DRAXIMAGE DTPA- kit for the preparation of technetium tc 99m pentetate injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
DRAXIMAGE DTPA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DRAXIMAGE DTPA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Jubilant DraxImage Inc., dba Jubilant Radiopharma, Jubilant HollisterStier General Partnership. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DRAXIMAGE® DTPA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DRAXIMAGE® DTPA.
DRAXIMAGE® DTPA (kit for the preparation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection), for intravenous and inhalation use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1974RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DRAXIMAGE® DTPA is a kit for the preparation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection. Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for:
- Brain imaging in adults (1.1).
- Renal visualization, assessment of renal perfusion, and estimation of glomerular filtration rate in adult and pediatric patients (1.2).
- Lung ventilation imaging and evaluation of pulmonary embolism when paired with perfusion imaging in adult and pediatric patients (1.3).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- During preparation and handling, use water proof gloves and effective shielding, to minimize radiation exposure (2.1, 5.3).
- See the Full Prescribing Information for detailed information regarding recommended Dosage and Image Acquisition Instructions (2.2) and Instructions for Drug Preparation (2.4).
- Do not administer more than one dose (2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Kit for the preparation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection: 10 mL multiple dose vials containing up to 9250 MBq / mL (250 mCi / mL) at time of preparation (reconstitution) (3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or any component of this product (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported during post-approval diagnostic use of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection. Monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions (5.1).
- Image interpretation risks in lung ventilation studies: If proximal airway deposition is observed, consider additional diagnostic options (5.2).
- Radiation exposure risk: Technetium Tc 99m pentetate contributes to a patient’s overall long-term radiation exposure (2.1, 2.3, 5.3).
- Bronchospasm in lung ventilation studies: Inhalation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate solution may result in acute bronchoconstriction, especially in patients with heightened bronchoreactivity (5.4).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions reported with Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection include allergic reactions, rash, itching (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Jubilant DraxImage Inc. at 1-888-633-5343 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Brain Imaging
1.2 Renal Scintigraphy
1.3 Lung Ventilation Imaging
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety – Drug Handling
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Image Acquisition Instructions
2.3 Administration Instructions
2.4 Instructions for Drug Preparation
2.5 Determination of Radiochemical Purity
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Image Interpretation Risks in Lung Ventilation Studies
5.3 Radiation Exposure Risk
5.4 Bronchospasm in Lung Ventilation Studies
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Characteristics
11.2 Physical Characteristics
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety – Drug Handling
Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA injection is a radioactive drug and should be handled with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to the patient and healthcare worker. During preparation and handling, use water proof gloves and effective shielding, including syringe shields [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Image Acquisition Instructions
- The recommended dose ranges for intravenous or inhalation administration of DRAXIMAGE® DTPA, after reconstitution, are presented in Table 1 through Table 3.
- Do not administer more than one dose.
Table 1 Tc 99m Labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA Injection – Intravenous Administration, Adults Indication Route of Administration Dose Image Acquisition Brain Imaging Intravenous Injection 370 to 740 MBq
(10 to 20 mCi)Immediate dynamic imaging.
Obtain at least one blood-pool image in same position as flow.
Delayed images can be obtained 1 hour later.Renal Visualization and Perfusion Assessment Intravenous Injection 370 to 740 MBq
(10 to 20 mCi)Immediate dynamic imaging.
Static imaging 1 to 30 minutes after injection.Renal Visualization with Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate Intravenous Injection 111 to 185 MBq
(3 to 5 mCi)Immediate dynamic imaging.
Static imaging 1 to 30 minutes after injection.Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate (with no renal imaging) Intravenous Injection 7.4 to 18.5 MBq
(0.2 to 0.5 mCi)Blood sampling only is performed. Table 2 Tc 99m Labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA Injection – Intravenous Administration, Pediatric Patients Indication Route of Administration Dose Image Acquisition Renal Visualization and Perfusion Assessment Intravenous Injection 3.7 to 7.4 MBq/kg
(0.1 to 0.2 mCi/kg)
Minimum 37 MBq (1 mCi)
Maximum 185 MBq (5 mCi)Immediate dynamic imaging.
