VERZENIO- abemaciclib tablet
Verzenio by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Verzenio by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Eli Lilly and Company. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VERZENIO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VERZENIO.
VERZENIO® (abemaciclib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VERZENIO® is a kinase inhibitor indicated:
- in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. (1)
- in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy. (1)
- as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy and prior chemotherapy in the metastatic setting. (1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, and 200 mg. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Diarrhea: Instruct patients at the first sign of loose stools to initiate antidiarrheal therapy, increase oral fluids, and notify their healthcare provider. (5.1)
- Neutropenia: Monitor complete blood counts prior to the start of VERZENIO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. (2.2, 5.2)
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Severe and fatal cases of ILD/pneumonitis have been reported. Monitor for clinical symptoms or radiological changes indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue VERZENIO in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 ILD or pneumonitis. (2.2, 5.3)
- Hepatotoxicity: Increases in serum transaminase levels have been observed. Perform liver function tests (LFTs) before initiating treatment with VERZENIO. Monitor LFTs every two weeks for the first two months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. (2.2, 5.4)
- Venous Thromboembolism: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and treat as medically appropriate. (5.5)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥20%) were diarrhea, neutropenia, nausea, abdominal pain, infections, fatigue, anemia, leukopenia, decreased appetite, vomiting, headache, alopecia, and thrombocytopenia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Eli Lilly and Company at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose and Schedule
2.2 Dose Modification
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Diarrhea
5.2 Neutropenia
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
5.5 Venous Thromboembolism
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on VERZENIO
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VERZENIO® (abemaciclib) is indicated:
- in combination with an aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy for the treatment of postmenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
- in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of women with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy.
- as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression following endocrine therapy and prior chemotherapy in the metastatic setting.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose and Schedule
When used in combination with fulvestrant or an aromatase inhibitor, the recommended dose of VERZENIO is 150 mg taken orally twice daily.
- When given with VERZENIO, refer to the Full Prescribing Information for the recommended dose of the aromatase inhibitor being used.
- When given with VERZENIO, the recommended dose of fulvestrant is 500 mg administered on Days 1, 15, and 29; and once monthly thereafter. Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for fulvestrant. Pre/perimenopausal women treated with the combination of VERZENIO plus fulvestrant should be treated with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist according to current clinical practice standards.
When used as monotherapy, the recommended dose of VERZENIO is 200 mg taken orally twice daily.
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. VERZENIO may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Instruct patients to take their doses of VERZENIO at approximately the same times every day.
If the patient vomits or misses a dose of VERZENIO, instruct the patient to take the next dose at its scheduled time. Instruct patients to swallow VERZENIO tablets whole and not to chew, crush, or split tablets before swallowing. Instruct patients not to ingest VERZENIO tablets if broken, cracked, or otherwise not intact.
2.2 Dose Modification
Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended VERZENIO dose modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Tables 1-6. Discontinue VERZENIO for patients unable to tolerate 50 mg twice daily.
Table 1: VERZENIO Dose Modification for Adverse Reactions Dose Level VERZENIO Dose
Combination with Fulvestrant or an Aromatase InhibitorVERZENIO Dose
for MonotherapyRecommended starting dose 150 mg twice daily 200 mg twice daily First dose reduction 100 mg twice daily 150 mg twice daily Second dose reduction 50 mg twice daily 100 mg twice daily Third dose reduction not applicable 50 mg twice daily Table 2: VERZENIO Dose Modification and Management — Hematologic Toxicitiesa Abbreviation: CTCAE = Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
a If blood cell growth factors are required, suspend VERZENIO dose for at least 48 hours after the last dose of blood cell growth factor and until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 2. Resume at next lower dose unless already performed for the toxicity that led to the use of the growth factor. Growth factor use as per current treatment guidelines.
Monitor complete blood counts prior to the start of VERZENIO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. CTCAE Grade VERZENIO Dose Modifications Grade 1 or 2 No dose modification is required. Grade 3 Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 2.
Dose reduction is not required.Grade 3 recurrent, or
Grade 4Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 2.
Resume at next lower dose.Table 3: VERZENIO Dose Modification and Management — Diarrhea At the first sign of loose stools, start treatment with antidiarrheal agents and increase intake of oral fluids. CTCAE Grade VERZENIO Dose Modifications Grade 1 No dose modification is required. Grade 2 If toxicity does not resolve within 24 hours to ≤Grade 1, suspend dose until resolution. No dose reduction is required. Grade 2 that persists or recurs after resuming the same dose despite maximal supportive measures Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Grade 3 or 4 or requires hospitalization Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Table 4: VERZENIO Dose Modification and Management — Hepatotoxicity Abbreviations: ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, ULN = upper limit of normal.
Monitor ALT, AST, and serum bilirubin prior to the start of VERZENIO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. CTCAE Grade for ALT and AST VERZENIO Dose Modifications Grade 1 (>ULN-3.0 x ULN)
Grade 2 (>3.0-5.0 x ULN),
WITHOUT increase in total bilirubin above 2 x ULNNo dose modification is required. Persistent or Recurrent Grade 2, or Grade 3 (>5.0-20.0 x ULN), WITHOUT increase in total bilirubin above 2 x ULN Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to baseline or Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Elevation in AST and/or ALT >3 x ULN WITH total bilirubin >2 x ULN, in the absence of cholestasis Discontinue VERZENIO. Grade 4 (>20.0 x ULN) Discontinue VERZENIO. Table 5: VERZENIO Dose Modification and Management for Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis CTCAE Grade VERZENIO Dose Modifications Grade 1 or 2 No dose modification is required. Persistent or recurrent Grade 2 toxicity that does not resolve with maximal supportive measures within 7 days to baseline or Grade 1 Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to baseline or ≤Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Grade 3 or 4 Discontinue VERZENIO. Table 6: VERZENIO Dose Modification and Management for Other Toxicitiesa a Excluding diarrhea, hematologic toxicity, hepatotoxicity, and ILD/pneumonitis.
CTCAE Grade VERZENIO Dose Modifications Grade 1 or 2 No dose modification is required. Persistent or recurrent Grade 2 toxicity that does not resolve with maximal supportive measures within 7 days to baseline or Grade 1 Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to baseline or ≤Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Grade 3 or 4 Suspend dose until toxicity resolves to baseline or ≤Grade 1.
Resume at next lower dose.Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for coadministered aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant for dose modifications and other relevant safety information.
Dose Modification for Use with Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of the strong CYP3A inhibitor ketoconazole.
With concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors other than ketoconazole, in patients with recommended starting doses of 200 mg twice daily or 150 mg twice daily, reduce the VERZENIO dose to 100 mg twice daily. In patients who have had a dose reduction to 100 mg twice daily due to adverse reactions, further reduce the VERZENIO dose to 50 mg twice daily. If a patient taking VERZENIO discontinues a CYP3A inhibitor, increase the VERZENIO dose (after 3-5 half-lives of the inhibitor) to the dose that was used before starting the strong inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
With concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors, monitor for adverse reactions and consider reducing the VERZENIO dose in 50 mg decrements as demonstrated in Table 1, if necessary.
Dose Modification for Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh-C), reduce the VERZENIO dosing frequency to once daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for coadministered aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant for dose modification requirements for severe hepatic impairment.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
50 mg tablets: oval beige tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “50” on the other side.
100 mg tablets: oval white to practically white tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “100” on the other side.
150 mg tablets: oval yellow tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “150” on the other side.
200 mg tablets: oval beige tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “200” on the other side.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurred in 81% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor in MONARCH 3, 86% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2, and 90% of patients receiving VERZENIO alone in MONARCH 1. Grade 3 diarrhea occurred in 9% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor in MONARCH 3, 13% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2, and in 20% of patients receiving VERZENIO alone in MONARCH 1. Episodes of diarrhea have been associated with dehydration and infection.
