FINACEA FOAM- azelaic acid aerosol, foam
FINACEA FOAM by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
FINACEA FOAM by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., ASM Aerosol-Service AG. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FINACEA FOAM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FINACEA FOAM.
FINACEA® (azelaic acid) Foam, 15% for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Finacea Foam is indicated for the topical treatment of inflammatory papules and pustules of mild to moderate rosacea. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Foam, 15% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Isolated cases of hypopigmentation occurred after azelaic acid use. (5.1)
- Azelaic acid has been reported to cause irritation of the eyes. Therefore, avoid contact with the eyes and mucous membranes. (5.2)
- Contents are flammable. Instruct the patient to avoid fire, flame, and smoking during and immediately following application. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In clinical studies, the most frequently observed adverse reactions in ≥ 0.5% of subjects treated with Finacea Foam included local site pain (6.2%), pruritus (2.5%), dryness (0.7%), and erythema (0.7%). (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare at 1-866-463-3634 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Skin Reactions
5.2 Eye and Mucous Membranes Irritation
5.3 Flammability
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Apply Finacea Foam twice daily (morning and evening) to the entire facial area (cheeks, chin, forehead, and nose). For a single application, dispense the smallest amount of foam necessary to adequately cover the affected area(s) with a thin layer.
- Shake well before use.
- Cosmetics may be applied after the application of Finacea Foam has dried.
- Avoid the use of occlusive dressings or wrappings.
- Finacea Foam should be used continuously over 12 weeks.
- Reassess patients if no improvement is observed upon completing 12 weeks of therapy.
- Not for oral, ophthalmic or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Skin Reactions
There have been isolated reports of hypopigmentation after use of azelaic acid. Because azelaic acid has not been well studied in patients with dark complexion, monitor these patients for early signs of hypopigmentation.
5.2 Eye and Mucous Membranes Irritation
Azelaic acid has been reported to cause irritation of the eyes. Avoid contact with the eyes, mouth and other mucous membranes. If Finacea Foam does come in contact with the eyes, wash the eyes with large amounts of water and consult a physician if eye irritation persists.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Hypopigmentation [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Eye and Mucous Membranes Irritation [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Finacea Foam was evaluated for the treatment of papulopustular rosacea in two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 12-week clinical trials involving a total of 1362 (Finacea Foam, 15%: 681; vehicle: 681) subjects. Overall, 95.7% of subjects were White, 73.4% were female, and the mean age was 50.6 years.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 0.5% of Subjects Treated with Finacea Foam Compared with Subjects Treated with Vehicle
System/Organ Class
PreferredFinacea Foam, 15%
(N=681)
n (%)
Vehicle
(N=681)
n (%)
General disorders and application site conditions
Application site pain*
42 (6.2%)
10 (1.5%)
Application site pruritus
17 (2.5%)
2 (0.3%)
Application site dryness
5 (0.7%)
5 (0.7%)
Application site erythema
5 (0.7%)
6 (0.9%)
- * “Application site pain” is a term used to describe disagreeable skin sensations, including burning, stinging, paraesthesia and tenderness.
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
Hypersensitivity, rash and worsening of asthma have been reported from the postmarketing experience of azelaic acid-containing formulations. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Therefore, Finacea Foam should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Dermal embryofetal developmental toxicology studies have not been performed with azelaic acid, 15% foam. Oral embryofetal developmental studies were conducted with azelaic acid in rats, rabbits, and cynomolgus monkeys. Azelaic acid was administered during the period of organogenesis in all three animal species. Embryotoxicity was observed in rats, rabbits, and monkeys at oral doses of azelaic acid that generated some maternal toxicity. Embryotoxicity was observed in rats given 2500 mg/kg/day [162 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area (BSA)], rabbits given 150 or 500 mg/kg/day (19 or 65 times the MRHD based on BSA) and cynomolgus monkeys given 500 mg/kg/day (65 times the MRHD based on BSA) azelaic acid. No teratogenic effects were observed in the oral embryofetal developmental studies conducted in rats, rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys.
