REPATHA- evolocumab injection, solution REPATHA- evolocumab kit
REPATHA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
REPATHA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amgen USA Inc., Amgen, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use REPATHA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for REPATHA.
REPATHA (evolocumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REPATHA is a PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9) inhibitor antibody indicated:
- to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and coronary revascularization in adults with established cardiovascular disease. (1.1)
- as an adjunct to diet, alone or in combination with other lipid-lowering therapies (e.g., statins, ezetimibe), for treatment of adults with primary hyperlipidemia (including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). (1.2)
- as an adjunct to diet and other LDL-lowering therapies (e.g., statins, ezetimibe, LDL apheresis) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) who require additional lowering of LDL-C. (1.3)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer subcutaneously. (2.1)
- Adults with established cardiovascular disease or primary hyperlipidemia (including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia): 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly in abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. (2.1)
- HoFH: 420 mg once monthly. (2.1)
- The 420 mg dose of REPATHA can be administered:
○ over 9 minutes by using the single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge, or
○ by giving 3 injections consecutively within 30 minutes using the single-use prefilled autoinjector or single-use prefilled syringe. (2.2)
- See Dosage and Administration for important administration instructions. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with a history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to REPATHA. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Allergic Reactions: Angioedema, rash, and urticaria have occurred. If signs or symptoms of serious allergic reactions occur, discontinue treatment with REPATHA, treat according to the standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions in clinical trials in primary hyperlipidemia (including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) (> 5% of patients treated with REPATHA and occurring more frequently than placebo): nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, influenza, back pain, and injection site reactions. (6)
Common adverse reactions in the cardiovascular outcomes trial (> 5% of patients treated with REPATHA and occurring more frequently than placebo): diabetes mellitus, nasopharyngitis and upper respiratory tract infection. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amgen Medical Information at 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2019
- to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and coronary revascularization in adults with established cardiovascular disease. (1.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events
1.2 Primary Hyperlipidemia (Including Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
1.3 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Immunogenicity
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events
14.2 Primary Hyperlipidemia (Including Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
14.3 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events
In adults with established cardiovascular disease, REPATHA® is indicated to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and coronary revascularization.
1.2 Primary Hyperlipidemia (Including Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
REPATHA is indicated as an adjunct to diet, alone or in combination with other lipid-lowering therapies (e.g., statins, ezetimibe), for the treatment of adults with primary hyperlipidemia to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
-
2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of REPATHA in adults with established cardiovascular disease or in adults with primary hyperlipidemia (including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia [HeFH]) is either 140 mg every 2 weeks OR 420 mg once monthly, based on patient preference for dosing frequency and injection volume. When switching dosage regimens, administer the first dose of the new regimen on the next scheduled date of the prior regimen.
The recommended subcutaneous dosage of REPATHA in patients with HoFH is 420 mg once monthly. In patients with HoFH, measure LDL-C levels 4 to 8 weeks after starting REPATHA, since response to therapy will depend on the degree of LDL-receptor function.
When monitoring LDL-C for patients receiving REPATHA 420 mg once monthly, note that LDL-C can vary considerably during the dosing interval in some patients [see Clinical Studies (14)].
If a dose is missed, instruct the patient to administer REPATHA within 7 days from the missed dose and resume the patient’s original schedule.
- If an every-2-week dose is not administered within 7 days, instruct the patient to wait until the next dose on the original schedule.
- If a once-monthly dose is not administered within 7 days, instruct the patient to administer the dose and start a new schedule based on this date.
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
- The 420 mg dose of REPATHA can be administered:
○ over 9 minutes by using the single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge, or
○ by giving 3 injections consecutively within 30 minutes using the single-use prefilled autoinjector or single-use prefilled syringe.
- Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on how to prepare and administer REPATHA prior to use, according to the Instructions for Use, including aseptic technique. Instruct patients and/or caregivers to read and follow the Instructions for Use each time they use REPATHA.
- Keep REPATHA in the refrigerator. Prior to use, allow REPATHA to warm to room temperature for at least 30 minutes for the single-use prefilled autoinjector or single-use prefilled syringe and for at least 45 minutes for the single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge. Do not warm in any other way. Alternatively, for patients and caregivers, REPATHA can be kept at room temperature at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) in the original carton. However, under these conditions, REPATHA must be used within 30 days [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
- Visually inspect REPATHA for particles and discoloration prior to administration. REPATHA is a clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use if the solution is cloudy or discolored or contains particles.
- Administer REPATHA subcutaneously into areas of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm that are not tender, bruised, red, or indurated using a single-use prefilled syringe, single-use prefilled autoinjector, or single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge.
- Do not co-administer REPATHA with other injectable drugs at the same administration site.
- Rotate the site of each subcutaneous administration.
- If an every-2-week dose is not administered within 7 days, instruct the patient to wait until the next dose on the original schedule.
-
3
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
REPATHA is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution available as follows:
- Injection: 140 mg/mL solution in a single-use prefilled syringe
- Injection: 140 mg/mL solution in a single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector
- Injection: 420 mg/3.5 mL solution in a single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge)
- Injection: 140 mg/mL solution in a single-use prefilled syringe
-
4
CONTRAINDICATIONS
REPATHA is contraindicated in patients with a history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to REPATHA. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema have occurred in patients treated with REPATHA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., angioedema, rash, urticaria) have been reported in patients treated with REPATHA, including some that led to discontinuation of therapy. If signs or symptoms of serious allergic reactions occur, discontinue treatment with REPATHA, treat according to the standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve [see Contraindications (4)].
-
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the label:
- Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adults with Primary Hyperlipidemia (including Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
The data described below reflect exposure to REPATHA in 8 placebo-controlled trials that included 2651 patients treated with REPATHA, including 557 exposed for 6 months and 515 exposed for 1 year (median treatment duration of 12 weeks). The mean age of the population was 57 years, 49% of the population were women, 85% White, 6% Black, 8% Asians, and 2% other races.
Adverse Reactions in a 52-Week Controlled Trial
In a 52-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (Study 3 [DESCARTES, NCT01516879]), 599 patients received 420 mg of REPATHA subcutaneously once monthly [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The mean age was 56 years (range: 22 to 75 years), 23% were older than 65 years, 52% women, 80% White, 8% Black, 6% Asian; 6% identified as Hispanic ethnicity. Adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of REPATHA-treated patients, and more frequently than in placebo-treated patients in DESCARTES, are shown in Table 1. Adverse reactions led to discontinuation of treatment in 2.2% of REPATHA-treated patients and 1% of placebo-treated patients. The most common adverse reaction that led to REPATHA treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo was myalgia (0.3% versus 0% for REPATHA and placebo, respectively).
Table 1. Adverse Reactions Occurring in Greater than or Equal to 3% of REPATHA-treated Patients and More Frequently than with Placebo in DESCARTES Placebo
(N = 302)
%REPATHA
(N = 599)
%Nasopharyngitis 9.6 10.5 Upper respiratory tract infection 6.3 9.3 Influenza 6.3 7.5 Back pain 5.6 6.2 Injection site reactions† 5.0 5.7 Cough 3.6 4.5 Urinary tract infection 3.6 4.5 Sinusitis 3.0 4.2 Headache 3.6 4.0 Myalgia 3.0 4.0 Dizziness 2.6 3.7 Musculoskeletal pain 3.0 3.3 Hypertension 2.3 3.2 Diarrhea 2.6 3.0 Gastroenteritis 2.0 3.0 † includes erythema, pain, bruising
Adverse Reactions in Seven Pooled 12-Week Controlled Trials
In seven pooled 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, 993 patients received 140 mg of REPATHA subcutaneously every 2 weeks and 1059 patients received 420 mg of REPATHA subcutaneously monthly. The mean age was 57 years (range: 18 to 80 years), 29% were older than 65 years, 49% women, 85% White, 5% Black, 9% Asian; 5% identified as Hispanic ethnicity. Adverse reactions reported in at least 1% of REPATHA-treated patients, and more frequently than in placebo-treated patients, are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Occurring in Greater than 1% of REPATHA-treated Patients and More Frequently than with Placebo in Pooled 12-Week Trials Placebo
(N = 1224)
%REPATHA†
(N = 2052)
%Nasopharyngitis 3.9 4.0 Back pain 2.2 2.3 Upper respiratory tract infection 2.0 2.1 Arthralgia 1.6 1.8 Nausea 1.2 1.8 Fatigue 1.0 1.6 Muscle spasms 1.2 1.3 Urinary tract infection 1.2 1.3 Cough 0.7 1.2 Influenza 1.1 1.2 Contusion 0.5 1.0 † 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly combined
Adverse Reactions in Eight Pooled Controlled Trials (Seven 12-Week Trials and One 52-Week Trial)
The adverse reactions described below are from a pool of the 52-week trial (DESCARTES) and seven 12-week trials. The mean and median exposure durations of REPATHA in this pool of eight trials were 20 weeks and 12 weeks, respectively.
Local Injection Site Reactions
Injection site reactions occurred in 3.2% and 3.0% of REPATHA-treated and placebo-treated patients, respectively. The most common injection site reactions were erythema, pain, and bruising. The proportions of patients who discontinued treatment due to local injection site reactions in REPATHA-treated patients and placebo-treated patients were 0.1% and 0%, respectively.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions occurred in 5.1% and 4.7% of REPATHA-treated and placebo-treated patients, respectively. The most common allergic reactions were rash (1.0% versus 0.5% for REPATHA and placebo, respectively), eczema (0.4% versus 0.2%), erythema (0.4% versus 0.2%), and urticaria (0.4% versus 0.1%).
Adverse Reactions in the Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial
In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled cardiovascular outcomes trial (Study 1 [REPATHA Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial, FOURIER, NCT01764633]), 27,525 patients received at least one dose of REPATHA or placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The mean age was 62.5 years (range: 40 to 86 years), 45% were 65 years or older, 9% were 75 years or older, 25% women, 85% White, 2% Black and 10% Asian; 8% identified as Hispanic ethnicity. Patients were exposed to REPATHA or placebo for a median of 24.8 months; 91% of patients were exposed for ≥ 12 months, 54% were exposed for ≥ 24 months and 5% were exposed for ≥ 36 months.
