These highlights do not include all the information needed to use memantine hydrochloride tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for memantine hydrochloride tablets. MEMANTINE hydrochloride tablets USP, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 2003
Memantine Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Memantine Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE- memantine tablet
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use memantine hydrochloride tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for memantine hydrochloride tablets.
MEMANTINE hydrochloride tablets USP, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2003 INDICATIONS AND USAGEMemantine hydrochloride tablets, USP are an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (≥ 5 % and greater than placebo) are dizziness, headache, confusion and constipation. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 9/2014 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Memantine hydrochloride tablets, USP are indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended starting dose of memantine hydrochloride tablets is 5 mg once daily. The dose should be increased in 5 mg increments to 10 mg/day (5 mg twice daily), 15 mg/day (5 mg and 10 mg as separate doses), and 20 mg/day (10 mg twice daily). The minimum recommended interval between dose increases is one week. The dosage shown to be effective in controlled clinical trials is 20 mg/day.
Memantine hydrochloride tablets can be taken with or without food. If a patient misses a single dose of memantine hydrochloride tablets, that patient should not double up on the next dose. The next dose should be taken as scheduled. If a patient fails to take memantine hydrochloride tablets for several days, dosing may need to be resumed at lower doses and retitrated as described above.
Special Populations: Renal Impairment: A target dose of 5 mg twice daily is recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 5 to 29 mL/min based on the Cockroft-Gault equation).
Hepatic Impairment: Memantine hydrochloride tablets should be administered with caution to patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Memantine hydrochloride 5 mg tablets are white, film-coated, round unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and 103 on the other side.
Memantine hydrochloride 10 mg tablets are white, film-coated, round unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and 104 on the other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Memantine hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to memantine hydrochloride or to any excipients used in the formulation.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Genitourinary Conditions
Conditions that raise urine pH may decrease the urinary elimination of memantine resulting in increased plasma levels of memantine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Memantine was evaluated in eight double-blind placebo-controlled trials involving a total of 1,862 dementia (Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia) patients (940 patients treated with memantine and 922 patients treated with placebo) for a treatment period up to 28 weeks.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation
In placebo-controlled trials in which dementia patients received doses of memantine up to 20 mg/day, the likelihood of discontinuation because of an adverse reaction was the same in the memantine group (10.1%) as in the placebo group (11.5%). No individual adverse reaction was associated with the discontinuation of treatment in 1% or more of memantine-treated patients and at a rate greater than placebo.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
In double-blind placebo-controlled trials involving dementia patients, the most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and higher than placebo) in patients treated with memantine were dizziness, headache, confusion and constipation. Table 1 lists all adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with memantine and at an incidence greater than placebo.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in Controlled Clinical Trials in at Least 2% of Patients Receiving Memantine Hydrochloride and at a Higher Frequency than Placebo-treated Patients.
|
Adverse Reaction |
Placebo (n = 922) % |
Memantine (n = 940) % |
|
Body as a Whole | ||
|
Fatigue |
1 |
2 |
|
Pain |
1 |
3 |
|
Cardiovascular System | ||
|
Hypertension |
2 |
4 |
|
Central and Peripheral Nervous System | ||
|
Dizziness |
5 |
7 |
|
Headache |
3 |
6 |
|
Gastrointestinal System | ||
|
Constipation |
3 |
5 |
|
Vomiting |
2 |
3 |
|
Musculoskeletal System | ||
|
Back pain |
2 |
3 |
|
Psychiatric Disorders | ||
|
Confusion |
5 |
6 |
|
Somnolence |
2 |
3 |
|
Hallucination |
2 |
3 |
|
Respiratory System | ||
|
Coughing |
3 |
4 |
|
Dyspnea |
1 |
2 |
The overall profile of adverse reactions and the incidence rates for individual adverse reactions in the subpopulation of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease were not different from the profile and incidence rates described above for the overall dementia population.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of memantine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These reactions include:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Agranulocytosis, leukopenia (including neutropenia), pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Cardiac Disorders: Cardiac failure congestive.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatitis.
Psychiatric Disorders: Suicidal ideation.
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Acute renal failure (including increased creatinine and renal insufficiency).