Diarrhea incidence was greatest during the first month of VERZENIO dosing. In MONARCH 3, the median time to onset of the first diarrhea event was 8 days, and the median duration of diarrhea for Grades 2 and 3 were 11 and 8 days, respectively. In MONARCH 2, the median time to onset of the first diarrhea event was 6 days, and the median duration of diarrhea for Grades 2 and 3 were 9 days and 6 days, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. In MONARCH 3, 19% of patients with diarrhea required a dose omission and 13% required a dose reduction. In MONARCH 2, 22% of patients with diarrhea required a dose omission and 22% required a dose reduction. The time to onset and resolution for diarrhea were similar across MONARCH 3, MONARCH 2, and MONARCH 1.
Instruct patients that at the first sign of loose stools, they should start antidiarrheal therapy such as loperamide, increase oral fluids, and notify their healthcare provider for further instructions and appropriate follow up. For Grade 3 or 4 diarrhea, or diarrhea that requires hospitalization, discontinue VERZENIO until toxicity resolves to ≤Grade 1, and then resume VERZENIO at the next lower dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.2 Neutropenia
Neutropenia occurred in 41% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor in MONARCH 3, 46% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2, and 37% of patients receiving VERZENIO alone in MONARCH 1. A Grade ≥3 decrease in neutrophil count (based on laboratory findings) occurred in 22% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor in MONARCH 3, 32% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2, and in 27% of patients receiving VERZENIO in MONARCH 1. In MONARCH 3, the median time to first episode of Grade ≥3 neutropenia was 33 days, and in MONARCH 2 and MONARCH 1 was 29 days. In MONARCH 3, median duration of Grade ≥3 neutropenia was 11 days, and for MONARCH 2 and MONARCH 1 was 15 days [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor complete blood counts prior to the start of VERZENIO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. Dose interruption, dose reduction, or delay in starting treatment cycles is recommended for patients who develop Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Febrile neutropenia has been reported in <1% of patients exposed to VERZENIO in the MONARCH studies. Two deaths due to neutropenic sepsis were observed in MONARCH 2. Inform patients to promptly report any episodes of fever to their healthcare provider [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Severe, life-threatening, or fatal interstitial lung disease (ILD) and/or pneumonitis can occur in patients treated with VERZENIO and other CDK4/6 inhibitors. Across clinical trials (MONARCH 1, MONARCH 2, and MONARCH 3), 3.3% of VERZENIO-treated patients had ILD/pneumonitis of any grade, 0.6% had Grade 3 or 4, and 0.4% had fatal outcomes. Additional cases of ILD/pneumonitis have been observed in the postmarketing setting, with fatalities reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Symptoms may include hypoxia, cough, dyspnea, or interstitial infiltrates on radiologic exams. Infectious, neoplastic, and other causes for such symptoms should be excluded by means of appropriate investigations.
Dose interruption or dose reduction is recommended for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2 ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue VERZENIO in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 ILD or pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
In MONARCH 3, Grade ≥3 increases in ALT (6% versus 2%) and AST (3% versus 1%) were reported in the VERZENIO and placebo arms, respectively. In MONARCH 2, Grade ≥3 increases in ALT (4% versus 2%) and AST (2% versus 3%) were reported in the VERZENIO and placebo arms, respectively.
In MONARCH 3, for patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor with Grade ≥3 ALT increased, median time to onset was 61 days, and median time to resolution to Grade <3 was 14 days. In MONARCH 2, for patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant with Grade ≥3 ALT increased, median time to onset was 57 days, and median time to resolution to Grade <3 was 14 days. In MONARCH 3, for patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor with Grade ≥3 AST increased, median time to onset was 71 days, and median time to resolution was 15 days. In MONARCH 2, for patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant with Grade ≥3 AST increased, median time to onset was 185 days, and median time to resolution was 13 days.
Monitor liver function tests (LFTs) prior to the start of VERZENIO therapy, every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, monthly for the next 2 months, and as clinically indicated. Dose interruption, dose reduction, dose discontinuation, or delay in starting treatment cycles is recommended for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2, or Grade 3 or 4, hepatic transaminase elevation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.5 Venous Thromboembolism
In MONARCH 3, venous thromboembolic events were reported in 5% of patients treated with VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor as compared to 0.6% of patients treated with an aromatase inhibitor plus placebo. In MONARCH 2, venous thromboembolic events were reported in 5% of patients treated with VERZENIO plus fulvestrant as compared to 0.9% of patients treated with fulvestrant plus placebo. Venous thromboembolic events included deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pelvic venous thrombosis, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, subclavian and axillary vein thrombosis, and inferior vena cava thrombosis. Across the clinical development program, deaths due to venous thromboembolism have been reported.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and treat as medically appropriate.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action, VERZENIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of abemaciclib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused teratogenicity and decreased fetal weight at maternal exposures that were similar to the human clinical exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the maximum recommended human dose.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VERZENIO and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Venous Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
MONARCH 3: VERZENIO in Combination with an Aromatase Inhibitor (Anastrozole or Letrozole) as Initial Endocrine-Based Therapy
Postmenopausal Women with HR-positive, HER2-negative locoregionally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer with no prior systemic therapy in this disease setting
MONARCH 3 was a study of 488 women receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor or placebo plus an aromatase inhibitor. Patients were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg of VERZENIO or placebo orally twice daily, plus physician's choice of anastrozole or letrozole once daily. Median duration of treatment was 15.1 months for the VERZENIO arm and 13.9 months for the placebo arm. Median dose compliance was 98% for the VERZENIO arm and 99% for the placebo arm.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 43% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus anastrozole or letrozole. Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions in ≥5% of patients were diarrhea and neutropenia. VERZENIO dose reductions due to diarrhea of any grade occurred in 13% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor compared to 2% of patients receiving placebo plus an aromatase inhibitor. VERZENIO dose reductions due to neutropenia of any grade occurred in 11% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor compared to 0.6% of patients receiving placebo plus an aromatase inhibitor.
Permanent treatment discontinuation due to an adverse event was reported in 13% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor and in 3% of patients receiving placebo plus an aromatase inhibitor. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation for patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor were diarrhea (2%), ALT increased (2%), infection (1%), venous thromboembolic events (VTE) (1%), neutropenia (0.9%), renal impairment (0.9%), AST increased (0.6%), dyspnea (0.6%), pulmonary fibrosis (0.6%) and anemia, rash, weight decreased and thrombocytopenia (each 0.3%).
Deaths during treatment or during the 30-day follow up, regardless of causality, were reported in 11 cases (3%) of VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor treated patients versus 3 cases (2%) of placebo plus an aromatase inhibitor treated patients. Causes of death for patients receiving VERZENIO plus an aromatase inhibitor included: 3 (0.9%) patient deaths due to underlying disease, 3 (0.9%) due to lung infection, 3 (0.9%) due to VTE event, 1 (0.3%) due to pneumonitis, and 1 (0.3%) due to cerebral infarction.
The most common adverse reactions reported (≥20%) in the VERZENIO arm and ≥2% than the placebo arm were diarrhea, neutropenia, fatigue, infections, nausea, abdominal pain, anemia, vomiting, alopecia, decreased appetite, and leukopenia (Table 7). The most frequently reported (≥5%) Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were neutropenia, diarrhea, leukopenia, increased ALT, and anemia. Diarrhea incidence was greatest during the first month of VERZENIO dosing. The median time to onset of the first diarrhea event was 8 days, and the median durations of diarrhea for Grades 2 and for Grade 3 were 11 days and 8 days, respectively. Most diarrhea events recovered or resolved (88%) with supportive treatment and/or dose reductions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Nineteen percent of patients with diarrhea required a dose omission and 13% required a dose reduction. The median time to the first dose reduction due to diarrhea was 38 days.
Table 7: Adverse Reactions ≥10% of Patients Receiving VERZENIO Plus Anastrozole or Letrozole and ≥2% Higher Than Placebo Plus Anastrozole or Letrozole in MONARCH 3 a Includes all reported preferred terms that are part of the Infections and Infestations system organ class. Most common infections (>1%) include upper respiratory tract infection, lung infection, and pharyngitis.
