EMBLAVEO- aztreonam and avibactam powder, for solution
EMBLAVEO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
EMBLAVEO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by AbbVie Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EMBLAVEO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EMBLAVEO.
EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
EMBLAVEO is a combination of aztreonam, a monobactam antibacterial, and avibactam, a beta-lactamase inhibitor, that when used in combination with metronidazole, is indicated in patients 18 years and older who have limited or no alternative options for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) including those caused by the following susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Enterobacter cloacae complex, Citrobacter freundii complex, and Serratia marcescens. Approval of this indication is based on limited clinical safety and efficacy data for EMBLAVEO. (1.1)
Usage to Reduce Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of EMBLAVEO and other antibacterial drugs, EMBLAVEO should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.2)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage in Adults based on Estimated Creatinine Clearance (CLcr) (2.1, 2.2) Estimated CLcr (mL/min)a Doseb Infusion Time Dosing Intervalc Loading Maintenance Greater than 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 2.67 g (aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams) EMBLAVEO 2 g (aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams) 3 hours Every 6 hours Greater than 30 to less than or equal to 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 2.67 g (aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams) EMBLAVEO 1 g (aztreonam 0.75 grams and avibactam 0.25 grams) 3 hours Every 6 hours Greater than 15 to less than or equal to 30 mL/min EMBLAVEO 1.8 g (aztreonam 1.35 grams and avibactam 0.45 grams) EMBLAVEO 0.9 g (aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams) 3 hours Every 8 hours Less than or equal to 15 mL/min, including on hemodialysisd EMBLAVEO 1.33 g (aztreonam 1 gram and avibactam 0.33 grams) EMBLAVEO 0.9 g (aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams)
3 hours Every 12 hours aCalculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula.
bAztreonam-avibactam is a combination product in a fixed 3:1 ratio. A single loading dose is followed by maintenance doses beginning at the next dosing interval.
cDosing interval is calculated from the start of one infusion to the start of the subsequent infusion.
dBoth aztreonam and avibactam are removed by hemodialysis; thus, administer EMBLAVEO after hemodialysis, on hemodialysis days.DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam) for injection is a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial containing 2 g (1.5 grams aztreonam and 0.5 grams avibactam). (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity to the components of EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam). (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions were noted in patients treated with EMBLAVEO including rash, flushing, and bronchospasm. In case of hypersensitivity reactions, immediately discontinue EMBLAVEO and initiate appropriate medications and/or supportive care. (5.1)
-
Serious Skin Disorders: Cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported in association with aztreonam (a component of EMBLAVEO) in patients undergoing bone marrow transplant with multiple risk factors. Discontinue EMBLAVEO if serious skin reaction occurs. (5.2)
-
Hepatic Adverse Reactions: Elevations in hepatic transaminases have been observed during treatment with EMBLAVEO. If transaminase elevations are noted, consider discontinuation of EMBLAVEO, if clinically indicated, and monitor the patient for resolution of any pertinent clinical and laboratory findings. (5.3)
- Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): CDAD has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including EMBLAVEO. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of greater than 5% were hepatic adverse reactions, anemia, diarrhea, hypokalemia, and pyrexia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatchSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections
1.2 Usage to Reduce Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Adults with Estimated Creatinine Clearance Greater than 50 mL/min
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults with Estimated Creatinine Clearance Less than or Equal to 50 mL/min
2.3 Preparation of EMBLAVEO Solution for Administration
2.4 Drug Compatibility
2.5 Storage of Reconstituted and Diluted EMBLAVEO Solutions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Serious Skin Disorders
5.3 Hepatic Adverse Reactions
5.4 Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea
5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 OAT 1 and 3 Transport Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections
EMBLAVEO, in combination with metronidazole, is indicated in patients 18 years and older who have limited or no alternative options for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) including those caused by the following susceptible gram-negative microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Enterobacter cloacae complex, Citrobacter freundii complex, and Serratia marcescens. Approval of this indication is based on limited clinical safety and efficacy data for EMBLAVEO [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
1.2 Usage to Reduce Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of EMBLAVEO and other antibacterial drugs, EMBLAVEO should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Adults with Estimated Creatinine Clearance Greater than 50 mL/min
Table 1 shows the recommended dosage to be administered by intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours in adults with estimated creatinine clearance (CLcr) greater than 50 mL/min.
Table 1. Recommended dosage for adults with estimated CLcr greater than 50 mL/mina Type of Infection Recommended Doses for EMBLAVEO
(aztreonam and avibactam)bDosing Intervalc Treatment duration Complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI)d Loading EMBLAVEO 2.67 g
(aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams)
Every 6 hours
5 to 14 daysMaintenance EMBLAVEO 2 g
(aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams)aCalculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula.
bAztreonam-avibactam is a combination product in a fixed 3:1 ratio. A single loading dose is followed by maintenance doses beginning at the next dosing interval.
cDosing interval is calculated from the start of one infusion to the start of the subsequent infusion.
dFor treatment of cIAI, administer metronidazole concurrently.2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adults with Estimated Creatinine Clearance Less than or Equal to 50 mL/min
Table 2 shows the recommended dosage to be administered by intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours in adults with estimated creatinine clearance (CLcr) less than or equal to 50 mL/min. In patients with renal impairment, close monitoring of estimated CLcr is advised. In some patients, the CLcr estimated from serum creatinine can change quickly, especially early in the course of treatment for the infection. For treatment of cIAI, administer metronidazole concurrently.
