CLEMASTINE FUMARATE tablet
Clemastine Fumarate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clemastine Fumarate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Genus Lifesciences. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Clemastine belongs to the benzhydryl ether group of antihistaminic compounds. The chemical name is (+)-(2R)-2-[2-[[(R)-p-Chloro-α-methyl-α-phenylbenzyl]-oxy]ethyl]-1-methylpyrrolidine fumarate (1:1).
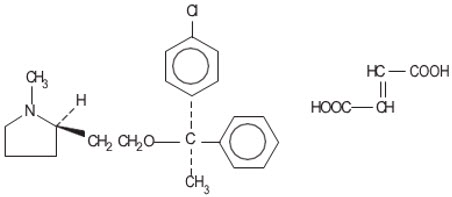
C21H26C1NO∙C4H4O4 M.W. 459.97 Each tablet for oral administration contains 2.68 mg of clemastine fumarate, USP.
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, povidone, pregelatinized starch and stearic acid.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Clemastine fumarate is an antihistamine with anticholinergic (drying) and sedative side effects. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for cell receptor sites on effector cells. The inherently long duration of antihistaminic effects of clemastine fumarate has been demonstrated in wheal and flare studies. In normal human subjects who received histamine injections over a 24-hour period, the antihistaminic activity of clemastine reached a peak at 5 to 7 hours, persisted for 10 to 12 hours and, in some cases, for as long as 24 hours. Pharmacokinetic studies in man utilizing 3H and 14C labeled compound demonstrates that: clemastine is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, peak plasma concentrations are attained in 2 to 4 hours, and urinary excretion is the major mode of elimination.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clemastine Fumarate Tablets USP, 2.68 mg are indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis such as sneezing, rhinorrhea, pruritus, and lacrimation. Clemastine Fumarate Tablets USP, 2.68 mg are also indicated for the relief of mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema. It should be noted that clemastine fumarate is indicated for the dermatologic indications at the 2.68 mg dosage level only.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Usage in Nursing Mothers
Because of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally and for newborns and prematures in particular, antihistamine therapy is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Usage in Lower Respiratory Disease
Antihistamines should not be used to treat lower respiratory tract symptoms including asthma. Antihistamines are also contraindicated in the following conditions:
Hypersensitivity to clemastine fumarate or other antihistamines of similar chemical structure.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy (see Drug Interactions section).
-
WARNINGS
Antihistamines should be used with considerable caution in patients with: narrow angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, and bladder neck obstruction.
Usage in Children
Safety and efficacy of clemastine fumarate have not been established in children under the age of 12 years.
Usage in Pregnancy
Experience with this drug in pregnant women is inadequate to determine whether there is exists a potential for harm to the developing fetus.
Usage with CNS Depressants
Clemastine has additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants (hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, etc.).
- PRECAUTIONS
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Transient drowsiness, the most common adverse reaction associated with clemastine fumarate, occurs relatively frequently and may require discontinuation of therapy in some instances.
Antihistaminic Compounds
It should be noted that the following reactions have occurred with one or more antihistamines and, therefore, should be kept in mind when prescribing drugs belonging to this class, including clemastine. The most frequent adverse reactions are italicized.
- General: Urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration, chills, dryness of the mouth, nose, and throat.
- Cardiovascular System: Hypotension, headache, palpitations, tachycardia, extrasystoles.
- Hematologic System: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
- Nervous System: Sedation, sleepiness, dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, euphoria, paresthesias, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, acute labyrinthitis, hysteria, neuritis, convulsions.
- GI System: Epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
- GU System: Urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses.
- Respiratory System: Thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest and wheezing, nasal stuffiness.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation.
Stimulation is particularly likely in children. Atropine-like signs and symptoms: dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing; and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur.
If vomiting has not occurred spontaneously the conscious patient should be induced to vomit. This is best done by having him drink a glass of water or milk after which he should be made to gag. Precautions against aspiration must be taken, especially in infants and children. If vomiting is unsuccessful gastric lavage is indicated within 3 hours after ingestion and even later if large amounts of milk or cream were given beforehand. Isotonic and 1/2 isotonic saline is the lavage solution of choice.
Saline cathartics, such as milk of magnesia, by osmosis draw water into the bowel and therefore, are valuable for their action in rapid dilution of bowel content.
Stimulants should not be used.
Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Clemastine Fumarate Tablets USP, 2.68 mg are white, round, scored tablets debossed with "NH" and "268". Tablets are packaged in bottles of 30 (NDC: 64950-268-03) and 100 (NDC: 64950-268-10)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2.68 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC: 64950-268-10
Clemastine
Fumarate
Tablets, USP2.68 mg
Rx only
100 TabletsGenus
Lifesciences Inc.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLEMASTINE FUMARATE
clemastine fumarate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 64950-268 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Clemastine Fumarate (UNII: 19259EGQ3D) (CLEMASTINE - UNII:95QN29S1ID) Clemastine Fumarate 2.68 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) LACTOSE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: J2B2A4N98G) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code NH;268 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 64950-268-03 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/20/2024 2 NDC: 64950-268-10 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/20/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA073283 11/20/2024 Labeler - Genus Lifesciences (113290444)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.