VERAFLOX- pradofloxacin suspension
Veraflox by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Veraflox by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Elanco US Inc., KVP Pharma Veterin Produkte GmbH, Bayer AG. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
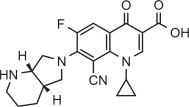
Pradofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic and belongs to the class of quinoline carboxylic acid derivatives. Its chemical name is: 7-[(4aS) octahydro-6H-pyrrolo [3, 4-b] pyridine-6yl]-8-cyano-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinoline carboxylic acid. Each mL of VERAFLOX Oral Suspension provides 25 mg of pradofloxacin.
- INDICATION
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Shake well before use. To ensure a correct dosage, body weight should be determined as accurately as possible. The dose of VERAFLOX is 7.5 mg/kg (3.4 mg/lb) body weight once daily for 7 consecutive days. Use the syringe provided to ensure accuracy of dosing to the nearest 0.1 mL. Rinse syringe between doses.
A sample of the lesion should be obtained for culture and susceptibility testing prior to beginning antibacterial therapy. Once results become available, continue with appropriate therapy. If acceptable response to treatment is not observed, or if no improvement is seen within 3 to 4 days, then the diagnosis should be re-evaluated and appropriate alternative therapy considered.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DO NOT USE IN DOGS. Pradofloxacin has been shown to cause bone marrow suppression in dogs. Dogs may be particularly sensitive to this effect, potentially resulting in severe thrombocytopenia and neutropenia.
Quinolone-class drugs have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested, the dog being particularly sensitive to this side effect.
Pradofloxacin is contraindicated in cats with a known hypersensitivity to quinolones.
-
WARNINGS
Human Warnings:
Not for human use. Keep out of reach of children.
Individuals with a history of quinolone hypersensitivity should avoid this product. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. In case of ocular contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water immediately for at least 20 seconds. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure, or in case of accidental ingestion. In humans, there is a risk of photosensitization within a few hours after exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight. Do not eat, drink or smoke while handling this product.
It is recommended that used syringes be kept out of reach of children and disposed of properly.
Animal Warnings:
For use in cats only.
The administration of pradofloxacin for longer than 7 days induced reversible leukocyte, neutrophil, and lymphocyte decreases in healthy, 12-week-old kittens (see Animal Safety section). If an unexplained drop in leukocyte, neutrophil, and/or lymphocyte counts is noted during pradofloxacin therapy, discontinuation of treatment is recommended.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Prescribing antibacterial drugs in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to treated animals and may increase the risk of the development of drug-resistant animal pathogens.
The use of fluoroquinolones in cats has been associated with the development of retinopathy and/or blindness. Such products should be used with caution in cats.
Quinolones have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species.
The safety of pradofloxacin in immune-compromised cats (i.e., cats infected with feline leukemia virus and/or feline immunodeficiency virus) has not been evaluated.
Quinolones should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation that may lead to convulsive seizures.
The safety of pradofloxacin in cats younger than 12 weeks of age has not been evaluated.
The safety of pradofloxacin in cats that are used for breeding or that are pregnant and/or lactating has not been evaluated.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Compounds (e.g., sucralfate, antacids and multivitamins) containing divalent and trivalent cations (e.g., iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and zinc) may substantially interfere with the absorption of quinolones resulting in a decrease in product bioavailability. Therefore, the concomitant oral administration of quinolones with foods, supplements, or other preparations containing these compounds should be avoided.
The dosage of theophylline should be reduced when used concurrently with quinolones. Cimetidine has been shown to interfere with the metabolism of quinolones and should be used with care when used concurrently. Concurrent use of quinolones with oral cyclosporine should be avoided. Concurrent administration of quinolones may increase the action of oral anticoagulants.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In a multi-site field study, 282 cats (ages 0.3 to 19 years) were evaluated for safety when given either VERAFLOX at a dose of 7.5 mg/kg (3.4 mg/lb) or placebo (vehicle without active ingredient) at a dose of 0.14 mL/lb (0.3 mL/kg). Each group was treated once daily for 7 consecutive days. Adverse reactions are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Number of Adverse Reactions Among Cats Treated with Pradofloxacin (N=190) or Vehicle (N=92)* * Some cats may have experienced more than one adverse reaction or more than one occurrence of the same adverse reaction during the study. Adverse Reactions
Pradofloxacin
Vehicle
Diarrhea / loose stools
7
2
Leukocytosis with neutrophilia
4
6
Elevated CPK levels
4
4
Sneezing
4
1
Hematuria
2
2
Hypersalivation
2
1
Pruritus
2
0
Inappetence
1
3
Lethargy
1
2
Cardiac murmur
1
1
Reclusive behavior
1
1
Vomiting
1
1
Bacteriuria
1
0
Lymphadenopathy
1
0
Polydipsia
1
0
Upper respiratory infection
1
0
The Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provides additional occupational safety information.