Skin Disorders: Stevens Johnson syndrome.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that Make the Urine Alkaline
The clearance of memantine was reduced by about 80% under alkaline urine conditions at pH 8. Therefore, alterations of urine pH towards the alkaline condition may lead to an accumulation of the drug with a possible increase in adverse effects. Urine pH is altered by diet, drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, sodium bicarbonate) and clinical state of the patient (e.g., renal tubular acidosis or severe infections of the urinary tract). Hence, memantine should be used with caution under these conditions.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. Pregnancy Category B
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of memantine in pregnant women. Memantine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Memantine given orally to pregnant rats and pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis was not teratogenic up to the highest doses tested (18 mg/kg/day in rats and 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits, which are 9 and 30 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis).
Slight maternal toxicity, decreased pup weights and an increased incidence of non-ossified cervical vertebrae were seen at an oral dose of 18 mg/kg/day in a study in which rats were given oral memantine beginning pre-mating and continuing through the postpartum period. Slight maternal toxicity and decreased pup weights were also seen at this dose in a study in which rats were treated from day 15 of gestation through the postpartum period. The no-effect dose for these effects was 6 mg/kg, which is 3 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when memantine is administered to a nursing mother.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The majority of people with Alzheimer’s disease are 65 years and older. In the clinical studies of memantine the mean age of patients was approximately 76; over 90% of patients were 65 years and older, 60% were 75 years and older, and 12% were at or above 85 years of age. The efficacy and safety data presented in the clinical trial sections were obtained from these patients. There were no clinically meaningful differences in most adverse events reported by patient groups ≥ 65 years old and < 65 year old.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. A dosage reduction is recommended in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Memantine should be administered with caution to patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Signs and symptoms most often accompanying memantine overdosage in clinical trials and from worldwide marketing experience, alone or in combination with other drugs and/or alcohol, include agitation, asthenia, bradycardia, confusion, coma, dizziness, ECG changes, increased blood pressure, lethargy, loss of consciousness, psychosis, restlessness, slowed movement, somnolence, stupor, unsteady gait, visual hallucinations, vertigo, vomiting, and weakness. The largest known ingestion of memantine worldwide was 2 grams in a patient who took memantine in conjunction with unspecified antidiabetic medications. The patient experienced coma, diplopia, and agitation, but subsequently recovered. Fatal outcome has been very rarely reported with memantine, and the relationship to memantine was unclear.
Because strategies for the management of overdose are continually evolving, it is advisable to contact a poison control center to determine the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose of any drug. As in any cases of overdose, general supportive measures should be utilized, and treatment should be symptomatic. Elimination of memantine can be enhanced by acidification of urine.
11 DESCRIPTION
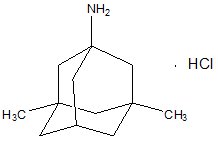
Memantine hydrochloride is an orally active NMDA receptor antagonist. The chemical name for memantine hydrochloride is 1-Amino-3,5-dimethyladamantane hydrochloride with the following structural formula:
The molecular formula is C12H21NHCl and the molecular weight is 215.76. Memantine hydrochloride, USP occurs as a fine white to off-white powder and is soluble in water.
Memantine hydrochloride is available as tablets. Memantine hydrochloride tablets, USP are available for oral administration as round, film-coated tablets containing 5 mg and 10 mg of memantine hydrochloride. The tablets also contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, talc and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Persistent activation of central nervous system N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors by the excitatory amino acid glutamate has been hypothesized to contribute to the symptomatology of Alzheimer’s disease. Memantine is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect through its action as a low to moderate affinity uncompetitive (open-channel) NMDA receptor antagonist which binds preferentially to the NMDA receptor-operated cation channels. There is no evidence that memantine prevents or slows neurodegeneration in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Memantine showed low to negligible affinity for GABA, benzodiazepine, dopamine, adrenergic, histamine and glycine receptors and for voltage-dependent Ca2+, Na+ or K+ channels. Memantine also showed antagonistic effects at the 5HT3 receptor with a potency similar to that for the NMDA receptor and blocked nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with one-sixth to one-tenth the potency.
In vitro studies have shown that memantine does not affect the reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by donepezil, galantamine, or tacrine.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration memantine is highly absorbed with peak concentrations reached in about 3 to 7 hours. Memantine has linear pharmacokinetics over the therapeutic dose range. Food has no effect on the absorption of memantine.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of memantine is 9 to 11 L/kg and the plasma protein binding is low (45%).
