HYRNUO- sevabertinib tablet, film coated
HYRNUO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
HYRNUO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Bayer AG, Sharp Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HYRNUO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HYRNUO.
HYRNUO® (sevabertinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
HYRNUO is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) activating mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have received a prior systemic therapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR). Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 10 mg of sevabertinib. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Diarrhea: At the first sign of diarrhea or increased bowel movement frequency, instruct patients to start an antidiarrheal treatment, and to increase their fluid and electrolyte intake. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity. (5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin at baseline prior to administration of HYRNUO, every 2 weeks during the first month, and then monthly thereafter as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity. (5.2)
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis: Monitor patients for new or worsening symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Discontinue HYRNUO upon confirmation of ILD/pneumonitis. (5.3)
- Ocular Toxicity: Promptly refer patients presenting with new or worsening eye symptoms to an ophthalmologist. Interrupt, reduce the dose or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity. (5.4)
- Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation: Monitor amylase and lipase regularly during treatment. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity. (5.5)
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions (>20%): diarrhea, rash, paronychia, stomatitis, and nausea.
- Most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥2%): decreased potassium, increased lipase, decreased lymphocyte count, decreased sodium, increased amylase, increased ALT, and increased AST. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-888-842-2937 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, reduce HYRNUO dosage. (2.4, 7.1).
- Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Monitor patients for increased HYRNUO-associated adverse reactions (2.3, 7.1)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. (7.1)
- Certain CYP3A Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with CYP3A substrates where minimal increases in concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions unless otherwise recommended in the Prescribing Information of the CYP3A substrate. (7.2)
- Certain P-gp Substrates: Refer to the Prescribing Information for P-gp substrates where minimal increases in concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Diarrhea
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
5.4 Ocular Toxicity
5.5 Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation
5.6 Embryo-fetal toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on HYRNUO
7.2 Effects of HYRNUO on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 TKD Activating Mutations
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
HYRNUO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) activating mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)], and who have received a prior systemic therapy.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC based on the presence of HER2 (ERBB2) TKD activating mutations in tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Information on FDA-approved tests is available at http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of HYRNUO is 20 mg orally twice daily with food, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Swallow tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew tablets.
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, take the missed dose as soon as you remember prior to the next scheduled dose. Do not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for the missed dose.
Vomited Dose
If a dose is vomited, do not take an additional dose. Resume dosing at the next scheduled time.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dosage reductions for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended HYRNUO Dosage Reductions for Adverse Reactions Dose Reduction Dosage Modification First 10 mg twice daily Second 10 mg once daily Permanently discontinue HYRNUO in patients who are unable to tolerate 10 mg once daily. The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended HYRNUO Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity* Dosage Modification - * Grades based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) Version 5.0.
Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Intolerable Grade 2 or Grade 3 - Interrupt HYRNUO until recovery to Grade ≤1.
- Resume HYRNUO at the same dose or the next lower dose.
- For recurrence, resume HYRNUO at the next lower dose.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Grade 2, 3 or 4 ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin or Grade 3 total bilirubin - Interrupt HYRNUO until recovery to Grade ≤1 or baseline.
- Resume HYRNUO at the next lower dose.
ALT or AST ≥ 3× ULN with total bilirubin ≥ 2× ULN or Grade 4 total bilirubin - Permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] Any Grade - Permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Ocular toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] Grade 2 - Interrupt HYRNUO until recovery to Grade ≤1.
- Resume HYRNUO at the next lower dose.
- For recurrence, permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Grade 3 or Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] Grade 3 - Interrupt HYRNUO until recovery to Grade ≤2 or baseline.
- Resume HYRNUO at the next lower dose.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue HYRNUO.
Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Intolerable or recurrent Grade 2 or Grade 3 - Interrupt HYRNUO until recovery to Grade ≤1.
- Resume HYRNUO at the same dose or the next lower dose.
- For recurrence, resume HYRNUO at the next lower dose.
