VETMEDIN SOLUTION- pimobendan solution
Vetmedin Solution by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Vetmedin Solution by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Caution:
-
Description:
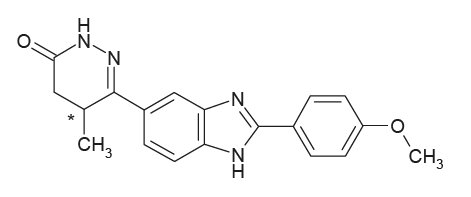
VETMEDIN® Solution (pimobendan oral solution) is a clear to yellow to slightly green to slightly brown aqueous solution containing 1.5 mg/mL pimobendan. Pimobendan, a benzimidazole-pyridazinone derivative, is a non-sympathomimetic, non-glycoside inotropic drug with vasodilatative properties. The chemical name of pimobendan is 4,5-dihydro-6-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-5-yl]-5-methyl-3(2H)-pyridazinone.
The structural formula of pimobendan is:
-
Indications:
VETMEDIN Solution (pimobendan oral solution) is indicated for the management of the signs of mild, moderate, or severe congestive heart failure in dogs due to clinical myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) or dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). VETMEDIN Solution is indicated for use with concurrent therapy for congestive heart failure (e.g., furosemide, etc.) as appropriate on a case-by-case basis.
-
Dosage and Administration:
Always provide the Client Information Sheet to the dog owner with each prescription.
VETMEDIN Solution should be administered orally at a total daily dose of 0.23 mg/lb (0.5 mg/kg) body weight. The total daily dose should be divided into 2 equal portions administered approximately 12 hours apart (i.e., morning and evening).
The syringe is calibrated to deliver the appropriate morning or evening dose when drawn to the dog’s nearest weight in pounds.
VETMEDIN Solution should be administered directly into the mouth. Do not mix into food.
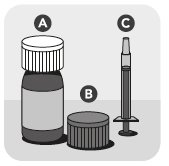
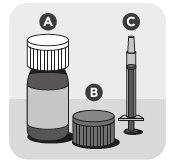
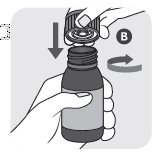
VETMEDIN Solution includes an amber glass bottle sealed with a white cap (A), an orange cap with integrated plastic plug (B), and an orange dosing syringe (C).
Do not shake the bottle before or during use to avoid foaming.
VETMEDIN Solution should be administered using the orange dosing syringe provided in the package. At the time of first use, the white cap should be removed and discarded. Once the orange cap has been screwed onto the bottle and the integrated plastic plug is in place, the dosing syringe fits onto the plug. The dosing syringe has 1 pound incremental marks. Each dose should be rounded to the nearest 1 pound increment (e.g., a dose for a dog 5.5 lb or greater should be rounded up to 6 lb).
An in-use video demonstration can be found using the URL https://go.boehringer.com/q7lKE or the QR code below.
Close the bottle tightly using the orange cap. After administration, clean the outside of the syringe by wiping with a clean, dry cloth or tissue after each use. If the syringe clogs, rinse without removing the plunger by using water and wiping the outside of the syringe dry with a clean cloth or tissue.
- Contraindications:
-
Warnings:
User Safety Warnings: Not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans.
Wash hands after use. This product may cause eye irritation. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, flush affected eye(s) immediately and thoroughly with water. If wearing contact lenses, flush the eyes first with water and then remove the lens(es) and continue to flush thoroughly with water. If eye irritation continues, seek medical advice and provide this product information to the physician.
Exposure to product may induce a local or systemic allergic reaction in sensitized individuals.
Animal Safety Warnings: Keep VETMEDIN Solution in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
Only for use in dogs with clinical evidence of heart failure. At 3 and 5 times the recommended dosage, administered over a 6-month period of time, pimobendan caused an exaggerated hemodynamic response in the normal dog heart, which was associated with cardiac pathology (See Target Animal Safety).
-
Precautions:
The safety of VETMEDIN Solution has not been established in dogs with asymptomatic heart disease or in heart failure caused by etiologies other than MMVD or DCM. The safe use of VETMEDIN Solution has not been evaluated in dogs younger than 6 months of age, dogs with congenital heart defects, dogs with diabetes mellitus or other serious metabolic diseases, dogs used for breeding, or pregnant or lactating bitches.