Static imaging 1 to 30 minutes after injection.Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate (with no renal imaging) Intravenous Injection 7.4 to 18.5 MBq
(0.2 to 0.5 mCi)Blood sampling only is performed. Table 3 Tc 99m Labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA – Aerosol Inhalation Administration * For lung imaging performed after perfusion imaging, target count rate should be approximately three times that of perfusion count rate. Indication Route of Administration Dose Image Acquisition Lung Ventilation
AdultsAerosol Inhalation 925 to 1850 MBq (25 to 50 mCi) in the nebulizer to achieve a lung dose of approximately 18.5 to 37 MBq (0.5 to 1.0 mCi) For lung imaging performed prior to perfusion imaging, the target administered dose to the lungs is achieved after 3 to 5 minutes of inhalation or at an imaging count rate of 50,000 to 100,000 per minute*. Lung Ventilation
Pediatric PatientsAerosol Inhalation 925 MBq (25 mCi) in the nebulizer to achieve a lung dose of approximately 18.5 MBq (0.5 mCi) For lung imaging performed prior to perfusion imaging, the target administered dose to the lungs is achieved at an imaging count rate of approximately 10,000 to 50,000 per minute*. 2.3 Administration Instructions
- Use aseptic technique for all drug preparation and handling.
- Visually inspect the Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA injection after reconstitution for particulate matter prior to administration. Do not use or administer if there is evidence of foreign matter or the solution is not clear.
- Measure the patient dose by a radioactivity calibration system immediately prior to administration.
- Instruct the patient to increase fluid intake and to void frequently for the next 4 to 6 hours after Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA administration by injection to minimize the radiation dose to the bladder.
- Use the selected nebulizer in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Instruct the patient to rinse their mouth and expectorate after Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA administration by inhalation to minimize the radiation dose to the mouth and esophagus.
2.4 Instructions for Drug Preparation
- The prepared solution can either be administered via intravenous injection or aerosolized by nebulizer for inhalation use.
- Before reconstitution, inspect the integrity of the vial.
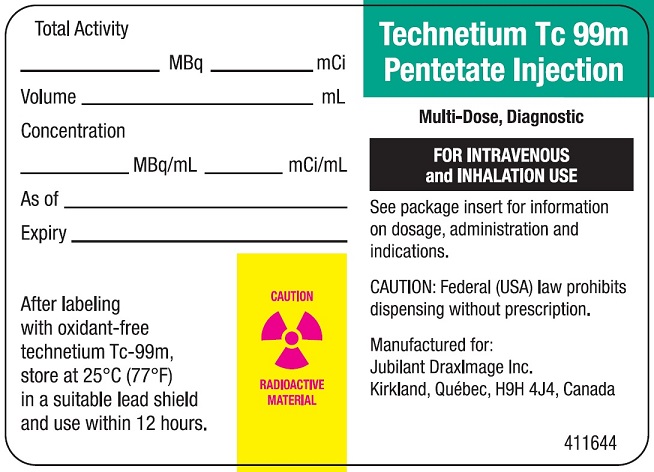
- Add 2 to 10 mL [maximum amount 18.5 gigabecquerels (500 mCi)] of sodium pertechnetate Tc 99m injection USP to the reaction vial. The volume of pertechnetate added should be balanced by the removal of the same volume of air. Cover the vial shield and invert to mix the contents.
- Assay the preparation in a calibrator, record the radio assay information on the label with radiation warning symbol, and affix it to the reaction vial.
- After reconstitution, store the solution at 25°C (77°F) in a lead shield and discard after 12 hours; excursions permitted between 15 and 30°C (59 and 86°F).
- Allow the preparation to stand for 15 minutes before determining the radiochemical purity of Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA injection.
- After reconstitution, do not vent the vial.
2.5 Determination of Radiochemical Purity
- Two ITLC-SG (1 x 10 cm)
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP (for determination of reduced hydrolyzed technetium)
- Acetone (for determination of free pertechnetate)
- Two glass test tubes (18 mm x 150 mm) with stoppers
- System A: Add 1 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP in an 18 mm x 150 mm test tube. Place the stopper and allow the atmosphere in the tube to equilibrate for 1 minute.