Grade 4 Permanently discontinue HYRNUO. 2.4 Dosage Modifications for Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, reduce HYRNUO dosage as shown in Table 3. After the CYP3A inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the HYRNUO dosage that was used prior to initiating the inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Table 3: Recommended HYRNUO Dosage Modifications for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A Inhibitors Current Dosage Recommended Dosage 20 mg twice daily 10 mg twice daily 10 mg twice daily 10 mg once daily 10 mg once daily Withhold HYRNUO until strong CYP3A inhibitor is discontinued - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Diarrhea
HYRNUO can cause severe diarrhea that can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], diarrhea was reported in 86% of patients who received HYRNUO including Grade 3 in 15%. The median time to first onset of any grade diarrhea was four days. Dosage interruptions occurred in 15% of patients, and dose reductions occurred in 12% of patients.
At the first sign of diarrhea or increased bowel movement frequency, instruct patients to start an antidiarrheal treatment (e.g., loperamide [refer to full Prescribing Information]), and to increase their fluid and electrolyte intake. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
HYRNUO can cause severe hepatotoxicity characterized by elevations of liver function tests. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], based on adverse reaction data, hepatotoxicity occurred in 24% of patients treated with HYRNUO including 3% Grade 3. Based on laboratory data, 35% of patients treated with HYRNUO experienced increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), including 2.3% Grade 3. Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 35% of patients treated with HYRNUO, including 2.3% Grade 3. Increased bilirubin occurred in 12% of patients treated with HYRNUO. The median time to first onset of AST or ALT elevation was 1.4 (range 0.2 to 14.5) months. HYRNUO was interrupted for an adverse reaction of hepatotoxicity in 4.1% of patients, the dose was reduced in 4.1% and permanently discontinued in 0.4%.
Monitor liver function tests including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin at baseline prior to the first administration of HYRNUO, every 2 weeks for the first month, and then monthly thereafter as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on the severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
HYRNUO can cause severe interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ILD/pneumonitis occurred in two patients (0.7%) treated with HYRNUO, including 0.4% Grade 3. One patient required interruption of HYRNUO.
Monitor patients for new or worsening symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Discontinue HYRNUO upon confirmation of ILD/pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Ocular Toxicity
HYRNUO can cause ocular toxicity. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ocular toxicity occurred in 14% of patients treated with HYRNUO, including 11% Grade 1, 2.6% Grade 2 and 0.4% Grade 3 (one case of corneal epithelial microcysts with temporary unilateral blindness).
Promptly refer patients presenting with new or worsening eye symptoms to an ophthalmologist. Interrupt, reduce the dose or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation
HYRNUO can cause elevations of amylase and lipase levels. In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], based on laboratory data, increased amylase occurred in 32% of patients treated with HYRNUO, including 3.2% Grade 3 or 4. Increased lipase elevation occurred in 40% of patients treated with HYRNUO, including 10% Grade 3 or 4. Two patients (0.7%) required interruption of HYRNUO due to increased lipase and 3 (1.1%) required interruption of HYRNUO due to increased amylase. The median time to onset of increased amylase/lipase was 1.4 months (range 0.2 to 17 months).
Monitor amylase and lipase regularly during treatment with HYRNUO. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HYRNUO based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Embryo-fetal toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, HYRNUO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of sevabertinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in alterations to growth at maternal exposures ≥0.18 times the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the clinical dose of 20 mg twice daily. Animal studies with disrupted or depleted HER2/EGFR and in vitro assays have demonstrated that inhibition of HER2 and/or EGFR results in structural abnormalities, alteration to growth, and embryo-fetal and infant mortality.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to HYRNUO at 20 mg orally twice daily in 268 patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC harboring HER2 and/or other mutations from the SOHO-01 study [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Among 268 patients who received HYRNUO, 35% were exposed for greater than 6 months and 12% were exposed for greater than 1 year. In this pooled safety population, the most common (>20%) adverse reactions were diarrhea, rash, stomatitis, and paronychia. The most common (≥2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased potassium, increased lipase, decreased lymphocyte count, decreased sodium, increased amylase, increased ALT, and increased AST.
