VIVITROL- naltrexone kit
VIVITROL by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
VIVITROL by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alkermes, Inc., Packaging Coordinators, LLC, Sharp Corporation, Oso Biopharmaceutcals. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIVITROL® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VIVITROL.
VIVITROL (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension), for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1984INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- VIVITROL contains naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, and is indicated for the treatment of alcohol dependence in patients who are able to abstain from alcohol in an outpatient setting prior to initiation of treatment with VIVITROL. Patients should not be actively drinking at the time of initial VIVITROL administration (1.1).
- VIVITROL is indicated for the prevention of relapse to opioid dependence, following opioid detoxification (1.2).
- VIVITROL should be part of a comprehensive management program that includes psychosocial support (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider. The recommended dose of VIVITROL is 380 mg delivered intramuscularly (IM) as a gluteal injection, every 4 weeks or once a month, alternating buttocks for each subsequent injection, using the carton components provided (2 and 16.1).
Prior to initiating VIVITROL, an opioid-free duration of a minimum of 7–10 days is recommended for patients, to avoid precipitation of opioid withdrawal that may be severe enough to require hospitalization (5.3).
VIVITROL must not be administered intravenously or subcutaneously.
The entire dose pack should be stored in the refrigerator (2 to 8°C, 36 to 46°F) (2.5 and 16.1).
Do not expose the product to temperatures above 25°C (77°F). VIVITROL should not be frozen (2.5).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
VIVITROL is an injectable suspension containing 380 mg of naltrexone in a microsphere formulation and 4 mL diluent (3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
VIVITROL is contraindicated in:
- Patients receiving opioid analgesics (5.3).
- Patients with current physiologic opioid dependence (5.3).
- Patients in acute opioid withdrawal (5.3).
- Any individual who has failed the naloxone challenge test or has a positive urine screen for opioids (4).
- Patients who have previously exhibited hypersensitivity to naltrexone, polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG), carboxymethylcellulose, or any other components of the diluent (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Vulnerability to Opioid Overdose: Following VIVITROL treatment opioid tolerance is reduced from pretreatment baseline, and patients are vulnerable to potentially fatal overdose at the end of a dosing interval, after missing a dose, or after discontinuing VIVITROL treatment. Attempts to overcome blockade may also lead to fatal overdose (5.1).
- Injection Site Reactions: VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider. In some cases, injection site reactions may be very severe. Some cases of injection site reactions required surgical intervention (5.2).
- Precipitation of Opioid Withdrawal: Opioid-dependent and opioid-using patients, including those being treated for alcohol dependence, should be opioid-free before starting VIVITROL treatment, and should notify healthcare providers of any recent opioid use. An opioid-free duration of a minimum of 7-10 days is recommended for patients to avoid precipitation of opioid withdrawal that may be severe enough to require hospitalization. (5.3).
- Hepatotoxicity: Cases of hepatitis and clinically significant liver dysfunction were observed in association with VIVITROL treatment during the clinical development program and in the postmarketing period. Discontinue use of VIVITROL in the event of symptoms or signs of acute hepatitis (5.4).
- Depression and Suicidality: Monitor patients for the development of depression or suicidal thinking (5.5).
- When Reversal of VIVITROL Blockade Is Required for Pain Management: In an emergency situation in patients receiving VIVITROL, suggestions for pain management include regional analgesia or use of non-opioid analgesics (5.6).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse events seen most frequently in association with VIVITROL therapy for alcohol dependence (i.e, those occurring in ≥5% and at least twice as frequently with VIVITROL than placebo) include nausea, vomiting, injection site reactions (including induration, pruritus, nodules and swelling), muscle cramps, dizziness or syncope, somnolence or sedation, anorexia, decreased appetite or other appetite disorders (6).
The adverse events seen most frequently in association with VIVITROL therapy in opioid-dependent patients (i.e., those occurring in ≥2% of patients treated with VIVITROL and at least twice as frequently with VIVITROL than placebo) were hepatic enzyme abnormalities, injection site pain, nasopharyngitis, insomnia, and toothache (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alkermes, Inc. at 1-800-VIVITROL (1-800-848-4876) and/or email: usmedinfo@alkermes.com or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Naltrexone antagonizes the effects of opioid-containing medicines, such as cough and cold remedies, antidiarrheal preparations, and opioid analgesics (7).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Alcohol Dependence
1.2 Opioid Dependence
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
2.2 Reinitiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued
2.3 Switching From Oral Naltrexone
2.4 Switching from Buprenorphine, Buprenorphine/Naloxone, or Methadone
2.5 Directions for Use
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Vulnerability to Opioid Overdose
5.2 Injection Site Reactions
5.3 Precipitation of Opioid Withdrawal
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
5.5 Depression and Suicidality
5.6 When Reversal of VIVITROL Blockade Is Required for Pain Management
5.7 Eosinophilic Pneumonia
5.8 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
5.9 Intramuscular Injections
5.10 Alcohol Withdrawal
5.11 Interference with Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Frequently Asked Questions About Administering VIVITROL:
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Treatment with VIVITROL should be part of a comprehensive management program that includes psychosocial support.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
Prior to initiating VIVITROL, an opioid-free duration of a minimum of 7–10 days is recommended for patients, to avoid precipitation of opioid withdrawal that may be severe enough to require hospitalization [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
The recommended dose of VIVITROL is 380 mg delivered intramuscularly every 4 weeks or once a month. The injection should be administered by a healthcare provider as an intramuscular (IM) gluteal injection, alternating buttocks for each subsequent injection, using the carton components provided [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. The needles provided in the carton are customized needles. VIVITROL must not be injected using any other needle. The needle lengths (either 1 1/2 or 2 inches) may not be adequate in every patient because of body habitus. Body habitus should be assessed prior to each injection for each patient to assure that needle length is adequate for intramuscular administration. For patients with a larger amount of subcutaneous tissue overlying the gluteal muscle, the administering healthcare provider may utilize the supplied 2-inch needle with needle protection device to help ensure that the injectate reaches the intramuscular mass. For very lean patients, the 1 1/2-inch needle may be appropriate to prevent the needle contacting the periosteum. Either needle may be used for patients with average body habitus. Healthcare providers should ensure that the VIVITROL injection is given correctly, and should consider alternate treatment for those patients whose body habitus precludes an intramuscular gluteal injection with one of the provided needles.
2.2 Reinitiation of Treatment in Patients Previously Discontinued
There are no data to specifically address reinitiation of treatment. Patients reinitiating treatment with VIVITROL should be opioid-free at the time of dose administration [see Indications and Usage (1), Contraindications (4), and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.3 Switching From Oral Naltrexone
There are no systematically collected data that specifically address the switch from oral naltrexone to VIVITROL.
2.4 Switching from Buprenorphine, Buprenorphine/Naloxone, or Methadone
There are no systematically collected data that specifically address the switch from buprenorphine or methadone to VIVITROL; however, review of postmarketing case reports have indicated that some patients may experience severe manifestations of precipitated withdrawal when being switched from opioid agonist therapy to opioid antagonist therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Patients transitioning from buprenorphine or methadone may be vulnerable to precipitation of withdrawal symptoms for as long as 2 weeks. Healthcare providers should be prepared to manage withdrawal symptomatically with non-opioid medications.
2.5 Directions for Use
VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
To ensure proper dosing, it is important that you follow the preparation and administration instructions outlined in this document.
VIVITROL must be suspended only in the diluent supplied in the carton and must be administered only with one of the administration needles supplied in the carton. The microspheres, diluent, preparation needle, and an administration needle with needle protection device are required for preparation and administration. Two thin-walled 1 1/2-inch needles with needle protection device and two 2-inch thin-walled needles with needle protection device have been provided to accommodate varying patient body habitus. For patients with a larger amount of subcutaneous tissue overlying the gluteal muscle, the administering healthcare provider may utilize the supplied 2-inch needle with needle protection device to help ensure that the injectate reaches the intramuscular mass. For very lean patients, the 1 1/2-inch needle may be appropriate to prevent the needle contacting the periosteum. Either needle may be used for patients with average body habitus. A spare administration needle of each size is provided in case of clogging [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. Do not substitute any other components for the components of the carton.
Prior to preparation, allow drug to reach room temperature (approximately 45 minutes).
Parenteral products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. A properly mixed suspension will be milky white, will not contain clumps, and will move freely down the wall of the vial [see Directions for Use, illustration below].
Keep out of reach of children.
Prepare and administer the VIVITROL suspension using aseptic technique.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of a needlestick:
- Do not intentionally disengage the needle protection device.
- Discard bent or damaged needle into a sharps container and use the spare needle provided. Do not attempt to straighten the needle or engage needle protection device if the needle is bent or damaged.
- Do not mishandle the needle protection device in a way that could lead to protrusion of the needle.
- Do not use free hand to press sheath over needle.
THE CARTON SHOULD NOT BE EXPOSED TO TEMPERATURES EXCEEDING 25°C (77°F).
