THYMOGLOBULIN (anti-thymocyte globulin- rabbit injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Thymoglobulin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Thymoglobulin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Genzyme Corporation, Genzyme Polyclonals S.A.S., Genzyme Ireland Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use THYMOGLOBULIN® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for THYMOGLOBULIN.
THYMOGLOBULIN (anti-thymocyte globulin [rabbit]) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
THYMOGLOBULIN should only be used by physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy in transplantation. (5.1)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The first dose should be infused over at least 6 hours; doses on subsequent days should be infused over at least 4 hours. (2.2)
- Premedication with corticosteroids, acetaminophen, and/or an antihistamine prior to each infusion is recommended. (2.2)
- The THYMOGLOBULIN dose should be reduced by one-half if the white blood cell (WBC) count is between 2,000 and 3,000 cells/mm3 or if the platelet count is between 50,000 and 75,000 cells/mm3. Stopping THYMOGLOBULIN treatment should be considered if the WBC count falls below 2,000 cells/mm3 or if the platelet count falls below 50,000 cells/mm3. (2.3)
Indication Dose Prophylaxis of acute rejection 1.5 mg/kg of body weight administered daily for 4 to 7 days Treatment of acute rejection 1.5 mg/kg of body weight administered daily for 7 to 14 days For complete dosing instructions, see full prescribing information. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Single-dose 10 mL vial containing 25 mg of anti-thymocyte globulin (rabbit) lyophilized, sterile powder. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Allergy or anaphylactic reaction to rabbit proteins or to any product excipients, or active acute or chronic infections which contraindicate any additional immunosuppression (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- THYMOGLOBULIN should only be used by physicians experienced in immunosuppressant therapy in transplantation. (5.1)
- Immune-mediated reactions: THYMOGLOBULIN infusion could result in an anaphylactic reaction. (5.2)
- Infusion-associated reactions: Close compliance with the recommended infusion time may reduce the incidence and severity of infusion-associated reactions. (5.3)
- Hematologic effects: low counts of platelets and white blood cells have been identified and are reversible following dose adjustments. Monitor total white blood cell and platelet counts. (5.4)
- Infection: Infections and reactivation of infections have been reported. Monitor patients and administer anti-infective prophylaxis. (5.5)
- Malignancy: Incidence of malignancies may increase. (5.6)
- Immunization with attenuated live vaccines is not recommended for patients who have recently received THYMOGLOBULIN. (5.7)
- THYMOGLOBULIN may interfere with rabbit antibody–based immunoassays and with cross-match or panel-reactive antibody cytotoxicity assays. (5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities (incidence >5% higher than comparator) are urinary tract infection, abdominal pain, hypertension, nausea, shortness of breath, fever, headache, anxiety, chills, increased potassium levels in the blood, low counts of platelets and white blood cells. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genzyme Corporation at 1-800-633-1610 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dosing Regimen
2.3 Dose Modifications
2.4 Recommended Concomitant Medication
2.5 Instructions for Dilution and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Management of Immunosuppression
5.2 Immune-Mediated Reactions
5.3 Infusion-Associated Reactions
5.4 Hematologic Effects
5.5 Infection
5.6 Malignancy
5.7 Immunizations
5.8 Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection in Patients Receiving a Kidney Transplant
14.2 Treatment of Acute Rejection in Patients Receiving a Kidney Transplant
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: IMMUNOSUPPRESSION
THYMOGLOBULIN should only be used by physicians experienced in immunosuppressive therapy in transplantation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
THYMOGLOBULIN is intended for intravenous use only.
2.1 Dosing Information
Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection
The recommended dosage of THYMOGLOBULIN for prophylaxis of acute rejection in patients receiving a kidney transplant is 1.5 mg/kg of body weight administered daily with the first dose initiated prior to reperfusion of the donor kidney. The usual duration of administration is 4 to 7 days.
2.2 Recommended Dosing Regimen
Administer the first dose of THYMOGLOBULIN over a minimum of 6 hours; administer doses on subsequent days over at least 4 hours [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Premedication with corticosteroids, acetaminophen, and/or an antihistamine 1 hour prior to each infusion of THYMOGLOBULIN is recommended and may reduce the incidence and intensity of infusion-associated reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
2.3 Dose Modifications
Monitor patients for adverse reactions during and after infusion. Monitor total white blood cell and platelet counts during and after THYMOGLOBULIN therapy.
Reduce the THYMOGLOBULIN dose by one-half if the white blood cell (WBC) count is between 2,000 and 3,000 cells/mm3 or if the platelet count is between 50,000 and 75,000 cells/mm3. Consider stopping THYMOGLOBULIN treatment if the WBC count falls below 2,000 cells/mm3 or if the platelet count falls below 50,000 cells/mm3.
2.4 Recommended Concomitant Medication
THYMOGLOBULIN is used with concomitant immunosuppressants.
