VIOKACE- pancrelipase tablet
Viokace by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Viokace by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Allergan, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIOKACE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VIOKACE
VIOKACE® (pancrelipase) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VIOKACE® is a combination of porcine-derived lipases, proteases, and amylases. VIOKACE, in combination with a proton pump inhibitor, is indicated in adults for the treatment of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatectomy. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
VIOKACE is not interchangeable with any other pancrelipase product. VIOKACE tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not crush or chew tablets. (2.1) Dosing should not exceed the recommended maximum dosage set forth by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conferences Guidelines. (2.2)
- Begin with 500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal to a maximum of 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or less than or equal to 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day), or less than 4,000 lipase units/g fat ingested per day. (2.2)
- Individualize dosage based on clinical symptoms, the degree of steatorrhea present and the fat content of the diet. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Fibrosing colonopathy is associated with high-dose use of pancreatic enzyme replacement. Exercise caution when doses of VIOKACE exceed 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or greater than 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day). (5.1)
- To avoid irritation of oral mucosa, do not chew VIOKACE or retain in the mouth. (5.2)
- Exercise caution when prescribing VIOKACE to patients with gout, renal impairment, or hyperuricemia. (5.3)
- There is theoretical risk of viral transmission with all pancreatic enzyme products including VIOKACE. (5.4)
- Exercise caution when administering pancrelipase to a patient with a known allergy to proteins of porcine origin. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adverse reactions occurring in at least 2 chronic pancreatitis or pancreatectomy patients (greater than or equal to 7%) receiving VIOKACE are biliary tract stones and anal pruritus. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan USA, Inc. at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- The safety and effectiveness of VIOKACE in pediatric patients have not been established. (8.4)
- VIOKACE use in pediatric patients may result in suboptimal growth due to tablet degradation in the gastric environment. In general, delayed-release (enteric-coated) capsules should be used for pediatric patients. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2020
- Begin with 500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal to a maximum of 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or less than or equal to 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day), or less than 4,000 lipase units/g fat ingested per day. (2.2)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration
2.2 Dosage
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fibrosing Colonopathy
5.2 Potential for Irritation to Oral Mucosa
5.3 Potential for Risk of Hyperuricemia
5.4 Potential for Viral Exposure from the Product Source
5.5 Allergic Reactions
5.6 Potential for Exacerbation of Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Dosing and Administration
17.2 Fibrosing Colonopathy
17.3 Allergic Reactions
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
VIOKACE is not interchangeable with any other pancrelipase product.
VIOKACE is orally administered. Therapy should be initiated at the lowest recommended dose and gradually increased. The dosage of VIOKACE should be individualized based on clinical symptoms, the degree of steatorrhea present, and the fat content of the diet as described in the Limitations on Dosing below [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.1 Administration
Since VIOKACE is not enteric-coated, it should be taken in combination with a proton pump inhibitor [see Indications and Usage (1)].
VIOKACE should be taken during meals or snacks, with sufficient fluid. Tablets should be swallowed whole. Do not crush or chew tablets. Care should be taken to ensure that no drug is retained in the mouth to avoid mucosal irritation.
2.2 Dosage
Dosage recommendations for pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy were published following the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conferences.1,2,3 VIOKACE should be administered in a manner consistent with the recommendations of the Conferences provided in the following paragraph. Only the adult dosing guidelines are shown below. Patients may be dosed on a fat ingestion-based or actual body weight-based dosing scheme.
Additional recommendations for pancreatic enzyme therapy in patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatectomy are based on a clinical trial conducted in these populations.
Enzyme dosing should begin with 500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal to a maximum of 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or less than or equal to 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day), or less than 4,000 lipase units/g fat ingested per day.
Usually, half of the prescribed VIOKACE dose for an individualized full meal should be given with each snack. The total daily dosage should reflect approximately three meals plus two or three snacks per day.
In one clinical trial, patients received VIOKACE at a dose of 125,280 lipase units per meal while consuming 100 g of fat per day [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Lower starting doses recommended in the literature are consistent with the 500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal lowest starting dose recommended for adults in the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conferences Guidelines.1, 2, 3, 4 The initial starting dose and increases in the dose per meal should be individualized based on clinical symptoms, the degree of steatorrhea present, and the fat content of the diet.
