AZTREONAM injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Aztreonam by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Aztreonam by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hospira, Inc., Hospira Australia Pty Ltd, Curia Italy S.r.l.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Aztreonam for Injection, USP contains the active ingredient aztreonam, a monobactam. It was originally isolated from Chromobacterium violaceum. It is a synthetic bactericidal antibiotic.
The monobactams, having a unique monocyclic beta-lactam nucleus, are structurally different from other beta-lactam antibiotics (eg, penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins). The sulfonic acid substituent in the 1-position of the ring activates the beta-lactam moiety; an aminothiazolyl oxime side chain in the 3-position and a methyl group in the 4-position confer the specific antibacterial spectrum and beta-lactamase stability.
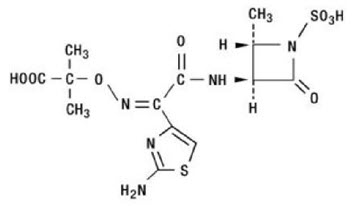
Aztreonam is designated chemically as (Z)-2-[[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[[(2S,3S)-2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfo-3-azetidinyl]carbamoyl]methylene]amino]oxy]-2-methylpropionic acid.
Structural formula:
Aztreonam for Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, sodium-free, lyophilized, off-white to slightly yellowish solid, containing approximately 780 mg arginine per gram of aztreonam. Following constitution, the product is for intramuscular or intravenous use. Aqueous solutions of the product have a pH in the range of 4.5 to 7.5.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
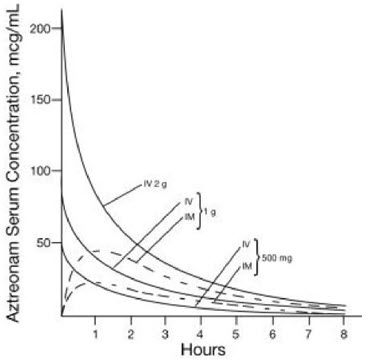
Single 30-minute intravenous infusions of 500 mg, 1 g, and 2 g doses of aztreonam for injection in healthy subjects produced aztreonam peak serum levels of 54 mcg/mL, 90 mcg/mL, and 204 mcg/mL, respectively, immediately after administration; at 8 hours, serum levels were 1 mcg/mL, 3 mcg/mL, and 6 mcg/mL, respectively (Figure 1). Single 3-minute intravenous injections of the same doses resulted in serum levels of 58 mcg/mL, 125 mcg/mL, and 242 mcg/mL at 5 minutes following completion of injection.
Serum concentrations of aztreonam in healthy subjects following completion of single intramuscular injections of 500 mg and 1 g doses are depicted in Figure 1; maximum serum concentrations occur at about 1 hour. After identical single intravenous or intramuscular doses of aztreonam for injection, the serum concentrations of aztreonam are comparable at 1 hour (1.5 hours from start of intravenous infusion) with similar slopes of serum concentrations thereafter.
The serum levels of aztreonam following single 500 mg or 1 g (intramuscular or intravenous) or 2 g (intravenous) doses of aztreonam for injection exceed the MIC90 for Neisseria sp., Haemophilus influenzae, and most genera of the Enterobacteriaceae for 8 hours (for Enterobacter sp., the 8-hour serum levels exceed the MIC for 80% of strains). For Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a single 2 g intravenous dose produces serum levels that exceed the MIC90 for approximately 4 to 6 hours. All of the above doses of aztreonam for injection result in average urine levels of aztreonam that exceed the MIC90 for the same pathogens for up to 12 hours.
When aztreonam pharmacokinetics were assessed for adult and pediatric patients, they were found to be comparable (down to 9 months old). The serum half-life of aztreonam averaged 1.7 hours (1.5 to 2) in subjects with normal renal function, independent of the dose and route of administration. In healthy subjects, based on a 70 kg person, the serum clearance was 91 mL/min and renal clearance was 56 mL/min; the apparent mean volume of distribution at steady-state averaged 12.6 liters, approximately equivalent to extracellular fluid volume.
In elderly patients, the mean serum half-life of aztreonam increased and the renal clearance decreased, consistent with the age-related decrease in creatinine clearance. The dosage of aztreonam for injection should be adjusted accordingly (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Renal Impairment in Adult Patients).
In patients with impaired renal function, the serum half-life of aztreonam is prolonged (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Renal Impairment in Adult Patients). The serum half-life of aztreonam is only slightly prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment since the liver is a minor pathway of excretion.