-
Adverse Reactions:
The safety and effectiveness of VETMEDIN Solution was established by demonstrating bioequivalence with VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets. (See Clinical Pharmacology).
Pre-Approval Experience: Clinical findings/adverse reactions were recorded in a 56-day field study of dogs with congestive heart failure (CHF) due to MMVD (256 dogs) or DCM (99 dogs). Dogs were treated with either VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets (175 dogs) or the active control enalapril maleate (180 dogs). Dogs in both treatment groups received additional background cardiac therapy (See Effectiveness for details and the difference in digoxin administration between treatment groups).
The VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets group had the following prevalence (percent of dogs with at least one occurrence) of common adverse reactions/new clinical findings (not present in a dog prior to beginning study treatments): poor appetite (38%), lethargy (33%), diarrhea (30%), dyspnea (29%), azotemia (14%), weakness and ataxia (13%), pleural effusion (10%), syncope (9%), cough (7%), sudden death (6%), ascites (6%), and heart murmur (3%). Prevalence was similar in the active control group.
The prevalence of renal failure was higher in the active control group (4%) compared to the VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets group (1%).
Adverse reactions/new clinical findings were seen in both treatment groups and were potentially related to CHF, the therapy of CHF, or both. The following adverse reactions/new clinical findings are listed according to body system and are not in order of prevalence:
CHF death, sudden death, chordae tendineae rupture, left atrial tear, arrhythmias overall, tachycardia, syncope, weak pulses, irregular pulses, increased pulmonary edema, dyspnea, increased respiratory rate, coughing, gagging, pleural effusion, ascites, hepatic congestion, decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, melena, weight loss, lethargy, depression, weakness, collapse, shaking, trembling, ataxia, seizures, restlessness, agitation, pruritus, increased water consumption, increased urination, urinary accidents, azotemia, dehydration, abnormal serum electrolyte, protein, and glucose values, mild increases in serum hepatic enzyme levels, and mildly decreased platelet counts.
See Table 1 for mortality due to CHF (including euthanasia, natural death, and sudden death) and for the development of new arrhythmias (not present in a dog prior to beginning study treatments) by treatment group and type of heart disease (MMVD or DCM) in the 56-day field study.
Table 1: CHF Death and New Arrhythmias in the 56-Day Field Study
VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets Group
Active Control Group
Dogs that died due to CHF
14.3%
n = 175
14.4%
n = 180
9 of 126 dogs with MMVD
16 of 130 dogs with MMVD
16 of 49 dogs with DCM
10 of 50 dogs with DCM
Dogs that developed new arrhythmiasa
39.4%
n = 175
45.0%
n = 180
45 of 126 dogs with MMVD
59 of 130 dogs with MMVD
24 of 49 dogs with DCM
22 of 50 dogs with DCM
a New arrhythmias included supraventricular premature beats and tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block, sinus bradycardia, ventricular premature beats and tachycardia, and bundle branch block.
Following the 56-day masked field study, 137 dogs in the VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets group were allowed to continue on VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets in an open-label extended-use study without restrictions on concurrent therapy. The adverse reactions/new clinical findings in the extended-use study were consistent with those reported in the 56-day study, with the following exception: One dog in the extended-use study developed acute cholestatic liver failure after 140 days on VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets and furosemide.
Post-Approval Experience (2023):
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting for VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA/CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events reported in dogs are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency:
Diarrhea, lethargy, anorexia, emesis, cough, tachycardia, ataxia, dyspnea, convulsion, elevated liver enzymes (ALT, ALP), increased BUN and/or creatinine, tremors, hyperactivity, pruritus, syncope, allergic reactions (including allergic edema/facial edema, erythema, and hives), hypotension, hypertension, coagulation abnormalities (including thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage and petechia), and hyperglycemia (with or without diabetes mellitus).
Death has been reported in some cases.