The safety profile of REPATHA in this trial was generally consistent with the safety profile described above in the 12- and 52-week controlled trials involving patients with primary hyperlipidemia (including HeFH). Serious adverse events occurred in 24.8% and 24.7% of REPATHA-treated and placebo-treated patients, respectively. Adverse events led to discontinuation of study treatment in 4.4% of patients assigned to REPATHA and 4.2% assigned to placebo. Common adverse reactions (> 5% of patients treated with REPATHA and occurring more frequently than placebo) included diabetes mellitus (8.8% REPATHA, 8.2% placebo), nasopharyngitis (7.8% REPATHA, 7.4% placebo), and upper respiratory tract infection (5.1% REPATHA, 4.8% placebo).
Among the 16,676 patients without diabetes mellitus at baseline, the incidence of new-onset diabetes mellitus during the trial was 8.1% in patients assigned to REPATHA compared with 7.7% in those assigned to placebo.
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
In a 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 49 patients with HoFH (Study 6 [TESLA, NCT01588496]), 33 patients received 420 mg of REPATHA subcutaneously once monthly [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. The mean age was 31 years (range: 13 to 57 years), 49% were women, 90% White, 4% Asian, and 6% other. The adverse reactions that occurred in at least two (6.1%) REPATHA-treated patients, and more frequently than in placebo-treated patients, included:
- Upper respiratory tract infection (9.1% versus 6.3%)
- Influenza (9.1% versus 0%)
- Gastroenteritis (6.1% versus 0%)
- Nasopharyngitis (6.1% versus 0%)
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to REPATHA in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
The immunogenicity of REPATHA has been evaluated using an electrochemiluminescent bridging screening immunoassay for the detection of binding anti-drug antibodies. For patients whose sera tested positive in the screening immunoassay, an in vitro biological assay was performed to detect neutralizing antibodies.
In a pool of placebo- and active-controlled clinical trials, 0.3% (48 out of 17,992) of patients treated with at least one dose of REPATHA tested positive for the development of binding antibodies. Patients whose sera tested positive for binding antibodies were further evaluated for neutralizing antibodies; none of the patients tested positive for neutralizing antibodies.
There was no evidence that the presence of anti-drug binding antibodies impacted the pharmacokinetic profile, clinical response, or safety of REPATHA, but the long-term consequences of continuing REPATHA treatment in the presence of anti-drug binding antibodies are unknown.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of REPATHA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Allergic reactions: Angioedema
- Influenza-like illness
-
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to REPATHA during pregnancy.
Please contact 1-877-311-8972 or https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/repatha/ to enroll in or to obtain information about the registry.
Risk Summary
There are no data available on use of REPATHA in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, there were no effects on pregnancy or neonatal/infant development when monkeys were subcutaneously administered evolocumab from organogenesis through parturition at dose exposures up to 12 times the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose of 420 mg every month. In a similar study with another drug in the PCSK9 inhibitor antibody class, humoral immune suppression was observed in infant monkeys exposed to that drug in utero at all doses. The exposures where immune suppression occurred in infant monkeys were greater than those expected clinically. No assessment for immune suppression was conducted with evolocumab in infant monkeys. Measurable evolocumab serum concentrations were observed in the infant monkeys at birth at comparable levels to maternal serum, indicating that evolocumab, like other IgG antibodies, crosses the placental barrier. FDA’s experience with monoclonal antibodies in humans indicates that they are unlikely to cross the placenta in the first trimester; however, they are likely to cross the placenta in increasing amounts in the second and third trimester. Consider the benefits and risks of REPATHA and possible risks to the fetus before prescribing REPATHA to pregnant women.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In cynomolgus monkeys, no effects on embryo-fetal or postnatal development (up to 6 months of age) were observed when evolocumab was dosed during organogenesis to parturition at 50 mg/kg once every 2 weeks by the subcutaneous route at exposures 30- and 12-fold the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC. No test of humoral immunity in infant monkeys was conducted with evolocumab.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of evolocumab in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for REPATHA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from REPATHA or from the underlying maternal condition. Human IgG is present in human milk, but published data suggest that breast milk antibodies do not enter the neonatal and infant circulation in substantial amounts.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of REPATHA in combination with diet and other LDL-C-lowering therapies in adolescents with HoFH who require additional lowering of LDL-C were established based on data from a 12-week, placebo-controlled trial that included 10 adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years old) with HoFH [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. In this trial, 7 adolescents received REPATHA 420 mg subcutaneously once monthly and 3 adolescents received placebo. The effect of REPATHA on LDL-C was generally similar to that observed among adult patients with HoFH. Including experience from open-label, uncontrolled studies, a total of 14 adolescents with HoFH have been treated with REPATHA, with a median exposure duration of 9 months. The safety profile of REPATHA in these adolescents was similar to that described for adult patients with HoFH.
The safety and effectiveness of REPATHA have not been established in pediatric patients with HoFH who are younger than 13 years old.
The safety and effectiveness of REPATHA have not been established in pediatric patients with primary hyperlipidemia or HeFH.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In controlled trials, 7656 (41%) patients treated with REPATHA were ≥ 65 years old and 1500 (8%) were ≥ 75 years old. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B). No data are available in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
11
DESCRIPTION
Evolocumab is a human monoclonal immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) directed against human proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9). Evolocumab has an approximate molecular weight (MW) of 144 kDa and is produced in genetically engineered mammalian (Chinese hamster ovary) cells.
REPATHA is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution for subcutaneous administration. Each 1 mL single-use prefilled syringe and single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector contains 140 mg evolocumab, acetate (1.2 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.1 mg), proline (25 mg) in Water for Injection, USP. Sodium hydroxide may be used to adjust to a pH of 5.0. Each single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge) delivers a 3.5 mL solution containing 420 mg evolocumab, acetate (4.2 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.35 mg), proline (89 mg) in Water for Injection, USP. Sodium hydroxide may be used to adjust to a pH of 5.0.
-
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Evolocumab is a human monoclonal IgG2 directed against human proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9). Evolocumab binds to PCSK9 and inhibits circulating PCSK9 from binding to the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR), preventing PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation and permitting LDLR to recycle back to the liver cell surface. By inhibiting the binding of PCSK9 to LDLR, evolocumab increases the number of LDLRs available to clear LDL from the blood, thereby lowering LDL-C levels.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following single subcutaneous administration of 140 mg or 420 mg of evolocumab, maximum suppression of circulating unbound PCSK9 occurred by 4 hours. Unbound PCSK9 concentrations returned toward baseline when evolocumab concentrations decreased below the limit of quantitation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Evolocumab exhibits non-linear kinetics as a result of binding to PCSK9. Administration of the 140 mg dose in healthy volunteers resulted in a Cmax mean (standard deviation [SD]) of 18.6 (7.3) μg/mL and AUClast mean (SD) of 188 (98.6) dayμg/mL. Administration of the 420 mg dose in healthy volunteers resulted in a Cmax mean (SD) of 59.0 (17.2) μg/mL and AUClast mean (SD) of 924 (346) dayμg/mL. Following a single 420 mg intravenous dose, the mean (SD) systemic clearance was estimated to be 12 (2) mL/hr. An approximate 2- to 3-fold accumulation was observed in trough serum concentrations (Cmin [SD] 7.21 [6.6]) following 140 mg doses administered subcutaneously every 2 weeks or following 420 mg doses administered subcutaneously monthly (Cmin [SD] 11.2 [10.8]), and serum trough concentrations approached steady-state by 12 weeks of dosing.
Absorption
Following a single subcutaneous dose of 140 mg or 420 mg evolocumab administered to healthy adults, median peak serum concentrations were attained in 3 to 4 days, and estimated absolute bioavailability was 72%.
Distribution
Following a single 420 mg intravenous dose, the mean (SD) steady-state volume of distribution was estimated to be 3.3 (0.5) L.
Metabolism and Elimination
Two elimination phases were observed for REPATHA. At low concentrations, the elimination is predominately through saturable binding to target (PCSK9), while at higher concentrations the elimination of REPATHA is largely through a non-saturable proteolytic pathway. REPATHA was estimated to have an effective half-life of 11 to 17 days.
Specific Populations
The pharmacokinetics of evolocumab were not affected by age, gender, race, or creatinine clearance across all approved populations [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
The exposure of evolocumab decreased with increasing body weight. These differences are not clinically meaningful.
Renal Impairment
Since monoclonal antibodies are not known to be eliminated via renal pathways, renal function is not expected to impact the pharmacokinetics of evolocumab.
In a clinical trial of 18 patients with either normal renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] ≥ 90 mL/min/1.73 m2, n = 6), severe renal impairment (eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, n = 6), or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) receiving hemodialysis (n = 6), exposure to evolocumab after a single 140 mg subcutaneous dose was decreased in patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD receiving hemodialysis. Reductions in PCSK9 levels in patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD receiving hemodialysis was similar to those with normal renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 140 mg subcutaneous dose of evolocumab in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment, a 20-30% lower mean Cmax and 40-50% lower mean AUC were observed as compared to healthy patients; however, no dose adjustment is necessary in these patients.
Pregnancy
The effect of pregnancy on evolocumab pharmacokinetics has not been studied [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Drug Interaction Studies
An approximately 20% decrease in the Cmax and AUC of evolocumab was observed in patients co-administered with a high-intensity statin regimen. This difference is not clinically meaningful and does not impact dosing recommendations.
-
13
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of evolocumab was evaluated in a lifetime study conducted in the hamster at dose levels of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg administered every 2 weeks. There were no evolocumab-related tumors at the highest dose at systemic exposures up to 38- and 15-fold the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC. The mutagenic potential of evolocumab has not been evaluated; however, monoclonal antibodies are not expected to alter DNA or chromosomes.
There were no adverse effects on fertility (including estrous cycling, sperm analysis, mating performance, and embryonic development) at the highest dose in a fertility and early embryonic developmental toxicology study in hamsters when evolocumab was subcutaneously administered at 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg every 2 weeks. The highest dose tested corresponds to systemic exposures up to 30- and 12-fold the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC. In addition, there were no adverse evolocumab-related effects on surrogate markers of fertility (reproductive organ histopathology, menstrual cycling, or sperm parameters) in a 6-month chronic toxicology study in sexually mature monkeys subcutaneously administered evolocumab at 3, 30, and 300 mg/kg once weekly. The highest dose tested corresponds to 744- and 300-fold the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
During a 3-month toxicology study of 10 and 100 mg/kg once every 2 weeks evolocumab in combination with 5 mg/kg once daily rosuvastatin in adult monkeys, there were no effects of evolocumab on the humoral immune response to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) after 1 to 2 months exposure. The highest dose tested corresponds to exposures 54- and 21-fold higher than the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC. Similarly, there were no effects of evolocumab on the humoral immune response to KLH (after 3 to 4 months exposure) in a 6-month study in cynomolgus monkeys at dose levels up to 300 mg/kg once weekly evolocumab corresponding to exposures 744- and 300-fold greater than the recommended human doses of 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly, respectively, based on plasma AUC.
