LASIX ONYU- furosemide injection
LASIX ONYU by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LASIX ONYU by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by SQ Innovation, Inc., Sharp Sterile Manufacturing, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Lasix® ONYU safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Lasix® ONYU. Lasix® ONYU (furosemide injection), for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lasix ONYU is a loop diuretic indicated for the treatment of edema in adult patients with chronic heart failure. (1.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The Infusor is pre-programmed to deliver 30 mg of Lasix ONYU over the first hour then 12.5 mg per hour for the subsequent 4 hours. (2.1)
- Lasix ONYU is not for chronic use and should be replaced with oral diuretics as soon as practical. (2.1)
- See Full Prescribing Information for important administration instructions. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 80 mg per 2.67 mL in a single-dose prefilled cartridge co-packaged with a single-use Disposable Unit of the Infusor. (3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities: Monitor serum electrolytes, CO2, BUN, creatinine, glucose, and uric acid. (5.1)
- Worsening Renal Function: Monitor for dehydration and azotemia. (5.2)
- Ototoxicity: Avoid higher than recommended doses. (5.3, 7.1)
- Acute Urinary Retention: Monitor patients with symptoms of urinary retention. (5.4)
- Incomplete Dosing: Fluid contact and certain patient movements during treatment may cause the On-body Infusor to prematurely terminate infusion. Ensure patients can detect and respond to alarms. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions during treatment with the Lasix ONYU Infusor were administration site and skin reactions: erythema, bruising, edema, and infusion site pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact SQ Innovation, at 1-855-452-7496 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Aminoglycoside antibiotics: Increased potential ototoxicity of the antibiotics. Avoid combination. (7.1)
- Ethacrynic acid: Risk of ototoxicity. Avoid combination. (7.1)
- Salicylates: Risk of salicylate toxicity. (7.1)
- Cisplatin and nephrotoxic drugs: Risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. (7.1)
- Lithium: Risk of lithium toxicity. (7.1)
- Renin-angiotensin inhibitors: Increased risk of hypotension and renal failure. (7.1)
- Adrenergic blocking drugs: Risk of potentiation. (7.1)
- Drugs undergoing renal tubular secretion: Risk of toxicity potentiation. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Congestion
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities
5.2 Worsening Renal Function
5.3 Ototoxicity
5.4 Acute Urinary Retention
5.5 Incomplete Dosing
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Furosemide on Other Drugs
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on Furosemide
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage
The Infusor with single-dose prefilled cartridge delivers 30 mg of Lasix ONYU over the first hour followed by 12.5 mg per hour for the subsequent 4 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. Administer Lasix ONYU once or twice daily as needed for edema. Lasix ONYU is not for chronic use and should be replaced with oral diuretics as soon as practical.
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
Lasix ONYU is intended for use in a setting where the patient can limit their activity for the duration of administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
The Infusor for Lasix ONYU is not compatible with use in an MRI setting.
Inspect Lasix ONYU prefilled cartridge prior to administration. Lasix ONYU is a clear to slightly yellow solution. Do not use Lasix ONYU if solution is discolored or cloudy [see Description (11)] .
Refer to the Instructions for Use for additional information.
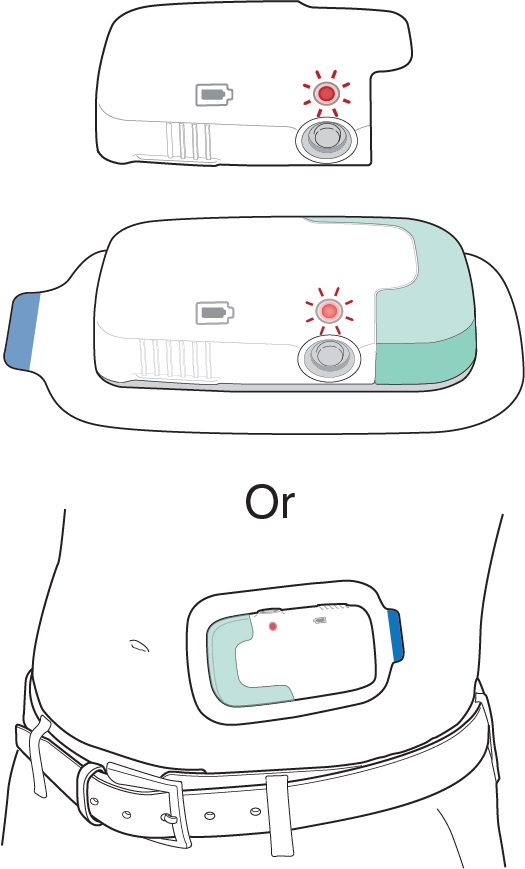
Push the Lasix ONYU prefilled cartridge into Disposable Unit. Slide the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit together until the Status Light on the Reusable Unit turns on. The Infusor will remain ready to start infusion for 7 hours.
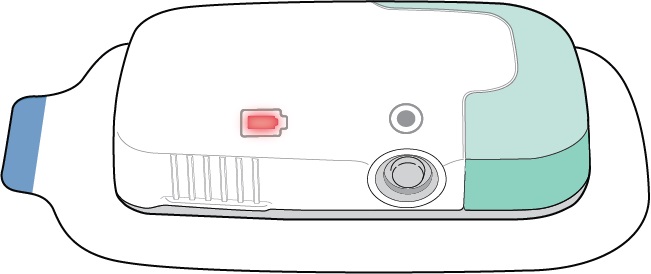
Peel away the paper liner on the Infusor and apply onto a clean, dry area of the abdomen between the top of the beltline and the bottom of the ribcage that is not tender, bruised, red, or indurated. Make sure the Status Lights and the Start/Stop Button are facing up in a horizontal position.
Start the injection by firmly pressing and holding the Start/Stop Button until you hear the motor and see the blue Status Light change to flashing slowly.
Do not remove until the injection is complete which is signaled by the solid blue Status Light and the OK tone (one long beep).
Rotate the site of each subcutaneous administration.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities
Furosemide may cause fluid, electrolyte, and metabolic abnormalities such as hypovolemia, hypokalemia, azotemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia, or hyperuricemia, particularly in patients receiving higher doses, patients with inadequate oral electrolyte intake, and in elderly patients. Excessive diuresis may cause dehydration and blood volume reduction with circulatory collapse and possible vascular thrombosis and embolism, particularly in elderly patients. Serum electrolytes, CO2, BUN, creatinine, glucose, and uric acid should be monitored frequently during furosemide therapy.
5.2 Worsening Renal Function
Furosemide can cause dehydration and azotemia. If increasing azotemia and oliguria occur during treatment of severe progressive renal disease, discontinue furosemide [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.3 Ototoxicity
Cases of tinnitus and reversible or irreversible hearing impairment and deafness have been reported with furosemide. Reports usually indicate that furosemide ototoxicity is associated with rapid injection, severe renal impairment, the use of higher than recommended doses, hypoproteinemia or concomitant therapy with aminoglycoside antibiotics, ethacrynic acid, or other ototoxic drugs. If the physician elects to use high-dose parenteral therapy, controlled intravenous infusion is advisable (for adults, an infusion rate not exceeding 4 mg furosemide per minute has been used) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.4 Acute Urinary Retention
In patients with severe symptoms of urinary retention (because of bladder emptying disorders, prostatic hyperplasia, urethral narrowing), the administration of furosemide can cause acute urinary retention related to increased production and retention of urine. These patients require careful monitoring, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
5.5 Incomplete Dosing
The Lasix ONYU Infusor should not come in contact with water or any other fluids (blood or drug product). Fluid contact with the Infusor circuit board can lead to device errors and premature termination of infusion.
The Lasix ONYU is intended for use in a setting where the patient can limit their activity for the duration of administration. Certain patient movements may cause interruption of device adherence to skin and premature termination of infusion.
Lasix ONYU should only be used in patients who can detect and respond to alarms to ensure a complete dose is administered. -
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of furosemide were identified in clinical trials or post-marketing reports. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably, or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions are categorized below by organ system and listed by decreasing severity.
Gastrointestinal System Reactions: pancreatitis, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), increased liver enzymes, anorexia, oral and gastric irritation, cramping, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting.
Systemic Hypersensitivity Reactions: severe anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions (e.g., with shock), systemic vasculitis, interstitial nephritis, necrotizing angiitis.
Central Nervous System Reactions: tinnitus and hearing loss, paresthesias, vertigo, dizziness, headache, blurred vision, xanthopsia.
Hematologic Reactions: aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, anemia, eosinophilia.
