ACYCLOVIR- acyclovir sodium injection, solution
Acyclovir by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Acyclovir by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC , Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is a synthetic nucleoside analog, active against herpes viruses. It is a sterile, aqueous solution for intravenous infusion, containing 50 mg acyclovir per mL in Water for Injection, USP. The concentration is equivalent to 54.9 mg of acyclovir sodium per mL in Water for Injection, USP. The sodium content is approximately 5.1 mg/mL. The pH range of the solution is 10.85 to 11.50. Further dilution of Acyclovir Sodium Injection in an appropriate intravenous solution must be performed before infusion (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Administration).
The chemical name of acyclovir sodium is 9-[(2-Hydroxyethoxy)methyl] guanine, and has the following structural formula:
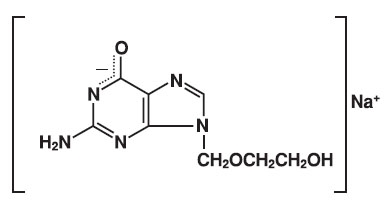
Acyclovir sodium is a white, crystalline powder with the molecular formula C8H10N5NaO3 and a molecular weight of 247.19. The maximum solubility in water at 25°C exceeds 100 mg/mL. At physiologic pH, acyclovir sodium exists as the unionized form with a molecular weight of 225 and a maximum solubility in water at 37°C of 2.5 mg/mL. The pka’s of acyclovir are 2.27 and 9.25.
-
VIROLOGY
Mechanism of Antiviral Action
Acyclovir is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue with in vitro and in vivo inhibitory activity against herpes simplex virus types 1 (HSV-1), 2 (HSV-2) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
The inhibitory activity of acyclovir is highly selective due to its affinity for the enzyme thymidine kinase (TK) encoded by HSV and VZV. This viral enzyme converts acyclovir into acyclovir monophosphate, a nucleotide analogue. The monophosphate is further converted into diphosphate by cellular guanylate kinase and into triphosphate by a number of cellular enzymes. In vitro, acyclovir triphosphate stops replication of herpes viral DNA. This is accomplished in three ways: 1) competitive inhibition of viral DNA polymerase, 2) incorporation into and termination of the growing viral DNA chain, and 3) inactivation of the viral DNA polymerase. The greater antiviral activity of acyclovir against HSV compared to VZV is due to its more efficient phosphorylation by the viral TK.
Antiviral Activities
The quantitative relationship between the in vitro susceptibility of herpes viruses to antivirals and the clinical response to therapy has not been established in humans, and virus sensitivity testing has not been standardized. Sensitivity testing results, expressed as the concentration of drug required to inhibit by 50% the growth of virus in cell culture (IC50), vary greatly depending upon a number of factors. Using plaque-reduction assays, the IC50 against herpes simplex virus isolates ranges from 0.02 to 13.5 mcg/mL for HSV-1 and from 0.01 to 9.9 mcg/mL for HSV-2. The IC50 for acyclovir against most laboratory strains and clinical isolates of VZV ranges from 0.12 to 10.8 mcg/mL. Acyclovir also demonstrates activity against the Oka vaccine strain of VZV with a mean IC50 of 1.35 mcg/mL.
Drug Resistance
Resistance of HSV and VZV to acyclovir can result from qualitative or quantitative changes in the viral TK and/or DNA polymerase. Clinical isolates of HSV and VZV with reduced susceptibility to acyclovir have been recovered from immunocompromised patients, especially with advanced HIV infection. While most of the acyclovir-resistant mutants isolated thus far from such patients have been found to be TK-deficient mutants, other mutants involving the viral TK gene (TK partial and TK altered) and DNA polymerase have been isolated. TK-negative mutants may cause severe disease in infants and immunocompromised adults. The possibility of viral resistance to acyclovir should be considered in patients who show poor clinical response during therapy.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of acyclovir after intravenous administration have been evaluated in adult patients with normal renal function during Phase 1/2 studies after single doses ranging from 0.5 to 15 mg/kg and after multiple doses ranging from 2.5 to 15 mg/kg every 8 hours. Proportionality between dose and plasma levels is seen after single doses or at steady-state after multiple dosing. Average steady-state peak and trough concentrations from 1-hour infusions administered every 8 hours are given in Table 1.
