JAVADIN- clonidine hydrochloride oral solution
JAVADIN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
JAVADIN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use JAVADIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for JAVADIN.
JAVADINTM(clonidine hydrochloride) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1974
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- JAVADIN is a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, indicated for the treatment of hypertension in adult patients to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure has been shown to reduce the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Initial dosage is 0.1 mg orally twice daily with or without food (morning and bedtime) (2.1)
- Titrate in increments of 0.1 mg per day at weekly intervals if necessary until the desired response is achieved. (2.1)
- The therapeutic doses most commonly used have ranged from 0.2 mg to 0.6 mg per day, given in divided doses. (2.1)
- Maximum recommended daily dose is 2.4 mg. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral Solution: 0.02 mg/mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
JAVADIN is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to clonidine (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Bradycardia, Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities, and Symptomatic Hypotension: Clonidine may cause bradycardia, conduction abnormalities, and hypotension. Titrate slowly in patients with syncope, heart block, or vascular disease. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate. Avoid drugs affecting sinus or AV node function. (5.1)
- Rebound Hypertension: Abrupt discontinuation of JAVADIN may cause rebound hypertension, especially with high doses or beta-blocker use. Taper gradually over 2–4 days. Continue administration up to 4 hours before surgery and resume promptly postoperatively; monitor blood pressure closely. (5.2)
- Sedation and Somnolence: Clonidine may cause sedation; caution patients who operate machinery or drive. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most frequent adverse reactions are dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation and sedation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc., at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Sedating Drugs: Clonidine may potentiate the CNS-depressive effects of alcohol, barbiturates or other sedating drugs. (7)
- Tricyclic Antidepressants: May reduce the hypotensive effect of clonidine. (7)
- Neuroleptics: May induce or exacerbate the orthostatic regulation disturbances (e.g., orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, fatigue). (7)
- Drugs Known to Affect Sinus Node Function or AV Nodal Conduction: Caution is warranted in patients receiving clonidine concomitantly with agents known to affect sinus node function or AV nodal conduction (e.g., digitalis, calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers) due to a potential for additive effects such as bradycardia and AV block. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Renal Impairment: Patients with renal impairment may require a lower initial dose and should be closely monitored. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Bradycardia, Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities, and Symptomatic Hypotension
5.2 Rebound Hypertension
5.3 Sedation and Somnolence
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JAVADIN is indicated for the treatment of hypertension in adult patients, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes. There are no controlled trials demonstrating risk reduction with JAVADIN.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
JAVADIN may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. -
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Dosage should be individualized based on response. The recommended initial dosage is 0.1 mg orally twice daily (morning and bedtime).
Dosage can be titrated in increments of 0.1 mg per day at weekly intervals as necessary. Doses should be taken twice a day, with either an equal or higher split dosage being given at bedtime. The therapeutic doses most commonly employed have ranged from 0.2 mg to 0.6 mg per day, given in divided doses. Maximum recommended daily dose is 2.4 mg, but doses as high as this have rarely been employed.2.2 Administration Instructions
A calibrated measuring device, such as an oral dosing syringe or oral dosing cup, is recommended to measure and deliver the prescribed dose accurately. A household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device.
Administer JAVADIN (clonidine hydrochloride) oral solution with or without food. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
JAVADIN may be administered up to 4 hours before surgery and resume as soon as possible post-operatively [see Warning and Precaution (5.2)]. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
JAVADIN is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to clonidine. [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Bradycardia, Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities, and Symptomatic Hypotension
Treatment with clonidine can cause bradycardia, cardiac conduction abnormalities, and symptomatic hypotension [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The sympatholytic action of clonidine may worsen sinus node dysfunction and atrioventricular (AV) block, especially in patients taking other sympatholytic drugs. There have been post-marketing reports of patients with conduction abnormalities and/or taking other sympatholytic drugs who developed severe bradycardia requiring intravenous (IV) atropine, IV isoproterenol, and temporary cardiac pacing while taking clonidine.
Titrate JAVADIN slowly in patients with a history of syncope, cardiac conduction abnormalities, and those with underlying conditions that may be worsened by hypotension and bradycardia; e.g., heart block, bradycardia, cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, or chronic renal failure. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate and adjust dosages accordingly in patients treated concomitantly with antihypertensives or other drugs that can reduce blood pressure or heart rate or increase the risk of syncope Avoid the use of drugs that can affect the sinus node function or AV node conduction [see Drug Interactions (7)].
In patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as symptomatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration, advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated.5.2 Rebound Hypertension
Abrupt discontinuation of JAVADIN can cause rebound hypertension with elevated plasma catecholamines, especially with higher doses or concomitant beta-blocker use. Symptoms of abrupt discontinuation include tachycardia, rapid blood pressure elevation, headache, nervousness, and agitation. Serious cases of hypertensive encephalopathy, stroke, and death have been reported after abrupt clonidine discontinuation. To reduce the risk of rebound hypertension, taper clonidine gradually over 2-4 days. If rebound hypertension occurs, reverse hypertensive crisis with oral clonidine or IV phentolamine. When discontinuing concurrent beta-blocker therapy, withdraw the beta-blocker several days before beginning clonidine taper.
Administration of JAVADIN should be continued up to 4 hours before surgery and resumed as soon as possible thereafter. Blood pressure should be carefully monitored during surgery and additional measures to control blood pressure should be available if required.5.3 Sedation and Somnolence
Clonidine may cause sedation. Patients who engage in potentially hazardous activities, such as operating machinery or driving, should be advised of possible sedative effects of clonidine. Avoid use with other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, as this combination may cause excessive drowsiness or sedation [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Bradycardia, Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities, and Symptomatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Rebound Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Sedation and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Most adverse effects are mild and tend to diminish with continued therapy. The most frequent (which appear to be dose-related) are dry mouth (40%), drowsiness (33%); dizziness (16%); constipation and sedation (10%, respectively).
The following less frequent adverse experiences have also been reported in patients receiving clonidine hydrochloride tablets, but in many cases patients were receiving concomitant medication and a causal relationship has not been established.
Body as a Whole: Fatigue, headache, pallor, malaise, weakness, and withdrawal syndrome.
Cardiovascular: Bradycardia, congestive heart failure, electrocardiographic abnormalities (i.e., sinus node arrest, junctional bradycardia, high degree AV block and arrhythmias), orthostatic symptoms, palpitations, syncope, and tachycardia.
Central Nervous System: Agitation, anxiety, delirium, hallucinations (including visual and auditory), insomnia, mental depression, behavioral changes, paresthesia, sleep disorder, and vivid dreams or nightmares.
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, constipation, nausea, and vomiting.
Hematologic: Thrombocytopenia.
Hepatobiliary: Hepatitis and transaminitis.
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema, hives, pruritus, rash, and urticaria.
Metabolic: Transient elevation of blood glucose or serum creatine phosphokinase, and weight gain.
Musculoskeletal: Leg cramps and muscle or joint pain.
Ophthalmological: Accommodation disorder, blurred vision, burning of the eyes, decreased lacrimation, and dryness of eyes.
Renal and Urinary: Difficulty in micturition, nocturia, and urinary retention.
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Gynecomastia. erectile dysfunction, and loss of libido.
Vascular: Raynaud's phenomenon. -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The interactions of JAVADIN with co-administration of other drugs have not been studied. The drug interaction data provided in this section is based on oral immediate-release clonidine formulations.
Table 1 displays clinically important drug interactions with JAVADIN.
Table 1: Clinically Important Drug Interactions with JAVADIN.
Antihypertensive drugs Clinical Implication
Concomitant use of antihypertensive drugs with clonidine potentiates the hypotensive effects of clonidine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Intervention
Monitor blood pressure and heart rate, and adjust dosage of JAVADIN accordingly in patients treated concomitantly with antihypertensivesCNS depressants
Clinical Implication
Concomitant use of CNS depressants with clonidine potentiates the sedating effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Intervention
Avoid concomitant use of CNS depressants with JAVADIN.Drugs that affect sinus node function or AV node conduction (e.g., digitalis, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers) Clinical Implication
Concomitant use of drugs that affect sinus node function or AV node conduction with clonidine potentiate bradycardia and risk of AV block [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Intervention
Avoid concomitant use of drugs that affect sinus node function or AV node conduction with JAVADIN.