-
CONTACT INFORMATION
For product questions, to report adverse reactions, or for a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), call Elanco Product & Veterinary Support at 888-545-5973.
For additional information about reporting adverse drug experiences for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics:
Pradofloxacin is rapidly absorbed following oral administration of VERAFLOX to fasted cats, with peak serum concentrations occurring in less than 1 hour. However, food markedly diminishes the serum bio-availability of pradofloxacin; mean peak serum concentrations (Cmax) are reduced 53% and mean exposures (AUC) are decreased by 26%. The relative bioavailability of pradofloxacin, when administered as the 2.5% oral suspension to fed and fasted cats, is provided in Table 2 and Figure 1.
Table 2. Mean (1 SD) serum pradofloxacin derived pharmacokinetics parameters in cats (N =12) following a 5mg/kg oral dose of VERAFLOX under fasted and fed conditions. VERAFLOX
5 mg/kg DoseParameter
Fasted
Fed
Cmax (ng/mL)
2116 (549)
999 (400)
Tmax (hr)
0.8
1.4
AUC0-24
9111 (1939)
6745 (1524)
Half-Life (hr)
7.3 (1.7)
6.4 (1.2)
Approximately 30% of the total drug concentrations are bound to plasma proteins in drug concentrations ranging from 150 to 1500 ng/mL. Dose proportional increases in drug concentrations are observed when the oral suspension is administered to fasted cats in doses ranging from 2.5 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg. Due to its short elimination half life, there is minimal pradofloxacin accumulation following multiple daily administrations.
Pharmacodynamics:
Pharmacodynamics was determined using in vitro susceptibility that showed the pathogens Pasteurella multocida, Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, and Streptococcus spp. had a pradofloxacin MIC90 of ≤0.015 to 0.12 ug/mL. The pharmacodynamics metrics (Cmax/ MIC90 and AUC/MIC90) were estimated using linear regression analysis of free drug steady-state pradofloxacin pharmacokinetics parameters from fasted cats and a pradofloxacin MIC90 value of 0.12 ug/mL. The 95% Confidence Intervals about predicted mean Cmax/MIC90 and AUC/MIC90 values were 15 to 17 and 70 to 81, respectively. It was concluded that the magnitude of the Cmax/ MIC90 and AUC/MIC90 values is predictive of product effectiveness when an oral dose of 7.5 mg/kg body weight of the pradofloxacin liquid formulation is administered to fasted cats. In addition, effectiveness was shown for cats dosed at 7.5 mg/kg body weight and fed free choice, or within two hours of dosing, in a field study.
Microbiology:
VERAFLOX is bactericidal, with activity against Gram-negative, Gram-positive, and anaerobic bacteria. The mechanism of action is dual targeting through inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for pradofloxacin against Pasteurella multocida, Streptococcus canis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus felis, and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from skin infections (wounds and abscesses) in cats in a U.S. field study from 2008 to 2009 are listed in Table 3. Only two isolates from two pradofloxacin Treatment Failure cases had elevated pradofloxacin MICs (non-hemolytic Staph. aureus - MIC = 2 μg/mL; E. coli - MIC = 4 μg/mL).
