SYNAREL- nafarelin acetate spray, metered
Synarel by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Synarel by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc, Pharmacia & Upjohn Company LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate) Nasal Solution is intended for administration as a spray to the nasal mucosa. Nafarelin acetate, the active component of SYNAREL Nasal Solution, is a decapeptide with the chemical name: 5-oxo-L-prolyl-L-histidyl-L-tryptophyl-L-seryl-L-tyrosyl-3-(2-naphthyl)-D-alanyl-L-leucyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-glycinamide acetate. Nafarelin acetate is a synthetic analog of the naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Nafarelin acetate has the following chemical structure:
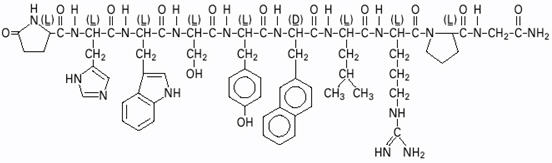
∙ x CH3COOH ∙ y H2O (1 ⩽ x ⩽ 2; 2 ⩽ y ⩽ 8)
SYNAREL Nasal Solution contains nafarelin acetate (2 mg/mL, content expressed as nafarelin base) in a solution of benzalkonium chloride, glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), sorbitol, and purified water.
After priming the pump unit for SYNAREL, each actuation of the unit delivers approximately 100 µL of the spray containing approximately 200 µg nafarelin base. The contents of one spray bottle are intended to deliver at least 60 sprays.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Nafarelin acetate is a potent agonistic analog of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). At the onset of administration, nafarelin stimulates the release of the pituitary gonadotropins, LH and FSH, resulting in a temporary increase of gonadal steroidogenesis. Repeated dosing abolishes the stimulatory effect on the pituitary gland. Twice daily administration leads to decreased secretion of gonadal steroids by about 4 weeks; consequently, tissues and functions that depend on gonadal steroids for their maintenance become quiescent.
In children, nafarelin acetate was rapidly absorbed into the systemic circulation after intranasal administration. Maximum serum concentrations (measured by RIA) were achieved between 10 and 45 minutes. Following a single dose of 400 µg base, the observed peak concentration was 2.2 ng/mL, whereas following a single dose of 600 µg base, the observed peak concentration was 6.6 ng/mL. The average serum half-life of nafarelin following intranasal administration of a 400 µg dose was approximately 2.5 hours. It is not known and cannot be predicted what the pharmacokinetics of nafarelin will be in children given a dose above 600 µg.
In adult women, nafarelin acetate was rapidly absorbed into the systemic circulation after intranasal administration. Maximum serum concentrations (measured by RIA) were achieved between 10 and 40 minutes. Following a single dose of 200 µg base, the observed average peak concentration was 0.6 ng/mL (range 0.2 to 1.4 ng/mL), whereas following a single dose of 400 µg base, the observed average peak concentration was 1.8 ng/mL (range 0.5 to 5.3 ng/mL). Bioavailability from a 400 µg dose averaged 2.8% (range 1.2 to 5.6%). The average serum half-life of nafarelin following intranasal administration was approximately 3 hours. About 80% of nafarelin acetate was bound to plasma proteins at 4°C. Twice daily intranasal administration of 200 or 400 µg of SYNAREL in 18 healthy women for 22 days did not lead to significant accumulation of the drug. Based on the mean Cmin levels on Days 15 and 22, there appeared to be dose proportionality across the two dose levels.
After subcutaneous administration of 14C-nafarelin acetate to men, 44–55% of the dose was recovered in urine and 18.5–44.2% was recovered in feces. Approximately 3% of the administered dose appeared as unchanged nafarelin in urine. The 14C serum half-life of the metabolites was about 85.5 hours. Six metabolites of nafarelin have been identified of which the major metabolite is Tyr-D(2)-Nal-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2(5–10). The activity of the metabolites, the metabolism of nafarelin by nasal mucosa, and the pharmacokinetics of the drug in hepatically- and renally-impaired patients have not been determined.
There appeared to be no significant effect of rhinitis, i.e., nasal congestion, on the systemic bioavailability of SYNAREL; however, if the use of a nasal decongestant for rhinitis is necessary during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing with SYNAREL.
When used regularly in girls and boys with central precocious puberty (CPP) at the recommended dose, SYNAREL suppresses LH and sex steroid hormone levels to prepubertal levels, affects a corresponding arrest of secondary sexual development, and slows linear growth and skeletal maturation. In some cases, initial estrogen withdrawal bleeding may occur, generally within 6 weeks after initiation of therapy. Thereafter, menstruation should cease.
In clinical studies the peak response of LH to GnRH stimulation was reduced from a pubertal response to a prepubertal response (< 15 mlU/mL) within one month of treatment.
Linear growth velocity, which is commonly pubertal in children with CPP, is reduced in most children within the first year of treatment to values of 5 to 6 cm/year or less. Children with CPP are frequently taller than their chronological age peers; height for chronological age approaches normal in most children during the second or third year of treatment with SYNAREL. Skeletal maturation rate (bone age velocity—change in bone age divided by change in chronological age) is usually abnormal (greater than 1) in children with CPP; in most children, bone age velocity approaches normal (1) during the first year of treatment. This results in a narrowing of the gap between bone age and chronological age, usually by the second or third year of treatment. The mean predicted adult height increases.
In clinical trials, breast development was arrested or regressed in 82% of girls, and genital development was arrested or regressed in 100% of boys. Because pubic hair growth is largely controlled by adrenal androgens, which are unaffected by nafarelin, pubic hair development was arrested or regressed only in 54% of girls and boys.
Reversal of the suppressive effects of SYNAREL has been demonstrated to occur in all children with CPP for whom one-year post-treatment follow-up is available (n=69). This demonstration consisted of the appearance or return of menses, the return of pubertal gonadotropin and gonadal sex steroid levels, and/or the advancement of secondary sexual development. Semen analysis was normal in the two ejaculated specimens obtained thus far from boys who have been taken off therapy to resume puberty. Fertility has not been documented by pregnancies and the effect of long-term use of the drug on fertility is not known.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE FOR CENTRAL PRECOCIOUS PUBERTY
(For Endometriosis, See Reverse Side)
SYNAREL is indicated for treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP) (gonadotropin-dependent precocious puberty) in children of both sexes.
The diagnosis of central precocious puberty (CPP) is suspected when premature development of secondary sexual characteristics occurs at or before the age of 8 years in girls and 9 years in boys, and is accompanied by significant advancement of bone age and/or a poor adult height prediction. The diagnosis should be confirmed by pubertal gonadal sex steroid levels and a pubertal LH response to stimulation by native GnRH. Pelvic ultrasound assessment in girls usually reveals enlarged uterus and ovaries, the latter often with multiple cystic formations. Magnetic resonance imaging or CT-scanning of the brain is recommended to detect hypothalamic or pituitary tumors, or anatomical changes associated with increased intracranial pressure. Other causes of sexual precocity, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, testotoxicosis, testicular tumors and/or other autonomous feminizing or masculinizing disorders must be excluded by proper clinical hormonal and diagnostic imaging examinations.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
1. Hypersensitivity to GnRH, GnRH agonist analogs or any of the excipients in SYNAREL;
2. Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding;
3. Use in pregnancy or in women who may become pregnant while receiving the drug. SYNAREL may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Major fetal abnormalities were observed in rats, but not in mice or rabbits after administration of SYNAREL during the period of organogenesis. There was a dose-related increase in fetal mortality and a decrease in fetal weight in rats [see Pregnancy]. The effects on rat fetal mortality are expected consequences of the alterations in hormonal levels brought about by the drug. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus;
4. Use in women who are breast-feeding [see Nursing Mothers].
-
WARNINGS
The diagnosis of central precocious puberty (CPP) must be established before treatment is initiated. Regular monitoring of CPP patients is needed to assess both patient response as well as compliance. This is particularly important during the first 6 to 8 weeks of treatment to assure that suppression of pituitary-gonadal function is rapid. Testing may include LH response to GnRH stimulation and circulating gonadal sex steroid levels. Assessment of growth velocity and bone age velocity should begin within 3 to 6 months of treatment initiation.