The safety of HYRNUO at 20 mg orally twice daily was evaluated in 136 patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC harboring HER2 activating mutations who had received prior systemic therapy in the SOHO-01 study [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Among 136 patients who received HYRNUO, 46% were exposed greater than 6 months and 15% were exposed for greater than 1 year. The median age of patients who received HYRNUO was 62 years (range: 29 to 91); 63% female; 65% Asian, 27% White, 3.7% Black or African American; and 2.2% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
The most common adverse reactions (>20%) in patients who received HYRNUO were diarrhea, rash, paronychia, stomatitis, and nausea. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥2%) were potassium decreased, lipase increased, lymphocyte count decreased, sodium decreased, amylase increased, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) increased.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 31% of patients who received HYRNUO. Serious adverse reactions in ≥2% of patients were diarrhea (6%), pneumonia (3.7%), dyspnea (2.2%), and pleural effusion (2.2%).
Permanent discontinuation of HYRNUO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3.7% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation were corneal epithelial microcysts, hepatic function abnormal, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, pain in extremity and dyspnea (0.7%, 1 patient each).
Dosage interruptions of HYRNUO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 46% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in dosage interruptions in >3% of patients were diarrhea, hypokalemia, nausea, decreased appetite, and pneumonia.
Dose reductions of HYRNUO due to adverse reactions occurred in 28% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in dose reductions in >2% of patients were diarrhea, rash, and hypokalemia.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions in SOHO-01 (Groups D and E).
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with NSCLC with HER2 Activating Mutations Who Received HYRNUO in SOHO-01 (Groups D and E) Adverse Reaction* HYRNUO
N = 136All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4†
(%)- * Graded per NCI CTCAE version 5.
- † All were Grade 3, except for dyspnea (0.7%, Grade 4).
- ‡ Includes diarrhea, enterocolitis.
- § Includes cheilitis, mouth ulceration, mucosal inflammation, stomatitis.
- ¶ Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper.
- # Includes dermatitis acneiform, eczema, eczema asteatotic, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, rash, rash erythematous, rash maculopapular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, skin exfoliation.
- Þ Includes ingrowing nail, nail disorder, onychoclasis, onycholysis, onychomadesis, paronychia.
- ß Includes dry skin, xeroderma.
- à Includes asthenia, fatigue.
- è Includes blindness unilateral, cataract, conjunctivitis, conjunctivitis allergic, corneal epithelial microcysts, dry eye, eye discharge, eye pain, lacrimation increased, ocular hyperemia, ocular hypertension, ocular toxicity, vision blurred, visual acuity reduced, visual impairment, xerophthalmia.
- ð Includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional.
Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea‡ 87 18 Stomatitis§ 29 1.5 Nausea 21 1.5 Vomiting 15 2.2 Abdominal pain¶ 10 0 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash# 66 1.5 ParonychiaÞ 33 0 Dry skinß 20 0 Pruritus 14 1.5 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased appetite 18 2.9 Investigations Weight decreased 19 0.7 General disorders and administration site conditions Fatigueà 13 0.7 Eye disorders Ocular toxicityè 16 0.7 Respiratory disorders Dyspneað 10 1.5 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received HYRNUO included edema (8%), cardiac arrhythmia (6%; includes arrhythmia, atrioventricular block complete, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, supraventricular extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia, tachycardia) and alopecia (3.7%).
Table 5 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities observed in SOHO-01 (Groups D and E).
Table 5: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥20%) That Worsened from Baseline in Patients with NSCLC with HER2 Activating Mutations in SOHO-01 (Groups D and E) Laboratory Abnormality HYRNUO
N=136*All Grades
(%)†Grade 3 or 4‡
(%)- * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 103 to 135 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
- † Graded per NCI CTCAE version 5 using only numeric values.
- ‡ All were Grade 3, except for calcium decreased (0.7%, Grade 4) and amylase increased (1.5%; Grade 4)
- § Graded per NCI CTCAE version 4.03 using only numeric values.