-
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events
Study 1 (FOURIER, NCT01764633) was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, event-driven trial in 27,564 (13,784 REPATHA, 13,780 placebo) adult patients with established cardiovascular disease and with LDL-C ≥ 70 mg/dL and/or non-HDL-C ≥ 100 mg/dL despite high- or moderate-intensity statin therapy. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either subcutaneous injections of REPATHA (140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly) or placebo; 86% used the every-2-week regimen throughout the trial. The median follow-up duration was 26 months. Overall, 99.2% of patients were followed until the end of the trial or death.
The mean (SD) age at baseline was 63 (9) years, with 45% being at least 65 years old; 25% were women. The trial population was 85% White, 2% Black, and 10% Asian; 8% identified as Hispanic ethnicity. Regarding prior diagnoses of cardiovascular disease, 81% had prior myocardial infarction, 19% prior non-hemorrhagic stroke, and 13% had symptomatic peripheral arterial disease. Selected additional baseline risk factors included hypertension (80%), diabetes mellitus (1% type 1; 36% type 2), current daily cigarette smoking (28%), New York Heart Association class I or II congestive heart failure (23%), and eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (6%). Most patients were on a high- (69%) or moderate-intensity (30%) statin therapy at baseline, and 5% were also taking ezetimibe. Most patients were taking at least one other cardiovascular medication including anti-platelet agents (93%), beta blockers (76%), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (56%), or angiotensin receptor blockers (23%). On stable background lipid-lowering therapy, the median [Q1, Q3] LDL-C at baseline was 92 [80, 109] mg/dL; the mean (SD) was 98 (28) mg/dL.
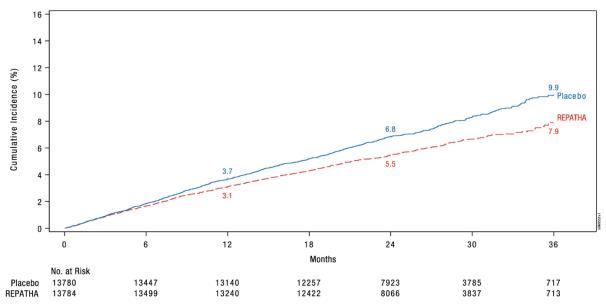
REPATHA significantly reduced the risk for the primary composite endpoint (time to first occurrence of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or coronary revascularization; p < 0.0001) and the key secondary composite endpoint (time to first occurrence of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke; p < 0.0001). The Kaplan-Meier estimates of the cumulative incidence of the primary and key secondary composite endpoints over time are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 below.
The results of primary and secondary efficacy endpoints are shown in Table 3 below.
Table 3. Effect of REPATHA on Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Established Cardiovascular Disease in FOURIER Placebo REPATHA REPATHA
vs. Placebo
N = 13780
n (%)Incidence
Rate (per
100 patient
years)
N = 13784
n (%)Incidence
Rate (per
100
patient
years)Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)
Primary composite endpoint Time to first occurrence of
cardiovascular death,
myocardial infarction, stroke,
coronary revascularization,
hospitalization for unstable
angina1563 (11.3) 5.2 1344 (9.8) 4.5 0.85
(0.79, 0.92)Key secondary composite endpoint Time to first occurrence of
cardiovascular death,
myocardial infarction, stroke1013 (7.4) 3.4 816 (5.9) 2.7 0.80
(0.73, 0.88)Other secondary endpoints Time to cardiovascular death 240 (1.7) 0.8 251 (1.8) 0.8 1.05
(0.88, 1.25)Time to death by any causea 426 (3.1) 1.4 444 (3.2) 1.5 1.04
(0.91, 1.19)Time to first fatal or non-fatal
myocardial infarction639 (4.6) 2.1 468 (3.4) 1.6 0.73
(0.65, 0.82)Time to first fatal or non-fatal stroke 262 (1.9) 0.9 207 (1.5) 0.7 0.79
(0.66, 0.95)Time to first coronary revascularization 965 (7.0) 3.2 759 (5.5) 2.5 0.78
(0.71, 0.86)Time to first hospitalization for unstable anginab 239 (1.7) 0.8 236 (1.7) 0.8 0.99
(0.82, 1.18)a Time to death by any cause is not a component of either the primary composite endpoint or key secondary composite endpoint.
b Not a prespecified endpoint; an ad hoc analysis was performed to ensure results are provided for each individual component of the primary endpoint.Figure 1. Estimated Cumulative Incidence of Primary Composite Endpoint Over 3 Years in FOURIER
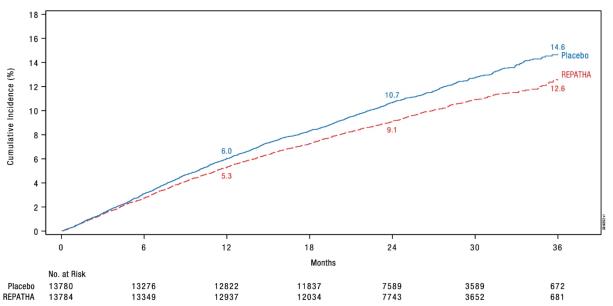
Figure 2. Estimated Cumulative Incidence of Key Secondary Composite Endpoint Over 3 Years in FOURIER
The difference between REPATHA and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -63% (95% CI: -63%, -62%) and from baseline to Week 72 was -57% (95% CI: -58%, -56%). At Week 48, the median [Q1, Q3] LDL-C was 26 [15, 46] mg/dL in the REPATHA group, with 47% of patients having LDL-C < 25 mg/dL.
Considering all assessments, among the patients treated with REPATHA, 10401 (76%) had at least one LDL-C value < 25 mg/dL. Although not a randomized comparison, the safety profile was similar between REPATHA-treated patients with post-baseline LDL-C < 25 mg/dL compared with REPATHA-treated patients with higher post-baseline LDL-C (LDL-C ≥ 40 mg/dL).
In EBBINGHAUS (NCT02207634), a substudy of 1974 patients enrolled in the FOURIER trial, REPATHA was non-inferior to placebo on selected cognitive function domains as assessed with the use of neuropsychological function tests over a median follow-up of 19 months.
14.2 Primary Hyperlipidemia (Including Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia)
Study 2 (LAPLACE-2, NCT01763866) was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled 12-week trial in which patients were initially randomized to an open-label specific statin regimen for a 4-week lipid stabilization period followed by random assignment to subcutaneous injections of REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks, REPATHA 420 mg once monthly, or placebo for 12 weeks. The trial included 1896 patients with hyperlipidemia who received REPATHA, placebo, or ezetimibe as add-on therapy to daily doses of statins (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, or simvastatin). Ezetimibe was also included as an active control only among those assigned to background atorvastatin. Overall, the mean age at baseline was 60 years (range: 20 to 80 years), 35% were ≥ 65 years old, 46% women, 94% White, 4% were Black, and 1% Asian; 5% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. After 4 weeks of background statin therapy, the mean baseline LDL-C ranged between 77 and 127 mg/dL across the five background therapy arms.
The difference between REPATHA and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -71% (95% CI: -74%, -67%; p < 0.0001) and -63% (95% CI: -68%, -57%; p ˂ 0.0001) for the 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly dosages, respectively. The difference between REPATHA and ezetimibe in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -45% (95% CI: -52%, -39%; p < 0.0001) and -41% (95% CI: -47%, -35%; p ˂ 0.0001) for the 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly dosages, respectively. For additional results see Table 4 and Figure 3.
Table 4. Effect of REPATHA on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Hyperlipidemia on Background Statin Regimens (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in LAPLACE-2) Treatment Group LDL-C Non-HDL-C Apo B Total Cholesterol REPATHA every 2 weeks vs. Placebo every 2 weeks
(Background statin: atorvastatin 10 mg or 80 mg; rosuvastatin 5 mg or 40 mg; simvastatin 40 mg)Placebo every 2 weeks (n = 281) 8 6 5 4 REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks† (n = 555) -63 -53 -49 -36 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-71
(-74, -67)
-59
(-62, -55)
-55
(-58, -52)
-40
(-43, -38)
REPATHA once monthly vs. Placebo once monthly
(Background statin: atorvastatin 10 mg or 80 mg; rosuvastatin 5 mg or 40 mg; simvastatin 40 mg)Placebo once monthly (n = 277) 4 5 3 2 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly (n = 562) -59 -50 -46 -34 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-63
(-68, -57)
-54
(-58, -50)
-50
(-53, -47)
-36
(-39, -33)
REPATHA every 2 weeks vs. Ezetimibe 10 mg daily
(Background statin: atorvastatin 10 mg or 80 mg)Ezetimibe 10 mg daily (n = 112) -17 -16 -14 -12 REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks† (n = 219) -63 -52 -49 -36 Mean difference from Ezetimibe
(95% CI)-45
(-52, -39)-36
(-41, -31)-35
(-40, -31)-24
(-28, -20)REPATHA once monthly vs. Ezetimibe 10 mg daily
(Background statin: atorvastatin 10 mg or 80 mg)Ezetimibe 10 mg daily (n = 109) -19 -16 -11 -12 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly (n = 220) -59 -50 -46 -34 Mean difference from Ezetimibe
(95% CI)-41
(-47, -35)-35
(-40, -29)-34
(-39, -30)-22
(-26, -19)Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence.
† 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly yield similar reductions in LDL-C
Figure 3. Effect of REPATHA on LDL-C in Patients with Hyperlipidemia when Combined with Statins (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in LAPLACE-2)
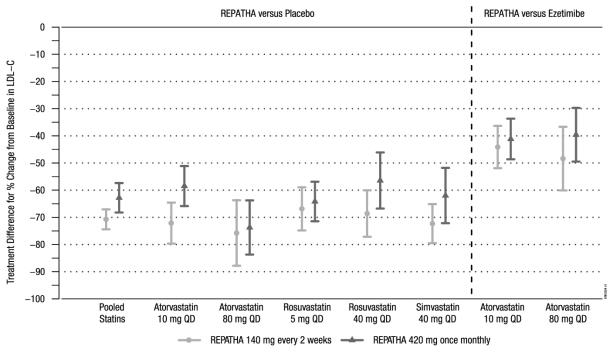
Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherenceError bars indicate 95% confidence intervals
Study 3 (DESCARTES, NCT01516879) was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trial that included 901 patients with hyperlipidemia who received protocol-determined background lipid-lowering therapy of a cholesterol-lowering diet either alone or in addition to atorvastatin (10 mg or 80 mg daily) or the combination of atorvastatin 80 mg daily with ezetimibe. After stabilization on background therapy, patients were randomly assigned to the addition of placebo or REPATHA 420 mg administered subcutaneously once monthly. Overall, the mean age at baseline was 56 years (range: 25 to 75 years), 23% were ≥ 65 years, 52% women, 80% White, 8% Black, and 6% Asian; 6% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. After stabilization on the assigned background therapy, the mean baseline LDL-C ranged between 90 and 117 mg/dL across the four background therapy groups.
