MELOXIVET- meloxicam injection, solution
Meloxivet by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Meloxivet by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dechra Veterinary Products. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: Repeated use of meloxicam in cats has been associated with acute renal failure and death. Do not administer additional injectable or oral meloxicam to cats. See Contraindications, Warnings, and Precautions for detailed information.
-
DESCRIPTION
Description:
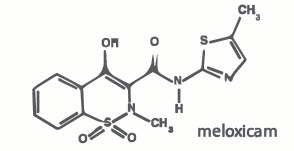
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class. Each mL of this sterile product for injection contains meloxicam 5.0 mg, alcohol 15%, glycofurol 10%, poloxamer 188 5%, sodium chloride 0.6%, glycine 0.5% and meglumine 0.3%, in water for injection, pH adjusted with sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Dosage and Administration:
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risk of Meloxivet and other treatment options before deciding to use Meloxivet. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual response.
Dogs: Meloxivet Injection should be administered initially as a single dose at 0.09 mg/lb (0.2 mg/kg) body weight intravenously (IV) or subcutaneously (SQ), followed, after 24 hours, by meloxicam oral suspension at the daily dose of 0.045 mg/lb (0.1 mg/kg) body weight, either mixed with food or placed directly in the mouth.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Warnings:
Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans. For IV or SQ injectable use in dogs. All dogs should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before administering any NSAID. Appropriate laboratory testing to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data is recommended prior to, and periodically during use of any NSAID in dogs.
Owner should be advised to observe their dogs for signs of potential drug toxicity.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Precautions:
The safe use of Meloxivet Injection in dogs younger than 6 months of age, dogs used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating bitches has not been evaluated. Meloxicam is not recommended for use in dogs with bleeding disorders, as safety has not been established in dogs with these disorders. Safety has not been established for intramuscular (IM) administration in dogs. When administering Meloxivet Injection, use a syringe of appropriate size to ensure precise dosing. As a class, cyclo-oxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal and hepatic toxicity. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse events varies with the individual patient. Dogs that have experienced adverse reactions from one NSAID may experience adverse reactions from another NSAID. Patients at greatest risk for renal toxicity are those that are dehydrated, on concomitant diuretic therapy, or those with existing renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully approached. NSAIDs may inhibit the prostaglandins that maintain normal homeostatic function. Such anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or preexisting disease that has not been previously diagnosed.
Since NSAIDs possess the potential to induce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/or perforations, concomitant use with other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, should be avoided. If additional pain medication is needed after the administration of the total daily dose of meloxicam oral suspension, a non-NSAID or noncorticosteroid class of analgesia should be considered. The use of another NSAID is not recommended. Consider appropriate washout times when switching from corticosteroid use or from one NSAID to another in dogs. The use of concomitantly protein-bound drugs with Meloxivet Injection has not been studied in dogs. Commonly used protein-bound drugs include cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit metabolism of Meloxivet Injection has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy. The effect of cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the potential for thromboembolic occurrence or a hypercoagulable state has not been studied.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reactions:
Dogs: A field study involving 224 dogs was conducted. Based on the results of this study, GI abnormalities (vomiting, soft stools, diarrhea, and inappetence) were the most common adverse reactions associated with the administration of meloxicam. The following table lists adverse reactions and the numbers of dogs that experienced them during the study. Dogs may have experienced more than one episode of the adverse reaction during the study.
Adverse Reactions Observed During Field Study Clinical Observation Meloxicam (n = 109) Placebo (n = 115) Vomiting 31 15 Diarrhea/Soft Stool 15 11 Inappetence 3 0 Bloody Stool 1 0 In foreign suspected adverse drug reaction (SADR) reporting, adverse reactions related to meloxicam administration included: auto-immune hemolytic anemia (1 dog), thrombocytopenia (1 dog), polyarthritis (1 dog), nursing puppy lethargy (1 dog), and pyoderma (1 dog).