Some patients may not show suppression of the pituitary-gonadal axis by clinical and/or biochemical parameters. This may be due to lack of compliance with the recommended treatment regimen and may be rectified by recommending that the dosing be done by caregivers. If compliance problems are excluded, the possibility of gonadotropin independent sexual precocity should be reconsidered and appropriate examinations should be conducted. If compliance problems are excluded and if gonadotropin independent sexual precocity is not present, the dose of SYNAREL may be increased to 1800 µg/day administered as 600 µg tid.
Psychiatric events have been reported in patients taking GnRH agonists. Postmarketing reports with this class of drugs includes symptoms of emotional lability, such as crying, irritability, impatience, anger, and aggression. Monitor for development or worsening of psychiatric symptoms during treatment with SYNAREL.
Post-marketing reports of convulsions have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists. These have included patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions such as bupropion and SSRIs. Convulsions have also been reported in patients in the absence of any of the conditions mentioned above.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
As with other drugs that stimulate the release of gonadotropins or that induce ovulation, in adult women with endometriosis ovarian cysts have been reported to occur in the first two months of therapy with SYNAREL. Many, but not all, of these events occurred in women with polycystic ovarian disease. These cystic enlargements may resolve spontaneously, generally by about four to six weeks of therapy, but in some cases may require discontinuation of drug and/or surgical intervention. The relevance, if any, of such events in children is unknown.
Information for Patients, Patients' Parents or Guardians
An information pamphlet for patients is included with the product. Patients and their caregivers should be aware of the following information:
1. Reversibility of the suppressive effects of nafarelin has been demonstrated by the appearance or return of menses, by the return of pubertal gonadotropin and gonadal sex steroid levels, and/or by advancement of secondary sexual development. Semen analysis was normal in the two ejaculated specimens obtained thus far from boys who have been taken off therapy to resume puberty. Fertility has not been documented by pregnancies and the effect of long-term use of the drug on fertility is not known.
2. Patients and their caregivers should be adequately counseled to assure full compliance; irregular or incomplete daily doses may result in stimulation of the pituitary-gonadal axis.
3. Inform parents that reports of convulsions have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists. Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions may be at increased risk [see Warnings].
4. Inform caregivers that reports of convulsions have been observed in patients receiving GnRH agonists. Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, cerebrovascular disorders, central nervous system anomalies or tumors, and patients on concomitant medications that have been associated with convulsions may be at increased risk [see Warnings].
5. During the first month of treatment with SYNAREL, some signs of puberty, e.g., vaginal bleeding or breast enlargement, may occur. This is the expected initial effect of the drug. Such changes should resolve soon after the first month. lf such resolution does not occur within the first two months of treatment, this may be due to lack of compliance or the presence of gonadotropin independent sexual precocity. If both possibilities are definitively excluded, the dose of SYNAREL may be increased to 1800 µg/day administered as 600 µg tid.
6. Patients with intercurrent rhinitis should consult their physician for the use of a topical nasal decongestant. If the use of a topical nasal decongestant is required during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing with SYNAREL.
Sneezing during or immediately after dosing with SYNAREL should be avoided, if possible, since this may impair drug absorption.
Drug Interactions
No pharmacokinetic-based drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with SYNAREL. However, because nafarelin acetate is a peptide that is primarily degraded by peptidase and not by cytochrome P-450 enzymes, and the drug is only about 80% bound to plasma proteins at 4°C, drug interactions would not be expected to occur.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies of nafarelin were conducted in rats (24 months) at doses up to 100 µg/kg/day and mice (18 months) at doses up to 500 µg/kg/day using intramuscular doses (up to 110 times and 560 times the maximum recommended human intranasal dose, respectively). These multiples of the human dose are based on the relative bioavailability of the drug by the two routes of administration. As seen with other GnRH agonists, nafarelin acetate given to laboratory rodents at high doses for prolonged periods induced proliferative responses (hyperplasia and/or neoplasia) of endocrine organs. At 24 months, there was an increase in the incidence of pituitary tumors (adenoma/carcinoma) in high-dose female rats and a dose-related increase in male rats. There was an increase in pancreatic islet cell adenomas in both sexes, and in benign testicular and ovarian tumors in the treated groups. There was a dose-related increase in benign adrenal medullary tumors in treated female rats. In mice, there was a dose-related increase in Harderian gland tumors in males and an increase in pituitary adenomas in high-dose females. No metastases of these tumors were observed. It is known that tumorigenicity in rodents is particularly sensitive to hormonal stimulation.
Mutagenicity studies were performed with nafarelin acetate using bacterial, yeast, and mammalian systems. These studies provided no evidence of mutagenic potential.
Reproduction studies in male and female rats have shown full reversibility of fertility suppression when drug treatment was discontinued after continuous administration for up to 6 months. The effect of treatment of prepubertal rats on the subsequent reproductive performance of mature animals has not been investigated.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
See Contraindications. Intramuscular SYNAREL was administered to rats during the period of organogenesis at 0.4, 1.6, and 6.4 µg/kg/day (about 0.5, 2, and 7 times the maximum recommended human intranasal dose based on the relative bioavailability by the two routes of administration). An increase in major fetal abnormalities was observed in 4/80 fetuses at the highest dose. A similar, repeat study at the same doses in rats and studies in mice and rabbits at doses up to 600 µg/kg/day and 0.18 µg/kg/day, respectively, failed to demonstrate an increase in fetal abnormalities after administration during the period of organogenesis. In rats and rabbits, there was a dose-related increase in fetal mortality and a decrease in fetal weight with the highest dose.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical trials of 155 pediatric patients, 2.6% reported symptoms suggestive of drug sensitivity, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, urticaria, rash, and pruritus.
In these 155 patients treated for an average of 41 months and as long as 80 months (6.7 years), adverse events most frequently reported (>3% of patients) consisted largely of episodes occurring during the first 6 weeks of treatment as a result of the transient stimulatory action of nafarelin upon the pituitary-gonadal axis:
- acne (10%)
- transient breast enlargement (8%)
- vaginal bleeding (8%)
- emotional lability (6%) [see Warnings]
- transient increase in pubic hair (5%)
- body odor (4%)
- seborrhea (3%)
Hot flashes, common in adult women treated for endometriosis, occurred in only 3% of treated children and were transient. Other adverse events thought to be drug-related, and occurring in >3% of patients were rhinitis (5%) and white or brownish vaginal discharge (3%). Approximately 3% of patients withdrew from clinical trials due to adverse events.
In one male patient with concomitant congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and who had discontinued treatment 8 months previously to resume puberty, adrenal rest tumors were found in the left testis. Relationship to SYNAREL is unlikely.
Regular examinations of the pituitary gland by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computer assisted tomography (CT) of children during long-term nafarelin therapy as well as during the post-treatment period has occasionally revealed changes in the shape and size of the pituitary gland. These changes include asymmetry and enlargement of the pituitary gland, and a pituitary microadenoma has been suspected in a few children. The relationship of these findings to SYNAREL is not known.
