ZINC SULFATE- zinc sulfate injection injection
Zinc Sulfate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Zinc Sulfate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Apotex Corp. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZINC SULFATE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZINC SULFATE INJECTION.
ZINC SULFATE injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1957INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Zinc sulfate injection is a trace element indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of zinc for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Pharmacy Bulk Package. Not for direct intravenous infusion. (2.1)
- See full prescribing information for information on preparation, administration, and general dosing considerations. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4)
Recommended Dosage and Monitoring (2.5)
- Zinc sulfate injection provides 5 mg/mL of zinc.
- Zinc sulfate injection in a concentration of 1 mg/mL is recommended for use in pediatric patients, particularly those weighing less than 12 kg.
- Individualize the dosage based upon the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and the contribution of oral or enteral zinc intake.
- Adults: The recommended adult dosage is 3 mg/day for metabolically stable patients, with potential need for a higher daily dosage in monitored patients with small bowel fluid loss or excess stool or ileostomy output.
- Pediatrics: The recommended dosage in pediatric patients is shown by age and estimated weight. The dosages in the table are general recommendations intended for most pediatric patients. However, based on clinical requirements, some patients may require a higher dosage.
Population Estimated Weight for Age Recommended Daily Dosage Pediatric Patients 10 kg and above 50 mcg/kg (up to 3 mg/day) 5 kg to less than 10 kg 100 mcg/kg Term Neonates 3 kg to less than 5 kg 250 mcg/kg* Preterm Neonates Less than 3 kg 400 mcg/kg *Term neonates have higher requirements in the first 3 months of life
- Monitor zinc concentrations and signs and symptoms of zinc deficiency, especially in pediatric patients, during treatment. Zinc concentrations may vary depending on the assay used and the laboratory reference range. The collection, processing, and storage of the blood samples for zinc analysis should be performed according to the laboratory’s sample requirements. Zinc concentrations in hemolyzed samples are falsely elevated due to release of zinc from erythrocytes. The lower end of the reported range in healthy adults in serum is 60 mcg/dL.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates: If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. (5.1)
- Vein Damage and Thrombosis: Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or more must be infused through a central catheter. (2.1, 5.2)
- Aluminum Toxicity: Increase risk in patients with renal impairment, including preterm infants (5.3, 8.4)
- Monitoring and Laboratory Tests: Monitor fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count and coagulation parameters throughout treatment. (5.4, 2.4)
- Copper Deficiency: If signs and symptoms develop, interrupt treatment with zinc sulfate injection and check zinc, copper, and ceruloplasmin levels. (5.5)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: If reactions occur, discontinue zinc sulfate injection and initiate appropriate medical treatment. (5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
No zinc-related adverse reactions in patients receiving intravenously administered parenteral nutrition solutions containing zinc within the recommended dosage range. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition Container
2.4 Dosing Considerations
2.5 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring in Adult and Pediatric Patients
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
5.2 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
5.3 Aluminum Toxicity
5.4 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
5.5 Copper Deficiency
5.6 Hypersensitivity Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics:
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
Zinc sulfate injection is supplied as a pharmacy bulk package for admixing use only. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, zinc sulfate injection must be transferred to a separate parenteral nutrition container, diluted and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
The final parenteral nutrition solution is for intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein. The choice of a central or peripheral venous route should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Zinc sulfate injection is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, zinc sulfate injection must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
- Zinc sulfate injection is to be prepared only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area). The key factor in the preparation is careful aseptic technique to avoid inadvertent touch contamination during mixing of solutions and addition of other nutrients.
- Visually inspect the diluted parenteral nutrition solution containing zinc sulfate injection for particulate matter before admixing, after admixing, and prior to administration.
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition Container
- Inspect zinc sulfate injection bulk pharmacy package for particulate matter.
- Transfer zinc sulfate injection to the parenteral nutrition container following the admixture of amino acids, dextrose, lipid emulsion (if added), and electrolytes solutions.
- Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the parenteral nutrition container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Apotex Corp. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives to the parenteral nutrition container, use aseptic technique.