In these patients with hyperlipidemia on a protocol-determined background therapy, the difference between REPATHA 420 mg once monthly and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 52 was -55% (95% CI: -60%, -50%; p ˂ 0.0001) (Table 5 and Figure 4). For additional results see Table 5.
Table 5. Effect of REPATHA on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Hyperlipidemia* (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 52 in DESCARTES) Treatment Group LDL-C Non-HDL-C Apo B Total Cholesterol Placebo once monthly (n = 302) 8 8 2 5 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly (n = 599) -47 -39 -38 -26 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-55
(-60, -50)-46
(-50, -42)
-40
(-44, -37)-31
(-34, -28)
Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
* Prior to randomization, patients were stabilized on background therapy consisting of a cholesterol-lowering diet either alone or in addition to atorvastatin (10 mg or 80 mg daily) or the combination of atorvastatin 80 mg daily with ezetimibe.
Figure 4. Effect of REPATHA 420 mg Once Monthly on LDL-C in Patients with Hyperlipidemia in DESCARTES
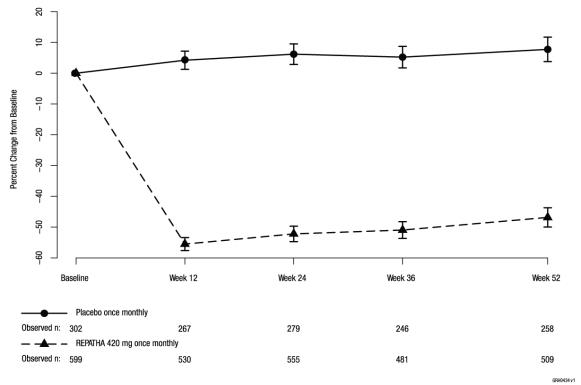
Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals
Study 4 (MENDEL-2, NCT01763827) was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled, 12-week trial that included 614 patients with hyperlipidemia who were not taking lipid-lowering therapy at baseline. Patients were randomly assigned to receive subcutaneous injections of REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks, REPATHA 420 mg once monthly, or placebo for 12 weeks. Blinded administration of ezetimibe was also included as an active control. Overall, the mean age at baseline was 53 years (range: 20 to 80 years), 18% were ≥ 65 years old, 66% were women, 83% White, 7% Black, and 9% Asian; 11% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean baseline LDL-C was 143 mg/dL.
The difference between REPATHA and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -55% (95% CI: -60%, -50%; p < 0.0001) and -57% (95% CI: -61%, -52%; p ˂ 0.0001) for the 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly dosages, respectively. The difference between REPATHA and ezetimibe in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -37% (95% CI: -42%, -32%; p < 0.0001) and -38% (95% CI: -42%, -34%; p ˂ 0.0001) for the 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly dosages, respectively. For additional results see Table 6.
Table 6. Effect of REPATHA on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Hyperlipidemia (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in MENDEL-2) Treatment Group LDL-C Non-HDL-C Apo B Total Cholesterol Placebo every 2 weeks (n = 76) 1 0 1 0 Ezetimibe 10 mg daily (n = 77) -17 -14 -13 -10 REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks† (n = 153) -54 -47 -44 -34 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-55
(-60, -50)-47
(-52, -43)-45
(-50, -41)-34
(-37, -30)Mean difference from Ezetimibe
(95% CI)-37
(-42, -32)-33
(-37, -29)-32
(-36, -27)-23
(-27, -20)Placebo once monthly (n = 78) 1 2 2 0 Ezetimibe 10 mg daily (n = 77) -18 -16 -13 -12 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly (n = 153) -56 -49 -46 -35 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-57
(-61, -52)-51
(-54, -47)-48
(-52, -44)-35
(-38, -32)Mean difference from Ezetimibe
(95% CI)-38
(-42, -34)-32
(-36, -29)-33
(-36, -29)-23
(-26, -20)Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
† 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly yield similar reductions in LDL-C
Study 5 (RUTHERFORD-2, NCT01763918) was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial in 329 patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) on statins with or without other lipid-lowering therapies. Patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous injections of REPATHA 140 mg every two weeks, 420 mg once monthly, or placebo. HeFH was diagnosed by the Simon Broome criteria (1991). In Study 5, 38% of patients had clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The mean age at baseline was 51 years (range: 19 to 79 years), 15% of the patients were ≥ 65 years old, 42% were women, 90% were White, 5% were Asian, and 1% were Black. The average LDL-C at baseline was 156 mg/dL with 76% of the patients on high-intensity statin therapy.
The differences between REPATHA and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -61% (95% CI: -67%, -55%; p < 0.0001) and -60% (95% CI: -68%, -52%; p < 0.0001) for the 140 mg every 2 weeks and 420 mg once monthly dosages, respectively. For additional results see Table 7 and Figure 5.
Table 7. Effect of REPATHA on Lipid Parameters in Patients with HeFH (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in RUTHERFORD-2) Treatment Group LDL-C Non-HDL-C Apo B Total Cholesterol Placebo every 2 weeks (n = 54) -1 -1 -1 -2 REPATHA 140 mg every 2 weeks† (n = 110) -62 -56 -49 -42 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-61
(-67, -55)-54
(-60, -49)-49
(-54, -43)-40
(-45, -36)Placebo once monthly (n = 55) 4 4 4 2 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly (n = 110) -56 -49 -44 -37 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-60
(-68, -52)-53
(-60, -46)-48
(-55, -41)-39
(-45, -33)Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
† 140 mg every 2 weeks or 420 mg once monthly yield similar reductions in LDL-C
Figure 5. Effect of REPATHA on LDL-C in Patients with HeFH (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in RUTHERFORD-2)
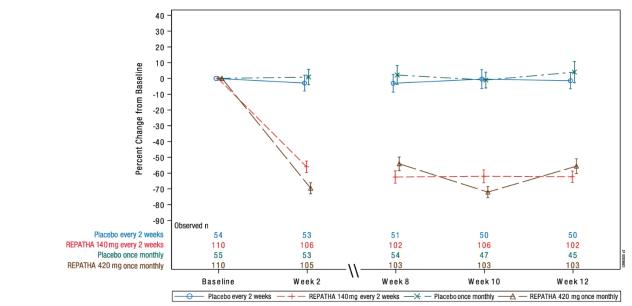
N = number of patients randomized and dosed in the full analysis set
Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals
14.3 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
Study 6 (TESLA, NCT01588496) was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial in 49 patients (not on lipid-apheresis therapy) with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). In this trial, 33 patients received subcutaneous injections of 420 mg of REPATHA once monthly and 16 patients received placebo as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering therapies (e.g., statins, ezetimibe). The mean age at baseline was 31 years, 49% were women, 90% White, 4% were Asian, and 6% other. The trial included 10 adolescents (ages 13 to 17 years), 7 of whom received REPATHA. The mean LDL-C at baseline was 349 mg/dL with all patients on statins (atorvastatin or rosuvastatin) and 92% on ezetimibe. The diagnosis of HoFH was made by genetic confirmation or a clinical diagnosis based on a history of an untreated LDL-C concentration > 500 mg/dL together with either xanthoma before 10 years of age or evidence of HeFH in both parents.
The difference between REPATHA and placebo in mean percent change in LDL-C from baseline to Week 12 was -31% (95% CI: -44%, -18%; p < 0.0001). For additional results see Table 8.
Patients known to have two LDL-receptor negative alleles (little to no residual function) did not respond to REPATHA.
Table 8. Effect of REPATHA on Lipid Parameters in Patients with HoFH (Mean % Change from Baseline to Week 12 in TESLA) Treatment Group LDL-C Non-HDL-C Apo B Total
CholesterolPlacebo once monthly (n = 16) 9 8 4 8 REPATHA 420 mg once monthly
(n = 33)-22 -20 -17 -17 Mean difference from placebo
(95% CI)-31
(-44, -18)-28
(-41, -16)-21
(-33, -9)-25
(-36, -14)Estimates based on a multiple imputation model that accounts for treatment adherence
-
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
REPATHA is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution for subcutaneous administration supplied in a single-use prefilled syringe, a single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector, or a single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge). Each single-use prefilled syringe or single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector of REPATHA is designed to deliver 1 mL of 140 mg/mL solution. Each single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge) is designed to deliver 420 mg evolocumab in 3.5 mL solution.
140 mg/mL single-use prefilled syringe 1 pack NDC: 72511-750-01
NDC: 55513-750-01140 mg/mL single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector 1 pack NDC: 55513-760-01 140 mg/mL single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector 2 pack NDC: 72511-760-02
NDC: 55513-760-02140 mg/mL single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector 3 pack NDC: 55513-760-03 420 mg/3.5 mL single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge) 1 pack NDC: 72511-770-01
NDC: 55513-770-01Pharmacy
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
For Patients/Caregivers
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton. Alternatively, REPATHA can be kept at room temperature at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) in the original carton; however, under these conditions, REPATHA must be used within 30 days. If not used within the 30 days, discard REPATHA.
Protect REPATHA from direct light and do not expose to temperatures above 25°C (77°F).
-
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling [Patient Information and Instructions for Use (IFU)] before the patient starts using REPATHA, and each time the patient gets a refill as there may be new information they need to know.
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with REPATHA. Advise patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to discontinue REPATHA and seek medical attention promptly, if such symptoms occur.
Provide guidance to patients and caregivers on proper subcutaneous administration technique, including aseptic technique, and how to use the single-use prefilled autoinjector, single-use prefilled syringe, or single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge correctly (see Instructions for Use leaflet). Inform patients that it may take up to 15 seconds to administer REPATHA using the single-use prefilled autoinjector or single-use prefilled syringe and about 9 minutes to administer REPATHA using the single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge.