Post-Marketing
Pituitary apoplexy: During post-marketing surveillance, rare cases of pituitary apoplexy (a clinical syndrome secondary to infarction of the pituitary gland) have been reported after the administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. In a majority of these cases, a pituitary adenoma was diagnosed, with a majority of pituitary apoplexy cases occurring within 2 weeks of the first dose, and some within the first hour. In these cases, pituitary apoplexy has presented as sudden headache, vomiting, visual changes, ophthalmoplegia, altered mental status, and sometimes cardiovascular collapse. Immediate medical attention has been required.
Psychiatric adverse events: Emotional lability, such as crying, irritability, impatience, anger, and aggression has been observed with GnRH agonists [see Warnings]; Depression, including rare reports of suicidal ideation and attempt, has been reported for GnRH agonists in children treated for central precocious puberty. Many, but not all, of these patients had a history of psychiatric illness or other comorbidities with an increased risk of depression.
-
OVERDOSAGE
In experimental animals, a single subcutaneous administration of up to 60 times the recommended human dose (on a µg/kg basis, not adjusted for bioavailability) had no adverse effects. At present, there is no clinical evidence of adverse effects following overdosage of GnRH analogs.
Based on studies in monkeys, SYNAREL is not absorbed after oral administration.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For the treatment of central precocious puberty (CPP), the recommended daily dose of SYNAREL is 1600 µg. The dose can be increased to 1800 µg daily if adequate suppression cannot be achieved at 1600 µg/day.
The 1600 µg dose is achieved by two sprays (400 µg) into each nostril in the morning (4 sprays) and two sprays into each nostril in the evening (4 sprays), a total of 8 sprays per day. The 1800 µg dose is achieved by 3 sprays (600 µg) into alternating nostrils three times a day, a total of 9 sprays per day. The patient's head should be tilted back slightly, and 30 seconds should elapse between sprays.
If the prescribed therapy has been well tolerated by the patient, treatment of CPP with SYNAREL should continue until resumption of puberty is desired.
There appeared to be no significant effect of rhinitis, i.e., nasal congestion, on the systemic bioavailability of SYNAREL; however, if the use of a nasal decongestant for rhinitis is necessary during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing with SYNAREL.
Sneezing during or immediately after dosing with SYNAREL should be avoided, if possible, since this may impair drug absorption.
At 1600 µg/day, a bottle of SYNAREL provides about a 7-day supply (about 56 sprays). If the daily dose is increased, increase the supply to the patient to ensure uninterrupted treatment for the duration of therapy.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Each 0.5 ounce bottle (NDC: 0025-0166-08) contains 8 mL SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate) Nasal Solution 2 mg/mL (as nafarelin base), and is supplied with a metered spray pump that delivers 200 µg of nafarelin per spray. A dust cover and a leaflet of patient instructions are also included.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Synarel®
(nafarelin acetate)
nasal solutionENDOMETRIOSIS (FOR CENTRAL PRECOCIOUS PUBERTY, SEE REVERSE SIDE)
PHYSICIAN LABELING
-
DESCRIPTION
SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate) Nasal Solution is intended for administration as a spray to the nasal mucosa. Nafarelin acetate, the active component of SYNAREL Nasal Solution, is a decapeptide with the chemical name: 5-oxo-L-prolyl-L-histidyl-L-tryptophyl-L-seryl-L-tyrosyl-3-(2-naphthyl)-D-alanyl-L-leucyl-L-arginyl-L-prolyl-glycinamide acetate. Nafarelin acetate is a synthetic analog of the naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Nafarelin acetate has the following chemical structure:
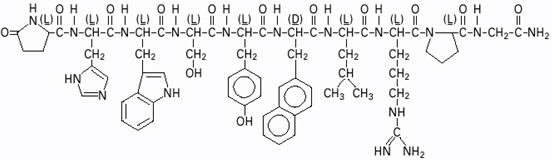
∙ x CH3COOH ∙ y H2O (1 ⩽ x ⩽ 2; 2 ⩽ y ⩽ 8)
SYNAREL Nasal Solution contains nafarelin acetate (2 mg/mL, content expressed as nafarelin base) in a solution of benzalkonium chloride, glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), sorbitol, and purified water.
After priming the pump unit for SYNAREL, each actuation of the unit delivers approximately 100 µL of the spray containing approximately 200 µg nafarelin base. The contents of one spray bottle are intended to deliver at least 60 sprays.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Nafarelin acetate is a potent agonistic analog of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). At the onset of administration, nafarelin stimulates the release of the pituitary gonadotropins, LH and FSH, resulting in a temporary increase of ovarian steroidogenesis. Repeated dosing abolishes the stimulatory effect on the pituitary gland. Twice daily administration leads to decreased secretion of gonadal steroids by about 4 weeks; consequently, tissues and functions that depend on gonadal steroids for their maintenance become quiescent.
Nafarelin acetate is rapidly absorbed into the systemic circulation after intranasal administration. Maximum serum concentrations (measured by RIA) were achieved between 10 and 40 minutes. Following a single dose of 200 µg base, the observed average peak concentration was 0.6 ng/mL (range 0.2 to 1.4 ng/mL), whereas following a single dose of 400 µg base, the observed average peak concentration was 1.8 ng/mL (range 0.5 to 5.3 ng/mL). Bioavailability from a 400 µg dose averaged 2.8% (range 1.2 to 5.6%). The average serum half-life of nafarelin following intranasal administration is approximately 3 hours. About 80% of nafarelin acetate is bound to plasma proteins at 4°C. Twice daily intranasal administration of 200 or 400 µg of SYNAREL in 18 healthy women for 22 days did not lead to significant accumulation of the drug. Based on the mean Cmin levels on Days 15 and 22, there appeared to be dose proportionality across the two dose levels.
After subcutaneous administration of 14C-nafarelin acetate to men, 44–55% of the dose was recovered in urine and 18.5–44.2% was recovered in feces. Approximately 3% of the administered dose appeared as unchanged nafarelin in urine. The 14C serum half-life of the metabolites was about 85.5 hours. Six metabolites of nafarelin have been identified of which the major metabolite is Tyr-D(2)-Nal-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2(5–10). The activity of the metabolites, the metabolism of nafarelin by nasal mucosa, and the pharmacokinetics of the drug in hepatically- and renally-impaired patients have not been determined.
There appeared to be no significant effect of rhinitis, i.e., nasal congestion, on the systemic bioavailability of SYNAREL; however, if the use of a nasal decongestant for rhinitis is necessary during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing of SYNAREL.
In controlled clinical studies, SYNAREL at doses of 400 and 800 µg/day for 6 months was shown to be comparable to danazol, 800 mg/day, in relieving the clinical symptoms of endometriosis (pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, and dyspareunia) and in reducing the size of endometrial implants as determined by laparoscopy. The clinical significance of a decrease in endometriotic lesions is not known at this time and, in addition, laparoscopic staging of endometriosis does not necessarily correlate with severity of symptoms.
In a single controlled clinical trial, intranasal SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate) at a dose of 400 µg per day was shown to be clinically comparable to intramuscular leuprolide depot, 3.75 mg monthly, for the treatment of the symptoms (dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia and pelvic pain) associated with endometriosis.
SYNAREL 400 µg daily induced amenorrhea in approximately 65%, 80%, and 90% of the patients after 60, 90, and 120 days, respectively. In the first, second, and third post-treatment months, normal menstrual cycles resumed in 4%, 82%, and 100%, respectively, of those patients who did not become pregnant.
At the end of treatment, 60% of patients who received SYNAREL, 400 µg/day, were symptom free, 32% had mild symptoms, 7% had moderate symptoms, and 1% had severe symptoms. Of the 60% of patients who had complete relief of symptoms at the end of treatment, 17% had moderate symptoms 6 months after treatment was discontinued, 33% had mild symptoms, 50% remained symptom free, and no patient had severe symptoms.
