinary Bladder Tumors
5.6 Hypoglycemia
5.7 Macular Edema
5.8 Ovulation
5.9 Macrovascular Outcomes
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Laboratory Abnormalities
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
7.2 CYP2C8 Inducers
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
13.3 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Monotherapy
14.2 Combination Therapy
16 HOW SUPPLIED/ STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions
17.2 FDA-Approved Medication Guide
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE
- Thiazolidinediones, including ACTOS, cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure in some patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- After initiation of ACTOS, and after dose increases, monitor patients carefully for signs and symptoms of heart failure (e.g., excessive, rapid weight gain, dyspnea, and/or edema). If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOS must be considered.
- ACTOS is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure.
- Initiation of ACTOS in patients with established New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy
ACTOS is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in multiple clinical settings [see Clinical Studies (14)].
1.2 Important Limitation of Use
ACTOS exerts its antihyperglycemic effect only in the presence of endogenous insulin. ACTOS should not be used to treat type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, as it would not be effective in these settings.
Use caution in patients with liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations for all patients
ACTOS should be taken once daily and can be taken without regard to meals.
The recommended starting dose for patients without congestive heart failure is 15 mg or 30 mg once daily.
The recommended starting dose for patients with congestive heart failure (NYHA Class I or II) is 15 mg once daily.
The dose can be titrated in increments of 15 mg up to a maximum of 45 mg once daily based on glycemic response as determined by HbA1c.
After initiation of ACTOS or with dose increase, monitor patients carefully for adverse reactions related to fluid retention such as weight gain, edema, and signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Liver tests (serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) should be obtained prior to initiating ACTOS. Routine periodic monitoring of liver tests during treatment with ACTOS is not recommended in patients without liver disease. Patients who have liver test abnormalities prior to initiation of ACTOS or who are found to have abnormal liver tests while taking ACTOS should be managed as described under Warnings and Precautions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Concomitant use with an insulin secretagogue or insulin
If hypoglycemia occurs in a patient co-administered ACTOS and an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea), the dose of the insulin secretagogue should be reduced.
If hypoglycemia occurs in a patient co-administered ACTOS and insulin, the dose of insulin should be decreased by 10% to 25%. Further adjustments to the insulin dose should be individualized based on glycemic response.
2.3 Coadministration with strong CYP2C8 inhibitors
Coadministration of ACTOS and gemfibrozil, a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor, increases pioglitazone exposure approximately 3-fold. Therefore, the maximum recommended dose of ACTOS is 15 mg daily when used in combination with gemfibrozil or other strong CYP2C8 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not initiate in patients with NYHA Class III or IV heart failure [see Boxed Warning].
Do not use in patients with a history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to ACTOS or any of its ingredients.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Congestive Heart Failure
ACTOS, like other thiazolidinediones, can cause dose-related fluid retention when used alone or in combination with other antidiabetic medications and is most common when ACTOS is used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate congestive heart failure. Patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure. If congestive heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOS must be considered [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Edema
In controlled clinical trials, edema was reported more frequently in patients treated with ACTOS than in placebo-treated patients and is dose-related [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In postmarketing experience, reports of new onset or worsening edema have been received.
ACTOS should be used with caution in patients with edema. Because thiazolidinediones, including ACTOS, can cause fluid retention, which can exacerbate or lead to congestive heart failure, ACTOS should be used with caution in patients at risk for congestive heart failure. Patients treated with ACTOS should be monitored for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)].
5.3 Hepatic Effects
There have been postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking ACTOS, although the reports contain insufficient information necessary to establish the probable cause. There has been no evidence of drug-induced hepatotoxicity in the ACTOS controlled clinical trial database to date [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients with type 2 diabetes may have fatty liver disease or cardiac disease with episodic congestive heart failure, both of which may cause liver test abnormalities, and they may also have other forms of liver disease, many of which can be treated or managed. Therefore, obtaining a liver test panel (serum alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST], alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) and assessing the patient is recommended before initiating ACTOS therapy. In patients with abnormal liver tests, ACTOS should be initiated with caution.
Measure liver tests promptly in patients who report symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice. In this clinical context, if the patient is found to have abnormal liver tests (ALT greater than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range), ACTOS treatment should be interrupted and investigation done to establish the probable cause. ACTOS should not be restarted in these patients without another explanation for the liver test abnormalities.
Patients who have serum ALT greater than three times the reference range with serum total bilirubin greater than two times the reference range without alternative etiologies are at risk for severe drug-induced liver injury, and should not be restarted on ACTOS. For patients with lesser elevations of serum ALT or bilirubin and with an alternate probable cause, treatment with ACTOS can be used with caution.
5.4 Fractures
In PROactive (the Prospective Pioglitazone Clinical Trial in Macrovascular Events), 5238 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of macrovascular disease were randomized to ACTOS (N=2605), force-titrated up to 45 mg daily or placebo (N=2633) in addition to standard of care. During a mean follow-up of 34.5 months, the incidence of bone fracture in females was 5.1% (44/870) for ACTOS versus 2.5% (23/905) for placebo. This difference was noted after the first year of treatment and persisted during the course of the study. The majority of fractures observed in female patients were nonvertebral fractures including lower limb and distal upper limb. No increase in the incidence of fracture was observed in men treated with ACTOS (1.7%) versus placebo (2.1%). The risk of fracture should be considered in the care of patients, especially female patients, treated with ACTOS and attention should be given to assessing and maintaining bone health according to current standards of care.
5.5 Urinary Bladder Tumors
Tumors were observed in the urinary bladder of male rats in the two-year carcinogenicity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. In two 3-year trials in which ACTOS was compared to placebo or glyburide, there were 16/3656 (0.44%) reports of bladder cancer in patients taking ACTOS compared to 5/3679 (0.14%) in patients not taking ACTOS. After excluding patients in whom exposure to study drug was less than one year at the time of diagnosis of bladder cancer, there were six (0.16%) cases on ACTOS and two (0.05%) cases on placebo.
A five-year interim report of an ongoing 10-year observational cohort study found a non-significant increase in the risk for bladder cancer in subjects ever exposed to ACTOS, compared to subjects never exposed to ACTOS (HR 1.2 [95% CI 0.9 – 1.5]). Compared to never exposure, a duration of ACTOS therapy longer than 12 months was associated with an increase in risk (HR 1.4 [95% CI 0.9 – 2.1]), which reached statistical significance after more than 24 months of ACTOS use (HR 1.4 [95% CI 1.03 – 2.0]). Interim results from this study suggested that taking ACTOS longer than 12 months increased the relative risk of developing bladder cancer in any given year by 40% which equates to an absolute increase of 3 cases in 10,000 (from approximately 7 in 10,000 [without ACTOS] to approximately 10 in 10,000 [with ACTOS]).
There are insufficient data to determine whether pioglitazone is a tumor promoter for urinary bladder tumors. Consequently, ACTOS should not be used in patients with active bladder cancer and the benefits of glycemic control versus unknown risks for cancer recurrence with ACTOS should be considered in patients with a prior history of bladder cancer.
5.6 Hypoglycemia
Patients receiving ACTOS in combination with insulin or other anti-diabetic medications (particularly insulin secretagogues such as sulfonylureas) may be at risk for hypoglycemia. A reduction in the dose of the concomitant anti-diabetic medication may be necessary to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.7 Macular Edema
Macular edema has been reported in postmarketing experience in diabetic patients who were taking ACTOS or another thiazolidinedione. Some patients presented with blurred vision or decreased visual acuity, but others were diagnosed on routine ophthalmologic examination.
Most patients had peripheral edema at the time macular edema was diagnosed. Some patients had improvement in their macular edema after discontinuation of the thiazolidinedione.
Patients with diabetes should have regular eye exams by an ophthalmologist according to current standards of care. Patients with diabetes who report any visual symptoms should be promptly referred to an ophthalmologist, regardless of the patient's underlying medications or other physical findings [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.8 Ovulation
Therapy with ACTOS, like other thiazolidinediones, may result in ovulation in some premenopausal anovulatory women. As a result, these patients may be at an increased risk for pregnancy while taking ACTOS [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. This effect has not been investigated in clinical trials, so the frequency of this occurrence is not known. Adequate contraception in all premenopausal women treated with ACTOS is recommended.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Fractures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Over 8500 patients with type 2 diabetes have been treated with ACTOS in randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trials, including 2605 patients with type 2 diabetes and macrovascular disease treated with ACTOS in the PROactive clinical trial. In these trials, over 6000 patients have been treated with ACTOS for 6 months or longer, over 4500 patients have been treated with ACTOS for one year or longer, and over 3000 patients have been treated with ACTOS for at least 2 years.