Administer prophylactic antifungal and antibacterial therapy if clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Antiviral prophylactic therapy is recommended for patients who are seropositive for cytomegalovirus (CMV) at the time of transplant and for CMV-seronegative patients scheduled to receive a kidney from a CMV-seropositive donor [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.5 Instructions for Dilution and Administration
Reconstitution
After calculating the number of vials needed, using aseptic technique, reconstitute each vial of THYMOGLOBULIN with 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI).
- Allow THYMOGLOBULIN vials to reach room temperature before reconstituting the lyophilized product.
- Aseptically remove caps to expose rubber stoppers.
- Clean stoppers with germicidal or alcohol swab.
- Aseptically reconstitute each vial of THYMOGLOBULIN lyophilized powder with the 5 mL of SWFI.
- Rotate vial gently until powder is completely dissolved. Each reconstituted vial contains 25 mg or 5 mg/mL of THYMOGLOBULIN.
- Inspect solution for particulate matter after reconstitution. Should some particulate matter remain, continue to gently rotate the vial until no particulate matter is visible. If particulate matter persists, discard this vial.
Dilution
- Transfer the contents of the calculated number of THYMOGLOBULIN vials into the bag of infusion solution (saline or dextrose). Recommended volume: per one vial of THYMOGLOBULIN use 50 mL of infusion solution (total volume usually between 50 to 500 mL). Discard unused portion.
- Mix the solution by inverting the bag gently only once or twice.
Infusion
Administer THYMOGLOBULIN under strict medical supervision in a hospital setting, and carefully monitor patients during the infusion.
THYMOGLOBULIN is less likely to produce side effects when administered at the recommended flow rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for the infusion administration set. Infuse through a 0.22 micrometer filter into a high-flow vein.
- Set the flow rate to deliver the dose over a minimum of 6 hours for the first dose and over at least 4 hours for subsequent doses.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
THYMOGLOBULIN is contraindicated in patients with history of allergy or anaphylactic reaction to rabbit proteins or to any product excipients, or who have active acute or chronic infections that contraindicate any additional immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Management of Immunosuppression
To prevent over-immunosuppression, physicians may wish to decrease the dose of the maintenance immunosuppression regimen during the period of THYMOGLOBULIN use.
Dosing for THYMOGLOBULIN is different from dosing for other anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) products, because protein composition and concentrations vary depending on the source of ATG. The prescribing physician must ensure that the dose prescribed is appropriate for the ATG product being administered.
5.2 Immune-Mediated Reactions
Serious immune-mediated reactions, including anaphylaxis or severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS), have been reported with the use of THYMOGLOBULIN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Fatal anaphylaxis has been reported. If an anaphylactic reaction occurs, terminate the infusion immediately. Provide emergency treatment, such as 0.3 mL to 0.5 mL aqueous epinephrine (1:1000 dilution) subcutaneously and other resuscitative measures including oxygen, intravenous fluids, antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines, and airway management, as clinically indicated.
5.3 Infusion-Associated Reactions
Cases consistent with cytokine release syndrome (CRS) have been reported with rapid infusion rates. CRS is attributed to the release of cytokines by activated monocytes and lymphocytes. Severe acute CRS can cause serious cardiorespiratory events and/or death [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Close compliance with the recommended dosage and infusion time may reduce the incidence and severity of infusion-associated reactions (IARs). Slowing the infusion rate may minimize many of these IARs.
Reactions at the infusion site may include pain, swelling, and redness of the skin.
5.4 Hematologic Effects
Low counts of platelets and white blood cells (including low counts of lymphocytes and neutrophils) have been identified and are reversible following dose adjustments. Total white blood cell and platelet counts should be monitored [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Infection
THYMOGLOBULIN is routinely used in combination with other immunosuppressive agents. Infections (bacterial, fungal, viral and protozoal), reactivation of infection (particularly cytomegalovirus [CMV]) and sepsis have been reported after THYMOGLOBULIN administration in combination with multiple immunosuppressive agents. These infections can be fatal.
Monitor patients carefully and administer appropriate anti-infective treatment when indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Malignancy
Use of immunosuppressive agents, including THYMOGLOBULIN, may increase the incidence of malignancies, including lymphoma or lymphoproliferative disorders. These events have been associated with fatal outcome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities (incidence >5% higher than comparator) are urinary tract infection, abdominal pain, hypertension, nausea, shortness of breath, fever, headache, anxiety, chills, increased potassium levels in the blood, and low counts of platelets and white blood cells.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection
The efficacy and safety of THYMOGLOBULIN compared to Active Comparator for the prophylaxis of acute rejection in patients receiving a kidney transplant were evaluated in a randomized, open-label, international, multicenter trial in patients receiving solitary kidneys from deceased donors (n=278). There were more Adverse Reactions (incidence >5%) occurring within 12 months of transplantation in the THYMOGLOBULIN group than in the Active Comparator group (Table 1).
Table 1: Adverse Reactions* and Laboratory Abnormalities Reported More Frequently (incidence† >5%) Following THYMOGLOBULIN versus Active Comparator‡ Adverse Reaction
[n (%)†]THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=141)Active Comparator
(N=137)- * Adverse reactions are treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) reported as related to the study agent in at least 1 patient.
