MOTEGRITY- prucalopride tablet, film coated
MOTEGRITY by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
MOTEGRITY by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Shire US Manufacturing Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MOTEGRITY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MOTEGRITY.
MOTEGRITY (prucalopride) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018INDICATIONS AND USAGE
MOTEGRITY™ is a serotonin-4 (5-HT4) receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults. (1.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg of prucalopride (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Suicidal Ideation and Behavior: Monitor patients for persistent worsening of depression and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Instruct patients to discontinue MOTEGRITY immediately and contact their healthcare provider if their depression is persistently worse, or they experience emerging suicidal thoughts or behaviors. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) are headache, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal distension, dizziness, vomiting, flatulence, and fatigue. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Shire at 1-800-828-2088 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
MOTEGRITY can be taken with or without food. The recommended dosage by patient population is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage Regimen and Dosage Adjustments by Population Population with CIC Recommended Oral Dose Regimen Adults 2 mg once daily Patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance (CrCL) less than 30 mL/min) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5 and 8.6)]. 1 mg once daily - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
MOTEGRITY is contraindicated in patients with:
- A history of hypersensitivity to MOTEGRITY. Reactions including dyspnea, rash, pruritus, urticaria, and facial edema have been observed [(see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Intestinal perforation or obstruction due to structural or functional disorder of the gut wall, obstructive ileus, severe inflammatory conditions of the intestinal tract such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and toxic megacolon/megarectum.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
In clinical trials, suicides, suicide attempts, and suicidal ideation have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A causal association between treatment with MOTEGRITY and an increased risk of suicidal ideation and behavior has not been established.
Monitor all patients treated with MOTEGRITY for persistent worsening of depression or the emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Counsel patients, their caregivers, and family members of patients to be aware of any unusual changes in mood or behavior and alert the healthcare provider. Instruct patients to discontinue MOTEGRITY immediately and contact their healthcare provider if they experience any of these symptoms.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below represent 2530 patients (1251 received MOTEGRITY 2 mg once daily and 1279 received placebo) with CIC from 6 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials of 12 weeks to 24 weeks in duration. In these trials overall, patients were primarily female (76%) and white (76%). The mean age was 47 years (range 17 to 95 years) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 2 below summarizes the incidence (%) of common adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of patients with CIC receiving either 2 mg of MOTEGRITY once daily or placebo and at an incidence greater than in the placebo group from the six double-blind placebo-controlled trials described above.
Table 2: Common Adverse Reactions* in Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials of CIC of at least 12 Weeks Duration Adverse Reaction MOTEGRITY
2 mg Once Daily
N=1251†
%Placebo
N=1279
%- * Reported in ≥2% of patients receiving MOTEGRITY and a rate higher than patients receiving placebo.
- † Includes 93 patients who started on MOTEGRITY 1 mg and increased to MOTEGRITY 2 mg.
- ‡ Includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, abdominal discomfort, and epigastric discomfort.
Headache 19 9 Abdominal pain‡ 16 11 Nausea 14 7 Diarrhea 13 5 Abdominal distension 5 4 Dizziness 4 2 Vomiting 3 2 Flatulence 3 2 Fatigue 2 1 Less Common Adverse Reactions
Less common adverse reactions occurring in <2% of patients receiving MOTEGRITY 2 mg once daily include:
Gastrointestinal disorders: abnormal gastrointestinal sounds
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: decreased appetite
Nervous system disorders: migraine
Renal and urinary disorders: pollakiuria
Diarrhea
Of the patients who reported diarrhea, 70% (110 out of 157) reported it in the first week of treatment. Diarrhea typically resolved within a few days in 73% (80 out of 110) of those patients. Severe diarrhea was reported in 1.8% of patients treated with MOTEGRITY 2 mg compared to 1% of patients in the placebo group, and had a similar onset and duration as diarrhea overall.
Headache
Of the patients who reported headache, 66% (157 out of 237) treated with MOTEGRITY 2 mg once daily reported onset in the first 2 days of treatment. Symptoms typically resolved within a few days in 65% (102 out of 157) of those patients.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In the 6 clinical trials described above, 5% of patients treated with 2 mg of MOTEGRITY once daily discontinued due to adverse reactions, compared to 3% of patients in the placebo group. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were nausea (2% MOTEGRITY, 1% placebo), headache (1% MOTEGRITY, 1% placebo), diarrhea (1% MOTEGRITY, <1% placebo), or abdominal pain (1% MOTEGRITY, 1% placebo).