In six pooled 16 to 26-week placebo-controlled monotherapy and 16 to 24-week add-on combination therapy trials, the incidence of withdrawals due to adverse events was 4.5% for patients treated with ACTOS and 5.8% for comparator-treated patients. The most common adverse events leading to withdrawal were related to inadequate glycemic control, although the incidence of these events was lower (1.5%) with ACTOS than with placebo (3.0%).
In the PROactive trial, the incidence of withdrawals due to adverse events was 9.0% for patients treated with ACTOS and 7.7% for placebo-treated patients. Congestive heart failure was the most common serious adverse event leading to withdrawal occurring in 1.3% of patients treated with ACTOS and 0.6% of patients treated with placebo.
Common Adverse Events: 16 to 26-Week Monotherapy Trials
A summary of the incidence and type of common adverse events reported in three pooled 16 to 26-week placebo-controlled monotherapy trials of ACTOS is provided in Table 1. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly in patients treated with ACTOS than in patients who received placebo. None of these adverse events were related to ACTOS dose.
Table 1: Three Pooled 16 to 26 Week Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials of ACTOS Monotherapy: Adverse Events Reported at an Incidence > 5% and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS than in Patients Treated with Placebo % of Patients Placebo
N=259ACTOS
N=606Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 8.5 13.2 Headache 6.9 9.1 Sinusitis 4.6 6.3 Myalgia 2.7 5.4 Pharyngitis 0.8 5.1 Common Adverse Events: 16 to 24-Week Add-on Combination Therapy Trials
A summary of the overall incidence and types of common adverse events reported in trials of ACTOS add-on to sulfonylurea is provided in Table 2. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly with the highest tested dose of ACTOS.
Table 2: 16 to 24 Week Clinical Trials of ACTOS Add-on to Sulfonylurea Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema." 16-Week Placebo-Controlled Trial
Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS 30 mg + Sulfonylurea than in Patients Treated with Placebo + Sulfonylurea% of Patients Placebo
+ Sulfonylurea
N=187ACTOS 15 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=184ACTOS 30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=189Edema 2.1 1.6 12.7 Headache 3.7 4.3 5.3 Flatulence 0.5 2.7 6.3 Weight Increased 0 2.7 5.3 24-Week Non-Controlled Double-Blind Trial
Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS 45 mg + Sulfonylurea than in Patients Treated with ACTOS 30 mg + Sulfonylurea% of Patients ACTOS 30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351ACTOS 45 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351Hypoglycemia 13.4 15.7 Edema 10.5 23.1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 12.3 14.8 Weight Increased 9.1 13.4 Urinary Tract Infection 5.7 6.8 A summary of the overall incidence and types of common adverse events reported in trials of ACTOS add-on to metformin is provided in Table 3. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly with the highest tested dose of ACTOS.
Table 3: 16 to 24 Week Clinical Trials of ACTOS Add-on to Metformin Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema." 16-Week Placebo-Controlled Trial
Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS + Metformin than in Patients Treated with Placebo + Metformin% of Patients Placebo
+ Metformin
N=160ACTOS 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=168Edema 2.5 6.0 Headache 1.9 6.0 24-Week Non-Controlled Double-Blind Trial Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS 45 mg + Metformin than in Patients Treated with
ACTOS 30 mg + Metformin% of Patients ACTOS 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=411ACTOS 45 mg
+ Metformin
N=416Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 12.4 13.5 Edema 5.8 13.9 Headache 5.4 5.8 Weight Increased 2.9 6.7 Table 4 summarizes the incidence and types of common adverse events reported in trials of ACTOS add-on to insulin. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly with the highest tested dose of ACTOS.
Table 4: 16 to 24 Week Clinical Trials of ACTOS Add-on to Insulin Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema." 16-Week Placebo-Controlled Trial
Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS 30 mg + Insulin than in Patients Treated with Placebo + Insulin% of Patients Placebo
+Insulin
N=187ACTOS 15 mg
+ Insulin
N=191ACTOS 30 mg
+ Insulin
N=188Hypoglycemia 4.8 7.9 15.4 Edema 7.0 12.6 17.6 Upper Respiratory Tract Infection 9.6 8.4 14.9 Headache 3.2 3.1 6.9 Weight Increased 0.5 5.2 6.4 Back Pain 4.3 2.1 5.3 Dizziness 3.7 2.6 5.3 Flatulence 1.6 3.7 5.3 24-Week Non-Controlled Double-Blind Trial
Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with ACTOS 45 mg + Insulin than in Patients Treated with ACTOS 30 mg + Insulin% of Patients ACTOS 30 mg
+ Insulin
N=345ACTOS 45 mg
+ Insulin
N=345Hypoglycemia 43.5 47.8 Edema 22.0 26.1 Weight Increased 7.2 13.9 Urinary Tract Infection 4.9 8.7 Diarrhea 5.5 5.8 Back Pain 3.8 6.4 Blood Creatine Phosphokinase Increased 4.6 5.5 Sinusitis 4.6 5.5 Hypertension 4.1 5.5 A summary of the overall incidence and types of common adverse events reported in the PROactive trial is provided in Table 5. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly in patients treated with ACTOS than in patients who received placebo.
Table 5: PROactive Trial: Incidence and Types of Adverse Events Reported in > 5% of Patients Treated with ACTOS and More Commonly than Placebo % of Patients Placebo
N=2633ACTOS
N=2605Mean duration of patient follow-up was 34.5 months. Hypoglycemia 18.8 27.3 Edema 15.3 26.7 Cardiac Failure 6.1 8.1 Pain in Extremity 5.7 6.4 Back Pain 5.1 5.5 Chest Pain 5.0 5.1 Congestive Heart Failure: A summary of the incidence of adverse events related to congestive heart failure is provided in Table 6 for the 16 to 24-week add-on to sulfonylurea trials, for the 16 to 24-week add-on to insulin trials, and for the 16 to 24-week add-on to metformin trials. None of the events were fatal.
Table 6: Treatment –Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Patients Treated with ACTOS or Placebo Added on to a Sulfonylurea Number (%) of Patients Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled Double Blind Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Sulfonylurea
N=187ACTOS 15 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=184ACTOS 30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=189ACTOS 30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351ACTOS 45 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351At least one congestive
heart failure event2 (1.1%) 0 0 1 (0.3%) 6 (1.7%) Hospitalized 2 (1.1%) 0 0 0 2 (0.6%) Patients Treated with ACTOS or Placebo Added on to Insulin Number (%) of Patients Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled
Double Blind Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Insulin
N=187ACTOS 15 mg
+ Insulin
N=191ACTOS 30 mg
+ Insulin
N=188ACTOS 30 mg
+ Insulin
N=345ACTOS 45 mg
+ Insulin
N=345At least one congestive heart failure event 0 2 (1.0%) 2 (1.1%) 3 (0.9%) 5 (1.4%) Hospitalized 0 2 (1.0%) 1 (0.5%) 1 (0.3%) 3 (0.9%) Patients Treated with ACTOS or Placebo Added on to Metformin Number (%) of Patients Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled
Double Blind Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Metformin
N=160ACTOS 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=168ACTOS 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=411ACTOS 45 mg
+ Metformin
N=416At least one congestive heart failure event 0 1 (0.6%) 0 1 (0.2%) Hospitalized 0 1 (0.6%) 0 1 (0.2%) Patients with type 2 diabetes and NYHA class II or early class III congestive heart failure were randomized to receive 24 weeks of double-blind treatment with either ACTOS at daily doses of 30 mg to 45 mg (n=262) or glyburide at daily doses of 10 mg to 15 mg (n=256). A summary of the incidence of adverse events related to congestive heart failure reported in this study is provided in Table 7.