Table 1: Acyclovir Peak and Trough Concentrations at Steady-State
Dosage Regimen
CSSmax
CSStrough
5 mg/kg q 8 h
(n=8)
9.8 mcg/mL
range: 5.5 to 13.8
0.7 mcg/mL
range: 0.2 to 1
10 mg/kg q 8 h
(n=7)
22.9 mcg/mL
range: 14.1 to 44.1
1.9 mcg/mL
range: 0.5 to 2.9
Concentrations achieved in the cerebrospinal fluid are approximately 50% of plasma values. Plasma protein binding is relatively low (9% to 33%) and drug interactions involving binding site displacement are not anticipated.
Renal excretion of unchanged drug is the major route of acyclovir elimination accounting for 62% to 91% of the dose. The only major urinary metabolite detected is 9-carboxymethoxymethylguanine accounting for up to 14.1% of the dose in patients with normal renal function.
The half-life and total body clearance of acyclovir are dependent on renal function as shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Acyclovir Half-life and Total Body Clearance
Creatinine Clearance
(mL/min/1.73 m2)
Total Body Clearance
Half-Life
(hr)
(mL/min/1.73 m2)
(mL/min/kg)
>80
50-80
15-50
0 (Anuric)
2.5
3
3.5
19.5
327
248
190
29
5.1
3.9
3.4
0.5
Special Populations
Adults with Impaired Renal Function
Acyclovir was administered at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg to 6 adult patients with severe renal failure. The peak and trough plasma levels during the 47 hours preceding hemodialysis were 8.5 mcg/mL and 0.7 mcg/mL, respectively.
Consult DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section for recommended adjustments in dosing based upon creatinine clearance.
Pediatrics
Acyclovir pharmacokinetics were determined in 16 pediatric patients with normal renal function ranging in age from 3 months to 16 years at doses of approximately 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg every 8 hours (Table 3). Concentrations achieved at these regimens are similar to those in adults receiving 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg every 8 hours, respectively (Table 1). Acyclovir pharmacokinetics were determined in 12 patients ranging in age from birth to 3 months at doses of 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 15 mg/kg every 8 hours (Table 3).
Table 3: Acyclovir Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Patients (Mean ± SD)
Parameter
Birth to 3 Months of Age
(n=12)
3 Months to 12 Years of Age (n=16)
CL (mL/min/kg)
4.46 ± 1.61
8.44 ± 2.92
VDSS (L/kg)
1.08 ± 0.35
1.01 ± 0.28
Elimination half-life
(hours)
3.80 ± 1.19
2.36 ± 0.97
Geriatrics
Acyclovir plasma concentrations are higher in geriatric patients compared to younger adults, in part due to age-related changes in renal function. Dosage reduction may be required in geriatric patients with underlying renal impairment (see PRECAUTIONS,Geriatric Use).
-
CLINICAL TRIALS
Herpes Simplex Infections in Immuocompromised Patients
A multicenter trial of acyclovir at a dose of 250 mg/m2 every 8 hours (750 mg/m2/day) for 7 days was conducted in 98 immunocompromised patients (73 adults and 25 children) with orofacial, esophageal, genital and other localized infections (52 treated with acyclovir and 46 with placebo). Acyclovir decreased virus excretion, reduced pain, and promoted healing of lesions.
Initial Episodes of Herpes Genitalis
In placebo-controlled trials, 58 patients with initial genital herpes were treated with intravenous acyclovir 5 mg/kg or placebo (27 patients treated with acyclovir and 31 treated with placebo) every 8 hours for 5 days. Acyclovir decreased the duration of viral excretion, new lesion formation, and duration of vesicles, and promoted healing of lesions.
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Sixty-two patients ages 6 months to 79 years with brain biopsy-proven herpes simplex encephalitis were randomized to receive either acyclovir (10 mg/kg every 8 hours) or vidarabine (15 mg/kg/day) for 10 days (28 were treated with acyclovir and 34 with vidarabine). Overall mortality at 12 months for patients treated with acyclovir was 25% compared to 59% for patients treated with vidarabine. The proportion of patients treated with acyclovir functioning normally or with only mild sequelae (e.g., decreased attention span) was 32% compared to 12% of patients treated with vidarabine.
Patients less than 30 years of age and those who had the least severe neurologic involvement at time of entry into study had the best outcome with treatment with acyclovir. An additional controlled study performed in Europe demonstrated similar findings.
Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
Two hundred and two infants with neonatal herpes simplex infections were randomized to receive either acyclovir 10 mg/kg every 8 hours (n=107) or vidarabine 30 mg/kg/day (n=95) for 10 days. Outcomes are presented in Table 4.