Table 2. Recommended dosage for adults with estimated CLcr less than or equal to 50 mL/min Estimated CLcr (mL/min)a Recommended Dose for EMBLAVEO
(aztreonam and avibactam)b,cDosing Intervald Greater than 30 to less than or equal to 50 mL/min Loading EMBLAVEO 2.67 g
(aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams)Every 6 hours Maintenance EMBLAVEO 1 g
(aztreonam 0.75 grams and avibactam 0.25 grams)Greater than 15 to less than or equal to 30 mL/min Loading EMBLAVEO 1.8 g
(aztreonam 1.35 grams and avibactam 0.45 grams)Every 8 hours Maintenance EMBLAVEO 0.9 g
(aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams)Less than or equal to 15, including on hemodialysise Loading EMBLAVEO 1.33 g
(aztreonam 1 gram and avibactam 0.33 grams)Every 12 hours Maintenance EMBLAVEO 0.9 g
(aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams)aCalculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula
bAztreonam-avibactam is a combination product in a fixed 3:1 ratio. A single loading dose is followed by maintenance doses beginning at the next dosing interval.
cThe total duration of treatment is for 5 days to 14 days.
dDosing interval is calculated from the start of one infusion to the start of the subsequent infusion.
eBoth aztreonam and avibactam are hemodialyzable; thus, administer EMBLAVEO after hemodialysis on hemodialysis days.2.3 Preparation of EMBLAVEO Solution for Administration
EMBLAVEO is supplied as a lyophilized powder, which must be reconstituted and subsequently diluted, using aseptic technique prior to intravenous infusion. Prepare the reconstituted and diluted solutions of EMBLAVEO using the steps described below.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
a) Reconstitute the powder in the EMBLAVEO vial with 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection.
b) Mix the reconstituted vial gently and ensure that the contents are dissolved completely.
- The reconstituted EMBLAVEO solution is not for direct injection. The reconstituted solution must be diluted before intravenous infusion.
- The reconstituted EMBLAVEO solution will have an approximate aztreonam concentration of 127 mg/mL and an approximate avibactam concentration of 42.3 mg/mL. The final volume is approximately 12 mL.
c) Prepare the required dose for intravenous infusion by withdrawing the appropriate volume determined from Table 3 from the reconstituted vial. Discard unused portion.
Table 3. Preparation of EMBLAVEO Doses for Intravenous Infusion Dose (EMBLAVEO) Volume to withdraw from Constituted Vial for Further Dilution to 50 mL to 250 mL Estimated CLcra (mL/min) EMBLAVEO (g) (aztreonam (grams) and avibactam (grams))
LoadingGreater than 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 2.67 g (aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams) 15.7 mL
(requires two vials; discard unused portions)Greater than 30 mL/min to less than or equal to 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 2.67 g (aztreonam 2 grams and avibactam 0.67 grams) 15.7 mL
(requires two vials; discard unused portions)Greater than 15 mL/min to less than or equal to 30 mL/min EMBLAVEO 1.8 g (aztreonam 1.35 grams and avibactam 0.45 grams) 10.6 mL Less than or equal to 15 mL/min EMBLAVEO 1.33 g (aztreonam 1 gram and avibactam 0.33 grams) 7.9 mL
MaintenanceGreater than 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 2 g (aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams) Entire contents of one vial (approximately 12 mL) Greater than 30 mL/min to less than or equal to 50 mL/min EMBLAVEO 1 g (aztreonam 0.75 grams and avibactam 0.25 grams) 5.9 mL Greater than 15 mL/min to less than or equal to 30 mL/min EMBLAVEO 0.9 g (aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams) 5.3 mL Less than or equal to 15 mL/min EMBLAVEO 0.9 g (aztreonam 0.675 grams and avibactam 0.225 grams) 5.3 mL aCalculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula d) Before infusion, dilute the withdrawn volume of the reconstituted EMBLAVEO solution further to 50 mL to 250 mL in an infusion bag containing any of the following: 0.9 % sodium chloride for injection or 5% dextrose solution for injection or lactated Ringer’s injection, to achieve an aztreonam concentration of 2.7 mg/mL to 40 mg/mL and an avibactam concentration of 0.9 mg/mL to 13.3 mg/mL.
e) Mix gently and ensure that the contents are dissolved completely. Visually inspect the diluted EMBLAVEO solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration (the color of the EMBLAVEO infusion solution for administration ranges from clear, colorless to yellow).