Table 7: Treatment –Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) in Patients with NYHA Class II or III Congestive Heart Failure Treated with ACTOS or Glyburide Number (%) of Subjects ACTOS
N=262Glyburide
N=256Death due to cardiovascular causes (adjudicated) 5 (1.9%) 6 (2.3%) Overnight hospitalization for worsening CHF (adjudicated) 26 (9.9%) 12 (4.7%) Emergency room visit for CHF (adjudicated) 4 (1.5%) 3 (1.2%) Patients experiencing CHF
progression during study35 (13.4%) 21 (8.2%) Congestive heart failure events leading to hospitalization that occurred during the PROactive trial are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8: Treatment –Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) in PROactive Trial Number (%) of Patients Placebo
N=2633ACTOS
N=2605At least one hospitalized congestive heart failure event 108 (4.1%) 149 (5.7%) Fatal 22 (0.8%) 25 (1.0%) Hospitalized, non-fatal 86 (3.3%) 124 (4.7%) Cardiovascular Safety: In the PROactive trial, 5238 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of macrovascular disease were randomized to ACTOS (N=2605), force-titrated up to 45 mg daily or placebo (N=2633) in addition to standard of care. Almost all patients (95%) were receiving cardiovascular medications (beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates, diuretics, aspirin, statins and fibrates). At baseline, patients had a mean age of 62 years, mean duration of diabetes of 9.5 years, and mean HbA1c of 8.1%. Mean duration of follow-up was 34.5 months.
The primary objective of this trial was to examine the effect of ACTOS on mortality and macrovascular morbidity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were at high risk for macrovascular events. The primary efficacy variable was the time to the first occurrence of any event in a cardiovascular composite endpoint that included all-cause mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) including silent MI, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, cardiac intervention including coronary artery bypass grafting or percutaneous intervention, major leg amputation above the ankle, and bypass surgery or revascularization in the leg. A total of 514 (19.7%) patients treated with ACTOS and 572 (21.7%) placebo-treated patients experienced at least one event from the primary composite endpoint (hazard ratio 0.90; 95% Confidence Interval: 0.80, 1.02; p=0.10).
Although there was no statistically significant difference between ACTOS and placebo for the 3-year incidence of a first event within this composite, there was no increase in mortality or in total macrovascular events with ACTOS. The number of first occurrences and total individual events contributing to the primary composite endpoint is shown in Table 9.
Table 9: PROactive: Number of First and Total Events for Each Component within the Cardiovascular Composite Endpoint Cardiovascular Events Placebo
N=2633ACTOS
N=2605First Events
n (%)Total events
nFirst Events
n (%)Total events
nCABG = coronary artery bypass grafting; PCI = percutaneous intervention Any event 572 (21.7) 900 514 (19.7) 803 All-cause mortality 122 (4.6) 186 110 (4.2) 177 Non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) 118 (4.5) 157 105 (4.0) 131 Stroke 96 (3.6) 119 76 (2.9) 92 Acute coronary syndrome 63 (2.4) 78 42 (1.6) 65 Cardiac intervention (CABG/PCI) 101 (3.8) 240 101 (3.9) 195 Major leg amputation 15 (0.6) 28 9 (0.3) 28 Leg revascularization 57 (2.2) 92 71 (2.7) 115 Weight Gain: Dose-related weight gain occurs when ACTOS is used alone or in combination with other anti-diabetic medications. The mechanism of weight gain is unclear but probably involves a combination of fluid retention and fat accumulation.
Tables 10 and 11 summarize the changes in body weight with ACTOS and placebo in the 16 to 26-week randomized, double-blind monotherapy and 16 to 24-week combination add-on therapy trials and in the PROactive trial.
Table 10: Weight Changes (kg) from Baseline during Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trials Control Group
(Placebo)ACTOS
15 mgACTOS
30 mgACTOS
45 mgMedian
(25th/75th percentile)Median
(25th/75th percentile)Median
(25th/75th percentile)Median
(25th/75th percentile)Monotherapy
(16 to 26 weeks)-1.4 (-2.7/0.0)
N=2560.9 (-0.5/3.4)
N=791.0 (-0.9/3.4)
N=1882.6 (0.2/5.4)
N=79
Combination Therapy
(16 to 24 weeks)Sulfonylurea -0.5 (-1.8/0.7)
N=1872.0 (0.2/3.2)
N=1833.1 (1.1/5.4)
N=5284.1 (1.8/7.3)
N=333Metformin -1.4 (-3.2/0.3)
N=160N/A 0.9 (-1.3/3.2)
N=5671.8 (-0.9/5.0)
N=407Insulin 0.2 (-1.4/1.4)
N=1822.3 (0.5/4.3)
N=1903.3 (0.9/6.3)
N=5224.1 (1.4/6.8)
N=338Table 11: Median Change in Body Weight in Patients Treated with ACTOS Versus Patients Treated with Placebo During the Double-Blind Treatment Period in the PROactive Trial Placebo ACTOS Median
(25th/75th
percentile)Median
(25th/75th
percentile)Note: median exposure for both ACTOS and Placebo was 2.7 years. Change from Baseline to Final Visit (kg) -0.5 (-3.3, 2.0)
N=2581+3.6 (0.0, 7.5)
N=2560Edema: Edema induced from taking ACTOS is reversible when ACTOS is discontinued. The edema usually does not require hospitalization unless there is coexisting congestive heart failure. A summary of the frequency and types of edema adverse events occurring in clinical investigations of ACTOS is provided in Table 12.
Table 12: Adverse Events of Edema in Patients Treated with ACTOS Number (%) of Patients Placebo ACTOS
15 mgACTOS
30 mgACTOS
45 mgNote: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema." Monotherapy (16 to 26 weeks) 3 (1.2%)
N=2592(2.5%)
N= 8113 (4.7%)
N= 27511 (6.5%)
N=169Combined Therapy
(16 to 24 weeks)Sulfonylurea 4 (2.1%)
N=1873(1.6%)
N=18461 (11.3%)
N=54081 (23.1%)
N=351Metformin 4 (2.5%)
N=160N/A 34 (5.9%)
N=57958 (13.9%)
N=416Insulin 13 (7.0%)
N=18724(12.6%)
N=191109(20.5%)
N=53390 (26.1%)
N=345Table 13: Adverse Events of Edema in Patients in the PROactive Trial Number (%) of Patients Placebo
N=2633ACTOS
N=2605Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema." 419 (15.9%) 712 (27.3%) Hepatic Effects: There has been no evidence of ACTOS-induced hepatotoxicity in the ACTOS controlled clinical trial database to date. One randomized, double-blind, 3-year trial comparing ACTOS to glyburide as add-on to metformin and insulin therapy was specifically designed to evaluate the incidence of serum ALT elevation to greater than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range, measured every 8 weeks for the first 48 weeks of the trial then every 12 weeks thereafter. A total of 3/1051 (0.3%) patients treated with ACTOS and 9/1046 (0.9%) patients treated with glyburide developed ALT values >3 times the upper limit of the reference range. None of the patients treated with ACTOS in the ACTOS controlled clinical trial database to date have had a serum ALT > 3 times the upper limit of the reference range and a corresponding total bilirubin >2 times the upper limit of the reference range, a combination predictive of the potential for severe drug-induced liver injury.
Hypoglycemia: In the ACTOS clinical trials, adverse events of hypoglycemia were reported based on clinical judgment of the investigators and did not require confirmation with fingerstick glucose testing.
In the 16-week add-on to sulfonylurea trial, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3.7% with ACTOS 30 mg and 0.5% with placebo. In the 16-week add-on to insulin trial, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 7.9% with ACTOS 15 mg, 15.4% with ACTOS 30 mg, and 4.8% with placebo.
The incidence of reported hypoglycemia was higher with ACTOS 45 mg compared to ACTOS 30 mg in both the 24-week add-on to sulfonylurea trial (15.7% vs. 13.4%) and in the 24-week add-on to insulin trial (47.8% vs. 43.5%).
Three patients in these four trials were hospitalized due to hypoglycemia. All three patients were receiving ACTOS 30 mg (0.9%) in the 24-week add-on to insulin trial. An additional 14 patients reported severe hypoglycemia (defined as causing considerable interference with patient's usual activities) that did not require hospitalization. These patients were receiving ACTOS 45 mg in combination with sulfonylurea (n=2) or ACTOS 30 mg or 45 mg in combination with insulin (n=12).
Urinary Bladder Tumors: Tumors were observed in the urinary bladder of male rats in the two-year carcinogenicity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. In two 3-year trials in which ACTOS was compared to placebo or glyburide, there were 16/3656 (0.44%) reports of bladder cancer in patients taking ACTOS compared to 5/3679 (0.14%) in patients not taking ACTOS. After excluding patients in whom exposure to study drug was less than one year at the time of diagnosis of bladder cancer, there were six (0.16%) cases on ACTOS and two (0.05%) cases on placebo. There are too few events of bladder cancer to establish causality.
