SITAVIG- acyclovir tablet, delayed release
Sitavig by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sitavig by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by EPI Health, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SITAVIG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SITAVIG.
SITAVIG (acyclovir) buccal tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 1982INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SITAVIG is indicated for the treatment of recurrent herpes labialis (cold sores) in immunocompetent adults (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
50 mg buccal tablets (3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Known hypersensitivity to acyclovir, milk protein concentrate, or any other component of the product (4).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥1%) are: headache and application site pain (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact EPI Health, LLC at 1-800-499-4468 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Due to the low dose and minimal systemic absorption of SITAVIG, drug interactions are unlikely (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Nursing Mothers: Caution should be exercised when administered to a nursing woman (8.3).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 12/2017
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Basic Dosing Information
2.2 Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Immunocompromised Patients
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions for Use
17.2 Adverse Reactions
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Basic Dosing Information
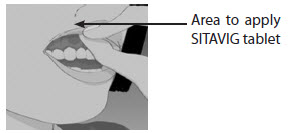
One SITAVIG 50 mg buccal tablet should be applied as a single dose to the upper gum region (canine fossa).
2.2 Administration Instructions
SITAVIG should be applied within one hour after the onset of prodromal symptoms and before the appearance of any signs of herpes labialis lesions. The tablet should be applied with a dry finger immediately after taking it out of the blister. The tablet should be placed to the upper gum just above the incisor tooth (canine fossa) and held in place with a slight pressure over the upper lip for 30 seconds to ensure adhesion. For comfort the rounded side should be placed to the upper gum, but either side of the tablet can be applied. Tablet should be applied on the same side of the mouth as the herpes labialis symptoms.
Once applied, SITAVIG stays in position and gradually dissolves during the day. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In addition,
- SITAVIG should not be crushed, chewed, sucked or swallowed.
- Food and drink can be taken normally when SITAVIG is in place. Avoid any situations which may interfere with adhesion of the tablet such as chewing gum, touching or pressing the tablet after placement, wearing upper dentures, and brushing teeth. If the teeth need to be cleaned while the tablet is in place, rinse the mouth gently. Drink plenty of liquids in the case of dry mouth.
- If SITAVIG does not adhere or falls off within the first 6 hours, the same tablet should be repositioned immediately. If the tablet cannot be repositioned, a new tablet should be placed.
- If SITAVIG is swallowed within the first 6 hours, the patient should drink a glass of water and a new tablet should be applied. [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- SITAVIG does not need to be reapplied if the tablet falls out or is swallowed after the first 6 hours
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The overall safety of SITAVIG was assessed in 378 adult subjects having at least 4 herpes labialis episodes the previous year.
One randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial was conducted in patients with recurrent herpes labialis (cold sores). In this trial, 378 HSV infected subjects used SITAVIG as a single dose, and 397 subjects used placebo.
Selected treatment emergent adverse events without regard to causality and reported in at least 1% of patients can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1 Selected Treatment Emergent Adverse Events reported in at least 1% of patients Event SITAVIG
N = 378Placebo
N = 397Nervous System Disorders Headache 3% 3% Dizziness 1% 1% Lethargy 1% 0 Gastrointestinal system Disorders Gingival Pain 1% 0.3% Aphthous Stomatitis 1% 0 Administration Site Conditions Application Site Pain 1% 1% Application Site Irritation 1% 0 Skin and Subcutaneous Disorders Erythema 1% 0.3% Rash 1% 0.3% The treatment emergent adverse events considered related to treatment that occurred in greater than or equal to 1% of patients included headache (1% SITAVIG vs. 2% placebo) and application site pain (1% both arms). There was no discontinuation of SITAVIG due to adverse drug reactions. Most treatment related adverse events were mild or moderate in severity. One report of headache from both treatment arms was classified as severe.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No interaction studies have been performed with SITAVIG. Acyclovir is primarily eliminated unchanged in the urine via active tubular secretion. Drugs administered concomitantly that compete with tubular secretion may increase acyclovir plasma concentrations. However, due to the low dose and minimal systemic absorption of SITAVIG, systemic drug interactions are unlikely.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
No studies with SITAVIG have been performed in pregnant women. Systemic exposure of acyclovir following buccal administration of SITAVIG is minimal. SITAVIG should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of systemic acyclovir in pregnant women. A prospective epidemiologic registry of acyclovir use during pregnancy between 1984 and 1999 followed 749 pregnancies in women exposed to systemic acyclovir during the first trimester of pregnancy resulting in 756 outcomes. The occurrence rate of birth defects approximated that found in the general population. However, the size of the registry was insufficient to evaluate the risk for less common defects or to permit reliable or definitive conclusions regarding the safety of acyclovir in pregnant women and their developing fetuses.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
SITAVIG should not be administered during labor and delivery as there is no experience with SITAVIG.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether topically applied acyclovir is excreted in breast milk. Systemic exposure following buccal administration is minimal.