Average urine concentrations of aztreonam were approximately 1,100 mcg/mL, 3,500 mcg/mL, and 6,600 mcg/mL within the first 2 hours following single 500 mg, 1 g, and 2 g intravenous doses of aztreonam for injection (30-minute infusions), respectively. The range of average concentrations for aztreonam in the 8- to 12-hour urine specimens in these studies was 25 to 120 mcg/mL. After intramuscular injection of single 500 mg and 1 g doses of aztreonam for injection, urinary levels were approximately 500 mcg/mL and 1,200 mcg/mL, respectively, within the first 2 hours, declining to 180 mcg/mL and 470 mcg/mL in the 6- to 8-hour specimens. In healthy subjects, aztreonam is excreted in the urine about equally by active tubular secretion and glomerular filtration. Approximately 60% to 70% of an intravenous or intramuscular dose was recovered in the urine by 8 hours. Urinary excretion of a single parenteral dose was essentially complete by 12 hours after injection. About 12% of a single intravenous radiolabeled dose was recovered in the feces. Unchanged aztreonam and the inactive beta-lactam ring hydrolysis product of aztreonam were present in feces and urine.
Intravenous or intramuscular administration of a single 500 mg or 1 g dose of aztreonam for injection every 8 hours for 7 days to healthy subjects produced no apparent accumulation of aztreonam or modification of its disposition characteristics; serum protein binding averaged 56% and was independent of dose. An average of about 6% of a 1 g intramuscular dose was excreted as a microbiologically inactive open beta-lactam ring hydrolysis product (serum half-life approximately 26 hours) of aztreonam in the 0- to 8-hour urine collection on the last day of multiple dosing.
Renal function was monitored in healthy subjects given aztreonam; standard tests (serum creatinine, creatinine clearance, BUN, urinalysis, and total urinary protein excretion) as well as special tests (excretion of N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, alanine aminopeptidase, and β2-microglobulin) were used. No abnormal results were obtained.
Aztreonam achieves measurable concentrations in the following body fluids and tissues:
Table 1: Extravascular Concentrations of Aztreonam After a Single Parenteral Dose* Fluid or Tissue Dose
(g)Route Hours
Post-injectionNumber of Patients Mean Concentration
(mcg/mL or mcg/g)- * Tissue penetration is regarded as essential to therapeutic efficacy, but specific tissue levels have not been correlated with specific therapeutic effects.
Fluids
bile
1
IV
2
10
39
blister fluid
1
IV
1
6
20
bronchial secretion
2
IV
4
7
5
cerebrospinal fluid
(inflamed meninges)2
IV
0.9 to 4.3
16
3
pericardial fluid
2
IV
1
6
33
pleural fluid
2
IV
1.1 to 3
3
51
synovial fluid
2
IV
0.8 to 1.9
11
83
Tissues
atrial appendage
2
IV
0.9 to 1.6
12
22
endometrium
2
IV
0.7 to 1.9
4
9
fallopian tube
2
IV
0.7 to 1.9
8
12
fat
2
IV
1.3 to 2
10
5
femur
2
IV
1 to 2.1
15
16
gallbladder
2
IV
0.8 to 1.3
4
23
kidney
2
IV
2.4 to 5.6
5
67
large intestine
2
IV
0.8 to 1.9
9
12
liver
2
IV
0.9 to 2
6
47
lung
2
IV
1.2 to 2.1
6
22
myometrium
2
IV
0.7 to 1.9
9
11
ovary
2
IV
0.7 to 1.9
7
13
prostate
1
IM
0.8 to 3
8
8
skeletal muscle
2
IV
0.3 to 0.7
6
16
skin
2
IV
0 to 1
8
25
sternum
2
IV
1
6
6
The concentration of aztreonam in saliva at 30 minutes after a single 1 g intravenous dose (9 patients) was 0.2 mcg/mL; in human milk at 2 hours after a single 1 g intravenous dose (6 patients), 0.2 mcg/mL, and at 6 hours after a single 1 g intramuscular dose (6 patients), 0.3 mcg/mL; in amniotic fluid at 6 to 8 hours after a single 1 g intravenous dose (5 patients), 2 mcg/mL. The concentration of aztreonam in peritoneal fluid obtained 1 to 6 hours after multiple 2 g intravenous doses ranged between 12 mcg/mL and 90 mcg/mL in 7 of 8 patients studied.