- System B: Repeat with Acetone in a separate test tube.
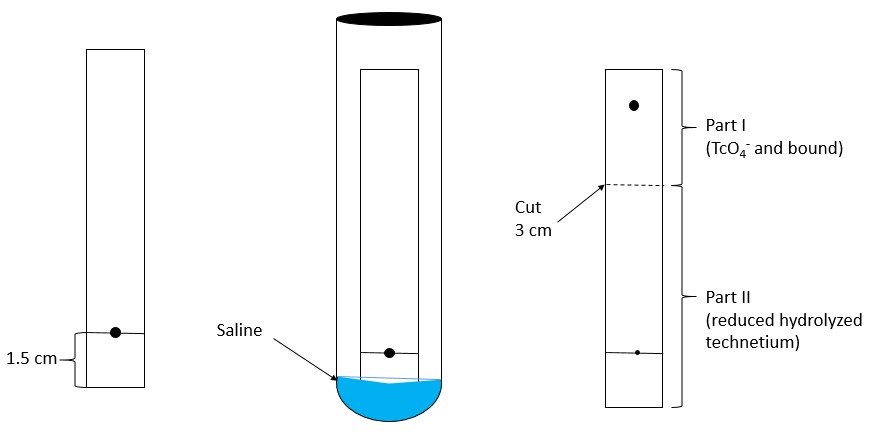
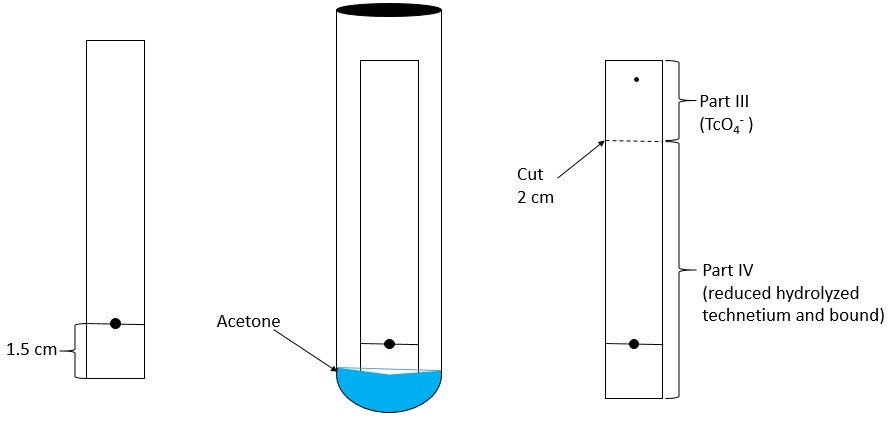
- Mark each chromatographic strip with a pencil mark 1.5 cm (see Figure 1 and Figure 2) from one end of the strip (mark as origin).
- Place one drop (approximately 0.01 - 0.02 mL) of the Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection at the origin.
- For System A (saline), do not allow the strip to dry.
- For System B (acetone), dry the strip using a gentle stream of nitrogen gas.
- Place each strip with the origin end towards the bottom of the previously equilibrated test tube to develop (the origin must be above the surface of the solvent).
- Place stopper in the test tube and keep upright.
- When the solvent front has reached the top of the strip, remove the strip with forceps and allow it to dry.
Step 5:
System A – Determination of reduced hydrolyzed technetium:- In System A (saline), reduced hydrolyzed technetium (99mTcO2) stays at the origin (Rf 0 to 0.1), while the bound technetium and free pertechnetate (99mTcO4–) migrates to the solvent front (Rf 0.85 to 1.0).
- Cut the dried strip 3 cm from the origin.
- The short piece is marked as Part I and the long piece is marked as Part II.
- Count the pieces in a counter and determine the percentage of reduced hydrolyzed technetium according to the following formula:
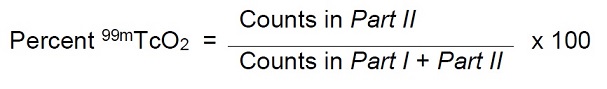
System B – Determination of free pertechnetate:
- In System B (acetone), the bound technetium and reduced hydrolyzed technetium (99mTcO2) stay at the origin (Rf 0 to 0.1), while free pertechnetate (99mTcO4–) migrates to the solvent front (Rf 0.85 to 1.0).