-
Contact Information:
To report suspected adverse reactions, to obtain a Safety Data Sheet (SDS), or for technical assistance, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. at 1-888-637-4251. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact the FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or at https://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
- Information for Dog Owners:
-
Clinical Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action: Pimobendan exerts a stimulatory myocardial effect by a dual mechanism of action consisting of an increase in calcium sensitivity of cardiac myofilaments and inhibition of phosphodiesterase (Type III). Pimobendan exhibits vasodilating activity by inhibiting phosphodiesterase III activity.
Pharmacodynamics: In normal dogs instrumented with left ventricular (LV) pressure transducers, pimobendan increased LV dP/dtmax (a measure of contractility of the heart) in a dose dependent manner between 0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg orally. The effect was still present 8 hours after dosing. There was a delay between peak blood levels of pimobendan and active metabolite and the maximum physiologic response (peak LV dP/dtmax). Blood levels of pimobendan and active metabolite began to drop before maximum contractility was seen. Repeated oral administration of pimobendan did not result in evidence of tachyphylaxis (decreased positive inotropic effect) or drug accumulation (increased positive inotropic effect). Laboratory studies indicate that the positive inotropic effect of pimobendan may be attenuated by the concurrent use of a β-adrenergic blocker or a calcium channel blocker.
Pharmacokinetics: VETMEDIN Solution was compared to VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets in a randomized, masked, four-period, two-sequence single-dose full replicative cross-over bioequivalence study. Twenty-four Beagle dogs (12 male/12 female), ranging in age from 1 to 10 years and weighing between 9.0 and 16.5 kg at enrollment were administered a 5 mg total dose of VETMEDIN Solution and VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets on two separate occasions. Using the mixed scaling approach, reference-scaled average bioequivalence (RSABE) was demonstrated. Mean pharmacokinetic parameters from this study are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Arithmetic mean (± standard deviation) pimobendan plasma pharmacokinetic parameters after a 5 mg (0.29 – 0.41 mg/kg) oral administration of VETMEDIN Solution to male and female Beagle dogs in a laboratory bioequivalence study.
Parameter
Estimate
N
Cmax (ng/mL)
24.0 ± 18.3
48
Tmaxa (h)
0.75 (0.25 – 3)
48
AUClast (h*ng/mL)
38.8 ± 26.2
48
AUCinf (h*ng/mL)
39.0 ± 26.5
47
t½ (h)
0.9 ± 0.4
47
aMedian (Range)
Cmax =maximum plasma concentration
Tmax = time to maximum plasma concentration
AUClast = area under the curve from the time of dosing to the last quantifiable plasma concentration
AUCinf = area under the curve from the time of dosing extrapolated to infinity
t½ = half-life
N = observations
The bioequivalence study also demonstrated similar AUC and Cmax of the active metabolite between VETMEDIN Solution and VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets. Pimobendan is oxidatively demethylated to a pharmacologically active metabolite, which is then conjugated with sulfate or glucuronic acid and excreted mainly via feces.
The AUClast of VETMEDIN Solution is 37% lower and the Cmax is 39% lower in the fed state compared to the fasted state (N=12 dogs). Statistical comparisons, where appropriate, were made using natural log transformed data and geometric means.
-
Effectiveness:
The effectiveness of VETMEDIN Solution was established by demonstrating bioequivalence with VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets. (See Clinical Pharmacology).
In a double-masked, multi-site, 56-day field study, 355 dogs with modified New York Heart Association‡ (NYHA) Class II, III, or IV CHF due to MMVD or DCM were randomly assigned to either the active control (enalapril maleate) or the VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets treatment group. Of the 355 dogs, 52% were male and 48% were female; 72% were diagnosed with MMVD and 28% were diagnosed with DCM; 34% had Class II, 47% had Class III, and 19% had Class IV CHF. Dogs ranged in age and weight from 1 to 17 years and 3.3 to 191 lbs, respectively. The most common breeds were mixed breed, Doberman Pinscher, Cocker Spaniel, Miniature/Toy Poodle, Maltese, Chihuahua, Miniature Schnauzer, Dachshund, and Cavalier King Charles Spaniel. The 180 dogs (130 MMVD, 50 DCM) in the active control group received enalapril maleate (0.5 mg/kg once or twice daily), and all but 2 received furosemide. Per protocol, all dogs with DCM in the active control group received digoxin. The 175 dogs (126 MMVD, 49 DCM) in the VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets group received pimobendan (0.5 mg/kg/day divided into 2 portions that were not necessarily equal, and the portions were administered approximately 12 hours apart), and all but 4 received furosemide. Digoxin was optional for treating supraventricular tachyarrhythmia in either treatment group, as was the addition of a β-adrenergic blocker if digoxin was ineffective in controlling heart rate. After initial treatment at the clinic on Day 1, dog owners were to administer the assigned product and concurrent medications for up to 56±4 days.