2.4 Drug Compatibility
The EMBLAVEO solution for administration is compatible with Sterile Water for Injection, for reconstitution and any of the following diluents for further dilution of the reconstituted solution:
- 0.9% Sodium chloride injection
- 5% Dextrose injection
- Lactated Ringer's injection
The compatibility of EMBLAVEO with other medicinal products has not been established. EMBLAVEO should not be mixed with or physically added to solutions containing other medicinal products.
2.5 Storage of Reconstituted and Diluted EMBLAVEO Solutions
Reconstituted Solution
Upon reconstitution with Sterile Water for Injection, the reconstituted EMBLAVEO solution may be held for up to 60 minutes at 30°C (86°F) under ambient light prior to transfer and dilution in a suitable infusion bag.
Diluted Reconstituted Solution
Following dilution of the reconstituted solution with 0.9% sodium chloride injection or 5 % dextrose injection or lactated Ringer’s injection, EMBLAVEO solution in the infusion bags may be stored based on conditions outlined in Table 4.
Table 4. Storage of Diluted Solutions Diluent used for Dilution following Reconstitution Storage 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection
Or Lactated Ringer’s InjectionRefrigerate at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours followed by 12 hours at not more than 30°C (86°F) under ambient light. Discard unused portion. 5% Dextrose Injection Refrigerate at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours followed by 4 hours at not more than 30°C (86°F) under ambient light. Discard unused portion. - The reconstituted EMBLAVEO solution is not for direct injection. The reconstituted solution must be diluted before intravenous infusion.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam) for injection is supplied as a white to slightly yellow sterile lyophilized powder for reconstitution in a single-dose, sterile, clear glass vial containing:
2 g aztreonam and avibactam (1.5 grams aztreonam and 0.5 grams avibactam (equivalent to 0.542 grams of avibactam sodium)).
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
EMBLAVEO is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the components of EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions were noted in patients treated with EMBLAVEO, including rash, flushing, and bronchospasm [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Prior to treatment, it should be established if the patient has a history of hypersensitivity reactions to components of EMBLAVEO (aztreonam and avibactam). In case of hypersensitivity reactions, immediately discontinue EMBLAVEO and initiate appropriate medications and/or supportive care.
5.2 Serious Skin Disorders
Cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported in association with aztreonam (a component of EMBLAVEO) in patients undergoing bone marrow transplant with multiple risk factors including sepsis, radiation therapy, and other concomitantly administered drugs associated with toxic epidermal necrolysis. Discontinue EMBLAVEO if a serious skin reaction occurs.
5.3 Hepatic Adverse Reactions
Elevations in hepatic transaminases have been observed during treatment with EMBLAVEO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitoring of liver-related laboratory tests is recommended while on treatment, particularly in patients with baseline liver comorbidities or on concomitant hepatotoxic medications. If transaminase elevations are noted, consider discontinuing EMBLAVEO, if clinically indicated, and monitor the patient for resolution of any pertinent clinical and laboratory findings.
5.4 Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported for nearly all systemic antibacterial drugs, including EMBLAVEO, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial drugs alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of C. difficile. C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary because CDAD has been reported to occur more than 2 months after the administration of antibacterial drugs. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, antibacterial drugs not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Manage fluid and electrolyte levels as appropriate, supplement protein intake, monitor antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and institute surgical evaluation as clinically indicated.
5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing EMBLAVEO in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria [see Indications and Usage (1.2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in the Warnings and Precautions section:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Serious Skin Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials Experience in Adult Patients
Three clinical trials, Trial 1, Trial 2, and Trial 3, underly the EMBLAVEO clinical development program. Trial 1 was a randomized, comparative trial conducted in patients with cIAI and hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP) (not an approved indication for EMBLAVEO), while Trials 2 and 3 were smaller, noncomparative trials conducted in patients with cIAI as well as other serious infections caused by gram negative pathogens expressing metallo-beta-lactamases. The safety data from Trial 1 are summarized below.
In Trial 1, EMBLAVEO was evaluated in a comparative clinical trial in patients with cIAI or HABP/VABP; note that EMBLAVEO is not approved for the treatment of HABP/VABP. Trial 1 evaluated 275 patients treated with EMBLAVEO and 137 patients treated with comparator (meropenem +/- colistin); 203 EMBLAVEO-treated patients had a diagnosis of cIAI while 72 EMBLAVEO-treated patients had a diagnosis of HABP/VABP (not an approved indication for EMBLAVEO).
Patients received treatment with EMBLAVEO 2 grams (aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams) or comparator for 5 to 14 days. Patients randomized to EMBLAVEO received a loading dose of aztreonam and avibactam administered by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes immediately followed by an extended loading dose infused over 3 hours, followed by maintenance doses infused over 3 hours every 6 hours based on the participant’s creatinine clearance. Patients with cIAI randomized to EMBLAVEO also received metronidazole 500 mg administered by intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 8 hours.