Limitations on Dosing
Dosing should not exceed the recommended maximum dosage set forth by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conferences Guidelines.1,2,3 If symptoms and signs of steatorrhea persist, the dosage may be increased by the healthcare professional. Patients should be instructed not to increase the dosage on their own. There is great inter-individual variation in response to enzymes; thus, a range of doses is recommended. Changes in dosage may require an adjustment period of several days. If doses are to exceed 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal, further investigation is warranted. Doses greater than 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or greater than 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day) should be used with caution and only if they are documented to be effective by 3-day fecal fat measures that indicate a significantly improved coefficient of fat absorption. Doses greater than 6,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal have been associated with colonic stricture, indicative of fibrosing colonopathy, in children less than 12 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Patients currently receiving higher doses than 6,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal should be examined and the dosage either immediately decreased or titrated downward to a lower range.
-
3
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
The active ingredient in VIOKACE evaluated in clinical trials is lipase. VIOKACE is dosed in lipase units.
Other active ingredients include protease and amylase. Each VIOKACE tablet strength contains the specified amounts of lipase, protease, and amylase as follows:
- 10,440 USP units of lipase; 39,150 USP units of protease; 39,150 USP units of amylase tablets are tan, round, biconvex and have VIO9111 engraved on one side and 9111 on the other side.
- 20,880 USP units of lipase; 78,300 USP units of protease; 78,300 USP units of amylase tablets are tan, oval, biconvex with V16 engraved on one side and 9116 on the other side.
- 10,440 USP units of lipase; 39,150 USP units of protease; 39,150 USP units of amylase tablets are tan, round, biconvex and have VIO9111 engraved on one side and 9111 on the other side.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fibrosing Colonopathy
Fibrosing colonopathy has been reported following treatment with different pancreatic enzyme products.5,6 Fibrosing colonopathy is a rare, serious adverse reaction initially described in association with high-dose pancreatic enzyme use, usually over a prolonged period of time and most commonly reported in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. The underlying mechanism of fibrosing colonopathy remains unknown. Doses of pancreatic enzyme products exceeding 6,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal have been associated with colonic stricture in children less than 12 years of age.1 Patients with fibrosing colonopathy should be closely monitored because some patients may be at risk of progressing to stricture formation. It is uncertain whether regression of fibrosing colonopathy occurs.1 It is generally recommended, unless clinically indicated, that enzyme doses should be less than 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or less than 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day) or less than 4,000 lipase units/g fat ingested per day [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Doses greater than 2,500 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal (or greater than 10,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per day) should be used with caution and only if they are documented to be effective by 3-day fecal fat measures that indicate a significantly improved coefficient of fat absorption. Patients receiving higher doses than 6,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal should be examined and the dosage either immediately decreased or titrated downward to a lower range.
5.2 Potential for Irritation to Oral Mucosa
Care should be taken to ensure that no drug is retained in the mouth to avoid irritation of oral mucosa, and/or loss of enzyme activity. VIOKACE should not be crushed or chewed [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)].
5.3 Potential for Risk of Hyperuricemia
Caution should be exercised when prescribing VIOKACE to patients with gout, renal impairment, or hyperuricemia. Porcine-derived pancreatic enzyme products contain purines that may increase blood uric acid levels.
5.4 Potential for Viral Exposure from the Product Source
VIOKACE is sourced from pancreatic tissue from pigs used for food consumption. Although the risk that VIOKACE will transmit an infectious agent to humans has been reduced by testing for certain viruses during manufacturing and by inactivating certain viruses during manufacturing, there is a theoretical risk for transmission of viral disease, including diseases caused by novel or unidentified viruses. Thus, the presence of porcine viruses that might infect humans cannot be definitely excluded. However, no cases of transmission of an infectious illness associated with the use of porcine pancreatic extracts have been reported.
5.5 Allergic Reactions
Caution should be exercised when administering pancrelipase to a patient with a known allergy to proteins of porcine origin. Rarely, severe allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, asthma, hives, and pruritus, have been reported with other pancreatic enzyme products with different formulations of the same active ingredient (pancrelipase). The risks and benefits of continued VIOKACE treatment in patients with severe allergy should be taken into consideration with the overall clinical needs of the patient.