The entire carton should be stored in the refrigerator (2 to 8°C, 36 to 46°F). Unrefrigerated, VIVITROL microspheres can be stored at temperatures not exceeding 25°C (77°F) for no more than 7 days prior to administration. Do not expose unrefrigerated product to temperatures above 25°C (77°F). VIVITROL should not be frozen.
Parenteral products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.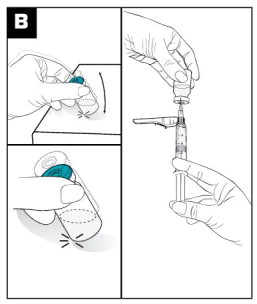
- Remove the carton from refrigeration. Prior to preparation, allow drug to reach room temperature (approximately 45 minutes).
- To ease mixing, firmly tap the VIVITROL microspheres vial on a hard surface, ensuring the powder moves freely. (see Figure B)
- Remove flip-off caps from both vials. DO NOT USE IF FLIP-OFF CAPS ARE BROKEN OR MISSING.
- Wipe the vial tops with an alcohol swab.
- Place the 1-inch preparation needle on the syringe and withdraw 3.4 mL of the diluent from the diluent vial. Some diluent will remain in the diluent vial. (see Figure B)
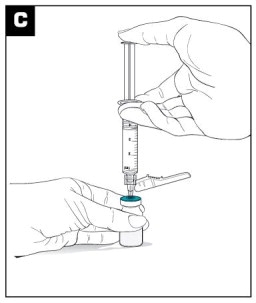
Inject the 3.4 mL of diluent into the VIVITROL microsphere vial. (see Figure C) 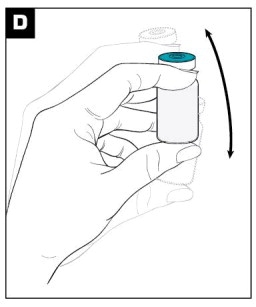
Mix the powder and diluent by vigorously shaking the vial for approximately 1 minute. (see Figure D)
Ensure that the dose is thoroughly suspended prior to proceeding to Step E.
A PROPERLY MIXED SUSPENSION WILL BE MILKY WHITE, WILL NOT CONTAIN CLUMPS, AND WILL MOVE FREELY DOWN THE WALLS OF THE VIAL.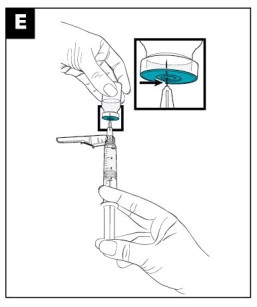
- Immediately after suspension, withdraw 4.2 mL of the suspension into the syringe using the same preparation needle. (see Figure E)
- Select the appropriate needle for an intramuscular injection based on patient's body habitus:
- 1 1/2-inch TERUMO® Needle
- 2-inch TERUMO® Needle
- Remove the preparation needle and replace with appropriately selected administration needle for immediate use.
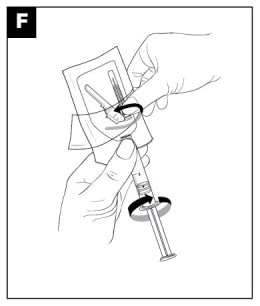
- Peel the blister pouch of the selected administration needle open halfway. Grip the base of the needle, not the safety sheath. Attach the luer connection to the syringe with an easy clockwise twisting motion. (see Figure F)
- Seat the needle firmly on the needle protection device with a push and clockwise twist.
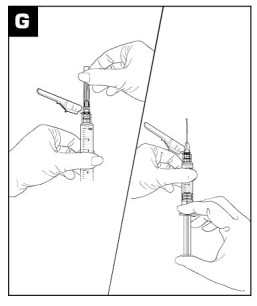
- Move the safety sheath away from the needle and toward the syringe barrel. Pull the sheath away from the needle -do not twist the sheath because it could result in loosening the needle.
- Prior to injecting, tap the syringe to release any air bubbles, then push gently on the plunger until 4 mL of the suspension remains in the syringe. (see Figure G)
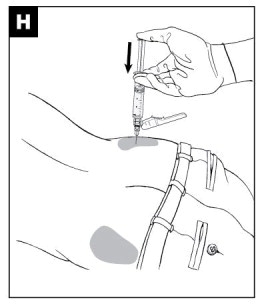
- Using a circular motion, clean the injection site with the alcohol swab. Let the site dry before injecting. Do not touch the site again before giving injections.
- Administer the suspension by deep intramuscular (IM) injection into a gluteal muscle, alternating buttocks per monthly injection. Remember to aspirate for blood before injection. (see Figure H)
- If blood aspirates or the needle clogs, do not inject. Change to the spare needle provided in the carton and administer into an adjacent site in the same gluteal region, again aspirating for blood before injection.
- Inject the suspension in a smooth and continuous motion.
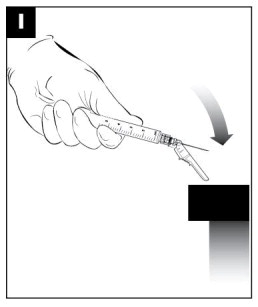
After the injection is administered, cover the needle by pressing the needle protection device against a flat surface using a one-handed technique to activate the safety mechanism away from self and others. (see Figure I) 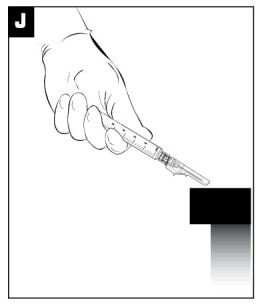
Visually confirm needle is fully engaged into the needle protection device. (see Figure J)
DISPOSE OF USED AND UNUSED ITEMS IN PROPER WASTE CONTAINERS. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
VIVITROL is contraindicated in:
- Patients receiving opioid analgesics [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Patients with current physiologic opioid dependence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Patients in acute opioid withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Any individual who has failed the naloxone challenge test or has a positive urine screen for opioids [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Patients who have previously exhibited hypersensitivity to naltrexone, PLG, carboxymethylcellulose, or any other components of the diluent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Vulnerability to Opioid Overdose
After opioid detoxification, patients are likely to have reduced tolerance to opioids. VIVITROL blocks the effects of exogenous opioids for approximately 28 days after administration. However, as the blockade wanes and eventually dissipates completely, patients who have been treated with VIVITROL may respond to lower doses of opioids than previously used, just as they would have shortly after completing detoxification. This could result in potentially life-threatening opioid intoxication (respiratory compromise or arrest, circulatory collapse, etc.) if the patient uses previously tolerated doses of opioids. Cases of opioid overdose with fatal outcomes have been reported in patients who used opioids at the end of a dosing interval, after missing a scheduled dose, or after discontinuing treatment.
Patients should be alerted that they may be more sensitive to opioids, even at lower doses, after VIVITROL treatment is discontinued, especially at the end of a dosing interval (i.e., near the end of the month that VIVITROL was administered), or after a dose of VIVITROL is missed. It is important that patients inform family members and the people closest to the patient of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
There is also the possibility that a patient who is treated with VIVITROL could overcome the opioid blockade effect of VIVITROL. Although VIVITROL is a potent antagonist with a prolonged pharmacological effect, the blockade produced by VIVITROL is surmountable. The plasma concentration of exogenous opioids attained immediately following their acute administration may be sufficient to overcome the competitive receptor blockade. This poses a potential risk to individuals who attempt, on their own, to overcome the blockade by administering large amounts of exogenous opioids. Any attempt by a patient to overcome the antagonism by taking opioids is especially dangerous and may lead to life-threatening opioid intoxication or fatal overdose. Patients should be told of the serious consequences of trying to overcome the opioid blockade [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Injection Site Reactions
VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
VIVITROL injections may be followed by pain, tenderness, induration, swelling, erythema, bruising, or pruritus; however, in some cases injection site reactions may be very severe. In the clinical trials, one patient developed an area of induration that continued to enlarge after 4 weeks, with subsequent development of necrotic tissue that required surgical excision. In the postmarketing period, additional cases of injection site reaction with features including induration, cellulitis, hematoma, abscess, sterile abscess, and necrosis, have been reported. Some cases required surgical intervention, including debridement of necrotic tissue. Some cases resulted in significant scarring. The reported cases occurred primarily in female patients.
VIVITROL is administered as an intramuscular gluteal injection, and inadvertent subcutaneous injection of VIVITROL may increase the likelihood of severe injection site reactions. The needles provided in the carton are customized needles. VIVITROL must not be injected using any other needle. The needle lengths (either 1 1/2 or 2 inches) may not be adequate in every patient because of body habitus. Body habitus should be assessed prior to each injection for each patient to assure that the proper needle is selected and that the needle length is adequate for intramuscular administration. For patients with a larger amount of subcutaneous tissue overlying the gluteal muscle, the administering healthcare provider may utilize the supplied 2-inch needle with needle protection device to help ensure that the injectate reaches the intramuscular mass. For very lean patients, the 1 1/2-inch needle may be appropriate to prevent the needle contacting the periosteum. Either needle may be used for patients with average body habitus. Healthcare providers should ensure that the VIVITROL injection is given correctly, and should consider alternate treatment for those patients whose body habitus precludes an intramuscular gluteal injection with one of the provided needles.