Dermatologic Hypersensitivity Reactions: toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, erythema multiforme, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, purpura, photosensitivity, rash.
Cardiovascular Reactions: orthostatic hypotension, increase in cholesterol and triglyceride serum levels.
Administration Site and Skin Reactions: erythema, bruising, edema, infusion site pain.
Other Reactions: glycosuria, muscle spasm, weakness, restlessness, urinary bladder spasm, thrombophlebitis, transient injection site pain following intramuscular injection, fever.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Furosemide on Other Drugs
Table 1: Effects of Furosemide on Other Drugs Drug/Substance Class or Name Drug Interaction Effect Recommendations Aminoglycoside antibiotics Furosemide may increase the ototoxic potential of aminoglycoside antibiotics, especially in the presence of impaired renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Avoid combination except in life-threatening situations. Ethacrynic acid Possibility of ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Avoid concomitant use with ethacrynic acid. Salicylates May experience salicylate toxicity at lower doses because of competitive renal excretory sites. Monitor for symptoms of salicylate toxicity. Cisplatin
Cisplatin and nephrotoxic drugsThere is a risk of ototoxic effects if cisplatin and furosemide are given concomitantly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
NephrotoxicityAdminister furosemide at lower doses and with positive fluid balance when used to achieve forced diuresis during cisplatin treatment. Monitor renal function. Paralytic agents Furosemide has a tendency to antagonize the skeletal muscle relaxing effect of tubocurarine and may potentiate the action of succinylcholine. Monitor for skeletal muscle effect. Lithium Furosemide reduces lithium’s renal clearance and adds a high-risk of lithium toxicity. Avoid concomitant use with lithium. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers May lead to severe hypotension and deterioration in renal function, including renal failure. Monitor for changes in blood pressure and renal function and interrupt or reduce the dosage of furosemide, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers if needed. Antihypertensive drugs Furosemide may add to or potentiate the therapeutic effect of other antihypertensive drugs. Monitor for changes in blood pressure and adjust the dose of other antihypertensive drugs if needed. Adrenergic blocking drugs or peripheral adrenergic blocking drugs Potentiation occurs. Monitor for changes in blood pressure and adjust the dose of adrenergic blocking drugs if needed. Norepinephrine Furosemide may decrease arterial responsiveness (vasoconstricting effect) to norepinephrine. Monitor blood pressure (or mean arterial pressure). Chloral hydrate In isolated cases, intravenous administration of furosemide within 24 hours of taking chloral hydrate may lead to flushing, sweating attacks, restlessness, nausea, increase in blood pressure, and tachycardia. Concomitant use with chloral hydrate is not recommended. Methotrexate and other drugs undergoing renal tubular secretion Furosemide may decrease renal elimination of other drugs that undergo tubular secretion. High-dose treatment of furosemide may result in elevated serum levels of these drugs and may potentiate their toxicity. Monitor serum levels of drugs undergoing renal tubular secretion and adjust the dose if needed. Cephalosporin Furosemide can increase the risk of cephalosporin-induced nephrotoxicity even in the setting of minor or transient renal impairment. Monitor for changes in renal function. Cyclosporine Increased risk of gouty arthritis secondary to furosemide-induced hyperuricemia and cyclosporine impairment of renal urate excretion. Monitor serum urate levels. Thyroid hormones High doses (> 80 mg) of furosemide may inhibit the binding of thyroid hormones to carrier proteins and result in transient increase in free thyroid hormones, followed by an overall decrease in total thyroid hormone levels. Monitor the total thyroid hormone levels. 7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on Furosemide
Table 2: Effect of Other Drugs on Furosemide Drug/Substance Class or Name Drug Interaction Effect Recommendations Phenytoin Phenytoin interferes directly with renal action of furosemide.
Monitor diuretic effects of furosemide and adjust the dose of furosemide if needed. Methotrexate and other drugs undergoing renal tubular secretion May reduce the effect of furosemide. High-dose treatment of methotrexate and these other drugs may result in elevated serum levels of furosemide and may potentiate the toxicity of furosemide. Monitor for enhanced toxicity of furosemide. Indomethacin Coadministration of indomethacin may reduce the natriuretic and antihypertensive effects of furosemide in some patients by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis.
Indomethacin may also affect plasma renin levels, aldosterone excretion, and renin profile evaluation.Patients receiving both indomethacin and furosemide should be observed closely to determine if the desired diuretic and/or antihypertensive effect of furosemide is achieved. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from published observational studies, case reports, and post marketing reports, from decades of use, have not demonstrated a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes with furosemide use during pregnancy. Untreated congestive heart failure can lead to adverse outcomes for the mother and the fetus (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, furosemide has been shown to cause unexplained maternal deaths and abortions in rabbits when administered orally during organogenesis at 4 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on body surface area (BSA) and oral bioavailability corrections, presumably secondary to volume depletion (see Data).
The background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo/fetal Risk
Pregnant women with congestive heart failure are at increased risk for pre-term birth. Stroke volume and heart rate increase during pregnancy, increasing cardiac output, especially during the first trimester.
Clinical classification of heart disease may worsen with pregnancy and lead to maternal death and/or stillbirth. Closely monitor pregnant patients for destabilization of their heart failure.
Data
Animal Data
The effects of furosemide on embryonic and fetal development and on pregnant dams were studied in mice, rats, and rabbits.
Furosemide caused unexplained maternal deaths and abortions in rabbits at the lowest dose of 25 mg/kg (approximately 4 times the human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections). In another study, a dose of 50 mg/kg (approximately 7 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections) also caused maternal deaths and abortions when administered to rabbits between Days 12 and 17 of gestation. In a third study, none of the pregnant rabbits survived an oral dose of 100 mg/kg. Data from the above studies indicate fetal lethality that can precede maternal deaths.
The results of the mouse study and one of the three rabbit studies also showed an increased incidence and severity of hydronephrosis (distention of the renal pelvis and, in some cases, of the ureters) in fetuses of treated dams as compared with the incidence of fetuses from the control group.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The presence of furosemide has been reported in human breast milk. There are no data on the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Doses of furosemide associated with clinically significant diuresis may impair milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for furosemide and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from furosemide or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy for pediatric use have not been established [see Indications and Usage (1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Controlled clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of subjects to determine whether subjects aged 65 and over respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for the elderly patients should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Lasix ONYU is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
The principal signs and symptoms of overdose with Lasix ONYU are dehydration, blood volume reduction, hypotension, electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia, and hypochloremic alkalosis, and are extensions of its diuretic action.
The concentration of furosemide in biological fluids associated with toxicity or death is not known.
Treatment of overdosage is supportive and consists of replacement of excessive fluid and electrolyte losses. Serum electrolytes, carbon dioxide level, and blood pressure should be determined frequently. Adequate drainage must be assured in patients with urinary bladder outlet obstruction (such as prostatic hypertrophy).
Hemodialysis does not accelerate furosemide elimination.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Lasix ONYU (furosemide injection) for subcutaneous use is a loop diuretic. Chemically, it is 4-chloro-N-furfuryl-5-sulfamoylanthranilic acid.
Furosemide is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in alcohol, freely soluble in dilute alkali solutions, and insoluble in dilute acids. The structural formula is as follows:
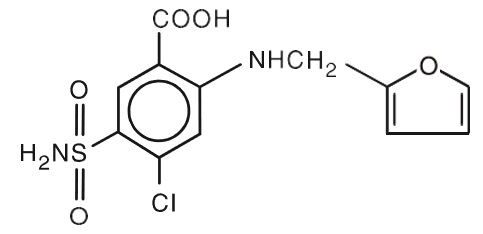
Molecular Formula: C12H11ClN2O5S
Molecular Weight: 330.75 g/mol
Lasix ONYU is a single-dose prefilled cartridge co-packaged with a single-use Disposable Unit of the Infusor.
The single-dose prefilled cartridge contains 80 mg furosemide in a 2.67 mL sterile, clear to slightly yellow, and nonpyrogenic aqueous solution. The pH of Lasix ONYU, 7.5, differs from that of Furosemide Injection, USP. Each 1 mL dose of Lasix ONYU contains 30 mg of furosemide and the following inactive ingredients: betadex sulfobutyl ether sodium (300 mg), hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment if needed, sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment if needed, tromethamine (3 mg), and water for injection (q.s.).