- Cut the dried strip 2 cm from the solvent front end.
- The short piece is marked Part III and the long piece is marked Part IV.
- Count the pieces in a counter and determine the percentage of free pertechnetate according to the following formula:

- Determine the radiochemical purity according to the following formula:
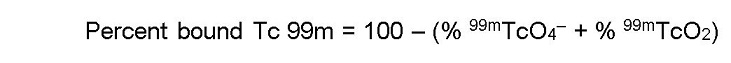
- Use Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection only if the radiochemical purity is 90% or greater.
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated radiation absorbed dose to various organs from an intravenous injection of Tc 99m pentetate in patients with normal and abnormal renal function is shown respectively in Table 4 and Table 5.
Table 4 Estimated Radiation Absorbed Dose for Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection in Patients With Normal Renal Function Following Intravenous Injection Absorbed Dose Per Unit Activity Administered (μGy/MBq) Organ Adult 15 Years 10 Years 5 Years 1 Year Adrenals 1.4 1.8 2.7 4.0 7.2 Bone surfaces 2.4 2.9 4.3 6.1 10 Brain 0.86 1.1 1.7 2.8 4.9 Breast 0.72 0.92 1.3 2.2 4.1 Gallbladder wall 1.5 2.1 3.8 5.0 6.1 Gastrointestinal tract Esophagus 1.0 1.3 1.9 3.0 5.4 Stomach wall 1.3 1.7 2.8 4.0 6.8 Small intestine wall 2.5 3.1 4.9 7.0 10 Colon wall 3.1 3.9 6.0 8.1 11 Upper large intestine wall 2.1 2.8 4.3 6.5 9.2 Lower large intestine wall 4.3 5.4 8.2 10 13 Heart wall 1.2 1.5 2.2 3.3 5.9 Kidneys 4.4 5.3 7.5 11 18 Liver 1.2 1.6 2.5 3.8 6.4 Lungs 1.0 1.3 2.0 3.0 5.5 Muscles 1.6 2.0 3.0 4.3 6.8 Ovaries 4.2 5.3 7.7 10 13 Pancreas 1.4 1.8 2.8 4.3 7.4 Red marrow 1.5 1.8 2.7 3.7 5.7 Skin 0.87 1.0 1.7 2.6 4.4 Spleen 1.3 1.6 2.6 3.9 6.8 Testes 2.9 4.0 6.8 9.4 13 Thymus 1.0 1.3 1.9 3.0 5.4 Thyroid 1.0 1.3 2.1 3.3 6.0 Urinary bladder wall 62 78 110 150 170 Uterus 7.9 9.6 15 18 22 Remaining organs 1.7 2.1 3.0 4.2 6.6 Effective dose per unit activity
(μSv/MBq)4.9 6.3 9.4 12 16 Table 5 Estimated Radiation Absorbed Dose for Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection in Patients With Abnormal Renal Function Following Intravenous Injection Absorbed Dose Per Unit Activity Administered (μGy/MBq) Organ Adult 15 Years 10 Years 5 Years 1 Year Adrenals 4.1 5.1 7.6 11 21 Bone surfaces 6.0 7.1 11 15 28 Brain 2.8 3.5 5.7 9.1 16 Breast 2.3 3.0 4.2 6.8 13 Gallbladder wall 4.2 5.7 9.2 13 16 Gastrointestinal tract Esophagus 3.3 4.2 6.2 9.6 17 Stomach wall 3.8 5.0 7.9 11 19 Small intestine wall 4.5 5.6 8.5 13 22 Colon wall 4.5 5.8 8.7 13 22 Upper large intestine wall 4.3 5.6 8.1 13 21 Lower large intestine wall 4.9 6.1 9.5 13 23 Heart wall 3.7 4.7 7.0 10 18 Kidneys 7.7 9.2 13 19 32 Liver 3.7 4.6 7.1 11 19 Lungs 3.3 4.2 6.2 9.5 17 Muscles 3.2 4.0 6.1 9.1 17 Ovaries 5.0 6.2 9.2 14 23 Pancreas 4.3 5.3 8.0 12 21 Red marrow 3.4 4.2 6.4 9.3 16 Skin 2.2 2.6 4.2 6.7 12 Spleen 3.8 4.7 7.3 11 19 Testes 3.5 4.5 6.9 10 18 Thymus 3.3 4.2 6.2 9.6 17 Thyroid 3.4 4.2 6.7 11 19 Urinary bladder wall 21 27 39 50 66 Uterus 6.1 7.4 11 16 25 Remaining organs 3.3 4.1 6.3 9.7 17 Effective dose per unit activity
(μSv/MBq)4.6 5.8 8.7 13 21 The estimated radiation absorbed dose to various organs from the inhalation of Tc 99m Pentetate Injection is shown in Table 6.