Adverse Reactions of Special Interest
Adverse reactions of special interest were evaluated in a pool of 28 completed clinical trials (19 double-blind and 9 open-label) for MOTEGRITY at doses including 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg, or 4 mg per day in adult patients with CIC (the recommended dosage of MOTEGRITY for CIC is 2 mg once daily). The total exposure in the double-blind trials was 565 patient-years in the MOTEGRITY group, 384 patient-years in the placebo group, and 2769 patient-years in the double-blind and open-label clinical trials.
Cardiovascular Safety Analysis
In an evaluation by an independent adjudication committee of all potential major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke, the standardized incidence rate (IR) per 1000 patient-years for MACE for MOTEGRITY was compared with the IR for placebo.
In the double-blind trials, the IR for MACE was 3.5 (2 patients out of 3366; 1 patient on 2 mg and 1 patient on 4 mg) in the MOTEGRITY group and 5.2 (2 patients out of 2019) in the placebo group. When combining the double-blind and open-label trials, the IR for MACE was 3.3 (9 patients out of 4472, doses ranging between 0.5 to 4 mg) for MOTEGRITY.
Suicidal Ideation and Behavior
In the double-blind trials, one patient reported a suicide attempt 7 days after the end of treatment with MOTEGRITY 2 mg once daily; none were reported in patients on placebo. In the open-label trials, two patients reported a suicide attempt and another patient reported suicidal ideation. Completed suicide was reported in two patients, previously treated with MOTEGRITY 2 mg or 4 mg; both discontinued MOTEGRITY for at least one month prior to the event.
Observational Cardiovascular Cohort Study
The overall cardiovascular safety of MOTEGRITY was assessed using European healthcare databases in a population-based, retrospective, observational, cohort study of adults with constipation. New users of MOTEGRITY (N=5715) were matched to new users of polyethylene glycol 3350 (PEG) (N=29,372) to estimate the standardized incidence rate ratio (SIRR) for MACE, pooled across four data sources. The 95% confidence interval for the pooled estimate of the SIRR did not demonstrate an increased MACE risk and excluded a pre-specified safety margin of a three-fold risk of MACE during prucalopride use relative to PEG use.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of prucalopride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions: dyspnea, rash, pruritus, urticaria, and facial edema [see Contraindications (4)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports with prucalopride use in pregnant women are insufficient to identify any drug-associated risks of miscarriage, major birth defects, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed with prucalopride administration during the period of organogenesis to pregnant rats and rabbits at doses up to approximately 390 times and 780 times, respectively, the recommended human dose of 2 mg/day (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In oral embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits, prucalopride was administered to pregnant animals at doses of 5, 20, and 80 mg/kg/day throughout the period of organogenesis. No adverse embryofetal developmental effects were observed in either rats or rabbits up to the highest oral dose of 80 mg/kg/day (about 390 times and 780 times the recommended human dose of 2 mg/day, respectively, based on body surface area).
In an oral pre- and post-natal development study in rats, prucalopride was administered at doses of 5, 20, and 80 mg/kg/day. At the 80-mg/kg dose(about 390 times the recommended human dose of 2 mg/day, based on body surface area), a slight decrease in overall survival rate of pups after 7 days was observed, which could be due to maternal toxicity observed at this dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Prucalopride is present in breast milk (see Data). There are no data on the effects of prucalopride on the breastfed child or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for MOTEGRITY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from MOTEGRITY or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In an open-label study in 8 healthy lactating women in the weaning stage, plasma and milk samples were collected at predose (day 1 and 4), and then 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours (day 4) after a 2-mg dose of prucalopride was administered once daily for 4 days. Prucalopride is excreted in breast milk with a milk to plasma AUC ratio of 2.65:1; the average amount passed to the infant was estimated to be 1.74 mcg/kg/day, which is about 6% of the maternal dose, adjusted for body weight. The prucalopride concentration detected in breast milk during weaning may not reflect the prucalopride concentration in breast milk during full milk production.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MOTEGRITY have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 2484 patients treated with MOTEGRITY 1 mg or 2 mg once daily in 6 controlled trials of at least 12-week duration in patients with CIC, 15% were 65 years of age and over, and 5% were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14)]. No overall differences in safety and effectiveness were observed between elderly and younger patients.
In an additional 4-week double-blind, placebo-controlled dose escalation study in 89 elderly nursing home residents with CIC (PRU-USA-26, NCT00627692), no unanticipated safety issues were identified.
Elderly subjects had higher prucalopride exposure compared to younger subjects. However, the effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of prucalopride appeared to be related to decreased renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Adjust the dosage in elderly patients based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild and moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance at least 30 mL/min, as determined from a 24-hour urine collection in the clinical trial).