Aztreonam given intravenously rapidly reaches therapeutic concentrations in peritoneal dialysis fluid; conversely, aztreonam given intraperitoneally in dialysis fluid rapidly produces therapeutic serum levels.
Concomitant administration of probenecid or furosemide and aztreonam causes clinically insignificant increases in the serum levels of aztreonam. Single-dose intravenous pharmacokinetic studies have not shown any significant interaction between aztreonam and concomitantly administered gentamicin, nafcillin sodium, cephradine, clindamycin, or metronidazole. No reports of disulfiram-like reactions with alcohol ingestion have been noted; this is not unexpected since aztreonam does not contain a methyl-tetrazole side chain.
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Aztreonam is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Aztreonam has activity in the presence of some beta-lactamases, both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Mechanism of Resistance
Resistance to aztreonam is primarily through hydrolysis by beta-lactamase, alteration of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), and decreased permeability.
Interaction with Other Antimicrobials
Aztreonam and aminoglycosides have been shown to be synergistic in vitro against most strains of P. aeruginosa, many strains of Enterobacteriaceae, and other Gram-negative aerobic bacilli.
Aztreonam has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms:
- Citrobacter species
- Enterobacter species
- Escherichia coli
- Haemophilus influenzae (including ampicillin-resistant and other penicillinase-producing strains)
- Klebsiella oxytoca
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia species
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90% of the following microorganisms exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for aztreonam. However, the efficacy of aztreonam in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Aerobic Gram-negative microorganisms:
- Aeromonas hydrophila
- Morganella morganii
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including penicillinase-producing strains)
- Pasteurella multocida
- Proteus vulgaris
- Providencia stuartii
- Providencia rettgeri
- Yersinia enterocolitica
Aztreonam and aminoglycosides have been shown to be synergistic in vitro against most strains of P. aeruginosa, many strains of Enterobacteriaceae, and other Gram-negative aerobic bacilli.
Alterations of the anaerobic intestinal flora by broad-spectrum antibiotics may decrease colonization resistance, thus permitting overgrowth of potential pathogens, eg, Candida and Clostridium species. Aztreonam has little effect on the anaerobic intestinal microflora in in vitro studies. Clostridium difficile and its cytotoxin were not found in animal models following administration of aztreonam (see ADVERSE REACTIONS: Gastrointestinal).
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Aztreonam for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, aztreonam for injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Aztreonam for Injection is indicated for the treatment of the following infections caused by susceptible Gram-negative microorganisms:
Urinary Tract Infections (complicated and uncomplicated), including pyelonephritis and cystitis (initial and recurrent) caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella oxytoca1, Citrobacter species1, and Serratia marcescens1.
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter species, and Serratia marcescens1.
Septicemia caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis1, Serratia marcescens1, and Enterobacter species.
Skin and Skin-Structure Infections, including those associated with postoperative wounds, ulcers, and burns, caused by Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Serratia marcescens, Enterobacter species, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Citrobacter species1.
Intra-abdominal Infections, including peritonitis caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species including K. pneumoniae, Enterobacter species including E. cloacae1, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Citrobacter species1 including C. freundii1, and Serratia species1 including S. marcescens1.
Gynecologic Infections, including endometritis and pelvic cellulitis caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae1, Enterobacter species1 including E. cloacae1, and Proteus mirabilis1.
Aztreonam for Injection is indicated for adjunctive therapy to surgery in the management of infections caused by susceptible organisms, including abscesses, infections complicating hollow viscus perforations, cutaneous infections, and infections of serous surfaces. Aztreonam for Injection is effective against most of the commonly encountered Gram-negative aerobic pathogens seen in general surgery.
- 1 Efficacy for this organism in this organ system was studied in fewer than 10 infections.
Concurrent Therapy
Concurrent initial therapy with other antimicrobial agents and aztreonam for injection is recommended before the causative organism(s) is known in seriously ill patients who are also at risk of having an infection due to Gram-positive aerobic pathogens. If anaerobic organisms are also suspected as etiologic agents, therapy should be initiated using an anti-anaerobic agent concurrently with aztreonam for injection (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Certain antibiotics (eg, cefoxitin, imipenem) may induce high levels of beta-lactamase in vitro in some Gram-negative aerobes such as Enterobacter and Pseudomonas species, resulting in antagonism to many beta-lactam antibiotics including aztreonam. These in vitro findings suggest that such beta-lactamase inducing antibiotics not be used concurrently with aztreonam. Following identification and susceptibility testing of the causative organism(s), appropriate antibiotic therapy should be continued.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Both animal and human data suggest that aztreonam for injection is rarely cross-reactive with other beta-lactam antibiotics and weakly immunogenic. Treatment with aztreonam can result in hypersensitivity reactions in patients with or without prior exposure (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has any history of hypersensitivity reactions to any allergens.