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Post-Approval Experience (Rev. 2009):
The following adverse reactions are based on post-approval adverse drug event reporting. The categories are listed in decreasing order of frequency by body system:
Gastrointestinal: vomiting, diarrhea, melena, gastrointestinal ulceration
Urinary: azotemia, elevated creatinine, renal failure
Neurological/Behavioral: lethargy, depression
Hepatic: elevated liver enzymes
Dermatologic: pruritusDeath has been reported as an outcome of the adverse events listed above. Acute renal failure and death have been associated with the use of meloxicam in cats.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
CONTACT INFORMATION:
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Dechra Veterinary Products at (866) 933-2472.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
-
INFORMATION FOR OWNERS/CAREGIVERS
Information for Dog Owners:
Meloxicam, like other NSAIDs, is not free from adverse reactions. Owners should be advised of the potential for adverse reactions and be informed of the clinical signs associated with NSAID intolerance. Adverse reactions may include vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, decreased appetite and behavioral changes. Dog owners should be advised when their pet has received a meloxicam injection. Dog owners should contact their veterinarian immediately if possible adverse reactions are observed, and dog owners should be advised to discontinue meloxicam therapy.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Clinical Pharmacology:
Meloxicam has nearly 100% bioavailability when administered orally or after subcutaneous injection in dogs. The terminal elimination half-life after a single dose is estimated to be approximately 24 hrs (+/- 30%) in dogs regardless of route of administration. Drug bioavailability, volume of distribution, and total systemic clearance remain constant up to 5 times the recommended dose for use in dogs. However, there is some evidence of enhanced drug accumulation and terminal elimination half-life prolongation when dogs are dosed for 45 days or longer.
Peak drug concentrations of 0.734 mcg/mL can be expected to occur within 2.5 hours following a 0.2 mg/kg subcutaneous injection in dogs. Based upon intravenous administration in Beagle dogs, the meloxicam volume of distribution in dogs (Vdλ) is approximately 0.32 L/kg and the total systemic clearance is 0.01 L/hr/kg. The drug is 97% bound to canine plasma proteins.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Effectiveness:
Dogs: The effectiveness of meloxicam injection was demonstrated in a field study involving a total of 224 dogs representing various breeds, all diagnosed with osteoarthritis. This placebo-controlled, masked study was conducted for 14 days. Dogs received a subcutaneous injection of 0.2 mg/kg meloxicam injection on day 1. The dogs were maintained on 0.1 mg/kg oral meloxicam from days 2 through 14. Variables evaluated by veterinarians included lameness, weight-bearing, pain on palpation, and overall improvement. Variables assessed by owners included mobility, ability to rise, limping, and overall improvement. In this field study, dogs showed clinical improvement with statistical significance after 14 days of meloxicam treatment for all variables.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Animal Safety:
Dogs: 3 Day Target Animal Safety Study - In a three day safety study, meloxicam injection was administered intravenously to Beagle dogs at 1, 3, and 5 times the recommended dose (0.2, 0.6 and 1.0 mg/kg) for three consecutive days. Vomiting occurred in 1 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. Fecal occult blood was detected in 3 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. No clinically significant hematologic changes were seen, but serum chemistry changes were observed. Serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was significantly increased in one 1× dog and two of the 5× dogs. One dog in the 5× group had a steadily increasing GGT over 4 days, although the values remained within the reference range. Decreases in total protein and albumin occurred in 2 of 6 dogs in the 3× group and 3 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. Increases in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) occurred in 3 of 6 dogs in the 1× group, 2 of 6 dogs in the 3× group and 2 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. Increased creatinine occurred in 2 dogs in the 5× group. Increased urine protein excretion was noted in 2 of 6 dogs in the control group, 2 of 6 dogs in the 1× group, 2 of 6 dogs in the 3× group, and 5 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. Two dogs in the 5× group developed acute renal failure by Day 4. Bicarbonate levels were at or above normal levels in 1 of the 3× dogs and 2 of the 5× dogs.
Histological examination revealed gastrointestinal lesions ranging from superficial mucosal hemorrhages and congestion to erosions. Mesenteric lymphadenopathy was identified in 2 of 6 dogs in the 1× group, 4 of 6 dogs in the 3× group, and 5 of 6 dogs in the 5× group. Renal changes ranged from dilated medullary and cortical tubules and inflammation of the interstitium, to necrosis of the tip of the papilla in 2 of 6 dogs in the 1× group, 2 of 6 dogs in the 3× group, and 4 of 6 dogs in the 5× group.