Hematology Hemoglobin decreased 47 1.5 Lymphocyte count decreased 32 6 White blood cell decreased 21 0.7 Chemistry Lipase increased 48 12 Potassium decreased 45 13 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 41 3 Magnesium decreased 40 0 Alanine aminotransferase increased 37 3 Glucose increased§ 36 0.7 Albumin decreased 32 1.5 Amylase increased 31 3.8 Calcium decreased 28 1.5 Creatinine increased 27 0 Sodium decreased 26 4.4 Alkaline phosphatase increased 24 0 Triglycerides increased 22 0 Laboratory abnormalities in <20% of patients who received HYRNUO include blood bilirubin increased (14%; all were Grades 1 and 2).
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on HYRNUO
Table 6 describes drug interactions where concomitant use of another drug affects HYRNUO.
Table 6: Drug Interactions that Affect HYRNUO Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors Prevention or management Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: - Avoid concomitant use of HYRNUO with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
- If concomitant use cannot be avoided, reduce HYRNUO dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: - Monitor patients for increased HYRNUO-associated adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Mechanism and Clinical Effect - Sevabertinib is a CYP3A substrate.
- Concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor may increase sevabertinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of HYRNUO-associated adverse reactions.
Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers Prevention or management - Avoid concomitant use of HYRNUO with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers.
Mechanism and Clinical Effect - Sevabertinib is a CYP3A substrate.
- Concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A inducer may decrease sevabertinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may decrease the effectiveness of HYRNUO.
7.2 Effects of HYRNUO on Other Drugs
Table 7 describes drug interactions where concomitant use of HYRNUO affects another drug.
Table 7: HYRNUO Drug Interactions that Affect Other Drugs Certain CYP3A Substrates Prevention or management - Avoid concomitant use of HYRNUO with CYP3A substrates where minimal increases in the concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions unless otherwise recommended in the Prescribing Information of the CYP3A substrate.
Mechanism and Clinical Effect - Sevabertinib is a weak to moderate CYP3A inhibitor.
- Sevabertinib increases exposure of CYP3A substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
Certain P-gp Substrates Prevention or management - Refer to the Prescribing Information for P-gp substrates where minimal increases in the concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions.
Mechanism and Clinical Effect - Sevabertinib is a P-gp inhibitor.
- Sevabertinib increases exposure of P-gp substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
CYP1A1 Substrates Prevention or management - Refer to the Prescribing Information of CYP1A1 substrates.
Mechanism and Clinical Impact - Sevabertinib is an inhibitor of CYP1A1 in vitro.
- Sevabertinib may increase exposure of CYP1A1 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], HYRNUO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of HYRNUO in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. In embryo-fetal development studies, oral administration of sevabertinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in alterations to growth at maternal exposures ≥0.18 times the human exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) at the clinical dose of 20 mg twice daily. Animal studies with disrupted or depleted HER2/EGFR and in vitro assays have demonstrated that inhibition of HER2 and/or EGFR results in structural abnormalities, alteration to growth, and embryo-fetal and infant mortality (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies, sevabertinib was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis from gestation day 6 to 17 at doses ranging from 1.5 to 11 mg/kg/day. Sevabertinib treatment resulted in maternal toxicity (reduced body weight and body weight gain) and a reduction in fetal weights at ≥6 mg/kg/day (≥0.18 times the human exposure based on AUC at the clinical dose).
Additional Nonclinical Data
A literature-based assessment of the effects on reproduction in mouse models with disrupted or depleted HER2/EGFR demonstrated that HER2/EGFR is critically important in reproductive and developmental processes including blastocyst implantation, placental development, and embryo-fetal/postnatal survival and development.