Tricyclic antidepressants Clinical Implication
Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants with clonidine can increase blood pressure and may counteract the hypotensive effects of clonidine. Intervention
Monitor blood pressure and adjust dosage of JAVADIN as needed. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Prolonged experience with clonidine in pregnant women over several decades, based on published literature, including controlled trials, a retrospective cohort study and case reports, have not identified a drug associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal embryofetal studies, increased resorptions were seen in rats and mice administered oral clonidine hydrochloride from implantation through organogenesis at approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of clonidine hydrochloride to pregnant rabbits during the period of embryo/fetal organogenesis at doses of up to 0.08 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the oral maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 2.4 mg/day) produced no developmental effects. In pregnant rats, however, doses as low as 0.015 mg/kg/day (~1/16 the oral MRHD on a mg/kg basis) were associated with increased resorptions in a study in which dams were treated continuously from 2 months prior to mating and throughout gestation. Increased resorptions were not associated with treatment at the same or at higher dose levels when treatment of the dams was restricted to gestation days 6-15. Increases in resorptions were observed in both rats and mice at 0.5 mg/kg/day (2 and 1 times the MRHD in rats and mice, respectively) or higher when the animals were treated on gestation days 1-14; 0.5 mg/kg/day was the lowest dose employed in this study.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on published lactation studies, clonidine hydrochloride is present in human milk at relative infant doses ranging from 4.1 to 8.4% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage. Although in most cases, there were no reported adverse effects in breastfed infants exposed to clonidine, there is one case report of sedation, hypotonia, and apnea in an infant exposed to clonidine through breast milk. If an infant is exposed to clonidine hydrochloride through breastmilk, monitor for symptoms of hypotension and bradycardia, such as sedation, lethargy, tachypnea and poor feeding (see Clinical Considerations). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for JAVADIN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from clonidine or from the underlying maternal condition. Exercise caution when JAVADIN is administered to a nursing woman.
Clinical Considerations
Monitor breastfeeding infants exposed to JAVADIN through breast milk for symptoms of hypotension and/or bradycardia such as sedation, lethargy, tachypnea, and poor feeding.8.6 Renal Impairment
The half-life of clonidine increases in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Patients with renal impairment may start from a lower dose. Since only a minimal amount of clonidine is removed during routine hemodialysis, there is no need to give supplemental JAVADIN following dialysis.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Hypertension may develop early and may be followed by hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, hypothermia, drowsiness, decreased or absent reflexes, weakness, irritability and miosis. The frequency of CNS depression may be higher in pediatric patients than adults. Large overdoses may result in reversible cardiac conduction defects or dysrhythmias, apnea, coma and seizures. Signs and symptoms of overdose generally occur within 30 minutes to two hours after exposure. Dialysis is not likely to significantly enhance the elimination of clonidine.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
JAVADIN (clonidine hydrochloride) oral solution is a central alpha-2 adrenergic agonist hypotensive agent available as a 0.02 mg/mL solution for oral administration.
Clonidine hydrochloride is an imidazoline derivative and exists as a mesomeric compound. The chemical name is 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline hydrochloride. Its molecular formula is C9H9Cl2N3, HCl which corresponds to a molecular weight of 266.5. The following is the structural formula:
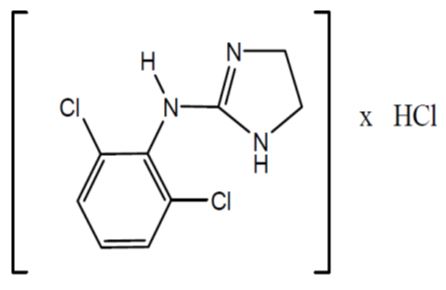
Clonidine hydrochloride USP is a white or almost white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water, and ethanol and slightly soluble in Chloroform.
JAVADIN is a clear colorless oral solution. Each mL contains 0.02 mg of clonidine hydrochloride (equivalent to 0.0173 mg of clonidine). The inactive ingredients are: mixed berry flavor, purified water, sodium chloride, sodium propionate, sucralose. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Clonidine stimulates alpha-adrenoreceptors in the brain. Clonidine is not a central nervous system stimulant. Clonidine is a known antihypertensive agent. By stimulating alpha-adrenoreceptors in the brain stem, clonidine reduces sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system and decreases peripheral resistance, renal vascular resistance, heart rate, and blood pressure.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The patient’s blood pressure declines within 30 to 60 minutes after an oral dose, the maximum decrease occurring within 2 to 4 hours. Renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate remain essentially unchanged. Normal postural reflexes are intact; therefore, orthostatic symptoms are mild and infrequent. The antihypertensive effect is reached at plasma concentrations between about 0.2 and 2.0 ng/mL in patients with normal excretory function. A further rise in the plasma levels will not enhance the antihypertensive effect.