Each single-dose of Lasix ONYU is administered via an electromechanical (battery powered, microprocessor controlled) Infusor, pre-programmed to deliver 80 mg of Lasix ONYU over 5-hours using a bi-phasic delivery profile. The Infusor consists of a custom Reusable Unit which can be used for close to 50 treatments. The Reusable Unit is used with a Disposable Unit and single-dose prefilled cartridge which are provided together for the user as a Lasix ONYU Kit. The Disposable Unit must be discarded after use.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Furosemide primarily inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the proximal and distal tubules and in the loop of Henle. The high degree of diuresis is largely due to the unique site of action. The action on the distal tubule is independent of any inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase and aldosterone.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In patients with NYHA Class II and Class III heart failure, subcutaneous administration of Lasix ONYU (30 mg furosemide over the first hour followed by 12.5 mg per hour for the subsequent 4 hours, total 80 mg furosemide within 5 hours) produced similar diuresis and natriuresis to intravenous administration (single 80 mg bolus) at 8- and 24-hour post-dose. The duration of diuretic effect with Lasix ONYU is at least 8 hours after initiation of dosing.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In patients with NYHA Class II and Class III heart failure, subcutaneous infusion of Lasix ONYU (30 mg furosemide over the first hour followed by 12.5 mg per hour for the subsequent 4 hours, 80 mg furosemide total), the bioavailability was 112% (90% CI: 104, 120%), with a median Tmax of 5 hours relative to 80 mg intravenous furosemide (single 80 mg bolus). The pharmacokinetic parameters of Lasix ONYU are presented in Table 3 below:
Table 3: Pharmacokinetic Data of Lasix ONYU Following Subcutaneous Infusion (n = 18) - * Mean ± SD
Dose C max
(ng/mL)*AUC t (ng×hr/mL)* T1/2 (hr)* AUC ∞
(ng×hr/mL)*Lasix ONYU: 30 mg subcutaneously infused over the first hour followed by 12.5 mg per hour for the subsequent 4 hours (total dose: 80 mg furosemide) 2010 ± 391
13000 ± 2510 3.7 ± 0.7
13100 ± 2550 Furosemide administered as single 80 mg bolus dose intravenously 13800 ± 4100 11900 ± 3380 3.7 ± 1.3 12000 ± 3400 The terminal half-life of furosemide is approximately 2 hours.
The impact of subcutaneous edema at the administration site of Lasix ONYU on drug absorption is unknown.
Distribution
Furosemide is extensively bound to plasma proteins, mainly to albumin. Plasma concentrations ranging from 1 mcg per mL to 400 mcg per mL are 91% to 99% bound in healthy individuals. The unbound fraction averages 2.3% to 4.1% at therapeutic concentrations.
Furosemide binding to albumin may be reduced in elderly patients.Elimination
Significantly more furosemide is excreted in urine following the intravenous injection than after the tablet or oral solution.
Furosemide is predominantly excreted unchanged in the urine.
The renal clearance of furosemide after intravenous administration in older healthy male subjects (60 to 70 years of age) is significantly less than in younger healthy male subjects (20 to 35 years of age).
Metabolism
Furosemide glucuronide is the only or at least the major biotransformation product of furosemide in humans.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Furosemide was tested for carcinogenicity by oral administration in one strain of mice and one strain of rats. A small but significantly increased incidence of mammary gland carcinomas occurred in female mice at a dose approximately 8 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections. There were marginal increases in uncommon tumors in male rats at a dose of 15 mg per kg (slightly greater than the maximum human dose) but not at 30 mg per kg.
Mutagenesis
Furosemide was devoid of mutagenic activity in various strains of Salmonella typhimurium when tested in the presence or absence of an in vitro metabolic activation system, and questionably positive for gene mutation in mouse lymphoma cells in the presence of rat liver S9 at the highest dose tested. Furosemide did not induce sister chromatid exchange in human cells in vitro, but other studies on chromosomal aberrations in human cells in vitro gave conflicting results. In Chinese hamster cells it induced chromosomal damage but was questionably positive for sister chromatid exchange. Studies on the induction by furosemide of chromosomal aberrations in mice were inconclusive. The urine of rats treated with this drug did not induce gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Impairment of Fertility
Furosemide produced no impairment of fertility in male or female rats, at 100 mg per kg per day (the maximum effective diuretic dose in the rat), approximately 7 times a human i.v. dose of 80 mg based on BSA and oral bioavailability corrections.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Lasix ONYU injection is a sterile, clear to slightly yellow, non-pyrogenic liquid supplied in a single-dose prefilled cartridge for subcutaneous infusion co-packaged with a Disposable Unit. The Infusor with single-dose prefilled cartridge is designed to deliver 80 mg of Lasix ONYU in 2.67 mL solution over 5 hours.
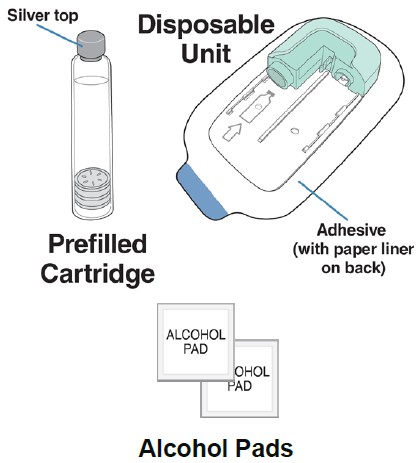
Lasix ONYU Kit: Carton containing one 80 mg/2.67 mL single-dose prefilled cartridge co-packaged with a Disposable Unit and two alcohol pads.
NDC 81137‐001‐15
Starter Kit: Carton containing three Lasix ONYU Kits co-packaged with one Reusable Unit and one wall charger.
NDC 81137‐001‐35
Store between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Protect Lasix ONYU from light. Do not remove the prefilled cartridge from carton until it is ready for use. Do not use if the solution is discolored or cloudy. Protect the Infusor from water.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling [Instructions for Use].
Advise the patient that Lasix ONYU should not come into contact with water or other fluids. Patients should check the device for alarms to ensure a complete dose is administered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Metabolic Abnormalities
Advise patients that they may experience symptoms from excessive fluid and/or electrolyte losses. The postural hypotension that sometimes occurs can usually be managed by getting up slowly. Potassium supplements and/or dietary measures may be needed to control or avoid hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients that furosemide may increase blood glucose levels and thereby affect urine glucose tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Photosensitivity
The skin of some patients may be more sensitive to the effects of sunlight while taking furosemide [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
For more information about Lasix® ONYU, go to www.Lasix-ONYU.com or call 1-855-452-7496 (1-855-4LASIX6).

Lasix® ONYU (furosemide injection 80 mg/2.67 mL) for subcutaneous use
Manufactured for:
SQ Innovation, Inc.
20 Burlington Mall Road, Suite 220
Burlington, MA 01803
USAPatent Protected
©2023 -
SQ InnovationInstructions for UseLasix® ONYU (lay-six on-yoo) (furosemide injection) 80 mg/2.67 mL (30 mg/mL) for Subcutaneous Use with Infusor
These Instructions for Use contains information on how to use Lasix ONYU with the Infusor.
Contact Information:
SQ Innovation, Inc.
Burlington, MA 01803, USA
Phone: 1-855-452-7496 (1-855-4LASIX6)
www.Lasix-ONYU.com1: Important Information You Need to Know
Before Using the Lasix ONYU Infusor
- Keep the Lasix ONYU Infusor out of sight and reach of children.
- The Lasix ONYU treatment is for adult patients only as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- For subcutaneous (under the skin) use only. The Lasix ONYU Infusor delivers the medicine just under the skin.
- Use on the stomach only. Do not use on any other area of the body.
- The Lasix ONYU Infusor is intended to be used by a single person and should not be shared.
- Do not use the Prefilled Cartridge if the solution is cloudy, yellow-brown or contains floating particles. It should be clear or light yellow. If it is not clear or light yellow, contact your healthcare provider to get a new one.
- Do not use any part of the Lasix ONYU Infusor if it has expired. If it is expired, contact your healthcare provider to get a new one.
- Do not use any part of the Lasix ONYU Infusor (Prefilled Cartridge, Disposable Unit, Reusable Unit or Charger) if it appears to be broken or damaged or does not work right. Use a new one or call SQ Innovation at 1-855-452-7496.
- Do not use a Disposable Unit if it was dropped as it may be damaged or contaminated. Use a new one.
- Do not use the Lasix ONYU Infusor if you can see the needle. Do not touch the needle or put the Lasix ONYU Infusor on your stomach, as you may get an injury. Go to Troubleshooting: You Can See the Needle for instructions on what to do.
- Do not use more than 1 Lasix ONYU Infusor at a time.
- Do not do more than 2 infusions in a 24-hour period.
- Do not use a Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge more than 1 time.

Before Starting a Treatment
-
Talk with your healthcare provider before using the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
Do not start an infusion unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider. - A healthcare provider should train you before using the Lasix ONYU Infusor by yourself.