Table 6 Estimated Radiation Absorbed Dose for Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection Administered by Inhalation Absorbed Dose Per Unit Activity Administered (μGy/MBq) Organ Adult 15 Years 10 Years 5 Years 1 Year Adrenals 2.1 2.9 4.4 6.7 12 Bone surfaces 1.9 2.4 3.5 5.3 9.8 Breast 1.9 1.9 3.3 4.8 7.8 Gastrointestinal tract Stomach wall 1.7 2.2 3.5 5.1 8.9 Small intestine wall 2.1 2.6 4.1 6.3 11 Upper large intestine wall 1.9 2.4 3.8 6.1 10 Lower large intestine wall 3.2 4.2 6.3 8.8 15 Kidneys 4.1 5.1 7.2 11 19 Liver 1.9 2.5 3.7 5.5 9.7 Lungs 17 26 36 54 100 Ovaries 3.3 4.1 6.1 8.9 15 Pancreas 2.1 2.6 4.0 6.1 11 Red marrow 2.7 3.4 4.7 6.2 9.6 Spleen 1.9 2.4 3.6 5.6 9.9 Testes 2.1 3.1 5.2 7.9 15 Thyroid 0.99 1.7 2.7 4.4 7.8 Urinary bladder wall 47 58 84 120 230 Uterus 5.9 7.2 11 16 27 Other tissue 1.8 2.2 3.2 4.9 8.6 Effective dose per unit activity
(μSv/MBq)5.9 8.0 11 17 31 -
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
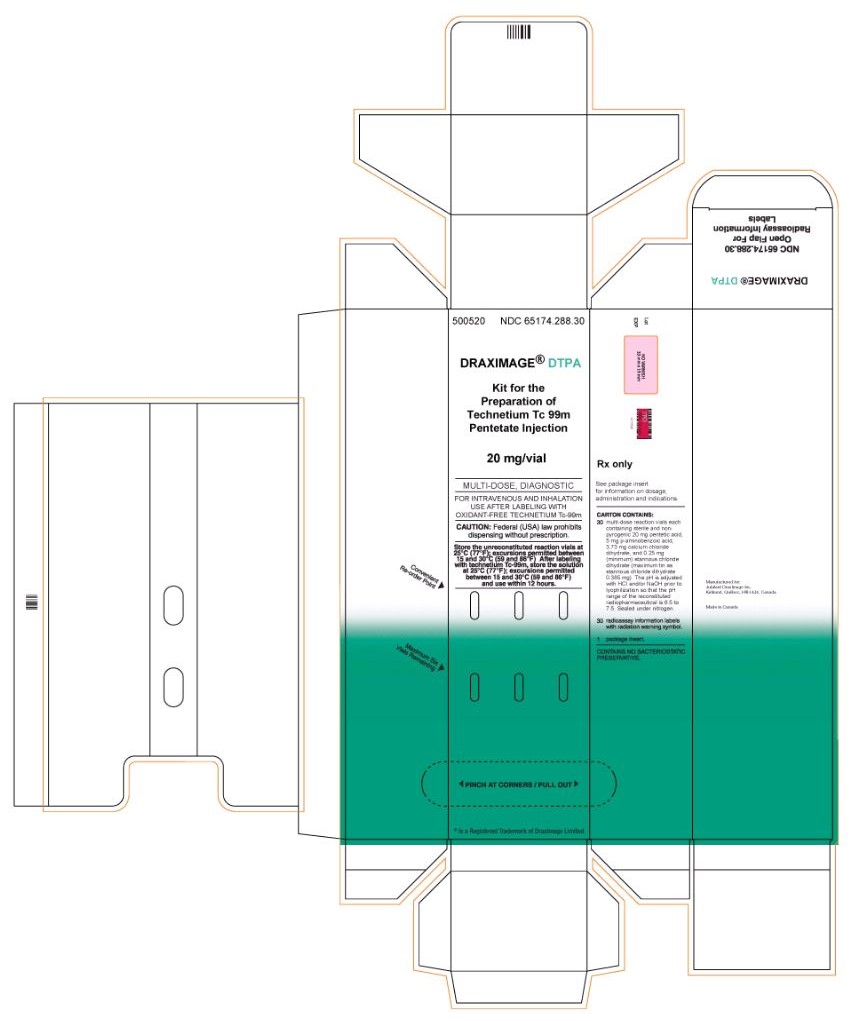
Kit for the preparation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection: multiple-dose 10 mL glass vial contains a non-radioactive (white) lyophilized powder with 20 mg of pentetic acid, 5 mg of p-aminobenzoic acid, 3.73 mg of calcium chloride dihydrate, and not less than 0.25 mg stannous chloride dihydrate and not more than 0.385 mg maximum tin expressed as stannous chloride dihydrate. The lyophilized product is sealed under an atmosphere of nitrogen.
Following reconstitution with the Technetium Tc 99m eluate, the radioactive solution produced is a clear solution not exceeding 9250 MBq/mL (250 mCi/mL) of Tc 99m.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or to any component of the product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported during post-approval diagnostic use of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection. Monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions and have access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment and personnel.
5.2 Image Interpretation Risks in Lung Ventilation Studies