- † Number (percentage) is shown regardless of causal relationship.
- ‡ basiliximab
- § Hyperkalemia: blood potassium ≥5.5 mmol/L; Leukopenia: WBC <3000 cells/mm3. Thrombocytopenia: platelet count <75,000 cells/mm3.
Urinary tract infection 55 (39%) 36 (26%) Pyrexia
(fever)39 (28%) 25 (18%) Headache 26 (18%) 17 (12%) Hyperlipidemia
(high lipids in blood)21 (15%) 9 (7%) Anxiety 20 (14%) 12 (9%) Chills 13 (9%) 5 (4%) Laboratory Abnormalities§ Hyperkalemia
(high potassium)81 (57%) 70 (51%) Leukopenia
(low white blood cell count)89 (63%) 20 (15%) Thrombocytopenia
(low platelet count)23 (16%) 7 (5%) Hematologic Abnormalities
The incidence of laboratory abnormalities of leukopenia with WBC<3000 cells/mm3 was 63% in THYMOGLOBULIN patients and 15% in Active Comparator patients. The incidence of thrombocytopenia laboratory abnormalities with platelets <75,000 cells/ mm3 within 1 month following transplantation was 16% in THYMOGLOBULIN patients and 5% in Active Comparator patients.
Malignancies
Six patients in the THYMOGLOBULIN group developed malignancies (Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoma of the cavum, Epstein-Barr virus-positive large B-cell lung lymphoma, Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoma of the brain, squamous cell carcinoma, renal cancer, and recurrent basal cell carcinoma). In the Active Comparator group, 1 patient developed renal cancer.
Infections
Infections occurred in 76% of THYMOGLOBULIN-treated patients (severe in 23%), and in 63% of Active Comparator-treated patients (severe in 15%).
Infections occurring in ≥5% of the patients in either treatment group during the 12-month follow-up are summarized in Table 2. Urinary tract infection was the most frequent type of infection, and was reported as severe in 9% of THYMOGLOBULIN-treated patients and in 2% of Active Comparator-treated patients. CMV infections were reported more frequently in the Active Comparator group, with an incidence of 6% (severe in 1%) in THYMOGLOBULIN-treated patients and of 18% (severe in 7%) in Active Comparator-treated patients. Patients who were CMV-positive at the time of transplant, as well as CMV-negative recipients of transplants from CMV-positive donors, were required to receive antiviral prophylaxis for 3 months after transplant.
Table 2: Infections Reported in ≥5% of Study Patients Infection THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=141)Active Comparator*
(N=137)All Severe/Unknown All Severe/Unknown - * basiliximab
- † Urinary tract infection group includes: Urinary tract infections, Urinary tract infection fungal, Urinary tract infection bacterial, Bacterial pyelonephritis, Urosepsis.
- ‡ Sepsis group includes: Sepsis, Escherichia sepsis, Staphylococcal bacteremia.
- § Lower respiratory tract and lung infections group includes: Lower respiratory tract and lung infections, and Pneumonia pseudomonal.
- ¶ The collective term "cytomegaloviral infections" includes CMV duodenitis, CMV gastritis, CMV hepatitis, CMV infection, and CMV viremia.
Urinary tract infections† 59 (42%) 12 (9%) 39 (29%) 3 (2%) Sepsis‡ 9 (6%) 5 (4%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) Lower respiratory tract and lung infections§ 18 (13%) 2 (1%) 16 (12%) 4 (3%) Upper respiratory tract infection 15 (11%) 0 15 (11%) 1 (1%) Nasopharyngitis 7 (5%) 0 9 (7%) 0 Cytomegaloviral infections¶ 8 (6%) 2 (1%) 21 (18%) 7 (7%) Herpes zoster 7 (5%) 0 2 (2%) 1 (1%) Oral candidiasis 8 (6%) 0 11 (8%) 0 Adverse Drug Reactions Occurring within 24 Hours and Infusion-Associated Reactions
Adverse reactions occurring during or within 24 hours of infusion in >5% of patients in the THYMOGLOBULIN group are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Adverse Drug Reactions* Occurring within 24 Hours of Infusion and with >5% Incidence in Patients who Received THYMOGLOBULIN Primary System Organ Class
n (%)THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=141)Active Comparator†
(N=137)- * Adverse reactions that occurred during or within 24 hours of an infusion, and where the incidence was higher in the THYMOGLOBULIN group.
