CUPRIC CHLORIDE injection, solution
CUPRIC CHLORIDE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
CUPRIC CHLORIDE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Cupric chloride injection USP, 0.4 mg/mL is a sterile, clear, colorless to light blue color, nonpyrogenic solution intended for use as an additive to intravenous solutions for total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Each mL of solution contains 1.07 mg cupric chloride dihydrate; 9 mg sodium chloride and water for injection.
The solution contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer. The pH is 2.0 (1.5 to 2.5); product may contain hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The osmolarity is 0.327 mOsmol/mL (calc.).
Cupric chloride, USP is chemically designated cupric chloride, dihydrate. Its molecular weight is 170.48 g/mol.
The molecular formula is CuCl2 2H2O and the structural formula is:
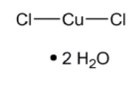
Cupric chloride, USP is a blue to blue-green crystalline compound freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol and slightly soluble in ether.
Sodium chloride, USP is chemically designated NaCl, a white crystalline compound freely soluble in water.
The semi-rigid vial is fabricated from a specially formulated polyolefin. It is a copolymer of ethylene and propylene. The small amount of water vapor that can pass through the plastic container wall will not significantly alter the drug concentration.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Copper is an essential nutrient which serves as a cofactor for serum ceruloplasmin, an oxidase necessary for proper formation of the iron carrier protein, transferrin. Copper also helps maintain normal rates of red and white blood cell formation.
Providing copper during TPN helps prevent development of the following deficiency symptoms: Leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, depressed ceruloplasmin levels, impaired transferrin formation, secondary iron deficiency and osteoporosis.
Normal serum copper values range from 80 mcg/dl to 163 mcg/dl (mean, approximately 110 mcg/dl). The serum copper level at which deficiency symptoms appear is not precisely defined. In the plasma, about 7% of copper is bound to albumin and amino acids. In the liver, about 93% of copper is bound to ceruloplasmin and released to the serum. The daily turnover of copper through ceruloplasmin is approximately 0.5 mg. Copper is primarily excreted through the bile and into the gastrointestinal tract where it is not reabsorbed. Copper is also eliminated through the kidneys.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cupric chloride injection is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to copper (see WARNINGS: Hypersensitivity Reactions).
-
WARNINGS
Hepatic Accumulation
Copper is primarily eliminated in the bile and excretion is decreased in patients with cholestasis and/or cirrhosis. Hepatic accumulation of copper has been reported in autopsies of patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition containing copper at dosages higher than recommended.
Administration of copper to patients with cholestasis and/or cirrhosis may cause hepatic accumulation of copper. Administration of copper to patients with Wilson disease, an inborn error of copper metabolism with a defect in hepatocellular copper transport, may cause both increased hepatic accumulation of copper and aggravation of the underlying hepatocellular degeneration.
For patients with cholestasis, biliary dysfunction, or cirrhosis, monitor hepatic and biliary function during long-term administration of cupric chloride injection. If a patient develops signs or symptoms of hepatobiliary disease during the use of cupric chloride injection, obtain serum concentrations of copper and ceruloplasmin and adjust the dose as indicated (see PRECAUTIONS: Hepatic Impairment).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Post-market safety reporting has identified copper hypersensitivity in women receiving copper-containing intrauterine devices, providing evidence that patients may experience hypersensitivity reactions when exposed to this metal. If hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., pruritis, angioedema, dyspnea, rash, urticaria) occur in patients receiving Cupric Chloride Injection in parenteral nutrition, discontinue the product and initiate appropriate medical treatment (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Aluminum Toxicity
This product contains aluminum that may be toxic. Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because their kidneys are immature and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which contain aluminum.
