DIGIFAB- ovine digoxin immune fab injection, powder, for solution
DigiFab by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DigiFab by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by BTG International Inc., Cangene bioPhamra Inc., Protherics UK Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DIGIFAB safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DIGIFAB.
DigiFab®, Digoxin Immune Fab (Ovine) For Intravenous Injection Only – Lyophilized Powder for Solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DIGIFAB is a digoxin immune fab (ovine) and is indicated for treatment of life-threatening or potentially life-threatening digoxin toxicity or overdose.(1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use only (2)
Clinical Conditions Dosage Acute ingestion of unknown amounts of digoxin and toxicity in the absence of a serum digitalis concentration or estimated ingestion amount Administer 20 vials of DIGIFAB.
Monitor for volume overload in small (< 20 Kg) children.
Start with 10 vials followed by an additional 10 vials, if needed, to avoid a febrile reaction.Chronic digoxin toxicity in the absence of a serum digitalis concentration Administer 6 vials of DIGIFAB in Adults and Children ≥ 20 Kg.
Administer 1 vial of DIGIFAB in Infants and Children < 20 Kg.Acute ingestion of known amounts of digoxin Dose (in vials) =
Amount of digoxin ingested (in mg)
0.5 mg/vialChronic digoxin toxicity and known serum digitalis concentration Dose (in vials) =
(Serum digoxin ng/mL)(weight in kg)
100DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
DIGIFAB is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized preparation. Each vial contains 40 mg of digoxin immune fab protein. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Rapid drop in serum potassium concentration after treatment with DIGIFAB. Monitor frequently, especially after the first several hours of DigiFab administration. (5.1)
- Anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity reactions are possible. Patients with allergies to papain, chymopapain, other papaya extracts, or the pineapple enzyme bromelain may be at risk for an allergic reaction to DIGIFAB.
- Clinically misleading reading of standard serum digoxin concentration may occur after administration of DIGIFABdue to interference with digitalis immunoassay measurements. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (>7%) are worsening congestive heart failure (13%), hypokalemia (13%) and worsening atrial fibrillation (7%). (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BTG 1-877-377-3784, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: No human or animal data. Use only if clearly needed. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 General
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.3 Use of DIGIFAB in Renal Failure
5.4 Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DIGIFAB is indicated for the treatment of patients with life-threatening or potentially life-threatening digoxin toxicity or overdose, including:
- Known suicidal or accidental consumption of fatal doses of digoxin: 10 mg or more of digoxin in healthy adults, or 4 mg (or more than 0.1 mg/kg) in healthy children, or ingestion of an amount that can cause steady state serum concentrations of ≥10 ng/mL;
- Chronic ingestions causing steady-state serum digoxin concentrations >6 ng/mL in adults or 4 ng/mL in children;
- Manifestations of life-threatening toxicity of digoxin overdose such as severe ventricular arrhythmias, progressive bradycardia, and second or third degree heart block not responsive to atropine, serum potassium levels exceeding 5.5 mEq/L in adults or 6 mEq/L in children with rapidly progressive signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For Intravenous Use Only
2.1 Dosage
General Guidelines:
Adjust the dosage of DIGIFAB according to the amount of digoxin to be neutralized.Summary of Dosing Guidelines Clinical Conditions Dosage Acute ingestion of
unknown amounts of
digoxin and toxicity in the
absence of a serum
digitalis concentration or
estimated ingestion amountAdminister 20 vials of DIGIFAB.
Monitor for volume overload in small
(<20 Kg) children.
Start with 10 vials followed by an
additional 10 vials, if needed, to avoid
a febrile reaction.Chronic digoxin toxicity in
the absence of a serum
digitalis concentrationAdminister 6 vials of DIGIFAB in
Adults and Children ≥ 20 Kg.
Administer 1 vial of DIGIFAB in Infants and Children < 20 Kg.Acute ingestion of known
amounts of digoxinDose (in vials) =
Amount of digoxin ingested (in mg)
0.5 mg/vialChronic digoxin toxicity
and known serum digitalis
concentrationDose (in vials) =
(Serum digoxind ng/mL)(weight in kg)
100Failure of the patient to respond to DIGIFAB should alert the physician to the possibility that the clinical problem may not be caused by digitalis toxicity.