- † basiliximab
Constipation 47 (33%) 23 (17%) Anemia
(low red blood cell count)35 (25%) 19 (14%) Hyperkalemia
(high potassium)33 (23%) 18 (13%) Hypertension
(elevated blood pressure)25 (18%) 19 (14%) Leukopenia and White blood cell count decreased 29 (21%) 0 Pyrexia
(fever)18 (13%) 3 (2%) Vomiting 17 (12%) 14 (10%) Thrombocytopenia
(low platelet count)13 (9%) 1 (1%) Abdominal pain 11 (8%) 6 (4%) Anxiety 10 (7%) 2 (2%) Hyperphosphatemia
(high phosphate)10 (7%) 2 (2%) Tachycardia
(fast heart rate)10 (7%) 5 (4%) Acidosis
(accumulation of acid in the body)9 (6%) 8 (6%) Diarrhea 9 (6%) 1 (1%) Hypokalemia
(low potassium)9 (6%) 4 (3%) Infusion-associated reactions
Adverse reactions that occurred within 24 hours after the completion of the THYMOGLOBULIN administration and are considered as possible infusion associated reactions (IARs) include the following: anxiety, confusional state, agitation, restlessness, headache, lethargy, dizziness, decreased sensitivity, fast heart rate, myocardial infarction, elevated blood pressure, decreased blood pressure, cough, throat irritation, reduced oxygen supply to tissues, shortness of breath, pulmonary edema, pain in mouth and throat, diarrhea, upper abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, abdominal discomfort, nausea, pruritus, rash, joint pain, fever, chills, lack of energy, localized edema, malaise, and chest pain.
Serum sickness was reported in 6 of 405 patients enrolled across completed studies where patients had been treated with THYMOGLOBULIN for the prophylaxis of acute rejection in patients receiving a kidney transplant. Anaphylactic shock was reported in 2 of 405 patients enrolled across completed studies.
Treatment of acute rejection
In the US Phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial (n=163) comparing the efficacy and safety of THYMOGLOBULIN and Active Comparator in the treatment of acute rejection in kidney transplant patients, adverse reactions occurring at least 5% more frequently in the THYMOGLOBULIN group than in the Active Comparator group are shown in Table 4. Malignancies were reported in 3 patients who received THYMOGLOBULIN and in 3 patients who received Active Comparator during the one-year follow-up period. These included two cases of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) in the THYMOGLOBULIN group and two cases of PTLD in the Active Comparator group.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions* Reported More Frequently (incidence ≥5%) Following THYMOGLOBULIN versus Active Comparator† Frequently Reported Events THYMOGLOBULIN
n=82Active Comparator
n=81- * Treatment-emergent adverse events/reactions (TEAE) are summarized.
- † Anti-thymocyte globulin equine (ATG-E)
Chills 47 (57%) 35 (43%) Leukopenia
(low white blood cell count)47 (57%) 24 (30%) Headache 33 (40%) 28 (35%) Abdominal pain 31 (38%) 22 (27%) Hypertension
(elevated blood pressure)30 (37%) 23 (28%) Nausea 30 (37%) 23 (28%) Dyspnea 23 (28%) 16 (20%) Hyperkalemia
(high potassium)22 (27%) 15 (19%) Myalgia 16 (20%) 10 (12%) Insomnia 16 (20%) 10 (12%) Hypotension
(decreased blood pressure)13 (16%) 6 (7%) Rash 11 (13%) 6 (7%) Sweating 11 (13%) 4 (5%) Malaise 11 (13%) 3 (4%) Acne 10 (12%) 4 (5%) Overdose 5 (6%) 0 Treatment-emergent thrombocytopenia was reported in 30 (37%) of patients following THYMOGLOBULIN infusion and in 36 (44%) of patients following Active Comparator infusion.
Infections occurring more frequently in the THYMOGLOBULIN group during the 3-month follow-up are summarized in Table 5. No significant differences were seen between the THYMOGLOBULIN and Active Comparator groups for all types of infections. The incidence of CMV infection was the same in both groups. Viral prophylaxis was by the center's discretion during antibody treatment, but all centers used ganciclovir infusion during treatment.
Table 5: Infections THYMOGLOBULIN
n=82Active Comparator*
n=81Body System No. of Patients (%) Total Reports No. of Patients (%) Total Reports - * ATG-E
Body as a Whole 30 (37) 36 22 (27) 29 Infection 25 (31) 26 19 (24) 21 Other 14 (17) 15 11 (14) 12 CMV 11 (13) 11 9 (11) 9 Sepsis 10 (12) 10 7 (10) 7 Digestive 5 (6) 5 3 (4) 3 Gastrointestinal moniliasis 4 (5) 4 1 (1) 1 Gastritis 1 (1) 1 0 (0) 0 Skin 4 (5) 4 0 (0) 0 Herpes simplex 4 (5) 4 0 (0) 0 Adverse reactions occurring during or shortly following THYMOGLOBULIN infusion (infusion-associated adverse reactions) are generally manageable or reversible. Adverse reactions occurring during or within 24 hours of infusion in at least 5% of patients in the THYMOGLOBULIN group are listed in Table 6.