Patients should be informed that any concerning injection site reactions should be brought to the attention of the healthcare provider [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Patients exhibiting signs of abscess, cellulitis, necrosis, or extensive swelling should be evaluated by a physician to determine if referral to a surgeon is warranted.
5.3 Precipitation of Opioid Withdrawal
The symptoms of spontaneous opioid withdrawal (which are associated with the discontinuation of opioid in a dependent individual) are uncomfortable, but they are not generally believed to be severe or necessitate hospitalization. However, when withdrawal is precipitated abruptly by the administration of an opioid antagonist to an opioid-dependent patient, the resulting withdrawal syndrome can be severe enough to require hospitalization. Review of postmarketing cases of precipitated opioid withdrawal in association with naltrexone treatment has identified cases with symptoms of withdrawal severe enough to require hospital admission, and in some cases, management in the intensive care unit.
To prevent occurrence of precipitated withdrawal in patients dependent on opioids, or exacerbation of a pre-existing subclinical withdrawal syndrome, opioid-dependent patients, including those being treated for alcohol dependence, should be opioid-free (including tramadol) before starting VIVITROL treatment. An opioid-free interval of a minimum of 7–10 days is recommended for patients previously dependent on short-acting opioids. Patients transitioning from buprenorphine or methadone may be vulnerable to precipitation of withdrawal symptoms for as long as two weeks.
If a more rapid transition from agonist to antagonist therapy is deemed necessary and appropriate by the healthcare provider, monitor the patient closely in an appropriate medical setting where precipitated withdrawal can be managed.
In every case, healthcare providers should always be prepared to manage withdrawal symptomatically with non-opioid medications because there is no completely reliable method for determining whether a patient has had an adequate opioid-free period. A naloxone challenge test may be helpful; however, a few case reports have indicated that patients may experience precipitated withdrawal despite having a negative urine toxicology screen or tolerating a naloxone challenge test (usually in the setting of transitioning from buprenorphine treatment). Patients should be made aware of the risks associated with precipitated withdrawal and encouraged to give an accurate account of last opioid use. Patients treated for alcohol dependence with VIVITROL should also be assessed for underlying opioid dependence and for any recent use of opioids prior to initiation of treatment with VIVITROL. Precipitated opioid withdrawal has been observed in alcohol-dependent patients in circumstances where the prescriber had been unaware of the additional use of opioids or co-dependence on opioids.
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
Cases of hepatitis and clinically significant liver dysfunction were observed in association with VIVITROL exposure during the clinical development program and in the postmarketing period. Transient, asymptomatic hepatic transaminase elevations were also observed in the clinical trials and postmarketing period. Although patients with clinically significant liver disease were not systematically studied, clinical trials did include patients with asymptomatic viral hepatitis infections. When patients presented with elevated transaminases, there were often other potential causative or contributory etiologies identified, including pre-existing alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B and/or C infection, and concomitant usage of other potentially hepatotoxic drugs. Although clinically significant liver dysfunction is not typically recognized as a manifestation of opioid withdrawal, opioid withdrawal that is precipitated abruptly may lead to systemic sequelae including acute liver injury.
Patients should be warned of the risk of hepatic injury and advised to seek medical attention if they experience symptoms of acute hepatitis. Use of VIVITROL should be discontinued in the event of symptoms and/or signs of acute hepatitis.
5.5 Depression and Suicidality
Alcohol- and opioid-dependent patients, including those taking VIVITROL, should be monitored for the development of depression or suicidal thinking. Families and caregivers of patients being treated with VIVITROL should be alerted to the need to monitor patients for the emergence of symptoms of depression or suicidality, and to report such symptoms to the patient's healthcare provider.
Alcohol Dependence
In controlled clinical trials of VIVITROL administered to adults with alcohol dependence, adverse events of a suicidal nature (suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, completed suicides) were infrequent overall, but were more common in patients treated with VIVITROL than in patients treated with placebo (1% vs 0%). In some cases, the suicidal thoughts or behavior occurred after study discontinuation, but were in the context of an episode of depression that began while the patient was on study drug. Two completed suicides occurred, both involving patients treated with VIVITROL.
Depression-related events associated with premature discontinuation of study drug were also more common in patients treated with VIVITROL (~1%) than in placebo-treated patients (0%).
In the 24-week, placebo-controlled pivotal trial in 624 alcohol-dependent patients, adverse events involving depressed mood were reported by 10% of patients treated with VIVITROL 380 mg, as compared to 5% of patients treated with placebo injections.
Opioid Dependence
In an open-label, long-term safety study conducted in the US, adverse events of a suicidal nature (depressed mood, suicidal ideation, suicide attempt) were reported by 5% of opioid-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL 380 mg (n=101) and 10% of opioid-dependent patients treated with oral naltrexone (n=20). In the 24-week, placebo-controlled pivotal trial that was conducted in Russia in 250 opioid-dependent patients, adverse events involving depressed mood or suicidal thinking were not reported by any patient in either treatment group (VIVITROL 380 mg or placebo).
5.6 When Reversal of VIVITROL Blockade Is Required for Pain Management
In an emergency situation in patients receiving VIVITROL, suggestions for pain management include regional analgesia or use of non-opioid analgesics. If opioid therapy is required as part of anesthesia or analgesia, patients should be continuously monitored in an anesthesia care setting by persons not involved in the conduct of the surgical or diagnostic procedure. The opioid therapy must be provided by individuals specifically trained in the use of anesthetic drugs and the management of the respiratory effects of potent opioids, specifically the establishment and maintenance of a patent airway and assisted ventilation.
Irrespective of the drug chosen to reverse VIVITROL blockade, the patient should be monitored closely by appropriately trained personnel in a setting equipped and staffed for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
5.7 Eosinophilic Pneumonia
In clinical trials with VIVITROL, there was one diagnosed case and one suspected case of eosinophilic pneumonia. Both cases required hospitalization, and resolved after treatment with antibiotics and corticosteroids. Similar cases have been reported in postmarketing use. Should a person receiving VIVITROL develop progressive dyspnea and hypoxemia, the diagnosis of eosinophilic pneumonia should be considered [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Patients should be warned of the risk of eosinophilic pneumonia, and advised to seek medical attention should they develop symptoms of pneumonia. Clinicians should consider the possibility of eosinophilic pneumonia in patients who do not respond to antibiotics.
5.8 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
Cases of urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylaxis have been observed with use of VIVITROL in the clinical trial setting and in postmarketing use. Patients should be warned of the risk of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. In the event of a hypersensitivity reaction, patients should be advised to seek immediate medical attention in a healthcare setting prepared to treat anaphylaxis. The patient should not receive any further treatment with VIVITROL.
5.9 Intramuscular Injections
As with any intramuscular injection, VIVITROL should be administered with caution to patients with thrombocytopenia or any coagulation disorder (e.g., hemophilia and severe hepatic failure).
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Accidental Opioid Overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Injection Site Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Precipitated Opioid Withdrawal [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Depression and Suicidality [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Eosinophilic Pneumonia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In all controlled and uncontrolled trials during the premarketing development of VIVITROL, more than 1100 patients with alcohol and/or opioid dependence have been treated with VIVITROL. Approximately 700 patients have been treated for 6 months or more, and more than 400 for 1 year or longer.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
Alcohol Dependence
In controlled trials of 6 months or less in alcohol-dependent patients, 9% of alcohol-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL discontinued treatment due to an adverse event, as compared to 7% of the alcohol-dependent patients treated with placebo. Adverse events in the VIVITROL 380 mg group that led to more dropouts than in the placebo-treated group were injection site reactions (3%), nausea (2%), pregnancy (1%), headache (1%), and suicide-related events (0.3%). In the placebo group, 1% of patients withdrew due to injection site reactions, and 0% of patients withdrew due to the other adverse events.
Common Adverse Reactions
Alcohol Dependence
Table 1 lists all treatment-emergent clinical adverse reactions, regardless of causality, occurring in ≥5% of patients with alcohol dependence, for which the incidence was greater in the combined VIVITROL group than in the placebo group. A majority of patients treated with VIVITROL in clinical studies had adverse reactions with a maximum intensity of “mild” or “moderate”.