VERZENIO plus
Anastrozole or Letrozole
N=327Placebo plus
Anastrozole or Letrozole
N=161All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Gastrointestinal Disorders Diarrhea 81 9 0 30 1 0 Nausea 39 <1 0 20 1 0 Abdominal pain 29 1 0 12 1 0 Vomiting 28 1 0 12 2 0 Constipation 16 <1 0 12 0 0 Infections and Infestations Infectionsa 39 4 <1 29 2 <1 Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Neutropenia 41 20 2 2 <1 <1 Anemia 28 6 0 5 1 0 Leukopenia 21 7 <1 2 0 <1 Thrombocytopenia 10 2 <1 2 <1 0 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 40 2 0 32 0 0 Influenza like illness 10 0 0 8 0 0 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Alopecia 27 0 0 11 0 0 Rash 14 <1 0 5 0 0 Pruritus 13 0 0 9 0 0 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 24 1 0 9 <1 0 Investigations Blood creatinine increased 19 2 0 4 0 0 Alanine aminotransferase increased 16 6 <1 7 2 0 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 15 3 0 7 1 0 Weight decreased 10 <1 0 3 <1 0 Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders Cough 13 0 0 9 0 0 Dyspnea 12 <1 <1 6 <1 0 Nervous System Disorders Dizziness 11 <1 0 9 0 0 Additional adverse reactions in MONARCH 3 include venous thromboembolic events (deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and pelvic venous thrombosis), which were reported in 5% of patients treated with VERZENIO plus anastrozole or letrozole as compared to 0.6% of patients treated with anastrozole or letrozole plus placebo.
Table 8: Laboratory Abnormalities ≥10% in Patients Receiving VERZENIO Plus Anastrozole or Letrozole and ≥2% Higher Than Placebo Plus Anastrozole or Letrozole in MONARCH 3 VERZENIO plus
Anastrozole or Letrozole
N=327Placebo plus
Anastrozole or Letrozole
N=161Laboratory Abnormality All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Creatinine increased 98 2 0 84 0 0 White blood cell decreased 82 13 0 27 <1 0 Anemia 82 2 0 28 0 0 Neutrophil count decreased 80 19 3 21 3 0 Lymphocyte count decreased 53 7 <1 26 2 0 Platelet count decreased 36 1 <1 12 <1 0 Alanine aminotransferase increased 48 6 <1 25 2 0 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 37 4 0 23 <1 0 Creatinine Increased
Abemaciclib has been shown to increase serum creatinine due to inhibition of renal tubular secretion transporters, without affecting glomerular function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Across the clinical studies, increases in serum creatinine (mean increase, 0.2-0.3 mg/dL) occurred within the first 28-day cycle of VERZENIO dosing, remained elevated but stable through the treatment period, and were reversible upon treatment discontinuation. Alternative markers such as BUN, cystatin C, or calculated GFR, which are not based on creatinine, may be considered to determine whether renal function is impaired.
MONARCH 2: VERZENIO in Combination with Fulvestrant
Women with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression on or after prior adjuvant or metastatic endocrine therapy
The safety of VERZENIO (150 mg twice daily) plus fulvestrant (500 mg) versus placebo plus fulvestrant was evaluated in MONARCH 2. The data described below reflect exposure to VERZENIO in 441 patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who received at least one dose of VERZENIO plus fulvestrant in MONARCH 2.
Median duration of treatment was 12 months for patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant and 8 months for patients receiving placebo plus fulvestrant.
Dose reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 43% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant. Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions in ≥5% of patients were diarrhea and neutropenia. VERZENIO dose reductions due to diarrhea of any grade occurred in 19% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant compared to 0.4% of patients receiving placebo and fulvestrant. VERZENIO dose reductions due to neutropenia of any grade occurred in 10% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant compared to no patients receiving placebo plus fulvestrant.
Permanent study treatment discontinuation due to an adverse event were reported in 9% of patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant and in 3% of patients receiving placebo plus fulvestrant. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation for patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant were infection (2%), diarrhea (1%), hepatotoxicity (1%), fatigue (0.7%), nausea (0.2%), abdominal pain (0.2%), acute kidney injury (0.2%), and cerebral infarction (0.2%).
Deaths during treatment or during the 30-day follow up, regardless of causality, were reported in 18 cases (4%) of VERZENIO plus fulvestrant treated patients versus 10 cases (5%) of placebo plus fulvestrant treated patients. Causes of death for patients receiving VERZENIO plus fulvestrant included: 7 (2%) patient deaths due to underlying disease, 4 (0.9%) due to sepsis, 2 (0.5%) due to pneumonitis, 2 (0.5%) due to hepatotoxicity, and one (0.2%) due to cerebral infarction.
The most common adverse reactions reported (≥20%) in the VERZENIO arm were diarrhea, fatigue, neutropenia, nausea, infections, abdominal pain, anemia, leukopenia, decreased appetite, vomiting, and headache (Table 9). The most frequently reported (≥5%) Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were neutropenia, diarrhea, leukopenia, anemia, and infections.
Table 9: Adverse Reactions ≥10% in Patients Receiving VERZENIO Plus Fulvestrant and ≥2% Higher Than Placebo Plus Fulvestrant in MONARCH 2 a Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, abdominal discomfort, abdominal tenderness.
b Includes upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, lung infection, pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, vaginal infection, sepsis.
c Includes neutropenia, neutrophil count decreased.
d Includes anemia, hematocrit decreased, hemoglobin decreased, red blood cell count decreased.
e Includes leukopenia, white blood cell count decreased.
f Includes platelet count decreased, thrombocytopenia.
g Includes asthenia, fatigue.
VERZENIO plus Fulvestrant
N=441Placebo plus Fulvestrant
N=223All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Gastrointestinal Disorders Diarrhea 86 13 0 25 <1 0 Nausea 45 3 0 23 1 0 Abdominal paina 35 2 0 16 1 0 Vomiting 26 <1 0 10 2 0 Stomatitis 15 <1 0 10 0 0 Infections and Infestations Infectionsb 43 5 <1 25 3 <1 Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Neutropeniac 46 24 3 4 1 <1 Anemiad 29 7 <1 4 1 0 Leukopeniae 28 9 <1 2 0 0 Thrombocytopeniaf 16 2 1 3 0 <1 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigueg 46 3 0 32 <1 0 Edema peripheral 12 0 0 7 0 0 Pyrexia 11 <1 <1 6 <1 0 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 27 1 0 12 <1 0 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Cough 13 0 0 11 0 0 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Alopecia 16 0 0 2 0 0 Pruritus 13 0 0 6 0 0 Rash 11 1 0 4 0 0 Nervous System Disorders Headache 20 1 0 15 <1 0 Dysgeusia 18 0 0 3 0 0 Dizziness 12 1 0 6 0 0 Investigations Alanine aminotransferase increased 13 4 <1 5 2 0 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 12 2 0 7 3 0 Creatinine increased 12 <1 0 <1 0 0 Weight decreased 10 <1 0 2 <1 0 Additional adverse reactions in MONARCH 2 include venous thromboembolic events (deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, subclavian vein thrombosis, axillary vein thrombosis, and DVT inferior vena cava), which were reported in 5% of patients treated with VERZENIO plus fulvestrant as compared to 0.9% of patients treated with fulvestrant plus placebo.
Table 10: Laboratory Abnormalities ≥10% in Patients Receiving VERZENIO Plus Fulvestrant and ≥2% Higher Than Placebo Plus Fulvestrant in MONARCH 2 VERZENIO plus Fulvestrant
N=441Placebo plus Fulvestrant
N=223All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Creatinine increased 98 1 0 74 0 0 White blood cell decreased 90 23 <1 33 <1 0 Neutrophil count decreased 87 29 4 30 4 <1 Anemia 84 3 0 33 <1 0 Lymphocyte count decreased 63 12 <1 32 2 0 Platelet count decreased 53 <1 1 15 0 0 Alanine aminotransferase increased 41 4 <1 32 1 0 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 37 4 0 25 4 <1 Creatinine Increased
Abemaciclib has been shown to increase serum creatinine due to inhibition of renal tubular secretion transporters, without affecting glomerular function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In clinical studies, increases in serum creatinine (mean increase, 0.2-0.3 mg/dL) occurred within the first 28-day cycle of VERZENIO dosing, remained elevated but stable through the treatment period, and were reversible upon treatment discontinuation. Alternative markers such as BUN, cystatin C, or calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which are not based on creatinine, may be considered to determine whether renal function is impaired.