- Read the step-by-step instructions (go to Chapter 2: How to Use the Lasix ONYU Infusor) before using the Lasix ONYU Infusor by yourself.
- You may watch the optional training video.

During a Treatment
- Start the infusion within 7 hours of preparing the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
- The infusion will last about 5 hours. During this time, you should limit your activities so that your bending movements are limited. Wearing the Lasix ONYU Infusor while riding in a car or airplane is not recommended. Be sure you have access to a bathroom after starting the infusion. You should urinate (pee) a lot and will need to make frequent bathroom visits.
- Frequent urination is to be expected during use of the Lasix ONYU Infusor. Be sure you have access to a bathroom for up to 8 hours after starting the infusion.
- Call your healthcare provider if you did not urinate a lot (at least 2 times during the 5-hour infusion).
- Do not apply lotions, oils, or ointments to the stomach area where you will apply the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
- Do not get the Lasix ONYU Infusor wet. Doing so may damage the Lasix ONYU Infusor. Do not shower, bathe, or swim while wearing the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
- Do not remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from the stomach until the infusion is done. Removing the Lasix ONYU Infusor before stopping it will expose the needle, and may injure you or others. Go to How to Stop the Lasix ONYU Infusor Early if you need to stop the infusion early.
- Do not use the Lasix ONYU Infusor in or around a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine.
- Do not use the Lasix ONYU Infusor within 12 inches of mobile phones, tablets, computers, or wireless accessories (for example: TV remote control, Bluetooth computer keyboard or mouse) during the 5-hour infusion. It may cause the Lasix ONYU Infusor to break.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
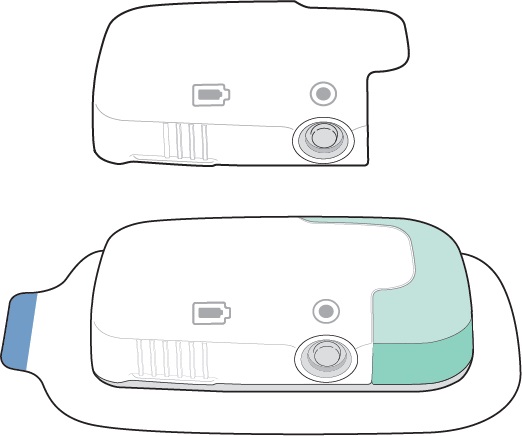
2: How to Use the Lasix ONYU Infusor
Inside the Box
Contents of the Lasix ONYU Kit

Note: The Single-Dose Prefilled Cartridge is referred to as Prefilled Cartridge throughout this Instructions for Use.
Contents of the Reusable Unit and Charger Box
Contents of the Lasix ONYU Starter Kit

Supplies not included:
- Cotton ball and small adhesive bandage (if needed) for Step 21 in End the Infusion.
- You will also need a sharps disposal container for Step 25 in Throw Away (Disposal), Cleaning, and Storage. You may obtain a free sharps disposal container from SQ Innovation. Visit www.Lasix-ONYU.com/sharps/ or call 1-855-452-7496 to have a container mailed
to you at no charge.
Get to Know the Lasix ONYU Infusor Parts
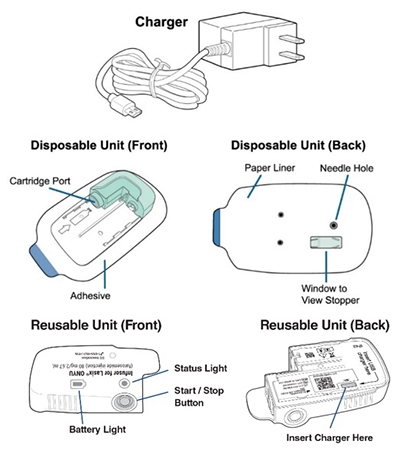
Get Ready for the Infusion

Do not start an infusion unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider.
Step 1
Gather the white Reusable Unit, Charger, and 1 Lasix ONYU Kit.
Only use the Charger that has been provided.
Do not use if the Disposable Unit was dropped or if any parts appear to be broken or damaged. Use a new one.
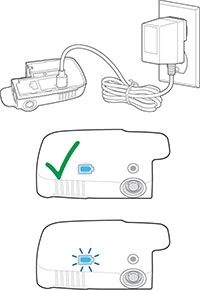
Step 2
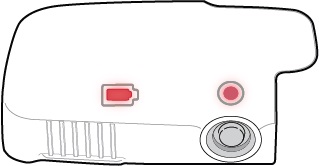
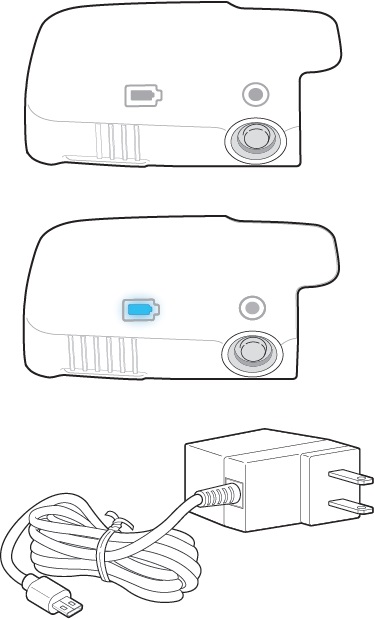
Charge the Reusable Unit. Plug the Charger into the back of the white Reusable Unit and a power outlet. Check the Battery Light:
- When the Battery Light turns solid blue, unplug the charger from the Reusable Unit. The Reusable Unit is ready to use.
- If the Battery Light is flashing blue, wait for charging to finish.
- If any lights are red, unplug the Charger and plug it back in. If the lights are still red, go to Troubleshooting: Lights and Tones Table for instructions.
Always charge the Reusable Unit before each infusion.
Prepare the Medicine
Step 3
Wash your hands with soap and water.
Step 4
Check the expiration date on the Lasix ONYU Kit.
Do not use if the expiration date has passed.

Step 5
Gather all supplies needed. On a clean, flat, well-lit work surface, open 1 Lasix ONYU Kit and remove the contents.
Do not open the contents until you are ready to start the infusion.
Do not use the Disposable Unit if the sealed packaging appears to be damaged. Use a new one.
Do not use the Disposable Unit if it was dropped or if any parts appear to be broken. Use a new one.

Step 6
Remove Prefilled Cartridge, Disposable Unit, and 2 alcohol pads from packaging:
- Remove the Prefilled Cartridge from its box and sealed tray.
- Remove the Disposable Unit from its sealed package.
Do not remove the paper liner from the back of the Disposable Unit.
Step 7
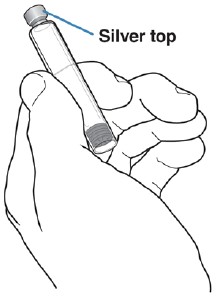
Check the Prefilled Cartridge appearance.
Do not use the Prefilled Cartridge if the medicine is cloudy, appears yellow-brown, or you see floating particles.
Step 8
Wipe the silver top of the Prefilled Cartridge with an alcohol pad.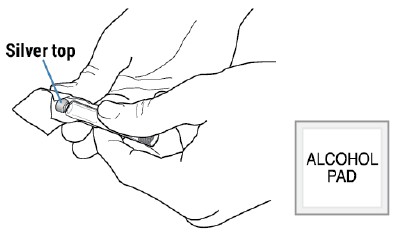
Step 9
Push the Prefilled Cartridge into the green Disposable Unit with the silver top inserted first.
The Prefilled Cartridge is fully inserted when the bottom of the Prefilled Cartridge is at the tip
of the arrow on the Disposable Unit.
Prepare the Lasix ONYU Infusor
Step 10
Check the following:
- The Reusable Unit Battery Light is solid blue, and
- The Charger is disconnected from the Reusable Unit.
Slide together the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit together until the Status Light on the Reusable Unit turns on.
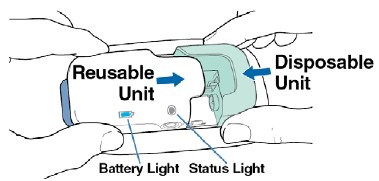
Step 11
Check the Status Light.
