EFFER-K UNFLAVORED- potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescent EFFER-K ORANGE- potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescent EFFER-K LEMON CITRUS- potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescent EFFER-K CHERRY BERRY- potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescent
Effer-K by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Effer-K by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Nomax Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
Description
Description: Effer-K® 25 mEq TABLETS (Potassium Bicarbonate Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution, USP) are intended for the preparation of an oral solution of potassium. Each tablet contains 2.5 g. potassium bicarbonate and 2.1 g. citric acid which in solution provides 25 mEq (978 mg) of elemental potassium as potassium citrate. Tablets also contain: SD flavors, microcrystalline cellulose, mineral oil, saccharine and talc. The orange tablets contain FD&C yellow No. 6 and FD&C yellow No, 6 lake. The lemon citrus tablets contain D&C yellow No. 10 and yellow No. 10 lake. The cherry berry tablets contain FD&C red No. 40 and FD&C red No. 40 lake. The unflavored tablets do not contain any natural or synthetic dyes, flavors or sweeteners.
Tablets are one inch in diameter round, flat face on both sides with large bevels. "EK-25" is imprinted on one side of the tablets. Each tablet is foil-pouched with the product description on one side of the pouch and the lot number, expiration and barcode on the other.
-
Clinical Pharmacology
Potassium ion is the principal intracellular cation of most body tissues, whereas sodium ion is relatively low in concentration. In extracellular fluid the opposite exists, sodium ion being principal and potassium ion being low. The situation is maintained by an active membrane-bound enzyme (Na+K+ATPase). This potassium ion concentration gradient is essential to conduct nerve impulses in such specialized tissues as the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle; and in addition, to maintain normal renal function, acid-base balance, and various cellular metabolic functions. Elimination values are 90% renal and 10% fecal.
Potassium depletion may occur if the rate of potassium ion loss by renal excretion and/or loss from the gastrointestinal tract exceeds the rate of potassium ion intake. Such depletion usually develops slowly as a consequence of prolonged therapy with oral diuretics, primary or secondary hyperaldosteronism, diabetic ketoacidosis, severe diarrhea, or inadequate replacement of potassium in patients on prolonged parenteral nutrition. Potassium depletion due to these causes is usually accompanied by a concomitant deficiency of chloride and is manifested by hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis. Potassium depletion may produce weakness, fatigue, mood or mental changes, nausea, vomiting, disturbances of cardiac rhythm (primarily ectopic beats), prominent U-waves in the electrocardiogram, and in advanced cases flaccid paralysis and/or impaired ability to concentrate urine.
-
Indications and Usage
- For therapeutic use in patients with hypokalemia with or without metabolic alkalosis; in chronic digitalis intoxication; and in patients with hypokalemic familial periodic paralysis.
- For prevention of potassium depletion when the dietary intake of potassium ion is inadequate in the following conditions; patients receiving digitalis and diuretics for congestive heart failure; hepatic cirrhosis with ascites; states of aldosterone excess with normal renal function; potassiumlosing nephropathy, and certain diarrheal states; long-term corticosteroid therapy.
- The use of potassium salts in patients receiving diuretics for uncomplicated essential hypertension or receiving certain antibiotics is often unnecessary when such patients have a normal dietary pattern. Serum potassium should be checked periodically, however, and, if hypokalemia occurs, dietary supplementation with potassium-containing foods may be adequate to control milder cases. In more severe cases supplementation with potassium salts may be indicated.
-
Contraindications
Potassium supplements are contraindicated in patients with hyperkalemia since a further increase in serum potassium concentration in such patients can produce cardiac arrest. Conditions predisposing to hyperkalemia include: chronic renal failure, acute metabolic acidosis, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, esophageal compression or delayed gastric emptying or intestinal obstruction/stricture or peptic ulcer. Potassium supplements should be used with caution and only where medically indicated in patients with familial periodic paralysis, myotonia congenita or severe/complete heart block. IMPORTANT: Potassium supplements are contraindicated in patients receiving potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g. spironolactone, triamterene) since such use may produce severe hyperkalemia.
-
Warnings
In patients with hyperkalemia and impaired mechanisms for excreting potassium the administration of potassium salts can produce hyperkalemia and cardiac arrest. This occurs most commonly in patients given potassium by the intravenous route but may also occur in patients given potassium orally. Potentially fatal hyperkalemia can develop rapidly and be asymptomatic.
The use of potassium salts in patients with chronic renal disease, or any other condition which impairs potassium excretion, requires particularly careful monitoring of the serum potassium concentration and appropriate dosage adjustment.