After oral administration of acyclovir, concentrations have been documented in breast milk in 2 women and ranged from 0.6 to 4.1 times the corresponding plasma levels. These concentrations would potentially expose the nursing infant to a dose of acyclovir up to 0.3 mg/kg/day.
There is no experience with SITAVIG in nursing mothers. SITAVIG should be administered to a nursing mother with caution.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of SITAVIG in pediatric patients have not been established. The ability of pediatric patients to comply with the application instructions has not been evaluated. Use in younger children is not recommended due to potential risk of choking.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Acyclovir absorption and systemic exposure following application of SITAVIG are minimal. Overdose is therefore unlikely [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Symptomatic and supportive care is the basis for management.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
SITAVIG (acyclovir) buccal tablet is applied topically to the gum and releases acyclovir as the buccal tablet gradually dissolves [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Acyclovir is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue active against herpes viruses. The chemical name of acyclovir is 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl]-6H-purin-6-one; it has a molecular formula of C8H11N5O3 and a molecular weight of 225. The structural formula is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Structural Formula of Acyclovir
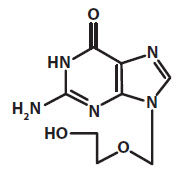
Acyclovir drug substance is a white or almost white crystalline powder.
SITAVIG contains 50 mg of acyclovir, USP and the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, USP; milk protein concentrate; sodium lauryl sulfate, NF; magnesium stearate, NF; microcrystalline cellulose, NF; povidone, USP; colloidal silicon dioxide, NF.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
Salivary
Single dose application of SITAVIG containing 50 mg of acyclovir to the buccal mucosa in 12 healthy volunteers provided mean maximum salivary concentrations of 440 μg/mL 8 hours after application of the tablet. The pharmacokinetic parameters of acyclovir in the saliva of healthy volunteers are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Pharmacokinetic (PK) Parameters of Acyclovir in Saliva Following Application of a Single SITAVIG 50 mg Tablet in Healthy Volunteers (N = 12) Salivary PK Parameters
(N = 12)Mean ±SD
(Min - Max)AUC0-24h (mcg.h/mL) 2900 ± 2400
(849 - 9450)Cmax (mcg/mL) 440 ± 241
(149 – 959)Tmax (hour) 7.95 ± 4.08
(3.07 – 18.05)In the Phase 3 study, the levels of acyclovir in saliva were measured within 24 hours of SITAVIG application in 56 patients with recurrent herpes labialis (mean value 88.1 micrograms per mL) and were within the range of those observed in the PK study in healthy volunteers.
In healthy volunteers, the median duration of buccal adhesion was 14 hours following application of a single SITAVIG 50 mg tablet.
Plasma
Plasma concentrations of acyclovir were measured in 12 healthy volunteers after a single-dose application of SITAVIG 50 mg buccal tablet. Acyclovir concentrations had a delayed appearance (undetectable at 5 hours) and were below the concentrations required for antiviral activity (range: 17.5 to 55.3 nanogram per mL).
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Acyclovir is a synthetic purine nucleoside that is phosphorylated intracellularly by the viral encoded thymidine kinase (TK) of HSV into acyclovir monophosphate, a nucleotide analogue. The monophosphate is further converted into diphosphate by cellular guanylate kinase and into triphosphate by a number of cellular enzymes. In a biochemical reaction, acyclovir triphosphate inhibits replication of herpes viral DNA by competing with nucleotides for binding to the viral DNA polymerase and by incorporation into and termination of the growing viral DNA chain. The cellular thymidine kinase of normal, uninfected cells does not use acyclovir effectively as a substrate, hence toxicity to mammalian host cells is low.
Antiviral activity
The quantitative relationship between the cell culture susceptibility of herpes viruses to antivirals and the clinical response to therapy has not been established in humans, and virus sensitivity testing has not been standardized. Sensitivity testing results, expressed as the concentration of drug required to inhibit by 50% the growth of virus in cell culture (EC50), vary greatly depending upon a number of factors. Using plaque-reduction assays on Vero cells, the median EC50 value of acyclovir against clinical herpes virus isolates (subjects receiving placebo) was 1.3 µM (range: < 0.56 to 3.3 µM).