Metabolism
Memantine undergoes partial hepatic metabolism. The hepatic microsomal CYP450 enzyme system does not play a significant role in the metabolism of memantine.
Elimination
Memantine is excreted predominantly (about 48%) unchanged in urine and has a terminal elimination half-life of about 60 to 80 hours.
The remainder is converted primarily to three polar metabolites which possess minimal NMDA receptor antagonistic activity: the N-glucuronide conjugate, 6-hydroxy memantine, and 1-nitroso-deaminated memantine. A total of 74% of the administered dose is excreted as the sum of the parent drug and the N-glucuronide conjugate. Renal clearance involves active tubular secretion moderated by pH dependent tubular reabsorption.
Pharmacokinetics in Specific Populations
Gender
Following multiple dose administration of memantine 20 mg daily, females had about 45% higher exposure than males, but there was no difference in exposure when body weight was taken into account.
Renal Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following single oral administration of 20 mg memantine hydrochloride in eight subjects with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance, CLcr, > 50 to 80 mL/min), eight subjects with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 49 mL/min), seven subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr 5 to 29 mL/min) and eight healthy subjects (CLcr > 80 mL/min) matched as closely as possible by age, weight and gender to the subjects with renal impairment. Mean AUC0-∞ increased by 4%, 60%, and 115% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects. The terminal elimination half-life increased by 18%, 41%, and 95% in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, compared to healthy subjects.
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild and moderate renal impairment. Dosage should be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Hepatic Impairment
Memantine pharmacokinetics were evaluated following the administration of single oral doses of 20 mg in eight subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, score 7 to 9) and eight subjects who were age-, gender-, and weight-matched to the hepatically-impaired subjects. There was no change in memantine exposure (based on Cmax and AUC) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. However, terminal elimination half-life increased by about 16% in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment as compared with healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment. Memantine should be administered with caution to patients with severe hepatic impairment as the pharmacokinetics of memantine have not been evaluated in that population.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Use with Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Coadministration of memantine with the AChE inhibitor donepezil hydrochloride did not affect the pharmacokinetics of either compound. Furthermore, memantine did not affect AChE inhibition by donepezil. In a 24-week controlled clinical study in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, the adverse event profile observed with a combination of memantine and donepezil was similar to that of donepezil alone.
Effect of Memantine on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
In vitro studies conducted with marker substrates of CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, -2A6, -2C9, -2D6, -2E1, -3A4) showed minimal inhibition of these enzymes by memantine. In addition, in vitro studies indicate that at concentrations exceeding those associated with efficacy, memantine does not induce the cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP1A2, -2C9, -2E1 and -3A4/5. No pharmacokinetic interactions with drugs metabolized by these enzymes are expected.
Pharmacokinetic studies evaluated the potential of memantine for interaction with warfarin, and buproprion. Memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics of the CYP2B6 substrate buproprion or its metabolite hydroxybuproprion. Furthermore, memantine did not affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of warfarin as assessed by the prothrombin INR.
Effect of Other Drugs on Memantine
Memantine is predominantly renally eliminated, and drugs that are substrates and/or inhibitors of the CYP450 system are not expected to alter the metabolism of memantine.
Drugs Eliminated via Renal Mechanisms
Because memantine is eliminated in part by tubular secretion, coadministration of drugs that use the same renal cationic system, including hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), triamterene (TA), metformin, cimetidine, ranitidine, quinidine, and nicotine, could potentially result in altered plasma levels of both agents. However, coadministration of memantine and HCTZ/TA did not affect the bioavailability of either memantine or TA, and the bioavailability of HCTZ decreased by 20%. In addition, coadministration of memantine with the antihyperglycemic drug Glucovance®* (glyburide and metformin hydrochloride) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of memantine, metformin and glyburide. Furthermore, memantine did not modify the serum glucose lowering effect of Glucovance®*, indicating the absence of a pharmacodynamic interaction.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There was no evidence of carcinogenicity in a 113-week oral study in mice at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (10 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] on a mg/m2 basis). There was also no evidence of carcinogenicity in rats orally dosed at up to 40 mg/kg/day for 71 weeks followed by 20 mg/kg/day (20 and 10 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis, respectively) through 128 weeks.
Memantine produced no evidence of genotoxic potential when evaluated in the in vitro S. typhimurium or E. coli reverse mutation assay, an in vitro chromosomal aberration test in human lymphocytes, an in vivo cytogenetics assay for chromosome damage in rats, and the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. The results were equivocal in an in vitro gene mutation assay using Chinese hamster V79 cells.