Clonidine hydrochloride in humans have demonstrated a moderate reduction (15% to 20%) of cardiac output in the supine position with no change in the peripheral resistance: at a 45° tilt there is a smaller reduction in cardiac output and a decrease of peripheral resistance. During long term therapy, cardiac output tends to return to control values, while peripheral resistance remains decreased. Slowing of the pulse rate has been observed in most patients given clonidine but the drug does not alter normal hemodynamic response to exercise.
Tolerance to the antihypertensive effect may develop in some patients, necessitating a reevaluation of therapy.
Other studies in patients have provided evidence of a reduction in plasma renin activity and in the excretion of aldosterone and catecholamines. The exact relationship of these pharmacologic actions to the antihypertensive effect of clonidine has not been fully elucidated.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Median time to peak clonidine plasma concentrations (Cmax) occurred at approximately 2.8 hours (range: 1 to 6 hours) following 0.3 mg oral dose of JAVADIN in healthy adult subjects under fasting conditions. The pharmacokinetics of clonidine is dose-proportional in the range of 0.1 to 0.6 mg.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of clonidine on oral administration is 70% to 80%.
Effect of Food
Food had no effect on plasma exposures of clonidine after administration of JAVADIN.
Distribution
Following intravenous administration, clonidine displays biphasic disposition with a distribution half-life of about 20 minutes. Clonidine crosses the placental barrier.
Elimination
Elimination half-life ranges from 12 to 16 hours.
Metabolism
About 50% of the absorbed dose is metabolized in the liver.
Excretion
Following oral administration, about 40% to 60% of the absorbed dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug in 24 hours.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
The half-life increases up to 41 hours in patients with severe impairment of renal function.
Clonidine is minimally removed during hemodialysis. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Chronic dietary administration of clonidine was not carcinogenic to rats (132 weeks) or mice (78 weeks) dosed, respectively, at up to 10 or 15 times the maximum recommended daily human dose as mg/kg (2 or 1 times the MRDHD on a mg/m2 basis).
Mutagenicity
There was no evidence of genotoxicity in the Ames test for mutagenicity or mouse micronucleus test for clastogenicity.
Impairment of Fertility
In a reproduction study fertility of female rats appeared to be adversely affected at dose levels of 0.5 and 2.0 mg/kg/day (2 and 8 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). Lower doses have not been adequately evaluated and a no adverse effect level could not be established. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
JAVADIN (clonidine hydrochloride) is a clear, colorless solution supplied in a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with child-resistant closure. The 0.02 mg/mL oral solution is available in bottles of 250 mL (NDC: 24338-115-01).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Sedation and Somnolence
Advise patients not to interrupt JAVADIN therapy without consulting their physician. They should be cautious of potential sedative effects, dizziness, or accommodation issues and avoid activities such as driving or operating machinery. Additionally, advise patients that the sedative effects may be increased by the use of alcohol, barbiturates, or other sedating drugs. [see Drug Interactions (7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Rebound Hypertension
Advise patients not to discontinue Clonidine therapy without consulting their physician, as sudden cessation can cause symptoms like tachycardia, rapid blood pressure elevation, headache, nervousness and agitation. The risk is higher with higher doses or ongoing beta-blocker use. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Bradycardia, cardiac conduction abnormalities, and symptomatic hypotension
Advise patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as symptomatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration, to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated.
Administration Information
Instruct patients or caregivers to use an oral dosing syringe or oral dosing cup to correctly measure the prescribed amount of medication. Inform patients that oral dosing syringes may be obtained from their pharmacy.
Manufactured for:
Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Woburn, MA 01801
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 24338-115-01
JAVADINTM (clonidine HCl) Oral Solution - Carton Label
0.02 mg/mL

JAVADINTM (clonidine HCl) Oral Solution - Container Label
0.02 mg/mL

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
JAVADIN
clonidine hydrochloride oral solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 24338-115 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: W76I6XXF06) (CLONIDINE - UNII:MN3L5RMN02) CLONIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE 20 ug in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) SODIUM PROPIONATE (UNII: DK6Y9P42IN) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 24338-115-01 1 in 1 CARTON 10/23/2025 1 250 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA220256 10/23/2025 Labeler - Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (117505635)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.