The median age of patients in Trial 1 treated with EMBLAVEO was 58 years, ranging between 18 and 87 years old. Patients treated with EMBLAVEO were predominantly male (66%) and White (59%). Approximately 40% (22% of cIAI and 89% of HABP/VABP; not an approved indication) of patients treated with EMBLAVEO had an APACHE II score greater than 10 at baseline.
Death occurred in 6.9% (19/275) of patients who received EMBLAVEO and in 8% (11/137) of patients who received comparator. In patients with cIAI, death occurred in 3.0% (6/203) of patients treated with EMBLAVEO and 2.9% (3/103) in patients treated with comparator. Overall, 3.6% (10/275) of the patients who received EMBLAVEO discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 3.6% (5/137) of patients treated with comparator.
Common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 5% of patients are noted in the table below.
Table 5: Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 5% of Patients in the EMBLAVEO Treatment Arm in Trial 1 Adverse Reactions EMBLAVEO ± Metronidazole
(N=275)
n (%)Meropenem ± Colistin
(N=137)
n (%)Hepatic adverse reactions* 40 (14.5) 16 (11.7) Anemia** 22 (8.0) 7 (5.1) Diarrhea 16 (5.8) 5 (3.6) Hypokalemia 16 (5.8) 4 (2.9) Pyrexia*** 16 (5.8) 7 (5.1) *Includes AR terms alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, hepatic function abnormal, hypertransaminasemia, transaminases increased, hepatic enzyme increased, liver injury
**Includes anemia, hemoglobin decreased
***Includes pyrexia, hyperpyrexia, hyperthermia, body temperature increasedHepatic Adverse Reactions
In Trial 1, 40/275 patients (15%) in the EMBLAVEO arm had hepatic adverse reactions compared to 16/137 (12%) in the comparator arm receiving meropenem with or without colistin. In Trial 1, 10 (3.8%) patients in the EMBLAVEO arm compared to 4 (3.1%) patients in the comparator arm had an ALT elevation greater than or equal to 5 x ULN. No Hy’s Law cases in the EMBLAVEO or comparator arm were seen in Trials 1, 2, and 3. EMBLAVEO was discontinued due to hepatic enzyme elevations in 4 patients in Trials 1, 2, and 3. The transaminase elevations resolved when EMBLAVEO was discontinued.
The following adverse reactions were reported in EMBLAVEO-treated patients at a rate of less than 5% in Trial 1:
-
Vascular disorders: Phlebitis, flushing, hypotension
-
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash (includes rash and rash macular), dermatitis (includes dermatitis allergic, dermatitis), erythema
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain (includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower), constipation
-
Nervous System Disorders: Mental status change (includes mental status changes, delirium, confusional state, and disorientation), dizziness, headache, sleep disorder (includes sleep disorder, insomnia), ageusia, asthenia
-
Infectious Diseases: Clostridioides difficile infection (includes Clostridioides difficile infection and Clostridioides difficile colitis)
-
Hematologic: Coagulopathy, leukocytosis (includes white blood cell count increased and leukocytosis), thrombocytopenia (includes thrombocytopenia, platelet count decreased); thrombocytosis (includes thrombocytosis, platelet count increased), eosinophilia
- Hypersensitivity: Bronchospasm
Additionally, adverse reactions that have been reported with aztreonam alone that were not reported in EMBLAVEO-treated patients in Trial 1 are listed below:
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylaxis, angioedema
Hematologic: Pancytopenia, neutropenia
Dermatologic: Purpura, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, urticaria, petechiae, pruritus, diaphoresis
Cardiovascular: Transient ECG changes (ventricular bigeminy and PVC)
Respiratory: Wheezing, dyspnea, chest pain
Hepatobiliary: Hepatitis, jaundice
Nervous System: Seizure, encephalopathy, vertigo, paresthesia
Musculoskeletal: Muscular aches
Special Senses: Tinnitus, diplopia, numb tongue, sneezing, nasal congestion, halitosis
Other: Vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis, breast tenderness
Body as a Whole: Malaise
Adverse Laboratory Changes reported with aztreonam alone that were not reported in EMBLAVEO-treated patients in Trial 1 are listed below:
Hematologic: Positive Coombs’ test
Renal: Increases in serum creatinine
Trial 2 was a noncomparative study of EMBLAVEO in 34 subjects with cIAI. Trial 3 was a comparative study of EMBLAVEO versus best available therapy in patients with serious infections due to multi-drug resistant gram-negative bacteria producing metallo-beta-lactamases (not an approved indication for EMBLAVEO); 12 patients were treated in the EMBLAVEO arm and 2 patients were treated in the comparator arm. The safety findings for the EMBLAVEO treatment arm in Trials 2 and 3 were similar to those of Trial 1.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 OAT 1 and 3 Transport Inhibitors
Concomitant use of organic anion transporter (OAT) 1 and OAT 3 transporter inhibitors (e.g., probenecid) with EMBLAVEO is not recommended. There is insufficient information to characterize the effect of concomitant use of OAT 1/3 transport inhibitors with EMBLAVEO [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data on the effects of EMBLAVEO use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Available data from case reports over several decades with aztreonam and over approximately a decade with avibactam have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other maternal or fetal outcomes.