DOSAGE CALCULATION
General
Methods for calculating a neutralizing dose of DIGIFAB, based on a known or estimated amount of digoxin or digitoxin in the body, are provided below. When using the dose calculation methods provided, the following guidelines should be considered:
- Inaccurate estimates of the amount of digitalis ingested or absorbed may occur due to non-steady state serum concentrations or due to digitalis assay limitations. Most serum digoxin assay kits are designed to measure concentrations less than 5 ng/mL; therefore, sample dilution is required to accurately measure serum concentrations > 5 ng/mL.
- Dosage calculations are based on a steady state volume of distribution of approximately 5 L/kg for digoxin, which is used to convert serum digoxin concentrations to total body burden of digoxin in milligrams. The volume of distribution is a population average and may vary among individuals. Many patients may require higher doses for complete neutralization and doses should usually be rounded up to the nearest whole vial.
- If toxicity has not adequately reversed after several hours, or appears to recur, re-administration of DIGIFAB, at a dose guided by clinical judgment, may be necessary. If a patient is in need of re-administration of DIGIFAB due to recurrent toxicity, or to a new toxic episode that occurs soon after the first episode, measurement of free (unbound) serum digitalis concentrations should be considered since Fab may still be present in the body.
- Failure of a patient to respond to DIGIFAB treatment may indicate that the clinical problem is not caused by digitalis intoxication. If there is no response to an adequate dose of DIGIFAB, the diagnosis of digitalis toxicity should be questioned.
Calculation for Ingestion of Known Amount:
- Each vial of DIGIFAB (40 mg of purified digoxin-specific Fab) binds approximately 0.5 mg of digoxin.
- The total number of vials required can be calculated by dividing the total body load of digoxin in milligrams (mg) by 0.5 mg per vial (see Formula 1).
- Following an acute ingestion, total body load will be approximately equal to the amount ingested in milligrams for either digoxin capsules or digitoxin.
- In case of digoxin tablet ingestion , the total body load will be approximately equal to the amount ingested (in mg) multiplied by the bioavailability of the tablet preparation, which is 0.8.
Table 1 gives dosage estimates in number of vials for adults and children who have ingested a single large dose of digoxin and for whom the approximate number of tablets or capsules is known. The dose of DIGIFAB (in number of vials) represented in Table 1 can be approximated using the following formula:
Dose = total digitalis body load in mg
(in # of vials) 0.5 mg of digitalis bound/vialTable 1 Approximate Dose of DIGIFAB for Reversal of a Single Large Digoxin Overdose *0.25 mg tablets with 80% bioavailability or 0.2 mg capsules with 100% bioavailability Number of Digoxin Tablets
or Capsules Ingested*Dose of DIGIFAB
# of vials25 10 50 20 75 30 100 40 150 60 200 80 If, after several hours, toxicity is not adequately reversed, or appears to recur, additional administration of DIGIFAB at a dose guided by clinical judgment may be required.
Calculations Based on Steady-State Serum Digoxin Concentrations:
Adults
Table 2 gives dosage estimates in number of vials for adult patients for whom a steady-state serum digoxin concentration is known. The dose of DIGIFAB (in number of vials) represented in Table 2 can be approximated using the following formula:
Formula 2 (see Table 2)
Dose = (Serum digoxin concentration in ng/mL)(weight in kg)
(in # of vials) 100Table 2 Adult Dose Estimate of DIGIFAB (in # of vials) from Steady-State Serum Digoxin Concentration v = vials Patient Weight
(kg)Serum Digoxin Concentration (ng/mL) 1 2 4 8 12 16 20 40 0.5v 1v 2v 3v 5v 7v 8v 60 0.5v 1v 3v 5v 7v 10v 12v 70 1v 2v 3v 6v 9v 11v 14v 80 1v 2v 3v 7v 10v 13v 16v 100 1v 2v 4v 8v 12v 16v 20v Children:
- Table 3 gives dosage estimates in milligrams for infants and small (< 20 Kg) children based on the steady-state serum digoxin concentration.
- The dose of DIGIFAB represented in Table 3 can be estimated by multiplying the dose (in number of vials) calculated from Formula 2 by the amount of DIGIFAB contained in a vial (40 mg/vial) (see Formula 3).