MOTEGRITY is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. A decreased dosage is recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min, as determined from a 24-hour urine collection in the clinical trial) [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Avoid MOTEGRITY in patients with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
An overdose may result in appearance of symptoms from an exaggeration of the known pharmacodynamic effects of prucalopride and includes headache, nausea, and diarrhea. Specific treatment is not available for MOTEGRITY overdose. Should an overdose occur, treat symptomatically and institute supportive measures, as required. Extensive fluid loss from diarrhea or vomiting may require correction of electrolyte disturbances.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
MOTEGRITY (prucalopride) tablets for oral use contain prucalopride succinate, a dihydrobenzofurancarboxamide that is a serotonin type 4 (5-HT4) receptor agonist. The IUPAC name is: 4-amino-5-chloro-N-[1-(3-methoxypropyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-carboxamide succinate.
The molecular formula is C18H26ClN3O3.C4H6O4 and the molecular weight is 485.96. The structural formula is:
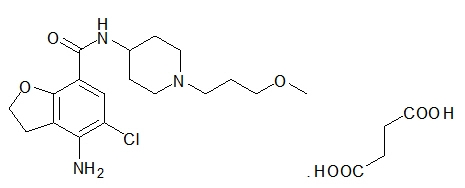
Prucalopride succinate is a white to almost white powder. It is highly soluble in acidic aqueous media and alkaline aqueous media up to a pH of approximately 9.
Each 1-mg film-coated tablet of MOTEGRITY contains 1 mg of prucalopride (equivalent to 1.32 mg prucalopride succinate), and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The coating for the 1-mg tablet contains hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3000, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Each 2-mg film-coated tablet of MOTEGRITY contains 2 mg of prucalopride (equivalent to 2.64 mg prucalopride succinate), and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The coating for the 2-mg tablet contains hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3000, titanium dioxide, triacetin, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, and FD&C Blue #2.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Prucalopride, a selective serotonin type 4 (5-HT4) receptor agonist, is a gastrointestinal (GI) prokinetic agent that stimulates colonic peristalsis (high-amplitude propagating contractions [HAPCs]), which increases bowel motility.
Prucalopride was devoid of effects mediated via 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT3, motilin or CCK-A receptors in vitro at concentrations exceeding 5-HT4 receptor affinity by 150-fold or greater. In isolated GI tissues from various animal species, prucalopride facilitated acetylcholine release to enhance the amplitude of contractions and stimulate peristalsis. In rats and dogs, prucalopride stimulated gastrointestinal motility with contractions starting from the proximal colon to the anal sphincter.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
High Amplitude Propagating Contractions
Following a single 2-mg dose of prucalopride in patients with CIC, prucalopride increased the number of high amplitude propagating contractions (HAPCs) during the first 12 hours as compared with an osmotic laxative treatment. In addition, prucalopride 4 mg once daily (2 times the maximum human recommended dose of 2 mg) for 7 days increased the amplitude of HAPCs in healthy subjects without affecting colonic phasic activity as compared with placebo.
Colonic Transit Time
An integrated analysis of 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-finding studies in 280 patients with CIC showed that after once daily treatment with 2 mg of prucalopride, the mean colonic transit time was reduced by 12 hours from a baseline of 65 hours for prucalopride 2 mg, compared to an increase of 0.5 hours from a baseline of 66 hours in the placebo group.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of prucalopride has been evaluated in healthy subjects and is dose-proportional within and beyond the therapeutic range (tested up to 20 mg, 10 times the maximum approved recommended dose). Prucalopride administered once daily displays time-independent kinetics during prolonged treatment. With once daily administration of 2 mg prucalopride, pharmacokinetic steady-state is attained within 3 to 4 days, and steady-state plasma concentrations fluctuate between trough and peak values of 2.5 and 7 ng/mL, respectively, with mean plasma AUC0-24h of 109 ng∙h/mL. The accumulation ratio after once daily dosing ranged from 1.9 to 2.3. The terminal half-life is approximately 1 day.
Pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with CIC are similar to those seen in healthy subjects.
Absorption
Following a single oral dose of 2 mg prucalopride in healthy subjects, peak plasma concentrations are observed within 2 to 3 hours after administration. The absolute oral bioavailability is >90%.
Effect of Food
Concomitant intake with a high-fat meal (1000 kcal total, 500 kcal from fat) does not influence the oral bioavailability of prucalopride [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Distribution
Prucalopride has a steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of 567 liters after intravenous administration. The plasma protein binding of prucalopride is approximately 30%.
Elimination
Renal excretion is the main route of elimination of prucalopride. Non-renal elimination contributes up to about 35% of the total. The plasma clearance of prucalopride averages 317 mL/min.