Aztreonam
Developmental toxicity studies in pregnant rats and rabbits with daily doses of aztreonam revealed no evidence of embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, or fetal malformations at doses 2.7- and 3.6-fold greater, respectively, than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for adults of 6.5 g per day. In a peri/postnatal development (PPND) study in rats, no aztreonam-induced changes in any maternal, fetal, or neonatal parameters were observed at a dose 2.7-fold greater than the MRHD.
Avibactam
Avibactam administered to pregnant rats was not associated with fetal malformations at doses 6 times the MRHD of 2.17 g per day. In pregnant rabbits, avibactam administered in doses greater than or equal to 5 times the MRHD was associated with increased post-implantation loss, lower mean fetal weights, delayed ossification of several bones and other anomalies. In a rat PPND study, there were no effects on pup growth and viability at doses up to 8 times the avibactam MRHD. A dose-related increase in the incidence of renal pelvic and ureter dilatation was observed in female weaning pups with renal pelvic dilatation persisting into adulthood (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Aztreonam
Developmental toxicity studies in pregnant rats and rabbits with daily doses of aztreonam up to 1800 and 1200 mg/kg, respectively, revealed no evidence of embryotoxicity or fetotoxicity or fetal malformations. These doses, based on body surface area, are 2.7- and 3.6-fold greater than the MRHD for adults of 6.5 g per day.
A peri/postnatal study in rats revealed no drug-induced changes in any maternal, fetal, or neonatal parameters. The highest dose used in this study, 1800 mg/kg/day, is 2.7 times the MRHD based on body surface area comparison.
Avibactam
Avibactam did not produce fetal malformations in pregnant rats or rabbits. In the rat, intravenous studies with 0, 250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day of avibactam during gestation days 6-17 showed no embryo-fetal toxicity at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day, approximately 6 times the MRHD (2.17 g/day) based on exposure (AUC).
Pregnant rabbits administered intravenous avibactam on gestation days 6-19 at 0, 100, 300 and 1000 mg/kg/day showed no effects on embryo-fetal development at a dose of 100 mg/kg, twice the MRHD based on AUC comparison. At doses greater than or equal to 300 mg/kg/day (5 times the MRHD based on AUC comparison), increased post-implantation loss, lower mean fetal weights, delayed ossification of several bones and other anomalies were observed.
In a rat pre-and post-natal study at up to 825 mg/kg/day intravenously (8 times the MRHD based on AUC), there were no effects on pup growth and viability. A dose-related increase in the incidence of renal pelvic and ureter dilatation was observed in female weaning pups that was not associated with pathological changes to renal parenchyma or renal function, with renal pelvic dilatation persisting after female weaning pups became adults.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Aztreonam is present in human milk at concentrations that are less than 1% of those determined in simultaneously obtained maternal serum. There are no data on the presence of avibactam in human milk. Avibactam is present in the milk of rats (see Data). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. There are no data on the effects of aztreonam or avibactam on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for EMBLAVEO and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed infant from EMBLAVEO or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In a rat pre- and post-natal study at doses up to 825 mg/kg/day intravenously (8 times the human exposure based on AUC), the exposure to avibactam was minimal in the pups in comparison to the dams. Exposure to avibactam was observed in both pups and milk on PND 7.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of EMBLAVEO in pediatric patients less than 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In Trials 1, 2, and 3, there were 103 patients in the EMBLAVEO treatment arm 65 years of age and older. Of these patients, 60 (58%) were between 65-74 years of age and 43 (42%) patients were 75 years of age and older. In comparison, there were 202 patients in the EMBLAVEO treatment arm less than 65 years of age. Clinical studies of EMBLAVEO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Aztreonam and avibactam (components of EMBLAVEO) are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to aztreonam and avibactam (components of EMBLAVEO) may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. No dosage adjustment is required in elderly patients based on age; the dose should be selected based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Aztreonam and avibactam, the components of EMBLAVEO, are primarily renally excreted. Plasma exposures of both aztreonam and avibactam increase with decreasing renal function, therefore dosage adjustments are recommended for EMBLAVEO to compensate for the slower rate of renal clearance in patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Monitor creatinine clearance in patients with changing renal function and adjust the dose of EMBLAVEO accordingly. Both aztreonam and avibactam are hemodialyzable; thus, EMBLAVEO should be administered after hemodialysis on hemodialysis days [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no information on the clinical signs and symptoms associated with an overdose of EMBLAVEO. Aztreonam and avibactam can be partially removed by hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No clinical information is available on the use of hemodialysis to treat EMBLAVEO overdosage.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
EMBLAVEO for injection, for intravenous use, is a combination product consisting of aztreonam and avibactam sodium.