Table 4: Mortality at 1 Year
HSV Disease Classification
Treatment Group
Acyclovir
(n=107)
Vidarabine
(n=95)
SEM* (n=85)
0/54
0/31
CNS† (n=71)
5/35
5/36
DISS‡ (n=46)
11/18
14/28
* SEM refers to localized infection with disease limited to skin, eye, and/or mouth.
† CNS refers to infection of the central nervous system with compatible neurologic and CSF findings.
‡ DISS refers to visceral organ involvement such as hepatitis or pneumonitis with or without CNS involvement.
Rates of neurologic sequelae at 1 year were comparable between the treatment groups.
Varicella-Zoster Infections in Immunocompromised Patients
A multicenter trial of acyclovir at a dose of 500 mg/m2 every 8 hours for 7 days was conducted in immunocompromised patients with zoster infections (shingles). Ninety-four (94) patients were evaluated (52 patients were treated with acyclovir and 42 with placebo). Acyclovir was superior to placebo as measured by reductions in cutaneous dissemination and visceral dissemination.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Herpes Simplex Infections in Immunocompromised Patients
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is indicated for the treatment of initial and recurrent mucosal and cutaneous herpes simplex (HSV-1 and HSV-2) in immunocompromised patients.
Initial Episodes of Herpes Genitalis
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is indicated for the treatment of severe initial clinical episodes of herpes genitalis in immuno-competent patients.
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is indicated for the treatment of herpes simplex encephalitis.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is intended for intravenous infusion only, and should not be administered topically, intramuscularly, orally, subcutaneously, or in the eye. Intravenous infusions must be given over a period of at least 1 hour to reduce the risk of renal tubular damage (see PRECAUTIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Renal failure, in some cases resulting in death, has been observed with acyclovir therapy (see ADVERSE REACTIONS,Observed During Clinical Practice and OVERDOSAGE). Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/ hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP/HUS), which has resulted in death, has occurred in immunocompromised patients receiving acyclovir therapy.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Precipitation of acyclovir crystals in renal tubules can occur if the maximum solubility of free acyclovir (2.5 mg/mL at 37°C in water) is exceeded or if the drug is administered by bolus injection. Ensuing renal tubular damage can produce acute renal failure.
Abnormal renal function (decreased creatinine clearance) can occur as a result of acyclovir administration and depends on the state of the patient’s hydration, other treatments, and the rate of drug administration. Concomitant use of other nephrotoxic drugs, pre-existing renal disease, and dehydration make further renal impairment with acyclovir more likely.
Administration of acyclovir by intravenous infusion must be accompanied by adequate hydration.
When dosage adjustments are required, they should be based on estimated creatinine clearance (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Approximately 1% of patients receiving intravenous acyclovir have manifested encephalopathic changes characterized by either lethargy, obtundation, tremors, confusion, hallucinations, agitation, seizures, or coma. Acyclovir should be used with caution in those patients who have underlying neurologic abnormalities and those with serious renal, hepatic, or electrolyte abnormalities, or significant hypoxia.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The data presented below include references to peak steady-state plasma acyclovir concentrations observed in humans treated with 30 mg/kg/day (10 mg/kg every 8 hours, dosing appropriate for treatment of herpes zoster or herpes encephalitis), or 15 mg/kg/day (5 mg/kg every 8 hours, dosing appropriate for treatment of primary genital herpes or herpes simplex infections in immunocompromised patients). Plasma drug concentrations in animal studies are expressed as multiples of human exposure to acyclovir at the higher and lower dosing schedules (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics).
Acyclovir was tested in lifetime bioassays in rats and mice at single daily doses of up to 450 mg/kg administered by gavage. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of tumors between treated and control animals, nor did acyclovir shorten the latency of tumors. At 450 mg/kg/day, plasma concentrations in both the mouse and rat bioassay were lower than concentrations in humans.
Acyclovir was tested in 16 in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicity assays. Acyclovir was positive in 5 of the assays.
Acyclovir did not impair fertility or reproduction in mice (450 mg/kg/day, PO) or in rats (25 mg/kg/day, SC). In the mouse study, plasma levels were the same as human levels, while in the rat study, they were 1 to 2 times human levels. At higher doses (50 mg/kg/day, SC) in rats and rabbits (1 to 2 and 1 to 3 times human levels, respectively) implantation efficacy, but not litter size, was decreased. In a rat peri- and post-natal study at 50 mg/kg/day, SC, there was a statistically significant decrease in group mean numbers of corpora lutea, total implantation sites, and live fetuses.