The determination of effectiveness (treatment success) for each case was based on improvement in at least 2 of the 3 following primary variables: modified NYHA classification, pulmonary edema score by a masked veterinary radiologist, and the investigator’s overall clinical effectiveness score (based on physical examination, radiography, electrocardiography, and clinical pathology). Attitude, pleural effusion, coughing, activity level, furosemide dosage change, cardiac size, body weight, survival, and owner observations were secondary evaluations contributing information supportive to product effectiveness and safety.
Based on protocol compliance and individual case integrity, 265 cases (134 VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets, 131 active control) were evaluated for treatment success on Day 29. See Table 3 for effectiveness results.
Table 3: Effectiveness Results for the 56-Day Field Study
VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets Group
Active Control Group
Treatment Success on
Day 29
80.7%
n = 134
76.3%
n = 131
88 of 101 dogs with MMVD
77 of 100 dogs with MMVD
20 of 33 dogs with DCM
23 of 31 dogs with DCM
Treatment Success on
Day 56
71.1%
n = 113
67.2%
n = 110
66 of 85 dogs with MMVD
56 of 85 dogs with MMVD
13 of 28 dogs with DCM
17 of 25 dogs with DCM
No increase in furosemide dose between Day 1 and Day 29
78.3%
n = 130
68.6%
n = 126
At the end of the 56-day study, dogs in the VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets group were enrolled in an unmasked field study to monitor safety under extended use, without restrictions on concurrent medications.
VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets were used safely in dogs concurrently receiving furosemide, digoxin, enalapril, atenolol, spironolactone, nitroglycerin, hydralazine, diltiazem, antiparasitic products (including heartworm disease prevention), antibiotics (metronidazole, cephalexin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, fluoroquinolones), topical ophthalmic and otic products, famotidine, theophylline, levothyroxine sodium, diphenhydramine, hydrocodone, metoclopramide, and butorphanol, and in dogs on sodium-restricted diets.
‡ The modified NYHA classification was historically used to stage dogs with heart disease.
A dog with modified NYHA Class II heart failure has fatigue, shortness of breath, coughing, etc. apparent when ordinary exercise is exceeded.
A dog with modified NYHA Class III heart failure is comfortable at rest, but exercise capacity is minimal.
A dog with modified NYHA Class IV heart failure has no capacity for exercise and disabling clinical signs are present even at rest.
-
Target Animal Safety:
The safety of VETMEDIN Solution was established by demonstrating bioequivalence with VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets. (See Clinical Pharmacology).
In a laboratory study, VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets were administered to 6 healthy Beagles per treatment group at 0 (control), 1, 3, and 5 times the recommended dosage for 6 months. See Table 4 for cardiac pathology results. The cardiac pathology/histopathology noted in the 3X and 5X dose groups is typical of positive inotropic and vasodilator drug toxicity in normal dog hearts, and is associated with exaggerated hemodynamic responses to these drugs. None of the dogs developed signs of heart failure and there was no mortality.
Table 4: Incidence of Cardiac Pathology/Histopathology in the Six-month Safety Study
Severe left ventricular hypertrophy with
multifocal subendocardial ischemic lesions
One 3X and two 5X dogsa
Moderate to marked myxomatous thickening of the mitral valves
Three 5X dogs
Myxomatous thickening of the chordae
tendineae
One 3X and two 5X dogs
Endocardial thickening of the left ventricular outflow tract
One 1X, two 3X, and two 5X dogs
Left atrial endocardial thickening (jet lesions) in 2 of the dogs that developed murmurs of mitral valve insufficiency
One 3X and one 5X dog
Granulomatous inflammatory lesion
in the right atrial myocardium
One 3X dog
aMost of the gross and histopathologic findings occurred in these three dogs
Murmurs of mitral valve insufficiency were detected in one 3X (Day 65) and two 5X dogs
(Days 135 and 163). These murmurs (grades II-III of VI) were not associated with clinical signs.