In a human-induced pluripotent stem cell-based assay, sevabertinib reduced cardiomyocyte and hepatocyte differentiation markers.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of sevabertinib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on a breastfed child or on milk production. In rats, sevabertinib or its metabolites are excreted in milk (see Data). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children from HYRNUO, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Animal Data
Following administration of radiolabeled sevabertinib to lactating rats, sevabertinib or its metabolites were excreted in milk. Sevabertinib-derived radioactivity concentrations were 13- to 26-times higher in milk than in plasma. Approximately 1.3% of the administered dose of sevabertinib-derived radioactivity was excreted into the milk.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
HYRNUO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating HYRNUO.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of HYRNUO have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 268 patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC harboring HER2 activating mutations who received HYRNUO at 20 mg twice daily in the SOHO-01study, 43% were 65 years and over and 13% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these older and younger patients. Grade 3 diarrhea was observed in 23% of patients age ≥75 years and 14% of patients <75 years old.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
HYRNUO tablets contain sevabertinib, a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name of the drug substance is 3-(3-chloro-2-methoxyanilino)-2-{3-[(2S)-1,4-dioxan-2-ylmethoxy]pyridin-4-yl}-1,5,6,7-tetrahydro-4H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridin-4-one hydrate. The molecular formula is C24H25ClN4O5 (anhydrate) and the molecular weight is 484.93 g/mol (anhydrate).
The structural formula is shown below:
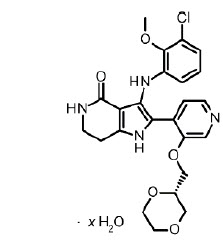
Sevabertinib is present as a non-stoichiometric hydrate as a white to off-white to yellow to pinkish powder. It is slightly soluble in aqueous solution at pH 2, and practically insoluble in aqueous solutions at pH 4.5 and above.
The strength of HYRNUO is based on the anhydrate form. Each HYRNUO tablet for oral use contains 10 mg of sevabertinib. The inactive ingredients are: cellulose microcrystalline, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate. The tablet film coating contains ferric oxide red, hypromellose 5 cP, and macrogol 3350.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sevabertinib is a reversible kinase inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). It also exhibits activity against epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
In vitro, sevabertinib inhibited the phosphorylation of HER2 and downstream signaling in cancer cells with HER2 alterations and proliferation of cancer cells overexpressing wild-type HER2 or harboring HER2 mutations.
In vivo, sevabertinib demonstrated antitumor activity in subcutaneous mouse xenograft models derived from human NSCLC tumors harboring an activating HER2 exon 20 mutation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationship
Higher sevabertinib exposure, across the dose range of 10 to 80 mg total daily dose (0.25 to 2 times the recommended dosage), was associated with an increased incidence of diarrhea (all grade and Grade ≥3) and rash.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At 2 times the maximum recommended dose, a mean increase in the QTc interval >20 ms was not observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Sevabertinib pharmacokinetics were observed at steady state in patients with advanced NSCLC harboring activating HER2 or EGFR mutations at the approved recommended dosage and are presented as mean (CV%), unless otherwise specified.
Sevabertinib maximum concentration (Cmax) is 902 (45%) ng/mL and total systemic exposure (AUC) is 6,640 (50%) ng*h/mL. Sevabertinib Cmax and AUC increase in a dose-proportional manner across the dose range of 10 mg to 80 mg (0.25 to 2 times the approved recommended total daily dose). Sevabertinib accumulation is approximately 1.7-fold for AUC and 1.3-fold for Cmax at the approved recommended dosage. Steady state is achieved within 3 days.
Absorption
Sevabertinib median (min, max) time to maximum concentrations (Tmax) is approximately 2 hours (0.5, 8.2 hours) after a single dose.
Effect of Food
Sevabertinib Cmax decreases by 56% and AUC decreases by 28% with a high-fat meal (1000 calories, 50% fat) in healthy subjects. No clinically significant differences in sevabertinib pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of a low-fat meal (400 calories, 25% fat).
Distribution
Sevabertinib apparent volume of distribution is 28 L (42%). Sevabertinib plasma protein binding is 95%. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio is 0.6.
Elimination
Sevabertinib effective half-life is approximately 8 hours (33%) with an apparent clearance of 3.1 L/hour (38%).
Metabolism
Sevabertinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A (major), CYP1A1 (minor), and glucuronidation (minor).