Table 1: Treatment-emergent Adverse Reactions (Reactions in ≥5% of patients with alcohol dependence treated with VIVITROL and occurring more frequently in the combined VIVITROL group than in the placebo group) Body System Adverse Reaction / Preferred Term Placebo Naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension N=214 400 mg
N=25380 mg
N=205190 mg
N=210All
N=440N % N % N % N % N % a) Includes the preferred terms: diarrhea NOS; frequent bowel movements; gastrointestinal upset; loose stools
b) Includes the preferred terms: abdominal pain NOS; abdominal pain upper; stomach discomfort; abdominal pain lower
c) Includes the preferred terms: nasopharyngitis; pharyngitis streptococcal; pharyngitis NOS
d) Includes the preferred terms: anxiety NEC; anxiety aggravated; agitation; obsessive compulsive disorder; panic attack; nervousness; posttraumatic stress
e) Includes the preferred terms: malaise; fatigue (these two comprise the majority of cases); lethargy; sluggishness
f) Includes the preferred terms: muscle cramps; spasms; tightness; twitching; stiffness; rigidity
g) Includes the preferred terms: rash NOS; rash papular; heat rash
h) Includes the preferred terms: headache NOS; sinus headache; migraine; frequent headaches
Gastrointestinal Disorders Nausea 24 11 8 32 68 33 53 25 129 29 Vomiting NOS 12 6 3 12 28 14 22 10 53 12 Diarrheaa) 21 10 3 12 27 13 27 13 57 13 Abdominal painb) 17 8 4 16 23 11 23 11 50 11 Dry Mouth 9 4 6 24 10 5 8 4 24 5 Infections & Infestations Pharyngitisc) 23 11 0 0 22 11 35 17 57 13 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia, sleep disorder 25 12 2 8 29 14 27 13 58 13 Anxietyd) 17 8 2 8 24 12 16 8 42 10 Depression 9 4 0 0 17 8 7 3 24 5 General Disorders & Administration Site Conditions Any ISR 106 50 22 88 142 69 121 58 285 65 Injection site tenderness 83 39 18 72 92 45 89 42 199 45 Injection site induration 18 8 7 28 71 35 52 25 130 30 Injection site pain 16 7 0 0 34 17 22 10 56 13 Other ISR (primarily nodules, swelling) 8 4 8 32 30 15 16 8 54 12 Injection site pruritus 0 0 0 0 21 10 13 6 34 8 Injection site ecchymosis 11 5 0 0 14 7 9 4 23 5 Asthenic conditionse) 26 12 3 12 47 23 40 19 90 20 Musculoskeletal & Connective Tissue Disorders Arthralgia, arthritis, joint stiffness 11 5 1 4 24 12 12 6 37 9 Back pain, back stiffness 10 5 1 4 12 6 14 7 27 6 Muscle crampsf) 3 1 0 0 16 8 5 2 21 5 Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Rashg) 8 4 3 12 12 6 10 5 25 6 Nervous System Disorders Headacheh) 39 18 9 36 51 25 34 16 94 21 Dizziness, syncope 9 4 4 16 27 13 27 13 58 13 Somnolence, sedation 2 1 3 12 8 4 9 4 20 5 Metabolism & Nutrition Disorders Anorexia, appetite decreased NOS, appetite disorder NOS 6 3 5 20 30 14 13 6 48 11 Opioid Dependence
In the open-label, long-term safety study conducted in the US, the commonly reported adverse reactions among the opioid-dependent patients in the study were similar to those commonly observed events in the alcohol-dependent populations in VIVITROL clinical trials as displayed in Table 1, above. For example, injection site reactions of all types, nausea and diarrhea occurred in more than 5% of patients on VIVITROL in the open-label study. In contrast, 48% percent, of the opioid-dependent patients had at least one adverse event in the “Infections and Infestations” Body System. Adverse Reactions/Preferred Terms of nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, and sinusitis were most commonly reported.
In the placebo-controlled study in opioid-dependent patients conducted in Russia, the overall frequency of adverse events was lower than in the U.S. population described above. Table 2 lists treatment-emergent clinical adverse events, regardless of causality, occurring in ≥2% of patients with opioid dependence, for which the incidence was greater in the VIVITROL group than in the placebo group. All adverse events were assessed as having a maximum intensity of “mild” or “moderate.”
Table 2: Treatment-emergent Clinical Adverse Events (Events in ≥2% of patients with opioid dependence treated with VIVITROL and occurring more frequently in the VIVITROL group than in the placebo group) Body System Adverse Event / Preferred Term Placebo
N=124VIVITROL 380 mg
N=126n % n % Investigations Alanine aminotransferase increased 7 6 16 13 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 3 2 13 10 Gamma-glutamyltransferase increased 4 3 9 7 Infections and Infestations Nasopharyngitis 3 2 9 7 Influenza 5 4 6 5 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia 1 1 8 6 Vascular Disorders Hypertension 4 3 6 5 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Injection site pain 1 1 6 5 Gastrointestinal Disorders Toothache 2 2 5 4 Nervous System Disorders Headache 3 2 4 3 Laboratory Tests
Eosinophil Count
In clinical trials, subjects on VIVITROL had increases in eosinophil counts relative to subjects on placebo. With continued use of VIVITROL, eosinophil counts returned to normal over a period of several months.
Platelet Count
VIVITROL 380 mg was associated with a decrease in platelet count. In clinical trials, alcohol-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL experienced a mean maximal decrease in platelet count of 17.8 × 103/μL, compared to 2.6 × 103/μL in placebo patients.
After 24 weeks of treatment, opioid-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL experienced a mean maximal decrease in platelet count of 62.8 × 103/μL, compared to 39.9 × 103/μL in placebo patients. In randomized controlled trials, VIVITROL was not associated with an increase in bleeding-related adverse events.
Hepatic Enzyme Elevations
In short-term, controlled trials, in alcohol-dependent patients, the incidence of AST elevations associated with VIVITROL treatment was similar to that observed with oral naltrexone treatment (1.5% each) and slightly higher than observed with placebo treatment (0.9%).
In the 6-month controlled trial conducted in opioid-dependent subjects, 89% had a baseline diagnosis of hepatitis C infection, and 41% had a baseline diagnosis of HIV infection. There were frequently observed elevated liver enzyme levels (ALT, AST, and GGT); these were more commonly reported as adverse events in the VIVITROL 380 mg group than in the placebo group. Patients could not enroll in this trial if they had a baseline ALT or AST value that was more than three times the upper limit of normal. More patients treated with VIVITROL in this study experienced treatment-emergent elevations in transaminases to more than three times the upper limit of normal than patients treated with placebo. Shifts to more than three times the upper limit of normal occurred in 20% of patients treated with VIVITROL as compared with 13% of placebo patients. Shifts in values of AST to more than three times the upper limit were also more common in the VIVITROL (14%) arm compared with the placebo (11%) arm. Opioid-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL experienced a mean maximal increase from baseline ALT levels of 61 IU/L compared with 48 IU/L in placebo patients. Similarly for AST, opioid-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL experienced a mean maximal increase from baseline AST levels of 40 IU/L compared with 31 IU/L in placebo patients.
Creatinine Phosphokinase
In short-term controlled trials in alcohol-dependent patients, more patients treated with VIVITROL 380 mg (11%) and oral naltrexone (17%) shifted from normal creatinine phosphokinase (CPK) levels before treatment to abnormal CPK levels at the end of the trials, compared to placebo patients (8%). In open-label trials, 16% of patients dosed for more than 6 months had increases in CPK. For both the oral naltrexone and VIVITROL 380 mg groups, CPK abnormalities were most frequently in the range of 1–2 × ULN. However, there were reports of CPK abnormalities as high as 4x ULN for the oral naltrexone group, and 35 × ULN for the VIVITROL 380 mg group. Overall, there were no differences between the placebo and naltrexone (oral or injectable) groups with respect to the proportions of patients with a CPK value at least three times the upper limit of normal. No factors other than naltrexone exposure were associated with the CPK elevations.
More opioid-dependent patients treated with VIVITROL 380 mg (39%) shifted from normal creatinine phosphokinase (CPK) levels before treatment to abnormal CPK levels during the study as compared to patients treated with placebo (32%). There were reports of CPK abnormalities as high as 41.8 × ULN for the placebo group, and 22.1 × ULN for the VIVITROL 380 mg group.
Other Events Observed During the VIVITROL Clinical Studies
The following is a list of treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported by alcohol- and/or opioid-dependent subjects treated with VIVITROL in all clinical trials. The listing does not include those events already listed in the previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, those events for which a drug cause was remote, those events that were so general as to be uninformative, and those events reported only once that did not have a substantial probability of being acutely life-threatening.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders – lymphadenopathy (including cervical adenitis), white blood cell count increased
Cardiac Disorders – angina pectoris, angina unstable, atrial fibrillation, cardiac failure congestive, coronary artery atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, palpitations
Eye Disorders – conjunctivitis, vision blurred
Gastrointestinal Disorders – abdominal discomfort, colitis, constipation, flatulence, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hemorrhoids, pancreatitis acute, paralytic ileus, perirectal abscess
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions – chest pain, chest tightness, chills, face edema, irritability, lethargy, pyrexia, rigors
Hepatobiliary Disorders – cholecystitis acute, cholelithiasis
Immune System Disorders – seasonal allergy, hypersensitivity reaction (including angioneurotic edema and urticaria)
Infections and Infestations – bronchitis, gastroenteritis, laryngitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, tooth abscess, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, advanced HIV disease in HIV-infected patients
Investigations – weight decreased, weight increased
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders – appetite increased, dehydration, heat exhaustion, hypercholesterolemia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders – joint stiffness, muscle spasms, myalgia, pain in limb
Nervous System Disorders – cerebral arterial aneurysm, convulsions, disturbance in attention, dysgeusia, mental impairment, migraine, ischemic stroke, paresthesia
Pregnancy, Puerperium, and Perinatal Conditions – abortion missed
Psychiatric Disorders – abnormal dreams, agitation, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, euphoric mood, delirium, libido decreased
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, dyspnea, pharyngolaryngeal pain, sinus congestion
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders – night sweats, pruritus, sweating increased
Vascular Disorders – deep venous thrombosis, hot flushes, pulmonary embolism
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse Events Following Patient Self-Administration
Adverse events including injection site reactions and precipitated opioid withdrawal syndrome resulting in serious outcomes, including hospitalization, have been reported following patient self-administration of VIVITROL. VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported during postmarketing surveillance.