While cross-reactivity of aztreonam with other beta-lactam antibiotics is rare, this drug should be administered with caution to any patient with a history of hypersensitivity to beta-lactams (eg, penicillins, cephalosporins, and/or carbapenems). Treatment with aztreonam can result in hypersensitivity reactions in patients with or without prior exposure to aztreonam. If an allergic reaction to aztreonam occurs, discontinue the drug and institute supportive treatment as appropriate (eg, maintenance of ventilation, pressor amines, antihistamines, corticosteroids). Serious hypersensitivity reactions may require epinephrine and other emergency measures (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including aztreonam for injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Rare cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported in association with aztreonam in patients undergoing bone marrow transplant with multiple risk factors including sepsis, radiation therapy, and other concomitantly administered drugs associated with toxic epidermal necrolysis.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Prescribing aztreonam in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
In patients with impaired hepatic or renal function, appropriate monitoring is recommended during therapy.
If an aminoglycoside is used concurrently with aztreonam, especially if high dosages of the former are used or if therapy is prolonged, renal function should be monitored because of the potential nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics.
The use of antibiotics may promote the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including Gram-positive organisms (Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis) and fungi. Should superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including aztreonam should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (eg, the common cold). When aztreonam is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by aztreonam or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with aztreonam have not been conducted using an intravenous route of administration. A 104-week rat inhalation toxicology study to assess the carcinogenic potential of aztreonam demonstrated no drug-related increase in the incidence of tumors. Rats were exposed to aerosolized aztreonam for up to 4 hours per day. Peak plasma levels of aztreonam averaging approximately 6.8 mcg/mL were measured in rats at the highest dose level.
Genetic toxicology studies performed with aztreonam in vitro (Ames test, mouse lymphoma forward mutation assay, gene conversion assay, chromosome aberration assay in human lymphocytes) and in vivo (mouse bone marrow cytogenetic assay) did not reveal evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential.
A two-generation reproduction study in rats at daily doses of 150, 600, or 2,400 mg/kg given prior to and during gestation and lactation, revealed no evidence of impaired fertility. Based on body surface area, the high dose is 2.9-fold greater than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) for adults of 8 g per day. There was a slightly reduced survival rate during the lactation period in the offspring of rats that received the highest dose, but not in offspring of rats that received lower doses of aztreonam.
Pregnancy
In pregnant women, aztreonam crosses the placenta and enters the fetal circulation.
Developmental toxicity studies in pregnant rats and rabbits with daily doses of aztreonam up to 1,800 and 1,200 mg/kg, respectively, revealed no evidence of embryotoxicity or fetotoxicity or teratogenicity. These doses, based on body surface area, are 2.2- and 2.9-fold greater than the MRHD for adults of 8 g per day. A peri/postnatal study in rats revealed no drug-induced changes in any maternal, fetal, or neonatal parameters. The highest dose used in this study, 1,800 mg/kg/day, is 2.2 times the MRHD based on body surface area.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of aztreonam on human pregnancy outcomes. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, aztreonam should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Aztreonam is excreted in human milk in concentrations that are less than 1% of concentrations determined in simultaneously obtained maternal serum; consideration should be given to temporary discontinuation of nursing and use of formula feedings.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of intravenous aztreonam for injection have been established in the age groups 9 months to 16 years. Use of aztreonam for injection in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of aztreonam for injection in adults with additional efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetic data from non-comparative clinical studies in pediatric patients. Sufficient data are not available for pediatric patients under 9 months of age or for the following treatment indications/pathogens: septicemia and skin and skin-structure infections (where the skin infection is believed or known to be due to H. influenzae type b). In pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis, higher doses of aztreonam for injection may be warranted (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, and CLINICAL STUDIES).
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of aztreonam for injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
In elderly patients, the mean serum half-life of aztreonam increased and the renal clearance decreased, consistent with the age-related decrease in creatinine clearance. Since aztreonam is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, renal function should be monitored and dosage adjustments made accordingly (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Renal Impairment in Adult Patients and Dosage in the Elderly).