No impairment of fertility or reproductive performance was seen in rats administered up to 18 mg/kg/day (9 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) orally from 14 days prior to mating through gestation and lactation in females, or for 60 days prior to mating in males.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Memantine induced neuronal lesions (vacuolation and necrosis) in the multipolar and pyramidal cells in cortical layers III and IV of the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial neocortices in rats, similar to those which are known to occur in rodents administered other NMDA receptor antagonists. Lesions were seen after a single dose of memantine. In a study in which rats were given daily oral doses of memantine for 14 days, the no-effect dose for neuronal necrosis was 6 times the maximum recommended human dose of 20 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis.
In acute and repeat-dose neurotoxicity studies in female rats, oral administration of memantine and donepezil in combination resulted in increased incidence, severity, and distribution of neurodegeneration compared with memantine alone. The no-effect levels of the combination were associated with clinically relevant plasma memantine and donepezil exposures.
The relevance of these findings to humans is unknown.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of memantine as a treatment for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease was demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies (Studies 1 and 2) conducted in the United States that assessed both cognitive function and day to day function. The mean age of patients participating in these two trials was 76 with a range of 50 to 93 years. Approximately 66% of patients were female and 91% of patients were Caucasian. A third study (Study 3), carried out in Latvia, enrolled patients with severe dementia, but did not assess cognitive function as a planned endpoint. Study Outcome Measures: In each U.S. study, the effectiveness of memantine was determined using both an instrument designed to evaluate overall function through caregiver-related assessment, and an instrument that measures cognition. Both studies showed that patients on memantine experienced significant improvement on both measures compared to placebo.
Day-to-day function was assessed in both studies using the modified Alzheimer’s disease Cooperative Study -Activities of Daily Living inventory (ADCS-ADL). The ADCS-ADL consists of a comprehensive battery of ADL questions used to measure the functional capabilities of patients. Each ADL item is rated from the highest level of independent performance to complete loss. The investigator performs the inventory by interviewing a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient. A subset of 19 items, including ratings of the patient’s ability to eat, dress, bathe, telephone, travel, shop, and perform other household chores has been validated for the assessment of patients with moderate to severe dementia. This is the modified ADCS-ADL, which has a scoring range of 0 to 54, with the lower scores indicating greater functional impairment.
The ability of memantine to improve cognitive performance was assessed in both studies with the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB), a multi-item instrument that has been validated for the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with moderate to severe dementia. The SIB examines selected aspects of cognitive performance, including elements of attention, orientation, language, memory, visuospatial ability, construction, praxis, and social interaction. The SIB scoring range is from 0 to 100, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive impairment.
Study 1 (Twenty Eight-Week Study): In a study of 28 weeks duration, 252 patients with moderate to severe probable Alzheimer’s disease (diagnosed by DSM-IV and NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini-Mental State Examination scores ≥ 3 and ≤ 14 and Global Deterioration Scale Stages 5 to 6) were randomized to memantine or placebo. For patients randomized to memantine, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased weekly by 5 mg/day in divided doses to a dose of 20 mg/day (10 mg twice a day).
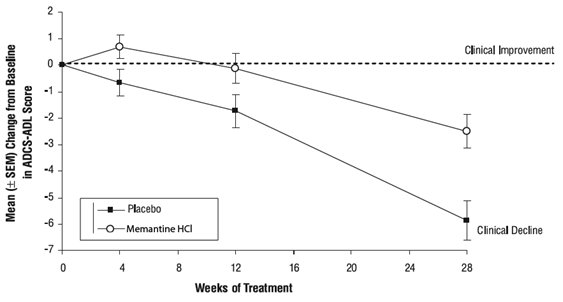
Effects on the ADCS-ADL: Figure 1 shows the time course for the change from baseline in the ADCS-ADL score for patients in the two treatment groups completing the 28 weeks of the study. At 28 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the ADCS-ADL change scores for the memantine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo was 3.4 units. Using an analysis based on all patients and carrying their last study observation forward (LOCF analysis), memantine treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 1: Time course of the change from baseline in ADCS-ADL score for patients completing 28 weeks of treatment.