No testicular abnormalities were seen in dogs given 50 mg/kg/day, IV for 1 month (1 to 3 times human levels) or in dogs given 60 mg/kg/day orally for 1 year (the same as human levels). Testicular atrophy and aspermatogenesis were observed in rats and dogs at higher dose levels.
Pregnancy: Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B.
Acyclovir administered during organogenesis was not teratogenic in the mouse (450 mg/kg/day, PO), rabbit (50 mg/kg/day, SC and IV) or rat (50 mg/kg/day, SC). These exposures resulted in plasma levels the same as, 4 and 9, and 1 and 2 times, respectively, human levels.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. A prospective epidemiologic registry of acyclovir use during pregnancy was established in 1984 and completed in April 1999. There were 749 pregnancies followed in women exposed to systemic acyclovir during the first trimester of pregnancy resulting in 756 outcomes. The occurrence rate of birth defects approximates that found in the general population. However, the small size of the registry is insufficient to evaluate the risk for less common defects or to permit reliable or definitive conclusions regarding the safety of acyclovir in pregnant women and their developing fetuses. Acyclovir should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Acyclovir concentrations have been documented in breast milk in two women following oral administration of acyclovir and ranged from 0.6 to 4.1 times corresponding plasma levels. These concentrations would potentially expose the nursing infant to a dose of acyclovir up to 0.3 mg/kg/day. Acyclovir should be administered to a nursing mother with caution and only when indicated.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of acyclovir did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has identified differences in the severity of CNS adverse events between elderly and younger patients (see ADVERSE REACTIONS,Observed During Clinical Practice). In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased renal function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse reactions listed below have been observed in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials in approximately 700 patients who received acyclovir at approximately 5 mg/kg (250 mg/m2) 3 times daily, and approximately 300 patients who received approximately 10 mg/kg (500 mg/m2) 3 times daily.
The most frequent adverse reactions reported during administration of acyclovir were inflammation or phlebitis at the injection site in approximately 9% of the patients, and transient elevations of serum creatinine or BUN in 5% to 10% (the higher incidence occurred usually following rapid [less than 10 minutes] intravenous infusion). Nausea and/or vomiting occurred in approximately 7% of the patients (the majority occurring in nonhospitalized patients who received 10 mg/kg). Itching, rash, or hives occurred in approximately 2% of patients. Elevation of transaminases occurred in 1% to 2% of patients.
The following hematologic abnormalities occurred at a frequency of less than 1%: anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia. In addition, anorexia and hematuria were observed.
Observed During Clinical Practice
In addition to adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been identified during post-approval use of Acyclovir Sodium Injection in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, potential causal connection to acyclovir, or a combination of these factors.
General: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, fatigue, fever, headache, pain, peripheral edema.
Digestive: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, gastrointestinal distress, nausea.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension.
Hematologic and Lymphatic: Disseminated intravascular coagulation, hemolysis,leukocytoclastic vasculitis, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy.
Hepatobiliary Tract and Pancreas: Elevated liver function tests, hepatitis, hyperbilirubinemia,jaundice.
Musculoskeletal: Myalgia.
Nervous: Aggressive behavior, agitation, ataxia, coma, confusion, delirium, dizziness, dysathria, encephalopathy, hallucinations, obtundation, paresthesia, psychosis, seizure, somnolence, tremor. These symptoms may be marked, particularly in older adults (see PRECAUTIONS).
Skin: Alopecia, erythema multiforme, photosensitive rash, pruritus, rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria. Severe local inflammatory reactions, including tissue necrosis, have occurred following infusion of acyclovir into extravascular tissues.
Special Senses: Visual abnormalities.
Urogenital: Renal failure, elevated blood urea nitrogen, elevated creatinine (see WARNINGS).
-
OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses involving ingestions of up to 20 g have been reported. Adverse events that have been reported in association with overdosage include agitation, coma, seizures, and lethargy. Precipitation of acyclovir in renal tubules may occur when the solubility (2.5 mg/mL) is exceeded in the intratubular fluid. Overdosage has been reported following bolus injections or inappropriately high doses, and in patients whose fluid and electrolyte balance were not properly monitored. This has resulted in elevated BUN and serum creatinine, and subsequent renal failure. In the event of acute renal failure and anuria, the patient may benefit from hemodialysis until renal function is restored (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CAUTION - RAPID OR BOLUS INTRAVENOUS INJECTION MUST BE AVOIDED (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
INTRAMUSCULAR OR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION MUST BE AVOIDED (see WARNINGS).