In patients with obstructive pulmonary disease there may be deposition of particles in the proximal airways influencing image quality and interfering with diagnostic interpretation, therefore to ensure diagnostic quality, careful use of the nebulizer to assure optimal particle delivery is essential. If interfering particle deposition occurs, consider additional diagnostic options.
5.3 Radiation Exposure Risk
Technetium Tc 99m contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk of cancer. Ensure safe handling and preparation procedures to protect patients and health care workers from unintentional radiation exposure. Use the lowest dose of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate necessary for imaging. Encourage patients to drink fluids and void as frequently as possible after intravenous administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)].
Radiation risks associated with the use of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate are greater in pediatric patients than in adults due to greater radiosensitivity and longer life expectancy.
5.4 Bronchospasm in Lung Ventilation Studies
As with other inhaled medications, inhalation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate solution may result in acute bronchoconstriction, especially in patients with heightened bronchoreactivity, such as patients with asthma or other lung or allergic disorders. Monitor all patients for bronchoconstriction.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been identified post-approval. Because these reactions are voluntarily reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their exact frequency or establish a causal relationship to Technetium Tc 99m pentetate exposure.
Adverse reactions are presented in decreasing order of reported frequency:
- Immune system disorders: allergic reaction, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema.
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: rash, itching, hives, erythema.
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: throat irritation, wheezing.
- Vascular disorders: hypotension, hypertension.
- Nervous system disorders: headache, fainting, dizziness.
- General disorders and administration site conditions: chills.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: nausea, vomiting.