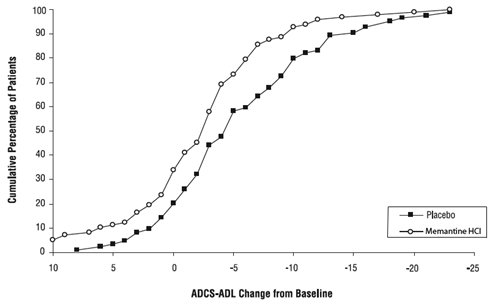
Figure 2 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the treatment groups who had attained at least the change in the ADCS-ADL shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine and placebo have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration (a negative change in ADCS-ADL compared to baseline), but that the memantine group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement. (In a cumulative distribution display, a curve for an effective treatment would be shifted to the left of the curve for placebo, while an ineffective or deleterious treatment would be superimposed upon or shifted to the right of the curve for placebo).
Figure 2: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 28 weeks of double-blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in ADCS-ADL scores.
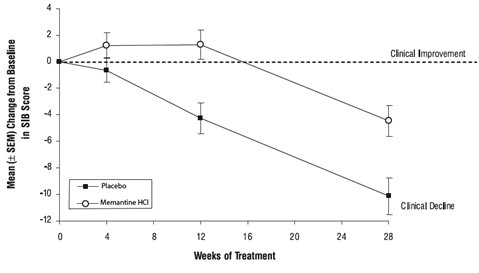
Effects on the SIB: Figure 3 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 28 weeks of the study. At 28 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the SIB change scores for the memantine-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo was 5.7 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Figure 3: Time course of the change from baseline in SIB score for patients completing 28 weeks of treatment.
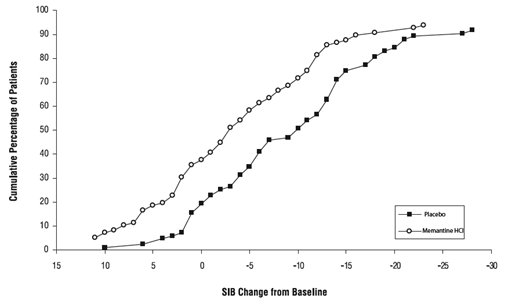
Figure 4 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each treatment group who had attained at least the measure of change in SIB score shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine and placebo have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration, but that the memantine group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement.
Figure 4: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 28 weeks of double-blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in SIB scores.
Study 2 (Twenty Four-Week Study): In a study of 24 weeks duration, 404 patients with moderate to severe probable Alzheimer’s disease (diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA criteria, with Mini-Mental State Examination scores ≥ 5 and ≤ 14) who had been treated with donepezil for at least 6 months and who had been on a stable dose of donepezil for the last 3 months were randomized to memantine or placebo while still receiving donepezil. For patients randomized to memantine, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased weekly by 5 mg/day in divided doses to a dose of 20 mg/day (10 mg twice a day).
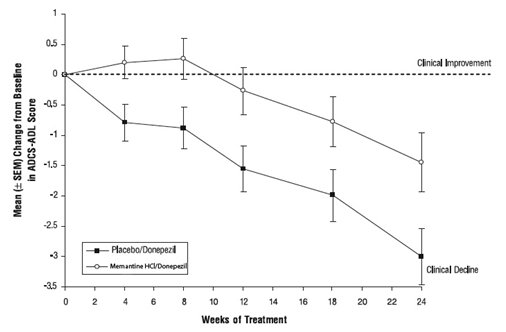
Effects on the ADCS-ADL: Figure 5 shows the time course for the change from baseline in the ADCS-ADL score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the ADCS-ADL change scores for the memantine/donepezil treated patients (combination therapy) compared to the patients on placebo/donepezil (monotherapy) was 1.6 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine/donepezil treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo/donepezil.
Figure 5: Time course of the change from baseline in ADCS-ADL score for patients completing 24 weeks of treatment.
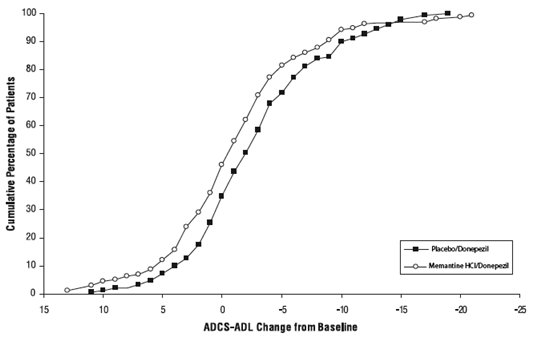
Figure 6 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the treatment groups who had attained at least the measure of improvement in the ADCS-ADL shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine/donepezil and placebo/donepezil have a wide range of responses and generally show deterioration, but that the memantine/donepezil group is more likely to show a smaller decline or an improvement.