-
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most serious adverse reactions reported with different pancreatic enzyme products of the same active ingredient (pancrelipase) that are described elsewhere in the label include fibrosing colonopathy, hyperuricemia and allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3 and 5.5)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The short-term safety of VIOKACE was assessed in a single, multicenter, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of 50 patients, ages 24-70 years, with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) due to chronic pancreatitis or pancreatectomy. VIOKACE Tablets (20,880 USP units of lipase per tablet) or placebo were administered as 22 tablets per day (6 tablets with 3 meals and 2 tablets with 2 of 3 snacks). Duration of exposure ranged from 6 to 7 days. The majority of the subjects were Caucasian (96%) and male (82%).
The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 7%) were biliary tract stones and anal pruritus. Table 1 enumerates adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1 patient (greater than or equal to 3%) treated with VIOKACE at a higher rate than with placebo. Two adverse reactions reported in greater than one patient were biliary tract stones and anal pruritus.
TABLE 1
Adverse Reactions Occurring in at Least 1 Patient (greater than or equal to 3%) in Chronic Pancreatitis or PancreatectomyTreatment Group MedDRA Primary System Organ Class/
Adverse ReactionsVIOKACE
(N=30)Placebo
(N=20)Blood And Lymphatic System Disorders Anemia 1 ( 3%) 0 Gastrointestinal Disorders Anal pruritus 2 ( 7%) 0 Abdominal pain 1 ( 3%) 0 Ascites 1 ( 3%) 0 Flatulence 1 ( 3%) 0 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Edema peripheral 1 ( 3%) 0 Hepatobiliary Disorders Biliary tract stones 2 ( 7%) 0 Hydrocholecystis 1 ( 3%) 0 Infections and Infestations Viral infection 1 ( 3%) 0 Nervous System Disorders Headache 1 ( 3%) 0 Renal and Urinary Disorders Renal cyst 1 ( 3%) 0 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Rash 1 ( 3%) 0 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Post-marketing data for VIOKACE have been available since 2003. The safety data are similar to that described below. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Pancreatic enzyme products (delayed and immediate-release) with different formulations of the same active ingredient (pancrelipase) have been used for the treatment of patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to cystic fibrosis and other conditions, such as chronic pancreatitis. The long-term safety profile of these products has been described in the medical literature. The most serious adverse events included fibrosing colonopathy, distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (DIOS), recurrence of pre-existing carcinoma, and severe allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, asthma, hives, and pruritus. The most commonly reported adverse events were gastrointestinal disorders, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation and nausea, and skin disorders including pruritus, urticaria and rash.
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Published data from case reports with pancrelipase use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Pancrelipase is minimally absorbed systematically; therefore, maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with pancrelipase.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of pancrelipase in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Pancrelipase is minimally absorbed systemically following oral administration, therefore maternal use is not expected to result in clinically relevant exposure of breastfed infants to the drug. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for VIOKACE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from VIOKACE or from the underlying maternal conditions.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VIOKACE in pediatric patients have not been established. In general, delayed-release (enteric-coated) capsules should be used for pediatric patients. Due to greater degradation in the gastric environment, VIOKACE, a non-enteric-coated, pancreatic enzyme replacement product, may have decreased bioavailability and therefore may be less efficacious than enteric-coated formulations.7, 8 Thus, use of VIOKACE in pediatric patients may increase the risk of inadequate treatment of pancreatic insufficiency and result in suboptimal weight gain, malnutrition and/or need for larger doses of pancreatic enzyme replacement [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] The efficacy of VIOKACE was established in adult patients with concomitant proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy. The long-term safety of PPI use in pediatric patients has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of VIOKACE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10
OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports of overdose in clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance with VIOKACE. Chronic high doses of pancreatic enzyme products have been associated with fibrosing colonopathy and colonic strictures [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. High doses of pancreatic enzyme products have been associated with hyperuricosuria and hyperuricemia, and should be used with caution in patients with a history of hyperuricemia, gout, or renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
11
DESCRIPTION
VIOKACE is a pancreatic enzyme preparation for oral administration consisting of pancrelipase, an extract derived from porcine pancreatic glands. Pancrelipase contains multiple enzyme classes, including porcine-derived lipases, amylases, and proteases.