Metabolism
Prucalopride is a substrate of CYP3A4, in vitro. In an oral dose study with radiolabeled prucalopride in healthy subjects, prucalopride made up 92 to 94% of the total radioactivity in plasma. There are 7 different known minor metabolites, the most abundant metabolite (O-desmethyl prucalopride acid) represents 0 to 1.7% of the total plasma exposure.
Excretion
Following oral administration of radiolabeled prucalopride in healthy subjects, 60 to 65% of the administered dose is excreted unchanged in urine and about 5% in feces. On average, 84.2% of administered radioactive dose was recovered in urine and 13.3% of the dose was recovered in feces. Seven metabolites were recovered in urine and feces, with the most abundant metabolite (O-desmethyl prucalopride acid) accounting for 3.2% and 3.1% of the dose in urine and feces, respectively. None of the other metabolites accounted for more than 3% of the dose. Renal elimination of prucalopride involves both passive filtration and active secretion.
Use in Specific Populations
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of a combined study population of 1343 subjects indicated that there were no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of prucalopride based on age (17-95 years), sex, race (89% white, 7% black, 4% other), or body weight (37-161 kg), after accounting for the effect of renal function.
Geriatric Patients
After once daily dosing of 1 mg, peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and AUC of prucalopride in geriatric subjects were 26% to 28% higher than in younger adult subjects. The effect of age appeared to be related to decreased renal function in the elderly. Additionally, a population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that age was not a significant covariate, after accounting for the effect of renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
After a single 2-mg oral dose, the mean AUC0-inf of prucalopride increased 1.23-fold in subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 60 to ≤89 mL/min), 1.4-fold in subjects with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to ≤59 mL/min), and 2.38-fold in subjects with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 15 to ≤29 mL/min), compared to subjects with normal renal function. The pharmacokinetics of prucalopride in patients with end-stage renal disease or undergoing dialysis is not fully known [see Dosage and Administration (2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
After a single oral dose of 2 mg, Cmax and AUC of prucalopride were on average 10 to 20% higher in subjects with moderate (Child-Pugh B) and severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment than in subjects with normal hepatic function. This effect is not considered to be clinically significant.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Effect of Prucalopride on Other Drugs
Effect of Other Drugs on Prucalopride
In Vitro Studies
Based on in vitro study results, the potential for prucalopride to inhibit CYP enzymes (1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4) and transporters (P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K, BSEP, and MRP2 transporters) or induce CYP enzymes (1A2, 2B6, and 3A4) is low at the clinical concentration.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in mice, prucalopride was given by daily oral gavage at doses of 10, 20, and 80 mg/kg. An increased incidence of mammary gland adenocarcinomas was observed in female mice at 80 mg/kg/day. The finding is considered rodent-specific. No significant neoplastic changes were seen in male mice dosed up to 80 mg/kg/day and in female mice dosed up to 20 mg/kg/day (exposure ratio of 219 and 24 times the human dosage of 2 mg per day in male and female mice, respectively, based on AUC).
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats, prucalopride was given by daily oral gavage at doses of 5, 20, and 80 mg/kg in males and 5, 10, and 40 mg/kg in females. In male and female rats there was a significant increase in the incidences of benign tumors, including hepatocellular adenomas, thyroid follicular adenomas, and mammary gland fibroadenomas. An increased incidence of pituitary adenomas, pancreas islet cell adenomas, and adrenal gland benign pheochromocytomas was also seen in male rats. The increases in neoplastic changes occurred primarily at the high dose of 80 mg/kg/day in male rats and 40 mg/kg/day in female rats (exposure ratios 556 times (males) and 495 times (females) the human dosage of 2 mg per day, based on AUC). There was no significant increase in tumor incidence at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day in male rats and up to 10 mg/kg/day in female rats (exposure ratios of 63 and 40 times the human dosage of 2 mg per day in male and female rats, respectively, based on AUC).
In a 12-month carcinogenicity study in neonatal mice, prucalopride was administered by oral gavage at total dosages of 75, 150, and 300 mg/kg given across 2 doses on day 8 of age (one-third of total dosage) and day 15 of age (two-thirds of total dosage). Prucalopride was not tumorigenic at doses up to 300 mg/kg (>1600 times the human exposure at 2 mg per day, based on AUC).
Mechanistic studies demonstrated that the increase in tumor incidence in rodents related to stimulation of prolactin in endocrine tissues was associated with dopamine D2 antagonist activity. The hepatic and thyroid tumors were due to induction of enzymes in liver and subsequent disruption of thyroid homeostasis.