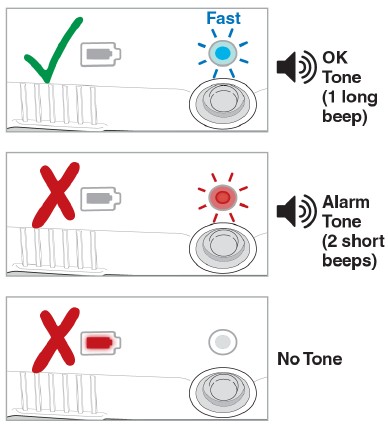
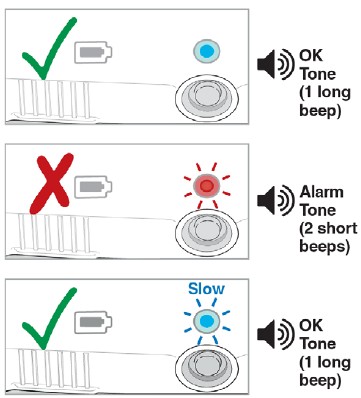
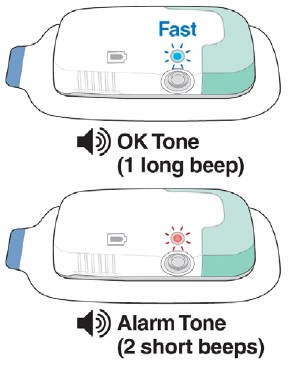
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing fast, and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), continue to Step 12. The Lasix ONYU Infusor is ready to start your infusion.
- The Lasix ONYU Infusor will remain ready to start infusion for 7 hours.
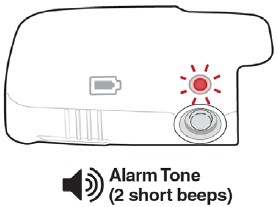
- If the Status Light is flashing red and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps), do not use the Lasix ONYU Infusor. Go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red for instructions.
- If the Battery Light is solid red, do not use the Lasix ONYU Infusor. Go to Troubleshooting: Checking the Reusable Unit Battery for instructions.
Prepare the Application Site
Step 12
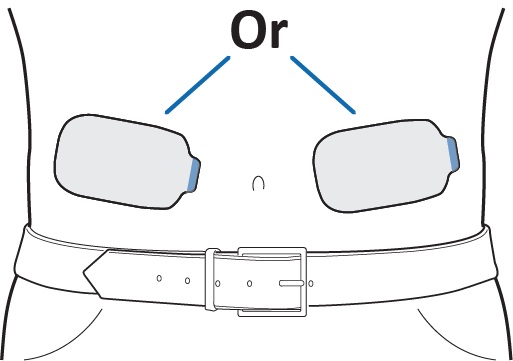
Choose a site on the stomach, above the beltline, to the left or right of the belly button.
Trim excessive hair at the site. This will help the Lasix ONYU Infusor stick to the skin.
Alternate (rotate) sites between left and right sides of the stomach with each infusion.Do not choose a site where:
- the skin is irritated, broken, tender, red, bruised, or hard,
- the skin is wet or sweaty,
- there are folds in the skin when standing up straight, or
- belts, waistbands, or tight clothing may rub against or move the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
Step 13
Wipe the site with an alcohol pad.
Let dry for at least 10 seconds.
Attach the Lasix ONYU Infusor
Step 14
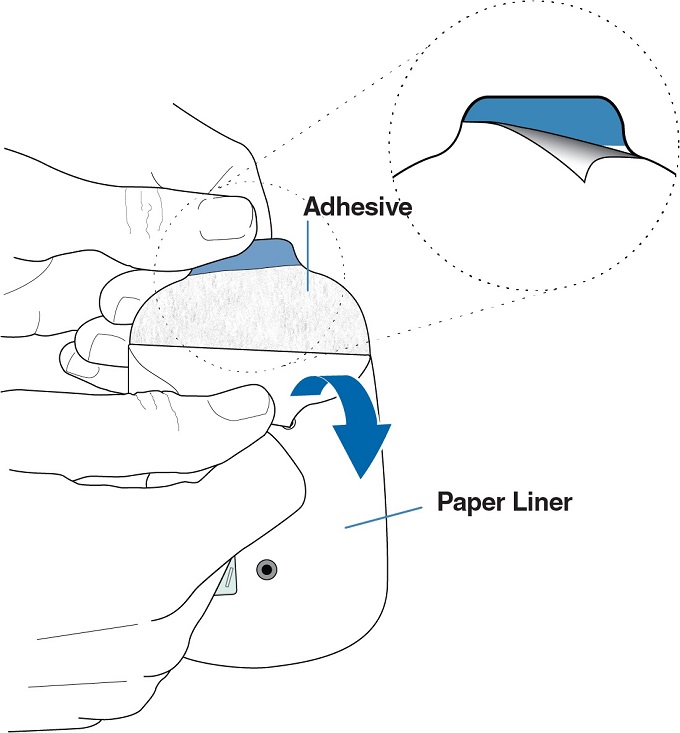
Hold the blue tab with one hand and use the other hand to peel off the paper liner from the adhesive on the back of the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
Leave the sticky adhesive on the Lasix ONYU Infusor. Only remove the paper liner.
Do not touch the sticky adhesive with your fingers or let it touch any surfaces before sticking the Lasix ONYU Infusor to your stomach.
Step 15
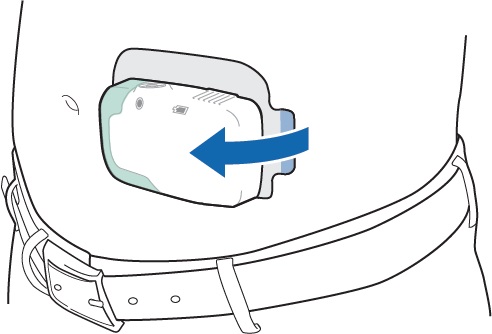
While standing up straight, press the Lasix ONYU Infusor onto the site on your stomach you wiped with the alcohol pad.
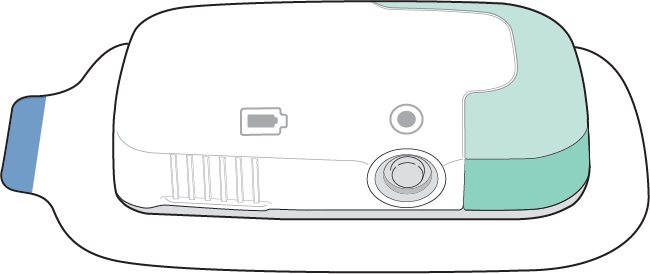
Make sure the Status Light and the Start/Stop Button are facing up in a horizontal position as shown, so you can see them when the Lasix ONYU Infusor is on your stomach.
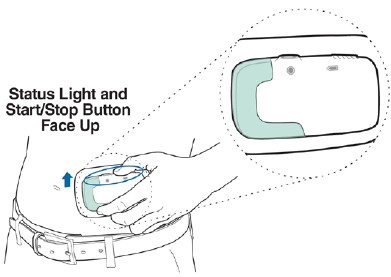
Step 16
Rub the edges of the adhesive with a finger to get the Lasix ONYU Infusor to stick well.
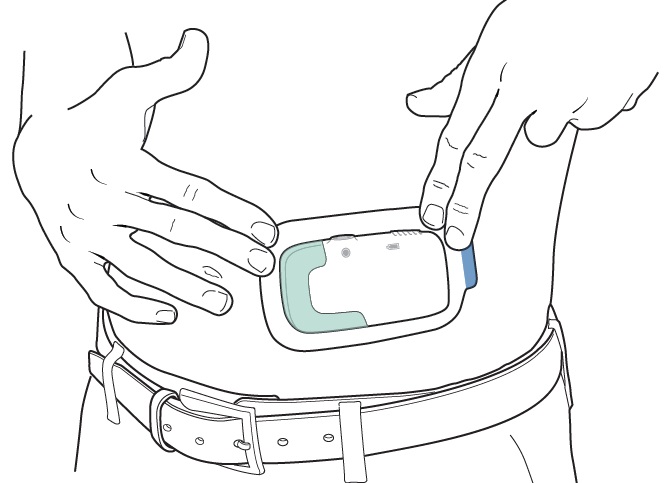
Start the Infusion
Start your infusion within 7 hours of connecting the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit. If more than 7 hours pass without starting your infusion, the Lasix ONYU Infusor will time out and the infusion cannot be delivered (go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red).
Step 17
Press and hold the Start/Stop Button until you hear the motor and see the blue Status Light change to flashing slow.
The needle will automatically insert into your skin after the Start/Stop Button is pressed. You may feel a slight pinch.
You will hear the motor start and stop often during your infusion. The motor runs for a few seconds at a time then pauses for several minutes.