- Administer smaller doses in children < 20 Kg requiring doses < 1mL with a tuberculin syringe after reconstituting 40 mg.
- For very small doses, a reconstituted vial can be diluted with 36 mL of sterile isotonic saline to achieve a concentration of 1 mg/mL.
Formula 3 (see Table 3)
Dose (in mg) = (Dose in # of vials) (40 mg/vial)
Table 3 Infants and Small (< 20 Kg) Children Dose Estimates of DIGIFAB (in mg) from Steady State Serum Digoxin Concentration * dilution of reconstituted vial to 1 mg/mL may be desirable Patient
Weight
(kg)Serum Digoxin Concentration (ng/mL) 1 2 4 8 12 16 20 1 0.4 mg* 1 mg* 1.5 mg* 3 mg* 5 mg 6.5 mg 8 mg 3 1 mg* 2.5 mg* 5 mg 10 mg 14 mg 19 mg 24 mg 5 2 mg* 4 mg 8 mg 16 mg 24 mg 32 mg 40 mg 10 4 mg 8 mg 16 mg 32 mg 48 mg 64 mg 80 mg 20 8 mg 16 mg 32 mg 64 mg 96 mg 128 mg 160 mg Calculation Based on Steady-State Digitoxin Concentrations:
The dose of DIGIFAB for digitoxin toxicity can be approximated by using the following formula (which differs from Formula 2 in the denominator due to a 10-fold decrease in the volume of distribution of digitoxin as compared to digoxin).
Dose = (Serum digitoxin concentration in ng/mL) (weight in kg)
(in # of vials) 1000If in any case, the dose estimated based on ingested amount (Formula 1) differs substantially from that calculated based on the serum digoxin or digitoxin concentration (Formulas 2 and 4), it may be preferable to use the higher dose estimate.
2.2 Preparation and Administration
- Each vial contains 40 mg of digoxin immune Fab protein and is intended for one time use only as it contains no preservatives
- Reconstitute each vial of DIGIFAB with 4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection USP and gently mix to provide a solution containing approximately 10 mg/mL of digoxin immune Fab protein.
- Use the reconstituted product promptly. If not used immediately, store under refrigeration at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) for up to 4 hours. Add the reconstituted product to an appropriate volume of 0.9% sodium chloride for injection.
- Visually inspect reconstituted vials for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if the solution is cloudy, turbid or if it contains particulates.
- Administer DIGIFAB slowly as an intravenous infusion over at least 30 minutes. Stop the infusion if infusion rate-related anaphylactoid-type reactions occur, such as hypotension, wheezing, or urticaria. The infusion can be re-started at a slower rate. Give DIGIFAB by bolus injection, if cardiac arrest is imminent. An increased incidence of infusion-related reactions may be expected with bolus injection.
- For infants and small children who may require very small doses, reconstitute the 40 mg vial as directed and administer undiluted using a tuberculin syringe. For very small doses, a reconstituted vial can be diluted with an additional 36 mL of isotonic saline to achieve a concentration of 1 mg/mL.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 General
Suicidal ingestion may result from more than one drug. Toxic effects of other drugs or poisons should not be overlooked, especially in cases where signs and symptoms of digitalis toxicity are not relieved by administration of DIGIFAB.
Rapid drop in serum potassium concentration may occur after treatment with DIGIFAB. Monitor frequently, especially after the first several hours of DIGIFAB administration (see 5.4 Laboratory Tests).
Patients with poor cardiac function may deteriorate secondary to the withdrawal of the inotropic action of digoxin by DIGIFAB. If needed, provide additional support by using other intravenous inotropes such as dopamine, dobutamine or vasodilators. However, take additional care not to aggravate the digitalis induced rhythm disturbances. Postpone re-digitalization, if possible, until the Fab fragments have been eliminated from the body, which may require several days, and patients with impaired renal function may require a week or longer.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and hypersensitivity reactions are possible. Carefully monitor all patients treated with DIGIFAB for signs and symptoms of an acute allergic reaction (e.g., urticaria, pruritus, erythema, angioedema, bronchospasm with wheezing or cough, stridor, laryngeal edema, hypotension, tachycardia) and treat immediately with appropriate emergency medical care (e.g., oxygen, diphenhydramine, corticosteroids, volume expansion and airway management), if one occurs.