Pancrelipase is a beige-white amorphous powder. It is miscible in water and practically insoluble in alcohol.
The active ingredient evaluated in clinical trials is lipase. VIOKACE is dosed by lipase units.
Other active ingredients include protease and amylase.
Inactive ingredients in VIOKACE include: colloidal silicon dioxide, crosscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, stearic acid and talc.
10,440 USP units of lipase; 39,150 USP units of protease; 39,150 USP units of amylase tablets are tan, round biconvex and have VIO9111 engraved on one side and 9111 on the other side.
20,880 USP units of lipase; 78,300 USP units of protease; 78,300 USP units of amylase tablets are tan, oval, biconvex with V16 engraved on one side and 9116 on the other side.
-
12
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The pancreatic enzymes in VIOKACE catalyze the hydrolysis of fats to monoglycerides, glycerol and free fatty acids, proteins into peptides and amino acids, and starches into dextrins and short chain sugars such as maltose and maltriose in the duodenum and proximal small intestine, thereby acting like digestive enzymes physiologically secreted by the pancreas.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14
CLINICAL STUDIES
The short-term safety and efficacy of VIOKACE were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study comparing VIOKACE Tablets (20,880 USP units of lipase per tablet) to placebo in 50 patients, ages 24 to 70, with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) due to chronic pancreatitis (CP) or pancreatectomy. Eighteen patients had a history of pancreatectomy (11 were treated with VIOKACE). All patients were maintained on a controlled high fat diet of 100 grams of fat per day. After a wash-out period (6 to 7 days), patients were randomized to a fixed dose of VIOKACE (22 tablets per day; 6 tablets per meal and 2 tablets with 2 of 3 snacks) or placebo, in combination with a proton pump inhibitor. Forty-nine patients completed the double-blind treatment period (6 to 7 days); 29 patients received VIOKACE, and 20 patients received placebo.
The coefficient of fat absorption (CFA) was determined by a 72-hour stool collection during both treatments, when both fat excretion and fat ingestion were measured.
The wash-out period mean CFA was 48% in the VIOKACE treatment group and was 57% in the placebo group. At the end of the double-blind treatment period, the mean CFA was 86% with VIOKACE treatment compared to 58% with placebo. The mean difference in CFA at the end of the double-blind treatment period was 28 percentage points in favor of VIOKACE treatment with 95% Confidence Interval of (21, 37) and p < 0.0001.
Subgroup analyses of the CFA results showed that mean change in CFA with VIOKACE treatment (from the washout period to the end of the double-blind period) was greater in patients with lower wash-out period CFA values than in patients with higher wash-out period CFA values.
Only 2 of the patients with a history of total pancreatectomy were treated with VIOKACE. One of these patients had a CFA of 12% during the wash-out period and a CFA of 90% at the end of the double-blind period; the other patient had a CFA of 38% during the wash-out period and a CFA of 77% at the end of the double-blind period. The remaining 9 patients with a history of partial pancreatectomy treated with VIOKACE had a mean CFA of 56% during the wash-out period and a mean CFA of 86% at the end of the double-blind period.
-
15
REFERENCES
1Borowitz DS, Grand RJ, Durie PR, et al. Use of pancreatic enzyme supplements for patients with cystic fibrosis in the context of fibrosing colonopathy. Journal of Pediatrics. 1995; 127: 681-684.
2Borowitz DS, Baker RD, Stallings V. Consensus report on nutrition for pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology Nutrition. 2002 Sep; 35: 246-259.
3Stallings VA, Start LJ, Robinson KA, et al. Evidence-based practice recommendations for nutrition-related management of children and adults with cystic fibrosis and pancreatic insufficiency: results of a systematic review. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2008; 108: 832-839.
4Dominguez-Munoz JE, Pancreatic enzyme therapy for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Current Gastroenterology Reports. 2007; 9: 116-122.