Table 6: Adverse Reactions* Occurring within 24 Hours of Infusion and with >5% Incidence in THYMOGLOBULIN Patients Adverse Reaction THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=82)Active Comparator*
(N=81)* Treatment-emergent adverse events that occurred during or within 24 hours of an infusion are summarized. - * ATG-E
Chills 45 (55%) 28 (35%) Leukopenia
(low white blood cell count)40 (49%) 10 (12%) Fever 38 (46%) 39 (48%) Nausea 24 (29%) 17 (21%) Thrombocytopenia
(low platelet count)24 (29%) 30 (37%) Headache 22 (27%) 22 (27%) Hypertension 22 (27%) 16 (20%) Pain 21 (26%) 19 (24%) Tachycardia
(fast heart rate)19 (23%) 16 (20%) Diarrhea 16 (20%) 15 (19%) Peripheral edema
(swelling)16 (20%) 13 (16%) Vomiting 16 (20%) 12 (15%) Abdominal pain 14 (17%) 13 (16%) Hyperkalemia
(increased potassium level)14 (17%) 12 (15%) Arthralgia
(joint pain)12 (15%) 11 (14%) Constipation 12 (15%) 16 (20%) Dyspnea
(shortness of breath)12 (15%) 11 (14%) Asthenia
(lack of energy)11 (13%) 11 (14%) Leukocytosis
(increased amount of white blood cells)11 (13%) 9 (11%) Anemia
(decreased amount of red blood cells or hemoglobin)10 (12%) 11 (14%) Back pain 10 (12%) 8 (10%) Hypokalemia
(decreased potassium level)10 (12%) 7 (9%) Insomnia 10 (12%) 4 (5%) Lung disorder 10 (12%) 6 (7%) Myalgia 9 (11%) 7 (9%) Dyspepsia 8 (10%) 6 (7%) Hypotension
(decreased blood pressure)8 (10%) 2 (3%) Acidosis
(accumulation of acid in the body)7 (9%) 4 (5%) Chest pain 7 (9%) 7 (9%) Malaise 7 (9%) 3 (4%) Anxiety 6 (7%) 8 (10%) Anorexia 5 (6%) 1 (1%) Cough increased 6 (7%) 8 (10%) Rash 6 (7%) 4 (5%) Edema 5 (6%) 12 (15%) Hypophosphatemia
(decreased phosphate)5 (6%) 3 (4%) Itchiness 5 (6%) 4 (5%) Sweating 5 (6%) 4 (5%) Treatment-emergent serum sickness was reported in 2 (2%) of patients following THYMOGLOBULIN infusion and in no patients following Active Comparator infusion.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of THYMOGLOBULIN. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infusion-Associated Reactions and Immune System Disorders
IARs may occur following the administration of THYMOGLOBULIN and may occur as soon as the first or second infusion during a single course of THYMOGLOBULIN treatment. Clinical manifestations of IARs have included the following signs and symptoms: fever, chills/rigors, dyspnea, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, hypotension or hypertension, malaise, rash, urticaria, decreased oxygen saturation, and/or headache. IARs with THYMOGLOBULIN are generally manageable with a reduction in infusion rates and/or with medications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Some of these reactions such as arthralgia/myalgia, lymphadenopathy, proteinuria, and decreased oxygen saturation tend to occur 5 to 15 days after THYMOGLOBULIN infusion and are consistent with serum sickness. Symptoms are manageable with corticosteroid treatment.
Serious and fatal anaphylactic reactions have been reported. The fatalities occurred in patients who did not receive epinephrine during the event [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
IARs consistent with cytokine release syndrome (CRS) have been reported. Severe and potentially life-threatening CRS cases have also been reported. Postmarketing reports of severe CRS have included cardiorespiratory dysfunction (including hypotension, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema, myocardial infarction, tachycardia, and/or death).
Hepatic Disorders
Transient reversible elevations in aminotransferases without any clinical signs or symptoms have also been reported during THYMOGLOBULIN administration.
Immunosuppression-Related Disorders
Infections, reactivation of infection, febrile neutropenia, and sepsis have been reported after THYMOGLOBULIN administration in combination with multiple immunosuppressive agents, which may be fatal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Malignancies including, but not limited to, lymphoproliferative disorders (LPD) and solid tumors have been reported. These events have been associated with fatal outcome. These adverse reactions were reported with use of a combination of multiple immunosuppressive agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No drug interaction studies have been performed.
THYMOGLOBULIN can stimulate the production of antibodies that cross-react with rabbit immune globulins [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of THYMOGLOBULIN in pediatric patients have not been established in controlled trials. However, based on limited European studies and U.S. compassionate use, the dose, efficacy, and adverse reaction profile are not thought to be different than for adults.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
THYMOGLOBULIN overdosage may result in leukopenia (including lymphopenia and neutropenia) and/ or thrombocytopenia, which can be managed with dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
THYMOGLOBULIN® (anti-thymocyte globulin [rabbit]) is a purified, pasteurized, immunoglobulin G, obtained by immunization of rabbits with human thymocytes. This immunosuppressive product contains cytotoxic antibodies directed against antigens expressed on human T-lymphocytes.
THYMOGLOBULIN is a sterile, lyophilized powder for intravenous administration after reconstitution with sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI). Each single-dose 10 mL vial contains 25 mg of anti-thymocyte globulin (rabbit), 50 mg glycine, 10 mg sodium chloride, and 50 mg mannitol.