Research indicates that patients with impaired kidney function, including premature neonates, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Laboratory Tests
Twice monthly serum assays for copper and/or ceruloplasmin are suggested for monitoring copper concentrations in long-term TPN patients. As ceruloplasmin is a cuproenzyme, ceruloplasmin assays may be depressed secondary to copper deficiency.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of cupric chloride injection have not been performed, nor have studies been done to assess mutagenesis or impairment of fertility.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when cupric chloride injection, 0.4 mg/mL is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of cupric chloride injection have been established in pediatric patients receiving parenteral nutrition (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with cupric chloride. It is also not known whether cupric chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Cupric chloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly indicated.
Geriatric Use
An evaluation of current literature revealed no clinical experience identifying differences in response between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Hepatic Impairment
Copper is primarily excreted in the bile. Excretion is decreased in patients with cholestasis and/or cirrhosis (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Hepatic accumulation of copper has been reported with long-term administration of parenteral nutrition at dosages higher than recommended (see WARNINGS: Hepatic Accumulation). For patients with cholestasis or cirrhosis, monitor hepatic and biliary function during long-term administration of cupric chloride injection. If a patient develops signs or symptoms of hepatobiliary disease during use of cupric chloride injection, obtain serum concentrations of copper and ceruloplasmin.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
-
OVERDOSAGE
Acute copper toxicity has been reported in patients with oral, intravenous, or subcutaneous administration. Clinical manifestations included metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, neurological signs, such as encephalopathy and multi-organ failure involving kidney, liver, blood and cardiovascular systems, which may be fatal. Chelating agents, such as D-penicillamine, can be used for treatment of acute toxicity. Long-term administration of parenteral copper above the recommended dosage may result in significant accumulation of copper in the liver, brain and other tissues with possible organ damage (see WARNINGS: Hepatic Accumulation).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Cupric chloride injection contains 0.4 mg of copper/mL and is administered intravenously only after dilution. The additive should be diluted in a volume of fluid not less than 100 mL.
- For the adult receiving TPN, the suggested additive dosage of copper is 0.3 mg/day to 0.5 mg/day.
- For pediatric patients, the suggested additive dosage of copper is 20 mcg/kg/day (0.05 mL/kg/day) up to a maximum of 500 mcg/day.
- This product is not appropriate for patients weighing less than 4 kg due to the inability to measure the appropriate amount of the product.
- Do not administer cupric chloride injection intramuscularly because the acidic pH of the solution may cause considerable tissue irritation.
Cupric chloride injection should only be used in conjunction with a pharmacy directed admixture program using aseptic technique in a laminar flow environment; it should be used promptly and in a single operation without any repeated penetrations. The solution contains no preservatives; discard the unused portion immediately after the admixture procedure is completed.
Cupric chloride injection should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use unless the solution is clear and the seal is intact.
Cupric ion may degrade ascorbic acid in TPN solutions. In order to avoid this loss of ascorbate, multivitamin additives should be added to TPN solutions immediately prior to infusion. Alternatively, the multivitamin additive may be added to one container of TPN solution, followed by copper in a subsequent container.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Cupric Chloride Injection USP, 0.4 mg/mL is available as sterile, clear, colorless to light blue color solution filled in 10 mL polypropylene vial with gray rubber stopper and orange flip-off seal.