Note: There is no conclusive evidence that potassium supplements lower blood pressure in hypertensive patients.
-
Precautions
The diagnosis of potassium depletion is ordinarily made by demonstrating hypokalemia in a patient with a clinical history suggesting some cause for potassium depletion. In interpreting the serum potassium level, the physician should bear in mind that acute alkalosis per se can produce hypokalemia in the absence of a deficit in total body potassium, while acute acidosis per se can increase the serum potassium concentration into the normal range even in the presence of a reduced total body potassium. The treatment of potassium depletion, particularly in the presence of cardiac disease, renal disease, or acidosis, requires careful attention to acid-base balance and appropriate monitoring of serum electrolytes, the electrocardiogram, and the clinical status of the patient.
Information for patients
To minimize the possibility of gastrointestinal irritation associated with the oral ingestion of concentrated potassium salt preparations, patients should be directed to dissolve each dose completely in the stated amount of water.
Each dose should be taken immediately after a meal or with food. Patients should avoid low-salt foods and salt substitutes, unless approved by physician. The patient should be cautioned to comply strictly with the regimen, particularly when taking diuretics or digitalis, to visit the physician regularly and to report at once any unusual symptoms (e.g. blackish stools, a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding). As with any other medicine, the patient should be counseled on this background information and advised to report to the physician any changes in routine (e.g. starting a fitness program). Proper storage and handling of the product is important. Tablets should not be removed from foil pouch until shortly before use.
Laboratory tests
Frequent clinical evaluation of the patient should include an ECG and a serum potassium level; also, as appropriate, renal function, serum magnesium and serum pH.
Drug Interactions
The simultaneous administration of potassium supplements and a potassium-sparing diuretic can produce severe hyperkalemia (see Contraindications). Potassium supplements should be used cautiously in patients who are using salt substitutes, because most of the latter contain substantial amounts of potassium. Such concomitant use could result in hyperkalemia.
Moreover, the following drugs may produce unfavorable interactions when used concomitantly with potassium supplements: angiotension-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), beta-adrenergic blocking drugs, heparin, low-salt foods, other potassium containing medications, digitalis glycosides and others.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Potassium is an essential constituent of the human diet. There are no data available on long-term potential for carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility in animals or in human beings.
Usage in Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Effer-K® 25mEq TABLETS (Potassium Bicarbonate Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution, USP). It is also not known whether these products can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Effer-K® 25mEq TABLETS (Potassium Bicarbonate Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution, USP) should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
-
Adverse Reactions
One of the most severe adverse effects is hyperkalemia (see Contraindications, Warnings and Overdosage). The most common adverse reactions to oral potassium salts are nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea. These symptoms are due to irritation of the gastrointestinal tract and are best managed by diluting the preparation further, taking the dose with meals, or reducing the dose. Skin rash has been reported rarely.
-
Overdosage
The administration of oral potassium salts to persons with normal excretory mechanisms for potassium rarely causes serious hyperkalemia. However, if excretory mechanisms are impaired or if potassium is administered too rapidly intravenously, potentially fatal hyperkalemia can result (see Contraindications and Warnings). It is important to recognize that initally hyperkalemia is usually asymptomatic and may be manifested only by an increased serum potassium concentration and characteristic electrocardiographic changes (peaking of T-waves, loss of P-wave, depression of S-T segment, and prolongation of the QT interval). Late manifestations include muscle paralysis and cardiovascular collapse from cardiac arrest.
Treatment measures for hyperkalemia include the elimination of foods and medications containing potassium and potassium-sparing diuretics, as well as ACE inhibitors, beta blocking agents, NSAIDs, heparin, and cyclosporine. In cases of life-threatening hyperkalemia, treatment measures may include: (1) intravenous administration of 300 to 500 ml/hr of 10% dextrose solution containing 10-20 units of insulin per 1,000 ml; (2) correction of acidosis, if present, with intravenous sodium bicarbonate; (3) use of exchange resins, hemodialysis, or peritoneal dialysis; (4) administration of a calcium salt to antagonize the cardiotoxic effects in patients whose electrocardiograms show appropriate characteristics, and who are not receiving digitalis glycosides; and (5) maintenance of a high urine output in suitable patients.
In treating hyperkalemia, it should be recalled that in patients who have been stabilized on digitalis, rapid lowering of serum potassium can produce digitalis toxicity.