Excretion
After a single oral dose of radiolabeled sevabertinib 40 mg to healthy subjects, approximately 84% of the dose was recovered in feces (14% unchanged) and approximately 10% in urine (1.3% unchanged).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant effects in the pharmacokinetics of sevabertinib were observed based on age (18 to 91 years), race (27% White, 65% Asian, 2.7% Black/African American), sex, body weight (29 to 155 kg), smoking status, eGFR 30 to < 90 mL/min, or mild hepatic impairment (AST > ULN and total bilirubin ≤ ULN; or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5× ULN and any AST). The effect of severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to <30 mL/min), end-stage renal disease (eGFR <15 mL/min), moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin >1.5 to 3× ULN and any AST) or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3× ULN and any AST) on sevabertinib pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Sevabertinib AUC increased 2.3-fold and Cmax 1.6-fold following concomitant use of itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) 200 mg once daily.
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Sevabertinib AUC decreased by 79% and Cmax by 57% following concomitant use of carbamazepine (strong CYP3A inducer) 600 mg once daily.
CYP3A Substrates: Midazolam (CYP3A substrate) AUC increased 2-fold and Cmax 1.8-fold following concomitant use of HYRNUO 20 mg twice daily.
P-gp Substrates: Dabigatran etexilate (P-gp substrate) AUC increased 1.4-fold following concomitant use of HYRNUO 20 mg twice daily.
BCRP Substrates: Rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate) AUC increased 1.3-fold and Cmax 1.4-fold following concomitant use of HYRNUO 20 mg twice daily.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in sevabertinib pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with esomeprazole (proton pump inhibitor).
In Vitro studies
CYP450 Enzymes: Sevabertinib inhibits CYP1A1 and CYP2C8 but does not inhibit CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, or CYP2E1. Sevabertinib does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP2C19.
Transporter Systems: Sevabertinib is a substrate of P-gp, and BCRP. Sevabertinib inhibits MATE1 and MATE2-K but does not inhibit OATP1B1, OATP1B3, MRP2, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, or OCT2.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with sevabertinib.
Mutagenesis
Sevabertinib was not genotoxic in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) and an in vitro micronucleus assay, or an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility studies have not been conducted with sevabertinib.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 TKD Activating Mutations
The efficacy of HYRNUO was evaluated in SOHO-01 (NCT05099172), an open-label, single-arm, multicenter, multi-cohort clinical study. Eligible patients (Groups D and E) were required to have previously treated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) activating mutations and have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) of 0 or 1. HER2 (ERBB2) activating mutations were determined in tumor tissue or plasma by local laboratories prior to enrollment. Patients with treated, stable and asymptomatic brain metastases were eligible. Patients with symptomatic CNS metastases, clinically significant cardiac disease, and history of steroid dependent interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis were excluded.
Patients received HYRNUO 20 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcomes were confirmed objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR), as assessed by Blinded Independent Central Review (BICR) using RECIST v1.1.
The efficacy population included 70 patients from Group D, and 52 patients from Group E, with advanced non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) activating mutations based on prospective local testing. Of the 122 patients in these combined cohorts, tumor tissue samples from 67.2% (82/122) of patients were retrospectively tested using Oncomine™ Dx Target Test (Life Technologies Corporation). While 92.7% (76/82) of samples were positive for HER2 (ERBB2) TKD activating mutations, 7.3% (6/82) were unevaluable, and there were no samples with negative status for HER2 (ERBB2) TKD activating mutations.
NSCLC Previously Treated, Naïve to HER2-Targeted Therapy: Group D
Efficacy was evaluated in 70 patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) TKD activating mutations who had received prior systemic therapy but were naïve to therapy targeting HER2 mutations. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics of the efficacy population were: median age 59 years (range 29 to 77 years); 67% female; 70% Asian, 23% White, 1.4% Black or African American, 6% race not reported; 2.9% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Patients had an ECOG performance status of either 0 (39%) or 1 (61%); 69% were never-smokers, 29% were former smokers and 2.9% were current smokers. All patients had adenocarcinoma histology. Ninety-one percent (91%) of patients had stage IV disease and 20% had stable brain metastases. The median number of prior therapies was 1 (range 1 to 8); 94% of patients received prior platinum-based chemotherapy, 71% received prior immunotherapy, and 69% received both in combination. Among the patients, 70% of patients had a Y772_A775dup (YVMA) exon 20 insertion.