An oral peri- and post-natal developmental study was conducted in rats. Azelaic acid was administered from gestational day 15 through day 21 postpartum up to a dose level of 2500 mg/kg/day. Embryotoxicity was observed in rats at an oral dose of 2500 mg/kg/day (162 times the MRHD based on BSA) that generated some maternal toxicity. In addition, slight disturbances in the post-natal development of fetuses was noted in rats at oral doses that generated some maternal toxicity (500 and 2500 mg/kg/day; 32 and 162 times the MRHD based on BSA). No effects on sexual maturation of the fetuses were noted in this study.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known if azelaic acid is secreted into human milk in vivo. No well-controlled studies of topically administered azelaic acid in nursing women are available. Nevertheless, the decision to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug should take into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of FinaceaFoam in children below the age of 18 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of FinaceaFoam, 18.8 percent were 65 and over, while 7.2 percent were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Finacea (azelaic acid) Foam contains 15% (w/w) azelaic acid, a naturally-occurring saturated dicarboxylic acid and is suspended in an oil-in-water emulsion vehicle for topical administration to affected skin area. Chemically, azelaic acid is 1,7-heptanedicarboxylic acid. The structural formula of azelaic acid is:
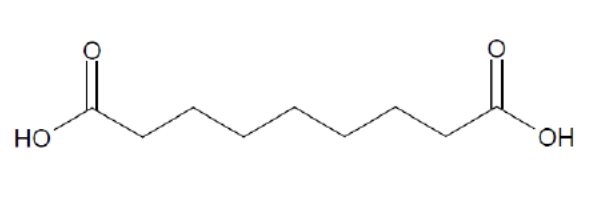
Azelaic acid has a molecular formula of C9 H16 O4 and a molecular weight of 188.22.
The aluminum containers are filled with hydrophilic emulsion, crimped with a continuous spray valve, and pressurized with propellants consisting of propane, butane, and isobutane. Each gram of Finacea Foam contains 0.15 g of azelaic acid. Finacea Foam also contains benzoic acid, cetostearyl alcohol, dimethyl isosorbide, medium-chain triglycerides, methylcellulose, mono- and di-glycerides, polyoxyl 40 stearate, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, purified water, sodium hydroxide, and xanthan gum as inactive ingredients.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism(s) by which azelaic acid interferes with the pathogenic events in rosacea are unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The efficacy of Finacea Foam is being driven by local mechanisms of azelaic acid within the skin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of azelaic acid and its metabolite pimelic acid was assessed in 21 adult subjects with moderate papulopustular rosacea with a minimum of 15 and no more than 50 inflammatory lesions (papules and/or pustules). Endogenous plasma concentrations of azelaic acid (range <1-105 ng/mL) and pimelic acid (range 0.69-27 ng/mL) were measured over various time points over 2 days prior to treatment initiation. The endogenous plasma concentrations varied widely across subjects and the mean ± SD values of endogenous azelaic acid plasma concentrations ranged between 4.5 ± 2.4 ng/mL and 14.6 ± 5.6 ng/mL and pimelic acid plasma concentrations ranged between 2.2 ± 1.1 ng/mL and 3.7 ± 3.1 ng/mL.
Following topical dermal applications of a mean dose of 0.94 g of Finacea Foam (141 mg azelaic acid) twice daily for 7 consecutive days, systemic concentrations of azelaic acid were at steady state by Day 5. On Day 7, a wide range of maximum azelaic acid (22.2 to 90.1 ng/mL) and pimelic acid (2.3-16.9 ng/mL) plasma concentrations (Cmax) was also observed after treatment with Finacea Foam. The mean ± SD Cmax for azelaic acid and pimelic acid were 51.8 ± 18.5 ng/mL and 5.0 ± 3.0 ng/mL, respectively. The mean ± SD systemic exposure of azelaic acid and pimelic acid within a dosing interval (AUC0-12h) were 442.0 ± 177.6 ng.h/mL and 43.4 ± 15.4 ng.h/mL, respectively.
Azelaic acid is mainly excreted unchanged in the urine, but undergoes some ß-oxidation to shorter chain dicarboxylic acids.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Systemic long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of azelaic acid. In a 26-week dermal carcinogenicity study using transgenic (Tg.AC) mice, Finacea Gel and the gel vehicle, when applied once or twice daily, did not increase the number of female Tg.AC animals with papillomas at the treatment site. No statistically significant increase in the number of animals with papillomas at the treatment site was observed in male Tg.AC animals after once daily application. After twice daily application, Finacea Gel and the gel vehicle induced a statistically significant increase in the number of male animals with papillomas at the treatment site when compared to untreated males. This suggests that the positive effect may be associated with the vehicle application. The clinical relevance of the findings in animals to humans is not clear.
Azelaic acid was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a battery of in vitro [Ames assay, HGPRT assay in V79 cells (Chinese hamster lung cells), and chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes] and in vivo (dominant lethal assay in mice and mouse micronucleus assay) genotoxicity tests.