VERZENIO Administered as a Monotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer (MONARCH 1)
Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who received prior endocrine therapy and 1-2 chemotherapy regimens in the metastatic setting
Safety data below are based on MONARCH 1, a single-arm, open-label, multicenter study in 132 women with measurable HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Patients received 200 mg VERZENIO orally twice daily until development of progressive disease or unmanageable toxicity. Median duration of treatment was 4.5 months.
Ten patients (8%) discontinued study treatment from adverse reactions due to (1 patient each) abdominal pain, arterial thrombosis, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased, blood creatinine increased, chronic kidney disease, diarrhea, ECG QT prolonged, fatigue, hip fracture, and lymphopenia. Forty-nine percent of patients had dose reductions due to an adverse reaction. The most frequent adverse reactions that led to dose reductions were diarrhea (20%), neutropenia (11%), and fatigue (9%).
Deaths due to adverse events during treatment or during the 30-day follow up were reported in 2% of patients. Cause of death in these patients was due to infection (2 patients) or pneumonitis (1 patient).
The most common reported adverse reactions (≥20%) were diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, abdominal pain, neutropenia, vomiting, infections, anemia, headache, and thrombocytopenia (Table 11). Severe (Grade 3 and 4) neutropenia was observed in patients receiving abemaciclib [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Table 11: Adverse Reactions (≥10% of Patients) in MONARCH 1 a Includes asthenia, fatigue.
b Includes neutropenia, neutrophil count decreased.
c Includes anemia, hematocrit decreased, hemoglobin decreased, red blood cell count decreased.
d Includes platelet count decreased, thrombocytopenia.
e Includes leukopenia, white blood cell count decreased.
VERZENIO
N=132All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Gastrointestinal Disorders Diarrhea 90 20 0 Nausea 64 5 0 Abdominal pain 39 2 0 Vomiting 35 2 0 Constipation 17 <1 0 Dry mouth 14 0 0 Stomatitis 14 0 0 Infections and Infestations Infections 31 5 2 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatiguea 65 13 0 Pyrexia 11 0 0 Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Neutropeniab 37 19 5 Anemiac 25 5 0 Thrombocytopeniad 20 4 0 Leukopeniae 17 5 <1 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 45 3 0 Dehydration 10 2 0 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Cough 19 0 0 Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Arthralgia 15 0 0 Nervous System Disorders Headache 20 0 0 Dysgeusia 12 0 0 Dizziness 11 0 0 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Alopecia 12 0 0 Investigations Creatinine increased 13 <1 0 Weight decreased 14 0 0 Table 12: Laboratory Abnormalities for Patients Receiving VERZENIO in MONARCH 1 VERZENIO
N=132All Grades
%Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Creatinine increased 98 <1 0 White blood cell decreased 91 28 0 Neutrophil count decreased 88 22 5 Anemia 68 0 0 Lymphocyte count decreased 42 13 <1 Platelet count decreased 41 2 0 ALT increased 31 3 0 AST increased 30 4 0 Creatinine Increased
Abemaciclib has been shown to increase serum creatinine due to inhibition of renal tubular secretion transporters, without affecting glomerular function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In clinical studies, increases in serum creatinine (mean increase, 0.2-0.3 mg/dL) occurred within the first 28-day cycle of VERZENIO dosing, remained elevated but stable through the treatment period, and were reversible upon treatment discontinuation. Alternative markers such as BUN, cystatin C, or calculated GFR, which are not based on creatinine, may be considered to determine whether renal function is impaired.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of VERZENIO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Respiratory disorders: Interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on VERZENIO
CYP3A Inhibitors
Strong and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors increased the exposure of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites to a clinically meaningful extent and may lead to increased toxicity.
Ketoconazole
Avoid concomitant use of ketoconazole. Ketoconazole is predicted to increase the AUC of abemaciclib by up to 16-fold [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Other Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
In patients with recommended starting doses of 200 mg twice daily or 150 mg twice daily, reduce the VERZENIO dose to 100 mg twice daily with concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors other than ketoconazole. In patients who have had a dose reduction to 100 mg twice daily due to adverse reactions, further reduce the VERZENIO dose to 50 mg twice daily with concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors. If a patient taking VERZENIO discontinues a strong CYP3A inhibitor, increase the VERZENIO dose (after 3-5 half-lives of the inhibitor) to the dose that was used before starting the inhibitor. Patients should avoid grapefruit products [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
With concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors, monitor for adverse reactions and consider reducing the VERZENIO dose in 50 mg decrements as demonstrated in Table 1, if necessary.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers decreased the plasma concentrations of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites and may lead to reduced activity. Avoid concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers and consider alternative agents [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, VERZENIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available human data informing the drug-associated risk. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. In animal reproduction studies, administration of abemaciclib during organogenesis was teratogenic and caused decreased fetal weight at maternal exposures that were similar to human clinical exposure based on AUC at the maximum recommended human dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2 to 4% and of miscarriage is 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats received oral doses of abemaciclib up to 15 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Doses ≥4 mg/kg/day caused decreased fetal body weights and increased incidence of cardiovascular and skeletal malformations and variations. These findings included absent innominate artery and aortic arch, malpositioned subclavian artery, unossified sternebra, bipartite ossification of thoracic centrum, and rudimentary or nodulated ribs. At 4 mg/kg/day in rats, the maternal systemic exposures were approximately equal to the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of abemaciclib in human milk, or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from VERZENIO, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during VERZENIO treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Based on animal studies, VERZENIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with VERZENIO.
Contraception
Females
VERZENIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during VERZENIO treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Males
Based on findings in animals, VERZENIO may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VERZENIO have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 900 patients who received VERZENIO in MONARCH 1, MONARCH 2, and MONARCH 3, 38% were 65 years of age or older and 10% were 75 years of age or older. The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) Grade 3 or 4 in patients ≥65 years of age across MONARCH 1, 2, and 3 were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, dehydration, leukopenia, anemia, infections, and ALT increased. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of VERZENIO were observed between these patients and younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr ≥30-89 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault [C-G]). The pharmacokinetics of abemaciclib in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min, C-G), end stage renal disease, or in patients on dialysis is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustments are necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B).
Reduce the dosing frequency when administering VERZENIO to patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
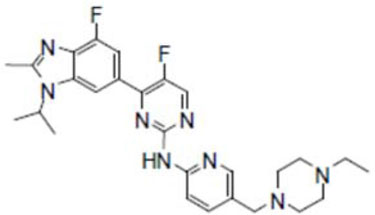
11 DESCRIPTION
Abemaciclib is a kinase inhibitor for oral administration. It is a white to yellow powder with the empirical formula C27H32F2N8 and a molecular weight 506.59.
The chemical name for abemaciclib is 2-Pyrimidinamine, N-[5-[(4-ethyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-2-pyridinyl]-5-fluoro-4-[4-fluoro-2-methyl-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-benzimidazol-6-yl]-. Abemaciclib has the following structure:
VERZENIO (abemaciclib) tablets are provided as immediate-release oval white, beige, or yellow tablets. Inactive ingredients are as follows: Excipients—microcrystalline cellulose 102, microcrystalline cellulose 101, lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, sodium stearyl fumarate, silicon dioxide. Color mixture ingredients—polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, iron oxide yellow, and iron oxide red.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Abemaciclib is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4 and CDK6). These kinases are activated upon binding to D-cyclins. In estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer cell lines, cyclin D1 and CDK4/6 promote phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (Rb), cell cycle progression, and cell proliferation. In vitro, continuous exposure to abemaciclib inhibited Rb phosphorylation and blocked progression from G1 into S phase of the cell cycle, resulting in senescence and apoptosis. In breast cancer xenograft models, abemaciclib dosed daily without interruption as a single agent or in combination with antiestrogens resulted in reduction of tumor size.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of abemaciclib were characterized in patients with solid tumors, including metastatic breast cancer, and in healthy subjects.