Aztreonam for Injection contains no sodium.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Local reactions such as phlebitis/thrombophlebitis following intravenous administration, and discomfort/swelling at the injection site following intramuscular administration occurred at rates of approximately 1.9% and 2.4%, respectively.
Systemic reactions (considered to be related to therapy or of uncertain etiology) occurring at an incidence of 1% to 1.3% include diarrhea, nausea and/or vomiting, and rash. Reactions occurring at an incidence of less than 1% are listed within each body system in order of decreasing severity:
Hypersensitivity—anaphylaxis, angioedema, bronchospasm
Hematologic—pancytopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, eosinophilia, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
Gastrointestinal—abdominal cramps; rare cases of C. difficile–associated diarrhea, including pseudomembranous colitis, or gastrointestinal bleeding have been reported. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment (see WARNINGS).
Dermatologic—toxic epidermal necrolysis (see WARNINGS), purpura, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, urticaria, petechiae, pruritus, diaphoresis
Cardiovascular—hypotension, transient ECG changes (ventricular bigeminy and PVC), flushing
Respiratory—wheezing, dyspnea, chest pain
Hepatobiliary—hepatitis, jaundice
Nervous System—seizure, confusion, encephalopathy, vertigo, paresthesia, insomnia, dizziness
Musculoskeletal—muscular aches
Special Senses—tinnitus, diplopia, mouth ulcer, altered taste, numb tongue, sneezing, nasal congestion, halitosis
Other—vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis, breast tenderness
Body as a Whole—weakness, headache, fever, malaise
Pediatric Adverse Reactions
Of the 612 pediatric patients who were treated with aztreonam for injection in clinical trials, less than 1% required discontinuation of therapy due to adverse events. The following systemic adverse events, regardless of drug relationship, occurred in at least 1% of treated patients in domestic clinical trials: rash (4.3%), diarrhea (1.4%), and fever (1.0%). These adverse events were comparable to those observed in adult clinical trials.
In 343 pediatric patients receiving intravenous therapy, the following local reactions were noted: pain (12%), erythema (2.9%), induration (0.9%), and phlebitis (2.1%). In the US patient population, pain occurred in 1.5% of patients, while each of the remaining 3 local reactions had an incidence of 0.5%.
The following laboratory adverse events, regardless of drug relationship, occurred in at least 1% of treated patients: increased eosinophils (6.3%), increased platelets (3.6%), neutropenia (3.2%), increased AST (3.8%), increased ALT (6.5%), and increased serum creatinine (5.8%).
In US pediatric clinical trials, neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count less than 1,000/mm3) occurred in 11.3% of patients (8/71) younger than 2 years receiving 30 mg/kg every 6 hours. AST and ALT elevations to greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal were noted in 15% to 20% of patients aged 2 years or above receiving 50 mg/kg every 6 hours. The increased frequency of these reported laboratory adverse events may be due to either increased severity of illness treated or higher doses of aztreonam for injection administered.
Adverse Laboratory Changes
Adverse laboratory changes without regard to drug relationship that were reported during clinical trials were:
Hepatic—elevations of AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), and alkaline phosphatase; signs or symptoms of hepatobiliary dysfunction occurred in less than 1% of recipients (see above).
Hematologic—increases in prothrombin and partial thromboplastin times, positive Coombs' test.
Renal—increases in serum creatinine.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage in Adult Patients
Aztreonam for Injection may be administered intravenously or by intramuscular injection. Dosage and route of administration should be determined by susceptibility of the causative organisms, severity and site of infection, and the condition of the patient.
Table 2: Aztreonam for Injection Dosage Guidelines for Adults* Type of Infection Dose Frequency
(hours)- * Maximum recommended dose is 8 g per day.
Urinary tract infections
500 mg or 1 g
8 or 12
Moderately severe systemic infections
1 g or 2 g
8 or 12
Severe systemic or life-threatening infections
2 g
6 or 8
Because of the serious nature of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, dosage of 2 g every six or eight hours is recommended, at least upon initiation of therapy, in systemic infections caused by this organism.
The intravenous route is recommended for patients requiring single doses greater than 1 g or those with bacterial septicemia, localized parenchymal abscess (eg, intra-abdominal abscess), peritonitis, or other severe systemic or life-threatening infections.
The duration of therapy depends on the severity of infection. Generally, aztreonam for injection should be continued for at least 48 hours after the patient becomes asymptomatic or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained. Persistent infections may require treatment for several weeks. Doses smaller than those indicated should not be used.