5Smyth RL, Ashby D, O’Hea U, et al. Fibrosing colonopathy in cystic fibrosis: results of a case-control study. Lancet. 1995; 346: 1247-1251.
6FitzSimmons SC, Burkhart GA, Borowitz DS, et al. High-dose pancreatic-enzyme supplements and fibrosing colonopathy in children with cystic fibrosis. New England Journal of Medicine. 1997; 336: 1283-1289.
7Gow R, Francis P, Bradbear R, et al. Comparative study of varying regimens to improve steatorrhoea and creatorrhoea in cystic fibrosis: effectiveness of an enteric-coated preparation with and without antacids and cimetidine. Lancet. November 14, 1981: 1071-1074.
8Ansaldi-Balocco N, Santini B, Sarchi C. Efficacy of pancreatic enzyme supplementation in children with cystic fibrosis: comparison of two preparations by random crossover study and a retrospective study of the same patients at two different ages. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988;7 Suppl 1:S40-5.
-
16
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VIOKACE tablets
10,440 USP units of lipase; 39,150 USP units of protease; 39,150 USP units of amylase
Each VIOKACE tablet is available as a tan, round, biconvex tablet with VIO9111 engraved on one side and 9111 on the other side supplied in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC: 58914-112-10).
VIOKACE tablets
20,880 USP units of lipase; 78,300 USP units of protease; 78,300 USP units of amylase
Each VIOKACE tablet is available as a tan, oval, biconvex tablet with V16 engraved on one side and 9116 on the other side supplied in bottles of 100 tablets (NDC: 58914-117-10).
Storage and Handling
Avoid heat. VIOKACE tablets should be stored in a dry place in the original container. Store at room temperature (20-25°C, 68-77°F), brief excursion permitted up to 40°C (104°F) for up to 24 hrs. After opening, keep the container tightly closed between uses to protect from moisture.
VIOKACE is dispensed in bottles containing a desiccant. The desiccant packet should not be eaten. The desiccant packet will protect the product from moisture.
-
17
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
“See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)”
17.1 Dosing and Administration
- Instruct patients and caregivers that VIOKACE should only be taken as directed by their doctor. Patients should be advised that the total daily dose should not exceed 10,000 lipase units/kg body weight/day unless clinically indicated. This needs to be especially emphasized for patients eating multiple snacks and meals per day. Patients should be informed that if a dose is missed, the next dose should be taken with the next meal or snack as directed. Doses should not be doubled [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- Instruct patients and caregivers that VIOKACE should always be taken with food. Patients should swallow the intact tablets with adequate amounts of liquid at mealtimes [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
17.2 Fibrosing Colonopathy
Advise patients and caregivers to follow dosing instructions carefully, as doses of pancreatic enzyme products exceeding 6,000 lipase units/kg of body weight per meal have been associated with colonic strictures in children below the age of 12 years [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
17.3 Allergic Reactions
Advise patients and caregivers to contact their healthcare professional immediately if allergic reactions to VIOKACE develop [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Instruct patients and caregivers that VIOKACE should only be taken as directed by their doctor. Patients should be advised that the total daily dose should not exceed 10,000 lipase units/kg body weight/day unless clinically indicated. This needs to be especially emphasized for patients eating multiple snacks and meals per day. Patients should be informed that if a dose is missed, the next dose should be taken with the next meal or snack as directed. Doses should not be doubled [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
VIOKACE ® (vye-oh-kase)
(pancrelipase)
tabletsRead this Medication Guide before you start taking VIOKACE and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. What is the most important information I should know about VIOKACE?
VIOKACE may increase your chance of having a rare bowel disorder called fibrosing colonopathy. This condition is serious and may require surgery. The risk of having this condition may be reduced by following the dosing instructions that your doctor gave you.
Call your doctor right away if you have any unusual or severe:
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
-
bloating
-
trouble passing stool (having bowel movements)
- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
What is VIOKACE? - VIOKACE is a prescription medicine used with a proton pump inhibitor medicine (PPI) to treat adults who cannot digest food normally. Adults with swelling of the pancreas that lasts a long time (chronic pancreatitis), or who have had some or all of their pancreas removed (pancreatectomy) may not digest food normally because they do not make enough enzymes or because their enzymes are not released into the bowel (intestine).