Reports From Other Intramuscular Drug Products Containing Polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG) Microspheres
Retinal Artery Occlusion
Retinal artery occlusion after injection with another drug product containing polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG) microspheres has been reported very rarely during postmarketing surveillance. This event has been reported in the presence of abnormal arteriovenous anastomosis. No cases of retinal artery occlusion have been reported during VIVITROL clinical trials or postmarketing surveillance. VIVITROL should be administered by intramuscular (IM) injection into the gluteal muscle, and care must be taken to avoid inadvertent injection into a blood vessel [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The available data from published case series with VIVITROL use in pregnant women are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are clinical considerations (see Clinical Considerations). Reproduction and developmental animal studies have not been conducted for VIVITROL. Daily oral administration of naltrexone to female rats and rabbits increased the incidence of early fetal loss at exposures ≥ 11 times and ≥ 2 times the human exposure, respectively. Daily oral administration of naltrexone to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not induce malformation at exposures up to 175 times and 14 times the human exposure, respectively (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Disease-associated maternal and embryo-fetal risk
Untreated opioid addiction in pregnancy is associated with adverse obstetrical outcomes such as low birth weight, preterm birth, and fetal death. In addition, untreated opioid addiction often results in continued or relapsing illicit opioid use.
Published studies have demonstrated that alcohol is associated with fetal harm including growth restriction, facial abnormalities, central nervous system abnormalities, behavioral disorders, and impaired intellectual development.
Animal Data
Reproduction and developmental studies have not been conducted for VIVITROL. Studies with naltrexone administered via the oral route have been conducted in pregnant rats and rabbits.
Daily oral administration of naltrexone has been shown to increase the incidence of early fetal loss when given to rats at doses ≥30 mg/kg/day (11 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison) and to rabbits at oral doses ≥60 mg/kg/day (2 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison).
Daily oral administration of naltrexone to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not induce malformations at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (175- and 14-times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison, respectively).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Naltrexone and its major metabolite, 6β-naltrexol, are present in human milk. There are no data on the effects on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. The developmental health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for naltrexone and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from naltrexone or the mother's underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of VIVITROL have not been established in the pediatric population. The pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL have not been evaluated in a pediatric population.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In trials of alcohol-dependent subjects, 2.6% (n=26) of subjects were >65 years of age, and one patient was >75 years of age. Clinical studies of VIVITROL did not include sufficient numbers of subjects age 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. No subjects over age 65 were included in studies of opioid-dependent subjects. The pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL have not been evaluated in the geriatric population.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL are not altered in subjects with mild renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance of 50-80 mL/min). Dose adjustment is not required in patients with mild renal impairment. VIVITROL pharmacokinetics have not been evaluated in subjects with moderate and severe renal insufficiency. Because naltrexone and its primary metabolite are excreted primarily in the urine, caution is recommended in administering VIVITROL to patients with moderate to severe renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL are not altered in subjects with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Groups A and B of the Child-Pugh classification). Dose adjustment is not required in subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. VIVITROL pharmacokinetics were not evaluated in subjects with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience with overdose of VIVITROL. Single doses up to 784 mg were administered to 5 healthy subjects. There were no serious or severe adverse events. The most common effects were injection site reactions, nausea, abdominal pain, somnolence, and dizziness. There were no significant increases in hepatic enzymes.
In the event of an overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
VIVITROL® (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) is supplied as a microsphere formulation of naltrexone for suspension, to be administered by intramuscular injection. Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist with little, if any, opioid agonist activity.
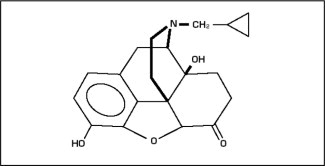
Naltrexone is designated chemically as morphinan-6-one, 17 (cyclopropylmethyl) 4,5-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-(5α) (CAS Registry # 16590-41-3). The molecular formula is C20H23NO4 and its molecular weight is 341.41 in the anhydrous form (ie, < 1% maximum water content). The structural formula is:
Naltrexone base anhydrous is an off-white to a light tan powder with a melting point of 168-170ºC (334-338ºF). It is insoluble in water and is soluble in ethanol.
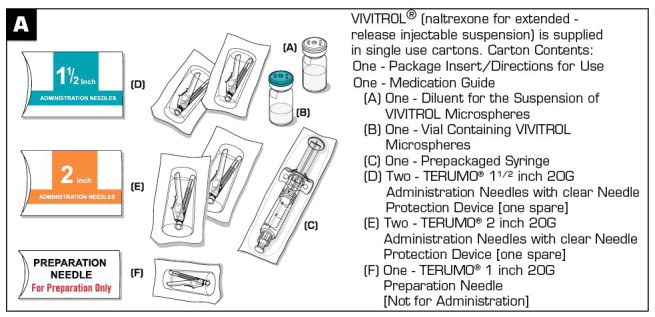
VIVITROL is provided as a carton containing a vial each of VIVITROL microspheres and diluent, one 5-mL syringe, one 1-inch 20-gauge preparation needle, two 1 1/2-inch 20-gauge and two 2-inch 20-gauge administration needles with needle protection device.
VIVITROL microspheres consist of a sterile, off-white to light tan powder that is available in a dosage strength of 380 mg of naltrexone per vial. Naltrexone is incorporated in 75:25 polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG) at a concentration of 337 mg of naltrexone per gram of microspheres.
The diluent is a clear, colorless solution. The composition of the diluent includes carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt, polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, and water for injection. The microspheres must be suspended in the diluent prior to injection.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of action
Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist with highest affinity for the mu opioid receptor. Naltrexone has little or no opioid agonist activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Naltrexone has few, if any, intrinsic actions besides its opioid blocking properties. However, it does produce some pupillary constriction, by an unknown mechanism.
The administration of VIVITROL is not associated with the development of tolerance or dependence. In subjects physically dependent on opioids, VIVITROL will precipitate withdrawal symptomatology.
Occupation of opioid receptors by naltrexone may block the effects of endogenous opioid peptides. It markedly attenuates or completely blocks, reversibly, the subjective effects of exogenous opioids. The neurobiological mechanisms responsible for the reduction in alcohol consumption observed in alcohol-dependent patients treated with naltrexone are not entirely understood. However, involvement of the endogenous opioid system is suggested by preclinical data.
Naltrexone blocks the effects of opioids by competitive binding at opioid receptors. This makes the blockade produced potentially surmountable, but overcoming full naltrexone blockade by administration of opioids may result in non-opioid receptor-mediated symptoms such as histamine release.
VIVITROL is not aversive therapy and does not cause a disulfiram-like reaction either as a result of opioid use or ethanol ingestion.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
VIVITROL is an extended-release, microsphere formulation of naltrexone designed to be administered by intramuscular (IM) gluteal injection every 4 weeks or once a month. After IM injection, the naltrexone plasma concentration time profile is characterized by a transient initial peak, which occurs approximately 2 hours after injection, followed by a second peak observed approximately 2-3 days later. Beginning approximately 14 days after dosing, concentrations slowly decline, with measurable levels for greater than 1 month.
Maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) for naltrexone and 6β-naltrexol (the major metabolite) following VIVITROL administration are dose proportional. Compared to daily oral dosing with naltrexone 50 mg over 28 days, total naltrexone exposure is 3 to 4-fold higher following administration of a single dose of VIVITROL 380 mg. Steady state is reached at the end of the dosing interval following the first injection. There is minimal accumulation (<15%) of naltrexone or 6β-naltrexol upon repeat administration of VIVITROL.
Elimination
-
The elimination half life of naltrexone following VIVITROL administration is 5-10 days and is dependent on the erosion of the polymer. The elimination half life of 6β-naltrexol following VIVITROL administration is 5-10 days.
Metabolism
Naltrexone is extensively metabolized in humans. Production of the primary metabolite, 6β-naltrexol, is mediated by dihydrodiol dehydrogenase, a cytosolic family of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 system is not involved in naltrexone metabolism. Two other minor metabolites are 2-hydroxy-3-methoxy-6β-naltrexol and 2-hydroxy-3-methoxy-naltrexone. Naltrexone and its metabolites are also conjugated to form glucuronide products.
