CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE aerosol, foam
Clobetasol Propionate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Clobetasol Propionate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Taro Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE FOAM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE FOAM.
CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE foam, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1985RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions (5.2) 04/2018 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Clobetasol propionate foam is a corticosteroid indicated for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis of the scalp and mild to moderate plaque psoriasis of non-scalp regions of the body excluding the face and intertriginous areas in patients 12 years and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Apply a thin layer to the affected skin areas twice daily. (2)
- Limit treatment to 2 consecutive weeks. (2)
- Do not use more than 50 grams per week or more than 21 capfuls per week. (2)
- Discontinue therapy when control is achieved. (2)
- Do not use with occlusive dressings unless directed by physician. (2)
- Avoid use on the face, groin, or axillae, or if skin atrophy is present at the treatment site. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Foam, 0.05% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Clobetasol propionate foam can cause reversible HPA axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency during and after withdrawal of treatment. Risk factors include the use of high-potency topical corticosteroid, use over a large surface area or to areas under occlusion, prolonged use, altered skin barrier, liver failure, and use in pediatric patients. Modify use should HPA axis suppression develop. (5.1, 8.4)
- Clobetasol propionate foam may increase the risk of cataract and glaucoma. If visual symptoms occur, consider referral to an ophthalmologist. (5.2)
- Clobetasol propionate foam is flammable. Avoid fire, flame, or smoking during and immediately following application. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 4%) are application site burning and other application site reactions. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
5.3 Allergic Contact Dermatitis
5.4 Flammable Contents
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Scalp Psoriasis
14.2 Non-scalp Psoriasis
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin layer of clobetasol propionate foam to the affected skin areas twice daily.
Clobetasol propionate foam is a super-high-potency topical corticosteroid; therefore, limit treatment to 2 consecutive weeks. Patients should not use greater than 50 grams per week or more than 21 capfuls per week because of the potential for the drug to suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved.
Clobetasol propionate foam should not be used with occlusive dressings unless directed by a physician.
Clobetasol propionate foam is for topical use only. It is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use.
Avoid contact with eyes. Wash hands after each application.
Avoid use on the face, groin, or axillae, or if skin atrophy is present at the treatment site.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Effects on Endocrine System
Clobetasol propionate foam can cause reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency. This may occur during treatment or after withdrawal of treatment. Factors that predispose a patient to HPA axis suppression include the use of high-potency steroids, large treatment surface areas, prolonged use, use of occlusive dressings, altered skin barrier, liver failure, and young age. Evaluation for HPA axis suppression may be done by using the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test.
In a trial evaluating the effects of clobetasol propionate foam on the HPA axis, 13 subjects applied clobetasol propionate foam to at least 20% of involved body surface area for 14 days. HPA axis suppression was identified in 5 out of 13 subjects (38%) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
If HPA axis suppression is documented, gradually withdraw the drug, reduce the frequency of application, or substitute with a less potent corticosteroid.
Cushing's syndrome and hyperglycemia may also occur due to the systemic effects of the topical corticosteroid. These complications are rare and generally occur after prolonged exposure to excessively large doses, especially of high-potency topical corticosteroids.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.2 Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Use of topical corticosteroids, including clobetasol propionate foam, may increase the risks of glaucoma and posterior subcapsular cataract. Glaucoma and cataracts have been reported in postmarketing experience with the use of topical corticosteroid products, including topical clobetasol products.
Avoid contact of clobetasol propionate foam with eyes. Advise patients to report any visual symptoms and consider referral to an ophthalmologist for evaluation.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Effects on Endocrine System [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In a controlled clinical trial involving 188 subjects with psoriasis of the scalp, there were no localized scalp adverse reactions reported in the subjects treated with clobetasol propionate foam. In 2 controlled clinical trials with clobetasol propionate foam in 360 subjects with psoriasis of non-scalp regions, localized adverse events that occurred in the subjects treated with clobetasol propionate foam included application site burning (10%), application site dryness (<1%), and other application site reactions (4%).
In larger controlled trials with other clobetasol propionate formulations, the most frequently reported local adverse reactions have included burning, stinging, irritation, pruritus, erythema, folliculitis, cracking and fissuring of the skin, numbness of the fingers, skin atrophy, and telangiectasia (all less than 2%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Local adverse reactions to topical corticosteroids may include: striae, itching, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, secondary infection, hypertrichosis, and miliaria.
Ophthalmic adverse reactions may include: cataracts, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and central serous chorioretinopathy.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on clobetasol propionate foam use in pregnant women to inform of a drug-associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes.