- Inspect the final parenteral nutrition solution containing zinc sulfate injection to ensure that:
- Precipitates have not formed during mixing or addition on additives.
- The emulsion has not separated, if lipid emulsion has been added. Separation of the emulsion can be visibly identified by a yellowish streaking or the accumulation of yellowish droplets in the admixed emulsion.
- Discard if any precipitates are observed.
Stability and Storage
- Penetrate vial closure only one time with a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set that allows measured dispensing of the contents.
- Use zinc sulfate injection for admixing promptly once the sterile transfer set has been inserted into the pharmacy bulk package container or not more than 4 hours at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) (25ºC/77ºF) after the container closure has been penetrated. Discard any remaining drug.
- Use parenteral nutrition solutions containing zinc sulfate injection promptly after mixing. Any storage of the admixture should be under refrigeration from 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) and limited to a period of time no longer than 9 days. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Discard any remaining admixture.
- Protect the admixed parenteral nutrition solution from light.
2.4 Dosing Considerations
- The dosage of the final parenteral nutrition solution containing zinc sulfate injection must be based on the concentrations of all components in the solution and the recommended daily nutritional requirements [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Consult the prescribing information of all added components to determine the recommended nutritional requirements for dextrose and lipid emulsion, as applicable.
- Prior to administration of parenteral nutrition solution containing zinc sulfate injection, correct severe fluid, electrolyte and acid-base disorders.
2.5 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring in Adult and Pediatric Patients
- Zinc sulfate injection provides 1 mg/mL or 5 mg/mL of zinc.
- Zinc sulfate injection in a concentration of 1 mg/mL is recommended for use in pediatric patients, particularly those weighing less than 12 kg.
- The dosage of zinc sulfate injection should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and the contribution of oral or enteral zinc intake.
Adults
The recommended adult dosage is 3 mg/day for metabolically stable patients, with potential need for a higher daily dosage in monitored patients with small bowel fluid loss or excess stool or ileostomy output.
Pediatric Patients
The recommended pediatric dosage is shown in Table 1 by age and estimated weight. The dosages in Table 1 are general recommendations intended for most pediatric patients. However, based on clinical requirements, some patients may require a higher dosage.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage of Zinc Sulfate Injection for Pediatric Patients by Age and Estimated Weight
Population Estimated Weight for Age Recommended Daily Dosage Pediatric patients 10 kg and above 50 mcg/kg (up to 3 mg/day) 5 kg to less than 10 kg 100 mcg/kg Term neonates 3 kg to less than 5 kg 250 mcg/kg* Preterm neonates Less than 3 kg 400 mcg/kg *Term neonates have higher requirements in the first 3 months of life
Monitoring
Monitor zinc concentrations during treatment. Also monitor patients clinically for signs and symptoms of zinc deficiency, especially in pediatrics. Zinc concentrations may vary depending on the assay used and the laboratory reference range. The collection, processing, and storage of the blood samples for zinc analysis should be performed according to the laboratory’s sample requirements. Zinc concentrations in hemolyzed samples are falsely elevated due to release of zinc from erythrocytes. The lower end of the reported range in healthy adults in serum is 60 mcg/dL.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Zinc sulfate injection is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to zinc [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. The cause of precipitate formation has not been determined in all cases; however, in some fatal cases, pulmonary emboli occurred as a result of calcium phosphate precipitates. Precipitation has occurred following passage through an in-line filter; invivo precipitate formation may also have occurred. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the parenteral nutrition infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. In addition to inspection of the solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)], the infusion set and catheter should also periodically be checked for precipitates.
5.2 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
Zinc sulfate injection has a low pH and must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions. It is not for direct intravenous infusion.
In addition, consider the osmolarity of the final parenteral nutrition solution in determining peripheral versus central administration. Solutions with an osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. The infusion of hypertonic nutrient solutions into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and/or thrombosis. The primary complication of peripheral access is venous thrombophlebitis, which manifests as pain, erythema, tenderness or a palpable cord. Remove the catheter as soon as possible, if thrombophlebitis develops.
5.3 Aluminum Toxicity
Zinc sulfate injection contains aluminum that may be toxic.
Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Preterm infants are particularly at risk for aluminum toxicity because the kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which also contain aluminum.
Patients with impaired kidney function, including preterm infants, who receive greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day of parenteral aluminum can accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
Exposure to aluminum from zinc sulfate injection is not more than 0.6 mcg/kg/day. When prescribing zinc sulfate injection for use in parenteral nutrition containing other small volume parenteral products, the total daily patient exposure to aluminum from the admixture should be considered and maintained at no more than 5 mcg/kg/day [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.4 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
Monitor zinc concentrations, fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count and coagulation parameters throughout treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.5 Copper Deficiency
Several post-marketing cases have reported that high doses of supplemental zinc (approximately 10 times the recommended dosage of 3 mg/day zinc sulfate injection in adults) taken over extended periods of time (i.e., months to years) may result in decreased enteral copper absorption and copper deficiency. The cases reported the following complications of copper deficiency: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, myeloneuropathy, and nephrotic-range proteinuria [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
If a patient develops signs and symptoms of copper deficiency during treatment with zinc sulfate injection, interrupt zinc treatment and check zinc, copper, and ceruloplasmin levels. Copper deficiency should be treated with supplemental copper administration and discontinuation of zinc supplementation.
5.6 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions to subcutaneously administered zinc-containing insulin products were identified in postmarketing case reports. Reported reactions included injection site induration, erythema, pruritus, papular rash, generalized urticaria, facial swelling, and dyspnea. Patients did not manifest symptoms after changing to zinc-free insulin or another insulin product with a reduced amount of zinc. In some cases, allergy testing confirmed the allergy to the zinc component of the insulin product. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue zinc sulfate injection and initiate appropriate medical treatment [see Contraindications (4)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
No zinc-related adverse reactions have been reported in clinical studies or post-marketing reports in patients receiving intravenously administered parenteral nutrition solutions containing zinc sulfate within the recommended dosage range.
The following were identified in clinical studies or post-marketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Adverse reactions with other components of parenteral nutrition solutions:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Adverse reactions with the use of zinc-containing products administered by other routes of administration:
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Administration of the approved recommended dose of zinc sulfate injection in parenteral nutrition is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with intravenous zinc sulfate.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo-Fetal Risk
Deficiency of trace elements, including zinc, is associated with adverse pregnancy and fetal outcomes. Pregnant women have an increased metabolic demand for trace elements, including zinc. Parenteral nutrition with zinc should be considered if a pregnant woman’s nutritional requirements cannot be fulfilled by oral or enteral intake.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Zinc is present in human milk. Administration of the approved recommended dose of zinc sulfate injection in parenteral nutrition is not expected to cause harm to a breastfed infant. There is no information on the effects of zinc sulfate on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for zinc sulfate injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from zinc sulfate injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Zinc sulfate injection is approved for use in the pediatric population, including neonates, as a source of zinc for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated. Safety and dosing recommendations in pediatric patients are based on published literature describing controlled studies of zinc-containing products in pediatric patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged parenteral nutrition treatment with zinc sulfate injection may be at higher risk of aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Reported clinical experience with intravenous zinc sulfate has not identified a difference in zinc requirements between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and additional nutritional intake provided orally or enterally to the patient.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There are reported cases of overdosage with intravenous zinc in parenteral nutrition:
- Seven adult patients received an inadvertent overdosage of 50 mg to 75 mg elemental zinc per day in parenteral nutrition solution for 26 to 60 days; 6 of the 7 patients developed hyperamylasemia (peak amylase values of 557 to 1,850 Klein units; normal: 130 to 310). Amylase was not reported in one patient. Serum zinc concentrations ranged from 310 to 670 mcg/dL. None of the patients developed clinical signs of pancreatitis. Five of the 7 patients died of septic complications.
- One adult patient died of infectious complications after receiving an inadvertent overdosage of 7.4 grams of zinc sulfate (equivalent to 1.2 grams of elemental zinc per day for 2.5 days) in parenteral nutrition solution over 60 hours. The serum zinc concentration was 4184 mcg/dL. Symptoms of zinc overdosage also included hyperamylasemia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, vomiting and diarrhea.