Injection Site Tolerance - Meloxicam injection was administered once subcutaneously to Beagle dogs at the recommended dose of 0.2 mg/kg and was well-tolerated by the dogs. Pain upon injection was observed in one of eight dogs treated with meloxicam. No pain or inflammation was observed post-injection. Long term use of meloxicam injection in dogs has not been evaluated.
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: Repeated use of meloxicam in cats has been associated with acute renal failure and death. Do not administer additional injectable or oral meloxicam to cats. See Contraindications, Warnings, and Precautions for detailed information.
-
DESCRIPTION
Description:
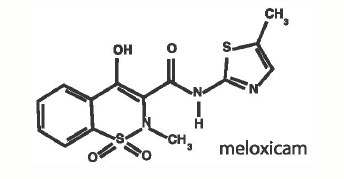
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class. Each mL of this sterile product for injection contains meloxicam 5.0 mg, alcohol 15%, glycofurol 10%, poloxamer 188 5%, sodium chloride 0.6%, glycine 0.5% and meglumine 0.3%, in water for injection, pH adjusted with sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Dosage and Administration:
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risk of Meloxivet and other treatment options before deciding to use Meloxivet. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual response.
Cats: Administer a single, one-time subcutaneous dose of Meloxivet Injection to cats at a dose of 0.14 mg/lb (0.3 mg/kg) body weight. Use of additional meloxicam or other NSAIDs is contraindicated. (See Contraindications). To ensure accuracy of dosing, the use of a 1 mL graduated syringe is recommended.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindications:
Cats with known hypersensitivity to meloxicam should not receive Meloxivet Injection. Additional doses of meloxicam or other NSAIDs in cats are contraindicated, as no safe dosage for repeated NSAID administration has been established (See Animal Safety). Do not use meloxicam in cats with pre-existing renal dysfunction.
-
WARNINGS
Warnings:
Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans. For subcutaneous (SQ) injectable use in cats. Do not use IV in cats.
Do not administer a second dose of meloxicam.
Do not follow the single, one-time dose of meloxicam with any other NSAID.
Do not administer meloxicam oral suspension following the single, one-time injectable dose of meloxicam.When administering any NSAID, appropriate laboratory testing to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data is recommended prior to use in dogs and cats. All cats should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before administering meloxicam. Do not repeat the single, one-time dose of meloxicam in cats.
Owner should be advised to observe their cats for signs of potential drug toxicity.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Precautions:
The safe use of Meloxivet Injection in cats younger than 4 months of age, cats used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating queens has not been evaluated.
Meloxicam is not recommended for use in cats with bleeding disorders, as safety has not been established in cats with these disorders. Safety has not been established for intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) use in cats. When administering Meloxivet Injection, use a syringe of appropriate size to ensure precise dosing.
As a class, cyclo-oxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal, and hepatic toxicity. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse events varies with the individual patient. Cats that have experienced adverse reactions from one NSAID may experience adverse reactions from another NSAID. NSAIDs may inhibit the prostaglandins that maintain normal homeostatic function. Such anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or pre- existing disease that has not been previously diagnosed.
Patients at greatest risk for adverse events are those that are dehydrated, on concomitant diuretic therapy, or those with existing renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully approached and monitored. Anesthetic drugs may affect renal perfusion; approach concomitant use of anesthetics and NSAIDs cautiously. Appropriate monitoring procedures should be employed during all surgical procedures. The use of perioperative parenteral fluids is recommended to decrease potential renal complications when using NSAIDs. If additional pain medication is needed after the single one-time dose of meloxicam, a non-NSAID class of analgesic may be necessary.
In one study1, one cat in each NSAID treatment group had increased intraoperative hemorrhage.
Since NSAIDs possess the potential to induce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/or gastrointestinal perforation, concomitant use of meloxicam with other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, should be avoided.
Consider appropriate washout times when switching from corticosteroid use to meloxicam in cats. As a single use product in cats, meloxicam should not be followed by additional NSAIDs or corticosteroids.