Table 3. Activity of VERAFLOX against Pathogens Isolated from Cats Treated with VERAFLOX in a Clinical Trial in the US in 2008. Disease
Pathogen
Clinical
Treatment
OutcomeNumber
of
IsolatesSample
Collection
(Time Relative
to Treatment)MIC50
μg/mLMIC90
μg/mLMIC Range
μg/mLSkin
InfectionsPasteurella
multocidaSuccess
40
Pre-Treatment
0.008
0.015
≤ 0.004 - 0.03
Failure
11
Pre-Treatment
0.008
0.008
≤ 0.004 - 0.015
Streptococcus
canisSuccess
13
Pre-Treatment
0.12
0.12
0.03 - 0.25
Failure
2
Pre-Treatment
0.06 - 0.12
Staphylococcus
aureusSuccess
10
Pre-Treatment
0.12
0.12
0.015 - 0.12
Failure
0
Staphylococcus
felisSuccess
13
Pre-Treatment
0.03
0.06
0.03 - 0.12
Failure
1
Pre-Treatment
0.06
Staphylococcus
pseud-
intermediusSuccess
10
Pre-Treatment
0.06
0.06
0.03 - 0.06
Failure
1
Pre-Treatment
0.03
-
EFFECTIVENESS
The clinical effectiveness of VERAFLOX was demonstrated in a multi-site (16 sites) field study. In this masked and randomized study, the effectiveness of VERAFLOX was compared to a placebo control (vehicle without active ingredient). Of the 282 cats enrolled in this study, 190 were treated with VERAFLOX once daily at 7.5 mg/kg (3.4 mg/lb) body weight for 7 consecutive days and 92 were treated with placebo once daily at 0.3 mL/kg body weight for 7 consecutive days. The effectiveness database included 182 cats: 66 placebo (vehicle)-treated cats and 116 VERAFLOX-treated cats. The analysis of this effectiveness database showed that the cure rate was greater in the VERAFLOX group on Day 15, as summarized in Table 4. Study cure rates were determined approximately 15 days after initiation of therapy. The statistical evaluation of the primary effectiveness endpoint (Study Cures) showed that VERAFLOX was different from placebo with 73.4% VERAFLOX study cures versus 38.9% placebo study cures.
Table 4: Day 15 Case Classification Treatment Group
Percent Cures
VERAFLOX
N= 11673.4%
Placebo
N= 6638.9%
P-value
0.0053
-
ANIMAL SAFETY
Target Animal Safety Study: Safety was evaluated in 32 healthy, 12-week-old kittens administered VERAFLOX once daily at doses of 0, 7.9, 23.7, or 39.5 mg/kg (0, 1, 3, and 5 times the recommended dose) for 21 consecutive days. Additional control (0X) and high-dose (5X) animals were maintained for 45 days after treatment cessation.
There were statistically significant decreases in neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes in the 3X and 5X groups compared to the controls. During the treatment period, one 3X cat and three 5X cats had absolute neutrophil counts below the reference range. Bone marrow cytology results consistent with bone marrow suppression (myeloid hypoplasia) were seen in the 3X neutropenic cat and two of the three 5X neutropenic cats. The 3X cat was neutropenic on the last day of the study prior to scheduled euthanasia, while absolute neutrophil values for the three 5X cats returned to normal either during treatment or after the cessation of treatment.
The most frequent abnormal clinical finding was soft feces. While this was seen in both treated and control groups, it was observed more frequently in the 3X and 5X kittens.
Ocular Safety Study: Ocular safety was evaluated in 20 healthy adult cats using pradofloxacin in capsules administered orally, once daily at doses of 30 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg for 23 days. No effects were seen in the following investigated ocular parameters: ophthalmic examinations, ERGs, and optical coherence tomography. Cats receiving 50 mg/kg/day of pradofloxacin showed mild weight loss. Cats receiving 30 and 50 mg/kg/day of pradofloxacin exhibited hypersalivation and vomiting throughout the study. Dose-dependent reductions in white blood cell counts were noted in the pradofloxacin-treated cats. One cat receiving 30 mg/kg/day of pradofloxacin exhibited minimal photoceptor degeneration on light and electron microscopy of a type that differed from enrofloxacin-treated cats (comparator used in this study); the effects of pradofloxacin on these retinal changes is unknown.
- STORAGE CONDITIONS
- HOW SUPPLIED
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 15 mL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VERAFLOX
pradofloxacin suspensionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58198-0039 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PRADOFLOXACIN (UNII: 6O0T5E048I) (PRADOFLOXACIN - UNII:6O0T5E048I) PRADOFLOXACIN 25 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58198-0039-1 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC: 58198-0039-3 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141344 01/21/2013 Labeler - Elanco US Inc. (966985624)
Trademark Results [Veraflox]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 VERAFLOX 85635337 4325861 Live/Registered |
Bayer Intellectual Property GmbH 2012-05-25 |
 VERAFLOX 85069348 4317497 Live/Registered |
Bayer Aktiengesellschaft 2010-06-23 |
 VERAFLOX 78195406 3092145 Dead/Cancelled |
Bayer Aktiengesellschaft 2002-12-17 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.