- One preterm infant born at 26 weeks gestation died of cardiac failure following a medication error in which the parenteral nutrition solution contained 330 mg/100 mL instead of 330 mcg/100 mL of zinc sulfate (overdosage of 1,000-fold).
Management
There is no known antidote for acute zinc toxicity. Management of zinc overdosage is supportive care based on presenting signs and symptoms.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
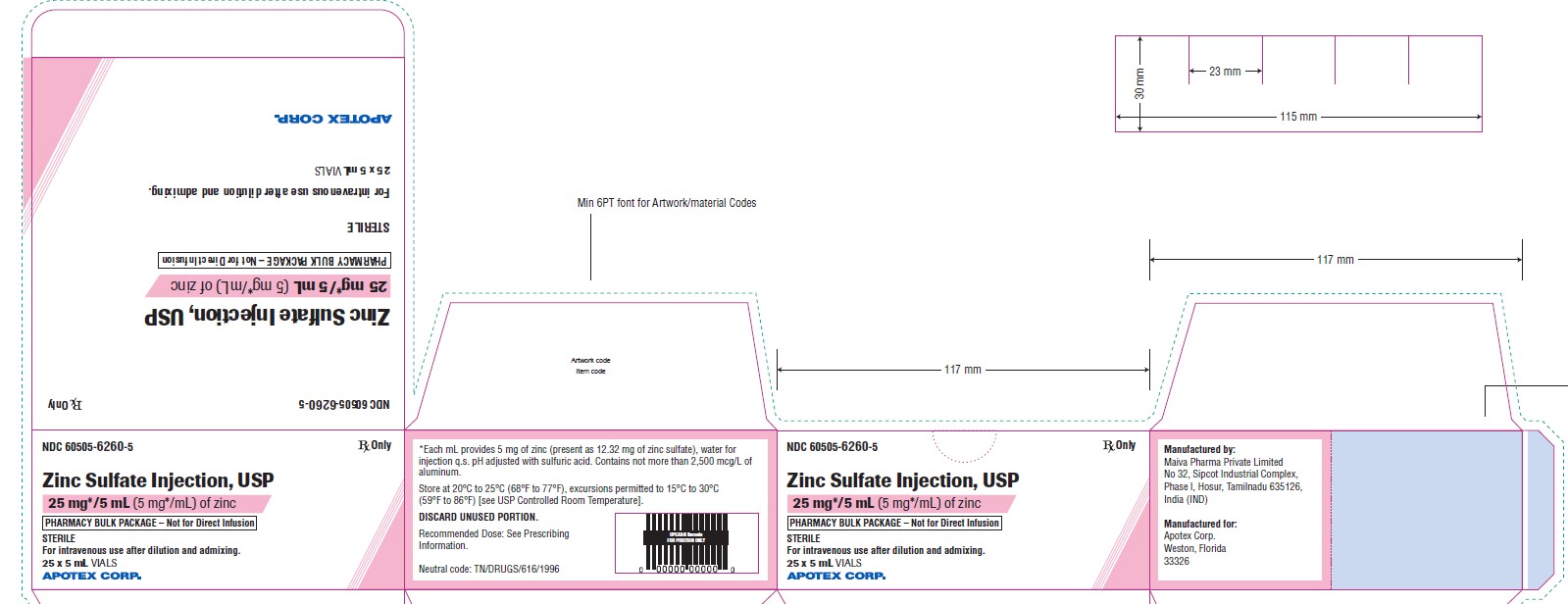
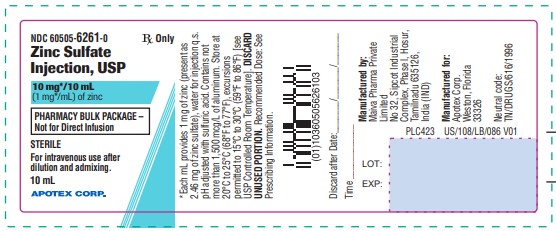
Zinc Sulfate Injection, USP is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, clear, colorless solution intended for use as a trace element and an additive to intravenous solutions for parenteral nutrition.