6.2 Laboratory Abnormalities
Hematologic Effects: ACTOS may cause decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit. In placebo-controlled monotherapy trials, mean hemoglobin values declined by 2% to 4% in patients treated with ACTOS compared with a mean change in hemoglobin of -1% to +1% in placebo-treated patients. These changes primarily occurred within the first 4 to 12 weeks of therapy and remained relatively constant thereafter. These changes may be related to increased plasma volume associated with ACTOS therapy and are not likely to be associated with any clinically significant hematologic effects.
Creatine Phosphokinase: During protocol-specified measurement of serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) in ACTOS clinical trials, an isolated elevation in CPK to greater than 10 times the upper limit of the reference range was noted in 9 (0.2%) patients treated with ACTOS (values of 2150 to 11400 IU/L) and in no comparator-treated patients. Six of these nine patients continued to receive ACTOS, two patients were noted to have the CPK elevation on the last day of dosing and one patient discontinued ACTOS due to the elevation. These elevations resolved without any apparent clinical sequelae. The relationship of these events to ACTOS therapy is unknown.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ACTOS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- New onset or worsening diabetic macular edema with decreased visual acuity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Postmarketing reports of congestive heart failure have been reported in patients treated with ACTOS, both with and without previously known heart disease and both with and without concomitant insulin administration.
In postmarketing experience, there have been reports of unusually rapid increases in weight and increases in excess of that generally observed in clinical trials. Patients who experience such increases should be assessed for fluid accumulation and volume-related events such as excessive edema and congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
An inhibitor of CYP2C8 (e.g., gemfibrozil) significantly increases the exposure (area under the serum concentration-time curve or AUC) and half-life of pioglitazone. Therefore, the maximum recommended dose of ACTOS is 15 mg daily if used in combination with gemfibrozil or other strong CYP2C8 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 CYP2C8 Inducers
An inducer of CYP2C8 (e.g., rifampin) may significantly decrease the exposure (AUC) of pioglitazone. Therefore, if an inducer of CYP2C8 is started or stopped during treatment with ACTOS, changes in diabetes treatment may be needed based on clinical response without exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of 45 mg for ACTOS [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ACTOS in pregnant women. Animal studies show increased rates of post-implantation loss, delayed development, reduced fetal weights, and delayed parturition at doses 10 to 40 times the maximum recommended human dose. ACTOS should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Clinical Considerations: Abnormal blood glucose concentrations during pregnancy are associated with a higher incidence of congenital anomalies, as well as increased neonatal morbidity and mortality. Most experts recommend the use of insulin during pregnancy to maintain blood glucose concentrations as close to normal as possible for patients with diabetes.
Animal Data: In animal reproductive studies, pregnant rats and rabbits received pioglitazone at doses up to approximately 17 (rat) and 40 (rabbit) times the maximum recommended human oral dose (MRHD) based on body surface area (mg/m2); no teratogenicity was observed [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.3)]. Increases in embryotoxicity (increased postimplantation losses, delayed development, reduced fetal weights, and delayed parturition) occurred in rats that received oral doses approximately 10 or more times the MRHD (mg/m2 basis). No functional or behavioral toxicity was observed in rat offspring. When pregnant rats received pioglitazone during late gestation and lactation, delayed postnatal development, attributed to decreased body weight, occurred in rat offspring at oral maternal doses approximately 2 or more times the MRHD (mg/m2 basis). In rabbits, embryotoxicity occurred at oral doses approximately 40 times the MRHD (mg/m2 basis).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ACTOS is secreted in human milk. Pioglitazone is secreted in the milk of lactating rats. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for ACTOS to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made to discontinue nursing or discontinue ACTOS, taking into account the importance of ACTOS to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ACTOS in pediatric patients have not been established.
Use in pediatric patients is not recommended for the treatment of diabetes due to lack of long-term safety data. Risks including fractures and other adverse effects associated with ACTOS have not been determined in this population [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 92 patients (15.2%) treated with ACTOS in the three pooled 16 to 26-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, monotherapy, trials were ≥65 years old and 2 patients (0.3%) were ≥75 years old. In the two pooled 16 to 24-week add-on to sulfonylurea trials, 201 patients (18.7 %) treated with ACTOS were ≥ 65 years old and 19 (1.8%) were ≥ 75 years old. In the two pooled 16 to 24 week add-on to metformin trials, 155 patients (15.5%) treated with ACTOS were ≥65 years old and 19 (1.9%) were ≥75 years old. In the two pooled 16 to 24 week add-on to insulin trials, 272 patients (25.4%) treated with ACTOS were ≥65 years old and 22 (2.1%) were ≥75 years old.
In PROactive, 1068 patients (41.0%) treated with ACTOS were ≥65 years old and 42 (1.6%) were ≥75 years old.
In pharmacokinetic studies with pioglitazone, no significant differences were observed in pharmacokinetic parameters between elderly and younger patients. These clinical experiences have not identified differences in effectiveness and safety between the elderly (≥ 65 years) and younger patients although small sample sizes for patients ≥75 years old limit conclusions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
During controlled clinical trials, one case of overdose with ACTOS was reported. A male patient took 120 mg per day for four days, then 180 mg per day for seven days. The patient denied any clinical symptoms during this period.
In the event of overdosage, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patient's clinical signs and symptoms.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ACTOS (pioglitazone hydrochloride) is an oral antidiabetic medication.
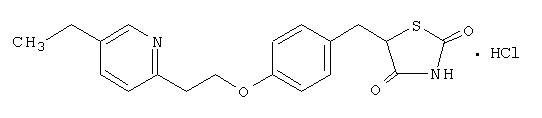
Pioglitazone [(±)-5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl) ethoxy] phenyl] methyl]-2,4-] thiazolidinedione monohydrochloride contains one asymmetric carbon, and the compound is synthesized and used as the racemic mixture. The two enantiomers of pioglitazone interconvert in vivo. No differences were found in the pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers. The structural formula is as shown:
Pioglitazone hydrochloride is an odorless white crystalline powder that has a molecular formula of C19H20N2O3SHCl and a molecular weight of 392.90 daltons. It is soluble in N,N-dimethylformamide, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, very slightly soluble in acetone and acetonitrile, practically insoluble in water, and insoluble in ether.
ACTOS is available as a tablet for oral administration containing 15 mg, 30 mg, or 45 mg of pioglitazone (as the base) formulated with the following excipients: lactose monohydrate NF, hydroxypropylcellulose NF, carboxymethylcellulose calcium NF, and magnesium stearate NF.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ACTOS is a thiazolidinedione that depends on the presence of insulin for its mechanism of action. ACTOS decreases insulin resistance in the periphery and in the liver resulting in increased insulin-dependent glucose disposal and decreased hepatic glucose output. Pioglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. Pioglitazone is an agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ). PPAR receptors are found in tissues important for insulin action such as adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and liver. Activation of PPARγ nuclear receptors modulates the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes involved in the control of glucose and lipid metabolism.
In animal models of diabetes, pioglitazone reduces the hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and hypertriglyceridemia characteristic of insulin-resistant states such as type 2 diabetes. The metabolic changes produced by pioglitazone result in increased responsiveness of insulin-dependent tissues and are observed in numerous animal models of insulin resistance.
Because pioglitazone enhances the effects of circulating insulin (by decreasing insulin resistance), it does not lower blood glucose in animal models that lack endogenous insulin.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Clinical studies demonstrate that ACTOS improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant patients. ACTOS enhances cellular responsiveness to insulin, increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal and improves hepatic sensitivity to insulin. In patients with type 2 diabetes, the decreased insulin resistance produced by ACTOS results in lower plasma glucose concentrations, lower plasma insulin concentrations, and lower HbA1c values. In controlled clinical trials, ACTOS had an additive effect on glycemic control when used in combination with a sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Patients with lipid abnormalities were included in clinical trials with ACTOS. Overall, patients treated with ACTOS had mean decreases in serum triglycerides, mean increases in HDL cholesterol, and no consistent mean changes in LDL and total cholesterol. There is no conclusive evidence of macrovascular benefit with ACTOS or any other antidiabetic medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In a 26-week, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging monotherapy study, mean serum triglycerides decreased in the 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg ACTOS dose groups compared to a mean increase in the placebo group. Mean HDL cholesterol increased to a greater extent in patients treated with ACTOS than in the placebo-treated patients. There were no consistent differences for LDL and total cholesterol in patients treated with ACTOS compared to placebo (Table 14).
