SEVELAMER CARBONATE powder, for suspension
sevelamer carbonate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
sevelamer carbonate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amneal Pharmaceuticals of New York LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SEVELAMER CARBONATE FOR ORAL SUSPENSION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SEVELAMER CARBONATE FOR ORAL SUSPENSION.
SEVELAMER CARBONATE for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions (5.1) 04/2020
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension is a phosphate binder indicated for the control of serum phosphorus in adults and children 6 years of age and older with chronic kidney disease on dialysis. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Starting dose of sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension is 0.8 or 1.6 grams administered orally three times per day with meals based on serum phosphorus levels for adult patients and based on body surface area (BSA) category for pediatric patients. (2.1)
- Titrate by 0.8 g per meal in two week intervals for adult patients as needed to obtain serum phosphorus target. (2.1)
- Titrate based on BSA category for pediatric patients in two week intervals for 6 weeks and then every 4 weeks as needed to obtain serum phosphorus target. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Powder: 0.8 g and 2.4 g packets (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious cases of dysphagia, bowel obstruction, bleeding gastrointestinal ulcers, colitis, ulceration, necrosis, and perforation have been associated with sevelamer use, some requiring hospitalization and surgery. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most of the safety experience is with sevelamer tablets and sevelamer hydrochloride. In long-term studies with sevelamer hydrochloride, which contains the same active moiety as sevelamer carbonate, the most common adverse events included: vomiting (22%), nausea (20%), diarrhea (19%), dyspepsia (16%), abdominal pain (9%), flatulence (8%), and constipation (8%). (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-835-5472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- For oral medication where a reduction in the bioavailability of that medication would have a clinically significant effect on its safety or efficacy, consider separation of the timing of administration and/or monitor clinical responses or blood levels of the concomitant medication. (7)
- Sevelamer did not alter the pharmacokinetics of digoxin, enalapril, iron, metoprolol and warfarin. (7)
- Sevelamer has demonstrated interaction with ciprofloxacin, mycophenolate mofetil, and therefore, these drugs should be dosed separately from sevelamer carbonate. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2020
- Starting dose of sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension is 0.8 or 1.6 grams administered orally three times per day with meals based on serum phosphorus levels for adult patients and based on body surface area (BSA) category for pediatric patients. (2.1)
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Sevelamer Carbonate Powder Preparation Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Gastrointestinal Adverse Events
5.2 Reductions in Vitamins D, E, K (clotting factors) and Folic Acid Levels
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.2 Cross-Over Study of Sevelamer Carbonate Powder and Sevelamer Hydrochloride Tablets
14.3 Clinical Study of Sevelamer Carbonate Powder and Tablets in Pediatric Patients
14.4 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control, Cross-Over Study in Hemodialysis Patients
14.5 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control in Hemodialysis Patients
14.6 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
14.7 Once-Daily versus Three-Times-Per-Day Dosing
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
Starting Dose for Adult Patients Not Taking a Phosphate Binder
The recommended starting dose of sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension is 0.8 to 1.6 g taken orally with meals based on serum phosphorus level. Table 1 provides recommended starting doses of sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension for adult patients not taking a phosphate binder.
Table 1: Starting Dose for Adult Dialysis Patients Not Taking a Phosphate Binder
Serum Phosphorus
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension
> 5.5 and < 7.5 mg/dL
0.8 g three times daily with meals
≥ 7.5 mg/dL
1.6 g three times daily with meals
Dose Titration for Adult Patients Taking Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension
Titrate the sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension dose by 0.8 g three times per day with meals at two-week intervals as necessary to achieve target serum phosphorus levels. Based on clinical studies, the average prescribed adult daily dose of sevelamer carbonate is approximately 7.2 g per day. The highest daily adult dose of sevelamer carbonate studied was 14 grams in CKD patients on dialysis.
Starting Dose for Pediatric Patients Not Taking a Phosphate Binder
The recommended starting dose for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is 0.8 g to 1.6 g taken three times per day with meals based on the patient’s body surface area (BSA) category; see Table 2.
Table 2: Recommended Starting Dosage and Titration Increment Based on Pediatric Patient’s Body Surface Area (m2)
BSA (m2)
Starting Dose Per
Meal/Snack
Titration Increases/Decreases
Per Dose
≥ 0.75 to < 1.2
0.8 g
Titrate by 0.4 g
≥ 1.2
1.6 g
Titrate by 0.8 g
Dose Titration for Pediatric Patients Taking Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension
Titrate the sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension dose as needed to achieve target levels at two-week intervals based on BSA category, as shown in Table 2.