10 mg/10 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package vial:
Each mL contains 1 mg of zinc present as 2.46 mg of zinc sulfate and water for injection q.s.
25 mg/5 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package vial:
Each mL contains 5 mg of zinc present as 12.32 mg of zinc sulfate and water for injection q.s.
All presentations do not contain preservatives.
The pH range is 2 to 4; pH may be adjusted with sulfuric acid.
1 mg/mL of Zinc Sulfate Injection, USP contains no more than 1,500 mcg/L of aluminum and has a calculated osmolarity of 33 mOsmol/L.
5 mg/mL of Zinc Sulfate Injection, USP contains not more than 2,500 mcg/L of aluminum and has a calculated osmolarity of 157.2 mOsmol/L.
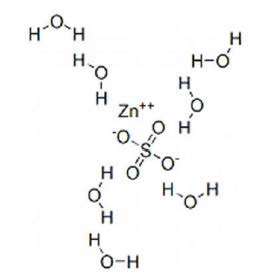
Zinc sulfate heptahydrate has a molecular weight of 287.6 g/mol and a formula of ZnSO4.7H2O.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zinc is an essential trace element. Zinc functions as a cofactor of various enzymes including DNA polymerases, RNA polymerases, alcohol dehydrogenase, and alkaline phosphatases. Zinc is a coordinator of protein structural folding, such as folding of “Zinc finger” motif that interacts with a variety of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. In addition, zinc is a catalyst of essential biochemical reactions, including activation of substrates of carbonic anhydrase in erythrocyte. Also, zinc is a signaling mediator modulating multiple signaling pathways.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Zinc sulfate exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic responses are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics:
Distribution
Over 85% of total body zinc is found in skeletal muscle and bone. Other organs containing zinc are the liver, kidney, skin, brain, and heart. In blood, zinc is mainly localized within erythrocytes. Approximately 80% of serum zinc is bound to albumin and the remainder to alpha2-macroglobulin and amino acids.
Elimination
In adults, zinc is primarily excreted via the gastrointestinal tract and eliminated in the feces. A smaller amount of zinc is excreted via the kidneys in the urine. Urinary zinc excretion rates in very low birth weight preterm infants are relatively high in the neonatal period, and they decline to a level on a body weight basis that is similar to that of normal adults by two months of age. Additionally, endogenous zinc loss occurs from hair, skin desquamation and sweat.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Zinc Sulfate Injection, USP is a clear, colorless solution supplied as:
- 10 mg/10 mL (1 mg/mL) of zinc in a 10 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package vial. Cartons of 25 vials (NDC: 60505-6261-5).
- 25 mg/5 mL (5 mg/mL) of zinc in a 5 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package vial. Cartons of 25 vials (NDC: 60505-6260-5).
Vial closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
For storage of admixed solution see Dosage and Administration (2.3).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients, caregivers or home healthcare providers of the following risks of zinc sulfate injection:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Copper deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
APOTEX INC.
ZINC SULFATE INJECTION, USP
25 mg/5 mL and 10 mg/10 mL
Manufactured by: Manufactured for: Maiva Pharma Private Limited Apotex Corp. No. 32, Sipcot Industrial Complex, Weston, Florida Phase-I, Hosur, Tamilnadu, 635126 India (IND) USA 33326 Revised: September 2024
Rev. 4
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25mg/5mL
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25mg/5mL
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/10 mL
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/10 mL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZINC SULFATE
zinc sulfate injection injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60505-6260 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ZINC SULFATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 89DS0H96TB) (Zinc Cation - UNII:13S1S8SF37) ZINC SULFATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM 5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sulfuric Acid (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60505-6260-5 25 in 1 CARTON 08/01/2024 1 NDC: 60505-6260-0 5 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA218059 08/01/2024 ZINC SULFATE
zinc sulfate injection injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60505-6261 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ZINC SULFATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 89DS0H96TB) (Zinc Cation - UNII:13S1S8SF37) ZINC SULFATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sulfuric Acid (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60505-6261-5 25 in 1 CARTON 01/15/2025 1 NDC: 60505-6261-0 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA218059 01/15/2025 Labeler - Apotex Corp (845263701)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.