- VIOKACE contains a mixture of digestive enzymes (including lipases, proteases, and amylases) from pig pancreas.
- It is not known if VIOKACE is safe and effective in children. Use of VIOKACE in children may result in poor nutrition and slowing of growth.
What should I tell my doctor before taking VIOKACE?
Before taking VIOKACE, tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- are allergic to pork (pig) products
- have a history of blockage of your intestines, or scarring or thickening of your bowel wall (fibrosing colonopathy)
- have gout, kidney disease, or a condition called high blood uric acid (hyperuricemia)
- have trouble swallowing tablets
- are lactose intolerant
- have any other medical condition
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if VIOKACE passes into your breast milk. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take VIOKACE.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take VIOKACE? - Take VIOKACE tablets exactly as your doctor tells you.
- You should not switch VIOKACE with any other pancreatic enzyme product without first talking to your doctor.
- Do not take more tablets in a day than the number your doctor tells you to take (total daily dose).
- Always take VIOKACE with a meal or a snack and enough liquid to swallow VIOKACE completely. If you eat a lot of meals or snacks in a day, be careful not to go over your total daily dose.
- Your doctor may change your dose based on the amount of fatty foods you eat or based on your weight.
- Your doctor should also prescribe a medicine for you called a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to decrease stomach acid. VIOKACE should be taken with a PPI to help prevent VIOKACE from breaking down in your stomach.
- Swallow VIOKACE tablets whole. Do not crush or chew the tablets. Be careful to make sure that no VIOKACE is left in your mouth. Crushing, chewing or holding the VIOKACE tablets in your mouth may cause irritation in your mouth, or change the way VIOKACE works in your body.
- If you forget to take VIOKACE, wait until your next meal and take your usual number of tablets. Take your next dose at your usual time. Do not take two doses at one time.
What are the possible side effects of VIOKACE?
VIOKACE may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about VIOKACE?”
-
Irritation of the inside of your mouth. This can happen if VIOKACE is not swallowed completely.
-
Increase in blood uric acid levels. This may cause worsening of swollen, painful joints (gout) caused by an increase in your blood uric levels.
- Allergic reactions, including trouble with breathing, skin rashes, or swollen lips.
The most common side effects of VIOKACE include:
- you can develop stones that form in your gallbladder and the tubes that carry bile to your small intestines.
- anal itching
VIOKACE and other pancreatic enzyme products are made from the pancreas of pigs, the same pigs people eat as pork. These pigs may carry viruses. Although it has never been reported, it may be possible for a person to get a viral infection from taking pancreatic enzyme products that come from pigs.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects of VIOKACE. For more information ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Allergan at 1-800-678-1605.How should I store VIOKACE?
- Store VIOKACE at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Avoid heat.
- Keep VIOKACE in a dry place and in its original container.
- After opening the bottle, keep it closed tightly between uses to protect from moisture.
- The VIOKACE bottle contains a desiccant packet to help keep your medicine dry (protect it from moisture). Do not eat or throw away the desiccant packet.
General information about the safe and effective use of VIOKACE
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use VIOKACE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VIOKACE to other people to take, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about VIOKACE. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about VIOKACE that is written for healthcare providers.
For more information, go to www.allergan.com or call toll-free 1-800-678-1605.What are the ingredients in VIOKACE?
Active ingredient: lipase, protease and amylase
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crosscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, stearic acid and talc.Distributed by:
Allergan USA, Inc.
Madison, NJ 07940
Marketed by:
Aptalis Pharma US, Inc
22 Inverness Center Parkway
Birmingham, Alabama 35242
Manufactured by:
Confab Laboratories, Inc.
St. Hubert, Canada
VIOKACE® is a registered trademark Allergan Sales, LLC.
©2020 Allergan. All rights reserved.This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 03/2020
v1.0MG0112
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Rx only
NDC# 58914-112-10
Viokace®
(pancrelipase)
Tablets
Each tablet contains:
10,440 USP Units Lipase
39,150 USP Units Amylase
39,150 USP Units Protease
VIOKACE® is dosed
based on lipase units
100 TABLETS
VIOKACE® tablets should
be swallowed whole. Do not
crush or chew tablets.