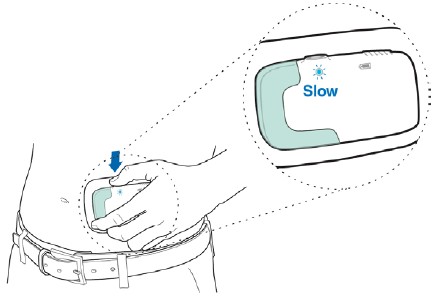
Step 18
Check the Status Light.
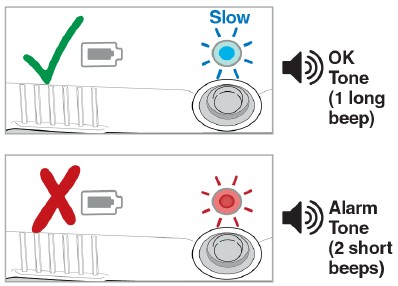
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing slow, and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the infusion has started. You will hear the motor running.
- If the Status Light is flashing red, and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps), the infusion did not start. Go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red for instructions.
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing fast, and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the infusion did not start. Repeat Step 17.
- For additional assistance go to Troubleshooting: Lights and Tones Table for instructions or call 1-855-452-7496.
During the Infusion
Step 19
Wait 5 hours for the Lasix ONYU Infusor to deliver the full infusion.
You will see the blue Status Light flashing slow and sometimes hear the motor running.
Check the Lasix ONYU Infusor every now and then to make sure it is working properly.
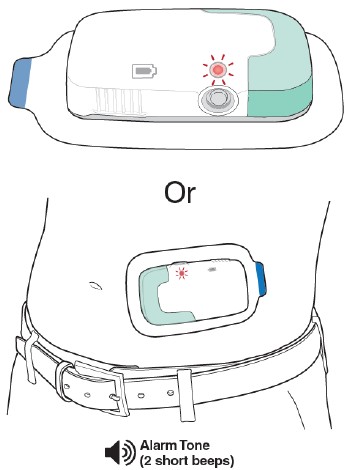
Do not remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from your stomach until the infusion is done. The infusion is complete when the Status Light is solid blue and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep). Go to Troubleshooting: How to Stop the Infusor Early if you need to stop the infusion early.

End the Infusion
Step 20
After 5 hours, check the Status Light.
- If the Status Light is solid blue, and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the infusion is done.
- If the Status Light is flashing red, and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps), an error happened. Go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red.
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing slow, and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the infusion is not done yet. Continue to wait.
The needle automatically pulls in (retracts) when the infusion is done. You may feel a slight pinch.
Step 21
When the infusion is done, remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from your stomach. Peel the Lasix ONYU Infusor off the skin by holding down the skin and pulling the blue tab away from the stomach.
You might have some discomfort after you remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor. This discomfort should quickly go away, but some redness of the skin may remain. If there is any bleeding, pat with a small cotton ball or apply a small adhesive bandage over the site.
Confirm the Infusion Worked
Step 22
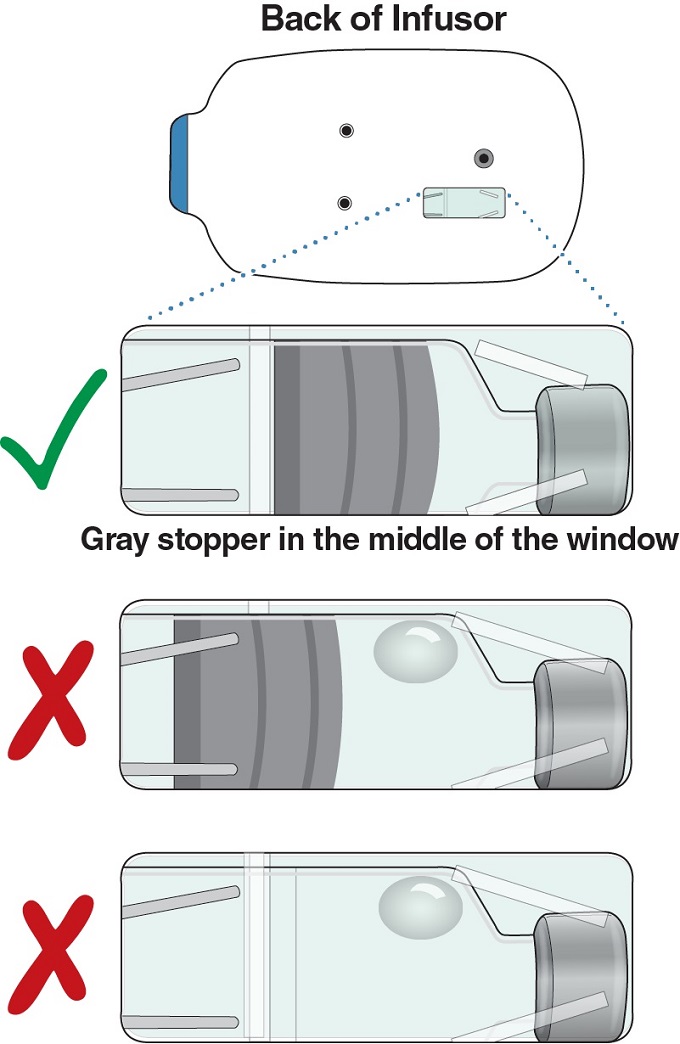
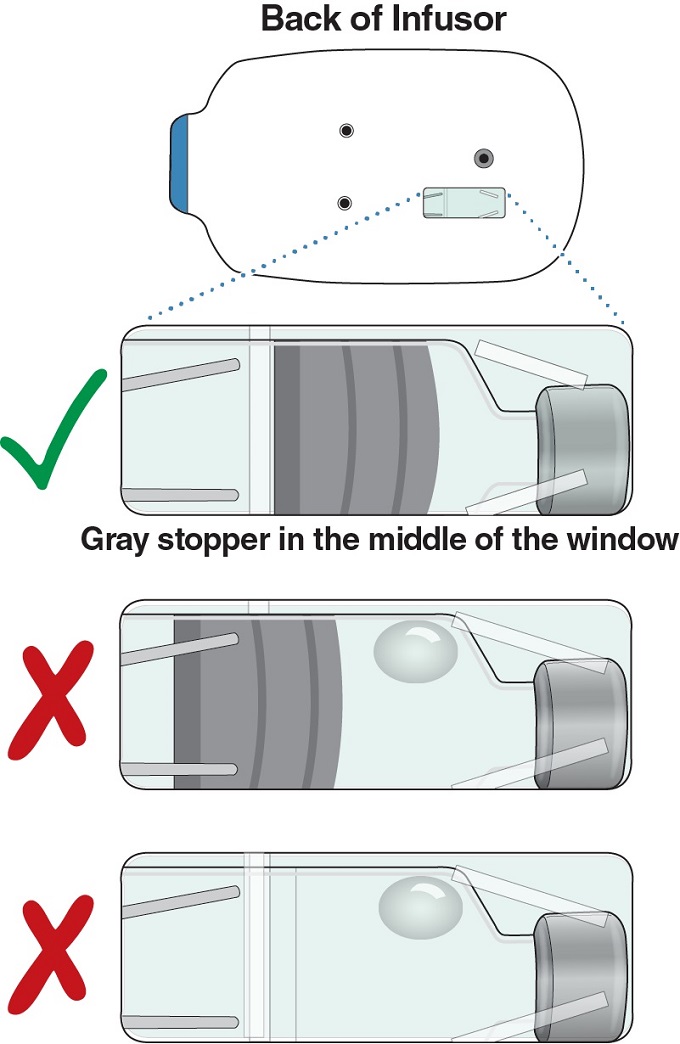
Look in the window on the back of the Infusor to check whether all the medicine was delivered.
- If the middle of the window is all gray (whole gray stopper is visible with very little or no liquid), all of the medicine was delivered.
If you see anything else (like a lot of liquid, a large bubble in the liquid, no gray stopper, or only part of the gray stopper), some of the medicine was not delivered. Call your healthcare provider right away.
Step 23
Confirm the medicine worked.
- If you urinate a lot (at least 2 times during the 5-hour infusion), the medicine worked.
- If you urinate less than 2 times (during the 5-hour infusion), the medicine may not have worked. Call your healthcare provider right away.