Advise latex-sensitive patients that the following components contain dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex) that may cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to latex: the needle cover of the glass single-use prefilled syringe and the single-use prefilled autoinjector.
The single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge is not made with natural rubber latex.
For more information about REPATHA, go to www.REPATHA.com or call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842).
REPATHA® (evolocumab)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799U.S. License Number 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/repatha/
© 2015-2019 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
V7
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
REPATHA® (ri-PAth-a)
(evolocumab)
injection, for subcutaneous useWhat is REPATHA?
REPATHA is an injectable prescription medicine used:
- in adults with cardiovascular disease to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and certain types of heart surgery.
- along with diet alone or together with other cholesterol-lowering medicines in adults with high blood cholesterol levels called primary hyperlipidemia (including a type of high cholesterol called heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia) to reduce low density lipoprotein (LDL) or bad cholesterol.
- along with diet and other LDL-lowering medicine in people with a type of high cholesterol called homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), who need additional lowering of LDL cholesterol.
Who should not use REPATHA?
Do not use REPATHA if you are allergic to evolocumab or to any of the ingredients in REPATHA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in REPATHA.What should I tell my healthcare provider before using REPATHA?
Before you start using REPATHA, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- are allergic to rubber or latex. The needle covers on the single-use prefilled syringes and within the needle caps on the single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjectors contain dry natural rubber. The single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge) is not made with natural rubber latex.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if REPATHA will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant while taking REPATHA.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take REPATHA or breastfeed.
How should I use REPATHA?
-
See the detailed “Instructions for Use” that comes with this patient information about the right way to prepare and give REPATHA.
- Use REPATHA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- REPATHA is given under the skin (subcutaneously), every 2 weeks or 1 time each month.
- REPATHA comes as a single-use (1 time) prefilled autoinjector (SureClick® autoinjector), as a single-use prefilled syringe or as a single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge). Your healthcare provider will prescribe the type and dose that is best for you.
- If your healthcare provider prescribes you the monthly dose, you may use:
○ a single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge to give the injection over 9 minutes, or
○ 3 separate injections in a row, using a different single-use prefilled syringe or single-use prefilled autoinjector for each injection. Give all of these injections within 30 minutes.
- If your healthcare provider decides that you or a caregiver can give REPATHA, you or your caregiver should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject REPATHA. Do not try to inject REPATHA until you have been shown the right way by your healthcare provider or nurse.
○ If you are using the prefilled autoinjector, put the yellow safety guard (needle inside) of the SureClick autoinjector on the skin before injecting.
-
Do not inject REPATHA together with other injectable medicines at the same injection site.
- Always check the label of your single-use prefilled autoinjector, single-use prefilled syringe, or single-use on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge to make sure you have the correct medicine and the correct dose of REPATHA before each injection.
- If you forget to use REPATHA or are not able to take the dose at the regular time, inject your missed dose as soon as you remember, as long as it is within 7 days of the missed dose.
○ If it is more than 7 days from the missed dose and you are using the every-2-week dose, inject the next dose based on your original schedule. This will put you back on your original schedule.
○ If it is more than 7 days from the missed dose and you are using the 1 time each-month dose, inject the dose and start a new schedule using this date.
- If your healthcare provider has prescribed REPATHA along with other cholesterol-lowering medicines, follow instructions from your healthcare provider. Read the patient information for those medicines.
- If you use more REPATHA than you should, talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- Do not stop using REPATHA without talking with your healthcare provider. If you stop using REPATHA, your cholesterol levels can increase.
What are possible side effects of REPATHA?
REPATHA can cause serious side effects including:
-
Serious allergic reactions. Some people taking REPATHA have had serious allergic reactions. Stop taking REPATHA and call your healthcare provider or seek emergency medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms:
○ trouble breathing or swallowing
○ raised bumps (hives)
○ rash, or itching
○ swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or arms
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of REPATHA. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of REPATHA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use REPATHA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give REPATHA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about REPATHA that is written for healthcare professionals.What are the ingredients in REPATHA? - Active Ingredient: evolocumab
- Inactive Ingredients: proline, glacial acetic acid, polysorbate 80, water for injection, and sodium hydroxide.
Manufactured by: Amgen Inc. One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799.
U.S. License Number 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/repatha/
©2017-2019 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
For more information about REPATHA, go to www.REPATHA.com or call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842).This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.Revised: 02/2019
V5
- in adults with cardiovascular disease to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and certain types of heart surgery.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Step 1: Prepare 1A Remove the on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge carton from the refrigerator. Wait at least 45 minutes before injecting for the on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge in the carton to naturally reach room temperature. - Do not try to warm the prefilled cartridge by using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave.
In any above cases, use a new on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge and call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. 1B Open the carton and peel away the white paper cover. Remove the plastic cover from the clear tray. 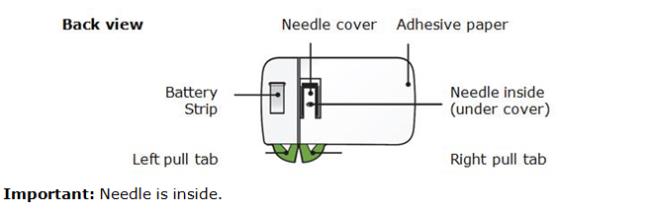
Leave the on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge in the clear tray until you are ready to inject. ● Do not touch the start button until the on-body infusor is on the skin and you are ready to inject. ● Do not use if the white paper cover is missing or damaged. 1C Gather all materials needed for your injection and then wash your hands well with soap and water. On a clean, well-lit work surface, place the: ● Clear tray containing the on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge ● Alcohol wipes ● Cotton ball or gauze pad ● Adhesive bandage ● Sharps disposal container 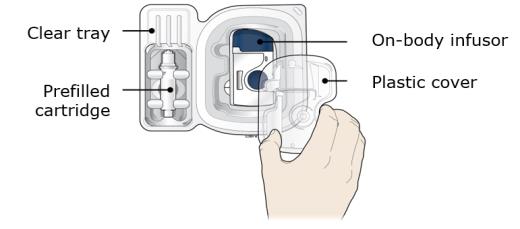
1D To securely attach the on-body infusor, prepare and clean an injection site that is less likely to have body hair, or you can trim the area. Use a firm and flat skin surface.
You can use:
● Your thigh
● Stomach area (abdomen), except for a two-inch area right around your navel
● Outer area of upper arm (only if someone else is giving the injection)
Clean your injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let your skin dry. ● Do not touch this area again before injecting. ● Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red or hard. Avoid injecting into areas with wrinkles, skin folds, scars, stretch marks, moles and excessive hair. 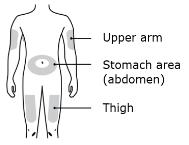
Step 2: Get ready 2A Open the on-body infusor by swinging the cartridge door to the right. Then, leave the door open. Do not close the cartridge door before the cartridge is loaded. If you accidently close the cartridge door, press on the left side of the door to release the door latch.
If you are still unable to open the door, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com.
Do not press the start button until you are ready to inject.

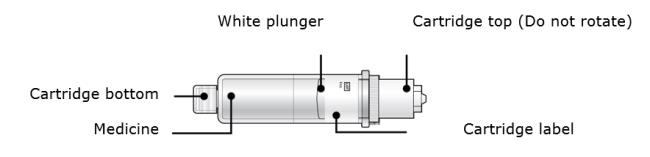
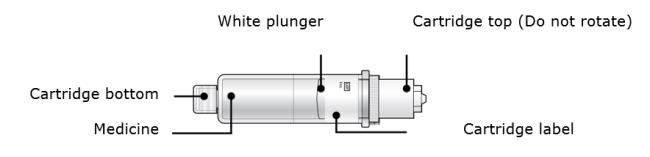
2B Inspect the cartridge. 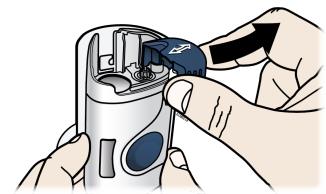
Check the expiration date: do not use if this date has passed.
Make sure the medicine in the cartridge is clear and colorless to slightly yellow.● Do not use if the medicine is cloudy or discolored or contains flakes or particles. ● Do not use if any part of the cartridge looks cracked or broken. ● Do not use if pieces of the cartridge are missing or not securely attached. In any above cases, use a new on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge and call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. 2C Clean the cartridge bottom. 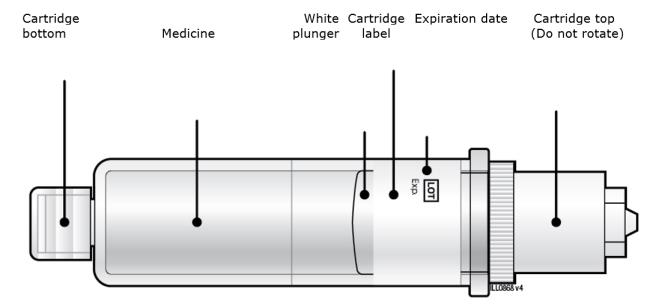
With 1 hand, hold the cartridge barrel and clean the cartridge bottom with an alcohol wipe. ● Do not remove or rotate the cartridge top or bottom. ● Do not touch the bottom of the cartridge after cleaning with alcohol wipe. 2D Load the cleaned cartridge into the on-body infusor and firmly press on the top until it is secured in place. Make sure that you give your injection within 5 minutes after loading the cartridge. Do not insert the cartridge more than 5 minutes before injection. This can dry out the medicine. 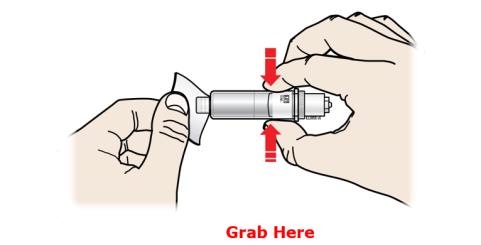
Insert the cartridge bottom first. ● Do not touch the start button until you have placed the loaded on-body infusor on your skin. 2E Swing the door to the left. Then, squeeze firmly until it snaps shut. Apply enough pressure when closing the door and make sure there is a “snap” before going to the next step. 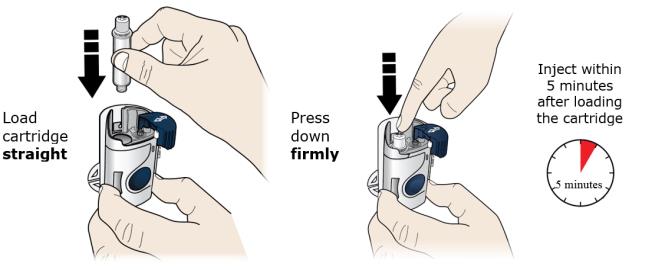
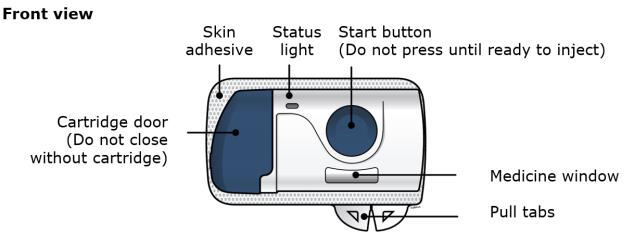
Make sure the cartridge fits securely in the on-body infusor before you close the door. ● Do not close the door if the cartridge is missing or not fully inserted. ● Do not touch the start button until you have placed the loaded on-body infusor on your skin. Important: After you load the on-body infusor, go to the next step right away. Step 3: Inject 3A Peel away both green pull tabs to show the adhesive. The on-body infusor is on when the blue status light flashes. 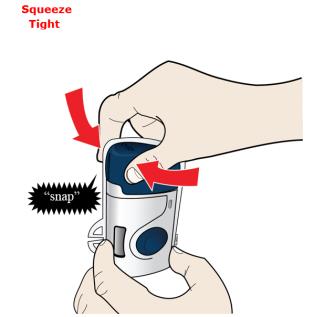
You must remove both green pull tabs to turn the loaded on-body infusor on. You will hear beeping and see a flashing blue status light. -
Do not pull the skin adhesive backing off the on-body infusor.