Dispense the enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.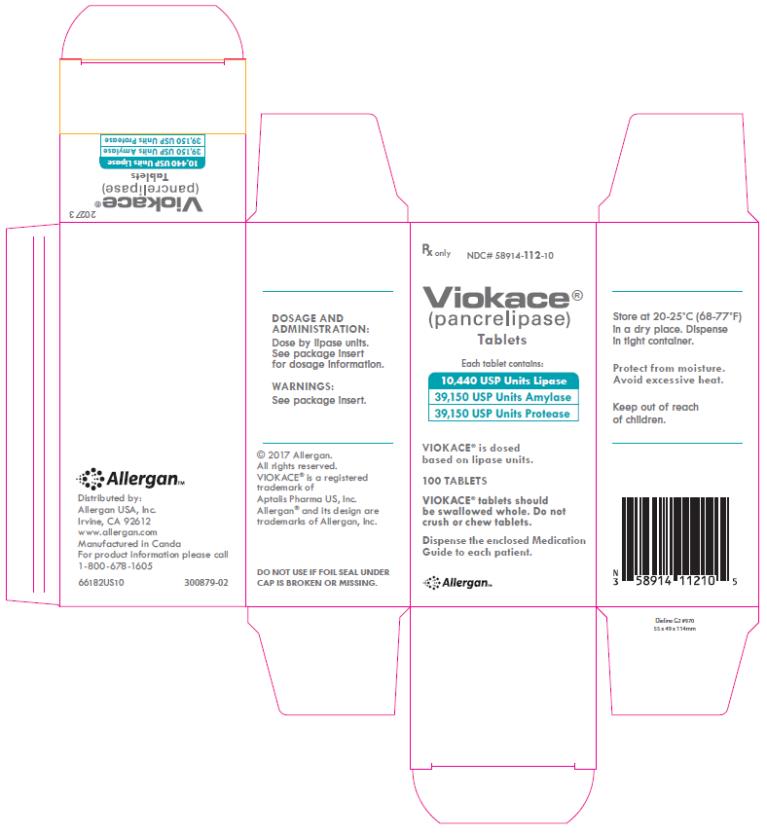
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Rx only
NDC# 58914-117-10
Viokace®
(pancrelipase)
Tablets
Each tablet contains:
20,880 USP Units Lipase
78,300 USP Units Amylase
78,300 USP Units Protease
VIOKACE® is dosed
based on lipase units
100 TABLETS
VIOKACE® tablets should
be swallowed whole. Do not
crush or chew tablets.
Dispense the enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VIOKACE
pancrelipase tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58914-112 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PANCRELIPASE LIPASE (UNII: 8MYC33932O) (PANCRELIPASE LIPASE - UNII:8MYC33932O) PANCRELIPASE LIPASE 10440 [USP'U] PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE (UNII: 3560D81V50) (PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE - UNII:3560D81V50) PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE 39150 [USP'U] PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE (UNII: YOJ58O116E) (PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE - UNII:YOJ58O116E) PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE 39150 [USP'U] Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color BROWN (tan) Score no score Shape ROUND (round biconvex) Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code VIO9111;9111 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58914-112-10 1 in 1 CARTON 03/01/2012 1 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA022542 03/01/2012 VIOKACE
pancrelipase tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58914-117 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PANCRELIPASE LIPASE (UNII: 8MYC33932O) (PANCRELIPASE LIPASE - UNII:8MYC33932O) PANCRELIPASE LIPASE 20880 [USP'U] PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE (UNII: 3560D81V50) (PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE - UNII:3560D81V50) PANCRELIPASE PROTEASE 78300 [USP'U] PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE (UNII: YOJ58O116E) (PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE - UNII:YOJ58O116E) PANCRELIPASE AMYLASE 78300 [USP'U] Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color BROWN (tan) Score no score Shape ROUND (round biconvex) Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code V16;9116 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58914-117-10 1 in 1 CARTON 03/01/2012 1 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA022542 03/01/2012 Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497)
Trademark Results [Viokace]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 VIOKACE 77896647 4533794 Live/Registered |
ALLERGAN SALES, LLC 2009-12-18 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.