Significantly less 6β-naltrexol is generated following IM administration of VIVITROL compared to administration of oral naltrexone due to a reduction in first-pass hepatic metabolism.
Excretion
Elimination of naltrexone and its metabolites occurs primarily via urine, with minimal excretion of unchanged naltrexone.
Specific Populations
Geriatric: Pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL have not been evaluated in the geriatric population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Sex: In a study in healthy subjects (n=18 females and 18 males), sex did not influence the pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL.
Renal Insufficiency: A population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated mild renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance of 50-80 mL/min) had little or no influence on VIVITROL pharmacokinetics and that no dosage adjustment is necessary. VIVITROL pharmacokinetics have not been evaluated in subjects with moderate and severe renal insufficiency [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Insufficiency: The pharmacokinetics of VIVITROL are not altered in subjects with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Groups A and B of the Child-Pugh classification). VIVITROL pharmacokinetics were not evaluated in subjects with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies: Because naltrexone is not a substrate for CYP drug metabolizing enzymes, inducers or inhibitors of these enzymes are unlikely to change the clearance of VIVITROL. An in vitro CYP inhibition study demonstrated that naltrexone is not an inhibitor of major CYP enzymes (CYP 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, 3A4). An in vitro CYP induction study demonstrated that naltrexone is not an inducer of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2.
-
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with VIVITROL.
Carcinogenicity studies of oral naltrexone hydrochloride (administered via the diet) have been conducted in rats and mice.
In a two-year carcinogenicity study in rats, there were small increases in the numbers of testicular mesotheliomas in males and tumors of vascular origin in males and females. The incidence of testicular mesothelioma in males given naltrexone at a dietary dose of 100 mg/kg/day (3-times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison) was 6%, compared with a maximum historical incidence of 4%. The incidence of vascular tumors in males and females given dietary doses of 100 mg/kg/day was 4% but only the incidence in females was increased compared with a maximum historical control incidence of 2% (3 and 32 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison in males and females, respectively). There was no evidence of carcinogenicity in a 2-year dietary study with naltrexone in male and female mice (12 and 3 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison, respectively). The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
Mutagenesis: Naltrexone was negative in the following in vitro genotoxicity studies: bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test), the heritable translocation assay, CHO cell sister chromatid exchange assay, and the mouse lymphoma gene mutation assay. Naltrexone was also negative in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. In contrast, naltrexone tested positive in the following assays: Drosophila recessive lethal frequency assay, non-specific DNA damage in repair tests with E. coli and WI-38 cells, and urinalysis for methylated histidine residues.
Impairment of Fertility: Daily oral administration of naltrexone caused a significant increase in pseudopregnancy and a decrease in pregnancy rates in rats at 100 mg/kg/day (75 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison). There was no effect on male fertility at this dose level (6 times the human exposure based on an AUC(0-28d) comparison). The relevance of these observations to human fertility is not known.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Alcohol Dependence
The efficacy of VIVITROL in the treatment of alcohol dependence was evaluated in a 24-week, placebo-controlled, multi-center, double-blind, randomized trial of alcohol-dependent (DSM-IV criteria) outpatients. Subjects were treated with an injection every 4 weeks of VIVITROL 190 mg, VIVITROL 380 mg or placebo. Oral naltrexone was not administered prior to the initial or subsequent injections of study medication. Psychosocial support was provided to all subjects in addition to medication.
Subjects treated with VIVITROL 380 mg demonstrated a greater reduction in days of heavy drinking than those treated with placebo. Heavy drinking was defined as self-report of 5 or more standard drinks consumed on a given day for male patients and 4 or more drinks for female patients. Among the subset of patients (n=53, 8% of the total study population) who abstained completely from drinking during the week prior to the first dose of medication, compared with placebo-treated patients, those treated with VIVITROL 380 mg had greater reductions in the number of drinking days and the number of heavy drinking days. In this subset, patients treated with VIVITROL were also more likely than placebo-treated patients to maintain complete abstinence throughout treatment. The same treatment effects were not evident among the subset of patients (n=571, 92% of the total study population) who were actively drinking at the time of treatment initiation.
Opioid Dependence
The efficacy of VIVITROL in the treatment of opioid dependence was evaluated in a 24-week, placebo-controlled, multi-center, double-blind, randomized trial of opioid-dependent (DSM-IV) outpatients, who were completing or had recently completed detoxification. Subjects were treated with an injection every 4 weeks of VIVITROL 380 mg or placebo. Oral naltrexone was not administered prior to the initial or subsequent injections of study medication. Standardized, manual-based psychosocial support was provided on a biweekly basis to all subjects in addition to medication.
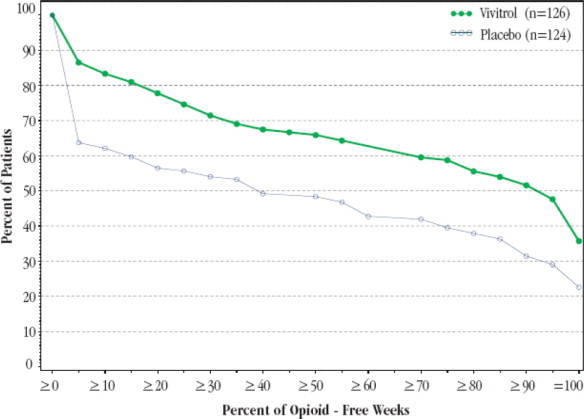
Figure 1, below, displays the cumulative percentage of subjects with opioid-free weeks ranging from no visits (0%) to all visits (100%). An opioid-free week was one in which urine drug test results were negative for opioids and self-reported opioid use was also zero. An initial period of engagement in treatment was permitted during which opiate use, if it occurred, was not considered in the analysis. Subjects discontinuing from the trial were assumed to have had opioid-use weeks for the weeks after dropout.
The cumulative percentage of subjects achieving each observed percentage of opioid-free weeks was greater in the VIVITROL group compared to the placebo group. Complete abstinence (opioid-free at all weekly visits) was sustained by 23% of subjects in the placebo group compared with 36% of subjects in the VIVITROL group from Week 5 to Week 24.
Figure 1: Subjects Sustaining Varying Percentages of Opioid-Free Weeks
A greater percentage of subjects in the VIVITROL group remained in the study compared to the placebo group.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VIVITROL (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension) is supplied in single-use cartons. Each carton contains one 380 mg vial of VIVITROL microspheres, one vial containing 4 mL (to deliver 3.4 mL) of diluent for the suspension of VIVITROL, one 5-mL prepackaged syringe, one 1-inch 20-gauge needle, two 1 1/2-inch 20-gauge needles and two 2-inch 20-gauge needles with needle protection devices: NDC: 65757-300-01.
VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
16.1 Storage and Handling
The entire dose pack should be stored in the refrigerator (2 to 8°C, 36 to 46°F). Unrefrigerated, VIVITROL can be stored at temperatures not exceeding 25°C (77°F) for no more than 7 days prior to administration. Do not expose the product to temperatures above 25°C (77°F). VIVITROL should not be frozen.
Parenteral products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. A properly mixed suspension will be milky white, will not contain clumps, and will move freely down the wall of the vial [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Keep out of Reach of Children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Physicians should include the following issues in discussions with patients for whom they prescribe VIVITROL:
- Advise patients that if they previously used opioids, they may be more sensitive to lower doses of opioids and at risk of accidental overdose should they use opioids when their next dose is due, if they miss a dose, or after VIVITROL treatment is discontinued. It is important that patients inform family members and the people closest to the patient of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose.
- Advise patients that because VIVITROL can block the effects of opioids, patients will not perceive any effect if they attempt to self-administer heroin or any other opioid drug in small doses while on VIVITROL. Further, emphasize that administration of large doses of heroin or any other opioid to try to bypass the blockade and get high while on VIVITROL may lead to serious injury, coma, or death.
- Inform patients on VIVITROL that they may not experience the expected effects from opioid-containing analgesic, antidiarrheal, or antitussive medications.
- Instruct patients that VIVITROL must be prepared and administered by a healthcare provider.
- Advise patients that a reaction at the site of VIVITROL injection may occur. Reactions include pain, tenderness, induration, swelling, erythema, bruising, or pruritus. Serious injection site reactions including necrosis may occur. Some of these injection site reactions have required surgery. Patients should be advised to seek medical attention for worsening skin reactions.
- Advise patients that they should be off all opioids, including opioid-containing medicines, for a minimum of 7 – 10 days before starting VIVITROL in order to avoid precipitation of opioid withdrawal. Patients transitioning from buprenorphine or methadone may be vulnerable to precipitation of withdrawal symptoms for as long as two weeks. Ensure that patients understand that withdrawal precipitated by administration of an opioid antagonist may be severe enough to require hospitalization if they have not been opioid-free for an adequate period of time, and is different from the experience of spontaneous withdrawal that occurs with discontinuation of opioid in a dependent individual. Advise patients that they should not take VIVITROL if they have any symptoms of opioid withdrawal. Advise all patients, including those with alcohol dependence, that it is imperative to notify healthcare providers of any recent use of opioids or any history of opioid dependence before starting VIVITROL to avoid precipitation of opioid withdrawal.