Mutagenesis
Prucalopride was tested in a battery of assays, including the Ames bacterial mutation assay in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli, mouse lymphoma assay, chromosomal aberration assays in human lymphocytes, micronucleus test in mice, Vitotox test, and in vitro Unscheduled DNA Synthesis (UDS) studies. Prucalopride tested positive in the Ames bacterial mutation assay in the S. typhimurium TA100 strain, at concentrations ≥500 mcg/plate, both in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. Prucalopride was negative in other assays evaluating mutagenesis, including in vitro mammalian-based assays (e.g., mouse lymphoma assay, chromosomal aberration assays in human lymphocytes) and in vivo tests (e.g., micronucleus test in mice, a UDS test, a gene mutation assay in Big Blue transgenic rats, and a 32P-postlabeling study in target tissues identified in the carcinogenicity studies, including liver, mammary gland, thyroid, and adrenal tissues). Based on the weight of evidence, prucalopride does not appear to have a mutagenic potential.
Impairment of Fertility
In an oral fertility and early embryonic development study performed in rats at doses of 5, 20, and 80 mg/kg/day, there was no evidence of adverse effects on fertility at doses up to 20 mg/kg. At the highest dose of 80 mg/kg (about 390 times the recommended human dose of 2 mg/day, based on body surface area), an increase in pre-coital interval, pseudo-pregnancies, and pre-implantation loss were seen. These effects could be secondary to increased prolactin secretion with prucalopride treatment.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In safety pharmacology studies, no relevant effects were observed in any of the cardiovascular studies at concentrations at least 50 times the human therapeutic Cmax. Prucalopride had no effect on potassium current in hERG-transfected HEK cells at concentrations up to 1 micromolar (50 times the human therapeutic Cmax). At concentrations ≥3 micromolar, concentration-dependent inhibition of the current was observed (IC50=22 micromolar; 1100 times the human therapeutic Cmax). In studies in pigs, minor and transient increases in heart rate and blood pressure were noted upon first exposure to prucalopride, at plasma levels at least 10 times the human therapeutic Cmax.
In repeated-dose toxicology studies in male rats, increases in heart weight (up to 9%) were observed at doses of 20 mg/kg/day or higher (at least 75 times the human therapeutic AUC). Cardiac histology revealed an increase in focal infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells in the heart at a dose of 80 mg/kg/day (at least 785 times the human therapeutic AUC). In dogs, no changes in heart rate, blood pressure, electrocardiogram parameters, heart weight, or cardiac histology were observed at any dose tested (the highest dose of 30 mg/kg/day was 572 times the human therapeutic AUC).
In vitro studies demonstrated no effect of prucalopride on either contractile responses in human, canine, and porcine coronary arteries at concentrations up to 10 micromolar (500 times the human clinical Cmax) or on platelet aggregation at concentrations up to 200 nanomolar (10 times the human clinical Cmax).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of MOTEGRITY for the treatment of CIC was evaluated in six double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trials in 2484 adult patients (Studies 1 to 6; see Table 3). Studies 1 through 5 were 12-week treatment duration and Study 6 included 24 weeks of treatment. Patients less than 65 years were dosed with MOTEGRITY 2 mg once daily. In Studies 2 and 6, the geriatric patients started on MOTEGRITY 1 mg once daily and, if necessary, the dose was increased to 2 mg after 2 or 4 weeks of treatment in the event of insufficient response at 1 mg; of these patients 81% increased to 2 mg. Overall, the majority of patients were female (76%) and white (76%), and also included Asian (19%) and black (3%). The mean adult age was 47±16 years (range 17 to 95 years) and the mean duration of constipation was 16±15 years with 28% of patients having chronic constipation for at least 20 years.
Table 3: Main Studies in the MOTEGRITY Clinical Program Study Number Duration Study 1 (PRU-CRC-3001, NCT01116206) 12 Weeks Study 2 (SPD555-302, NCT01147926) 12 Weeks Study 3 (PRU-INT-6, NCT00488137) 12 Weeks Study 4 (PRU-USA-11, NCT00483886) 12 Weeks Study 5 (PRU-USA-13, NCT00485940) 12 Weeks Study 6 (SPD-555-401, NCT01424228) 24 Weeks Eligible patients required a history of chronic constipation defined as having fewer than 3 spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) per week that resulted in a feeling of complete evacuation (complete, spontaneous bowel movement [CSBM]) and 1 or more of the following symptoms for greater than 25% of bowel movements in the preceding 3 months, with symptoms onset more than 6 months prior to screening:
- Lumpy or hard stools
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation
- Straining at defecation
Patients who never had SBMs were eligible. In Study 1, eligibility also included sensation of ano-rectal obstruction or blockade or the need for digital manipulation in more than 25% of bowel movements. In all studies, patients were excluded if constipation was due to secondary causes or suspected to be drug-induced.