The use of concomitantly protein-bound drugs with Meloxivet Injection has not been studied in cats. Commonly used protein-bound drugs include cardiac, anticonvulsant and behavioral medications. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit metabolism of Meloxivet Injection has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
The effect of cyclo-oxygenase inhibition and the potential for thromboembolic occurrence or a hypercoagulable state has not been studied.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reactions:
Cats: A field study involving 138 cats was conducted. Of the 72 cats receiving meloxicam injection, six cats (8.3%) experienced post-treatment elevated serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. The pre-treatment values were in the normal range. Of the 66 cats in the butorphanol treatment group, no cats experienced post-treatment elevated serum blood urea nitrogen levels. Nine cats (12.5%) receiving meloxicam Injection had post-treatment anemia. Pre-treatment, these cats all had hematocrit and hemoglobin values in the normal range. Four cats (6.1%) in the butorphanol treatment group had post-treatment anemia. All but one cat, who had a mild anemia pre-treatment (hematocrit=21% and hemoglobin=7.0 g/dL) had normal pre-treatment values. Twenty-four hours after the injection with meloxicam injection, one cat experienced pain upon palpation of the injection site.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Foreign Experience:
Repeated use in cats has been associated with acute renal failure and death. In studies used for the foreign approval of meloxicam injection in cats, lethargy, vomiting, inappetence, and transient pain immediately after injection were noted. Diarrhea and fecal occult blood have also been reported.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Post-Approval Experience (Rev. 2009):
The following adverse reactions are based on post-approval adverse drug event reporting. The categories are listed in decreasing order of frequency by body system:
Urinary: azotemia, elevated creatinine, elevated phosphorus, renal failure
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea
Neurologic/Behavioral: lethargy, depression
Hematologic: anemiaDeath has been reported as an outcome of the adverse events listed above. Acute renal failure and death have been associated with the use of meloxicam in cats.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
CONTACT INFORMATION:
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Dechra Veterinary Products at (866) 933-2472.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
-
INFORMATION FOR OWNERS/CAREGIVERS
Information For Cat Owners:
Meloxicam, like other NSAIDs, is not free from adverse reactions. Owners should be advised of the potential for adverse reactions and be informed of the clinical signs associated with NSAID intolerance. Adverse reactions may include vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, decreased appetite and behavioral changes.
Cat owners should be advised when their pet has received a meloxicam injection. Cat owners should contact their veterinarian immediately if possible adverse reactions are observed.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Clinical Pharmacology:
Meloxicam has nearly 100% bioavailability after subcutaneous injection in cats. The terminal elimination half life after a single dose is estimated to be approximately 15 hrs (+/-10%) in cats. Peak drug concentrations of 1.1 mcg/mL can be expected to occur within 1.5 hours following a 0.3 mg/kg subcutaneous injection in cats. The volume of distribution (Vdλ) in cats is approximately 0.27 L/kg, with an estimated total systemic clearance of 0.013 L/hr/kg. The drug is 97% bound to feline plasma proteins.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Effectiveness:
Cats: The effectiveness of meloxicam injection was demonstrated in a masked field study involving a total of 138 cats representing various breeds. This study used butorphanol as an active control. Cats received either a single subcutaneous injection of 0.3 mg/kg meloxicam injection or 0.4 mg/kg butorphanol prior to onychectomy, either alone or in conjunction with surgical neutering. All cats were premedicated with acepromazine, induced with propofol and maintained on isoflurane. Pain assessment variables evaluated by veterinarians included additional pain intervention therapy, gait/lameness score, analgesia score, sedation score, general impression score, recovery score, and visual analog scale score. Additionally, a cumulative pain score, which was the summation of the analgesia, sedation, heart rate and respiratory rate scores was evaluated. A palpometer was used to quantify the pain threshold.
A substantial number of cats required additional intervention in the 0-24 hour postsurgical period, with the majority of these interventions taking place within the first hour. Therefore, the percentage of cats in each group that received one or more interventions was designated as the primary assessment variable. Approximately half of the cats in each group received a pain intervention as a result of the first (time 0) post-surgical evaluation, i.e., extubation. At this point, the need to provide a pain intervention was not statistically significant between the two groups (p=0.7215). However, the median number of interventions was one per cat in the meloxicam group and two per cat in the butorphanol group and this difference was statistically significant (p=0.0021). The statistical evaluation supports the conclusion that the meloxicam test article is non-inferior to the butorphanol active control. Forty-eight of the 72 cats in the meloxicam group received one or more interventions (66.7%), and 47 of 66 cats in the butorphanol group received one or more interventions (71.2%). The number of interventions administered to the meloxicam group was less than the butorphanol group at 1, 3, 5, 8, 12, and 24 hours post-surgery.