Figure 6: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 24 weeks of double-blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in ADCS-ADL scores.
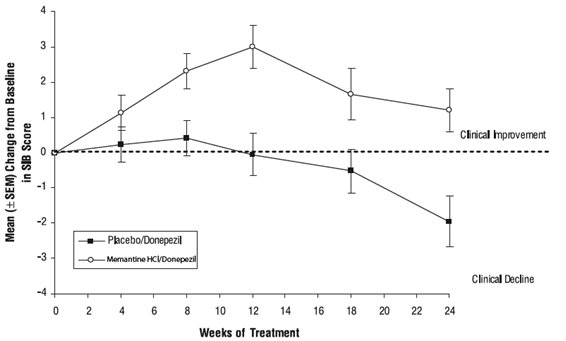
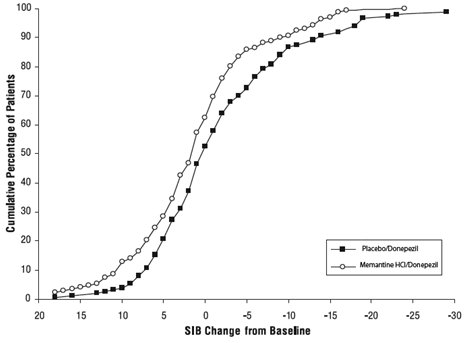
Effects on the SIB: Figure 7 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the mean difference in the SIB change scores for the memantine/donepezil-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo/donepezil was 3.3 units. Using an LOCF analysis, memantine/donepezil treatment was statistically significantly superior to placebo/donepezil.
Figure 7: Time course of the change from baseline in SIB score for patients completing 24 weeks of treatment.
Figure 8 shows the cumulative percentages of patients from each treatment group who had attained at least the measure of improvement in SIB score shown on the X axis. The curves show that both patients assigned to memantine/donepezil and placebo/donepezil have a wide range of responses, but that the memantine/donepezil group is more likely to show an improvement or a smaller decline.
Figure 8: Cumulative percentage of patients completing 24 weeks of double-blind treatment with specified changes from baseline in SIB scores.
Study 3 (Twelve-Week Study): In a double-blind study of 12 weeks duration, conducted in nursing homes in Latvia, 166 patients with dementia according to DSM-III-R, a Mini-Mental State Examination score of < 10, and Global Deterioration Scale staging of 5 to 7 were randomized to either memantine or placebo. For patients randomized to memantine, treatment was initiated at 5 mg once daily and increased to 10 mg once daily after one week. The primary efficacy measures were the care dependency subscale of the Behavioral Rating Scale for Geriatric Patients (BGP), a measure of day-to-day function, and a Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGI-C), a measure of overall clinical effect. No valid measure of cognitive function was used in this study. A statistically significant treatment difference at 12 weeks that favored memantine over placebo was seen on both primary efficacy measures. Because the patients entered were a mixture of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, an attempt was made to distinguish the two groups and all patients were later designated as having either vascular dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, based on their scores on the Hachinski Ischemic Scale at study entry. Only about 50% of the patients had computerized tomography of the brain. For the subset designated as having Alzheimer’s disease, a statistically significant treatment effect favoring memantine over placebo at 12 weeks was seen on both the BGP and CGI-C.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Memantine Hydrochloride Tablets, USP are available containing 5 mg and 10 mg of memantine hydrochloride, USP.
The 5 mg tablets are white, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and 103 on the other side:
NDC: 0378-1103-91
bottles of 60 tablets
NDC: 0378-1103-05
bottles of 500 tablets
The 10 mg tablets are white, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and 104 on the other side:
NDC: 0378-1104-91
bottles of 60 tablets
NDC: 0378-1104-05
bottles of 500 tablets
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
PHARMACIST: Dispense the Patient Information Leaflet with each prescription.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information Leaflet).
To assure safe and effective use of memantine hydrochloride tablets, the following information provided in the patient information section should be discussed with patients and caregivers.