Aztreonam
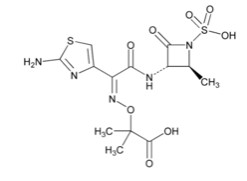
Aztreonam is a synthetic, monobactam antibacterial drug. Its chemical name is (Z)-2-[[[(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)[[(2S,3S)-2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfo-3-azetidinyl]carbamoyl]methylene]amino]oxy]-2-methylpropionic acid. Its molecular weight is 435.43 g/mol. The empirical formula is C13H17N5O8S2.
Figure 1. Chemical structure of aztreonam
Avibactam
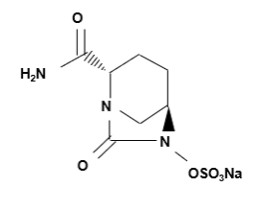
Avibactam sodium is a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Its chemical name is sodium [(2S,5R)-2-carbamoyl-7-oxo-1,6- diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-6-yl] sulfate. Its molecular weight is 287.23 g/mol. The empirical formula is C7H10N3O6SNa.
Figure 2. Chemical structure of avibactam sodium
EMBLAVEO 2 grams (aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams) for injection is a white to slightly yellow sterile powder for reconstitution consisting of aztreonam and avibactam packaged in glass vials. The formulation also contains inactive ingredient L-arginine 1170 mg/vial.
Each EMBLAVEO 2 grams single-dose vial contains 1.5 grams aztreonam and 0.5 grams avibactam (equivalent to 0.542 gram sterile avibactam sodium). The total sodium content of the mixture is approximately 44.6 mg/vial.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
As with other beta-lactam antimicrobial drugs, the time that unbound plasma concentrations of aztreonam exceed the EMBLAVEO minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against the infecting organism has been shown to best correlate with efficacy in a neutropenic murine thigh infection model with Enterobacterales. The time above a threshold concentration has been determined to be the parameter that best predicts the efficacy of avibactam in combination with aztreonam in in vitro and in vivo nonclinical models.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Avibactam does not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically significant extent at a dose 3 times the maximum approved EMBLAVEO recommended avibactam loading dose.
Aztreonam QT prolongation evaluations have not been conducted or reported in literature.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following single or multiple dosing, the Cmax and AUC of both aztreonam and avibactam (components of EMBLAVEO) increase in an approximate dose-proportional manner over a dose range of 500 mg to 2000 mg aztreonam (0.25 to 1 times the approved maximum recommended loading dose) and of 50 mg to 2000 mg avibactam (0.07 to 3 times the approved maximum recommended loading dose).
Aztreonam and avibactam (components of EMBLAVEO) pharmacokinetic properties are summarized in Table 6. There is minimal accumulation of aztreonam and avibactam following multiple intravenous 3-hour infusions of EMBLAVEO every 6 hours in patients with normal renal function.
Table 6: Pharmacokinetic (PK) Properties of Components of EMBLAVEO (Aztreonam and Avibactam) PK Parameter Aztreonam Avibactam Cmax, ss (mg/L)a,b, c 54.46 ± 17.22 11.29 ± 3.89 AUC0-24, ss (mgh/L)a,b,c 841.22 ± 317.59 165.7 ± 65.63 Distribution Binding to human plasma proteins 38 % 8 % Volume of distribution (Vss)c 21.4 ± 23 L 37.8 ± 73 L Elimination Clearance (CL)c 10.2 ± 22 L/hr 18 ± 39 L/hr Mean terminal half-life (t1/2)c 2.03 ± 0.69 hrs 2.04 ± 0.52 hrs Metabolism
Metabolic pathwaysAztreonam is minimally metabolized. No metabolism of avibactam was observed in human liver preparations (microsomes and hepatocytes). Unchanged avibactam was the major drug-related component in human plasma and urine following dosing with [14C]-avibactam Excretion Major route of elimination Renal excretion: tubular secretion and glomerular filtration % of dose excreted in urine, unchanged 64.2 % to 75.9 % 83.8 % to 100 % % of dose excreted in feces, changed and unchanged Approximately 12 % < 0.25 % Cmax, ss =maximum plasma concentration at steady-state; AUC0-24, ss=area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time zero up to 24 hrs at steady state; Vss = volume of distribution at steady state; mean = arithmetic mean; SD = standard deviation.
a2000 mg aztreonam + 670 mg avibactam IV infusion over 3 hours then 1500 mg aztreonam + 500 mg avibactam IV infusion over 3 hours every 6 hours.
bThere is no clinically significant PK differences (as measured by AUC and Cmax) between healthy adults and adults with cIAI (normal renal function).
cmean ± SD reported based on PK data from 97 adults with cIAISpecific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of aztreonam or avibactam were observed based on age (range: 18-89 years), sex (62.1% male), race (61.9% White, 27.7% Asian, and 3.4% Black), or BMI (10.4 to 62.5 kg/m2).