Table 14. Lipids in a 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Monotherapy Dose-Ranging Study Placebo ACTOS
15 mg
Once DailyACTOS
30 mg
Once DailyACTOS
45 mg
Once Daily- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p < 0.05 versus placebo
Triglycerides (mg/dL) N=79 N=79 N=84 N=77 Baseline (mean) 263 284 261 260 Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 4.8% -9.0%† -9.6%† -9.3%† HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) N=79 N=79 N=83 N=77 Baseline (mean) 42 40 41 41 Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 8.1% 14.1%† 12.2% 19.1%† LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) N=65 N=63 N=74 N=62 Baseline (mean) 139 132 136 127 Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 4.8% 7.2% 5.2% 6.0% Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) N=79 N=79 N=84 N=77 Baseline (mean) 225 220 223 214 Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 4.4% 4.6% 3.3% 6.4% In the two other monotherapy studies (16 weeks and 24 weeks) and in combination therapy studies with sulfonylurea (16 weeks and 24 weeks), metformin (16 weeks and 24 weeks ) or insulin (16 weeks and 24 weeks), the results were generally consistent with the data above.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following once daily administration of ACTOS, steady-state serum concentrations of both pioglitazone and its major active metabolites, M-III (keto derivative of pioglitazone) and M-IV (hydroxyl derivative of pioglitazone), are achieved within 7 days. At steady-state, M-III and M-IV reach serum concentrations equal to or greater than that of pioglitazone. At steady-state, in both healthy volunteers and patients with type 2 diabetes, pioglitazone comprises approximately 30% to 50% of the peak total pioglitazone serum concentrations (pioglitazone plus active metabolites) and 20% to 25% of the total AUC.
Maximum serum concentration (Cmax), AUC, and trough serum concentrations (Cmin) for pioglitazone and M-III and M-IV, increased proportionally with administered doses of 15 mg and 30 mg per day.
Absorption: Following oral administration of pioglitazone hydrochloride, peak concentrations of pioglitazone were observed within 2 hours. Food slightly delays the time to peak serum concentration (Tmax) to 3 to 4 hours, but does not alter the extent of absorption (AUC).
Distribution: The mean apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) of pioglitazone following single-dose administration is 0.63 ± 0.41 (mean ± SD) L/kg of body weight. Pioglitazone is extensively protein bound (> 99%) in human serum, principally to serum albumin. Pioglitazone also binds to other serum proteins, but with lower affinity. M-III and M-IV are also extensively bound (> 98%) to serum albumin.
Metabolism: Pioglitazone is extensively metabolized by hydroxylation and oxidation; the metabolites also partly convert to glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. Metabolites M-III and M-IV are the major circulating active metabolites in humans.
In vitro data demonstrate that multiple CYP isoforms are involved in the metabolism of pioglitazone. The cytochrome P450 isoforms involved are CYP2C8 and, to a lesser degree, CYP3A4 with additional contributions from a variety of other isoforms including the mainly extrahepatic CYP1A1. In vivo study of pioglitazone in combination with gemfibrozil, a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor showed that pioglitazone is a CYP2C8 substrate [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Urinary 6ß-hydroxycortisol/cortisol ratios measured in patients treated with ACTOS showed that pioglitazone is not a strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducer.
Excretion and Elimination: Following oral administration, approximately 15% to 30% of the pioglitazone dose is recovered in the urine. Renal elimination of pioglitazone is negligible, and the drug is excreted primarily as metabolites and their conjugates. It is presumed that most of the oral dose is excreted into the bile either unchanged or as metabolites and eliminated in the feces.
The mean serum half-life of pioglitazone and its metabolites (M-III and M-IV) range from 3 to 7 hours and 16 to 24 hours, respectively. Pioglitazone has an apparent clearance, CL/F, calculated to be 5 to 7 L/hr.
Renal Impairment: The serum elimination half-life of pioglitazone, M-III, and M-IV remains unchanged in patients with moderate (creatinine clearance 30 to 50 mL/min) and severe (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min) renal impairment when compared to subjects with normal renal function. Therefore, no dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment is required.
Hepatic Impairment: Compared with healthy controls, subjects with impaired hepatic function (Child-Turcotte-Pugh Grade B/C) have an approximate 45% reduction in pioglitazone and total pioglitazone (pioglitazone, M-III and M-IV) mean peak concentrations but no change in the mean AUC values. Therefore, no dose adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment is required.
There are postmarketing reports of liver failure with ACTOS and clinical trials have generally excluded patients with serum ALT >2.5× the upper limit of the reference range. Use caution in patients with liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Geriatric Patients: In healthy elderly subjects, peak serum concentrations of pioglitazone are not significantly different, but AUC values are approximately 21% higher than those achieved in younger subjects. The mean terminal half-life values of pioglitazone were also longer in elderly subjects (about 10 hours) as compared to younger subjects (about 7 hours). These changes were not of a magnitude that would be considered clinically relevant.
Pediatric Patients: Safety and efficacy of pioglitazone in pediatric patients have not been established. ACTOS is not recommended for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Gender: The mean Cmax and AUC values of pioglitazone were increased 20% to 60% in women compared to men. In controlled clinical trials, HbA1c decreases from baseline were generally greater for females than for males (average mean difference in HbA1c 0.5%). Because therapy should be individualized for each patient to achieve glycemic control, no dose adjustment is recommended based on gender alone.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Table 15: Effect of Pioglitazone Coadministration on Systemic Exposure of Other Drugs Co-administered Drug Pioglitazone Dosage
Regimen (mg)*Name and Dose Regimens Change in AUC† Change in Cmax† - * Daily for 7 days unless otherwise noted
- † % change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively.
45 mg
(N = 12)Warfarin Daily loading then maintenance doses based PT and INR values
Quick's Value = 35 ± 5%R-Warfarin ↓ 3% R-Warfarin ↓ 2% S-Warfarin ↓ 1% S-Warfarin ↑ 1% 45 mg
(N = 12)Digoxin 0.200 mg twice daily (loading dose) then
0.250 mg daily (maintenance dose, 7 days)↑ 15% ↑ 17% 45 mg daily
for 21 days
(N = 35)Oral Contraceptive [Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) 0.035 mg plus
Norethindrone (NE) 1 mg] for 21 daysEE ↓11% EE ↓13% NE ↑ 3% NE ↓ 7% 45 mg
(N = 23)Fexofenadine 60 mg twice daily for 7 days ↑ 30% ↑ 37% 45 mg
(N = 14)Glipizide 5 mg daily for 7 days ↓ 3% ↓ 8% 45 mg daily
for 8 days
(N = 16)Metformin 1000 mg single dose on 8 days ↓ 3% ↓ 5% 45 mg
(N = 21)Midazolam 7.5 mg single dose on day 15 ↓ 26% ↓ 26% 45 mg
(N = 24)Ranitidine 150 mg twice daily for 7 days ↑ 1% ↓1% 45 mg daily
for 4 days
(N = 24)Nifedipine ER 30 mg daily for 4 days ↓ 13% ↓ 17% 45 mg
(N = 25)Atorvastatin Ca 80 mg daily for 7 days ↓ 14% ↓ 23% 45 mg
(N = 22)Theophylline 400 mg twice daily for 7 days ↑ 2% ↑ 5% Table 16: Effect of Coadministered Drugs on Pioglitazone Systemic Exposure Coadministered Drug and Dosage Regimen Pioglitazone Dose Regimen
(mg)*Change
in AUC†Change
in Cmax†- * Daily for 7 days unless otherwise noted
- † Mean ratio (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 1-fold) % change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively.