Published data report a significantly increased risk of low birthweight with the use of greater than 300 grams of potent or very potent topical corticosteroid during a pregnancy. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus and to use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible (see Data). In animal reproduction studies, increased malformations, such as cleft palate and skeletal abnormalities, were observed after subcutaneous administration of clobetasol propionate to pregnant mice and rabbits. No comparison of animal exposure with human exposure was computed.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Multiple observational studies found no significant associations between maternal use of topical corticosteroids of any potency and congenital malformations, preterm delivery, or fetal mortality. However, when the dispensed amount of potent or very potent topical corticosteroid exceeded 300 g during the entire pregnancy, use was associated with an increase in low birth weight infants [adjusted RR, 7.74 (95% CI, 1.49 to 40.11)]. In addition, a small cohort study, in which 28 sub-Saharan women using potent topical corticosteroids (27/28 used clobetasol propionate 0.05%) for skin lightening during pregnancy, noted a higher incidence of low birth weight infants in the exposed group. The majority of exposed subjects treated large areas of the body (a mean quantity of 60 g/month (range, 12 to 170g) over long periods of time.
Animal Data
Embryofetal development studies conducted with clobetasol propionate in mice using the subcutaneous route resulted in fetotoxicity at the highest dose tested (1 mg/kg) and malformations at all dose levels tested down to 0.03 mg/kg. Malformations seen included cleft palate and skeletal abnormalities.
In an embryofetal development study in rabbits, subcutaneous administration of clobetasol propionate resulted in malformations at doses of 0.003 and 0.01 mg/kg. Malformations seen included cleft palate, cranioschisis, and other skeletal abnormalities.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of clobetasol propionate in breast milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and can suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. It is not known whether topical administration of clobetasol propionate could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for clobetasol propionate foam and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from clobetasol propionate foam or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breast milk, use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Advise breastfeeding women not to apply clobetasol propionate foam directly to the nipple and areola to avoid direct infant exposure.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of clobetasol propionate foam in patients younger than 12 years of age have not been established; therefore, use in children younger than 12 years is not recommended.
Because of a higher ratio of skin surface area to body mass, pediatric patients are at a greater risk than adults of systemic toxicity when they are treated with topical drugs. They are, therefore, also at greater risk of adrenal insufficiency upon the use of topical corticosteroids.
Rare systemic toxicities such as Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in pediatric patients especially those with prolonged exposure to large doses of high potency topical corticosteroids.
Local adverse reactions including striae have also been reported with use of topical corticosteroids in pediatric patients.
Avoid use of clobetasol propionate foam in the treatment of diaper dermatitis.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of clobetasol propionate foam did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
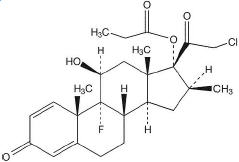
Clobetasol propionate foam, 0.05%, is a white thermolabile hydroethanolic aerosol foam containing the active ingredient, clobetasol propionate, USP, a synthetic corticosteroid, for topical use. Clobetasol, an analog of prednisolone, has a high degree of glucocorticoid activity and a slight degree of mineralocorticoid activity.
Clobetasol propionate is 21-chloro-9-fluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-16β-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17-propionate, with the empirical formula C25H32CIFO5, a molecular weight of 466.97.
The following is the chemical structure:
Clobetasol propionate is a white to almost white crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water.
Each gram of clobetasol propionate foam contains 0.5 mg clobetasol propionate, USP. The foam also contains cetyl alcohol, citric acid anhydrous, dehydrated alcohol (60%), polysorbate 60, potassium citrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Corticosteroids play a role in cellular signaling, immune function, inflammation, and protein regulation; however, the precise mechanism of action in corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a controlled pharmacokinetic trial, 5 of 13 subjects experienced reversible suppression of the adrenals at any time during the 14 days of therapy with clobetasol propionate foam applied to at least 20% of involved body surface area. Of the 13 subjects studied, 1 of 9 with psoriasis was suppressed after 14 days and all 4 of the subjects with atopic dermatitis had abnormal cortisol levels indicative of adrenal suppression at some time after starting therapy with clobetasol propionate foam (See Table 1 below).
Table 1: Subjects With Reversible HPA Axis Suppression at Any Time During Treatment Dermatosis Clobetasol Propionate Foam - * Clobetasol propionate foam is not indicated for non-scalp atopic dermatitis, as the safety and efficacy of clobetasol propionate foam in non-scalp atopic dermatitis has not been established. Use in children under 12 years of age is not recommended.