Efficacy results for SOHO-01 Group D are presented in Table 8.
Table 8: Efficacy Results for SOHO-01: Group D* Efficacy Parameter HYRNUO
N=70CI – Confidence Interval - * ORR 95% CI calculated using Clopper-Pearson method.
- † Observed proportion of responding patients with duration of response beyond landmark time.
- ‡ Kaplan-Meier estimate.
Objective Response Rate (ORR)*, (95% CI) 71% (59, 82) Complete Response 2.9% Partial Response 69% Duration of Response (DOR)† N=50 Median, months (95% CI)‡ 9.2 (6.3, 15.0) DOR ≥6 months† 54% DOR ≥12 months† 18% NSCLC Previously Treated, Including Prior HER2 Targeted Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs): Group E
Efficacy was evaluated in 52 patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) TKD activating mutations who had received prior systemic therapy including HER2-targeted ADCs.
Baseline demographic and disease characteristics of this efficacy population were: median age 65 years (range 35 to 91 years); 67% female; 62% Asian, 27% White, 6% Black or African American, 6% race not reported; 1.9% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Patients had an ECOG performance status of either 0 (29%) or 1 (71%); 65% were never-smokers, and 35% were former smokers. All patients had adenocarcinoma histology. Eighty-five percent (85%) of patients had stage IV disease and 29% had stable brain metastases. The median number of prior therapies was 2 (range 1 to 8), 77% of patients received prior platinum-based chemotherapy, 56% received prior immunotherapy, and 56% received both in combination. Among the patients, 77% of patients had a Y772_A775dup (YVMA) exon 20 insertion.
The ORR was 38% (95% CI 25, 53), with 6% of patients having a complete response and 33% of patients having a partial response. The median DOR was 7 months (95% CI 5.6, NE); ranging from 1+ to 17.2+ months based on the observed DOR. The observed proportion of responding patients with DOR of ≥6 months and ≥12 months was 60% and 10%, respectively.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
HYRNUO 10 mg tablets are supplied as red brown film-coated, round, biconvex tablets debossed with "SE" on one side and "10" on the other side.
HYRNUO tablets are packaged in a HDPE bottle of 120 tablets closed with a child-resistant screw cap.
NDC: 50419-397-01
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Diarrhea
Inform patients that HYRNUO can cause severe diarrhea. At the first sign of diarrhea or increased bowel movement frequency, instruct patients to start an antidiarrheal treatment (e.g., loperamide), to increase their fluid and electrolyte intake, and to immediately contact their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients that HYRNUO can cause severe hepatotoxicity characterized by elevations of liver function tests. Inform patients that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor hepatic function. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Inform patients that HYRNUO can cause severe ILD/pneumonitis. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Ocular Toxicity
Inform patients that HYRNUO can cause ocular toxicity. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening ocular symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Pancreatic Enzyme Elevation
Inform patients that HYRNUO can cause pancreatic enzyme elevation. Inform patients that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor pancreatic function. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms associated with pancreatic enzyme elevation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HYRNUO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Dosage and Administration
- Instruct patients to take HYRNUO twice daily with food. Each tablet should be swallowed whole [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Instruct patients that if a dose of HYRNUO is missed to take the missed dose as soon as they remember prior to the next scheduled dose. Advise patients not to take two doses together to make up for a missed dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Instruct patients that if a dose of HYRNUO is vomited not to take an additional dose but to take the next dose at the next scheduled time [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products. Inform patients to avoid St. John's wort, grapefruit, or grapefruit juice while taking HYRNUO [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
HYRNUO® (Her noo' oh)
(sevabertinib)
tablets, for oral useThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 11/2025 What is HYRNUO?
HYRNUO is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults with a type of lung cancer called non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that:- has spread within your chest or to other parts of the body, and
- has a certain abnormal human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) gene(s), and
- who have received a previous treatment (systemic therapy).
It is not known if HYRNUO is safe and effective in children.Before taking HYRNUO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have liver problems.