It is supplied as follows:
4 mg/10 mL (0.4 mg/mL)
1 Single-Dose Vial: NDC: 80830-2301-1
25 Vials in 1 Carton: NDC: 80830-2301-5
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad 382110, INDIA
Distributed by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 10-2025-03
-
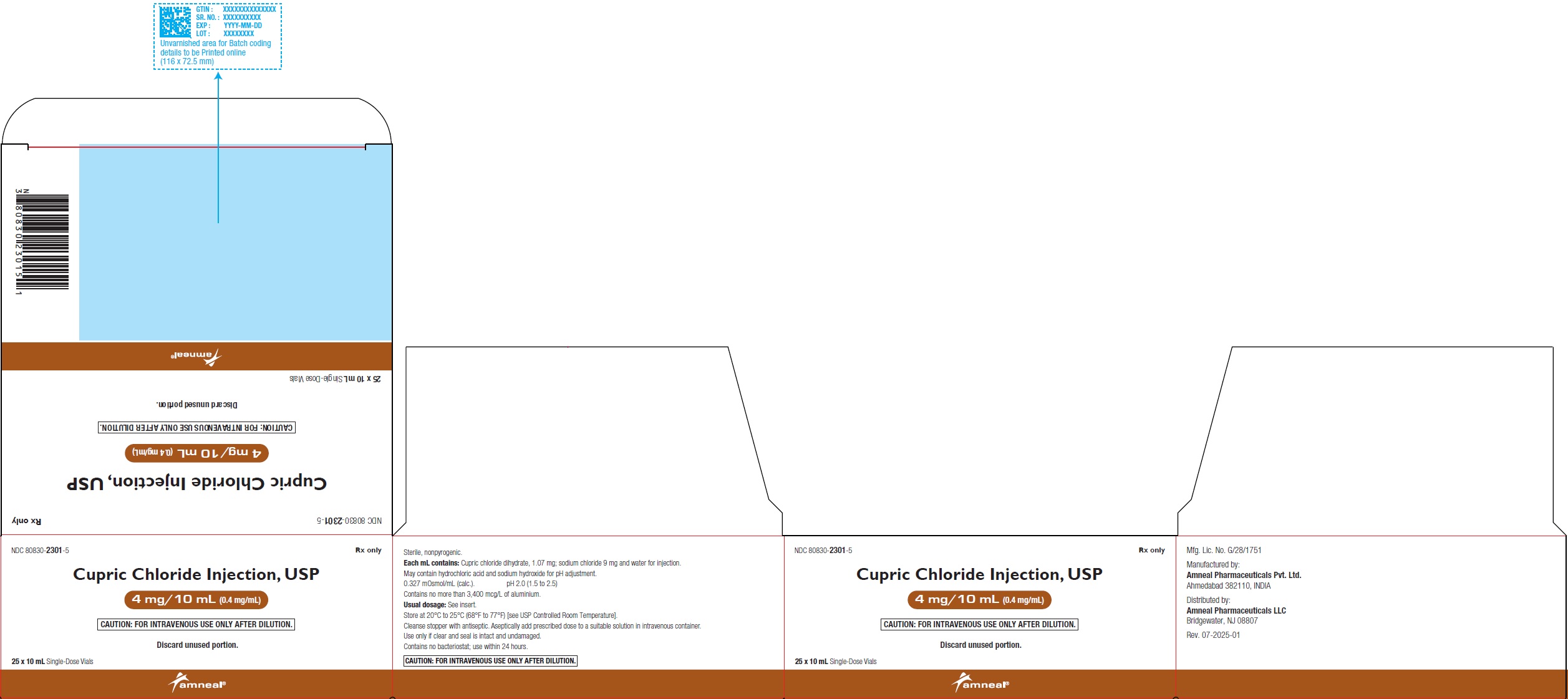
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 80830-2301-1
Cupric Chloride Injection USP, 4 mg/10 mL (0.4 mg/mL)
Vial label
Rx only
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC

NDC: 80830-2301-5
Cupric Chloride Injection USP, 4 mg/10 mL (0.4 mg/mL)
Carton label
Rx only
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CUPRIC CHLORIDE
cupric chloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 80830-2301 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CUPRIC CHLORIDE (UNII: S2QG84156O) (CUPRIC CATION - UNII:8CBV67279L) CUPRIC CATION 0.4 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 9 mg in 1 mL HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 80830-2301-5 25 in 1 CARTON 01/29/2026 1 NDC: 80830-2301-1 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA217287 01/29/2026 Labeler - Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited (675474666) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Amneal Pharmaceuticals Private Limited 675474666 analysis(80830-2301) , label(80830-2301) , manufacture(80830-2301) , pack(80830-2301) , sterilize(80830-2301)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.