- Advise patients that VIVITROL may cause liver injury. Patients should immediately notify their physician if they develop symptoms and/or signs of liver disease.
- Advise patients that they may experience depression while taking VIVITROL. It is important that patients inform family members and the people closest to the patient that they are taking VIVITROL and that they should call a doctor right away should they become depressed or experience symptoms of depression.
- Advise patients to carry documentation to alert medical personnel to the fact that they are taking VIVITROL (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension). This will help to ensure that patients obtain adequate medical treatment in an emergency.
- Advise patients that VIVITROL may cause an allergic pneumonia. Patients should immediately notify their physician if they develop signs and symptoms of pneumonia, including dyspnea, coughing, or wheezing.
- Advise patients that they should not take VIVITROL if they are allergic to VIVITROL or any of the microsphere or diluent components.
- Advise patients that they may experience nausea following the initial injection of VIVITROL. These episodes of nausea tend to be mild and subside within a few days post-injection. Patients are less likely to experience nausea in subsequent injections. Patients should be advised that they may also experience tiredness, headache, vomiting, decreased appetite, painful joints and muscle cramps.
- Advise patients that because VIVITROL is an intramuscular injection and not an implanted device, once VIVITROL is injected, it is not possible to remove it from the body.
- Advise patients that VIVITROL has been shown to treat alcohol and opioid dependence only when used as part of a treatment program that includes counseling and support.
- Advise patients that dizziness may occur with VIVITROL treatment, and they should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until they have determined how VIVITROL affects them.
- Advise patients to notify their physician if they:
- – become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with VIVITROL.
- – are breast-feeding.
- – experience respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea, coughing, or wheezing when taking VIVITROL.
- – experience any allergic reactions when taking VIVITROL.
- – experience other unusual or significant side effects while on VIVITROL therapy.
US Patent Nos. 5,792,477; 5,916,598; 6,194,006; 6,264,987; 6,331,317; 6,379,703; 6,379,704; 6,395,304; 6,403,114; 6,495,166; 6,534,092; 6,537,586; 6,596,316; 6,713,090; 6,667,061; 6,495,164; 6,939,033;5,650,173; 5,654,008; 6,540,393; 6,705,757; 6,861,016
17.1 Frequently Asked Questions About Administering VIVITROL:
-
Can I prepare the suspension prior to my patient's arrival?
No. You may remove the carton from the refrigerator prior to the patient's arrival, but once the diluent is added to the VIVITROL microspheres, the dose should be mixed and the suspension administered immediately. It is very important to use proper aseptic technique when preparing the suspension [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. -
How much time do I have between preparing and administering the dose?
It is recommended that the suspension be administered immediately once the product has been suspended and transferred into the syringe. If a few minutes' delay occurs after suspension but before transfer into the syringe [see Dosage and Administration (2.5; Figure D)], the vial can be inverted a few times to resuspend and then transferred into the syringe for immediate use [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. -
Can I use needles other than those provided in the carton?
No. The needles in the carton are specially designed for administration of VIVITROL. Do not make any substitutions for components of the carton [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. -
The suspension is milky white upon mixing with the diluent. Is this normal?
Yes. VIVITROL microspheres will form a milky suspension when mixed with the provided diluent [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. -
What if a needle clog occurs during administration of the product?
If a clog occurs during administration, the needle should be withdrawn from the patient, capped with the attached needle protection device, and replaced with the spare administration needle. Gently push on the plunger until a bead of the suspension appears at the tip of the needle. The remainder of the suspension should then be administered into an adjacent site in the same gluteal region [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
For additional information, visit www.vivitrol.com or call 1-800-848-4876
Manufactured and marketed by:
Alkermes, Inc.
852 Winter Street
Waltham, MA 02451-1420©2019 Alkermes. All rights reserved.
ALKERMES® and VIVITROL® are registered trademarks of Alkermes, Inc.
Printed in U.S.A.
REV: September 2019 -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
VIVITROL ®(viv-i-trol)
(naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension)
Read this Medication Guide before you start receiving VIVITROL injections and each time you receive an injection. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?
VIVITROL can cause serious side effects, including:
-
Risk of opioid overdose.
You can accidentally overdose in two ways.- VIVITROL blocks the effects of opioids, such as heroin or opioid pain medicines. Do not take large amounts of opioids, including opioid-containing medicines, such as heroin or prescription pain pills, to try to overcome the opioid-blocking effects of VIVITROL. This can lead to serious injury, coma, or death.
- After you receive a dose of VIVITROL, its blocking effect slowly decreases and completely goes away over time. If you have used opioid street drugs or opioid-containing medicines in the past, using opioids in amounts that you used before treatment with VIVITROL can lead to overdose and death. You may also be more sensitive to the effects of lower amounts of opioids:
- after you have gone through detoxification
- when your next VIVITROL dose is due
- if you miss a dose of VIVITROL
- after you stop VIVITROL treatment
It is important that you tell your family and the people closest to you of this increased sensitivity to opioids and the risk of overdose.
You or someone close to you should get emergency medical help right away if you:
- have trouble breathing
- become very drowsy with slowed breathing
- have slow, shallow breathing (little chest movement with breathing)
- feel faint, very dizzy, confused, or have unusual symptoms
-
Severe reactions at the site of the injection (injection site reactions). Some people on VIVITROL have had severe injection site reactions, including tissue death (necrosis). Some of these injection site reactions have required surgery. VIVITROL must be injected by a healthcare provider. Call your healthcare provider right away if you notice any of the following at any of your injection sites:
Tell your healthcare provider about any reaction at an injection site that concerns you, gets worse over time, or does not get better by two weeks after the injection.
- intense pain
- the area feels hard
- large area of swelling
- lumps
- blisters
- an open wound
- a dark scab
-
Sudden opioid withdrawal.
Anyone who receives a VIVITROL injection must not use any type of opioid (must be opioid-free) including street drugs, prescription pain medicines, cough, cold, or diarrhea medicines that contain opioids, or opioid dependence treatments, buprenorphine or methadone, for at least 7 to 14 days before starting VIVITROL. Using opioids in the 7 to 14 days before you start receiving VIVITROL may cause you to suddenly have symptoms of opioid withdrawal when you get the VIVITROL injection. Sudden opioid withdrawal can be severe and you may need to go to the hospital.
You must be opioid-free before receiving VIVITROL unless your healthcare provider decides that you don't need to go through detox first. Instead, your doctor may decide to give your VIVITROL injection in a medical facility that can treat you for sudden opioid withdrawal. -
Liver damage or hepatitis. Naltrexone, the active ingredient in VIVITROL, can cause liver damage or hepatitis.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems during treatment with VIVITROL:- stomach area pain lasting more than a few days
- dark urine
- yellowing of the whites of your eyes
- tiredness
Your healthcare provider may need to stop treating you with VIVITROL if you get signs or symptoms of a serious liver problem.
What is VIVITROL?
VIVITROL is a prescription injectable medicine used to:
- treat alcohol dependence. You should stop drinking before starting VIVITROL.
- prevent relapse to opioid dependence, after opioid detoxification.
This means that if you take opioids or opioid-containing medicines, you must stop taking them before you start receiving VIVITROL. See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?”
To be effective, treatment with VIVITROL must be used with other alcohol or drug recovery programs such as counseling. VIVITROL may not work for everyone.
It is not known if VIVITROL is safe and effective in children.
Who should not receive VIVITROL?
Do not receive VIVITROL if you:
- are using or have a physical dependence on opioid-containing medicines or opioid street drugs. See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?”
To see whether you have a physical dependence on opioid-containing medicines or opioid street drugs, your healthcare provider may give you a small injection of a medicine called naloxone. This is called a naloxone challenge test. If you get symptoms of opioid withdrawal after the naloxone challenge test, do not start treatment with VIVITROL at that time. Your healthcare provider may repeat the test after you have stopped using opioids to see whether it is safe to start VIVITROL. - are having opioid withdrawal symptoms. Opioid withdrawal symptoms may happen when you have been taking opioid-containing medicines or opioid street drugs regularly and then stop.
Symptoms of opioid withdrawal may include: anxiety, sleeplessness, yawning, fever, sweating, teary eyes, runny nose, goose bumps, shakiness, hot or cold flushes, muscle aches, muscle twitches, restlessness, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach cramps. See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?” Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms before taking VIVITROL. - are allergic to naltrexone or any of the ingredients in VIVITROL or the liquid used to mix VIVITROL (diluent). See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in VIVITROL and the diluent.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before receiving VIVITROL?
Before you receive VIVITROL, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have liver problems
- use or abuse street (illegal) drugs
- have hemophilia or other bleeding problems
- have kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if VIVITROL will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if VIVITROL passes into your milk, and if it can harm your baby. Naltrexone, the active ingredient in VIVITROL, is the same active ingredient in tablets taken by mouth that contain naltrexone. Naltrexone from tablets passes into breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about whether you will breastfeed or take VIVITROL. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take any opioid-containing medicines for pain, cough or colds, or diarrhea. See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?”