Therapy should be initiated as early as possible following onset of signs and symptoms of herpes infections.
A maximum dose equivalent to 20 mg/kg every 8 hours should not be exceeded for any patient.
Dosage
HERPES SIMPLEX INFECTIONS
MUCOSAL AND CUTANEOUS HERPES SIMPLEX (HSV-1 and HSV-2)
INFECTIONS IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PATIENTS:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older):
5 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Pediatrics (Under 12 years of age):
10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
SEVERE INITIAL CLINICAL EPISODES OF HERPES GENITALIS:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older):
5 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 5 days.
HERPES SIMPLEX ENCEPHALITIS:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older):
10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days.
Pediatrics (3 months to 12 years of age):
20 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days.
Neonatal Herpes Simplex Virus Infections (Birth to 3 months):
10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 10 days. In neonatal herpes simplex infections, doses of 15 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg (infused at a constant rate over 1 hour every 8 hours) have been used; the safety and efficacy of these doses are not known.
VARICELLA-ZOSTER INFECTIONS
ZOSTER IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PATIENTS:
Adults and Adolescents (12 years of age and older:
10 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Pediatrics (Under 12 years of age):
20 mg/kg infused at a constant rate over 1 hour, every 8 hours for 7 days.
Obese Patients
Obese patients should be dosed at the recommended adult dose using Ideal Body Weight.
PATIENTS WITH ACUTE OR CHRONIC RENAL IMPAIRMENT: Refer to DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section for recommended doses, and adjust the dosing interval as indicated in Table 5.
Table 5: Dosage Adjustments for Patients with Renal Impairment
Creatinine Clearance
(mL/min/1.73 m2)
Percent of
Recommended Dose
Dosing Interval
(hours)
>50
25 to 50
10 to 25
0 to 10
100%
100%
100%
50%
8
12
24
24
Hemodialysis
For patients who require dialysis, the mean plasma half-life of acyclovir during hemodialysis is approximately 5 hours. This results in a 60% decrease in plasma concentrations following a six-hour dialysis period. Therefore, the patient’s dosing schedule should be adjusted so that an additional dose is administered after each dialysis.
Peritoneal Dialysis
No supplemental dose appears to be necessary after adjustment of the dosing interval.
Administration
The calculated dose should be further diluted in an appropriate intravenous solution at a volume selected for administration during each 1 hour infusion. Infusion concentrations of approximately 7 mg/mL or lower are recommended. In clinical studies, the average 70 kg adult received between 60 and 150 mL of fluid per dose. Higher concentrations (e.g., 10 mg/mL) may produce phlebitis or inflammation at the injection site upon inadvertent extravasation. Standard, commercially available electrolyte and glucose solutions are suitable for intravenous administration; biologic or colloidal fluids (e.g., blood products, protein solutions, etc.) are not recommended.
Once diluted for administration, each dose should be used within 24 hours.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Acyclovir Sodium Injection is available as:
Product
No.
NDC
No.
Strength
PRX302510
63323-325-14
500 mg per 10 mL (50 mg per mL) Acyclovir Sodium Injection equivalent to acyclovir, in a 10 mL plastic vial, in packages of 10.
PRX302520
63323-325-24
1,000 mg per 20 mL (50 mg per mL) Acyclovir Sodium Injection equivalent to acyclovir, in a 20 mL plastic vial, in packages of 10.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Discard unused portion.
This container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
PREMIERPro™ Rx is a trademark of Premier, Inc., used under license.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Acyclovir 20 mL Single Dose Vial Label
NDC 63323-325-24
PRX302520
Acyclovir Sodium Injection
1,000 mg per 20 mL* (50 mg per mL)
For IV Infusion Only
Must Be Diluted Prior To Use
20 mL Single Dose Vial
Rx only

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY - Acyclovir 20 mL Single Dose Vial Tray Label
NDC 63323-325-24
PRX302520
Acyclovir Sodium Injection
1,000 mg per 20 mL* (50 mg per mL)
For IV Infusion Only
Must Be Diluted Prior To Use
20 mL Single Dose Vial
10 Vials
Rx only

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ACYCLOVIR
acyclovir sodium injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-325 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ACYCLOVIR SODIUM (UNII: 927L42J563) (ACYCLOVIR - UNII:X4HES1O11F) ACYCLOVIR 50 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-325-14 10 in 1 TRAY 10/17/2000 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 63323-325-24 10 in 1 TRAY 10/17/2000 2 20 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA074930 10/17/2000 Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC 840771732 MANUFACTURE(63323-325)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