During the first two months use of SYNAREL, some women experience vaginal bleeding of variable duration and intensity. In all likelihood, this bleeding represents estrogen withdrawal bleeding and is expected to stop spontaneously. If vaginal bleeding continues, the possibility of lack of compliance with the dosing regimen should be considered. If the patient is complying carefully with the regimen, an increase in dose to 400 µg twice a day should be considered.
There is no evidence that pregnancy rates are enhanced or adversely affected by the use of SYNAREL.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE FOR ENDOMETRIOSIS
(For Central Precocious Puberty, See Reverse Side)
SYNAREL is indicated for management of endometriosis, including pain relief and reduction of endometriotic lesions. Experience with SYNAREL for the management of endometriosis has been limited to women 18 years of age and older treated for 6 months.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
1. Hypersensitivity to GnRH, GnRH agonist analogs or any of the excipients in SYNAREL;
2. Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding;
3. Use in pregnancy or in women who may become pregnant while receiving the drug. SYNAREL may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Major fetal abnormalities were observed in rats, but not in mice or rabbits after administration of SYNAREL during the period of organogenesis. There was a dose-related increase in fetal mortality and a decrease in fetal weight in rats [see Pregnancy]. The effects on rat fetal mortality are expected consequences of the alterations in hormonal levels brought about by the drug. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus;
4. Use in women who are breast-feeding [see Nursing Mothers]. -
WARNINGS
Safe use of nafarelin acetate in pregnancy has not been established clinically. Before starting treatment with SYNAREL, pregnancy must be excluded.
When used regularly at the recommended dose, SYNAREL usually inhibits ovulation and stops menstruation. Contraception is not insured, however, by taking SYNAREL, particularly if patients miss successive doses. Therefore, patients should use nonhormonal methods of contraception. Patients should be advised to see their physician if they believe they may be pregnant. If a patient becomes pregnant during treatment, the drug must be discontinued and the patient must be apprised of the potential risk to the fetus.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
As with other drugs that stimulate the release of gonadotropins or that induce ovulation, ovarian cysts have been reported to occur in the first two months of therapy with SYNAREL. Many, but not all, of these events occurred in patients with polycystic ovarian disease. These cystic enlargements may resolve spontaneously, generally by about four to six weeks of therapy, but in some cases may require discontinuation of drug and/or surgical intervention.
Information for Patients
An information pamphlet for patients is included with the product. Patients should be aware of the following information:
1. Since menstruation should stop with effective doses of SYNAREL, the patient should notify her physician if regular menstruation persists. The cause of vaginal spotting, bleeding or menstruation could be noncompliance with the treatment regimen, or it could be that a higher dose of the drug is required to achieve amenorrhea. The patient should be questioned regarding her compliance. If she is careful and compliant, and menstruation persists to the second month, consideration should be given to doubling the dose of SYNAREL. If the patient has missed several doses, she should be counseled on the importance of taking SYNAREL regularly as prescribed.
2. Patients should not use SYNAREL if they are pregnant, breastfeeding, have undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding, or are allergic to any of the ingredients in SYNAREL.
3. Safe use of the drug in pregnancy has not been established clinically. Therefore, a nonhormonal method of contraception should be used during treatment. Patients should be advised that if they miss successive doses of SYNAREL, breakthrough bleeding or ovulation may occur with the potential for conception. If a patient becomes pregnant during treatment, she should discontinue treatment and consult her physician.
4. Those adverse events occurring most frequently in clinical studies with SYNAREL are associated with hypoestrogenism; the most frequently reported are hot flashes, headaches, emotional lability, decreased libido, vaginal dryness, acne, myalgia, and reduction in breast size. Estrogen levels returned to normal after treatment was discontinued. Nasal irritation occurred in about 10% of all patients who used intranasal nafarelin.
5. The induced hypoestrogenic state results in a small loss in bone density over the course of treatment, some of which may not be reversible. During one six-month treatment period, this bone loss should not be important. In patients with major risk factors for decreased bone mineral content such as chronic alcohol and/or tobacco use, strong family history of osteoporosis, or chronic use of drugs that can reduce bone mass such as anticonvulsants or corticosteroids, therapy with SYNAREL may pose an additional risk. In these patients the risks and benefits must be weighed carefully before therapy with SYNAREL is instituted. Repeated courses of treatment with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs are not advisable in patients with major risk factors for loss of bone mineral content.
6. Patients with intercurrent rhinitis should consult their physician for the use of a topical nasal decongestant. If the use of a topical nasal decongestant is required during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing with SYNAREL.
Sneezing during or immediately after dosing with SYNAREL should be avoided, if possible, since this may impair drug absorption.
7. Retreatment cannot be recommended since safety data beyond 6 months are not available.
Drug Interactions
No pharmacokinetic-based drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with SYNAREL. However, because nafarelin acetate is a peptide that is primarily degraded by peptidase and not by cytochrome P-450 enzymes, and the drug is only about 80% bound to plasma proteins at 4°C, drug interactions would not be expected to occur.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Administration of SYNAREL in therapeutic doses results in suppression of the pituitary-gonadal system. Normal function is usually restored within 4 to 8 weeks after treatment is discontinued. Therefore, diagnostic tests of pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during treatment and up to 4 to 8 weeks after discontinuation of therapy with SYNAREL may be misleading.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies of nafarelin were conducted in rats (24 months) at doses up to 100 µg/kg/day and mice (18 months) at doses up to 500 µg/kg/day using intramuscular doses (up to 110 times and 560 times the maximum recommended human intranasal dose, respectively). These multiples of the human dose are based on the relative bioavailability of the drug by the two routes of administration. As seen with other GnRH agonists, nafarelin acetate given to laboratory rodents at high doses for prolonged periods induced proliferative responses (hyperplasia and/or neoplasia) of endocrine organs. At 24 months, there was an increase in the incidence of pituitary tumors (adenoma/carcinoma) in high-dose female rats and a dose-related increase in male rats. There was an increase in pancreatic islet cell adenomas in both sexes, and in benign testicular and ovarian tumors in the treated groups. There was a dose-related increase in benign adrenal medullary tumors in treated female rats. In mice, there was a dose-related increase in Harderian gland tumors in males and an increase in pituitary adenomas in high-dose females. No metastases of these tumors were observed. It is known that tumorigenicity in rodents is particularly sensitive to hormonal stimulation.
Mutagenicity studies were performed with nafarelin acetate using bacterial, yeast, and mammalian systems. These studies provided no evidence of mutagenic potential.
Reproduction studies in male and female rats have shown full reversibility of fertility suppression when drug treatment was discontinued after continuous administration for up to 6 months. The effect of treatment of prepubertal rats on the subsequent reproductive performance of mature animals has not been investigated.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
See Contraindications. Intramuscular SYNAREL was administered to rats during the period of organogenesis at 0.4, 1.6, and 6.4 µg/kg/day (about 0.5, 2, and 7 times the maximum recommended human intranasal dose based on the relative bioavailability by the two routes of administration). An increase in major fetal abnormalities was observed in 4/80 fetuses at the highest dose. A similar, repeat study at the same doses in rats and studies in mice and rabbits at doses up to 600 µg/kg/day and 0.18 µg/kg/day, respectively, failed to demonstrate an increase in fetal abnormalities after administration during the period of organogenesis. In rats and rabbits, there was a dose-related increase in fetal mortality and a decrease in fetal weight with the highest dose.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Clinical Studies
In formal clinical trials of 1509 healthy adult patients, symptoms suggestive of drug sensitivity, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, urticaria, rash and pruritus occurred in 3 patients (approximately 0.2%).
As would be expected with a drug which lowers serum estradiol levels, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were those related to hypoestrogenism.