- have lung or breathing problems other than lung cancer.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. HYRNUO can harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider will do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with HYRNUO.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of HYRNUO.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during your treatment with HYRNUO.
Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant:- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 week after your last dose of HYRNUO.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you and your partner.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if HYRNUO passes into breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of HYRNUO.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. HYRNUO may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how HYRNUO works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take HYRNUO? - Take HYRNUO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking HYRNUO unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Take HYRNUO 2 times a day with food.
- Swallow HYRNUO tablets whole with a glass of water.
- Do not cut, crush or chew HYRNUO tablets.
- If you miss a dose of HYRNUO, take your prescribed dose as soon as you remember before the next scheduled dose. Do not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
- If you vomit after taking a dose of HYRNUO, do not make up the dose. Take your next dose at your regularly scheduled time.
What should I avoid while taking HYRNUO? - Avoid eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice during treatment with HYRNUO. Grapefruit may increase the amount of HYRNUO in your blood.
What are the possible side effects of HYRNUO?
HYRNUO may cause serious side effects, including:- diarrhea. Diarrhea is common and can be severe during treatment with HYRNUO and usually occurs in the first week of treatment. Diarrhea can cause the loss of body fluids (dehydration) and salts (electrolyte imbalances). At the first signs of diarrhea (loose stool) or increased bowel movements, tell your healthcare provider right away, drink plenty of fluids and start treatment for diarrhea as soon as possible. You should have an anti-diarrhea medicine available before you start taking HYRNUO.
- liver problems. HYRNUO can cause increases in liver blood tests which may be severe. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver function before you start taking and during treatment with HYRNUO. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs and symptoms of liver problems including:
- yellowing of the skin or white part of your eyes (jaundice)
- dark urine
- pale stools
- tiredness or weakness
- nausea or vomiting
- loss of appetite
- pain on the upper right side of your stomach
- lung problems. HYRNUO may cause severe lung problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any new or worsening symptoms of lung problems during treatment with HYRNUO, including:
- cough
- fever
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- eye problems. HYRNUO can cause eye problems that can lead to temporary loss of vision. Your healthcare provider may send you to see an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) if you develop new or worsening eye problems during treatment with HYRNUO.
-
pancreas problems. HYRNUO may cause increases in certain pancreatic lab tests (amylase and lipase). Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your pancreatic function before and during treatment with HYRNUO. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs and symptoms of pancreas problems, including:
- upper stomach pain that may spread to your back and get worse with eating
- weight loss
- nausea or vomiting
Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or completely stop your treatment with HYRNUO if you have certain side effects.
The most common side effects of HYRNUO include: - rash
- nail problems including infection and inflammation
- mouth sores
- nausea
- changes in certain blood tests
These are not all of the possible side effects of HYRNUO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store HYRNUO? - Store HYRNUO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- HYRNUO comes in a child-resistant container.
General information about the safe and effective use of HYRNUO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use HYRNUO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give HYRNUO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about HYRNUO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in HYRNUO?
Active ingredient: sevabertinib
Inactive ingredients: cellulose microcrystalline, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate. Tablet film coating: ferric oxide red, hypromellose 5 cP, and macrogol 3350.Manufactured for: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc., Whippany, NJ 07981 USA
For more information, call Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at Bayer at 1-888-842-2937 or go to www.HYRNUO-us.com - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Carton
NDC: 50419-397-01
Rx onlyHYRNUO®
(sevabertinib) tablets10 mg
— 120 film-coated tablets
— Oral useBAYER

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HYRNUO
sevabertinib tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 50419-397 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEVABERTINIB (UNII: 2A7VPM5RWH) (SEVABERTINIB - UNII:2A7VPM5RWH) SEVABERTINIB 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) CROSPOVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2S7830E561) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) Product Characteristics Color RED (red brown) Score no score Shape ROUND (biconvex) Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code SE;10 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 50419-397-01 120 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/19/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219972 11/19/2025 Labeler - Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. (005436809) Registrant - Bayer AG (323208116) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bayer AG 323208116 ANALYSIS(50419-397) , API MANUFACTURE(50419-397) , PACK(50419-397)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