-
Do not touch the skin adhesive.
-
Do not touch the start button until you have placed the loaded on-body infusor on your skin.
-
Do not touch the needle cover area.
-
Do not place the loaded on-body infusor on your body if the red status light flashes continuously.
- Do not fold the skin adhesive over onto itself.
3B Choose your on-body infusor injection site. Only use the outer arm if someone else is giving the injection. 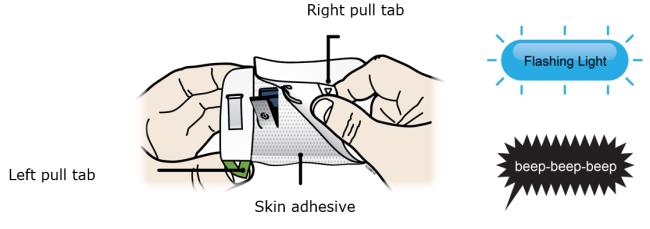
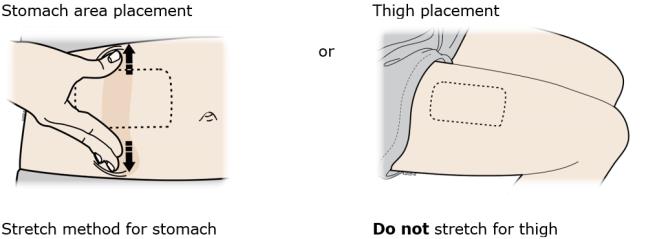
3C When the blue light flashes, the on-body infusor is ready. Keep the stretch (stomach area method only). Hold the loaded on-body infusor with the blue light visible, and place it on your skin. You may hear beeps. 
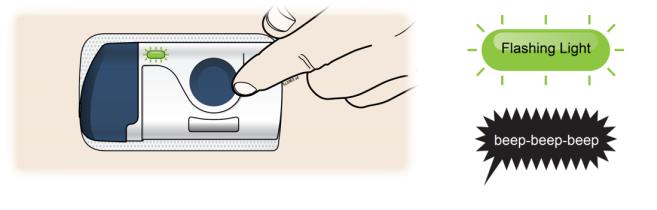
The loaded on-body infusor will lay flat on your body. Make sure all of the adhesive is attached to your skin. Run a finger around the adhesive edges to secure it. Make sure clothing does not get in the way of the loaded on-body infusor, and you can see the blue light at all times. ● Do not move the loaded on-body infusor after it has been placed onto your skin. 3D Firmly press and release the start button. A flashing green light and a click signals the injection has started. 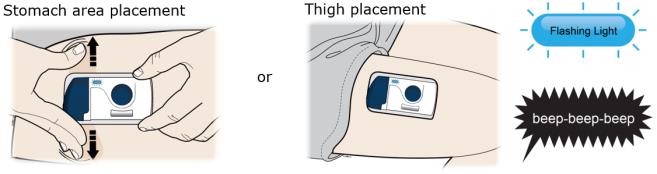
- You may hear a pumping sound.
- You may feel a pinch.
- Make sure you see a green, flashing status light.
- You may hear beeps that mean your injection has started.
3E The injection takes about nine minutes to finish. The status light turns solid green, and the device beeps, when done.
It is okay to hear a pumping sound start and stop during injection.
Injection is finished when: - The status light changes to solid green.
- You hear several beeps.
- The plunger fills medicine window all the way.

Step 4: Finish 4A When the injection is done, grab the skin adhesive to carefully peel the on-body infusor off skin. After removal, check the medicine window. The green light should now be off.

Check to see that the used plunger fills the medicine window all the way, and the green solid light turns off, letting you know all medicine has been injected. If the plunger did not fill the window, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. - The used on-body infusor will beep when removed from your skin.
- It is normal to see a few drops of fluid on your skin after you remove the used
on-body infusor.
4B Throw away the used on-body infusor in a sharps container. - The on-body infusor contains batteries, electronics, and a needle.
- Put the used on-body infusor in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the on-body infusor in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
○ made of a heavy-duty plastic,
○ can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
○ upright and stable during use,
○ leak-resistant, and
○ properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
-
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
- Do not recycle the on-body infusor or sharps disposal container or throw them into household trash.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.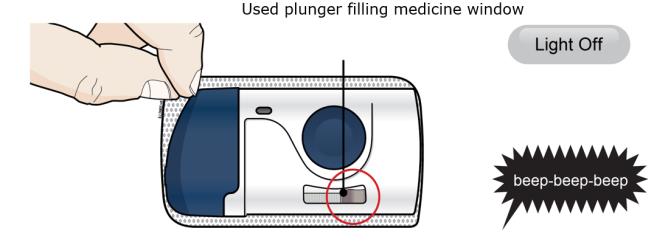
4C Check the injection site. If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on your injection site. Do not rub the injection site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed. Troubleshooting What do I do if the loaded on-body infusor status light continuously flashes red and I hear beeps? 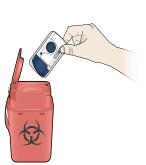
Stop using the loaded on-body infusor. If the on-body infusor is attached to your body, carefully remove it. Call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. Commonly Asked Questions What if I hear the on-body infusor beep and see a red blinking light when it is on my body? This means that an error has happened. When this happens, the injection will stop by itself. Remove the on-body infusor from your body by slowly and carefully peeling it off of your skin, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. What should I do if the on-body infusor comes off my body during the injection? Though unlikely, if the on-body infusor comes off during the injection, the on-body infusor will make a beeping sound, you will see the blinking red light, and the on-body infusor will stop. The loaded on-body infusor can no longer be used, and do not reapply to your body. Call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. What if I push the start button before I place the on-body infusor on my skin? If you have removed the adhesive backing and pressed the start button, the on-body infusor will make a beeping sound and you will see the blinking red light. The on-body infusor will stop. Stop using the on-body infusor, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. What if the on-body infusor does not beep and the blue status light does not blink when I remove the pull tabs? Check to see if both green pull tabs have been fully removed from the on-body infusor, including the adhesive paper over the battery strip and needle cover. If both green pull tabs have been fully removed and the on-body infusor still does not turn on, use a new on-body infusor and prefilled cartridge. Call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. What if I push the start button and nothing happens? Remove the on-body infusor by slowly and carefully peeling it away from your skin. Do not reapply the same on-body infusor that you have already placed on your skin. Call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. What if I cannot open the cartridge door to insert the cartridge? To open the on-body infusor door, press on the left side of the door to release the door latch. If you are still unable to open the door, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center DriveThousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799
© 2015-2017, 2019 Amgen Inc.
All rights reserved.
<part number> Revised: 04/2019 v5U.S. License Number 1080
Additional environmental conditions
Relative humidity range is 15% to 85%.
Altitude range is -984 feet to 11483 feet (-300 meters to 3500 meters).
During injection, keep the on-body infusor a minimum of 4 inches (10 cm) away from other electronics such as cellular phones.
Warning: Do not modify the device.
On-body infusor operating temperature range is 59°F to 104°F (15°C to 40°C).
www.devicepatents.com. SYMBOL TABLE




Do not re-use Serial number Type BF Applied Part Do not use if packaging is damaged On-Body Infusor containing
420 mg/ 3.5 mL (120 mg/mL)




Sterilized using ethylene oxide Refer to Instructions for Use Lot number Keep dry Open here -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for Use
Repatha® (ri-PAth-a)
(evolocumab)
Single-Use Prefilled SureClick® AutoinjectorGuide to parts Before use After use 

Important: Needle is inside the yellow safety guard Important Before you use a Single-Use Repatha SureClick autoinjector, read this important information:
- It is important that you do not try to give yourself or someone else the injection unless you have received training from your healthcare provider.
- The orange cap on the Repatha SureClick autoinjector contains a needle cover (located inside the cap) that contains dry natural rubber, which is made from latex. Tell your healthcare provider if you are allergic to latex.
- Keep the Repatha SureClick autoinjector in the original carton to protect from light during storage.
- Keep the Repatha SureClick autoinjector in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- If removed from the refrigerator, the Repatha SureClick autoinjector should be kept at room temperature at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) in the original carton and must be used within 30 days.
- Do not freeze the Repatha SureClick autoinjector or use a Repatha SureClick autoinjector that has been frozen.
-
Do not shake the Repatha SureClick autoinjector.
-
Do not remove the orange cap from the Repatha SureClick autoinjector until you are ready to inject.
-
Do not use the Repatha SureClick autoinjector if it has been dropped on a hard surface. Part of the Repatha SureClick autoinjector may be broken even if you cannot see the break. Use a new Repatha SureClick autoinjector, and call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842).
