CLINDACIN- clindamycin phosphate aerosol, foam
Clindacin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clindacin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Padagis. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLINDACIN® (CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE) FOAM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLINDACIN® (CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE) FOAM.
CLINDACIN® (CLINDAMYCIN PHOSPHATE) foam, 1%
For topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1970INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clindacin Foam is a lincosamide product indicated for acne vulgaris in patients 12 years and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Foam containing 1% clindamycin as clindamycin phosphate. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Clindacin Foam is contraindicated in individuals with a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis). (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Colitis: Clindamycin can cause severe colitis, which may result in death. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of clindamycin. Clindacin Foam should be discontinued if significant diarrhea occurs. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (>1%) are headache and application site reactions including burning, pruritus, and dryness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Medimetriks at 1-973-882-7512 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2022
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
5.2 Irritation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Erythromycin
7.2 Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Instructions for Use
17.2 Skin Irritation
17.3 Colitis
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Clindacin Foam is for topical use only, and not for oral, ophthalmic or intravaginal use.
Apply Clindacin Foam once daily to affected areas after the skin is washed with mild soap and allowed to fully dry. Use enough to cover the entire affected area.
If there has been no improvement after 6 to 8 weeks or if the condition becomes worse, treatment should be discontinued.
The contents of Clindacin Foam are flammable; avoid fire, flame and/or smoking during and immediately following application.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Colitis
Systemic absorption of clindamycin has been demonstrated following topical use of this product. Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported with the use of topical clindamycin. If significant diarrhea occurs, Clindacin Foam should be discontinued [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Severe colitis has occurred following oral or parenteral administration of clindamycin with an onset of up to several weeks following cessation of therapy. Antiperistaltic agents such as opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine may prolong and/or worsen severe colitis. Severe colitis may result in death.
Studies indicate a toxin(s) produced by Clostridia is one primary cause of antibiotic-associated colitis. The colitis is usually characterized by severe persistent diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps and may be associated with the passage of blood and mucus. Stool cultures for Clostridium difficile and stool assay for C. difficile toxin may be helpful diagnostically.
5.2 Irritation
Clindacin Foam can cause irritation. Concomitant topical acne therapy should be used with caution since a possible cumulative irritancy effect may occur, especially with the use of peeling, desquamating, or abrasive agents. If irritation or dermatitis occurs, clindamycin should be discontinued.
Avoid contact of Clindacin Foam with eyes, mouth, lips, other mucous membranes or areas of broken skin. If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water.
Clindacin Foam should be prescribed with caution in atopic individuals.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
A total of 439 subjects with mild to moderate acne vulgaris were treated once daily for 12 weeks with clindamycin phosphate foam.
The incidence of adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of the subjects in clinical trials comparing clindamycin phosphate foam and its vehicle is presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 1% of Subjects Adverse Reactions Number (%) of Subjects Clindamycin Phosphate Foam
N = 439Vehicle Foam
N = 154Headache 12 (3%) 1 (1%) Application site burning 27 (6%) 14 (9%) Application site pruritus 5 (1%) 5 (3%) Application site dryness 4 (1%) 5 (3%) Application site reaction, not otherwise specified 3 (1%) 4 (3%) In a contact sensitization study, none of the 203 subjects developed evidence of allergic contact sensitization to clindamycin phosphate foam.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of clindamycin phosphate foam: application site pain, application site erythema, diarrhea, urticaria, abdominal pain, hypersensitivity, rash, abdominal discomfort, nausea, seborrhea, application site rash, dizziness, pain of skin, colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis), and hemorrhagic diarrhea. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Abdominal pain and gastrointestinal disturbances, as well as gram-negative folliculitis, have also been reported in association with the use of topical formulations of clindamycin. Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin have been associated with severe colitis, which may end fatally.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Erythromycin
Clindamycin phosphate foam should not be used in combination with topical or oral erythromycin-containing products due to possible antagonism to its clindamycin component. In vitro studies have shown antagonism between these two antimicrobials. The clinical significance of this in vitro antagonism is not known.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on clindamycin phosphate foam use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with clindamycin phosphate foam. No evidence of fetal harm or malformations was observed in pregnant rats and mice administered daily subcutaneous or oral doses of clindamycin salts during organogenesis at doses that produced exposures up to 84 and 42 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of clindamycin phosphate foam based on body surface area (BSA) comparisons and assuming 100% absorption [see Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies have been conducted in rats and mice using subcutaneous or oral doses of clindamycin phosphate, clindamycin hydrochloride or clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride administered daily during organogenesis at doses up to the equivalent of 432 mg/kg/day clindamycin phosphate. These studies produced no evidence of fetal harm or malformations in rats or mice at exposures 84 or 42 times, respectively, the MRHD of clindamycin phosphate (i.e., 5 milliliters of clindamycin phosphate foam) based on BSA comparison and assuming 100% absorption.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of clindamycin in human milk, or the effects on the breast-fed child, or the effects on milk production following use of clindamycin phosphate foam. However, orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been reported to appear in breast milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for clindamycin phosphate foam and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from clindamycin phosphate foam or from the underlying maternal condition.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Clindacin Foam contains clindamycin (1%) as clindamycin phosphate.