If an anaphylactic reaction occurs during the infusion, terminate DIGIFAB administration at once and administer appropriate treatment. Balance the need for epinephrine against its potential risk in the setting of digitalis toxicity. Patients with known allergies to sheep protein are particularly at risk for an anaphylactic reaction, as are individuals who have previously received intact ovine antibodies or ovine Fab.
Do not administer DIGIFAB to patients with a known history of hypersensitivity to papaya or papain unless the benefits outweigh the risks and appropriate management for anaphylactic reactions is readily available. Prior treatment with digoxin-specific ovine immune Fab carries a theoretical risk of sensitization to ovine serum protein and possible diminution of the efficacy of the drug due to the presence of human antibodies against ovine Fab. To date, there have been no clinical reports of human anti-ovine immunoglobulin antibodies causing a reduction in binding of ovine digoxin immune Fab or neutralization response to ovine digoxin immune Fab.
5.3 Use of DIGIFAB in Renal Failure
The elimination half-life of DIGIFAB in renal failure has not been clearly defined. Monitor patients with severe renal failure who receive DIGIFAB for digitalis toxicity for a prolonged period for possible recurrence of toxicity.
Monitoring of free (unbound) digoxin concentrations after the administration may be appropriate in order to establish recrudescent toxicity in renal failure patients. 5
5.4 Laboratory Tests
DIGIFAB may interfere with digitalis immunoassay measurements. Thus, standard serum digoxin concentration measurements may be clinically misleading until the Fab fragments are eliminated from the body. This may take several days or a week or more in patients with markedly impaired renal function. Therefore, serum samples for digoxin concentration should be obtained before DIGIFAB administration, if at all possible. Such measurements would establish the level of serum digoxin at the time of diagnosis of digitalis intoxication.
At least 6 to 8 hours are required for equilibration of digoxin between serum and tissue, so absorption of the last dose may continue from the intestine. Therefore, serum measurements may be difficult to interpret if samples are drawn soon after the last digitalis dose.
The total serum digoxin concentration may rise precipitously following administration of DIGIFAB, but this will be almost entirely bound to the Fab fragment and therefore not able to react with receptors in the body.
Patients should be closely monitored, including temperature, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, and potassium concentration, during and after administration of DIGIFAB. Digoxin causes a shift of potassium from inside to outside the cell, such that severe intoxication can cause a life-threatening elevation of serum potassium. This may lead to increased urinary excretion of potassium so that a patient may have hyperkalemia but a whole body deficit of potassium. When the toxic effects of digoxin are reversed by DIGIFAB, potassium shifts back into the cell with a resulting decline in serum potassium concentration. This hypokalemia may develop rapidly. For these reasons, serum potassium concentration should be followed closely, especially during the first several hours after DIGIFAB administration. Cautious potassium supplementation should then be given when necessary.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (> 7%) related to DIGIFAB administration are worsening congestive heart failure (13%), hypokalemia (13%) and worsening atrial fibrillation (7%).
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In the clinical trials of DIGIFAB, 6 of 15 patients in the digoxin overdose study had a total of 17 adverse events. Three events occurred in one patient and consisted of the following: pulmonary edema, bilateral pleural effusion and renal failure. The events were determined to be likely due to the loss of digoxin inotropic support in combination with the patient’s underlying medical condition. Of 8 healthy volunteers who received DIGIFAB, two experienced an adverse reaction that was considered to be related to DIGIFAB. The reactions were; one episode of phlebitis of the infusion-site vein and one episode of transient postural hypotension.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with DIGIFAB. It is also not known whether DIGIFAB can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. DIGIFAB should be given to a pregnant woman only if clinically needed.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether DIGIFAB is excreted in human breast milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when DIGIFAB is administered to a nursing woman. DIGIFAB should be given to nursing mothers only if clinically needed.8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety data in pediatric population is limited. The pediatric dosing estimation is based on calculations for adult dosing.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Specific studies in elderly patients have not been conducted. Of the 15 patients given DIGIFAB for digoxin toxicity in one clinical trial, the average age of all patients was 64 years and over half of the patients (8 of the 15) were 65 years of age or older. The oldest patient studied was 86 years old. There is no evidence that the efficacy of DIGIFAB would be altered due to advanced age alone; however, elderly patients have a higher chance of having impaired renal function and therefore should be monitored more closely for recurrent toxicity (See 5.3 Use of DIGIFAB in renal failure).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
DIGIFAB [Digoxin Immune Fab (Ovine)] is a sterile, lyophilized preparation of digoxin-immune ovine Fab (monovalent) immunoglobulin fragments. These fragments are obtained from the blood of healthy sheep immunized with a digoxin derivative, digoxin-dicarboxymethoxylamine (DDMA), a digoxin analogue which contains the functionally essential cyclopentaperhydrophenanthrene: lactone ring moiety coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH).