- ‡ The half-life of pioglitazone increased from 6.5 h to 15.1 h in the presence of gemfibrozil [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7]
Gemfibrozil 600 mg
twice daily for 2 days
(N = 12)30 mg
single dose↑ 3.4-fold‡ ↑ 6% Ketoconazole 200 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 28)45 mg ↑ 34% ↑ 14% Rifampin 600 mg
daily for 5 days
(N = 10)30 mg
single dose↓ 54% ↓ 5% Fexofenadine 60 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 23)45 mg ↑ 1% 0% Ranitidine 150 mg
twice daily for 4 days
(N = 23)45 mg ↓ 13% ↓ 16% Nifedipine ER 30 mg
daily for 7 days
(N = 23)45 mg ↑ 5% ↑ 4% Atorvastatin Ca 80 mg
daily for 7 days
(N = 24)45 mg ↓ 24% ↓ 31% Theophylline 400 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 22)45 mg ↓ 4% ↓ 2% -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in male and female rats at oral doses up to 63 mg/kg (approximately 14 times the maximum recommended human oral dose of 45 mg based on mg/m2). Drug-induced tumors were not observed in any organ except for the urinary bladder. Benign and/or malignant transitional cell neoplasms were observed in male rats at 4 mg/kg/day and above (approximately equal to the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in male and female mice at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 11 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). No drug-induced tumors were observed in any organ.
Pioglitazone hydrochloride was not mutagenic in a battery of genetic toxicology studies, including the Ames bacterial assay, a mammalian cell forward gene mutation assay (CHO/HPRT and AS52/XPRT), an in vitro cytogenetics assay using CHL cells, an unscheduled DNA synthesis assay, and an in vivo micronucleus assay.
No adverse effects upon fertility were observed in male and female rats at oral doses up to 40 mg/kg pioglitazone hydrochloride daily prior to and throughout mating and gestation (approximately 9 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Heart enlargement has been observed in mice (100 mg/kg), rats (4 mg/kg and above) and dogs (3 mg/kg) treated orally with pioglitazone hydrochloride (approximately 11, 1, and 2 times the maximum recommended human oral dose for mice, rats, and dogs, respectively, based on mg/m2). In a one-year rat study, drug-related early death due to apparent heart dysfunction occurred at an oral dose of 160 mg/kg/day (approximately 35 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). Heart enlargement was seen in a 13-week study in monkeys at oral doses of 8.9 mg/kg and above (approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2), but not in a 52-week study at oral doses up to 32 mg/kg (approximately 13 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2).
13.3 Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
Pioglitazone was not teratogenic in rats at oral doses up to 80 mg/kg or in rabbits given up to 160 mg/kg during organogenesis (approximately 17 and 40 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2, respectively). Delayed parturition and embryotoxicity (as evidenced by increased postimplantation losses, delayed development and reduced fetal weights) were observed in rats at oral doses of 40 mg/kg/day and above (approximately 10 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). No functional or behavioral toxicity was observed in offspring of rats. In rabbits, embryotoxicity was observed at an oral dose of 160 mg/kg (approximately 40 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). Delayed postnatal development, attributed to decreased body weight, was observed in offspring of rats at oral doses of 10 mg/kg and above during late gestation and lactation periods (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Monotherapy
Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with durations from 16 to 26 weeks were conducted to evaluate the use of ACTOS as monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. These trials examined ACTOS at doses up to 45 mg or placebo once daily in a total of 865 patients.
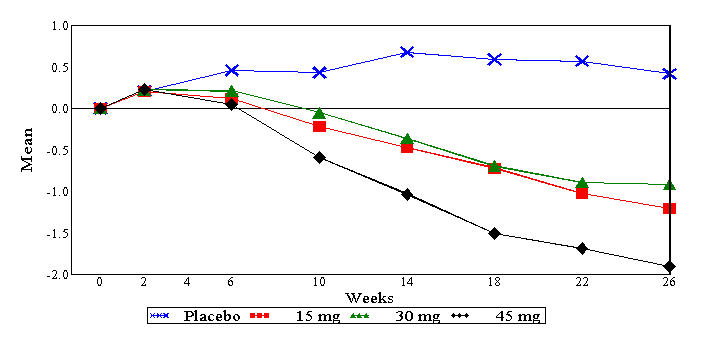
In a 26-week dose-ranging monotherapy trial, 408 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to receive 7.5 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg, or 45 mg of ACTOS, or placebo once daily. Therapy with any previous antidiabetic agent was discontinued 8 weeks prior to the double-blind period. Treatment with 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg of ACTOS produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) at endpoint compared to placebo (see Figure 1, Table 17).
Figure 1 shows the time course for changes in HbA1c in this 26-week study.
Figure 1 Mean Change from Baseline for HbA1c in a 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging Study (Observed Values) Table 17: Glycemic Parameters in a 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging Monotherapy Trial Placebo ACTOS
15 mg
Once
DailyACTOS
30 mg
Once
DailyACTOS
45 mg
Once
Daily- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. placebo
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=79 N=79 N=85 N=76 Baseline (mean) 10.4 10.2 10.2 10.3 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 0.7 -0.3 -0.3 -0.9 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-1.0†
(-1.6, -0.4)-1.0†
(-1.6, -0.4)-1.6†
(-2.2, -1.0)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=79 N=79 N=84 N=77 Baseline (mean) 268 267 269 276 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 9 -30 -32 -56 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-39†
(-63, -16)-41†
(-64, -18)-65†
(-89, -42)In a 24-week placebo-controlled monotherapy trial, 260 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to one of two forced-titration ACTOS treatment groups or a mock-titration placebo group. Therapy with any previous antidiabetic agent was discontinued 6 weeks prior to the double-blind period. In one ACTOS treatment group, patients received an initial dose of 7.5 mg once daily. After four weeks, the dose was increased to 15 mg once daily and after another four weeks, the dose was increased to 30 mg once daily for the remainder of the trial (16 weeks). In the second ACTOS treatment group, patients received an initial dose of 15 mg once daily and were titrated to 30 mg once daily and 45 mg once daily in a similar manner. Treatment with ACTOS, as described, produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo (Table 18).
Table 18: Glycemic Parameters in a 24-Week Placebo-Controlled Forced-Titration Monotherapy Trial Placebo ACTOS
30 mg*
Once
DailyACTOS
45 mg*
Once
Daily- * Final dose in forced titration
- † Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- ‡ p ≤ 0.05 vs. placebo
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=83 N=85 N=85 Baseline (mean) 10.8 10.3 10.8 Change from baseline (adjusted mean†) 0.9 -0.6 -0.6 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean†)
95% Confidence Interval-1.5‡
(-2.0, -1.0)-1.5‡
(-2.0, -1.0)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=78 N=82 N=85 Baseline (mean) 279 268 281 Change from baseline (adjusted mean†) 18 -44 -50 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean†)
95% Confidence Interval-62‡
(-82, -0.41)-68‡
(-88, -0.48)In a 16-week monotherapy trial, 197 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to treatment with 30 mg of ACTOS or placebo once daily. Therapy with any previous antidiabetic agent was discontinued 6 weeks prior to the double-blind period. Treatment with 30 mg of ACTOS produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo (Table 19).
Table 19: Glycemic Parameters in a 16-Week Placebo-Controlled Monotherapy Trial Placebo ACTOS 30 mg
Once Daily- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.050 vs. placebo
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=93 N=100 Baseline (mean) 10.3 10.5 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 0.8 -0.6 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-1.4†
(-1.8, -0.9)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=91 N=99 Baseline (mean) 270 273 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 8 -50 Difference from placebo (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-58†
(-77, -38)14.2 Combination Therapy
Three 16-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials were conducted to evaluate the effects of ACTOS (15 mg and/or 30 mg) on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately controlled (HbA1c ≥ 8%) despite current therapy with a sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin. In addition, three 24-week randomized, double-blind clinical trials were conducted to evaluate the effects of ACTOS 30 mg vs. ACTOS 45 mg on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who were inadequately controlled (HbA1c ≥ 8%) despite current therapy with a sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin. Previous diabetes treatment may have been monotherapy or combination therapy.
Add-on to Sulfonylurea Trials: Two clinical trials were conducted with ACTOS in combination with a sulfonylurea. Both studies included patients with type 2 diabetes on any dose of a sulfonylurea, either alone or in combination with another antidiabetic agent. All other antidiabetic agents were withdrawn at least 3 weeks prior to starting study treatment.
In the first study, 560 patients were randomized to receive 15 mg or 30 mg of ACTOS or placebo once daily for 16 weeks in addition to their current sulfonylurea regimen. Treatment with ACTOS as add-on to sulfonylurea produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo add-on to sulfonylurea (Table 20).