Clindamycin phosphate is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7(S)-chloro-substitution of the 7(R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic, lincomycin.
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate is methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl-trans-4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L-threo-α-D-galacto-octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate). The structural formula for clindamycin phosphate is represented below:
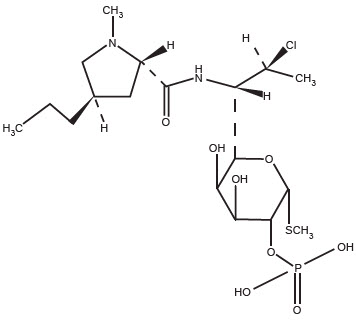
Molecular Formula: C18H34CIN2O8PS Molecular Weight: 504.97 g/mol
Clindacin Foam contains clindamycin (1%) as clindamycin phosphate, USP at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per gram in a thermolabile hydroethanolic foam vehicle consisting of cetyl alcohol, ethanol (58%), polysorbate 60, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Mechanism of action of clindamycin in acne vulgaris is unknown [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In an open label, parallel group study in 24 subjects with acne vulgaris, 12 subjects (3 male and 9 female) applied 4 grams of clindamycin phosphate foam once-daily for five days, and 12 subjects (7 male and 5 female) applied 4 grams of a clindamycin gel, 1%, once daily for five days. On Day 5, the mean Cmax and AUC(0-12) were 23% and 9% lower, respectively, for clindamycin phosphate foam than for the clindamycin gel, 1%.
Following multiple applications of clindamycin phosphate foam, less than 0.024% of the total dose was excreted unchanged in the urine over 12 hours on Day 5.
12.4 Microbiology
No microbiology studies were conducted in the clinical trials with this product.
Clindamycin binds to the 50S ribosomal subunits of susceptible bacteria and prevents elongation of peptide chains by interfering with peptidyl transfer, thereby suppressing protein synthesis. Clindamycin has been shown to have in vitro activity against Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), an organism that has been associated with acne vulgaris; however, the clinical significance of this activity against P. acnes was not examined in clinical studies with clindamycin phosphate foam. P. acnes resistance to clindamycin has been documented.
Inducible Clindamycin Resistance: The treatment of acne with antimicrobials is associated with the development of antimicrobial resistance in P. acnes as well as other bacteria (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes). The use of clindamycin may result in developing inducible resistance in these organisms. This resistance is not detected by routine susceptibility testing.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenicity of a 1.2% clindamycin phosphate gel similar to clindamycin phosphate foam was evaluated by daily topical administration to mice for two years. The topical doses used in this study were approximately 3 and 15 times higher than the MRHD of clindamycin phosphate from clindamycin phosphate foam, based on BSA comparison and assuming 100% absorption. No significant increase in tumors was noted in the treated animals.
The genotoxic potential of clindamycin was evaluated in an in vitro Ames assay and in an in vivo rat micronucleus test. Both tests were negative.
Reproduction studies in rats using oral doses of clindamycin hydrochloride and clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled clinical trial, subjects with mild to moderate acne vulgaris used clindamycin phosphate foam or the vehicle foam once daily for twelve weeks. Treatment response, defined as the proportion of subjects clear or almost clear, based on the Investigator Static Global Assessment (ISGA), and the mean percent reductions in lesion counts at the end of treatment in this study are shown in Table 2.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Clindacin® (clindamycin phosphate) Foam, 1% contains 10 mg of clindamycin as clindamycin phosphate, USP per gram. The white to off-white thermolabile foam is available as follows:
- 100 gram aerosol can - NDC 43538-179-10
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Flammable. Avoid fire, flame or smoking during and immediately following application.
Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not expose to heat or store at temperature above 120°F (49°C).
Keep out of reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
17.1 Instructions for Use
- Patients should be advised to wash their skin with mild soap and allow it to dry before applying Clindacin Foam.
- Patients should use enough Clindacin Foam to cover the face and to apply once daily.
- Patients should dispense Clindacin Foam directly into the cap or onto a cool surface.
- Patients should wash their hands after applying Clindacin Foam.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Clindacin® (klin-da-sin) (clindamycin phosphate) (klin-da-MYE-sin fos-fate) Foam, 1%Important Information: Clindacin Foam is for use on the skin only. Do not use Clindacin Foam in your eyes, mouth or vagina.
What is Clindacin Foam?
Clindacin Foam is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat acne vulgaris in people 12 years and older.
It is not known if Clindacin Foam is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.
Who should not use Clindacin Foam?