Psoriasis 1 of 9 Atopic Dermatitis* 4 of 4 12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from intact healthy skin. The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including the product formulation and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusion, inflammation, and/or other disease processes in the skin may also increase percutaneous absorption. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are metabolized, primarily in the liver, and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of clobetasol propionate foam or clobetasol propionate.
In a 90-day repeat-dose toxicity study in rats, topical administration of clobetasol propionate foam at dose concentrations from 0.001% to 0.1% or from 0.03 mg/kg/day to 0.3 mg/kg/day of clobetasol propionate resulted in a toxicity profile consistent with long-term exposure to corticosteroids including adrenal atrophy, histopathological changes in several organ systems indicative of severe immune suppression, and opportunistic fungal and bacterial infections. A no observable adverse effect level could not be determined in this study. Although the clinical relevance of the findings in animals to humans is not clear, sustained glucocorticoid-related immune suppression may increase the risk of infection and possibly the risk for carcinogenesis.
Clobetasol propionate was nonmutagenic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma test, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene conversion assay, and the E. coli B WP2 fluctuation test. In the in vivo mouse micronucleus test, a positive finding was observed at 24 hours, but not at 48 hours, following oral administration at a dose of 2,000 mg/kg.
Studies in the rat following subcutaneous administration of clobetasol propionate at dosage levels up to 0.05 mg/kg per day revealed that the females exhibited an increase in the number of resorbed embryos and a decrease in the number of living fetuses at the highest dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Scalp Psoriasis
A well-controlled clinical trial evaluated 188 subjects with moderate to severe scalp psoriasis. Subjects were treated twice daily for 2 weeks with one of 4 treatments: clobetasol propionate foam, vehicle foam, a commercially available clobetasol propionate solution (TEMOVATE® Scalp Application), or vehicle solution. The efficacy of clobetasol propionate foam in treating scalp psoriasis at the end of the 2 weeks' treatment was superior to that of vehicle (foam and solution), and was comparable to that of TEMOVATE Scalp Application (Table 2).
Table 2. Efficacy Results From a Controlled Clinical Trial in Scalp Psoriasis Clobetasol Propionate Foam
n (%)Vehicle Foam
n (%)- * Defined as a composite of an Investigator's Global Assessment of "completely clear" or "almost clear," a plaque thickness score of 0, an erythema score of 0 or 1, and a scaling score of 0 or 1 at endpoint, scored on a severity scale of 0 to 4.
Total number of subjects 62 31 Subjects with treatment success* 39 (63) 1 (3) Subjects with parameter Clear at endpoint (scalp psoriasis) Scaling - Clear at endpoint 42 (68) 3 (10) Erythema - Clear at endpoint 27 (44) 2 (6) Plaque Thickness - Clear at endpoint 41 (66) 3 (10) 14.2 Non-scalp Psoriasis
Another well-controlled clinical trial evaluated 279 subjects with mild to moderate plaque-type psoriasis (mean body surface area at baseline was 6.7% with a range from 1% to 20%) of non-scalp regions. Subjects were treated twice daily for 2 weeks with clobetasol propionate foam or vehicle foam. The face and intertriginous areas were excluded from treatment. The efficacy of clobetasol propionate foam in treating non-scalp psoriasis at the end of 2 weeks' treatment was superior to that of vehicle foam (Table 3).
Table 3. Efficacy Results From a Controlled Clinical Trial in Non-scalp Psoriasis Clobetasol Propionate Foam
n (%)Vehicle Foam
n (%)- * Defined as a composite of a Physician's Static Global Assessment score of 0 or 1, scaling score of 0 or 1, an erythema score of 0 or 1 and a plaque thickness score of 0, based on a severity scale of 0 to 5 at endpoint.