In controlled studies comparing SYNAREL (400 µg/day) and danazol (600 or 800 mg/day), adverse reactions most frequently reported and thought to be drug-related are shown in the figure below:
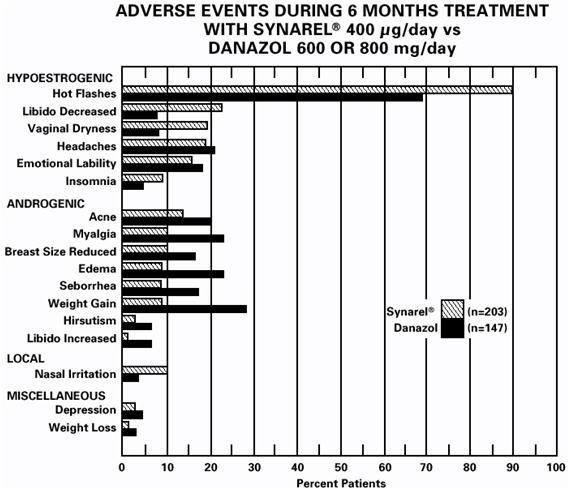
In addition, less than 1% of patients experienced paresthesia, palpitations, chloasma, maculopapular rash, eye pain, asthenia, lactation, breast engorgement, and arthralgia.
Changes in Bone Density
After six months of treatment with SYNAREL, vertebral trabecular bone density and total vertebral bone mass, measured by quantitative computed tomography (QCT), decreased by an average of 8.7% and 4.3%, respectively, compared to pretreatment levels. There was partial recovery of bone density in the post-treatment period; the average trabecular bone density and total bone mass were 4.9% and 3.3% less than the pretreatment levels, respectively. Total vertebral bone mass, measured by dual photon absorptiometry (DPA), decreased by a mean of 5.9% at the end of treatment.
After six months treatment with SYNAREL, bone mass as measured by dual x-ray bone densitometry (DEXA), decreased 3.2%. Mean total vertebral mass, re-examined by DEXA six months after completion of treatment, was 1.4% below pretreatment. There was little, if any, decrease in the mineral content in compact bone of the distal radius and second metacarpal. Use of SYNAREL for longer than the recommended six months or in the presence of other known risk factors for decreased bone mineral content may cause additional bone loss.
Changes in Laboratory Values During Treatment
Plasma enzymes
During clinical trials with SYNAREL, regular laboratory monitoring revealed that SGOT and SGPT levels were more than twice the upper limit of normal in only one patient each. There was no other clinical or laboratory evidence of abnormal liver function and levels returned to normal in both patients after treatment was stopped.
Lipids
At enrollment, 9% of the patients in the group taking SYNAREL 400 µg/day and 2% of the patients in the danazol group had total cholesterol values above 250 mg/dL. These patients also had cholesterol values above 250 mg/dL at the end of treatment.
Of those patients whose pretreatment cholesterol values were below 250 mg/dL, 6% in the group treated with SYNAREL and 18% in the danazol group, had post-treatment values above 250 mg/dL.
The mean (± SEM) pretreatment values for total cholesterol from all patients were 191.8 (4.3) mg/dL in the group treated with SYNAREL and 193.1 (4.6) mg/dL in the danazol group. At the end of treatment, the mean values for total cholesterol from all patients were 204.5 (4.8) mg/dL in the group treated with SYNAREL and 207.7 (5.1) mg/dL in the danazol group. These increases from the pretreatment values were statistically significant (p<0.05) in both groups.
Triglycerides were increased above the upper limit of 150 mg/dL in 12% of the patients who received SYNAREL and in 7% of the patients who received danazol.
At the end of treatment, no patients receiving SYNAREL had abnormally low HDL cholesterol fractions (less than 30 mg/dL) compared with 43% of patients receiving danazol. None of the patients receiving SYNAREL had abnormally high LDL cholesterol fractions (greater than 190 mg/dL) compared with 15% of those receiving danazol. There was no increase in the LDL/HDL ratio in patients receiving SYNAREL, but there was approximately a 2-fold increase in the LDL/HDL ratio in patients receiving danazol.
Other changes
In comparative studies, the following changes were seen in approximately 10% to 15% of patients. Treatment with SYNAREL was associated with elevations of plasma phosphorus and eosinophil counts, and decreases in serum calcium and WBC counts. Danazol therapy was associated with an increase of hematocrit and WBC.
Post-Marketing
Pituitary apoplexy: During post-marketing surveillance, rare cases of pituitary apoplexy (a clinical syndrome secondary to infarction of the pituitary gland) have been reported after the administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. In a majority of these cases, a pituitary adenoma was diagnosed, with a majority of pituitary apoplexy cases occurring within 2 weeks of the first dose, and some within the first hour. In these cases, pituitary apoplexy has presented as sudden headache, vomiting, visual changes, ophthalmoplegia, altered mental status, and sometimes cardiovascular collapse. Immediate medical attention has been required.
Cardiovascular adverse events: Cases of serious venous and arterial thromboembolism have been reported, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, and transient ischemic attack. Although a temporal relationship was reported in some cases, most cases were confounded by risk factors or concomitant medication use. It is unknown if there is a causal association between the use of GnRH analogs and these events.
-
OVERDOSAGE
In experimental animals, a single subcutaneous administration of up to 60 times the recommended human dose (on a µg/kg basis, not adjusted for bioavailability) had no adverse effects. At present, there is no clinical evidence of adverse effects following overdosage of GnRH analogs.
Based on studies in monkeys, SYNAREL is not absorbed after oral administration.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For the management of endometriosis, the recommended daily dose of SYNAREL is 400 µg. This is achieved by one spray (200 µg) into one nostril in the morning and one spray into the other nostril in the evening. Treatment should be started between days 2 and 4 of the menstrual cycle.
In an occasional patient, the 400 µg daily dose may not produce amenorrhea. For these patients with persistent regular menstruation after 2 months of treatment, the dose of SYNAREL may be increased to 800 µg daily. The 800 µg dose is administered as one spray into each nostril in the morning (a total of two sprays) and again in the evening.
The recommended duration of administration is six months. Retreatment cannot be recommended since safety data for retreatment are not available. If the symptoms of endometriosis recur after a course of therapy, and further treatment with SYNAREL is contemplated, it is recommended that bone density be assessed before retreatment begins to ensure that values are within normal limits.
There appeared to be no significant effect of rhinitis, i.e., nasal congestion, on the systemic bioavailability of SYNAREL; however, if the use of a nasal decongestant for rhinitis is necessary during treatment with SYNAREL, the decongestant should not be used until at least 2 hours following dosing with SYNAREL.
Sneezing during or immediately after dosing with SYNAREL should be avoided, if possible, since this may impair drug absorption.
At 400 µg/day, a bottle of SYNAREL provides a 30-day (about 60 sprays) supply. If the daily dose is increased, increase the supply to the patient to ensure uninterrupted treatment for the recommended duration of therapy.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Each 0.5 ounce bottle (NDC: 0025-0166-08) contains 8 mL SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate) Nasal Solution 2 mg/mL (as nafarelin base), and is supplied with a metered spray pump that delivers 200 µg of nafarelin per spray. A dust cover and a leaflet of patient instructions are also included.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
SYNAREL
nafarelin acetate
Nasal SprayPatient Instructions for Use
Introduction
Your doctor has prescribed SYNAREL Nasal Solution to treat your symptoms of endometriosis. This pamphlet has two purposes:
- 1.) to review information your doctor has given you about SYNAREL; and
- 2.) to give you information about how to use SYNAREL properly.