If you are being treated for alcohol dependence but also use or are addicted to opioid-containing medicines or opioid street drugs, it is important that you tell your healthcare provider before starting VIVITROL to avoid having sudden opioid withdrawal symptoms when you start VIVITROL treatment.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How will I receive VIVITROL?
- VIVITROL is injected by a healthcare provider, about 1 time each month.
- VIVITROL must be injected by a healthcare provider. Do not attempt to inject yourself with VIVITROL. Serious reactions, some that may require hospitalization, might happen.
- VIVITROL is given as an injection into a muscle in your buttocks using a special needle that comes with VIVITROL.
- After VIVITROL is injected, it lasts for a month and it cannot be removed from the body.
- If you miss your appointment for your VIVITROL injection, schedule another appointment as soon as possible. See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?”
- Whenever you need medical treatment, be sure to tell the treating healthcare provider that you are receiving VIVITROL injections and mention when you got your last dose. This is important because VIVITROL can also block the effects of opioid-containing medicines that might be prescribed for you for pain, cough or colds, or diarrhea.
- Carry written information with you at all times to alert healthcare providers that you are taking VIVITROL, so that they can treat you properly in an emergency. Ask your healthcare provider how you can get a wallet card to carry with you.
What should I avoid while receiving VIVITROL?
Do not drive a car, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how VIVITROL affects you. VIVITROL may make you feel dizzy and sleepy. See “What are the possible side effects of VIVITROL?”
What are the possible side effects of VIVITROL?
VIVITROL can cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about VIVITROL?”
-
Depressed mood. Sometimes this leads to suicide, or suicidal thoughts, and suicidal behavior. Tell your family members and people closest to you that you are taking VIVITROL.
You, a family member, or the people closest to you should call your healthcare provider right away if you become depressed or have any of the following symptoms of depression, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:- You feel sad or have crying spells.
- You are no longer interested in seeing your friends or doing things you used to enjoy.
- You are sleeping a lot more or a lot less than usual.
- You feel hopeless or helpless.
- You are more irritable, angry, or aggressive than usual.
- You are more or less hungry than usual or notice a big change in your body weight.
- You have trouble paying attention.
- You feel tired or sleepy all the time.
- You have thoughts about hurting yourself or ending your life.
-
Pneumonia. Some people receiving VIVITROL treatment have had a certain type of pneumonia that is caused by an allergic reaction. If this happens to you, you may need to be treated in the hospital. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms during treatment with VIVITROL:
- shortness of breath or wheezing
- coughing that does not go away
-
Serious allergic reactions. Serious allergic reactions can happen during or soon after an injection of VIVITROL. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms of a serious allergic reaction.
- skin rash
- swelling of your face, eyes, mouth, or tongue
- trouble breathing or wheezing
- chest pain
- feeling dizzy or faint
Common side effects of VIVITROL may include:
- nausea. Nausea may happen after your first VIVITROL injection and usually improves within a few days. Nausea is less likely with future injections of VIVITROL.
- sleepiness
- headache
- dizziness
- vomiting
- decreased appetite
- painful joints
- muscle cramps
- cold symptoms
- trouble sleeping
- toothache
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects of VIVITROL. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about VIVITROL
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about VIVITROL. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about VIVITROL that is written for health professionals.
For more information about VIVITROL call 1-800-848-4876, Option #1 or go to www.vivitrol.com.
What are the ingredients in VIVITROL?
Active ingredient: naltrexone
Inactive ingredients: polylactide-co-glycolide (PLG)
Diluent ingredients: carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt, polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, and water for injection
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured and marketed by:
Alkermes, Inc.
852 Winter Street
Waltham, MA 02451-1420
Revised: July 2019
Alkermes® and VIVITROL® are registered trademarks of Alkermes, Inc. -
Risk of opioid overdose.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-VIVITROL® COMMERCIAL KIT CARTON
NDC: 65757-300-01
Rx Only
VIVITROL®
(naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension)
380 mg/vial
VIVITROL must be injected by a healthcare provider.
Severe injection site reactions that required surgery and/or hospitalization have occurred with VIVITROL.
Healthcare provider: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient
Please see accompanying full prescribing information.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
Must reconstitute VIVITROL Microspheres with enclosed diluent prior to administration. Upon reconstitution with 3.4 mL diluent, each mL will contain 95 mg of naltrexone.
Each Carton Contains:
1) One vial of 380 mg of VIVITROL (naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension)*
2) One vial containing 4 mL of diluent†
3) One 5-mL prepackaged syringe
4) One 20-gauge 1-inch needle
5) Two 20-gauge 1½-inch safety needles
6) Two 20-gauge 2-Inch safety needles
*VIVITROL Microspheres: 380 mg of naltrexone per vial, contained in a biodegradable matrix of 75:25 polylactide-co-glycolide at a concentration of 337 mg of naltrexone per gram of microspheres.
†Diluent contains (carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt, polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, and sterile water for injection).
Storage:
Store in outer carton, refrigerated at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F).
If refrigeration is unavailable, product can be stored at temperatures not exceeding 25 °C (77 °F) for no more than 7 days prior to administration. Do not expose unrefrigerated product to temperatures above 25 °C (77 °F). Do not freeze.
Remove the carton from the refrigerator and allow it to come to room temperature prior to preparation.
Keep out of reach of children.
ALKERMES® and VIVITROL® are registered trademarks of Alkermes, Inc. Manufactured and marketed by Alkermes, Inc. www.vivitrol.com 1-800-848-4876
Alkermes®
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-VIVITROL ®MICROSPHERES VIAL LABEL
NDC: 65757-302-02
Rx Only
VIVITROL® Microspheres, 380 mg/vial
(naltrexone for extended-release injectable suspension)
Single-Use Vial. Discard unused portion. For gluteal intramuscular injection only. Must be diluted with the enclosed diluent prior to administration. Upon reconstitution with 3.4 mL diluent, each mL will contain 95 mg of naltrexone. See Package Insert for dose preparation and administration. Storage: Refrigerate at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). Manufactured and marketed by: Alkermes, Inc., Waltham, MA 02451
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-VIVITROL ®DILUENT VIAL LABEL
NDC: 65757-304-03
Rx Only
Diluent for use only with
VIVITROL ®microspheres, 4 mL/VialDiluent contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt, polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, and sterile water for injection. Single-Use Vial. Discard unused portion. Not for direct administration. See Package Insert for dose preparation. Storage: Refrigerate at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). 4 mL (to withdraw 3.4 mL for reconstitution).
Manufactured for: Alkermes, Inc., Waltham, MA 02451
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-VIVITROL ®DILUENT VIAL LABEL
NDC: 65757-304-03
Rx Only
Diluent for use only with
VIVITROL ®microspheres, 4 mL/vialDiluent contains carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt, polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, and sterile water for injection. Single-Use Vial. Discard unused portion. Not for direct administration. See Package Insert for dose preparation. Storage: Refrigerate at 2-8 °C (36-46 °F). 4 mL (to withdraw 3.4 mL for reconstitution). Manufactured for: Alkermes, Inc., Waltham, MA 02451 by OSO BioPharmaceuticals Mfg., LLC, Albuquerque, NM 87107
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VIVITROL
naltrexone kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 65757-300 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65757-300-01 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/13/2006 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 VIAL, GLASS 4 mL Part 2 1 VIAL, GLASS 4 mL Part 1 of 2 VIVITROL MICROSPHERE
naltrexone injection, powder, for suspension, extended releaseProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 65757-302 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength naltrexone (UNII: 5S6W795CQM) (naltrexone - UNII:5S6W795CQM) naltrexone 380 mg in 4 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65757-302-02 4 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021897 06/13/2006 Part 2 of 2 VIVITROL DILUENT
microsphere diluent injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC: 65757-304 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength carboxymethylcellulose sodium, unspecified form (UNII: K679OBS311) polysorbate 20 (UNII: 7T1F30V5YH) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 65757-304-03 4 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021897 06/13/2006 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021897 06/13/2006 Labeler - Alkermes, Inc. (185481132) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Alkermes, Inc. 858582083 MANUFACTURE(65757-300) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Packaging Coordinators, LLC 078525133 PACK(65757-300) , LABEL(65757-300) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sharp Corporation 143696495 REPACK(65757-300) , RELABEL(65757-300) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Oso Biopharmaceutcals 078268825 MANUFACTURE(65757-300)
Trademark Results [VIVITROL]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 VIVITROL 86681650 4895654 Live/Registered |
Alkermes, Inc. 2015-07-02 |
 VIVITROL 77578157 3681273 Live/Registered |
Alkermes, Inc. 2008-09-24 |
 VIVITROL 76414428 3104288 Live/Registered |
ALKERMES, INC. 2002-05-28 |
 VIVITROL 72206768 0795202 Dead/Expired |
STAMFORD CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES, INC. 1964-11-23 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.