The final product is prepared by isolating the immunoglobulin fraction of the ovine serum, digesting it with papain and isolating the digoxin-specific Fab fragments by affinity chromatography. These antibody fragments have a molecular weight of approximately 46,000 Da.
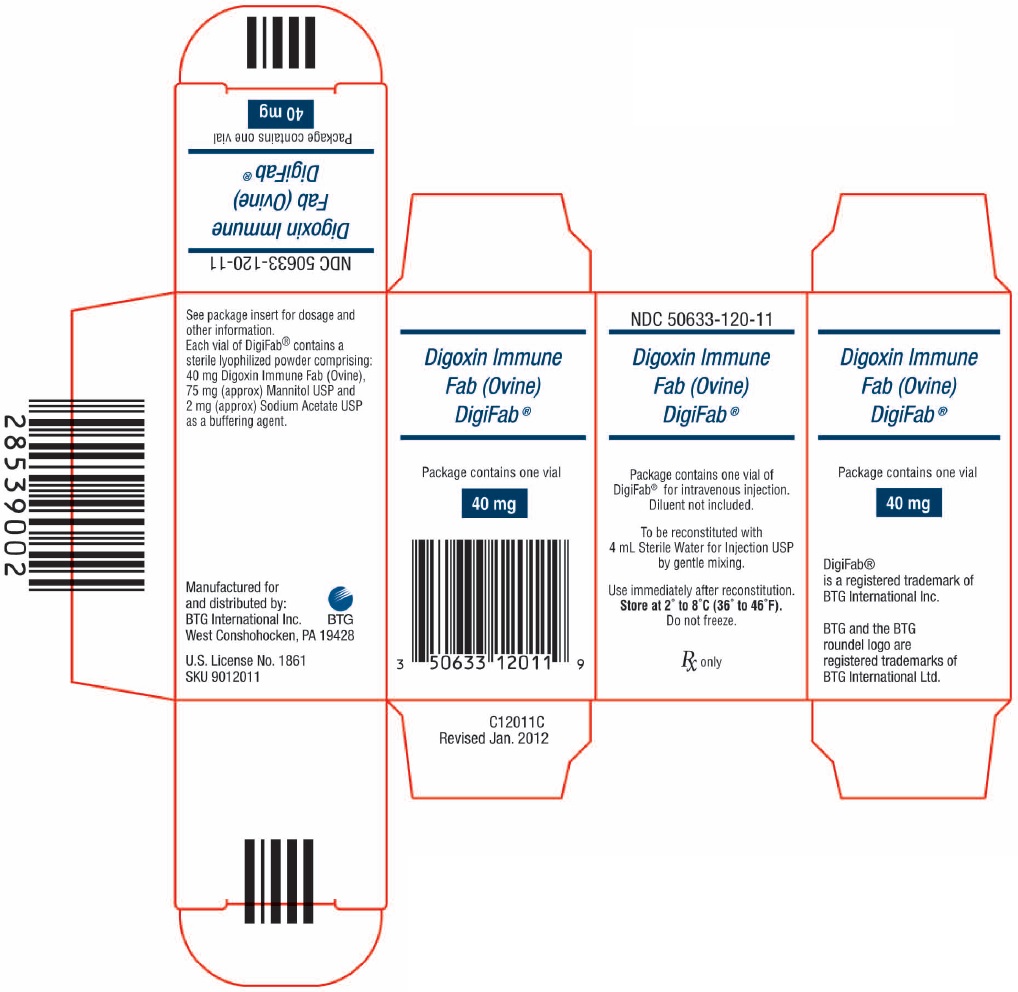
Each vial of DIGIFAB, which will bind approximately 0.5 mg digoxin, contains 40 mg of digoxin immune Fab, 75 mg (approx) of mannitol USP, and 2 mg (approx) sodium acetate USP as a buffering agent.