Following single and repeated twice daily dosing of 50 mg (0.3 times the approved recommended 150 mg dosage) to 200 mg of abemaciclib, the increase in plasma exposure (AUC) and Cmax was approximately dose proportional. Steady state was achieved within 5 days following repeated twice daily dosing, and the estimated geometric mean accumulation ratio was 2.3 (50% CV) and 3.2 (59% CV) based on Cmax and AUC, respectively.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of abemaciclib after a single oral dose of 200 mg is 45% (19% CV). The median Tmax of abemaciclib is 8.0 hours (range: 4.1-24.0 hours).
Effect of Food
A high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500 to 600 calories from fat) administered to healthy subjects increased the AUC of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites by 9% and increased Cmax by 26%.
Distribution
In vitro, abemaciclib was bound to human plasma proteins, serum albumin, and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in a concentration independent manner from 152 ng/mL to 5066 ng/mL. In a clinical study, the mean (standard deviation, SD) bound fraction was 96.3% (1.1) for abemaciclib, 93.4% (1.3) for M2, 96.8% (0.8) for M18, and 97.8% (0.6) for M20. The geometric mean systemic volume of distribution is approximately 690.3 L (49% CV).
In patients with advanced cancer, including breast cancer, concentrations of abemaciclib and its active metabolites M2 and M20 in cerebrospinal fluid are comparable to unbound plasma concentrations.
Elimination
The geometric mean hepatic clearance (CL) of abemaciclib in patients was 26.0 L/h (51% CV), and the mean plasma elimination half-life for abemaciclib in patients was 18.3 hours (72% CV).
Metabolism
Hepatic metabolism is the main route of clearance for abemaciclib. Abemaciclib is metabolized to several metabolites primarily by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4, with formation of N-desethylabemaciclib (M2) representing the major metabolism pathway. Additional metabolites include hydroxyabemaciclib (M20), hydroxy-N-desethylabemaciclib (M18), and an oxidative metabolite (M1). M2, M18, and M20 are equipotent to abemaciclib and their AUCs accounted for 25%, 13%, and 26% of the total circulating analytes in plasma, respectively.
Specific Populations
Age, Gender, and Body Weight
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis in patients with cancer, age (range 24-91 years), gender (134 males and 856 females), and body weight (range 36-175 kg) had no effect on the exposure of abemaciclib.
Patients with Renal Impairment
In a population pharmacokinetic analysis of 990 individuals, in which 381 individuals had mild renal impairment (60 mL/min ≤ CLcr <90 mL/min) and 126 individuals had moderate renal impairment (30 mL/min ≤ CLcr <60 mL/min), mild and moderate renal impairment had no effect on the exposure of abemaciclib [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min) on pharmacokinetics of abemaciclib is unknown.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 200 mg oral dose of abemaciclib, the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC0-INF of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2, M18, M20) in plasma increased 1.2-fold in subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A, n=9), 1.1-fold in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B, n=10), and 2.4-fold in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C, n=6) relative to subjects with normal hepatic function (n=10) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)]. In subjects with severe hepatic impairment, the mean plasma elimination half-life of abemaciclib increased to 55 hours compared to 24 hours in subjects with normal hepatic function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Ketoconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) is predicted to increase the AUC of abemaciclib by up to 16-fold.
Coadministration of 500 mg twice daily doses of clarithromycin (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) with a single 50 mg dose of VERZENIO (0.3 times the approved recommended 150 mg dosage) increased the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC0-INF of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2, M18, and M20) by 2.5-fold relative to abemaciclib alone in cancer patients.
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Verapamil and diltiazem (moderate CYP3A inhibitors) are predicted to increase the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2, M18, and M20) by approximately 1.6-fold and 2.4-fold, respectively.
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of 600 mg daily doses of rifampin (a strong CYP3A inducer) with a single 200 mg dose of VERZENIO decreased the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC0-INF of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2, M18, and M20) by approximately 70% in healthy subjects.
Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Efavirenz, bosentan, and modafinil (moderate CYP3A inducers) are predicted to decrease the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2, M18, and M20) by 53%, 41%, and 29%, respectively.
Loperamide: Co-administration of a single 8-mg dose of loperamide with a single 400 mg dose of abemaciclib in healthy subjects increased the relative potency adjusted unbound AUC0-INF of abemaciclib plus its active metabolites (M2 and M20) by 12%, which is not considered clinically relevant.
Endocrine Therapies: In clinical studies in patients with breast cancer, there was no clinically relevant effect of fulvestrant, anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane on abemaciclib pharmacokinetics.
Loperamide: In a clinical drug interaction study in healthy subjects, coadministration of a single 8 mg dose of loperamide with a single 400 mg abemaciclib (2.7 times the approved recommended 150 mg dosage) increased loperamide AUC0-INF by 9% and Cmax by 35% relative to loperamide alone. These increases in loperamide exposure are not considered clinically relevant.
Metformin: In a clinical drug interaction study in healthy subjects, coadministration of a single 1000 mg dose of metformin, a clinically relevant substrate of renal OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K transporters, with a single 400 mg dose of abemaciclib (2.7 times the approved recommended 150 mg dosage) increased metformin AUC0-INF by 37% and Cmax by 22% relative to metformin alone. Abemaciclib reduced the renal clearance and renal secretion of metformin by 45% and 62%, respectively, relative to metformin alone, without any effect on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) as measured by iohexol clearance and serum cystatin C.
Endocrine Therapies: In clinical studies in patients with breast cancer, there was no clinically relevant effect of abemaciclib on the pharmacokinetics of fulvestrant, anastrozole, letrozole, or exemestane.
CYP Metabolic Pathways: In a clinical drug interaction study in patients with cancer, multiple doses of abemaciclib (200 mg twice daily for 7 days) did not result in clinically meaningful changes in the pharmacokinetics of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 substrates. Abemaciclib is a substrate of CYP3A4, and time-dependent changes in pharmacokinetics of abemaciclib as a result of autoinhibition of its metabolism were not observed.
In Vitro Studies
Transporter Systems: Abemaciclib and its major active metabolites inhibit the renal transporters OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K at concentrations achievable at the approved recommended dosage. The observed serum creatinine increase in clinical studies with abemaciclib is likely due to inhibition of tubular secretion of creatinine via OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K [see Adverse Effects (6.1)]. Abemaciclib and its major metabolites at clinically relevant concentrations do not inhibit the hepatic uptake transporters OCT1, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3 or the renal uptake transporters OAT1 and OAT3.
Abemaciclib is a substrate of P-gp and BCRP. Abemaciclib and its major active metabolites, M2 and M20, are not substrates of hepatic uptake transporters OCT1, organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1), or OATP1B3.
Abemaciclib inhibits P-gp and BCRP. The clinical consequences of this finding on sensitive P-gp and BCRP substrates are unknown.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with abemaciclib.
Abemaciclib and its active human metabolites M2 and M20 were not mutagenic in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or clastogenic in an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells or human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Abemaciclib was not clastogenic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Studies to assess the effects of abemaciclib on fertility have not been performed. In repeat-dose toxicity studies up to 3-months duration, abemaciclib-related findings in the testis, epididymis, prostate, and seminal vesicle at doses ≥10 mg/kg/day in rats and ≥0.3 mg/kg/day in dogs included decreased organ weights, intratubular cellular debris, hypospermia, tubular dilatation, atrophy, and degeneration/necrosis. These doses in rats and dogs resulted in approximately 2 and 0.02 times, respectively, the exposure (AUC) in humans at the maximum recommended human dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
VERZENIO in Combination with an Aromatase Inhibitor (Anastrozole or Letrozole) (MONARCH 3)
Postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with no prior systemic therapy in this disease setting
MONARCH 3 was a randomized (2:1), double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in postmenopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor as initial endocrine-based therapy, including patients not previously treated with systemic therapy for breast cancer.