Throw Away (Disposal), Cleaning, and Storage
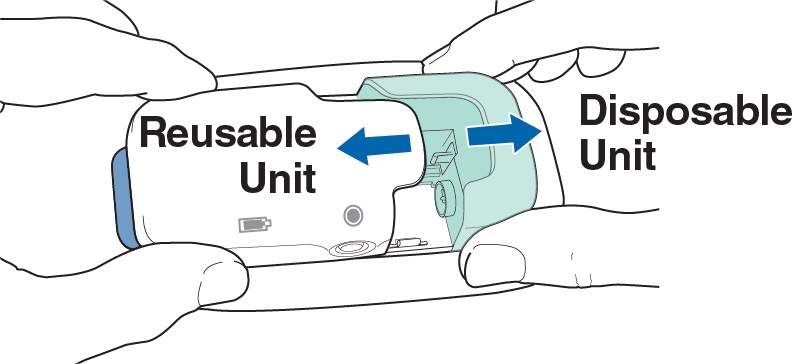
Step 24
Pull apart the green Disposable Unit and white Reusable Unit.
The Reusable Unit automatically turns off when the two parts are separated.
Step 25
Do not save and re-use the green Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge. They are for one-time use only.
Throw away the green Disposable Unit into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container.
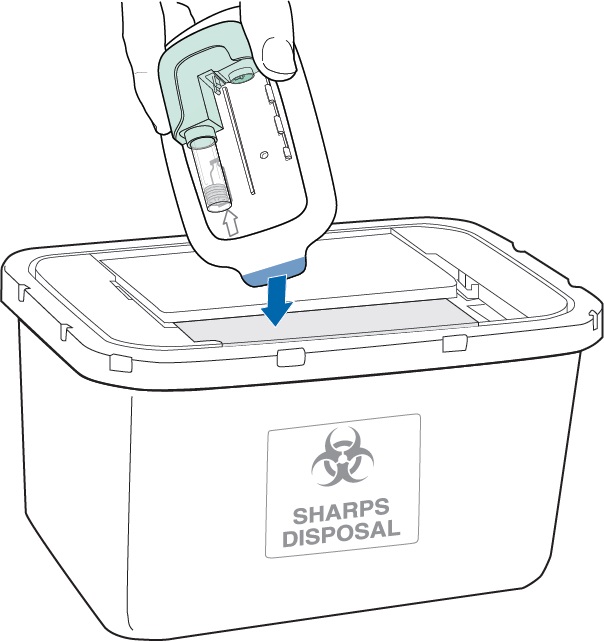
You may obtain a free sharps disposal container from SQ Innovation. Visit www.Lasix-ONYU.com/sharps/ or call 1-855-452-7496 to have a container mailed to you at no charge.
Alternatively, if you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your Sharps container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDAs website at:
https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safely-using-sharps-needles-and-syringes-home-work-and-travel/best-way-get-rid-used-needles-and-other-sharps
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.
Do not recycle the green Disposable Unit and used sharps disposal container or throw them away into household trash.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
Scan the code below with your phone for a sharps disposal location near you or call Safe Needle Disposal at 1-800-643-1643.

Step 26
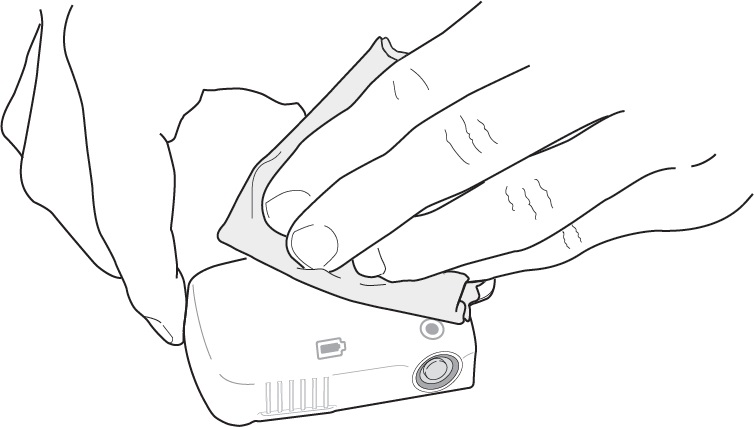
Wipe the white Reusable Unit with a clean, water-damp cloth to remove visible dirt right after use. Let dry completely before storing.
If needed, a mild detergent, like dish soap, may be added to the damp cleaning cloth.
Do not use harsh cleaners that contain bleach, alcohol, ammonia, or other solvents. These cleaners may damage the Reusable Unit.
Do not submerge the Reusable Unit in liquids or spray liquids directly on the surface. It contains parts that should not get wet.
Step 27
Store the Reusable Unit, Charger, and any remaining Lasix ONYU Kits for next use.
- Keep at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C).
- Do not refrigerate or freeze.
- Keep in a dark place to protect from light.
- Keep dry.
- Keep extra Prefilled Cartridges and Disposable Units in their original packaging until it is time to use them.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
3: Troubleshooting
Customer Service Contact Information
Contact Information:
SQ Innovation, Inc.
Burlington, MA 01803, USA
Phone: 1-855-452-7496 (1-855-4LASIX6)
www.Lasix-ONYU.comLights and Tones Table
Checking the Reusable Unit Battery
If the Battery Light is charged, the white Reusable Unit is able to deliver a full infusion. If the Battery Light is low, the Reusable Unit cannot deliver a full infusion and it needs to be charged.
Always charge the Reusable Unit before you use a new Disposable Unit (before each infusion).
Charging may take up to 20 minutes.
A. Battery Light is flashing blue
The Reusable Unit battery is being charged. Wait until the Battery Light turns solid blue before using the Lasix ONYU Infusor.
B. Battery Light is solid blue
The Reusable Unit battery is done charging and ready to use.
C. Battery Light is solid red before preparing the Lasix ONYU Infusor for use
The Reusable Unit battery is low and cannot deliver a full infusion.
Charge the Reusable Unit:
- Plug the Charger into the back of the Reusable Unit.
- Plug the other end of the Charger into a power outlet.
- Wait until the Battery Light turns solid blue.
D. Battery Light is solid red when the Disposable Unit and Reusable Unit are connected
The Reusable Unit battery is low and the Lasix ONYU Infusor will not start.
- Pull apart the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit.
- Put the Disposable Unit to the side while you charge the Reusable Unit (do not remove the Prefilled Cartridge from the Disposable Unit).
- Charge the Reusable Unit:
- Plug the Charger into the back of the Reusable Unit.
- Plug the other end of the Charger into a power outlet.
- Wait until the Battery Light turns solid blue.
- Follow instructions beginning with Step 10 in Prepare the Lasix ONYU Infusor to connect the Reusable Unit to the Disposable Unit.
The Reusable Unit Has Expired
When the Reusable Unit expires, the Lasix ONYU Infusor can no longer be used. The Reusable Unit needs to be replaced.
The Reusable Unit is expired if it does not light up at all after charging or the Status Light and the Battery Light are both solid red when the Reusable Unit is plugged in or when the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit are pulled apart.
Call 1-855-452-7496 for a replacement Reusable Unit, which will be shipped overnight when possible. Also call your healthcare provider.
The Reusable Unit should not be thrown away (disposed of) with household waste and should not be recycled in your local recycling program. Throw away the Reusable Unit according to local regulations for electronic devices with lithium batteries.
Alternatively, the Reusable Unit may be returned to SQ Innovation, free of charge, for proper and safe recycling. Go to Chapter 4 for more information.
The Status Light is Flashing Red
When an error happens inside the Lasix ONYU Infusor or the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit have been connected for 7 hours without starting infusion, the Status Light will flash red and you will hear a repeating Alarm Tone (2 short beeps).
This can happen in the following 2 situations:
- Before the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit are connected, see Section A below for what to do.
- After the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit are connected, see Section B below for what to do.
A. If the Status Light flashes red before the white Reusable Unit is connected to the green Disposable Unit, a device error happened. Follow the instructions below:
- Unplug the Charger (if it is connected).
- Press and hold the Start/Stop Button until the flashing red light turns off (1 second).
- Plug the charger into the Reusable Unit and a power outlet. Check the Lights:
- If the Battery Light is solid or flashing blue, the Reusable Unit is ready to use. Continue with Step 2 in Get Ready for the Infusion.
- If the Status Light is still flashing red, the Reusable Unit cannot be used. Call 1-855-452-7496 for a replacement Reusable Unit, which will be shipped overnight when possible. Also call your healthcare provider.
B. If the Status Light flashes red after connecting the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit, a device error happened or the Lasix ONYU Infusor timed out (because it was connected for 7 hours without starting the infusion). The Lasix ONYU Infusor cannot be used. Follow the steps below:
- If the Lasix ONYU Infusor is on the body, remove it from the stomach.
- If you can see the needle, do not touch the needle because you could get an injury.
- Pull apart the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit.