Total number of subjects 139 140 Subjects with treatment success* 39 (28) 4 (3) Physician's Static Global Assessment - Clear or almost clear at endpoint 94 (68) 30 (21) Scaling - Clear or almost clear at endpoint 101 (73) 42 (30) Erythema - Clear or almost clear at endpoint 88 (63) 35 (25) Plaque Thickness - Clear at endpoint 44 (32) 5 (4) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Clobetasol Propionate Foam, 0.05% contains 0.5 mg of clobetasol propionate, USP per gram. The white aerosol foam is available as follows:
- 50-g aluminum can
- 100-g aluminum can
- NDC: 51672-4193-3
- NDC: 51672-4193-7
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
FLAMMABLE. AVOID FIRE, FLAME, OR SMOKING DURING AND IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWING APPLICATION. Contents under pressure. Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not expose to heat or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
Keep out of reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use)
Effects on Endocrine System
Clobetasol propionate foam may cause HPA axis suppression. Advise patients that use of topical corticosteroids, including clobetasol propionate foam, may require periodic evaluation for HPA axis suppression. Topical corticosteroids may have other endocrine effects. Concomitant use of multiple corticosteroid-containing products may increase the total systemic exposure to topical corticosteroids. Patients should inform their physician(s) that they are using clobetasol propionate foam if surgery is contemplated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
Advise patients to report any visual symptoms to their healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Local Adverse Reactions
Report any signs of local adverse reactions to the physician. Advise patients that local reactions and skin atrophy are more likely to occur with occlusive use or prolonged use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus and to use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise a woman to use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Advise breastfeeding women not to apply clobetasol propionate foam directly to the nipple and areola to avoid direct infant exposure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Important Administration Instructions
Inform patients of the following:
- Avoid use of clobetasol propionate foam on the face, underarms, or groin areas unless directed by the physician.
- Do not occlude the treatment area with bandage or other covering, unless directed by the physician.
- Discontinue therapy when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, contact the physician.
- For proper dispensing of foam, hold the can upside down and depress the actuator. Dispensing directly onto hands is not recommended (unless the hands are the affected area), as the foam will begin to melt immediately upon contact with warm skin.
- Limit treatment to 2 consecutive weeks. Use no more than 50 grams of clobetasol propionate foam per week, or more than 21 capfuls per week.
- Avoid use of clobetasol propionate foam in the diaper area, as diapers or plastic pants may constitute occlusive dressing.
- The product is flammable; avoid heat, flame, and smoking when applying this product.
- Do not use other corticosteroid-containing products without first consulting with the physician.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Clobetasol Propionate
(kloe bay' ta sol proe' pee oh nate) Foam, 0.05%Important: Clobetasol propionate foam is for use on the skin only. Do not get clobetasol propionate foam in your eyes, mouth, or vagina. What is clobetasol propionate foam? Clobetasol propionate foam is a prescription corticosteroid medicine used in people 12 years of age and older for the treatment of: - moderate to severe plaque psoriasis of the scalp and
- mild to moderate plaque psoriasis of the skin except the face and areas where the skin may touch or rub together.
It is not known if clobetasol propionate foam is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age. Clobetasol propionate foam is not recommended in children under 12 years of age. Before using clobetasol propionate foam, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have had irritation or other skin reaction to a steroid medicine in the past.
- have a skin infection. You may need medicine to treat the skin infection before using clobetasol propionate foam.
- have diabetes.
- have adrenal gland problems.
- have liver problems.
- plan to have surgery.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if clobetasol propionate foam will harm your unborn baby. If you use clobetasol propionate foam during pregnancy, use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest time needed.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if clobetasol propionate passes into your breast milk. If you use clobetasol propionate foam while breastfeeding, use clobetasol propionate foam on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest time needed. Do not apply clobetasol propionate foam directly to the nipple and areola to avoid getting clobetasol propionate foam into your baby's mouth.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicine you take including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Do not use other products containing a corticosteroid medicine during treatment with clobetasol propionate foam without talking to your healthcare provider first. How should I use clobetasol propionate foam? See the "Instructions for Use" for detailed information about the right way to apply clobetasol propionate foam. - Use clobetasol propionate foam exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Apply a thin layer of clobetasol propionate foam to the affected skin areas 2 times each day.
- Avoid using clobetasol propionate foam on your face, underarms (armpits), groin area, or in areas with thinning skin (atrophy).
- Avoid using clobetasol propionate foam on skin in a diaper area.
- Do not bandage or cover your treated area unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Do not use clobetasol propionate foam for longer than 2 weeks in a row.
- You should not use more than 50 grams or 21 capfuls of clobetasol propionate foam in 1 week.
- Talk to your healthcare provider if your skin or scalp does not improve after 2 weeks of treatment with clobetasol propionate foam.
- Wash your hands after using clobetasol propionate foam.
What should I avoid while using clobetasol propionate foam? Clobetasol propionate foam is flammable. Avoid heat, flame, or smoking during and right after you apply clobetasol propionate foam to your skin. What are the possible side effects of clobetasol propionate foam? Clobetasol propionate foam may cause serious side effects, including: - Clobetasol propionate foam can pass through your skin. Too much clobetasol propionate foam passing through your skin can cause adrenal glands to stop working.