After reconstitution with 5 mL SWFI, each vial of reconstituted product contains approximately 5 mg/mL of THYMOGLOBULIN, of which >90% is rabbit gamma immune globulin (IgG). The reconstituted solution has a pH of 6.5 to 7.2.
Human red blood cells are used in the manufacturing process to deplete cross-reactive antibodies to non–T-cell antigens. The manufacturing process is validated to remove or inactivate potential exogenous viruses. All human red blood cells are from U.S.-registered or FDA-licensed blood banks. A virus removal step (nanofiltration, using a 20 nm filter) and a viral inactivation step (pasteurization, i.e., heat treatment of active ingredient at 60°C/10 hr) are performed for each lot. Each THYMOGLOBULIN lot is released following potency testing (lymphocytotoxicity and E-rosette inhibition assays), and cross-reactive antibody testing (hemagglutination, platelet agglutination, antiglomerular basement membrane antibody, and fibroblast toxicity assays on every lot).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action by which polyclonal antilymphocyte preparations suppress immune responses is not fully understood. Possible mechanisms by which THYMOGLOBULIN may induce immunosuppression in vivo include: T-cell clearance from the circulation and modulation of T-cell activation, homing, and cytotoxic activities. THYMOGLOBULIN includes antibodies against T-cell markers such as CD2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11a, CD18, CD25, CD44, CD45, HLA-DR, HLA Class I heavy chains, and ß2 micro-globulin. In vitro, THYMOGLOBULIN (concentrations >0.1 mg/mL) mediates T-cell suppressive effects via inhibition of proliferative responses to several mitogens. In patients, T-cell depletion is usually observed within a day after initiating THYMOGLOBULIN therapy.
THYMOGLOBULIN has not been shown to be effective for treating antibody-mediated (humoral) rejections.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After an intravenous dose of 1.25 to 1.5 mg/kg/day (over 4 hours for 7–11 days) 4–8 hours post infusion, THYMOGLOBULIN levels were on average 21.5 mcg/mL (10–40 mcg/mL) with a half-life of 2–3 days after the first dose, and 87 mcg/mL (23–170 mcg/mL) after the last dose.
During the THYMOGLOBULIN Phase 3 randomized trial for the treatment of acute rejection, of the 108 of 163 patients evaluated, anti-rabbit antibodies developed in 68% of the THYMOGLOBULIN-treated patients, and anti-horse antibodies developed in 78% of the Active Comparator-treated patients. No controlled studies have been conducted to study the effect of anti-rabbit antibodies on repeat use of THYMOGLOBULIN. However, to ensure that T-cell depletion is achieved upon retreatment with THYMOGLOBULIN, monitoring the lymphocyte count is recommended. T-cell counts based on data collected from a limited number of patients (n=12) in this study, are presented in the chart below. These data were collected using flow cytometry (FACSCAN, Becton-Dickinson).
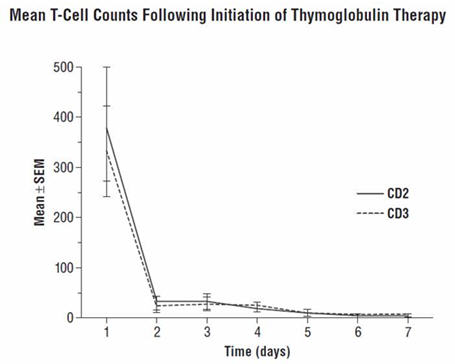
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection in Patients Receiving a Kidney Transplant
Study 1
THYMOGLOBULIN was evaluated in an open-label, randomized, active-controlled study in kidney transplant patients (n=278) at increased risk of acute rejection or delayed graft function.
The treatment failure rate within 12 months post-transplantation was statistically significantly lower in the THYMOGLOBULIN group than in the Active Comparator group (25% vs 38%; p=0.02), based on the composite endpoint (biopsy-proven acute rejection [BPAR], graft loss [GL], or death, with "lost to follow-up" considered as a treatment failure). The individual elements of the composite endpoint were BPAR (13% vs 21%), GL (8% vs 10%), and death (4% vs 4%) for the THYMOGLOBULIN and Active Comparator groups, respectively (Table 7).
Table 7: Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection – Treatment Failure within 12 Months (Study 1) Parameter THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=141)Active Comparator*
(N=137)Difference†
(95% CI)P-value‡ BPAR= biopsy-proven acute rejection; CI=confidence interval - * basiliximab
- † Two-sided 95% confidence intervals of difference between treatment groups (THYMOGLOBULIN – Active Comparator) are based on normal approximation of binomial distribution.
- ‡ P-value obtained by comparison of treatment groups using Fisher's exact test.
- § Lost to follow-up is defined as not having BPAR, GL, or death within 12 months after transplantation, and last visit date was prior to the lower bound of 12-month window (12 months ± 30 days after transplantation).