Please read this pamphlet carefully. If you still have questions after reading it or if you have questions at any time during your treatment with SYNAREL, be sure to check with your doctor.
SYNAREL is used to relieve the symptoms of endometriosis. The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium, and part of it is shed during menses. In endometriosis, endometrial tissue is also found outside the uterus and, like normal endometrial tissue, can bleed during a menstrual cycle. It is, in part, this monthly activity that causes you to have symptoms during your cycle. Most often, this out-of-place endometrial tissue is found around the uterus, ovaries, the intestine or other organs in the pelvis. Although some women with endometriosis have no symptoms, many have problems such as severe menstrual cramps, pain during sexual intercourse, low back pain, and painful bowel movements.
Endometrial tissue is affected by the body's hormones, especially estrogen, which is made by the ovaries. When estrogen levels are low, endometrial tissue shrinks (perhaps even disappears), and symptoms of endometriosis ease. SYNAREL temporarily reduces estrogen in the body and temporarily relieves the symptoms of endometriosis.
Important Information about SYNAREL
- You should not use SYNAREL if
- you are pregnant.
- you are breast feeding.
- you have abnormal vaginal bleeding that has not been checked into by your doctor.
- you are allergic to any of the ingredients of SYNAREL (nafarelin acetate, benzalkonium chloride, acetic acid, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, sorbitol, purified water).
- SYNAREL is a prescription medicine that should be used according to your doctor's directions. SYNAREL comes as a special nasal spray that gives a measured amount of medicine. To be effective, SYNAREL must be used every day, twice a day, for the whole treatment period.
- It is important to use a non-hormonal method of contraception (such as diaphragm with contraceptive jelly, IUD, condoms) while taking SYNAREL. You should not use birth control pills while taking SYNAREL.
- If you miss 1 or more doses of SYNAREL, vaginal bleeding (often called breakthrough bleeding) may occur. If you miss successive doses of SYNAREL and have not been using contraception as described above, release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) may occur, with the possibility of pregnancy. Under these circumstances you must see your physician to make sure you are not pregnant. If you should become pregnant while using SYNAREL, you must discuss the possible risks to the fetus and the choices available to you with your physician.
- Because SYNAREL works by temporarily reducing the body's production of estrogen, a female hormone produced by the ovary, you may have some of the same changes that normally occur at the time of menopause, when the body's production of estrogen naturally decreases. For the first two months after you start using SYNAREL, you may experience some irregular vaginal spotting or bleeding. The duration and intensity of this bleeding may vary; it may be similar to your usual menstruation, or it may be lighter or heavier. The duration may also vary from brief to prolonged. In any case, you can expect this bleeding to stop by itself. After the first two months of treatment with SYNAREL, you can expect a decrease in menstrual flow, and your periods may stop altogether. However, if you miss one or more doses of SYNAREL, you may continue to experience vaginal bleeding. If you continue to experience normal menstrual cycles after two months use of SYNAREL, you should see your doctor about the continued periods. Other changes due to decreased estrogen include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, headaches, mood changes, and decreased interest in sex. Most of these changes are caused by low estrogen levels and may occur during treatment with SYNAREL. Some patients may also experience acne, muscle pain, reduced breast size, and irritation of the tissues inside the nose. These symptoms should disappear after you stop taking the drug.
- When you take SYNAREL, your estrogen levels will be low. Low estrogen levels can result in a small loss of mineral from bone, some of which may not be reversible. During one six-month treatment period, this small loss of mineral from bone should not be important.
There are certain conditions that may increase the possibility of the thinning of your bones when you take a drug such as SYNAREL. They are:- excessive use of alcohol;
- smoking;
- family history of osteoporosis (thinning of the bones with fractures);
- taking other medications that can cause thinning of the bones.
- During studies, menstruation usually resumed within 2 to 3 months of stopping treatment with SYNAREL. At the end of treatment 60% of patients treated with SYNAREL were symptom free, 32% had mild symptoms, 7% had moderate symptoms and 1% had severe symptoms.
Of the 60% of patients who had complete relief of symptoms at the end of treatment, 17% had moderate symptoms at the end of the six month post-treatment period; 33% had mild symptoms; 50% were symptom free; no patient had severe symptoms. - Retreatment cannot be recommended since the safety of such retreatment is not known.
- It is all right to use a nasal decongestant spray while you are being treated with SYNAREL if you follow these simple rules. Use SYNAREL first. Wait at least 2 hours after using SYNAREL before you use the decongestant spray.
- You should avoid sneezing during or immediately after using SYNAREL, if possible, since sneezing may impair drug absorption.
Proper use of SYNAREL for Treatment of Endometriosis
- When you start to use SYNAREL, the first dose should be taken between the second and fourth day after the beginning of your menstrual bleeding. You should continue taking SYNAREL every day as prescribed.
Do not miss a single dose. - Unless your doctor has given you special instructions, follow the steps for using SYNAREL twice each day, about 12 hours between doses:
- once in the morning in one nostril (for example, 7 a.m.)
- once in the evening in the other nostril (for example, 7 p.m.)
- Because it is so important that you do not miss a single dose of SYNAREL, here are some suggestions to help you remember:
- Keep your SYNAREL in a place where you will be reminded to use it each morning and each evening — next to your toothbrush is one possibility.
- Keep track of each dose on a calendar.
- Make a note on your calendar on the day you start a new bottle of SYNAREL. You can also mark the date you started right on the bottle. Be sure to refill your prescription before the 30 days are up so you will have a new bottle on hand.
- A bottle of SYNAREL should not be used for longer than 30 days (60 sprays). Each bottle contains sufficient quantity of nasal solution for initial priming of the pump and 30 days (60 sprays) of treatment. At the end of 30 days, a small amount of liquid will be left in the bottle. Do not try to use up that leftover amount because you might get too low a dose, which could interfere with the effectiveness of your treatment. Dispose of the bottle and do not reuse.
- If your doctor increases your daily dose of SYNAREL, then your bottle will not last the standard 30 days. Please discuss this with your doctor to be sure that you have an adequate supply for uninterrupted treatment with SYNAREL to complete the recommended treatment period.
Preparation of the SYNAREL Nasal Spray unit
For use in your nose only.
Before you use SYNAREL nasal spray for the first time, you will need to prime it. This will ensure that you get the right dose of medicine each time you use it.
Important Tips about using SYNAREL
- Your pump should produce a fine mist, which can only happen by a quick and firm pumping action. It is normal to see some larger droplets of liquid within the fine mist. However, if SYNAREL comes out of the pump as a thin stream of liquid instead of a fine mist, SYNAREL may not work as well, and you should talk to your pharmacist.
- Be sure to clean the Spray Tip before and after every use. (See Step 4). Failure to do this may result in a clogged tip that may cause you not to get the right amount of medicine that is prescribed for you.
- The pump is made to deliver only a set amount of medicine, no matter how hard you pump it.
- Do Not try to make the tiny hole in the spray tip larger. If the hole is made larger the pump will deliver a wrong dose of SYNAREL.
Figure A 
To Prime the Pump:
Figure B
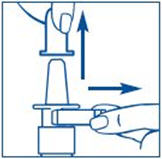
- 1. Remove and save the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover from the spray bottle (See Figure B).
Figure C
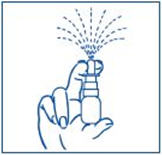
- 2. Hold the bottle in an upright position away from you. Put two fingers on the "shoulders" of the spray bottle and put your thumb on the bottom of the bottle. Apply pressure evenly to the "shoulders" and push down quickly and firmly 7 to 10 times, until you see a fine spray. Usually you will see the spray after about 7 pumps. (See Figure C).