Indirect blood pressure was unaffected by VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets at the label dose (1X). Mean diastolic blood pressure was decreased in the 3X group (74 mmHg) compared to the control group (82 mmHg). Mean systolic blood pressure was decreased in the 5X group (117 mmHg) compared to the control group (124 mmHg). None of the dogs had clinical signs of hypotension.
On 24-hour Holter monitoring, mean heart rate was increased in the 5X group (101 beats/min) compared to the control group (94 beats/min). Not counting escape beats, the 3X and 5X groups had slightly higher numbers of isolated ventricular ectopic complexes (VEs). The maximum number of non-escape VEs recorded either at baseline or in a control group dog was 4 VEs/24 hours. At either Week 4 or Week 20, three 3X group dogs had maximums of 33, 13, and 10 VEs/24 hours, and two 5X group dogs had maximums of 22 and 9 VEs/24 hours. One 1X group dog with no VEs at baseline had 6 VEs/24 hours at Week 4 and again at Week 20. Second-degree atrioventricular heart block was recorded in one 3X group dog at Weeks 4 and 20, and in one dog from each of the 1X and 5X groups at Week 20. None of the dogs had clinical signs associated with these electrocardiogram changes.
Treatment was associated with small differences in mean platelet counts (decreased in the 3X and 1X groups), potassium (increased in the 5X group), glucose (decreased in the 1X and 3X groups), and maximum blood glucose in glucose curves (increased in the 5X group).
All individual values for these variables were within the normal range. Three 1X and one 5X group dogs had mild elevations of alkaline phosphatase (less than two times normal).
Loose stools and vomiting were infrequent and self-limiting.
- Storage Information:
-
How Supplied:
VETMEDIN Solution (pimobendan oral solution): Available as 1.5 mg/mL, 50 mL fill volume, is supplied in a 60 mL amber glass bottle sealed with a white cap, an orange in-use cap with integrated plastic plug, and an orange dosing syringe.
NDC: 0010-4131-01
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Client Information Sheet
Vetmedin® Solution
(pimobendan oral solution)
1.5 mg/mL
Cardiac drug for oral use in dogs only
The Client Information Sheet contains important information about VETMEDIN® Solution
(pimobendan oral solution). You should read this information before you start giving VETMEDIN Solution and review it each time the prescription is refilled as there may be new information. This sheet does not take the place of instructions from your veterinarian. Talk with your veterinarian if you do not understand any of this information or if you want to know more about VETMEDIN Solution.
What is VETMEDIN Solution?
VETMEDIN Solution is used to manage the signs of congestive heart failure in dogs.
What should I tell my veterinarian about my dog before starting VETMEDIN Solution?
- Tell your veterinarian about other medications your pet is taking, including prescription drugs, over the counter drugs, heartworm preventives, flea & tick products, and vitamins and supplements, including herbal medications.
- Tell your veterinarian if your dog is pregnant, nursing, or you intend to breed him/her.
- Tell your veterinarian if your dog has any other serious health conditions.
- Tell your veterinarian if your dog has or develops any signs of disease progression, such as labored breathing, increased resting respiratory rates, fainting, abnormal heart rhythms, and coughing.
Talk to your veterinarian about the risks and benefits of giving VETMEDIN Solution to your dog.
What are some of the possible side effects of VETMEDIN Solution?
VETMEDIN Solution may cause side effects, even at the prescribed dose. Contact your veterinarian immediately if your dog develops a serious or concerning medical problem or side effect while taking VETMEDIN Solution.
The most common side effects reported in dogs treated with VETMEDIN Chewable Tablets are poor appetite, lack of energy (lethargy), diarrhea, and difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
To report a suspected adverse reaction (side effect), to obtain a Safety Data Sheet (SDS), or for technical assistance, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. at 1-888-637-4251.
For additional information about reporting side effects for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or https://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
How do I give VETMEDIN Solution to my dog?