- Cardiac disorders: cyanosis, tachycardia.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Limited available data with Technetium Tc 99m pentetate use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is transferred across the placenta (see Data). No animal reproductive studies have been conducted with Technetium Tc 99m pentetate. All radiopharmaceuticals have the potential to cause fetal harm depending on the fetal stage of development and the magnitude of the radiation dose. If considering Technetium Tc 99m pentetate administration to a pregnant woman, inform the patient about the potential for adverse pregnancy outcomes based on the radiation dose from Technetium Tc 99m pentetate and the gestational timing of exposure.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S., general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Human Data
Limited published literature describes Technetium Tc 99m pentetate crossing the placental barrier. No adverse fetal effects or radiation-related risks have been identified for diagnostic procedures involving less than 50 mGy, which represents less than 10 mGy fetal doses.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are limited data available in scientific literature on the presence of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate in human milk. There are no data available on the effects of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Based on the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission guidelines for breast feeding interruption after exposure to radiopharmaceuticals, breastfeeding interruption is not recommended for Technetium 99m pentetate at levels less than 1000 MBq (30 mCi). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Technetium Tc 99m pentetate, any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Technetium Tc 99m pentetate or from the underlying maternal condition.8.4 Pediatric Use
Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is indicated for lung ventilation and evaluation of pulmonary embolism when paired with perfusion imaging and for renal visualization, assessment of renal perfusion, and estimation of glomerular filtration rate in pediatric patients ages birth to less than 17 years of age. Pediatric use is supported by evidence from controlled studies in adults and dosing and safety are based on clinical experience.
The radiation risk of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is greater in pediatric patients than adults [See Warnings and Precautions, (5.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
No formal studies of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate in the elderly were performed to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Characteristics
DRAXIMAGE® DTPA is a kit for the preparation of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate injection, a radioactive diagnostic agent, for intravenous or inhalation use. Each multiple-dose 10 mL glass vial contains a sterile, non-pyrogenic, non-radioactive lyophilized powder of 20 mg of pentetic acid, 5 mg of p-aminobenzoic acid, 3.73 mg of calcium chloride dihydrate, and not less than 0.25 mg stannous chloride dihydrate and not more than 0.385 mg maximum tin expressed as stannous chloride dihydrate. The lyophilized product is sealed under an atmosphere of nitrogen. No bacteriostatic preservative is present. Its chemical name is:
Technetate (1-)99mTc,[N,N-bis[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl]-glycinato(5-)]-, sodium. The structure of the technetium labeled form is:
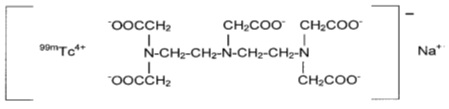
The pH is adjusted with HCl and/or NaOH prior to lyophilization so that the pH range of the reconstituted radiopharmaceutical is 6.5 to 7.5.
11.2 Physical Characteristics
Technetium Tc 99m decays by isomeric transition with a physical half-life of 6 hours. The principal photon that is useful for detection and imaging studies is listed in Table 7.
Table 7 Principal Radiation Emission Data Radiation Mean % per Disintegration Mean Energy (keV) Gamma-2 88.5 140.5 The air-kerma-rate (exposure-rate) constant for Technetium Tc 99m is 5.23 m2·pGy·(MBq)−1·s−1 [0.795 cm2·R·(mCi)−1·h−1]. A range of values for the relative radiation attenuation by the various thicknesses of lead is shown in Table 8. For example, the use of a 3 mm thickness of lead will attenuate the radiation emitted by a factor of about 1,000.
Table 8 Radiation Attenuation by Lead Shielding Shield Thickness (Pb) cm Coefficient of Attenuation 0.25 0.5 1 10-1 2 10-2 3 10-3 4 10-4 To correct for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions that remain at selected intervals after the time of calibration are shown in Table 9.
Table 9 Physical Decay Chart of Technetium 99mTc, Half Life: 6 Hours *Calibration Time Hours Fraction Remaining Hours Fraction Remaining 0* 1.000 5 0.562 1 0.891 6 0.501 2 0.794 8 0.398 3 0.708 10 0.316 4 0.631 12 0.251 -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Intravenous Administration
Following intravenous administration for brain and renal imaging, Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is distributed in the vascular compartment. It is cleared by the kidneys, which results in the ability to image the kidney.Aerosolized Inhalation Administration
Following inhalation of the aerosol, Technetium Tc 99m pentetate deposits on the epithelium of ventilated alveoli.12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Brain Imaging
Technetium Tc 99m pentetate with intravenous administration tends to accumulate in intra-cranial lesions with excessive neovascularity or an altered blood brain barrier. Technetium Tc 99m pentetate accumulation in the brain is prevented by an intact blood brain barrier. It does not accumulate in the choroid plexus.Renal Scintigraphy
The first few minutes after intravenous administration, Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is present in the vascular compartment within the renal system.Lung Ventilation Imaging
In patients with normal lungs, the deposition of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is homogeneous throughout the lungs. In patients with airway disease, the deposition patterns become inhomogeneous with irregular deposition of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate in the airways and alveolar regions of the lung.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After an intravenous administration, the pharmacokinetics of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate were studied by monitoring radioactivity in serial venous blood samples for 7 hours post-administration. The mean plasma clearance rate was 6.8 (L/h) and the mean plasma elimination half-life (t½) was 2.1 hours. The mean volume of distribution at steady state conditions calculated with clearance and mean residence time was 17 L. This relatively low volume of distribution after intravenous administration suggests that Technetium Tc 99m pentetate distributes to the extracellular fluid only. The rate of elimination of Technetium Tc 99m pentetate from the systemic circulation appears to be constant over an approximately 20-fold intravenous dose range.