Randomization was stratified by disease site (visceral, bone only, or other) and by prior (neo)adjuvant endocrine therapy (aromatase inhibitor versus other versus no prior endocrine therapy). A total of 493 patients were randomized to receive 150 mg VERZENIO or placebo orally twice daily, plus physician's choice of letrozole (80% of patients) or anastrozole (20% of patients). Patient median age was 63 years (range, 32-88 years) and the majority were White (58%) or Asian (30%). A total of 51% had received prior systemic therapy and 39% of patients had received chemotherapy, 53% had visceral disease, and 22% had bone-only disease.
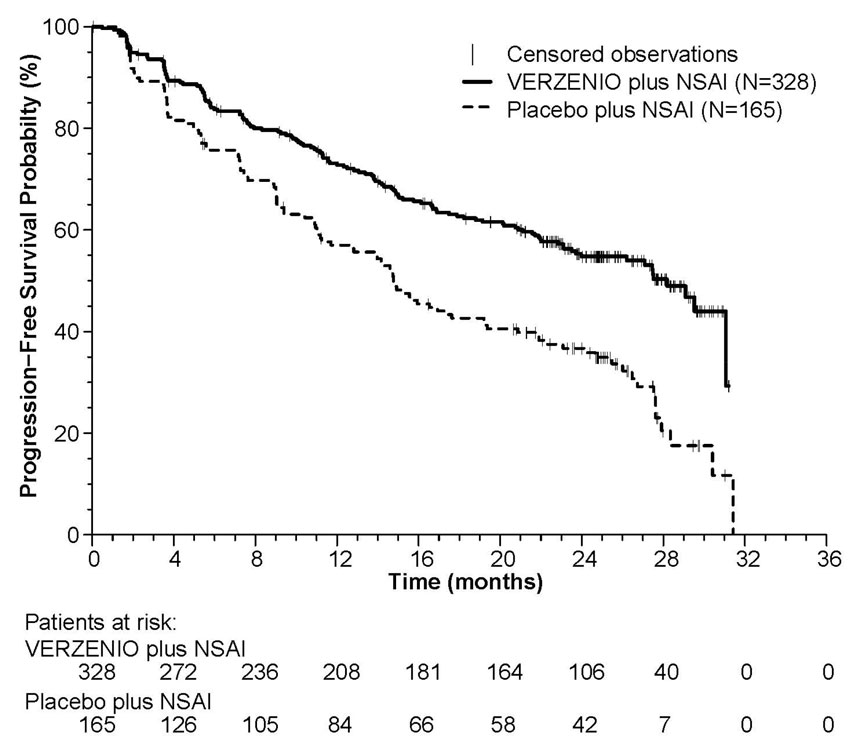
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 13 and Figure 1. PFS was evaluated according to RECIST version 1.1 and PFS assessment based on a blinded independent radiologic review was consistent with the investigator assessment. Consistent results were observed across patient stratification subgroups of disease site and prior (neo)adjuvant endocrine therapy. At the time of the PFS analysis, 19% of patients had died, and overall survival data were immature.
Table 13: Efficacy Results in MONARCH 3 (Investigator Assessment, Intent-to-Treat Population) Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval, NR = not reached.
a Complete response + partial response.
b Based upon confirmed responses.
VERZENIO plus
Anastrozole or LetrozolePlacebo plus
Anastrozole or LetrozoleProgression-Free Survival N=328 N=165 Number of patients with an event (n, %) 138 (42.1) 108 (65.5) Median (months, 95% CI) 28.2 (23.5, NR) 14.8 (11.2, 19.2) Hazard ratio (95% CI) 0.540 (0.418, 0.698) p-value <0.0001 Objective Response for Patients with Measurable Disease N=267 N=132 Objective response ratea,b (n, %) 148 (55.4) 53 (40.2) 95% CI 49.5, 61.4 31.8, 48.5 Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-Free Survival: VERZENIO plus Anastrozole or Letrozole versus Placebo plus Anastrozole or Letrozole (MONARCH 3)
VERZENIO in Combination with Fulvestrant (MONARCH 2)
Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer with disease progression on or after prior adjuvant or metastatic endocrine therapy
MONARCH 2 (NCT02107703) was a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study in women with HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer in combination with fulvestrant in patients with disease progression following endocrine therapy who had not received chemotherapy in the metastatic setting. Randomization was stratified by disease site (visceral, bone only, or other) and by sensitivity to prior endocrine therapy (primary or secondary resistance). Primary endocrine therapy resistance was defined as relapse while on the first 2 years of adjuvant endocrine therapy or progressive disease within the first 6 months of first line endocrine therapy for metastatic breast cancer. A total of 669 patients were randomized to receive VERZENIO or placebo orally twice daily plus intramuscular injection of 500 mg fulvestrant on days 1 and 15 of cycle 1 and then on day 1 of cycle 2 and beyond (28-day cycles). Pre/perimenopausal women were enrolled in the study and received the gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist goserelin for at least 4 weeks prior to and for the duration of MONARCH 2. Patients remained on continuous treatment until development of progressive disease or unmanageable toxicity.
Patient median age was 60 years (range, 32-91 years), and 37% of patients were older than 65. The majority were White (56%), and 99% of patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 0 or 1. Twenty percent (20%) of patients had de novo metastatic disease, 27% had bone-only disease, and 56% had visceral disease. Twenty-five percent (25%) of patients had primary endocrine therapy resistance. Seventeen percent (17%) of patients were pre- or perimenopausal.
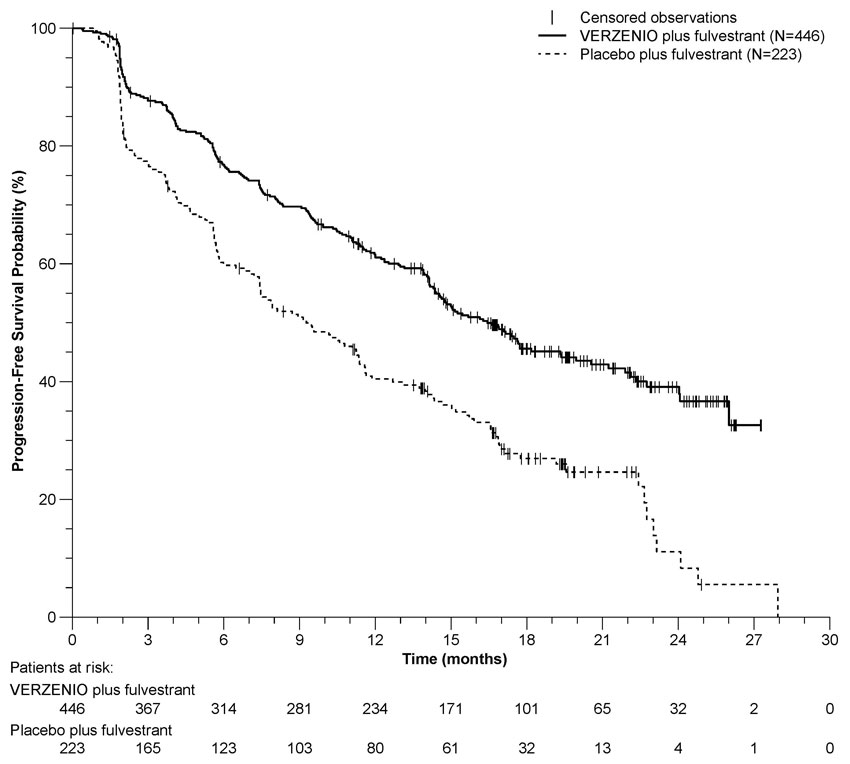
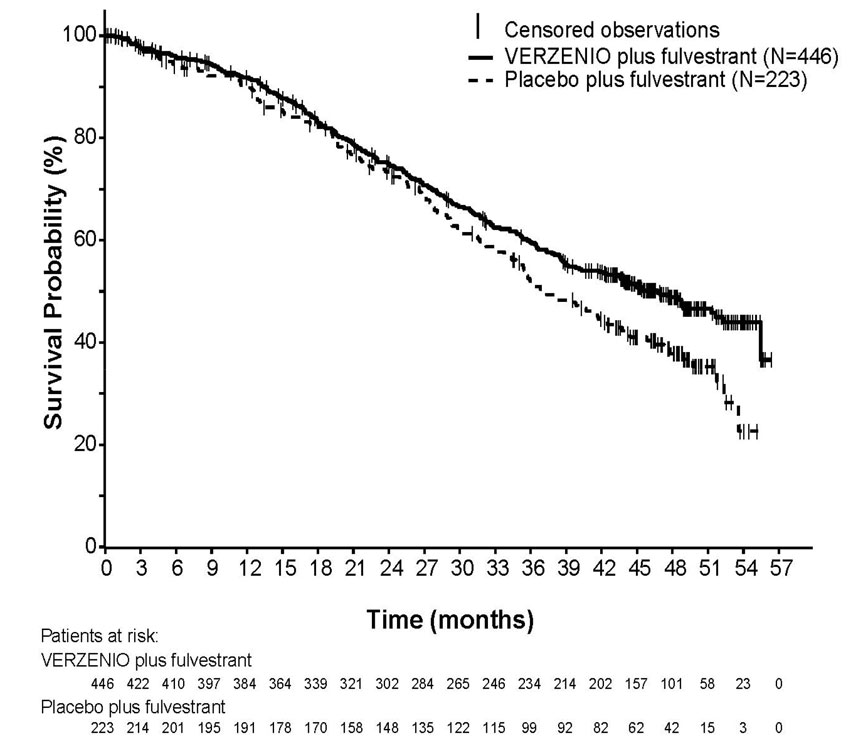
The efficacy results from the MONARCH 2 study are summarized in Table 14, Figure 2, and Figure 3. PFS assessment based on a blinded independent radiologic review was consistent with the investigator assessment. Consistent results were observed across patient stratification subgroups of disease site and endocrine therapy resistance for PFS and OS.