- Do not use the Repatha SureClick autoinjector after the expiration date.
Keep the Repatha SureClick autoinjector out of the sight and reach of children.Step 1: Prepare 1A Remove 1 Repatha SureClick autoinjector from the package. Carefully lift the autoinjector straight up out of the box.
Put the original package with any unused autoinjectors back in the refrigerator.
Wait at least 30 minutes for the autoinjector to reach room temperature before injecting.
This is important for administering the entire dose and helps minimize discomfort. Repatha may take longer to inject if it has not reached room temperature. Do not heat the autoinjector. Let it warm up on its own. -
Do not try to warm the autoinjector by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave.
-
Do not leave the autoinjector in direct sunlight.
-
Do not shake the autoinjector.
- Do not remove the orange cap from the autoinjector yet.
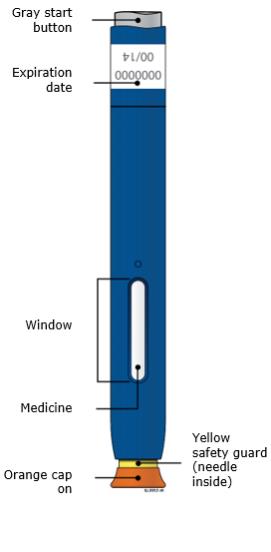
1B Inspect the Repatha SureClick autoinjector. 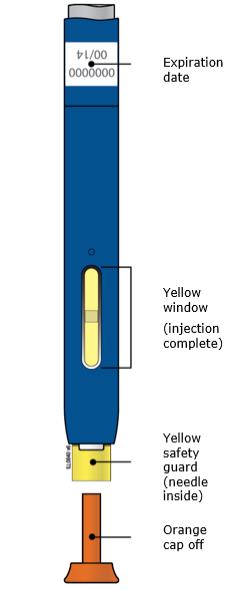
Check the expiration date. Do not use the Repatha SureClick autoinjector past the expiration date printed on the label.
Make sure the medicine in the window is clear and colorless to slightly yellow.
-
Do not use the autoinjector if the medicine is cloudy or discolored or contains particles.
-
Do not use the autoinjector if any part appears cracked or broken.
-
Do not use the autoinjector if the autoinjector has been dropped.
- Do not use the autoinjector if the orange cap is missing or not securely attached.
1C Gather all materials needed for your injection. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
On a clean, well-lit work surface, place the:
- New autoinjector
- Alcohol wipes
- Cotton ball or gauze pad
- Adhesive bandage
- Sharps disposal container (see Step 4: Finish)
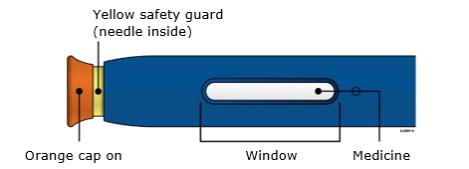
1D Prepare and clean your injection site. Only use these injection sites:
- Thigh
- Stomach (abdomen), except for a two-inch area around your belly button
- Outer area of upper arm (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
-
Do not touch this area again before injecting.
- Choose a different site each time you give yourself an injection. If you want to use the same injection site, make sure it is not the same spot you used for the last injection.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
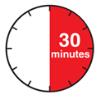
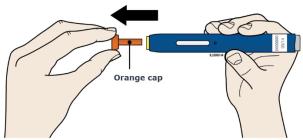
Step 2: Get ready 2A Pull the orange cap off only when you are ready to inject. Do not leave the orange cap off for more than five minutes. This can dry out the medicine. 
It is normal to see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle or yellow safety guard
-
Do not twist, bend, or wiggle the orange cap.
-
Do not put the orange cap back onto the autoinjector.
-
Do not put fingers into the yellow safety guard.
- Do not remove the orange cap from the autoinjector until you are ready to inject.
2B Create a firm surface at the selected injection site (thigh, stomach, or outer areas of the upper arm), by using either the Stretch method or the Pinch method. Stretch method:
Stretch the skin firmly by moving your thumb and fingers in opposite directions, creating an area about two inches wide.
or
Pinch method:

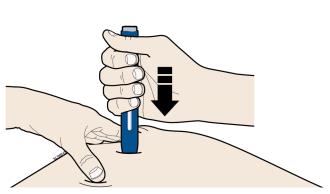
Pinch the skin firmly between your thumb and fingers, creating an area about two inches wide. Important: It is important to keep skin stretched or pinched while injecting. Step 3: Inject 3A Keep holding the stretched or pinched skin. With the orange cap off, put the yellow safety guard on your skin at 90 degrees. The needle is inside the yellow safety guard. Do not touch the gray start button yet. 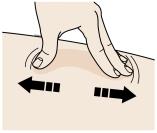
3B Firmly push down the autoinjector onto the skin until it stops moving. 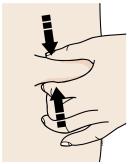
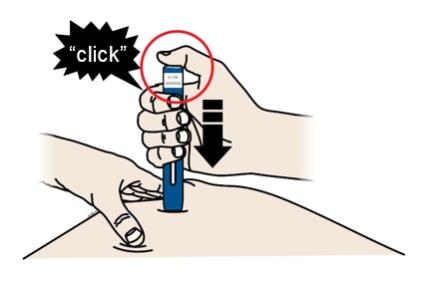
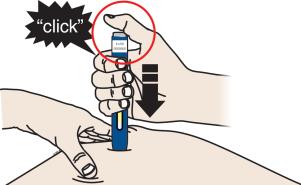
Important: You must push all the way down but do not touch the gray start button until you are ready to inject. 3C When you are ready to inject, press the gray start button. You will hear a click. 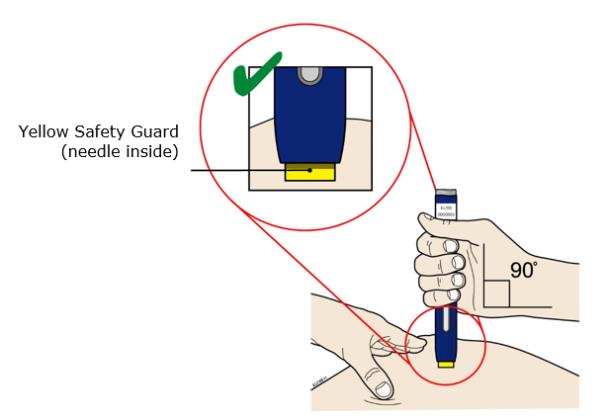
3D Keep pushing the autoinjector down on your skin. Then lift your thumb while still holding the autoinjector on your skin. Your injection could take about 15 seconds.
Window turns from clear to yellow when the injection is done. You may hear a second click.
NOTE: After you remove the autoinjector from your skin, the needle will be automatically covered. Important: When you remove the autoinjector, if the window has not turned yellow, or if it looks like the medicine is still injecting, this means you have not received a full dose. Call your healthcare provider immediately. Step 4: Finish 4A Throw away the used autoinjector and orange needle cap. 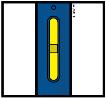
Put the used autoinjector and orange needle cap in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the autoinjector or orange cap in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.-
Do not reuse the autoinjector.
- Do not recap the autoinjector or put fingers into the yellow safety guard.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of reach of children. 4B Check the injection site. If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on your injection site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed.
Do not rub the injection site.Commonly Asked Questions What will happen if I press the gray start button before I am ready to do the injection on my skin?
You can lift your finger up off the gray start button and place the prefilled autoinjector back on your injection site. Then, you can push the gray start button again.Can I move the autoinjector around on my skin while I am choosing an injection site?
It is okay to move the autoinjector around on the injection site as long as you do not press the gray start button. However, if you press the gray start button and the yellow safety guard is pushed into the autoinjector, the injection will begin.Can I release the gray start button after I start my injection?
You can release the gray start button, but continue to hold the autoinjector firmly against your skin during the injection.Will the gray start button pop up after I release my thumb?
The gray start button may not pop up after you release your thumb if you held your thumb down during the injection. This is okay.What do I do if I did not hear a second click?
If you did not hear a second click, you can confirm a complete injection by checking that the window has turned yellow.Whom do I contact if I need help with the autoinjector or my injection?
A healthcare provider familiar with Repatha should be able to answer your questions. For more information, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com.This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center DriveThousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799
US License No: 1080
© 2015-2016,2018-2019 Amgen Inc.
All rights reserved.
<part number> Revised: 09/2019 v6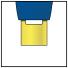
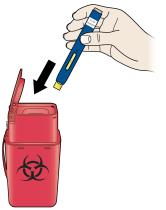
- It is important that you do not try to give yourself or someone else the injection unless you have received training from your healthcare provider.
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for use:
Repatha® (ri-PAth-a)
(evolocumab)
Single-Use Prefilled SyringeGuide to parts
Before use After use 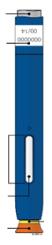
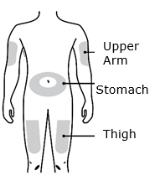
Important Before you use a Single-Use Repatha Prefilled Syringe, read this important information:
- It is important that you do not try to give yourself or someone else the injection unless you have received training from your healthcare provider.
- The gray needle cap on the Repatha prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber, which is made from latex. Tell your healthcare provider if you are allergic to latex.
Storage of Repatha:- Keep the Repatha prefilled syringe in the original carton to protect from light during storage.
- Keep the Repatha prefilled syringe in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- If removed from the refrigerator, the Repatha prefilled syringe should be kept at room temperature at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) in the original carton and must be used within 30 days.
- Do not freeze the Repatha prefilled syringe or use a Repatha prefilled syringe that has been frozen.
Do not:-
Do not use the Repatha prefilled syringe if the packaging is open or damaged.
-
Do not remove the gray needle cap from the Repatha prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject.
-
Do not use the Repatha prefilled syringe if it has been dropped onto a hard surface. Part of the Repatha prefilled syringe may be broken even if you cannot see the break. Use a new Repatha prefilled syringe and call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842).
- Do not use the Repatha prefilled syringe after the expiration date.
A healthcare provider who knows how to use the Repatha prefilled syringe should be able to answer your questions. For more information, call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com
Keep the Repatha prefilled syringe out of the sight and reach of children.Step 1: Prepare 1 A Remove the Repatha prefilled syringe carton from the refrigerator and wait 30 minutes. Wait at least 30 minutes for the prefilled syringe in the carton to reach room temperature before injecting. 