Absorption
Following inhalation Technetium Tc 99m pentetate was absorbed (Tmax <2 hours after inhalation) and distributed across the lung epithelium (bioavailability approximately 70%) and into the systemic circulation.Following intravenous administration, Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is distributed throughout the extracellular fluid space and is cleared from the body by the kidney.
The steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) was 17 L following an intravenous administration. Technetium Tc 99m pentetate distribution appears to be limited to the extravascular compartment.
A variable percentage of the Technetium Tc 99m pentetate binds to the serum proteins; this ranges from 3.7% following a single injection to approximately 10% if the material is continuously infused. Although the chelate gives useful information on the glomerular filtration rate, the variable percent which is protein bound leads to a measured renal clearance rate which is lower than that determined by inulin clearance.
Elimination
Metabolism
Technetium Tc 99m pentetate is not metabolized.Excretion
After either intravenous administration or inhalation, excretion is by glomerular filtration. The mean fraction of intravenously administered Technetium Tc 99m pentetate excreted in urine over 24 hours was 102%. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
DRAXIMAGE® DTPA is supplied as multiple dose kits consisting of 10 mL reaction vials containing a white, lyophilized powder with 20 mg of pentetic acid, 5 mg of p-aminobenzoic acid, 3.73 mg of calcium chloride dihydrate, and not less than 0.25 mg stannous chloride dihydrate and not more than 0.385 mg tin expressed as stannous chloride dihydrate.
The radionuclide is not part of the kit. Before reconstitution and radiolabeling with sodium pertechnetate Tc 99m injection USP, the contents of the kit are not radioactive.
The kits are supplied in the following formats:
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store the unreconstituted reaction vials at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15 and 30°C (59 and 86°F).
This radiopharmaceutical is approved for use by persons under license by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission or the relevant regulatory authority of an Agreement State.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING
INFORMATION
Administration Instructions
Intravenous Use
Advise patients to hydrate after administration of Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA injection and to void frequently to minimize radiation dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Inhalation Use
To minimize the potential of mouth and esophageal activity of Tc 99m labeled DRAXIMAGE® DTPA, advise the patient to rinse their mouth with water and spit it out prior to imaging [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the risk of fetal exposure to radiation if they undergo a radionuclide procedure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Radioactive Label
- Vial Label
- 5 Vials Carton
- 30 Vials Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DRAXIMAGE DTPA
kit for the preparation of technetium tc 99m pentetate injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 65174-288 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, RESPIRATORY (INHALATION) Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Pentetic Acid (UNII: 7A314HQM0I) (Pentetic Acid - UNII:7A314HQM0I) Pentetic Acid 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Aminobenzoic Acid (UNII: TL2TJE8QTX) 5 mg Calcium Chloride (UNII: M4I0D6VV5M) 3.73 mg Stannous Chloride (UNII: 1BQV3749L5) 0.25 mg Product Characteristics Color Score no score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65174-288-05 5 in 1 KIT; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/29/1989 2 NDC: 65174-288-30 30 in 1 KIT; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/29/1989 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA018511 12/29/1989 Labeler - Jubilant DraxImage Inc. (243604761) Registrant - Jubilant DraxImage Inc. (243604761) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Jubilant HollisterStier General Partnership 246762764 MANUFACTURE(65174-288)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.