-
Dosage and administration
Dosage and Administration: Adults- One Effer-K® flavored tablet, (Orange, Lemon Citrus or Cherry Berry) each containing 25 mEq (978 mg) of potassium, completely dissolved in 4 ounces of cold or ice water, 1 to 4 times daily, depending on the requirement of the patient. For Effer-K® unflavored tablets (each containing 25 mEq (978 mg) of potassium) we recommend completely dissolving one tablet in 12 to 16 ounces of cold juice of the patient's choice.
NOTE: It is suggested that any effervescent potassium tablets be taken with meals and sipped slowly over a 5 to 10 minute period.
-
How Supplied
Effer-K® 25 mEq TABLETS (Potassium Bicarbonate Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution, USP). Each tablet in solution provides 25 mEq of elemental potassium as potassium citrate. Store below 40˚C (104˚F) preferably between 15˚ and 30˚C (59˚ and 86˚F), in original hermetic packaging.
Tablets are one inch diameter round, flat face on both sides with large bevels. "EK 25" is imprinted one side of the tablets. Each tablet is pouched with the product description on one side of the pouch and the lot number, expiration date, and barcode on the other.
NDC: 51801-001-30 Orange-flavored, package of 30 tablets. NDC: 51801-005-30 Lemon Citrus-flavored, package of 30 tablets. NDC: 51801-001-40 Orange-flavored, package of 100 tablets. NDC: 51801-006-30 Cherry Berry-flavored, package of 30 tablets. NDC: 51801-007-30 Unflavored, package of 30 tablets. Nomax, Inc. St. Louis, MO 63123 - Made in USA
MSN 015-031Rev. 08/10
-
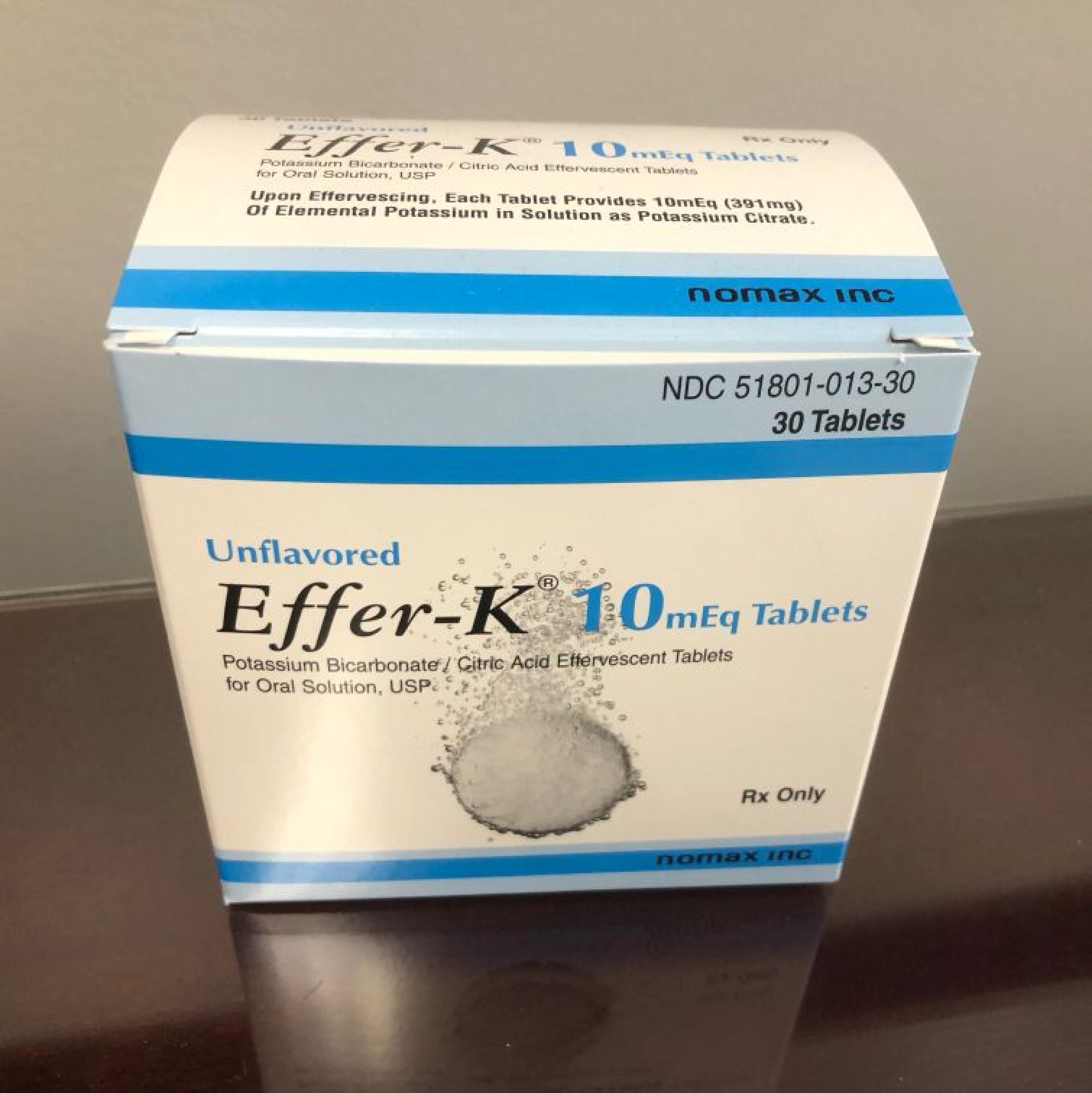
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Tablet Pouch Carton - Unflavored
NDC: 51801-007-30
30 TabletsEffer-K® 25 mEq Tablets
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
FOR ORAL SOLUTION, USPEach Tablet contains 25mEq (978 mg) of Potassium
Unflavored (Dissolve in 12-16 ounces of juice)
Rx Onlynomax inc

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Tablet Pouch Carton - Orange
NDC: 51801-001-30
30 TabletsEffer-K® 25 mEq Tablets
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
FOR ORAL SOLUTION, USPEach Tablet contains 25mEq (978 mg) of Potassium
Orange Flavored
Rx Onlynomax inc

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Tablet Pouch Carton - Lemon
NDC: 51801-005-30
30 TabletsEffer-K® 25 mEq Tablets
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
FOR ORAL SOLUTION, USPEach Tablet contains 25mEq (978 mg) of Potassium
Lemon Citrus Flavored
Rx Onlynomax inc

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Tablet Pouch Carton - Cherry
NDC: 51801-006-30
30 TabletsEffer-K® 25 mEq Tablets
POTASSIUM BICARBONATE EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
FOR ORAL SOLUTION, USPEach Tablet contains 25mEq (978 mg) of Potassium
Cherry Berry Flavored
Rx Onlynomax inc

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EFFER-K UNFLAVORED
potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescentProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51801-007 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) (BICARBONATE ION - UNII:HN1ZRA3Q20) POTASSIUM BICARBONATE 977.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 2100 mg MINERAL OIL (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) 34 mg TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) 20 mg CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) 100 mg Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 25mm Flavor Imprint Code EK;25 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51801-007-30 30 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2013 1 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 01/30/2013 EFFER-K ORANGE
potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescentProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51801-001 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) (BICARBONATE ION - UNII:HN1ZRA3Q20) POTASSIUM BICARBONATE 977.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 2100 mg MINERAL OIL (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) 34 mg TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) 20 mg CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) 100 mg Product Characteristics Color ORANGE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 25mm Flavor ORANGE Imprint Code EK;25 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51801-001-30 30 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2013 1 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51801-001-40 100 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2013 2 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 01/30/2013 EFFER-K LEMON CITRUS
potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescentProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51801-005 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) (BICARBONATE ION - UNII:HN1ZRA3Q20) POTASSIUM BICARBONATE 977.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 2100 mg MINERAL OIL (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) 34 mg TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) 20 mg CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) 100 mg Product Characteristics Color YELLOW Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 25mm Flavor LEMON (Lemon Citrus) Imprint Code EK;25 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51801-005-30 30 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2013 1 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 01/30/2013 EFFER-K CHERRY BERRY
potassium bicarbonate tablet, effervescentProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51801-006 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength POTASSIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: HM5Z15LEBN) (BICARBONATE ION - UNII:HN1ZRA3Q20) POTASSIUM BICARBONATE 977.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) 2100 mg MINERAL OIL (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) 34 mg TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) 20 mg CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) 100 mg Product Characteristics Color PINK Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 25mm Flavor CHERRY (Cherry Berry) Imprint Code EK;25 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51801-006-30 30 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2013 1 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER 01/30/2013 Labeler - Nomax Inc. (103220273) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Nomax Inc. 103220273 MANUFACTURE(51801-007, 51801-001, 51801-005, 51801-006)
Trademark Results [Effer-K]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 EFFER-K 73402235 1295554 Live/Registered |
Nomax, Inc. 1982-11-10 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.