- 3. The pump is now primed. Priming only needs to be done 1 time, when you start using a new bottle of SYNAREL. You will waste your medicine if you prime the pump every time you use it and may not have enough medicine for 30 days of treatment.
Figure D
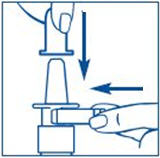
- 4.
Clean the Spray Tip after Priming:
- Hold the bottle in a horizontal position. Rinse the spray tip with warm water while wiping the tip with your finger or soft cloth for 15 seconds.
- Wipe the spray tip with a soft cloth or tissue to dry.
- Replace the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover on the spray bottle (See Figure D).
- Do Not try to clean the spray tip using a pointed object. Do Not take apart the pump.
How to use the SYNAREL Nasal Spray unit for the treatment of Endometriosis
Figure E
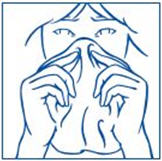
- 5. Gently blow your nose to clear both nostrils before you use SYNAREL nasal spray (See Figure E).
Figure F
- 6.
Clean the Spray Tip. Remove and save the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover from the spray bottle (See Figure F).
- Hold the bottle in a horizontal position. Rinse the spray tip with warm water while wiping the tip with your finger or soft cloth for 15 seconds.
- Wipe the spray tip with a soft cloth or tissue to dry.
- Do Not try to clean the spray tip using a pointed object.
- Do Not try to take apart the pump.
- 7. Bend your head forward and put the spray tip into one nostril. The tip should not reach too far into your nose. Aim the spray tip toward the back and outer side of your nose (See Figure G).
Figure H
- 8. Close the other nostril with your finger (See Figure H).
- 9. Apply pressure evenly to the "shoulders" and push down quickly and firmly. Pump the sprayer 1 time, at the same time as you sniff in gently. If the sprayer fails to deliver the dose clean the spray tip (See Step 6 Clean the Spray Tip).
Figure I
- 10.
Remove the spray tip from your nose and tilt your head backwards for a few seconds. This lets the SYNAREL spray spread over the back of your nose (See Figure I).
Do not spray in your other nostril unless your doctor has instructed you to do so.
Figure J
- 11. Clean the Spray Tip after use (See Step 4).
It is important that you clean the spray tip before and after every use. Failure to do this may result in a clogged tip that may cause you to get the wrong dose of medicine.
Important Reminder: Treatment with SYNAREL must be uninterrupted with no missed doses to be effective.
Make sure you use SYNAREL exactly as your doctor tells you. Make sure to note the date you start each bottle so you do not run out of medicine and miss doses.
Keep out of the reach of children and use carefully as directed.Storage Instructions: - Store SYNAREL at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Store the SYNAREL bottle upright.
- Keep SYNAREL out of the light.
- Do not freeze SYNAREL.
This product's label may have been updated. For current full prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.

LAB-0278-6.0
Revised: May 2017 -
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
SYNAREL (sin-na-rell)
(nafarelin acetate) nasal solutionWhat is the most important information I should know about SYNAREL?
- Some people taking GnRH agonists like SYNAREL have had new or worsened mental (psychiatric) problems. Mental (psychiatric) problems may include emotional symptoms such as:
- crying
- irritability
- restlessness (impatience)
- anger
- acting aggressive
- Some people taking GnRH agonists like SYNAREL have had seizures. The risk of seizures may be higher in people who:
- have a history of seizures.
- have a history of epilepsy.
- have a history of brain or brain vessel (cerebrovascular) problems or tumors.
- are taking a medicine that has been connected to seizures such as taking bupropion or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Call your child's doctor right away if your child has a seizure while taking SYNAREL.What is SYNAREL?
SYNAREL is a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) medicine used for the treatment of children with central precocious puberty (CPP).Do not give SYNAREL if your child: - is allergic to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), GnRH agonist medicines, or any of the ingredients in SYNAREL. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in SYNAREL.
- has unusual vaginal bleeding that has not been checked by her doctor.
- is pregnant or may become pregnant. SYNAREL can cause birth defects or loss of the baby. If your child becomes pregnant call your doctor.
- is breastfeeding or plans to breastfeed. It is not known if SYNAREL passes into breast milk. You and your child's doctor should decide if your child will take SYNAREL or breastfeed. Do not breastfeed while taking SYNAREL.
Before your child takes SYNAREL, tell your doctor about all of your child's medical conditions, including if they: - have a history of mental (psychiatric) problems.
- have or have had a history of seizures.
- have a history of epilepsy.
- have a history of brain or brain vessel (cerebrovascular) problems or tumors
- are taking a medicine that has been connected to seizures such as bupropion or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
How should your child take SYNAREL? - Your child's doctor should do tests to make sure your child has CPP before treating your child with SYNAREL.
- Keep all scheduled visits to the doctor. If scheduled doses are missed, your child may start having signs of puberty again. The doctor will do regular exams and blood tests to check for signs of puberty.
- Take SYNAREL exactly as your doctor tells you to take it. See detailed "Instructions for Use" at the end of this Medication Guide for information about the right way to use SYNAREL.
- Your child's doctor will tell you how much SYNAREL your child is to take and when to take it. If your doctor increases your child's daily dose of SYNAREL, 1 bottle will not last the standard 7 days. Talk with your child's doctor to make sure your child has enough SYNAREL to take their prescribed dose every day.
What should your child avoid while taking SYNAREL? - Your child should avoid sneezing while taking SYNAREL or right after using it, if possible. This could reduce the amount of medicine your child's body absorbs.
- If your child needs to use a nasal decongestant spray while being treated with SYNAREL, they should not use the decongestant spray for at least 2 hours after taking the dose of SYNAREL.
What are the possible side effects of SYNAREL?
SYNAREL may cause serious side effects, including:- See "What is the most important information I should know about SYNAREL"
- in the first month of treatment, SYNAREL can cause an increase in some hormones. During this time you may notice more signs of puberty in your child, including vaginal bleeding and breast enlargement in girls. Within 1 month of treatment, you should see signs in your child that puberty is stopping.
- allergic reactions such as shortness of breath, chest pain, hives, rash, and itching
- acne
- temporary increase in pubic hair
- body odor
- flaky, scaly skin
- hot flashes
- stuffy or runny nose (rhinitis)
- white or brown vaginal discharge
General Information about the safe and effective use of SYNAREL.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SYNAREL for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give SYNAREL to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about SYNAREL that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in SYNAREL?
Active ingredient: nafarelin acetate
Inactive ingredients: benzalkonium chloride, glacial acetic acid, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), sorbitol, and purified water - Some people taking GnRH agonists like SYNAREL have had new or worsened mental (psychiatric) problems. Mental (psychiatric) problems may include emotional symptoms such as:
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Instructions for Use
SYNAREL(sin-na-rell)
(nafarelin acetate)
nasal solutionFor use in the nose only.
Figure A 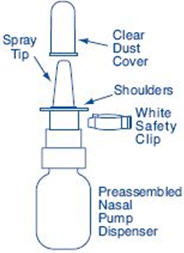
Before you use SYNAREL nasal spray for the first time, you will need to prime it. This will make sure that you get the right dose of medicine each time you use it. Priming only needs to be done 1 time, when you start using a new bottle of SYNAREL.
To Prime the Pump:
Figure B
- 1. Remove and save the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover from the spray bottle (See Figure B).
Figure C
- 2.
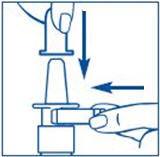
Hold the bottle in an upright position away from you. Put 2 fingers on the "shoulders" of the spray bottle and put your thumb on the bottom of the bottle. Apply pressure evenly to the "shoulders" and push down quickly and firmly 7 to 10 times, until you see a fine mist spray. Usually you will see the spray after about 7 pumps. (See Figure C). The pump is now primed.