Patients/caregivers should be instructed to follow the dose titration schedule provided by their physician or healthcare professional for memantine hydrochloride tablets. They should be warned not to use any tablets of memantine hydrochloride tablets that are damaged or show signs of tampering.
If a patient misses a single dose of memantine hydrochloride tablets, that patient should not double up on the next dose. The next dose should be taken as scheduled. If a patient fails to take memantine hydrochloride tablets for several days, dosing should not be resumed without consulting that patient’s healthcare professional.
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS, USP
(mem' an teen hye" droe klor' ide)
5 mg and 10 mg
Read this Patient Information that comes with memantine hydrochloride tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are memantine hydrochloride tablets?
Memantine hydrochloride tablets are a prescription medicine used for the treatment of moderate to severe dementia in people with Alzheimer’s disease. Memantine hydrochloride tablets belong to a class of medicines called NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) inhibitors.
It is not known if memantine hydrochloride tablets are safe and effective in children.
Who should not take memantine hydrochloride tablets?
Do not take memantine hydrochloride tablets if you are allergic to memantine or any of the ingredients in memantine hydrochloride tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in memantine hydrochloride tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before taking memantine hydrochloride tablets?
Before you take memantine hydrochloride tablets, tell your doctor if you:
- have or have had seizures
- have or have had problems passing urine
- have or have had bladder or kidney problems
- have liver problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if memantine hydrochloride tablets will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if memantine hydrochloride passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take memantine hydrochloride tablets or breastfeed.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking memantine hydrochloride tablets with certain other medicines may affect each other. Taking memantine hydrochloride tablets with other medicines can cause serious side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- other NMDA antagonists such as amantadine, ketamine, and dextromethorphan
- medicines that make your urine alkaline such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and sodium bicarbonate
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take memantine hydrochloride tablets?
- Your doctor will tell you how many memantine hydrochloride tablets to take and when to take it.
- Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Memantine hydrochloride tablets can be taken with food or without food.
- Do not use any tablets of memantine hydrochloride tablets that are damaged or show signs of tampering.
- If you forget to take one dose of memantine hydrochloride tablets, do not double up on the next dose. You should take only the next dose as scheduled.
- If you have forgotten to take memantine hydrochloride tablets for several days, you should not take the next dose until you talk to your doctor.
- If you take too many memantine hydrochloride tablets, call your doctor or poison control center at 1-800-222-1222 right away, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are the possible side effects of memantine hydrochloride tablets?
Memantine hydrochloride tablets may cause side effects, including:
The most common side effects of memantine hydrochloride tablets include:
- dizziness
- headache
- confusion
- constipation
These are not all the possible side effects of memantine hydrochloride tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store memantine hydrochloride tablets?
- Store memantine hydrochloride tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
What are the ingredients in memantine hydrochloride tablets?
Active ingredients: memantine hydrochloride, USP
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, talc and titanium dioxide.
Keep memantine hydrochloride tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of memantine hydrochloride tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not take memantine hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give memantine hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about memantine hydrochloride tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about memantine hydrochloride tablets that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about memantine hydrochloride tablets, call Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX).
This Patient Information Leaflet has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
* The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
REVISED SEPTEMBER 2014
MENT:R3ppt
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 5 mg
NDC: 0378-1103-91
Memantine
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP
5 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying
Patient Information Leaflet to each patient.
Rx only 60 Tablets
Each film-coated tablet
contains: Memantine
hydrochloride, USP 5 mg
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant
container as defined in the USP
using a child-resistant closure.
Keep container tightly closed.
Keep this and all medication
out of the reach of children.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
[See USP Controlled Room
Temperature.]
Usual Dosage: See accompanying
prescribing information.
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Mylan.com
RM1103D2
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 10 mg
NDC: 0378-1104-91
Memantine
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP
10 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying
Patient Information Leaflet to each patient.
Rx only 60 Tablets
Each film-coated tablet
contains: Memantine
hydrochloride, USP 10 mg
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant
container as defined in the USP
using a child-resistant closure.
Keep container tightly closed.
Keep this and all medication
out of the reach of children.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
[See USP Controlled Room
Temperature.]
Usual Dosage: See accompanying
prescribing information.
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Mylan.com
RM1104D2
| MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE
memantine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MEMANTINE HYDROCHLORIDE
memantine tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc. (059295980) |