Efficacy was assessed using information provided by patients in a daily diary.
Primary Efficacy Results
For the primary efficacy endpoint, a responder was defined as a patient with an average of 3 or more CSBMs per week, over the 12-week treatment period. In the Intent-to-Treat [ITT] population in the 6 trials, 1237 received MOTEGRITY 1 or 2 mg and 1247 received placebo. Table 4 summarizes the results.
Table 4: Efficacy Responder Rates in Placebo-Controlled Studies of CIC: Proportion of Patients with an Average Weekly Frequency of ≥3 CSBMs per Week over 12 Weeks of Treatment (ITT Population) Study MOTEGRITY 1 or 2 mg Once Daily Placebo Treatment Difference
(95% CI)p value N n (%) N n (%) p-value based on a Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test
N = number of patients per treatment group
n = number of respondersStudy 1 249 83 (33) 252 26 (10) 23
(16, 30)p<0.001 Study 2 177 67 (38) 181 32 (18) 20
(11, 29)p<0.001 Study 3 236 46 (19) 240 23 (10) 10
(4, 16)p=0.002 Study 4 190 55 (29) 193 25 (13) 16
(8, 24)p<0.001 Study 5 214 50 (24) 212 25 (12) 12
(4, 19)p<0.001 Study 6 171 43 (25) 169 34 (20) 5
(-4, 14)p=0.341 In all studies, improvement in the frequency of CSBMs/week was seen as early as week 1 and was maintained through week 12.
Across the six studies, the median time to first CSBM after dosing of MOTEGRITY on day 1 ranged from 1.4 to 4.7 days compared with 9.1 to 20.6 days in the placebo group. The median time to first SBM after dosing on day 1 ranged from 0.1 to 0.4 days in the MOTEGRITY group compared with 1.0 to 1.6 days in the placebo group.
Alternative Efficacy Endpoint
Using an alternative efficacy endpoint, a responder was defined as a patient who had at least 3 CSBMs and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline in a given week for at least 9 weeks out of the 12-week treatment period and for at least 3 of the last 4 weeks of the treatment period. The differences in response rates between MOTEGRITY and placebo in the 6 studies are shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Efficacy Responder Rates in Placebo-Controlled Studies of CIC - Proportion of Patients with an Average of ≥3 CSBMs/week and an Increase of ≥1 CSBM per Week for at Least 9 out of the 12 Weeks, Including 3 of the Last 4 Weeks (ITT Population) Study MOTEGRITY 1 or 2 mg Once Daily Placebo Treatment Difference
(95% CI)N n (%) N n (%) CSBM = complete spontaneous bowel movement
N = number of patients per treatment group
n = number of respondersStudy 1 249 65 (26) 252 22 (9) 17
(11, 24)Study 2 177 57 (32) 181 25 (14) 18
(10, 27)Study 3 236 30 (13) 240 13 (5) 8
(2, 12)Study 4 190 37 (19) 193 15 (8) 11
(5, 18)Study 5 214 34 (16) 212 11 (5) 11
(5, 16)Study 6 171 29 (17) 169 22 (13) 4
(-4, 12) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
MOTEGRITY tablets containing 1 mg prucalopride are white to off-white, round, biconvex film-coated tablets debossed with "PRU 1" on one side and no debossing on the other side. They are supplied as:
- NDC: 54092-546-01: HDPE bottle of 30 tablets, with child-resistant closure.
MOTEGRITY tablets containing 2 mg prucalopride are pink, round, biconvex film-coated tablets debossed with "PRU 2" on one side and no debossing on the other side. They are supplied as:
- NDC: 54092-547-01: HDPE bottle of 30 tablets, with child-resistant closure.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
- Suicidal Ideation and Behavior: Inform patients, their caregivers, and family members that suicidal ideation and behavior have been reported in patients treated with MOTEGRITY. Advise them to be aware of any unusual changes in mood or behavior, persistent worsening of symptoms of depression, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts or behavior. Instruct patients, caregivers, and family members that if any of these symptoms occur, they should discontinue MOTEGRITY immediately and contact their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for:
Shire US Inc.
300 Shire Way
Lexington, MA 02421For more information go to www.motegrity.com or call 1-800-828-2088
Motegrity is a trademark or registered trademark of Shire LLC, a wholly-owned, indirect subsidiary of Shire plc.
Shire and the Shire Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Shire Pharmaceutical Holdings Ireland Limited or its affiliates.
Copyright © 2018 Shire LLC.