Table 14: Efficacy Results in MONARCH 2 (Intent-to-Treat Population) Abbreviation: CI = confidence interval, OS = overall survival.
a Stratified by disease site (visceral metastases vs. bone-only metastases vs. other) and endocrine therapy resistance (primary resistance vs. secondary resistance)
b Data from a pre-specified interim analysis (77% of the number of events needed for the planned final analysis) with the p-value compared with the allocated alpha of 0.021.
c Complete response + partial response.
VERZENIO plus Fulvestrant Placebo plus Fulvestrant Progression-Free Survival
(Investigator Assessment)N=446 N=223 Number of patients with an event (n, %) 222 (49.8) 157 (70.4) Median (months, 95% CI) 16.4 (14.4, 19.3) 9.3 (7.4, 12.7) Hazard ratio (95% CI)a 0.553 (0.449, 0.681) p-valuea p<.0001 Overall Survivalb Number of deaths (n, %) 211 (47.3) 127 (57.0) Median OS in months (95% CI) 46.7 (39.2, 52.2) 37.3 (34.4, 43.2) Hazard ratio (95% CI)a 0.757 (0.606, 0.945) p-valuea p=.0137 Objective Response for Patients with Measurable Disease N=318 N=164 Objective response ratec (n, %) 153 (48.1) 35 (21.3) 95% CI 42.6, 53.6 15.1, 27.6 Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Progression-Free Survival: VERZENIO plus Fulvestrant
versus Placebo plus Fulvestrant (MONARCH 2)Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival: VERZENIO plus Fulvestrant versus Placebo plus Fulvestrant (MONARCH 2)
VERZENIO Administered as a Monotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer (MONARCH 1)
Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who received prior endocrine therapy and 1-2 chemotherapy regimens in the metastatic setting
MONARCH 1 (NCT02102490) was a single-arm, open-label, multicenter study in women with measurable HR-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer whose disease progressed during or after endocrine therapy, had received a taxane in any setting, and who received 1 or 2 prior chemotherapy regimens in the metastatic setting. A total of 132 patients received 200 mg VERZENIO orally twice daily on a continuous schedule until development of progressive disease or unmanageable toxicity.
Patient median age was 58 years (range, 36-89 years), and the majority of patients were White (85%). Patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 (55% of patients) or 1 (45%). The median duration of metastatic disease was 27.6 months. Ninety percent (90%) of patients had visceral metastases, and 51% of patients had 3 or more sites of metastatic disease. Fifty-one percent (51%) of patients had had one line of chemotherapy in the metastatic setting. Sixty-nine percent (69%) of patients had received a taxane-based regimen in the metastatic setting and 55% had received capecitabine in the metastatic setting. Table 15 provides the efficacy results from MONARCH 1.
Table 15: Efficacy Results in MONARCH 1 (Intent-to-Treat Population) Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval, NR = not reached.
a All responses were partial responses.
b Based upon confirmed responses.
VERZENIO 200 mg
N=132Investigator Assessed Independent Review Objective Response Ratea,b, n (%) 26 (19.7) 23 (17.4) 95% CI (%) 13.3, 27.5 11.4, 25.0 Median Duration of Response 8.6 months 7.2 months 95% CI (%) 5.8, 10.2 5.6, NR -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
VERZENIO 50 mg tablets are oval beige tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “50” on the other side.
VERZENIO 100 mg tablet are oval white to practically white tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “100” on the other side.
VERZENIO 150 mg tablets are oval yellow tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “150” on the other side.
VERZENIO 200 mg tablets are oval beige tablet with “Lilly” debossed on one side and “200” on the other side.
VERZENIO tablets are supplied in 7-day dose pack configurations as follows:
- 200 mg dose pack (14 tablets) – each blister pack contains 14 tablets (200 mg per tablet) (200 mg twice daily)
NDC: 0002-6216-54 - 150 mg dose pack (14 tablets) – each blister pack contains 14 tablets (150 mg per tablet) (150 mg twice daily)
NDC: 0002-5337-54 - 100 mg dose pack (14 tablets) – each blister pack contains 14 tablets (100 mg per tablet) (100 mg twice daily)
NDC: 0002-4815-54 - 50 mg dose pack (14 tablets) – each blister pack contains 14 tablets (50 mg per tablet) (50 mg twice daily)
NDC: 0002-4483-54 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved Patient Information.
Diarrhea
VERZENIO may cause diarrhea, which may be severe in some cases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Early identification and intervention is critical for the optimal management of diarrhea. Instruct patients that at the first sign of loose stools, they should start antidiarrheal therapy (for example, loperamide) and notify their healthcare provider for further instructions and appropriate follow up.
- Encourage patients to increase oral fluids.
- If diarrhea does not resolve with antidiarrheal therapy within 24 hours to ≤Grade 1, suspend VERZENIO dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Neutropenia
Advise patients of the possibility of developing neutropenia and to immediately contact their healthcare provider should they develop a fever, particularly in association with any signs of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
Advise patients to immediately report new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Venous Thromboembolism
Advise patients to immediately report any signs or symptoms of thromboembolism such as pain or swelling in an extremity, shortness of breath, chest pain, tachypnea, and tachycardia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during VERZENIO therapy and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during VERZENIO treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
- Inform patients to avoid concomitant use of ketoconazole. Dose reduction may be required for other strong CYP3A inhibitors or for moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7)].
- Grapefruit may interact with VERZENIO. Advise patients not to consume grapefruit products while on treatment with VERZENIO.
- Advise patients to avoid concomitant use of strong and moderate CYP3A inducers and to consider alternative agents [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7)].