Oral administration of azelaic acid at dose levels up to 2500 mg/kg/day (162 times the MRHD based on BSA) did not affect fertility or reproductive performance in male or female rats.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of Finacea Foam was evaluated in two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, 12-week clinical trials (Trials 1 and 2) in subjects with papulopustular rosacea, with a mean lesion count of 21.3 (range 12 to 50) inflammatory papules and pustules. A total of 1362 (active: 681; vehicle: 681) subjects aged 19 to 92 years (mean age = 50.6 years), 95.7% Caucasian, and 73.4% female participated in the trials. The following subjects were excluded: a) those with ocular rosacea, phymatous rosacea or plaque-type rosacea lesions; b) those with rosacea that requires systemic treatment; c) those who are known non-responders to azelaic acid, and d) those with a known hypersensitivity to any ingredients of the study drug. Finacea Foam or its vehicle were to be applied twice daily for 12 weeks; no other topical or systemic medication affecting the course of rosacea and/or evaluability was to be used during the studies. Subjects were instructed to avoid any food and beverages that, by their own experience, may provoke erythema, flushing and blushing, including spicy food, hot drinks and alcoholic beverages during the study. Subjects were also instructed to avoid use of products which may cause local irritation such as soaps, alcohol-containing cleansers, tinctures and astringents, abrasives and peeling agents during the study.
The efficacy endpoints were 1) nominal change in inflammatory lesion count from baseline and 2) success defined as a score of “clear” or “minimal” with at least 2-step reduction from baseline on a 5-point Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA). Details on IGA are specified below:
Clear
no papules and/or pustules; no erythema
Minimal
rare papules and/or pustules; faint, up to but not including mild erythema
Mild
few papules and/or pustules; mild erythema
Moderate
pronounced number of papules and/or pustules, but less than numerous papules and/or pustules; moderate erythema
Severe
numerous papules and/or pustules, occasionally with confluent areas of inflamed lesions; moderate to severe erythema
Finacea Foam was superior to its vehicle in the treatment of rosacea in reducing the number of inflammatory papules and pustules and demonstrating success according to IGA at the end of treatment (Table 2).
Table 2: IGA Success Rate and Nominal Change in Inflammatory Lesion Count from Baseline to End of the 12-Week Treatment Period
Trial 1
Trial 2
Finacea Foam, 15%
Vehicle
Finacea Foam, 15%
Vehicle
N=483
N=478
N=198
N=203
IGA success rate
32.1%
23.4%
43.4%
32.5%
Mean nominal change in inflammatory lesion count from baseline
-13.2
-10.3
-13.3
-9.5
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Finacea (azelaic acid) Foam 15% is a white to off-white emulsion supplied in a pressurized 50 g (NDC: 50419-829-01) aluminum can.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 25◦C (77◦F); excursions permitted between 15–30◦C (59–86◦F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
WARNING:Flammable. Avoid fire, flame, or smoking during and immediately following application. Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not expose to heat or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients using Finacea Foam of the following information and instructions:
- For external use only.
- Cleanse affected area(s) with a very mild soap or a soapless cleansing lotion and pat dry with a soft towel.
- Shake well before use.
- Avoid use of alcoholic cleansers, tinctures and astringents, abrasives and peeling agents.
- Avoid contact with the eyes, mouth and other mucous membranes. If Finacea Foam does come in contact with the eyes, wash the eyes with large amounts of water and consult your physician if eye irritation persists.
- If allergic reactions occur, discontinue use and consult your physician.
- Wash hands immediately following application of Finacea Foam.
- Cosmetics may be applied after the application of Finacea Foam has dried.
- Avoid the use of occlusive dressings and wrappings.
- To help manage rosacea, avoid any triggers that may provoke erythema, flushing, and blushing. These triggers can include spicy and thermally hot food and drinks such as hot coffee, tea, or alcoholic beverages.
- The propellant in Finacea Foam is flammable. Avoid fire, flame, or smoking during and immediately following application.
- Discard product 8 weeks after opening.
© 2015, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved.
Manufactured for:
Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Whippany, NJ 07981
Manufactured in Switzerland
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FINACEA FOAM
azelaic acid aerosol, foamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50419-829 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AZELAIC ACID (UNII: F2VW3D43YT) (AZELAIC ACID - UNII:F2VW3D43YT) AZELAIC ACID .15 g in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZOIC ACID (UNII: 8SKN0B0MIM) CETOSTEARYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2DMT128M1S) DIMETHYL ISOSORBIDE (UNII: SA6A6V432S) MEDIUM-CHAIN TRIGLYCERIDES (UNII: C9H2L21V7U) POLYOXYL 40 STEARATE (UNII: 13A4J4NH9I) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50419-829-01 1 in 1 CARTON 08/03/2015 1 50 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 50419-829-71 1 in 1 CARTON 08/03/2015 2 30 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 50419-829-72 1 in 1 CARTON 10/24/2016 3 15 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA207071 08/03/2015 Labeler - Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. (005436809) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations ASM Aerosol-Service AG 480286111 MANUFACTURE(50419-829)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