It is normal to see some larger droplets of liquid within the fine mist. However, if SYNAREL comes out of the pump as a thin stream of liquid instead of a fine mist, SYNAREL may not work as well, and you should talk to your pharmacist.
Figure D
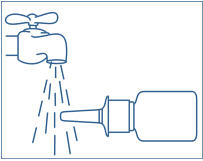
Figure E
- 3.
Clean the Spray Tip after Priming:
- Hold the bottle in sideways (horizontal) position (see Figure D).
Rinse the "spray tip" with warm water while wiping the tip with your finger or soft cloth for 15 seconds. - Wipe the spray tip with a soft cloth or tissue to dry.
- Replace the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover on the spray bottle. (See Figure E).
- Do not try to clean the spray tip using a pointed object.
- Do not take apart the pump.
- Hold the bottle in sideways (horizontal) position (see Figure D).
How to use the SYNAREL Nasal Spray for the treatment of Central Precocious Puberty
Figure F
- 4. Have your child blow their nose to clear both nostrils before using SYNAREL nasal spray (see Figure F). If the child is too young to blow their nose, you may need to clear the child's nostrils with a bulb syringe.
Figure G
- 5.
Clean the Spray Tip each time before and after using SYNAREL.
- Remove and save the white safety clip and the clear plastic dust cover from the spray bottle (See Figure G).
- Hold the bottle in sideways (horizontal) position. Rinse the spray tip with warm water while wiping the tip with your finger or soft cloth for 15 seconds.
- Wipe the spray tip with a soft cloth or tissue to dry.
- Do not try to clean the spray tip using a pointed object.
- Do not try to take apart the pump.
Figure H
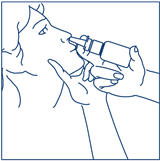
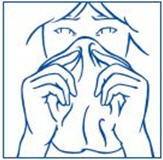
- 6. The child's head should be bent back a little and the spray tip put into one nostril. The tip should not reach too far into the nose. Aim the spray tip toward the back and outer side of the nose (See Figure H).
Figure I
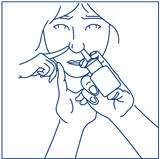
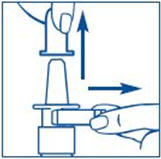
- 7. Close the other nostril with a finger (See Figure I).
Figure J
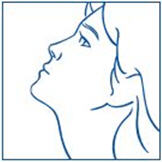
- 8. Remove the spray tip from the child's nose after all sprays are completed. Keep the child's head tilted back for a few seconds. This lets the SYNAREL spray spread over the back of the nose (See Figure J).
Figure K
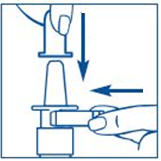
It is important that you clean the spray tip before and after every use. Not doing this may result in a clogged tip that may cause you to get the wrong dose of medicine.
How should I store SYNAREL?
- Store SYNAREL at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Store the SYNAREL bottle upright.
- Keep SYNAREL out of the light.
Keep SYNAREL and all medicines out of the reach of children.
For more information call 1-800-438-1985.
This Medication Guide and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for: Pfizer Inc., 235 East 42nd Street, New York, NY, 10017

LAB-1049-1.0
Revised: May 2017 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8 mL Bottle Label
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
NDC: 0025-0166-08Synarel®
(nafarelin acetate) nasal solution2 mg/mL (as nafarelin base)
SPRAY - FOR INTRANASAL USE ONLY.
Each actuation delivers approximately 200 mcg nafarelin.8 mL (60 metered sprays)
Rx only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 8 mL Bottle Carton
ALWAYS DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
Pfizer
NDC: 0025-0166-08Synarel®
(nafarelin acetate) nasal solution2 mg/mL (as nafarelin base)
SPRAY – FOR INTRANASAL USE ONLY
Each actuation delivers approximately
200 mcg nafarelin.Carton contains: 1 bottle of nasal solution with
spray pump, patient information and complete
prescribing information.Store upright.
8 mL (60 metered sprays)
Rx only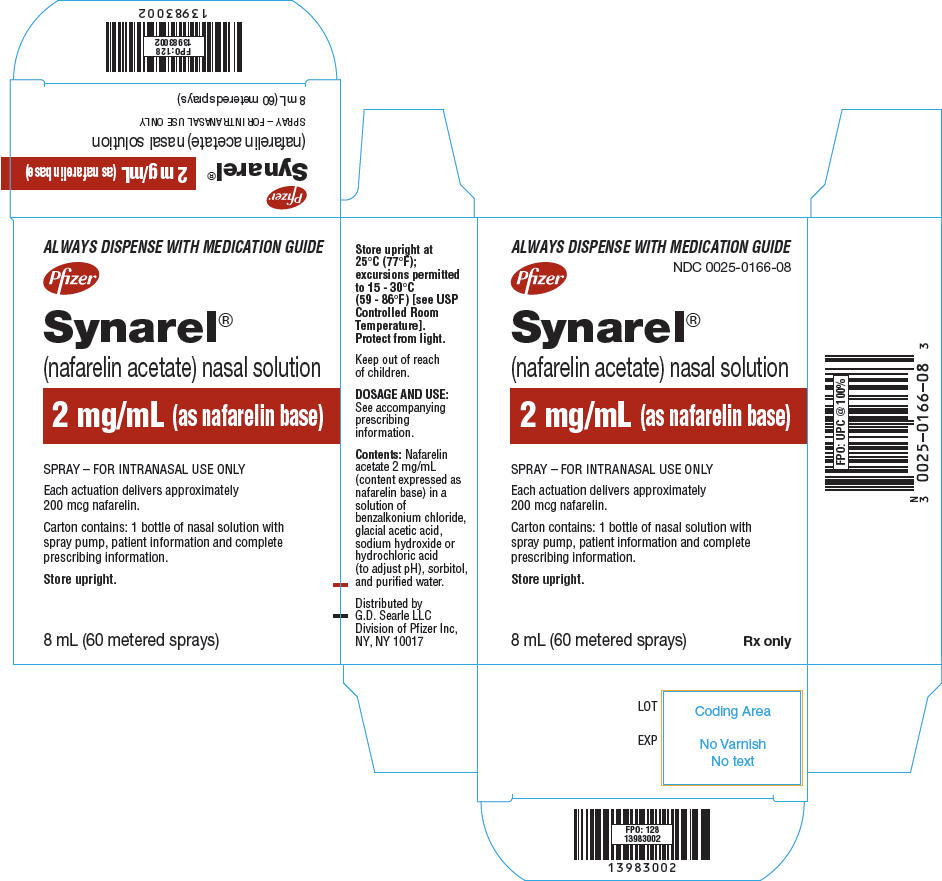
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SYNAREL
nafarelin acetate spray, meteredProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0025-0166 Route of Administration NASAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NAFARELIN ACETATE (UNII: 8ENZ0QJW4H) (NAFARELIN - UNII:1X0094V6JV) NAFARELIN 2 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0025-0166-08 1 in 1 CARTON 02/13/1990 1 8 mL in 1 BOTTLE, SPRAY; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA019886 02/13/1990 Labeler - G.D. Searle LLC Division of Pfizer Inc (829077085) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Pharmacia and Upjohn Company LLC 618054084 ANALYSIS(0025-0166) , LABEL(0025-0166) , MANUFACTURE(0025-0166) , PACK(0025-0166)
Trademark Results [Synarel]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 SYNAREL 75228431 2172477 Dead/Cancelled |
G. D. Searle & Co. 1997-01-21 |
 SYNAREL 73699567 1495608 Live/Registered |
SYNTEX (U.S.A.) INC. 1987-12-07 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