Patients with Renal Impairment
The disposition of aztreonam and avibactam were evaluated in non-infected subjects with CLcr >80 mL/min (as measured by Cockcroft-Gault method, n=6) administered the recommended general maintenance dosing regimen and with CLcr 32 to 37 mL/min (n=5) administered the recommended adjusted maintenance dosing regimen for CLcr >15 to ≤ 30 mL/min. Aztreonam AUC24 and Cmax at steady state is approximately 21% and 24% lower in the subjects with CLcr 32 to 37 mL/min compared to the CLcr >80 mL/min group. The avibactam AUC24 and Cmax at steady state are approximately 24% and 2% higher in the subjects with CLcr 32 to 37 mL/min, compared to the CLcr >80 mL/min group. Dosage adjustment for EMBLAVEO in patients with CLcr ≤ 50 mL/min is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
EMBLAVEO has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. As aztreonam and avibactam do not appear to undergo significant hepatic metabolism, the systemic clearance of either active substance is not expected to be significantly altered by hepatic impairment.
Dosage adjustments are not considered necessary for EMBLAVEO in patients with impaired hepatic function.
Geriatric Patients (Greater than or equal to 65 years)
Mean elimination half-life of both aztreonam and avibactam is increased, and plasma clearance decreased in the elderly, consistent with age-related reduction in renal clearance of aztreonam and avibactam.
Dosage adjustment for EMBLAVEO in geriatric patients should be based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
OAT1/3 inhibitors: No clinically significant differences in aztreonam pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with probenecid (OAT1/3 inhibitors). Concomitant administration of probenecid with aztreonam is reported to result in clinically insignificant increases in aztreonam exposure. No clinical studies have been conducted with avibactam and OAT1/3 inhibitors (e.g., probenecid) and the clinical impact of OAT inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of avibactam is not known.
Other: No drug-drug interaction was observed between aztreonam, avibactam, and metronidazole in clinical studies.
In Vitro Studies
Avibactam was not found to be an inhibitor of the following hepatic and renal transporters in vitro at clinically relevant concentrations: MDR1, BCRP, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, BSEP, MRP4, OCT1, or OCT2. Avibactam was not a substrate of MDR1, BCRP, MRP4, or OCT2, but was a substrate of human OAT1 and OAT3 kidney transporters based on results generated in human embryonic kidney cells expressing these transporters.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of action
EMBLAVEO is a combination of the monobactam antibacterial, aztreonam, and the beta-lactamase inhibitor, avibactam. Aztreonam inhibits bacterial peptidoglycan cell wall synthesis following binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs), which leads to bacterial cell lysis and death and is stable to class B beta-lactamase enzymes (metallo-beta-lactamases). Avibactam is a non-beta-lactam, beta-lactamase inhibitor that acts by forming a covalent adduct with the enzyme that is stable to hydrolysis. Avibactam inhibits both Ambler class A, class C and some class D beta-lactamases, including extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC), OXA-48 carbapenemases, and AmpC enzymes. Avibactam does not inhibit class B enzymes and is not able to inhibit some class D enzymes.
EMBLAVEO demonstrated in vitro activity against Enterobacterales isolates expressing beta-lactamases included in Ambler Class A (CTX-M-, TEM-, and SHV-type ESBLs; KPC carbapenemase), Class B (New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamases [NDM], Verona integron-encoded metallo-beta-lactamase [VIM], and imipenemases [IMP]), Class C (AmpC), and Class D (OXA-48-like).
Resistance
Resistance mechanisms to EMBLAVEO include beta-lactamase enzymes refractory to inhibition by avibactam and able to hydrolyze aztreonam, mutant or acquired PBPs, decreased outer membrane permeability, and active efflux pumps.
Interaction with Other Antimicrobials
No antagonism was demonstrated in in vitro studies between EMBLAVEO and amikacin, ciprofloxacin, colistin, daptomycin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, linezolid, metronidazole, tigecycline, tobramycin, and vancomycin against Enterobacterales.
Activity against bacteria in animal infection models
Avibactam restored the activity of aztreonam in animal models of infection (e.g., mouse thigh infection, mouse lung infection) caused by aztreonam non-susceptible NDM- and ESBL-producing E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates. However, the clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
Antimicrobial Activity
EMBLAVEO has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1.1)].
-
Citrobacter freundii complex
-
Escherichia coli
-
Enterobacter cloacae complex
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae
-
Klebsiella oxytoca
- Serratia marcescens
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro MIC less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for EMBLAVEO against isolates of similar genus or organism group. However, the safety and effectiveness of EMBLAVEO in treating clinical infections due to these bacteria have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials:
Aerobic Gram-negative organisms
-
Citrobacter koseri
-
Enterobacter spp.
-
Klebsiella aerogenes
-
Morganella morganii
-
Proteus mirabilis
-
Proteus vulgaris
-
Providencia rettgeri
-
Providencia stuartii
-
Raoultella ornithinolytica
-
Serratia spp.
- Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Susceptibility Test Methods
For specific information regarding susceptibility testing methods, interpretive criteria, and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for EMBLAVEO, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
-
Citrobacter freundii complex
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Aztreonam
Carcinogenicity studies with aztreonam have not been conducted using an intravenous route of administration. A 104-week rat inhalation toxicology study to assess the carcinogenic potential of aztreonam demonstrated no drug-related increase in the incidence of tumors. Rats were exposed to aerosolized aztreonam for up to 4 hours per day. Peak plasma levels of aztreonam averaging approximately 6.8 mcg/mL were measured in rats at the highest dose level.
Avibactam
Carcinogenicity studies with avibactam have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Aztreonam
Genetic toxicology studies performed with aztreonam in vitro (Ames test, mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay, gene conversion assay, chromosome aberration assay in human lymphocytes) and in vivo (mouse bone marrow cytogenetic assay) did not reveal evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential.
Avibactam
Avibactam was negative for genotoxicity in the Ames assay, unscheduled DNA synthesis, chromosomal aberration assay, and a rat micronucleus study.
Impairment of Fertility
Aztreonam
A two-generation reproduction study in rats at daily doses of 150, 600, or 2400 mg/kg/day given prior to and during gestation and lactation, revealed no evidence of impaired fertility. Based on body surface area, the high dose is 3.6-fold greater than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for adults of 6.5 g per day. There was a slightly reduced survival rate during the lactation period in the offspring of rats that received the highest dose, but not in offspring of rats that received lower doses of aztreonam.
Avibactam
Avibactam had no adverse effects on fertility of male and female rats given up to 1g/kg/day (approximately 4.5-fold higher than the MRHD of 2.17 g/day on a body surface area basis). There was a dose-related increase in the percentage of pre-and post-implantation loss relative to controls, resulting in a lower mean litter size at doses of 0.5 g/kg/day (approximately 2 times the MRHD on a body surface area basis) and greater with intravenous administration to female rats beginning 2 weeks prior to mating.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections
The determination of efficacy of EMBLAVEO was supported in part by the previous findings of the efficacy and safety of aztreonam for the treatment of cIAI. The contribution of avibactam to EMBLAVEO was primarily established in vitro and in animal models of infection [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]. EMBLAVEO was studied in one randomized, active-controlled, multicenter trial (Trial 1, NCT03329092) in patients with cIAI or hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia/ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP) (not an approved indication for EMBLAVEO). The trial was not designed with any formal hypotheses for inferential testing against the active comparator.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
EMBLAVEO 2 grams (aztreonam and avibactam) for injection is supplied as a sterile powder in single-dose, clear glass vial containing: 1.5 grams aztreonam and 0.5 grams avibactam (equivalent to 0.542 grams of avibactam sodium).
Vials (NDC# 0074-3878-01) are supplied in cartons containing 10 vials.
EMBLAVEO vials should be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect from light. Store in carton until time of use.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Serious Allergic Reactions
Advise patients, their families, or caregivers that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions, could occur that require immediate treatment. Ask them about any previous hypersensitivity reactions to EMBLAVEO, other beta-lactams, or other allergens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serious Skin Reactions
Advise patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations such as sudden onset of a severe rash or blistering or peeling skin, possibly accompanied by a high fever or joint pain (these may be signs of more serious medical conditions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Potentially Serious Diarrhea
Advise patients, their families, or caregivers that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs. Sometimes, frequent watery or bloody diarrhea may occur and may be a sign of a more serious intestinal infection. If severe watery or bloody diarrhea develops, tell them to contact his or her healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Antibacterial Resistance
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including EMBLAVEO should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When EMBLAVEO is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by EMBLAVEO or other antibacterial drugs in the future [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Distributed by:
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064EMBLAVEO and its design are trademarks of Allergan Pharmaceuticals International Limited, an AbbVie company.
© 2025 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
PAA232843
-
Principal Display Panel
NDC: 0074-3878-10
Rx Only
10 single-dose vials
Emblaveo™ 2g per vial*
(aztreonam and avibactam) for injection
*Aztreonam 1.5 grams and avibactam 0.5 grams (equivalent to 0.542 grams of avibactam sodium).
Single-Dose Vial. Discard Unused Portion
MUST BE RECONSTITUTED THEN DILUTED. FOR INTRAVENOUS INFUSION.

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EMBLAVEO
aztreonam and avibactam powder, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0074-3878 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AZTREONAM (UNII: G2B4VE5GH8) (AZTREONAM - UNII:G2B4VE5GH8) AZTREONAM 127 mg in 1 mL AVIBACTAM (UNII: 7352665165) (AVIBACTAM - UNII:7352665165) AVIBACTAM 42.3 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 99.1 mg in 1 mL Product Characteristics Color white (white to slightly yellow) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0074-3878-10 10 in 1 CARTON 02/07/2025 1 NDC: 0074-3878-01 12 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA217906 02/07/2025 Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370)
Trademark Results [EMBLAVEO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 EMBLAVEO 97773211 not registered Live/Pending |
Allergan Pharmaceuticals International Limited 2023-01-30 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.