-
Throw away the Disposable Unit with the Prefilled Cartridge into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container (see Step 25 in Throw Away (Disposal), Cleaning, and Storage). You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Determine the next steps:
- If the error happened before the infusion was started, get a new Lasix ONYU Kit and start over at Step 1 in Get Ready for the Infusion.
- If the error happened after the infusion was started, call your healthcare provider to see what to do because some of the medicine was not delivered.
You Can See the Needle
You may see the needle in one of these situations:
- You press the Start/Stop Button before the Lasix ONYU Infusor is placed on the stomach, see Section A below for what to do.
- You remove the Infusor before infusion is done or the Lasix ONYU Infusor falls off during the 5-hour infusion, see Section B below for what to do.
- The needle did not retract automatically after infusion, see Section C below for what to do.
Do not touch the needle because you could get an injury.
A. If you see the needle before the Lasix ONYU Infusor is placed on the stomach, you should start over with a new Lasix ONYU Kit. Follow the steps below:
- Press and hold the Start/Stop Button (4 seconds) until the Status Light flashes red and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps).
- Pull apart the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit.
-
Throw away the Disposable Unit with Prefilled Cartridge into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Return to Step 1 in Get Ready for the Infusion to start over with a new Lasix ONYU Kit. Be careful not to press the Start/Stop Button until after the Lasix ONYU Infusor is on the stomach.
B. If you see the needle because the Lasix ONYU Infusor fell off or it was removed before infusion was done, follow the steps below:
You should not stick the Infusor back on the stomach because it may fall off again.
- Press and hold the Start/StopButton (4 seconds) until the Status Light flashes red and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps).
- Pull apart the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit.
-
Throw away the Disposable Unit with the Prefilled Cartridge into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Call your healthcare provider to see what to do because some of the medicine was not delivered.
C. If you see the needle after the 5-hour infusion is done, the needle did not retract automatically. Follow the steps below:
- Carefully pull apart the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit.
-
Throw away the Disposable Unit with the Prefilled Cartridge into an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Continue with Step 26 and Step 27 in Throw Away (Disposal), Cleaning, and Storage to clean and store the Reusable Unit.
How to Stop the Lasix ONYU Infusor EarlyFollow these steps below if you need to stop the Lasix ONYU Infusor before the 5-hour infusion is finished. Do not remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from the stomach before stopping it. Removing the Lasix ONYU Infusor from the body before stopping it will expose the needle, and you could get an injury if you touch it.
-
Press and hold the Start/StopButton (4 seconds) until you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps) and the Status Light is flashing red.
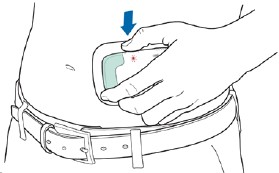
-
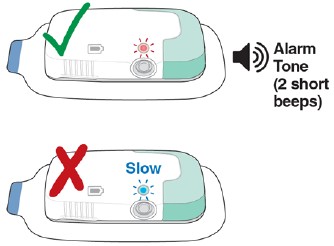
Confirm infusion was stopped. Check the Status Light:
- If the Status Light is flashing red and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps), infusion has stopped. The needle will retract shortly after you press the Start/Stop Button.
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing slow, the infusion did not stop. Repeat Step 1 in How to Stop the Lasix ONYU Infusor Early above.
- The infusion cannot be restarted. You must remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor and contact your healthcare provider. Follow the steps below:
- Remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from your stomach.
- Pull apart the white Reusable Unit and green Disposable Unit.
- Throw away the Disposable Unit withthe Prefilled Cartridge in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Call your healthcare provider because you did not get all of the medicine.
You Did Not Urinate (Pee) Much During Infusion
The Lasix ONYU Infusor delivers a diuretic medicine which should make you urinate a lot. If you do not urinate a lot (at least 2 times during the 5-hour infusion), there are two reasons this could have happened:
- The diuretic medicine, Lasix ONYU, was not effective for you, or
- The Lasix ONYU Infusor did not work properly.
In either case, it is important that you call your healthcare provider. Follow the steps below to determine whether the Lasix ONYU Infusor worked and if all the medicine was delivered:
- Remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from your stomach.
-
Look at the window on the back of the Lasix ONYU Infusor:
- If the middle of the window is all gray (whole gray stopper is visible with very little or no liquid), all the medicine was delivered. The Lasix ONYU Infusor worked.
- If you see anything else (like a lot of liquid, a large bubble in the liquid, no gray stopper, or only part of the gray stopper), some of the medicine was not delivered. You did not get a full infusion.
- Check your stomach: If you see or feel a lot of liquid on your stomach, you may not have received a full infusion due to the medicine leaking.
The Reusable Unit Does Not Light Up
This can happen in the following situations:
- The Reusable Unit has not been used for a long time or the Reusable Unit is expired, see Section A below for what to do.
- The Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit have been connected for more than 7 hours and infusion has not been started, see Section B below for what to do.
A. If the white Reusable Unit does not light up, try charging it, even if it has recently been charged. The Battery Light on the Reusable Unit must always be solid blue before connecting it to the Disposable Unit.
Follow the steps below:
- Plug the Charger into the back of the Reusable Unit and plug the other end of the Charger into a power outlet.
- Wait 20 minutes.
- Disconnect the Charger from the Reusable Unit and power outlet.
-
Check the Battery Light:
- If the Battery Light is solid blue, the Reusable Unit is ready to use.
- If the Battery Light did not light up after 20 minutes of charging, the Reusable Unit expired. Call 1-855-452-7496 for a replacement Reusable Unit, which will be shipped overnight when possible. Also call your healthcare provider. Go to Troubleshooting: The Reusable Unit Has Expired for more information.
- If you see other lights, go to Troubleshooting: Lights and Tones Table.
B. If the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit have been connected for more than 7 hours and infusion has not been started, the Lasix ONYU Infusor will automatically time out. The Lasix ONYU Infusor cannot be restarted.
Follow the steps below:
- If the Lasix ONYU Infusor is on the body, remove the Lasix ONYU Infusor from your stomach.
- If you can see the needle, do not touch the needle because you could get an injury.
- Pull apart the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit.
-
Throw away the Disposable Unit with the Prefilled Cartridge in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. You should not throw away the Disposable Unit in the household trash.
- Do not save and re-use the Disposable Unit or Prefilled Cartridge as the medicine may be contaminated. They are for one-time use only.
- Get a new Lasix ONYU Kit and start over at Step 1 in Get Ready for the Infusion.
The Lasix ONYU Infusor Will Not Start the Infusion
You press the Start/Stop Button and the infusion does not start.
This can happen in the following situations:
- The Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit are not properly connected, see Section A below for what to do.
- The Reusable Unit is powered off and both the Battery Light and Status Light are off, go to Troubleshooting: The Reusable Unit Does Not Light Up for what to do.
- A device error has happened and the Status Light is flashing red, go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red for what to do.
A. If the infusion does not start, follow the steps below:
- Firmly push the Reusable Unit and Disposable Unit together. There should be no gap or space between the parts when they are properly connected.
- Check the Status Light:
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing fast and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the Lasix ONYU Infusor is properly connected. The Lasix ONYU Infusor is ready to deliver infusion.
If the Lasix ONYU Infusor is not on the body, go to Step 12 in Prepare the Application site.
If the Lasix ONYU Infusor is on the body, go to Step 17 in Start the infusion. - If the Status Light is flashing red and you hear the Alarm Tone (2 short beeps), there is a problem with the Infusor. Go to Troubleshooting: The Status Light is Flashing Red to see what to do.
- If the Status Light is blue and flashing fast and you hear the OK Tone (1 long beep), the Lasix ONYU Infusor is properly connected. The Lasix ONYU Infusor is ready to deliver infusion.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 10/2025
SP110004US
Symbols
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LASIX ONYU
furosemide injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 81137-001 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FUROSEMIDE (UNII: 7LXU5N7ZO5) (FUROSEMIDE - UNII:7LXU5N7ZO5) FUROSEMIDE 30 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) BETADEX SULFOBUTYL ETHER SODIUM (UNII: 2PP9364507) 300 mg in 1 mL TROMETHAMINE (UNII: 023C2WHX2V) 3 mg in 1 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 81137-001-15 1 in 1 KIT 12/01/2025 1 1 in 1 CARTON 1 2.67 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package 2 NDC: 81137-001-35 3 in 1 KIT 06/15/2026 2 1 in 1 CARTON 2 2.67 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA217294 12/01/2025 Labeler - SQ Innovation, Inc. (117146655) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sharp Sterile Manufacturing, LLC 079589218 manufacture(81137-001) , label(81137-001) , pack(81137-001)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.