Cats receiving meloxicam injection showed improvement in the pain assessment variables.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Animal Safety:
Cats: 3 Day Target Animal Safety Study - In a three day safety study, subcutaneous meloxicam injection administration to healthy cats at up to 1.5 mg/kg (5× the recommended dose) resulted in vomiting in three cats (1 of 6 control cats and 2 of 6 cats in 5×) and loose stools in four cats (2 of 6 control cats and 2 of 6 cats in 5×). Fecal occult blood was detected in ten of the twenty four cats, including two cats in the control group. This was not a dose-related event.
Clinically significant hematologic changes seen included increased PT and APTT in two cats (1 of 6 control cats and 1 of 6 cats in 5×), and elevated white blood cell counts in cats having renal or GI tract lesions. Serum chemistry changes observed included decreased total protein in four of 24 cats (1 of 6 cats in 1×, 2 of 6 cats in 3× and 1 of 6 cats in 5×), concomitant increases in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine values in 2 of 6 cats in 5×.
Histological examination revealed gastrointestinal lesions ranging from inflammatory cell infiltration of the mucosa of the GI tract to erosions. Mesenteric lymphadenopathy was identified in 1 of 6 cats in 1×. Renal changes ranged from dilated medullary (2 of 6 cats in 1×, 1 of 6 cats in 3×, and 1 of 6 cats in 5×) and cortical (3 of 6 cats in 1×, 1 of 6 cats in 3×, and 3 of 6 cats in 5×) tubules and inflammation (2 of 6 cats in 1×, 2 of 6 cats in 3×, and 2 of 6 cats in 5×) or fibrosis (2 of 6 cats in 3× and 2 of 6 cats in 5×) of the interstitium to necrosis of the tip of the papilla (5 of 6 cats in 5×).
Subsequent oral dosing - In a nine day study with three treatment groups, meloxicam injection was given as a single subcutaneous injection using doses of 0 mg/kg (saline injection), 0.3 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg on Day 0. Meloxicam oral suspension, 1.5 mg/mL or saline was then administered orally once-daily at the same respective dose (0.3 or 0.6 mg/kg) for eight consecutive days. Clinical adverse reactions included vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and decreased food consumption in the treated groups, and one day of diarrhea in one control cat. The gross necropsy report includes observation of reddened GI mucosa in 3 of 4 cats in the 0.3 mg/kg group and 1 of 4 cats in the 0.6 mg/kg group. All saline-treated cats were normal. By Day 9, one cat in both the 0.3 mg/kg group and the 0.6 mg/kg group died and another cat in the 0.3 mg/kg group was moribund. The cause of death for these cats could not be determined, although the pathologist reported pyloric/duodenal ulceration in the cats in 0.6 mg/kg group. The safety studies demonstrate a narrow margin of safety.
Injection Site Tolerance - Histopathology of the injection sites revealed hemorrhage and inflammation, myofiber atrophy, panniculitis, fibrin deposition, and fibroblast proliferation. These findings were present in cats in all groups, with the 3× cats having the most present. No safe repeat dose has been established in cats.
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- HOW SUPPLIED
- REFERENCES
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Carton
NDC: 17033-051-20
Meloxivet™
(meloxicam)5 mg/mL Solution for Injection
Caution: Federal law restricts this
drug to use by or on the order of a
licensed veterinarian.Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
for use in dogs and cats onlyDechra
Net Contents: 20 mL
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200 - 727

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MELOXIVET
meloxicam injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 17033-051 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength meloxicam (UNII: VG2QF83CGL) (MELOXICAM - UNII:VG2QF83CGL) meloxicam 5 mg in 1 mL Product Characteristics Color Yellow (clear light yellow to yellow) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 17033-051-10 1 in 1 CARTON 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS 2 NDC: 17033-051-20 1 in 1 CARTON 2 20 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200727 11/15/2022 Labeler - Dechra Veterinary Products (362142734)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.