The product contains no preservatives and is intended for intravenous administration after reconstitution with 4 mL of Sterile Water for Injection USP.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
DIGIFAB has an affinity for digoxin in the range of 109 to 1010 M-1, which is greater than the affinity of digoxin for its sodium pump receptor, the presumed receptor for its therapeutic and toxic effects. When administered to the intoxicated patient, DIGIFAB binds to molecules of digoxin reducing free digoxin levels, which results in a shift in the equilibrium away from binding to the receptors, thereby reducing cardio-toxic effects. Fab-digoxin complexes are then cleared by the kidney and reticuloendothelial system.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of DIGIFAB were assessed in a randomized and controlled study of DIGIFAB and Digibind® (n=8) or Digibind® (n=8). The objective of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study was to compare parameters for DIGIFAB to those for Digibind®. and Digibind®, respectively) indicate considerable penetration from the circulation into the extracellular space and are consistent with previous reports of ovine Fab distribution, as are the elimination half-life values (15 hours and 23 hours for DIGIFAB and Digibind®, respectively).8-12 The elimination half-life of 15-20 hours in patients with normal renal function appears to be increased up to 10 fold in patients with renal impairment, although volume of distribution remains unaffected.12
The primary outcome measure for this study was the serum level of free (unbound) digoxin. The results demonstrated that both products reduced the level of free digoxin in the serum to below the limit of assay quantitation for several hours after Fab administration. Cumulative urinary excretion of digoxin was comparable for both products and exceeded 40% of the administered dose by 24 hours. These results demonstrate that DIGIFAB and Digibind® have equivalent pharmacodynamic effects on the digoxin parameters that are relevant to the treatment of digoxin toxicity.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal carcinogenicity and reproduction studies have not been conducted with DigiFab.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
No toxic effects were observed when DIGIFAB was administered to healthy male Sprague Dawley rats in equimolar doses sufficient to neutralize a 1 mg/kg dose of digoxin. In these studies, the physiologic changes produced by toxic serum concentrations of digoxin were ameliorated rapidly by the administration of DIGIFAB or comparator product Digibind®. Statistically equivalent responses were observed with both DIGIFAB and Digibind® to the following variables: PTQ index, heart rate, mean arterial pressure, ventilation, arterial blood gases, and serum potassium concentrations.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
One prospective multi-center safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetic study in patients presenting with life-threatening digoxin toxicity was conducted in U.S. and Finland.
The objective of the study was to demonstrate safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical response of DIGIFAB in patients. Results were compared to historical data on Digibind ®. Fifteen patients received doses of DIGIFAB based on its theoretical binding capacity for digoxin, and based on the known amount of digoxin ingested or on blood concentrations of digoxin at the time of admission.
Serum free digoxin concentrations fell to undetectable concentrations in all patients following DIGIFAB administration. Ten of the 15 patients studied who had baseline ECG abnormalities improved within 4 hours after the DIGIFAB infusion. The remaining 5 patients who had baseline ECG abnormalities remained unchanged throughout the 24-hour assessment period, and in one case through the 30-day follow up period. Seven out of the 15 patients (47%) studied had complete resolution of digoxin toxicity within 4 hours of DIGIFAB administration, and 14 patients (93%) were classified as having resolved their digoxin toxicity by 20 hours. In this study, where 2/15 patients had serum available for human anti-ovine antibody determination, there was no measurable immune response.
-
15 REFERENCES
- Kojis FG. Serum sickness and anaphylaxis: analysis of cases of 6,211 patients treated with horse serum for various infections. Am J Dis Children 1942; 64:93-143, 313-350.
- Quarre JP, Lecomte J, Lauwers D, Gilbert P, Thiriaux J. Allergy to latex and papain. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1995; 95(4):922.