Table 20: Glycemic Parameters in a 16-Week Placebo-Controlled, Add-on to Sulfonylurea Trial Placebo
+ SulfonylureaACTOS 15 mg
+ SulfonylureaACTOS 30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. placebo + sulfonylurea
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=181 N=176 N=182 Baseline (mean) 9.9 10.0 9.9 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 0.1 -0.8 -1.2 Difference from placebo + sulfonylurea (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-0.9†
(-1.2, -0.6)-1.3†
(-1.6, -1.0)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=182 N=179 N=186 Baseline (mean) 236 247 239 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 6 -34 -52 Difference from placebo + sulfonylurea (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-39†
(-52, -27)-58†
(-70, -46)In the second trial, 702 patients were randomized to receive 30 mg or 45 mg of ACTOS once daily for 24 weeks in addition to their current sulfonylurea regimen. The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in HbA1c was 1.6% for the 30 mg dose and 1.7% for the 45 mg dose (see Table 21). The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in FPG was 52 mg/dL for the 30 mg dose and 56 mg/dL for the 45 mg dose.
The therapeutic effect of ACTOS in combination with sulfonylurea was observed in patients regardless of the sulfonylurea dose.
Table 21: Glycemic Parameters in a 24-Week Add-on to Sulfonylurea Trial ACTOS 30 mg +
SulfonylureaACTOS 45 mg +
Sulfonylurea95% CI = 95% confidence interval - * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=340 N=332 Baseline (mean) 9.8 9.9 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -1.6 -1.7 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + sulfonylurea (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -0.1
(-0.4, 0.1)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=338 N=329 Baseline (mean) 214 217 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -52 -56 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + sulfonylurea (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -5
(-12, 3)Add-on to Metformin Trials: Two clinical trials were conducted with ACTOS in combination with metformin. Both trials included patients with type 2 diabetes on any dose of metformin, either alone or in combination with another antidiabetic agent. All other antidiabetic agents were withdrawn at least 3 weeks prior to starting study treatment.
In the first trial, 328 patients were randomized to receive either 30 mg of ACTOS or placebo once daily for 16 weeks in addition to their current metformin regimen. Treatment with ACTOS as add-on to metformin produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo add-on to metformin (see Table 22).
Table 22: Glycemic Parameters in a 16-Week Placebo-Controlled, Add-on to Metformin Trial Placebo
+ MetforminACTOS 30 mg
+ Metformin- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. placebo + metformin
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=153 N=161 Baseline (mean) 9.8 9.9 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 0.2 -0.6 Difference from placebo + metformin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-0.8†
(-1.2, -0.5)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=157 N=165 Baseline (mean) 260 254 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -5 -43 Difference from placebo + metformin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-38†
(-49, -26)In the second trial, 827 patients were randomized to receive either 30 mg or 45 mg of ACTOS once daily for 24 weeks in addition to their current metformin regimen. The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in HbA1c was 0.8% for the 30 mg dose and 1.0% for the 45 mg dose (see Table 23). The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in FPG was 38 mg/dL for the 30 mg dose and 51 mg/dL for the 45 mg dose.
Table 23: Glycemic Parameters in a 24-Week Add-on to Metformin Study ACTOS 30 mg +
MetforminACTOS 45 mg
+ Metformin95% CI = 95% confidence interval - * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. 30 mg daily ACTOS + metformin
Total Population HbA1C (%) N=400 N=398 Baseline (mean) 9.9 9.8 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -0.8 -1.0 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + Metformin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -0.2
(-0.5, 0.1)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=398 N=399 Baseline (mean) 233 232 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -38 -51 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + Metformin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -12†
(-21, -4)The therapeutic effect of ACTOS in combination with metformin was observed in patients regardless of the metformin dose.
Add-on to Insulin Trials: Two clinical trials were conducted with ACTOS in combination with insulin. Both trials included patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin, either alone or in combination with another antidiabetic agent. All other antidiabetic agents were withdrawn prior to starting study treatment. In the first trial, 566 patients were randomized to receive either 15 mg or 30 mg of ACTOS or placebo once daily for 16 weeks in addition to their insulin regimen. Treatment with ACTOS as add-on to insulin produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo add-on to insulin (see Table 24). The mean daily insulin dose at baseline in each treatment group was approximately 70 units. The majority of patients (75% overall, 86% treated with placebo, 77% treated with ACTOS 15 mg, and 61% treated with ACTOS 30 mg) had no change in their daily insulin dose from baseline to the final study visit. The mean change from baseline in daily dose of insulin (including patients with no insulin dose modifications) was -3 units in the patients treated with ACTOS 15 mg, -8 units in the patients treated with ACTOS 30 mg, and -1 unit in patients treated with placebo.
Table 24: Glycemic Parameters in a 16-Week Placebo-Controlled, Add-on to Insulin Trial Placebo
+ InsulinACTOS 15 mg
+ InsulinACTOS 30 mg
+ Insulin- * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. placebo + insulin
Total Population HbA1C (%) N=177 N=177 N=185 Baseline (mean) 9.8 9.8 9.8 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -0.3 -1.0 -1.3 Difference from placebo + Insulin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-0.7†
(-1.0, -0.5)-1.0†
(-1.3, -0.7)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=179 N=183 N=184 Baseline (mean) 221 222 229 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) 1 -35 -48 Difference from placebo + Insulin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-35†
(-51, -19)-49†
(-65, -33)In the second trial, 690 patients receiving a median of 60 units per day of insulin were randomized to receive either 30 mg or 45 mg of ACTOS once daily for 24 weeks in addition to their current insulin regimen. The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in HbA1c was 1.2% for the 30 mg dose and 1.5% for the 45 mg dose. The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in FPG was 32 mg/dL for the 30 mg dose and 46 mg/dL for the 45 mg dose (see Table 25). The mean daily insulin dose at baseline in both treatment groups was approximately 70 units. The majority of patients (55% overall, 58% treated with ACTOS 30 mg, and 52% treated with ACTOS 45 mg) had no change in their daily insulin dose from baseline to the final study visit. The mean change from baseline in daily dose of insulin (including patients with no insulin dose modifications) was -5 units in the patients treated with ACTOS 30 mg and -8 units in the patients treated with ACTOS 45 mg.
The therapeutic effect of ACTOS in combination with insulin was observed in patients regardless of the insulin dose.
Table 25: Glycemic Parameters in a 24-Week Add-on to Insulin Trial ACTOS 30 mg +
InsulinACTOS 45 mg +
Insulin95% CI = 95% confidence interval - * Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
- † p ≤ 0.05 vs. 30 mg daily ACTOS + insulin
Total Population HbA1c (%) N=328 N=328 Baseline (mean) 9.9 9.7 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -1.2 -1.5 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + Insulin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -0.3†
(-0.5, -0.1)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) N=325 N=327 Baseline (mean) 202 199 Change from baseline (adjusted mean*) -32 -46 Difference from 30 mg daily ACTOS + Insulin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI) -14†
(-25, -3) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/ STORAGE AND HANDLING
ACTOS is available in 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg tablets as follows:
15 mg tablet: White to off-white, round, convex, non-scored tablet with "ACTOS" on one side, and "15" on the other, available in:
NDC: 64764-151-04 Bottles of 30
NDC: 64764-151-05 Bottles of 90
NDC: 64764-151-06 Bottles of 50030 mg tablet: White to off-white, round, flat, non-scored tablet with "ACTOS" on one side, and "30" on the other, available in:
NDC: 64764-301-14 Bottles of 30
NDC: 64764-301-15 Bottles of 90
NDC: 64764-301-16 Bottles of 50045 mg tablet: White to off-white, round, flat, non-scored tablet with "ACTOS" on one side, and "45" on the other, available in:
NDC: 64764-451-24 Bottles of 30
NDC: 64764-451-25 Bottles of 90
NDC: 64764-451-26 Bottles of 500 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Medication Guide (17.2).
17.1 Instructions
- It is important to instruct patients to adhere to dietary instructions and to have blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin tested regularly. During periods of stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, medication requirements may change and patients should be reminded to seek medical advice promptly.
- Patients who experience an unusually rapid increase in weight or edema or who develop shortness of breath or other symptoms of heart failure while on ACTOS should immediately report these symptoms to a physician.
- Tell patients to promptly stop taking ACTOS and seek immediate medical advice if there is unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or dark urine as these symptoms may be due to hepatotoxicity.