Composite endpoint 35/141 (25%) 52/137 (38%) -13%
(-23.9% to -2.3%)0.02 BPAR 18/141 (13%) 29/137 (21%) -8%
(-17.2% to 0.4%)– Graft loss 11/141 (8%) 13/137 (10%) – – Death 6/141 (4%) 6/137 (4%) – – Lost to follow-up§ 7/141 (5%) 11/137 (8%) – – The composite endpoint is defined as the occurrence of any of the following: BPAR (Grade I–III), graft loss, death, or lost to follow-up. Except for patients counted as "lost to follow-up," a patient can be counted in more than one category for the individual components (BPAR, graft loss, death).
In Study 1, patients received either THYMOGLOBULIN (n=141) 1.5 mg/kg daily for a total of 5 doses (Day 0 to Day 4) or Active Comparator (n=137) 2 doses of 20 mg each (Day 0, Day 4). For both treatment groups, the first induction treatment was initiated prior to the reperfusion of the kidney. All patients received triple maintenance immunosuppression (cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, and corticosteroids) throughout the 12 months of the study.
Recipient disease characteristics were balanced between the 2 treatment groups with similar distribution of prior transplant, degree of sensitization and number of mismatched human leukocyte antigens (HLA). Overall, the mean percentage of pretransplant panel-reactive antibody (PRA) was 6% and the historical peak was 14%. The number of patients having a higher level of sensitization with PRA >20% was similar in the THYMOGLOBULIN (9%) and Active Comparator (10%) groups. The mean number of mismatched HLAs was evenly distributed across the 2 treatment groups.
Study 2
THYMOGLOBULIN was evaluated in an open-label, parallel-arm, randomized, active-controlled, investigator-sponsored study in kidney transplant patients (n=230) at higher immunological risk of rejection.
The noninferiority of THYMOGLOBULIN to Active Comparator was achieved with treatment failure rates of 25% versus 34%, with an estimated treatment group difference (THYMOGLOBULIN – Active Comparator) of -9% (95% CI: -19.9% to 3.6%), based on the composite endpoint (BPAR, GL, or death, with lost to follow-up considered as a treatment failure) in the 12 months after transplantation. The individual elements of the composite endpoint were BPAR (11% vs 21%), GL (15% vs 11%), and death (4% vs 3%) for the THYMOGLOBULIN and Active Comparator groups, respectively (Table 8).
Table 8: Prophylaxis of Acute Rejection – Treatment Failure within 12 Months (Study 2) Parameter THYMOGLOBULIN
(N=114)Active Comparator*
(N=116)Difference†
(95% CI)BPAR= biopsy-proven acute rejection; CI=confidence interval
The composite endpoint is defined as the occurrence of any of the following: BPAR (Grade I–III), graft loss, death, or lost to follow-up. A patient can be counted in more than one category with the exception of lost to follow-up.- * daclizumab
- † Two-sided 95% confidence intervals of difference between treatment groups (THYMOGLOBULIN – Active Comparator) are based on normal approximation of binomial distribution.
- ‡ Lost to follow-up is defined as not having BPAR (Grade I–III), GL, or death within 12 months post-transplantation, and last visit date was prior to the lower bound of 12 month window (12 months ± 30 days post-transplantation).
Composite endpoint 29 (25%) 39 (34%) -9%
(-19.9% to 3.6%)BPAR 12 (11%) 24 (21%) -10%
(-19.4% to -0.9%)Graft loss 17 (15%) 13 (11%) – Death 5 (4%) 4 (3%) – Lost to follow-up‡ 2 (2%) 3 (3%) – In Study 2, patients received either THYMOGLOBULIN (n=114) 1.25 mg/kg daily for a total of 8 doses (Day 0 to Day 7) or Active Comparator (n=116) 1 mg/kg (maximum dose 100 mg) on Days 0, 14, 28, 42, and 56. For both treatment groups, the first induction treatment was initiated prior to the beginning of the surgical procedure. All patients received triple maintenance immunosuppression (tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and corticosteroids) throughout the 12 months of the study.
Recipient disease characteristics were balanced between the 2 treatment groups, including similar distribution of prior transplant, degree of sensitization and number of HLA mismatches. The number of patients having prior transplants was 163 of 230 (71%). Overall, the mean percentage of pretransplant PRA was 35% and the historical peak was 72%. The number of patients having a higher level of sensitization with PRA >20% was similar in the THYMOGLOBULIN (55%) and Active Comparator (58%) groups. The mean number of HLA mismatches was evenly distributed across the 2 treatment groups.
14.2 Treatment of Acute Rejection in Patients Receiving a Kidney Transplant
A controlled, double-blind, multicenter, randomized clinical trial comparing THYMOGLOBULIN and Active Comparator was conducted at 28 US transplant centers in renal transplant patients (n=163) with biopsy-proven Banff Grade II (moderate), Grade III (severe), or steroid-resistant Grade I (mild) acute graft rejection. This clinical trial met the non-inferiority criteria for THYMOGLOBULIN relative to Active Comparator in reversing acute rejection episodes with a 20% non-inferiority margin. The overall weighted estimate of the treatment difference (THYMOGLOBULIN – Active Comparator success rate) was 11% with a lower 95% confidence bound of 0.07%. Therefore, THYMOGLOBULIN was not inferior to Active Comparator in reversing acute rejection episodes.