This is important for administering the entire dose and helps minimize discomfort. Repatha may take longer to inject if it has not reached room temperature. Do not heat the syringe. Let it warm up on its own.
Check that the name Repatha appears on the carton label.
Do not try to warm the Repatha prefilled syringe by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave. Do not leave the Repatha prefilled syringe in direct sunlight. Do not shake the Repatha prefilled syringe. 1 B Gather all materials needed for your injection. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. On a clean, well-lit, flat work surface, place: ● 1 Repatha prefilled syringe in carton ● Alcohol wipes ● Cotton ball or gauze pad ● Adhesive bandage ● Sharps disposal container (see Step 4: Finish) Check the expiration date on the Repatha prefilled syringe carton: do not use if this date has passed.

1 C Choose your injection site. 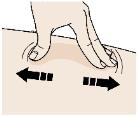
You can use:
- Thigh
- Stomach (abdomen), except for a two inch area around your belly button
Do not choose an area where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into areas with scars or stretch marks.
Choose a different site each time you give yourself an injection. If you need to use the same injection site, just make sure it is not the same spot on that site you used last time.1 D Clean your injection site. 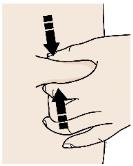
Clean your injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let your skin dry before injecting. Do not touch this area of skin again before injecting.
1 E Remove prefilled syringe from tray. 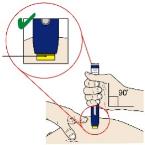
To remove: ● Peel paper off of tray. ● Place the tray on your hand. ● Turn the tray over and gently press the middle of the tray’s back to release the syringe into your palm. ● If prefilled syringe does not release from tray, gently press on back of tray Do not pick up or pull the prefilled syringe by the plunger rod or gray needle cap. This could damage the syringe. Do not remove the gray needle cap from the prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject. Always hold the prefilled syringe by the syringe barrel. 1 F Check the medicine and syringe. 
Always hold the prefilled syringe by the syringe barrel.
Check that:● the name Repatha appears on the prefilled syringe label. ● the medicine in the prefilled syringe is clear and colorless to slightly yellow. ● the expiration date on the prefilled syringe has not passed. If the expiration date has passed, do not use the prefilled syringe. Do not use the prefilled syringe if any part of the prefilled syringe appears cracked or broken. Do not use the prefilled syringe if the gray needle cap is missing or not securely attached. Do not use the prefilled syringe if the medicine is cloudy or discolored or contains particles. In any above cases, use a new prefilled syringe and call 1-844-REPATHA (1-844-737-2842) or visit www.REPATHA.com. Step 2: Get ready 2 A Carefully pull the gray needle cap straight out and away from your body. 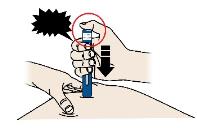
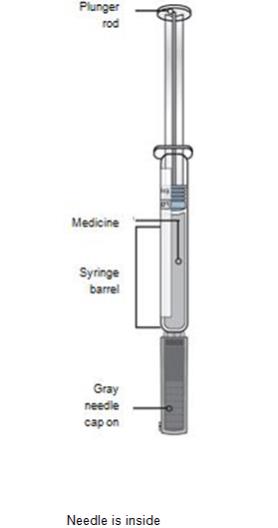
It is normal to see a drop of
medicine at the end of the needle.Place the cap in the sharps
disposal container right away.Do not twist or bend the gray needle cap. This can damage the needle. Do not put the gray needle cap back onto the prefilled syringe. Do not try to remove any air bubbles in the syringe before the injection. 2 B Pinch your injection site to create a firm surface. 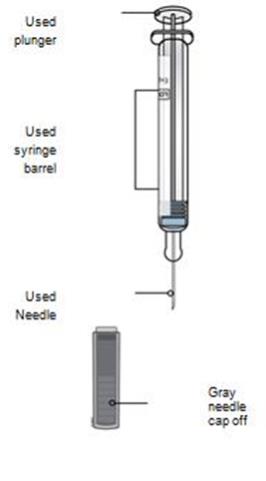
Pinch skin firmly between your thumb and fingers, creating an area about two inches wide.
It is important to keep the skin pinched while injecting.Step 3: Inject 3 A Hold the pinch. Insert the needle into skin using a 45 to 90 degree angle. 
Do not place your finger on the plunger rod while inserting the needle. 3 B Using slow and constant pressure, push the plunger rod all the way down until the syringe is empty. You may have to push harder on the plunger than for other injectable medicines. 
3 C When done, release your thumb, and gently lift the syringe off skin. 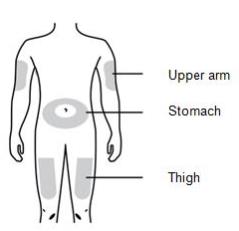
Do not put the gray needle cap back onto the used syringe. Step 4: Finish 4 A Place the used syringe in a sharps disposal container right away. 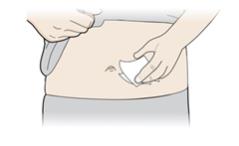
Do not reuse the used syringe. Do not use any medicine that is left in the used syringe.
- Put the used syringe in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the syringe in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
○ made of a heavy-duty plastic,
○ can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
○ upright and stable during use,
○ leak-resistant, and
○ properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Keep the used syringe and sharps container out of the sight and reach of children. 4 B Check the injection site. If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on your injection site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed. Do not rub the injection site. This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799
© 2015-2016 Amgen Inc.
All rights reserved.
<part number> Issued: 07/2016 v2 - It is important that you do not try to give yourself or someone else the injection unless you have received training from your healthcare provider.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
2 x 1 mL Prefilled Autoinjectors
NDC: 72511-760-02
Amgen®
Repatha® SureClick®
(evolocumab)
Injection
140 mg/mL 140 mg/mL
140 mg/mL
Prefilled Autoinjector
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Single-Use Only
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do Not Freeze or Shake.
Store in Carton to Protect from Light.
(see side panel for additional storage information)
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber.
Single Use
CAUTION, See package insert for full prescribing information and Instructions for Use
Rx Only
U.S. License No. 1080
No U.S. standard of potency.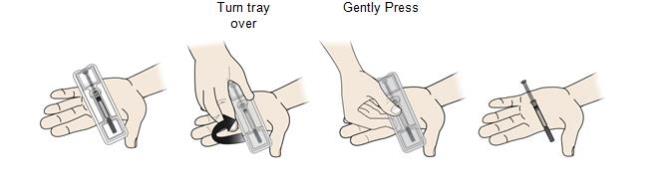
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
1 x 1 mL Prefilled Syringe
NDC: 72511-750-01
Amgen®
Repatha®
(evolocumab)
Injection
140 mg/mL
140 mg/mL
Prefilled Syringe
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Do Not Freeze or Shake.
Store in Carton to Protect from Light.
(see side panel for additional storage information)
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
Single UseRx Only
CAUTION, See package insert for full prescribing information and Instructions for Use
This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber.
Keep out of the sight and reach of children
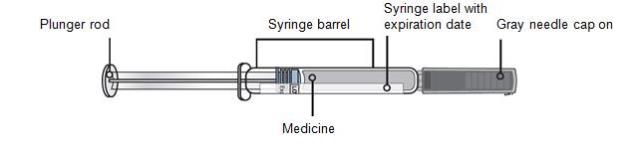
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
1 x 3.5 mL Prefilled Cartridge
1 On-Body Infusor
NDC: 72511-770-01
Amgen®
Repatha® Pushtronex® system
(evolocumab)
On-Body Infusor and Prefilled Cartridge
420 mg/3.5 mL
420 mg/3.5 mL
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Single-Use Only
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Do Not Freeze or Shake.
Store in Carton to Protect from Light.
(see side panel for additional storage information)
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
Refer to Instructions for Use
Do Not Use if Package is Damaged
On-Body Infusor Sterilized Using Ethylene Oxide
Keep Dry
Do not re-use
Type BF Applied Part
Relative Humidity
Range is 15% to 85%
Rx Only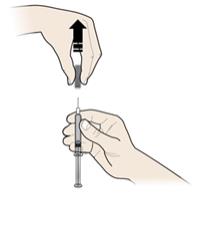
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
REPATHA
evolocumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72511-760 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength EVOLOCUMAB (UNII: LKC0U3A8NJ) (EVOLOCUMAB - UNII:LKC0U3A8NJ) EVOLOCUMAB 140 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PROLINE (UNII: 9DLQ4CIU6V) 25 mg in 1 mL ACETATE ION (UNII: 569DQM74SC) 1.2 mg in 1 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.10 mg in 1 mL SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72511-760-02 2 in 1 CARTON 10/09/2018 1 NDC: 72511-760-01 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125522 10/09/2018 REPATHA
evolocumab injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72511-750 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength EVOLOCUMAB (UNII: LKC0U3A8NJ) (EVOLOCUMAB - UNII:LKC0U3A8NJ) EVOLOCUMAB 140 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PROLINE (UNII: 9DLQ4CIU6V) 25 mg in 1 mL ACETATE ION (UNII: 569DQM74SC) 1.2 mg in 1 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.10 mg in 1 mL SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72511-750-01 1 in 1 CARTON 10/09/2018 1 1 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125522 10/09/2018 REPATHA
evolocumab kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72511-770 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72511-770-01 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 9: Other Type of Part 3 Combination Product (e.g., Drug/Device/Biological Product) 10/09/2018 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 1 CARTRIDGE 3.5 mL Part 1 of 1 REPATHA
evolocumab injection, solutionProduct Information Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength EVOLOCUMAB (UNII: LKC0U3A8NJ) (EVOLOCUMAB - UNII:LKC0U3A8NJ) EVOLOCUMAB 420 mg in 3.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PROLINE (UNII: 9DLQ4CIU6V) 89 mg in 3.5 mL ACETATE ION (UNII: 569DQM74SC) 4.2 mg in 3.5 mL POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) 0.35 mg in 3.5 mL SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 1 in 1 TRAY 1 3.5 mL in 1 CARTRIDGE; Type 9: Other Type of Part 3 Combination Product (e.g., Drug/Device/Biological Product) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125522 10/09/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125522 10/09/2018 Labeler - Amgen USA Inc. (962075045) Registrant - Amgen, Inc (039976196)
Trademark Results [REPATHA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 REPATHA 86436098 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Amgen Inc. 2014-10-27 |
 REPATHA 86066934 4837298 Live/Registered |
Amgen Inc. 2013-09-17 |
 REPATHA 76463628 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Amgen Inc. 2002-11-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.