- Cushing's syndrome, a condition that happens when the body is exposed to too much of the hormone cortisol.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia)
- Vision problems. Clobetasol propionate foam may increase your chance of developing vision problems such as cataract(s) and glaucoma. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop blurred vision or other vision problems during treatment with clobetasol propionate foam.
- Skin reactions at the treated skin site. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any skin reactions or skin infections.
- Effects on growth and weight in children.
Your healthcare provider may do certain blood tests to check for side effects. The most common side effects of clobetasol propionate foam include burning and skin reactions at the treated site. These are not all the possible side effects of clobetasol propionate foam. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. How should I store clobetasol propionate foam? - Store clobetasol propionate foam at room temperature between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Do not break through (puncture) the clobetasol propionate foam can.
- Never throw the can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
- Do not store clobetasol propionate foam near heat or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
Keep clobetasol propionate foam and all medicines out of the reach of children. General information about the safe and effective use of clobetasol propionate foam. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use clobetasol propionate foam for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give clobetasol propionate foam to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about clobetasol propionate foam that is written for health professionals. What are the ingredients in clobetasol propionate foam? Active ingredient: clobetasol propionate, USP, 0.05% Inactive ingredients: cetyl alcohol, citric acid anhydrous, dehydrated alcohol (60%), polysorbate 60, potassium citrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant. Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Dist. by:
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532
Revised: June 2018
20815-0618-2
85 -
Instructions for Use Clobetasol Propionate (kloe bay' ta sol proe' pee oh nate) Foam, 0.05%
Important: Clobetasol propionate foam is for use on the skin only. Do not get clobetasol propionate foam in your eyes, mouth or vagina.
How to apply clobetasol propionate foam:
Step 1: Remove the cap and save for further use.
Step 2: Before applying clobetasol propionate foam for the first time, break the tiny plastic piece at the base of the can's rim by gently pushing back (away from the piece) on the nozzle. (see Figure A)
Figure A
Step 3: Turn the can upside down. Push the button to dispense a small amount of clobetasole propionate foam into the cap of the can, or on your affected skin area. (see Figure B) This amount should be no more than 1½ capfuls, about the size of a golf ball.
Figure B
- Do not dispense clobetasol propionate foam directly onto your hands (unless your hands are the affected areas), because the foam will begin to melt right away on contact with your warm skin.
- If your fingers are warm, rinse them in cold water first. Be sure to dry them thoroughly before handling the foam.
- If the can seems warm or the foam seems runny, run the can under cold water.
Step 4: Using your fingertips, gently massage a thin layer of clobetasol propionate foam into the affected skin areas until the foam disappears. (see Figures C and D)
Figure C
Figure D
Step 5: If you are treating areas with hair, such as the scalp, move any hair away so that the foam can be applied directly to the affected areas. (see Figure E)
- Repeat until the affected areas are treated.
Figure E
Keep the foam away from your eyes, as it will sting and may cause eye problems if there is frequent contact with your eyes. If the foam gets in your eyes, rinse them well with cold water right away. If the stinging continues, contact your healthcare provider right away.
Step 6: Wash your hands after applying clobetasol propionate foam. (see Figure F)
Figure F
- Throw away any of the unused medicine that you dispensed out of the can.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Mfd. by:
Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Dist. by:
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
Hawthorne, NY 10532
Revised: June 2018
20815-0618-2
85 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 g Can Carton
NDC: 51672-4193-3
Clobetasol
Propionate
Foam
0.05%For Topical
Use Only.Not for Oral,
Ophthalmic or
Intravaginal Use.Keep this and all
medications out of the
reach of children.Rx only
50 gTARO

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CLOBETASOL PROPIONATE
clobetasol propionate aerosol, foamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51672-4193 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Clobetasol Propionate (UNII: 779619577M) (CLOBETASOL - UNII:ADN79D536H) Clobetasol Propionate 0.5 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength cetyl alcohol (UNII: 936JST6JCN) anhydrous citric acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) polysorbate 60 (UNII: CAL22UVI4M) potassium citrate (UNII: EE90ONI6FF) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) stearyl alcohol (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51672-4193-3 1 in 1 CARTON 10/04/2018 1 50 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51672-4193-7 1 in 1 CARTON 10/04/2018 2 100 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208779 10/04/2018 Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. 600072078 MANUFACTURE(51672-4193)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.