In the study, patients were randomized to receive 7 to 14 days of THYMOGLOBULIN (1.5 mg/kg/day) or Active Comparator (15 mg/kg/day). For the entire study, the two treatment groups were comparable with respect to donor and recipient characteristics. In Table 9, successful treatment is presented as those patients whose serum creatinine levels (14 days from the diagnosis of rejection) returned to baseline and whose graft was functioning on Day 30 after the end of therapy.
Table 9: Treatment of Acute Rejection – Response to Study Treatment by Rejection Severity Success/n Total Thymoglobulin Active Comparator* - * ATG-E
- † under null hypothesis (Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test)
Rejection Severity: Mild 9/10 (90%) 5/8 (63%) Moderate 44/58 (76%) 41/58 (71%) Severe 11/14 (72%) 8/14 (57%) Overall 64/82 (78%) 54/80 (68%) Weighted estimate of difference
(Thymoglobulin – Active Comparator*)11% Lower one-sided 95% confidence bound 0.07% p Value† 0.061 There were no statistically significant differences between the two treatments with respect to (1) serum creatinine levels 30 days after treatment relative to baseline, (2) improvement rate in post-treatment histology, (3) one-year post-rejection Kaplan-Meier patient survival (THYMOGLOBULIN 93%, n=82 and Active Comparator 96%, n=80), (4) Day 30 post-rejection graft survival and (5) one-year post-rejection graft survival (THYMOGLOBULIN 83%, n=82; Active Comparator 75%, n=80).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
THYMOGLOBULIN is supplied as a single-dose clear glass 10 mL vial containing 25 mg of lyophilized (solid) THYMOGLOBULIN. Each carton contains one THYMOGLOBULIN vial (NDC: 58468-0080-1).
16.2 Storage and Handling
- Store in refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
- Protect from light.
- Do not freeze.
- Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the label.
- Reconstituted THYMOGLOBULIN is physically and chemically stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature; however, room temperature storage is not recommended. As THYMOGLOBULIN contains no preservatives, reconstituted product should be used immediately.
- Infusion solutions of THYMOGLOBULIN must be used immediately.
- Any unused drug remaining after infusion must be discarded.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients receiving THYMOGLOBULIN that they will be monitored by a physician experienced in immunosuppressive therapy for the management of kidney transplant patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Infusion-Associated Reactions
Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of infusion-associated reactions (flu-like symptoms, e.g., fever, chills, nausea, muscle or joint pain) and the need to take premedications as prescribed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Allergic Reactions
Determine if the patient has known allergies to rabbits or rabbit proteins. Determine if the patient has had significant exposure to rabbits [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Infections
Inform patients of the increased risk of infection while taking immunosuppressive therapy. Instruct patients to immediately report signs or symptoms of infection and to take prophylactic anti-infectives as prescribed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Malignancies
Inform patients of the increased risk of malignancies, especially skin cancer, while taking immunosuppressive therapy. Instruct patients to limit exposure to sunlight and UV light by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen with a high protection factor [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Immunizations
Advise patients that they should not receive immunizations with live viral vaccines if they have been recently treated with THYMOGLOBULIN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Vial Carton
NDC: 58468-0080-1
Rx onlyThymoglobulin®
Anti-thymocyte Globulin (Rabbit)25 mg per vial
For Injection
For Intravenous InfusionOne single-dose vial
Discard unused portionSANOFI GENZYME

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
THYMOGLOBULIN
anti-thymocyte globulin (rabbit) injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58468-0080 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LAPINE T-LYMPHOCYTE IMMUNE GLOBULIN (UNII: D7RD81HE4W) (LAPINE T-LYMPHOCYTE IMMUNE GLOBULIN - UNII:D7RD81HE4W) LAPINE T-LYMPHOCYTE IMMUNE GLOBULIN 5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58468-0080-1 1 in 1 CARTON 12/30/1998 1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA103869 12/30/1998 Labeler - Genzyme Corporation (025322157) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genzyme Polyclonals S.A.S. 500026062 API MANUFACTURE(58468-0080) , MANUFACTURE(58468-0080) , ANALYSIS(58468-0080) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Genzyme Ireland Limited 985127419 MANUFACTURE(58468-0080) , ANALYSIS(58468-0080) , STERILIZE(58468-0080) , LABEL(58468-0080) , PACK(58468-0080)
Trademark Results [Thymoglobulin]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 THYMOGLOBULIN 75448584 2350683 Live/Registered |
GENZYME CORPORATION 1998-03-11 |
 THYMOGLOBULIN 74299700 1842635 Dead/Cancelled |
GENZYME CORPORATION 1992-07-31 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.