- Tell patients to promptly report any sign of macroscopic hematuria or other symptoms such as dysuria or urinary urgency that develop or increase during treatment as these may be due to bladder cancer.
- Tell patients to take ACTOS once daily. ACTOS can be taken with or without meals. If a dose is missed on one day, the dose should not be doubled the following day.
- When using combination therapy with insulin or other antidiabetic medications, the risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development should be explained to patients and their family members.
- Therapy with ACTOS, like other thiazolidinediones, may result in ovulation in some premenopausal anovulatory women. As a result, these patients may be at an increased risk for pregnancy while taking ACTOS. Therefore, adequate contraception should be recommended for all pre-menopausal women who are prescribed ACTOS.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Deerfield, IL 60015ACTOS is a trademark of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
©1999, 2006, 2010-2011 Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
July 2011
ACT003 R16 -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
ACTOS® (ak-TŌS)
(pioglitazone hydrochloride) tabletsRead this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking ACTOS and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. If you have any questions about ACTOS, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about ACTOS?
ACTOS can cause serious side effects, including new or worse heart failure.
- ACTOS can cause your body to keep extra fluid (fluid retention), which leads to swelling (edema) and weight gain. Extra body fluid can make some heart problems worse or lead to heart failure. Heart failure means your heart does not pump blood well enough
- Do not take ACTOS if you have severe heart failure
- If you have heart failure with symptoms (such as shortness of breath or swelling), even if these symptoms are not severe, ACTOS may not be right for you
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
- swelling or fluid retention, especially in the ankles or legs
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially when you lie down
- an unusually fast increase in weight
- unusual tiredness
ACTOS can have other serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of ACTOS?"
What is ACTOS?
ACTOS is a prescription medicine used with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) control in adults with type 2 diabetes. ACTOS is a diabetes medicine called pioglitazone hydrochloride that may be taken alone or with other diabetes medicines.
It is not known if ACTOS is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take ACTOS?
See "What is the most important information I should know about ACTOS?"
Do not take ACTOS if you:
- have severe heart failure
- are allergic to any of the ingredients in ACTOS. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ACTOS
Talk to your doctor before taking ACTOS if you have either of these conditions.
What should I tell my doctor before taking ACTOS?
Before you start taking ACTOS, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart failure
- have type 1 ("juvenile") diabetes or had diabetic ketoacidosis
- have a type of diabetic eye disease that causes swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema)
- have liver problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ACTOS will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while pregnant
- are a premenopausal woman (before the "change of life") who does not have periods regularly or at all. ACTOS may increase your chance of becoming pregnant. Talk to your doctor about birth control choices while taking ACTOS. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking ACTOS
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if ACTOS passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby. You should not take ACTOS if you breastfeed your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while breastfeeding
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
ACTOS and some of your other medicines can affect each other. You may need to have your dose of ACTOS or certain other medicines changed.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist before you start a new medicine. They will tell you if it is okay to take ACTOS with other medicines.
How should I take ACTOS?
- Take ACTOS exactly as your doctor tells you to take it
- Your doctor may change your dose of ACTOS. Do not change your ACTOS dose unless your doctor tells you to
- ACTOS may be prescribed alone or with other diabetes medicines. This will depend on how well your blood sugar is controlled
- Take ACTOS 1 time each day, with or without food
- If you miss a dose of ACTOS, take your next dose as prescribed unless your doctor tells you differently. Do not take two doses at one time the next day
- If you take too much ACTOS, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away
- If your body is under stress such as from a fever, infection, accident, or surgery the dose of your diabetes medicines may need to be changed. Call your doctor right away
- Stay on your diet and exercise programs and test your blood sugar regularly while taking ACTOS
- Your doctor should do certain blood tests before you start and while you take ACTOS
- Your doctor should also do hemoglobin A1C testing to check how well your blood sugar is controlled with ACTOS
- Your doctor should check your eyes regularly while you take ACTOS
- It may take 2 to 3 months to see the full effect of ACTOS on your blood sugar level.
What are the possible side effects of ACTOS?
ACTOS may cause serious side effects including:
- See "What is the most important information about ACTOS."
-
liver problems. Call your doctor right away if you have:
- nausea or vomiting
- stomach pain
- unusual or unexplained tiredness
- loss of appetite
- dark urine
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
- broken bones (fractures). Usually in the hand, upper arm, or foot in women. Talk to your doctor for advice on how to keep your bones healthy.
-
bladder cancer. There may be an increased chance of having bladder cancer when you take ACTOS. You should not take ACTOS if you are receiving treatment for bladder cancer. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of bladder cancer:
- blood or a red color in your urine
- an increased need to urinate
- pain while you urinate
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This can happen if you skip meals, if you also use another medicine that lowers blood sugar, or if you have certain medical problems. Lightheadedness, dizziness, shakiness, or hunger may happen if your blood sugar is too low. Call your doctor if low blood sugar levels are a problem for you
- diabetic eye disease with swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema). Tell your doctor right away if you have any changes in your vision. Your doctor should check your eyes regularly
- release of an egg from an ovary in a woman (ovulation) leading to pregnancy. Ovulation may happen when premenopausal women who do not have regular monthly periods take ACTOS. This can increase your chance of getting pregnant
The most common side effects of ACTOS include:
- cold-like symptoms (respiratory tract infection)
- headache
- sinus infection
- muscle pain
- sore throat
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the side effects of ACTOS. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ACTOS?
- Store ACTOS at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C). Keep ACTOS in the original container and protect from light
- Keep the ACTOS bottle tightly closed and protect from getting wet (away from moisture and humidity)
- Keep ACTOS and all medicines out of the reach of children
General information about the safe and effective use of ACTOS
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ACTOS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ACTOS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about ACTOS. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about ACTOS that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, go to www.actos.com or call 1-877-825-3327.
What are the ingredients in ACTOS?
Active Ingredient: pioglitazone hydrochloride
Inactive Ingredients: lactose monohydrate, hydroxypropylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose calcium, and magnesium stearate.
ACTOS is a trademark of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Deerfield, IL 60015
© 2009-2011 Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.July 2011
ACT003 R16
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

NDC: 68258-5230-03
30 Tablets
actos®
(pioglitazone HCl)
Tablets
15 mg
Each tablet contains pioglitazone hydrochloride equivalent to 15 mg pioglitazone.
Dispense with Medication Guide available in package insert or at www.actos.com
Rx Only -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 68258-3034-03
30 Tablets
actos®
(pioglitazone HCl)
Tablets
30 mg
Each tablet contains pioglitazone hydrochloride equivalent to 30 mg pioglitazone.
Dispense with Medication Guide available in package insert or at www.actos.com
Rx Only -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ACTOS
pioglitazone hydrochloride tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68258-5230(NDC:64764-151) Route of Administration OCCLUSIVE DRESSING TECHNIQUE Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength pioglitazone hydrochloride (UNII: JQT35NPK6C) (pioglitazone - UNII:X4OV71U42S) pioglitazone hydrochloride 15 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength carboxymethylcellulose calcium (UNII: UTY7PDF93L) hydroxypropyl cellulose (UNII: RFW2ET671P) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color white (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND (round, convex) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code ACTOS;15 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68258-5230-3 30 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021073 07/15/1999 ACTOS
pioglitazone hydrochloride tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68258-3034(NDC:64764-301) Route of Administration OCCLUSIVE DRESSING TECHNIQUE Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength pioglitazone hydrochloride (UNII: JQT35NPK6C) (pioglitazone - UNII:X4OV71U42S) pioglitazone hydrochloride 30 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength carboxymethylcellulose calcium (UNII: UTY7PDF93L) hydroxypropyl cellulose (UNII: RFW2ET671P) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color white (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND (round, flat) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code ACTOS;30 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68258-3034-3 30 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021073 07/15/1999 Labeler - Dispensing Solutions, Inc. (066070785) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dispensing Solutions, Inc. 066070785 relabel, repack
Trademark Results [Actos]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ACTOS 98408921 not registered Live/Pending |
Rosario, Gaspar 2024-02-16 |
 ACTOS 85796053 4632958 Live/Registered |
Lee, Seung-gu 2012-12-06 |
 ACTOS 75456152 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Data Everywhere, Inc. 1998-03-24 |
 ACTOS 75146715 2307686 Live/Registered |
TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY LIMITED 1996-08-07 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.