- Baur X, Chen Z, Rozynek P, Düser D, Raulf-Heimsoth M. Cross-reacting IgE antibodies recognizing latex allergens, including Hev b 1, as well as papain. Allergy 1995; 50(7):604-609.
- Wenger TL. Experience with digoxin immune fab (ovine) in patients with renal impairment. Am J of Emer Med 1991; 9(supp. 1):21-23.
- Valdes R, Jortani SA. Monitoring of unbound digoxin in patients with antidigoxin antigen-binding fragments: a model for the future ? Clin Chem 1998; 44(9):1883-1885.
- Kirkpatrick CHG, Digibind® Study Advisory Panel. Allergic histories and reactions of patients treated with digoxin immune fab (ovine) antibody. Am J of Emer Med 1991; 9(supp. 1):7-10.
- Ward, SB, Sjostrom L, and Ujhelyi MR. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and in vivo binding affinity of DigiTAb versus Digibind.Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 2000; 22:599-607.
- Hickey AR, Wenger TL, Carpenter VP, et al. Digoxin immune fab therapy in the management of digitalis intoxication: safety and efficacy results of an observational surveillance study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991; 17:590-598.
- Antman EM, Wenger TL, Butler VP, Haber E, and Smith TW. Treatment of 150 cases of life threatening digitalis intoxication with digoxin-specific fab antibody fragments. Circulation 1990; 81:1744-1752.
- Wenger TL, Butler VP Jr, Haber E, Smith TW. Treatment of 63 severely digitalis-toxic patients with digoxin-specific antibody fragments. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985; 5 (supp.):118A-123A.
- Schaumann W, Kaufmann B, Neubert P, Smolarz A. Kinetics of the fab fragments of digoxin antibodies and of bound digoxin in patients with severe digoxin intoxication. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1986; 30:527-533.
- Ujhelyi MR, Robert S. Pharmacokinetic aspects of digoxin-specific fab therapy in the management of digitalis toxicity. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995; 28(6):483-493.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
DigiFab is supplied as a carton that contains 1 vial of product (diluent not included).
- NDC: 50633-120-11
- Store at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F).
- Do not freeze.
- Use within 4 hours after reconstitution.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to contact their physician immediately if they experience any signs and symptoms of delayed allergic reactions or serum sickness (e.g., rash, pruritus, urticaria) after hospital discharge.
Manufactured for
and distributed by:BTG International Inc.
West Conshohocken, PA 19428U.S. License No. 1861
DIGIFAB is a registered trademark of BTG International Inc.
BTG and the BTG roundel logo are registered trademarks of BTG International Ltd.P12011E
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 50633-120-11 - 40 mg Carton Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DIGIFAB
ovine digoxin immune fab injection, powder, for solutionProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC: 50633-120 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OVINE DIGOXIN IMMUNE FAB (UNII: YB12NQZ1YN) (DIGOXIN - UNII:73K4184T59) OVINE DIGOXIN IMMUNE FAB 40 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) SODIUM ACETATE (UNII: 4550K0SC9B) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50633-120-11 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC: 50633-120-12 1 in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 6: Drug/Biologic Combination Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA103910 08/31/2001 Labeler - BTG International Inc. (617382395) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cangene bioPhamra Inc. 050783398 manufacture(50633-120) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Protherics UK Limited 536591589 api manufacture(50633-120)
Trademark Results [DigiFab]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 DIGIFAB 86887251 5031805 Live/Registered |
DigiFab Systems, Inc. 2016-01-26 |
 DIGIFAB 85098697 4372871 Live/Registered |
BTG INTERNATIONAL INC. 2010-08-03 |
 DIGIFAB 85071538 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
BTG International Inc. 2010-06-25 |
 DIGIFAB 79403315 not registered Live/Pending |
ÃAGDAS MAKINA ITHALAT IHRACAT 2024-02-01 |
 DIGIFAB 77701397 3704855 Live/Registered |
DigiFab Corporation 2009-03-27 |
 DIGIFAB 76176952 2795341 Live/Registered |
BTG INTERNATIONAL INC. 2000-12-04 |
 DIGIFAB 75512346 2353197 Dead/Cancelled |
DigiFab Corporation 1998-07-02 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.