Do not use Clindacin Foam if you:- have Crohn's disease
- have ulcerative colitis
- have had inflammation of the colon (colitis) or severe diarrhea with past antibiotic use
What should I tell my doctor before using Clindacin Foam?
Before using Clindacin Foam, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:- have or have had bowel problems (such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, colitis)
- have or have had eczema or other skin problems
- are planning to have surgery. Clindacin Foam may affect how certain medicines work that may be given during surgery.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Clindacin Foam may harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if clindamycin phosphate passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about using Clindacin Foam while breastfeeding. If you use Clindacin Foam while breastfeeding and Clindacin Foam is applied on the chest, take care to avoid getting Clindacin Foam into your baby's mouth.
Clindacin Foam may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how Clindacin Foam works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take medicine by mouth that contains erythromycin or use products on your skin that contain erythromycin.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Clindacin Foam?- Use Clindacin Foam exactly as your doctor tells you to use it. See the detailed "Instructions for Use" for directions about how to apply Clindacin Foam correctly.
- Wash your skin with mild soap and water and dry before applying Clindacin Foam.
- Apply Clindacin Foam 1 time each day to the affected skin area. You should apply enough Clindacin Foam to cover the entire affected area.
- Dispense Clindacin Foam directly into the cap. Do not dispense Clindacin Foam directly onto your hands or face, because the foam will begin to melt on contact with warm skin.
- Wash your hands after applying Clindacin Foam.
- Clindacin Foam is flammable. Avoid fire, flames, or smoking during and right after you apply Clindacin Foam to your skin.
- Avoid getting Clindacin Foam in or near your eyes, mouth, lips, or broken skin. If you get Clindacin Foam in your eyes, mouth, on lips or broken skin, rinse well with water.
Clindacin Foam may cause serious side effects, including:- Inflammation of the colon (colitis). Diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis has happened in people who use Clindacin Foam. Stop using Clindacin Foam and call your doctor right away if you have severe stomach (abdominal) cramps, watery diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea during treatment, and for several weeks after treatment, with Clindacin Foam.
- Skin irritation. Stop using Clindacin Foam and call your doctor if you develop skin irritation during treatment with Clindacin Foam.
These are not all the possible side effects of Clindacin Foam.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Clindacin Foam?- Store Clindacin Foam at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Clindacin Foam away from heat. Never throw the can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
- Do not store Clindacin Foam at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
- Do not break through (puncture) the Clindacin Foam can.
General information about the safe and effective use of Clindacin Foam.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Clindacin Foam for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Clindacin Foam to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
You can also ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Clindacin Foam that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Clindacin Foam?
Active ingredient: clindamycin phosphate
Inactive ingredients: cetyl alcohol, ethanol (58%), polysorbate 60, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol. The can is pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for Use
Clindacin® (klin-da-sin) (clindamycin phosphate) (klin-da-MYE-sin fos-fate) Foam, 1%Important Information: Clindacin Foam is for use on the skin only. Do not use Clindacin Foam in your eyes, mouth or vagina. 
Step 1: Remove the clear cap from the Clindacin Foam can. 
Step 2: Hold the can upright and firmly press the nozzle to dispense Clindacin Foam into the clear cap. 
- Dispense enough Clindacin Foam to cover the entire affected area.

- If the can seems warm or the foam seems runny, run the can under cold water.
Step 3: Pick up small amounts of Clindacin Foam with your fingertips and gently rub the foam into the affected area until the foam disappears. Step 4: Wash your hands after applying Clindacin Foam. - Throw away any of the unused medicine that you dispensed out of the can.
How should I store Clindacin Foam? - Store Clindacin Foam at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep Clindacin Foam away from heat. Never throw the can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
- Do not store Clindacin Foam at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
- Do not break through (puncture) the Clindacin Foam can.
The Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
MEDIMETRIKS
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
383 Route 46 West Fairfield, NJ 07004-2402 US www.medimetriks.com
Manufactured by Padagis, Yeruham, Israel
Iss: 04/22
IP053
4T500 EK J1 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 g Can Carton
NDC: 43538-179-10
Rx OnlyClindacin®
(Clindamycin Phosphate)Foam, 1%
MEDIMETRIKS
PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
100 g
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLINDACIN
clindamycin phosphate aerosol, foamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 43538-179 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength clindamycin phosphate (UNII: EH6D7113I8) (clindamycin - UNII:3U02EL437C) clindamycin 10 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) polysorbate 60 (UNII: CAL22UVI4M) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) stearyl alcohol (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) cetyl alcohol (UNII: 936JST6JCN) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 43538-179-10 1 in 1 CARTON 11/14/2022 1 100 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA090785 03/21/2010 Labeler - Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (019903816) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Padagis 600093611 MANUFACTURE(43538-179)
Trademark Results [Clindacin]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 CLINDACIN 85163653 4032724 Live/Registered |
Medimetriks Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2010-10-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.