Renal Impairment in Adult Patients
Prolonged serum levels of aztreonam may occur in patients with transient or persistent renal insufficiency. Therefore, the dosage of aztreonam for injection should be halved in patients with estimated creatinine clearances between 10 and 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 after an initial loading dose of 1 g or 2 g.
When only the serum creatinine concentration is available, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) may be used to approximate the creatinine clearance (Clcr). The serum creatinine should represent a steady-state of renal function.
Males: Clcr = weight (kg) × (140−age)
72 × serum creatinine (mg/dL)
Females: 0.85 × above valueIn patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 mL/min/1.73 m2), such as those supported by hemodialysis, the usual dose of 500 mg, 1 g, or 2 g should be given initially. The maintenance dose should be one-fourth of the usual initial dose given at the usual fixed interval of 6, 8, or 12 hours. For serious or life-threatening infections, in addition to the maintenance doses, one-eighth of the initial dose should be given after each hemodialysis session.
Dosage in the Elderly
Renal status is a major determinant of dosage in the elderly; these patients in particular may have diminished renal function. Serum creatinine may not be an accurate determinant of renal status. Therefore, as with all antibiotics eliminated by the kidneys, estimates of creatinine clearance should be obtained and appropriate dosage modifications made if necessary.
Dosage in Pediatric Patients
Aztreonam for Injection should be administered intravenously to pediatric patients with normal renal function. There are insufficient data regarding intramuscular administration to pediatric patients or dosing in pediatric patients with renal impairment (see PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use).
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
A total of 612 pediatric patients aged 1 month to 12 years were enrolled in uncontrolled clinical trials of aztreonam in the treatment of serious Gram-negative infections, including urinary tract, lower respiratory tract, skin and skin-structure, and intra-abdominal infections.
Preparation of Parenteral Solutions
General
Upon the addition of the diluent to the container, contents should be shaken immediately and vigorously. Use constituted solution immediately. Discard any remaining unused constituted solution.
Depending upon the concentration of aztreonam and diluent used, constituted aztreonam for injection yields a colorless to light straw yellow solution which may develop a slight pink tint on standing (potency is not affected). Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration whenever solution and container permit.
Admixtures with Other Antibiotics
Intravenous infusion solutions of aztreonam for injection not exceeding 2% w/v prepared with Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 0.9% or Dextrose Injection, USP 5%, to which clindamycin phosphate, gentamicin sulfate, tobramycin sulfate, or cefazolin sodium have been added at concentrations usually used clinically, are stable for up to 48 hours at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) or 7 days under refrigeration 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Ampicillin sodium admixtures with aztreonam in Sodium Chloride Injection, USP 0.9% are stable for 24 hours at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) and 48 hours under refrigeration 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F); stability in Dextrose Injection, USP 5% is 2 hours at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) and 8 hours under refrigeration 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Aztreonam-cloxacillin sodium and aztreonam-vancomycin hydrochloride admixtures are stable in Dianeal 137 (Peritoneal Dialysis Solution) with 4.25% Dextrose for up to 24 hours at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Aztreonam is incompatible with nafcillin sodium, cephradine, and metronidazole.
Other admixtures are not recommended since compatibility data are not available.
Intravenous Solutions
For Bolus Injection
The vial contents should be constituted with 6 mL to 10 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP.
For Infusion
If the vial contents are to be transferred to an appropriate infusion solution, each gram of aztreonam should be initially constituted with at least 3 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP. Further dilution may be obtained with one of the following intravenous infusion solutions:
- Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9%
- Ringer's Injection, USP
- Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP
- Dextrose Injection, USP, 5% or 10%
- Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 5%:0.9%, 5%:0.45%, or 5%:0.2%
- Sodium Lactate Injection, USP (M/6 Sodium Lactate)
- Ionosol® B and 5% Dextrose
- Isolyte® M with 5% Dextrose
- Normosol®-R
- Normosol®-R and 5% Dextrose
- Normosol®-M and 5% Dextrose
- Mannitol Injection, USP, 5% or 10%
- Lactated Ringer's and 5% Dextrose Injection
Intramuscular Solutions
The vial contents should be constituted with at least 3 mL of an appropriate diluent per gram aztreonam. The following diluents may be used:
- Sterile Water for Injection, USP
- Sterile Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, USP (with benzyl alcohol or with methyl- and propylparabens)
- Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9%
- Bacteriostatic Sodium Chloride Injection, USP (with benzyl alcohol)
Stability of Intravenous and Intramuscular Solutions
Aztreonam for Injection solutions for intravenous infusion at concentrations not exceeding 2% w/v must be used within 48 hours following constitution if kept at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) or within 7 days if refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Aztreonam for Injection solutions at concentrations exceeding 2% w/v, except those prepared with Sterile Water for Injection, USP or Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, should be used promptly after preparation; the 2 excepted solutions must be used within 48 hours if stored at controlled room temperature 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) or within 7 days if refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Intravenous Administration
Bolus Injection
A bolus injection may be used to initiate therapy. The dose should be slowly injected directly into a vein, or the tubing of a suitable administration set, over a period of 3 to 5 minutes (see next paragraph regarding flushing of tubing).