- Advise patients to inform their healthcare providers of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Dosing
- Instruct patients to take the doses of VERZENIO at approximately the same times every day and to swallow whole (do not chew, crush, or split them prior to swallowing) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- If patient vomits or misses a dose, advise the patient to take the next prescribed dose at the usual time [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Advise the patient that VERZENIO may be taken with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Marketed by: Lilly USA, LLC, Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
Copyright © 2017, 2020, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.VER-0006-USPI-20200330
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE CARTON – VERZENIO 50 mg 14ct
14 tablets
NDC: 0002-4483-54
Rx only
Verzenio™
(abemaciclib) tablets
50 mg dose
7-Day Supply
This 50 mg Dose Pack contains fourteen 50 mg tablets.
www.verzenio.com
LIFT TO OPEN
Lilly
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE CARTON – VERZENIO 100 mg 14ct
14 tablets
NDC: 0002-4815-54
Rx only
Verzenio™
(abemaciclib) tablets
100 mg dose
7-Day Supply
This 100 mg Dose Pack contains fourteen 100 mg tablets.
www.verzenio.com
LIFT TO OPEN
Lilly
-
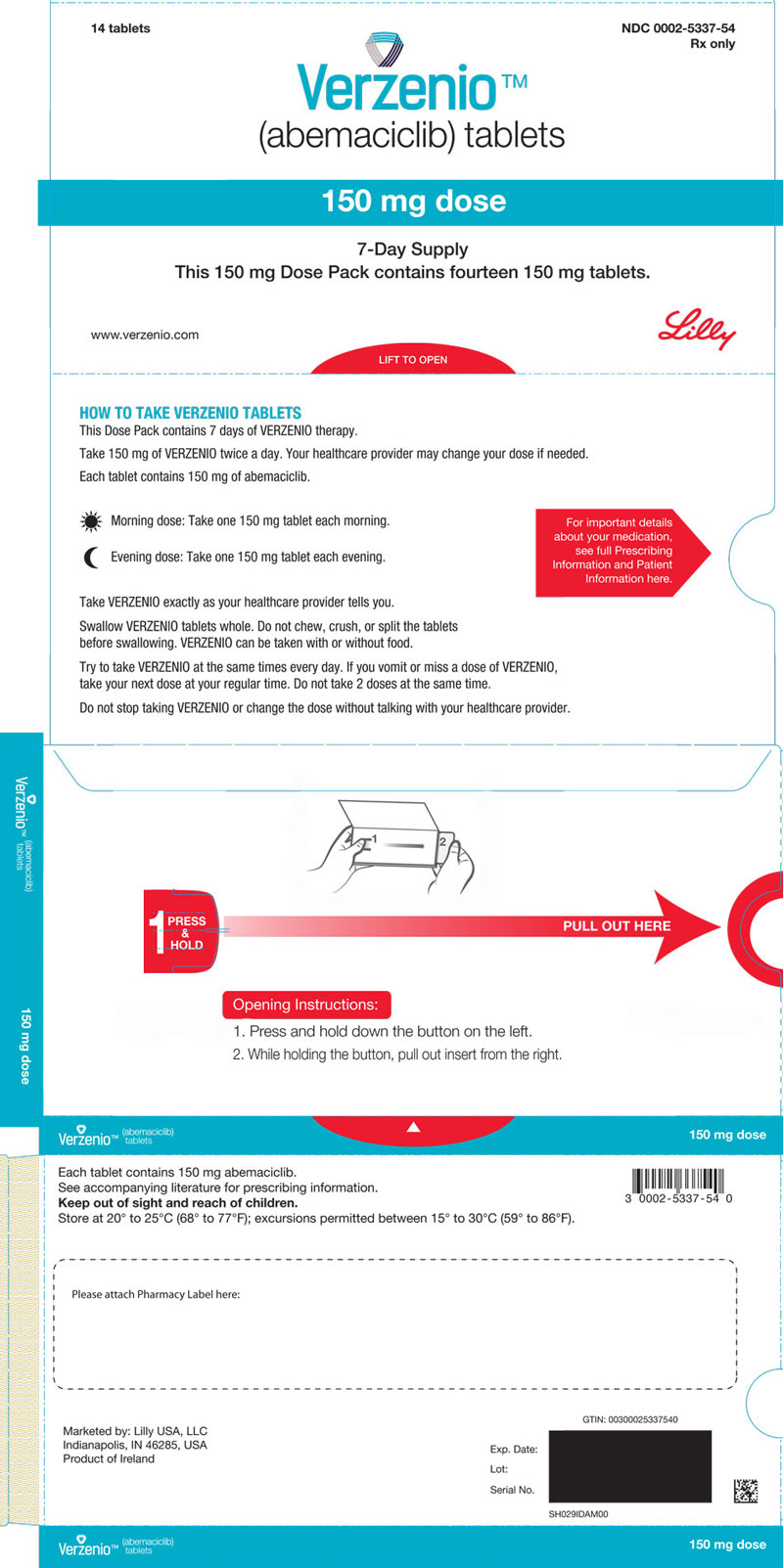
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE CARTON – VERZENIO 150 mg 14ct
14 tablets
NDC: 0002-5337-54
Rx only
Verzenio™
(abemaciclib) tablets
150 mg dose
7-Day Supply
This 150 mg Dose Pack contains fourteen 150 mg tablets.
www.verzenio.com
LIFT TO OPEN
Lilly
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE CARTON – VERZENIO 200 mg 14ct
14 tablets
NDC: 0002-6216-54
Rx only
Verzenio™
(abemaciclib) tablets
200 mg dose
7-Day Supply
This 200 mg Dose Pack contains fourteen 200 mg tablets.
www.verzenio.com
LIFT TO OPEN
Lilly
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VERZENIO
abemaciclib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-4483 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength abemaciclib (UNII: 60UAB198HK) (abemaciclib - UNII:60UAB198HK) abemaciclib 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Lactose Monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Polyvinyl Alcohol, Unspecified (UNII: 532B59J990) Polyethylene Glycol, Unspecified (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Ferric Oxide Yellow (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Ferric Oxide Red (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color white (beige) Score no score Shape oval (modified oval) Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;50 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-4483-54 1 in 1 CARTON 10/06/2017 1 14 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208716 09/28/2017 VERZENIO
abemaciclib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-4815 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength abemaciclib (UNII: 60UAB198HK) (abemaciclib - UNII:60UAB198HK) abemaciclib 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Lactose Monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Polyvinyl Alcohol, Unspecified (UNII: 532B59J990) Polyethylene Glycol, Unspecified (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color white (white) Score no score Shape oval (modified oval) Size 12mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;100 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-4815-54 1 in 1 CARTON 10/06/2017 1 14 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208716 09/28/2017 VERZENIO
abemaciclib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-5337 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength abemaciclib (UNII: 60UAB198HK) (abemaciclib - UNII:60UAB198HK) abemaciclib 150 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Lactose Monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Polyvinyl Alcohol, Unspecified (UNII: 532B59J990) Polyethylene Glycol, Unspecified (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Ferric Oxide Yellow (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color yellow (yellow) Score no score Shape oval (modified oval) Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;150 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-5337-54 1 in 1 CARTON 10/06/2017 1 14 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 0002-5337-63 1 in 1 CARTON 03/05/2020 2 4 in 1 CARTON 2 14 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208716 09/28/2017 VERZENIO
abemaciclib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0002-6216 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength abemaciclib (UNII: 60UAB198HK) (abemaciclib - UNII:60UAB198HK) abemaciclib 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Lactose Monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Sodium Stearyl Fumarate (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Polyvinyl Alcohol, Unspecified (UNII: 532B59J990) Polyethylene Glycol, Unspecified (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Ferric Oxide Yellow (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Ferric Oxide Red (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color white (beige) Score no score Shape oval (modified oval) Size 15mm Flavor Imprint Code Lilly;200 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0002-6216-54 1 in 1 CARTON 10/06/2017 1 14 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208716 09/28/2017 Labeler - Eli Lilly and Company (006421325)
Trademark Results [Verzenio]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 VERZENIO 87712095 5746611 Live/Registered |
Eli Lilly and Company 2017-12-07 |
 VERZENIO 87147864 5429204 Live/Registered |
Eli Lilly and Company 2016-08-23 |
 VERZENIO 85864138 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Eli Lilly and Company 2013-03-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.