Drug Resistance
Resistance of HSV to acyclovir can result from qualitative and quantitative changes in the viral TK and/or DNA polymerase. Clinical isolates of HSV with reduced susceptibility to acyclovir have been recovered from immunocompromised subjects, especially with advanced HIV infection. While most of the acyclovir-resistant mutant isolates from immunocompromised subjects thus far have been found to be TK-deficient, other mutant isolates involving the viral TK gene (TK partial and TK altered) or DNA polymerase have been identified. TK-negative mutants may cause severe disease in infants and immunocompromised adults.
The possibility of viral resistance to acyclovir should be considered in immunocompromised subjects who show poor clinical response during therapy.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Systemic exposure following buccal administration of acyclovir is minimal. Results from previous studies of carcinogenesis, mutagenesis and fertility for acyclovir are not included in the full prescribing information for SITAVIG due to the minimal exposure that results from buccal administration. Information on these studies following systemic exposure is available in the full prescribing information for acyclovir products approved for oral and parenteral administration.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Study in Patients with Recurrent Herpes Labialis (cold sores)
The efficacy and safety of SITAVIG was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, patient-initiated, multicenter trial comparing SITAVIG 50 mg administered as a single dose (n = 378) to placebo (n = 397) in patients with recurrent herpes labialis (cold sores). A total of 376 SITAVIG treated patients and 395 placebo treated patients were included in the Intent to Treat (ITT) efficacy population defined as all patients who took study treatment and who had a start date and time of treatment initiation recorded. The mean age was 41.0 years (range: 18-80 years) and the majority of patients were female (68.6%), and Caucasian (94.9%). All patients had at least 4 herpes episodes in the previous year of whom 68.4% had ≥ 5 episodes. Patients were instructed to initiate treatment within one hour after the onset of prodromal symptoms and before the appearance of any signs of herpes labialis lesions by applying the tablet to the buccal mucosa in the canine fossa. If the tablet was detached within the first 6 hours, subjects were instructed to reapply a tablet.
The mean and median durations of the recurrent herpes labialis episode (ITT population, n=771) were approximately half a day shorter in patients treated with SITAVIG compared with patients treated with placebo.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
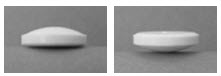
SITAVIG 50 mg buccal tablets are supplied as off-white tablets containing 50 mg of acyclovir. SITAVIG tablets have a rounded side and a flat side. SITAVIG tablets are packaged in blisters (NDC: 71403-049-02).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients should be informed that SITAVIG is not a cure for cold sores. See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
17.1 Instructions for Use
Read the Instructions for Use that comes with SITAVIG before you start using it. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Important:
SITAVIG should be applied to the area of the upper gum above the incisor tooth.
SITAVIG tablets should not be crushed, sucked, chewed or swallowed.
If it comes out before 6 hours have gone by, reapply it. If this does not work then a new tablet should be applied.
It should not be applied to the inside of the lip or cheek.
- Tablet should be applied on the same side of the mouth as the herpes labialis symptoms.
- Do not remove SITAVIG if it sticks to your upper gum. If SITAVIG does not stick or falls off of your upper gum within the first 6 hours that you apply it, place it back onto your upper gum. If it still does not stick, replace it with a new SITAVIG tablet.
- Do not re-apply SITAVIG if it falls out or you swallow it after it has been in place 6 hours or longer.
- If you swallow SITAVIG within the first 6 hours of applying it, drink a glass of water and place a new SITAVIG tablet onto your upper gum.
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issue: April/2013 Patient Information
SITAVIG (SIT-a-vig)
(acyclovir) buccal tabletsWhat is SITAVIG? - SITAVIG is a prescription medicine used to treat cold sores (herpes labialis) in adults with normal immune systems.
- It is not known if SITAVIG is safe and effective in children.
Who should not use SITAVIG?
Do not use SITAVIG if you are allergic to:- acyclovir or any of the ingredients in SITAVIG. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in SITAVIG.
- milk protein concentrate
Before using SITAVIG, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if SITAVIG will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if SITAVIG passes into your breast milk.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements.
How should I use SITAVIG?
See the detailed Instructions for Use for information about how to use SITAVIG.- Use SITAVIG exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Use SITAVIG within 1 hour after you have the first symptom of a cold sore, such as itching, redness, burning, or tingling, and before a cold sore appears.
- You may eat and drink while using SITAVIG.
- Do not crush, chew, suck, or swallow SITAVIG tablets.
- SITAVIG will slowly dissolve over time while in your mouth and should be left in place.
- Gently rinse your mouth with water to clean your teeth while SITAVIG is in place.