Infusion
With any intermittent infusion of aztreonam and another drug with which it is not pharmaceutically compatible, the common delivery tube should be flushed before and after delivery of aztreonam with any appropriate infusion solution compatible with both drug solutions; the drugs should not be delivered simultaneously. Any aztreonam infusion should be completed within a 20- to 60-minute period. With use of a Y-type administration set, careful attention should be given to the calculated volume of aztreonam solution required so that the entire dose will be infused. A volume control administration set may be used to deliver an initial dilution of aztreonam for injection (see Preparation of Parenteral Solutions: Intravenous Solutions: For Infusion) into a compatible infusion solution during administration; in this case, the final dilution of aztreonam should provide a concentration not exceeding 2% w/v.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Aztreonam for Injection, USP single-dose vials are supplied as follows:
Unit of Sale Strength Each NDC: 0409-0829-01
Carton containing 101 gram/vial
NDC: 0409-0829-11
Single-dose vialNDC: 0409-0830-01
Carton containing 102 grams/vial
NDC: 0409-0830-11
Single-dose vial - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 gram Vial Label
NDC: 0409-0829-11
Rx OnlyAztreonam for
Injection, USP
1 gram/vialFor Intravenous or Intramuscular use after constitution.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1 gram Vial Carton
10 x 1 gram Single-Dose Vials
NDC: 0409-0829-01
Contains 10 of NDC: 0409-0829-11Aztreonam
for Injection, USP
1 gram/vialFor Intravenous or Intramuscular use after constitution.
Rx only
Hospira
-
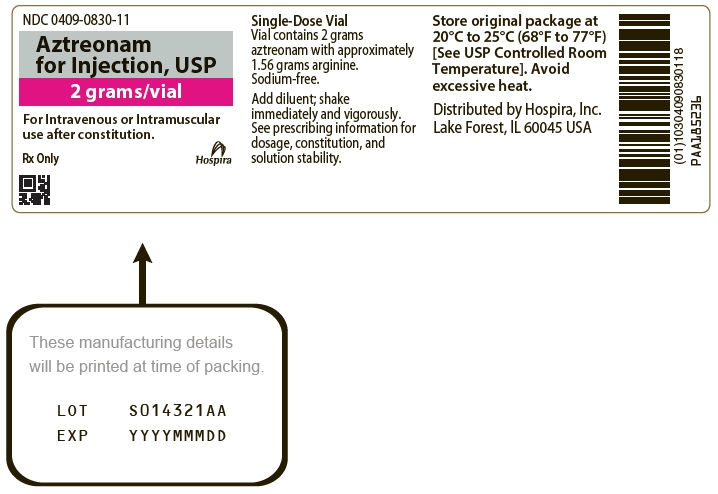