VETMEDIN Solution should be given to your dog directly in their mouth (orally) twice a day, about 12 hours apart. Do not mix into food.
Follow your veterinarian’s instructions for how much VETMEDIN Solution to give your dog. Because the dose is based on body weight, the dose you are prescribed to give your dog may be rounded to the nearest pound weight mark on the dosing syringe.
Your package of VETMEDIN Solution includes an amber glass bottle sealed with a white cap (A), an orange cap with integrated plastic plug (B), and an orange dosing syringe (C).
Do not shake the bottle before or during use to avoid foaming.
Give VETMEDIN Solution using the orange dosing syringe provided in the package. The dosing syringe fits onto the plug and has 1 pound marks to use for measuring the dose.
Please read the following instructions carefully prior to first use of VETMEDIN Solution.
A video demonstration can also be found using the URL https://go.boehringer.com/q7lKE or the QR code below.
At the time of first use
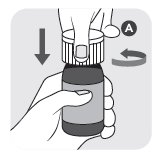
- 1) Open bottle in an upright position by pressing down on the white child resistant cap (A) and simultaneously turning the cap counterclockwise. Discard the white cap (A).
- 2) Close the bottle with the orange cap (B) by turning the cap clockwise. The orange cap contains a plastic plug which should automatically attach to the bottle opening. Ensure the cap is tightly closed to appropriately insert plug into the top of the bottle.
To dose your dog
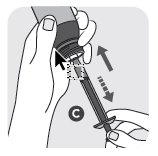
- 3) Remove the orange cap (B) from the bottle by pressing down on the orange child resistant cap and simultaneously turning the cap counterclockwise. Gently push the end of the orange dosing syringe (C) onto the plug. Turn the bottle and syringe upside down. Pull the plunger out and fill the dosing syringe to the dose weight prescribed by your veterinarian. Turn the bottle upright and remove the dosing syringe from the bottle. Replace the orange cap (B) onto the bottle and close tightly.
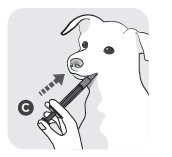
- 4) Put the end of the dosing syringe (C) into your dog´s mouth and push the plunger to give the prescribed dose.
- 5) After dosing, clean the outside of the syringe by wiping with a clean, dry cloth or tissue after each use. If the syringe clogs, rinse without removing the plunger by using water and wiping the outside of the syringe dry with a clean cloth or tissue.
If your dog vomits after being given VETMEDIN Solution, please contact your veterinarian. Unless directed otherwise, do not give additional VETMEDIN Solution again until the next scheduled dose.
What if my dog receives more VETMEDIN Solution than what is prescribed?
Contact your veterinarian as soon as possible.
What else should I know about VETMEDIN Solution?
VETMEDIN Solution is not for use in humans. Keep this and all medications out of reach of children.
Wash hands after use. This product may cause eye irritation. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, flush affected eye(s) immediately and thoroughly with water. If wearing contact lenses, flush the eyes first with water and then remove the lens(es) and continue to flush thoroughly with water. If eye irritation continues, seek medical advice and provide this product information to the physician.
Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans. It is important to show the treating physician a copy of the package insert, label, or this client information sheet. VETMEDIN Solution is a non-sympathomimetic, non-glycoside inotropic drug with vasodilatative properties.
This client information sheet contains a summary of important information about VETMEDIN Solution. For more detailed information about VETMEDIN Solution, talk with your veterinarian.
How should I store VETMEDIN Solution?
VETMEDIN Solution should be stored at room temperature at or below 77°F (25°C). Temperatures as high as 86°F (30°C) can be acceptable for short periods of time. Do not shake. Once the bottle is opened, use the contents within 8 weeks.
Keep VETMEDIN Solution in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
Revised 12/2023
- Principal Display Panel – 50 mL display carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VETMEDIN SOLUTION
pimobendan solutionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0010-4131 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PIMOBENDAN (UNII: 34AP3BBP9T) (PIMOBENDAN - UNII:34AP3BBP9T) PIMOBENDAN 1.5 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0010-4131-01 1 in 1 CARTON 1 50 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141575 11/11/2024 Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. (007134091)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.