- Drink more liquids if your mouth becomes dry while using SITAVIG.
What should I avoid while using SITAVIG?
You should avoid activities that may prevent SITAVIG from sticking to your gum, including: touching or pressing SITAVIG after you apply it, wearing upper dentures, chewing gum, and brushing your teeth during the treatment day.What are the possible side effects of SITAVIG?
The most common side effects of SITAVIG include: headache and pain where SITAVIG is applied.
These are not all the possible side effects of SITAVIG. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store SITAVIG? - Store SITAVIG between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep SITAVIG tablets dry.
General information about the safe and effective use of SITAVIG
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use SITAVIG for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SITAVIG to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SITAVIG that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in SITAVIG?
Active ingredient: acyclovir
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, milk protein concentrate, sodium lauryl sulfate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, colloidal silicon dioxide.
Manufactured By: Farméa, 10 rue Bouché Thomas, ZAC d'orgemont, 49 000 Angers - France
For more information call 1-800-499-4468. -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for Use
SITAVIG (SIT-a-vig)
(acyclovir) buccal tabletsRead the Instructions for Use that comes with SITAVIG before you start using it. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Important:
- SITAVIG should be applied within 1 hour after you have the first symptom of a cold sore, such as itching, redness, burning, or tingling, and before a cold sore appears.
- SITAVIG should be applied on the same side of your mouth as the cold sore symptoms.
- SITAVIG should be applied to your upper gum, just above your incisor tooth.
- SITAVIG should not be applied to the inside of your lip or your cheek.
- If SITAVIG does not stick to your upper gum or falls off of your upper gum within the first 6 hours after you apply it, the same tablet should be placed back onto your upper gum right away. If this SITAVIG tablet does not stay in place, apply another SITAVIG tablet to your upper gum.
- Do not re-apply SITAVIG if it falls out or you swallow it after it has been in place 6 hours or longer.
- If you swallow SITAVIG within the first 6 hours of applying it, drink a glass of water and place a new SITAVIG tablet onto your upper gum.
How to apply SITAVIG:
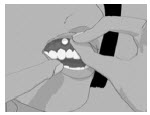
Step 1: Before you apply SITAVIG, find the area on your upper gum, just above either the left or the right incisor. The incisor tooth is the tooth just to the right or left of your two front teeth (See Figure A). This is where you should apply SITAVIG.
Figure AStep 2: Peel back the cover of the blister pack. Take 1 SITAVIG out of the blister pack. When removed from the blister pack, SITAVIG must be used right away. SITAVIG is round on one side and flat on the other side (See Figure B).
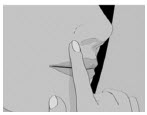
Figure BStep 3: Place the flat side of SITAVIG on your dry fingertip. Apply the round side of SITAVIG to your upper gum (See Figure C). The flat side will be facing the inside of your lip.
Figure CStep 4: Hold SITAVIG in place by applying a slight pressure with your finger on the outside of your upper lip, over the area where SITAVIG is placed, for 30 seconds. This will help SITAVIG stick to your gum (See Figure D).
Figure DStep 5: Leave the SITAVIG tablet in place until it dissolves. This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured By:
Farméa
10 rue Bouché Thomas
ZAC d'orgemont
49 000 Angers - FranceDistributed By:
EPI Health, LLC
Charleston, SC 29403
1-800-499-4468
www.epihealth.com
www.sitavig.comU.S. Pat. No.: 8,592,434 ; 8,747,896 and 8,791,127.
©EPI Health, LLC
Revision date: 12/2017
SIT-PI-0618
022932
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Blister Pack Carton
NDC: 71403-049-02
Sitavig®
(ACYCLOVIR)
Buccal Tablets50 mg
2 blisters
each blister contains one 50 mg
buccal tabletRx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SITAVIG
acyclovir tablet, delayed releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71403-049 Route of Administration BUCCAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ACYCLOVIR (UNII: X4HES1O11F) (ACYCLOVIR - UNII:X4HES1O11F) ACYCLOVIR 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYPROMELLOSE 2208 (15000 MPA.S) (UNII: Z78RG6M2N2) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Product Characteristics Color white Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code AL21 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71403-049-02 1 in 1 CARTON 03/20/2014 1 2 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA203791 03/20/2014 Labeler - EPI Health, Inc (080638894) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations EPI Health, Inc 080638894 manufacture(71403-049) , analysis(71403-049) , label(71403-049) , pack(71403-049)
Trademark Results [Sitavig]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SITAVIG 85247490 4044319 Live/Registered |
VECTANS PHARMA 2011-02-21 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.