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 gram Vial Label
NDC: 0409-0830-11
Aztreonam
for Injection, USP
2 grams/vialFor Intravenous or Intramuscular
use after constitution.Rx Only
Hospira
-
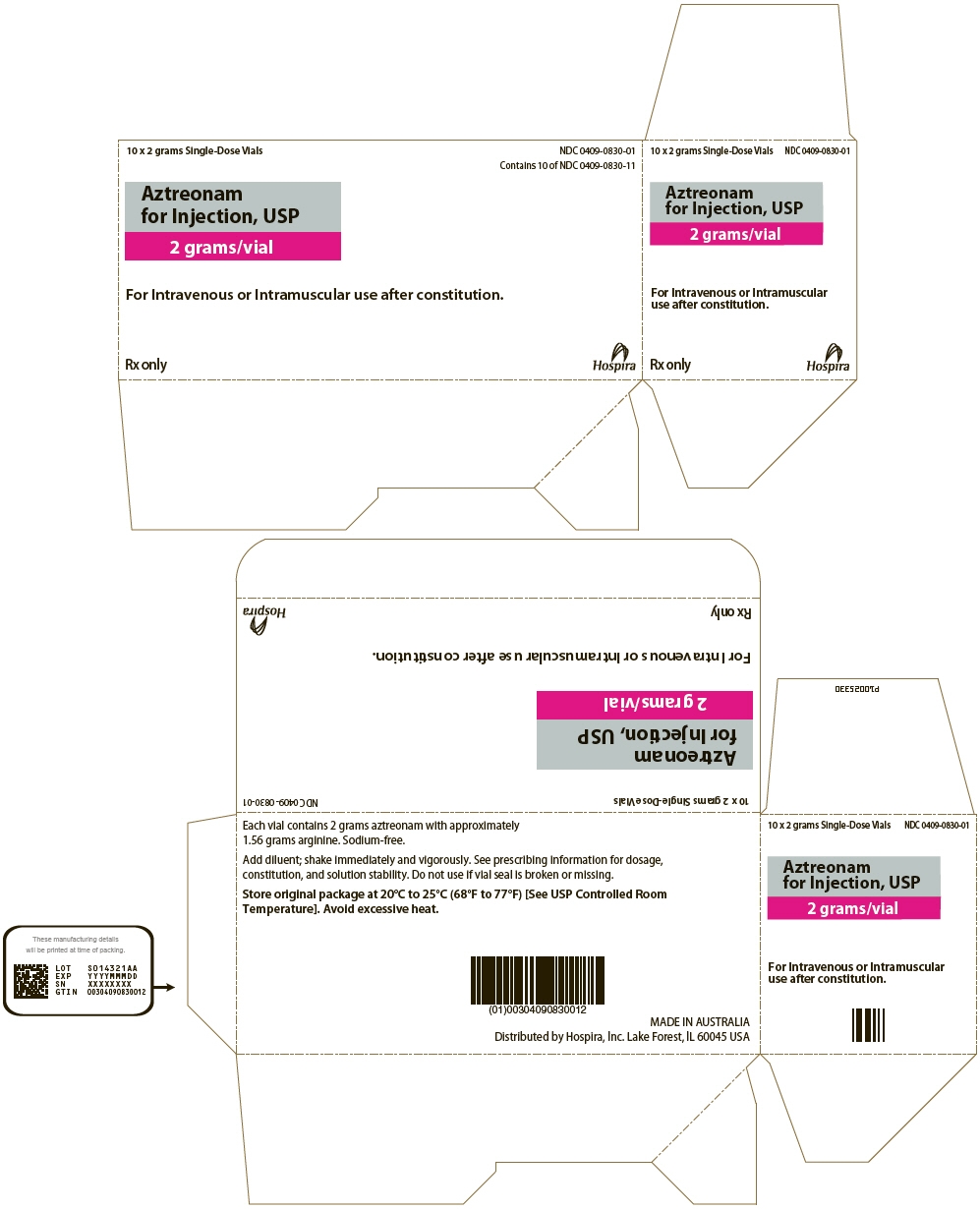
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 gram Vial Carton
10 x 2 grams Single-Dose Vials
NDC: 0409-0830-01
Contains 10 of NDC: 0409-0830-11Aztreonam
for Injection, USP
2 grams/vialFor Intravenous or Intramuscular use after constitution.
Rx only
Hospira
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AZTREONAM
aztreonam injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0409-0829 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AZTREONAM (UNII: G2B4VE5GH8) (AZTREONAM - UNII:G2B4VE5GH8) AZTREONAM 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 780 mg Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0409-0829-01 10 in 1 CARTON 01/24/2022 1 NDC: 0409-0829-11 1 in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206517 01/24/2022 AZTREONAM
aztreonam injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0409-0830 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AZTREONAM (UNII: G2B4VE5GH8) (AZTREONAM - UNII:G2B4VE5GH8) AZTREONAM 2 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ARGININE (UNII: 94ZLA3W45F) 1.56 g Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0409-0830-01 10 in 1 CARTON 01/24/2022 1 NDC: 0409-0830-11 1 in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA206517 01/24/2022 Labeler - Hospira, Inc. (141588017) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Hospira Australia Pty Ltd 758967652 ANALYSIS(0409-0829, 0409-0830) , MANUFACTURE(0409-0829, 0409-0830) , PACK(0409-0829, 0409-0830) , LABEL(0409-0829, 0409-0830)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.