All rights reserved.TRPI0
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: December 2018 PATIENT INFORMATION
MOTEGRITY™ (moe-teh'-gri-tee)
(prucalopride) tablets, for oral use
What is MOTEGRITY?
MOTEGRITY is a prescription medicine used in adults to treat a type of constipation called chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC). Idiopathic means the cause of the constipation is unknown.
It is not known if MOTEGRITY is safe and effective in children.Do not take MOTEGRITY if you: - are allergic to MOTEGRITY. Allergic reaction symptoms may include trouble breathing, rash, itching and swelling of your face, lips, tongue or throat.
- have a tear in your stomach or intestinal wall (bowel perforation), a bowel blockage (intestinal obstruction) or serious conditions of the intestinal wall such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
Before taking MOTEGRITY, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have or have had depression, suicidal thoughts or actions, or mood problems.
- have kidney problems. Your healthcare provider may give you a lower dose.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if MOTEGRITY will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Prucalopride can pass into your breastmilk. Talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take MOTEGRITY.
How should I take MOTEGRITY? - Take 1 MOTEGRITY tablet each day or as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Take MOTEGRITY exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take MOTEGRITY with or without food.
What are the possible side effects of MOTEGRITY?
MOTEGRITY may cause serious side effects, including:- unusual changes in mood or behavior, thoughts of hurting yourself, trying to hurt yourself, or suicide. Stop taking MOTEGRITY right away and tell your healthcare provider immediately if your depression gets worse, you feel sad, hopeless or begin to have thoughts of suicide, thoughts of hurting yourself or have tried to hurt yourself.
The most common side effects of MOTEGRITY include: - headache
- stomach area (abdominal) pain or bloating
- nausea
- diarrhea
- dizziness
- vomiting
- gas
- fatigue
These are not all the possible side effects of MOTEGRITY.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store MOTEGRITY? - Store MOTEGRITY at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store MOTEGRITY in the original container to protect from moisture.
General information about the safe and effective use of MOTEGRITY.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use MOTEGRITY for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MOTEGRITY to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about MOTEGRITY that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in MOTEGRITY?
Active ingredient: prucalopride
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. The coating contains hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 3000, titanium dioxide and triacetin. The 2 mg tablet also contains red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide and FD&C Blue #2.Manufactured for:
Shire US Inc.
300 Shire Way
Lexington, MA 02421
Motegrity is a trademark or registered trademark of Shire LLC, a wholly-owned, indirect subsidiary of Shire plc.
Shire and the Shire Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Shire Pharmaceutical Holdings Ireland Limited or its affiliates.
Copyright © 2018 Shire LLC.
All rights reserved. TRPIL0
For more information, call Shire at 1-800-828-2088, or go to www.MOTEGRITY.com. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 mg Tablet Bottle Label
Rx Only
NDC: 54092-546-01motegrity™
(prucalopride) tablets1 mg
Usual Dose: One tablet once daily.
30 Tablets
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg Tablet Bottle Label
Rx Only
NDC: 54092-547-01motegrity™
(prucalopride) tablets2 mg
Usual Dose: One tablet once daily.
30 Tablets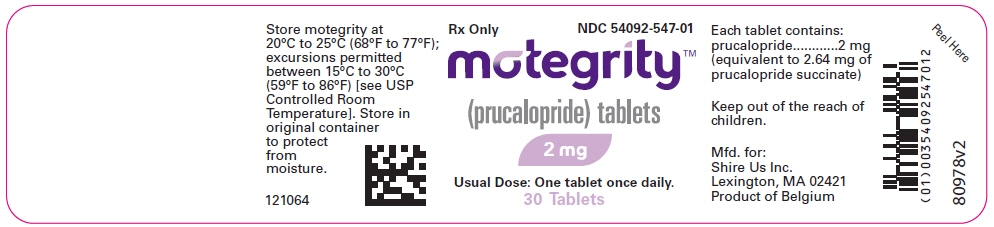
-
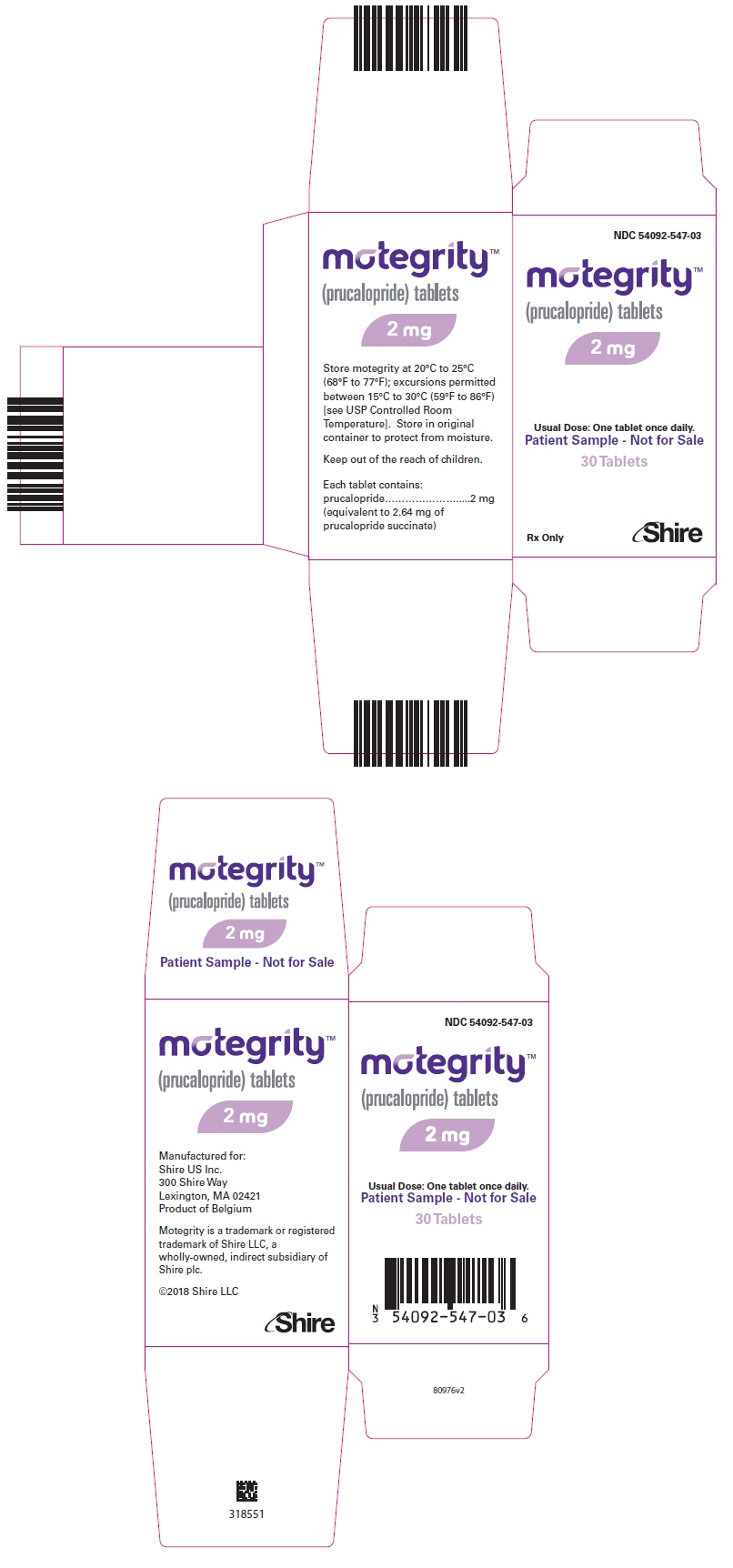
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC: 54092-547-03
motegrity™
(prucalopride) tablets2 mg
Usual Dose: One tablet once daily.
Patient Sample - Not for Sale30 Tablets
Rx Only
Shire
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MOTEGRITY
prucalopride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54092-546 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PRUCALOPRIDE SUCCINATE (UNII: 4V2G75E1CK) (PRUCALOPRIDE - UNII:0A09IUW5TP) PRUCALOPRIDE 1 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) TRIACETIN (UNII: XHX3C3X673) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3000 (UNII: SA1B764746) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND (biconvex) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code PRU;1 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54092-546-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/14/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA210166 12/14/2018 MOTEGRITY
prucalopride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54092-547 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PRUCALOPRIDE SUCCINATE (UNII: 4V2G75E1CK) (PRUCALOPRIDE - UNII:0A09IUW5TP) PRUCALOPRIDE 2 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) TRIACETIN (UNII: XHX3C3X673) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3000 (UNII: SA1B764746) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape ROUND (biconvex) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code PRU;2 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54092-547-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/14/2018 2 NDC: 54092-547-02 1 in 1 CARTON 12/14/2018 2 7 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 54092-547-03 1 in 1 CARTON 12/14/2018 3 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA210166 12/14/2018 Labeler - Shire US Manufacturing Inc. (964907406)
Trademark Results [MOTEGRITY]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 MOTEGRITY 87673187 5776458 Live/Registered |
Shire LLC 2017-11-06 |
 MOTEGRITY 87329871 5794940 Live/Registered |
Shire LLC 2017-02-09 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.