Switching from Sevelamer Hydrochloride Tablets
For adult patients switching from sevelamer hydrochloride tablets to sevelamer carbonate powder, use the same dose in grams.
Switching between Sevelamer Carbonate Tablets and Powder
Use the same dose in grams.
Switching from Calcium Acetate
Table 3 gives recommended starting doses of sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension based on a patient’s current calcium acetate dose.
Table 3: Starting Dose for Dialysis Patients Switching from Calcium Acetate to Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension
Calcium Acetate 667 mg
(Tablets per meal)
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension
1 tablet
0.8 g
2 tablets
1.6 g
3 tablets
2.4 g
2.2 Sevelamer Carbonate Powder Preparation Instructions
Sevelamer carbonate powder is available in 0.8 or 2.4 g packets. For dose increments of 0.4 g, use one half of a 0.8 g packet. Place the sevelamer carbonate powder in a cup and suspend in the amount of water described in Table 4.
Table 4: Sevelamer Carbonate Powder Preparation Instructions
Amount of Sevelamer Carbonate Powder
Minimum Amount of Water for Dose Preparation
(either ounces, mL, or tablespoon)
Ounces mL Tablespoons 0.4 g
1 30 2 0.8 g
1 30 2 2.4 g
2 60
4
Instruct patients to stir the mixture vigorously (it does not dissolve), resuspend, if necessary, right before administration, and drink the entire preparation within 30 minutes.
As an alternative to water, the entire contents of the packet may be pre-mixed with a small amount of food or beverage and consumed immediately (within 30 minutes) as part of the meal. Do not heat sevelamer carbonate powder (e.g., microwave) or add to heated foods or liquids.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Gastrointestinal Adverse Events
Patients with dysphagia, swallowing disorders, severe gastrointestinal (GI) motility disorders, including severe constipation, or major GI tract surgery were not included in the sevelamer carbonate clinical studies.
Cases of dysphagia and esophageal tablet retention have been reported in association with use of the tablet formulation of sevelamer, some requiring hospitalization and intervention. Consider using sevelamer suspension in patients with a history of swallowing disorders.
Cases of bowel obstruction, bleeding gastrointestinal ulcers, colitis, ulceration, necrosis, and perforation have also been reported with sevelamer use [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Inflammatory disorders may resolve upon sevelamer carbonate discontinuation. Treatment with sevelamer carbonate should be re-evaluated in patients who develop severe gastrointestinal symptoms.
5.2 Reductions in Vitamins D, E, K (clotting factors) and Folic Acid Levels
In preclinical studies in rats and dogs, sevelamer hydrochloride, which contains the same active moiety as sevelamer carbonate, reduced vitamins D, E, and K (coagulation parameters) and folic acid levels at doses of 6 to 10 times the recommended human dose. In short-term clinical trials, there was no evidence of reduction in serum levels of vitamins. However, in a one-year clinical trial, 25-hydroxyvitamin D (normal range 10 to 55 ng/mL) fell from 39 ± 22 ng/mL to 34 ± 22 ng/mL (p<0.01) with sevelamer hydrochloride treatment. Most (approximately 75%) patients in sevelamer hydrochloride clinical trials were receiving vitamin supplements.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
There are limited clinical trial data on the safety of sevelamer carbonate. However, because it contains the same active ingredient as the hydrochloride salt, the adverse event profiles of the two salts are expected to be similar. In a cross-over study in hemodialysis patients with treatment durations of eight weeks each and no washout, and another cross-over study in hemodialysis patients with treatment durations of four weeks each and no washout between treatment periods, the adverse reactions on sevelamer carbonate powder were similar to those reported for sevelamer hydrochloride.
In a parallel design study of sevelamer hydrochloride with treatment duration of 52 weeks, adverse reactions reported for sevelamer hydrochloride (n=99) were similar to those reported for the active-comparator group (n=101). Overall adverse reactions among those treated with sevelamer hydrochloride occurring in > 5% of patients included: vomiting (22%), nausea (20%), diarrhea (19%), dyspepsia (16%), abdominal pain (9%), flatulence (8%), and constipation (8%). A total of 27 patients treated with sevelamer and 10 patients treated with comparator withdrew from the study due to adverse reactions.
Based on studies of 8 to 52 weeks, the most common reason for withdrawal from sevelamer hydrochloride was gastrointestinal adverse reactions (3% to 16%).
In 143 peritoneal dialysis patients studied for 12 weeks using sevelamer hydrochloride, most common adverse reactions were similar to adverse reactions observed in hemodialysis patients. The most frequently occurring treatment emergent serious adverse reaction was peritonitis (8 reactions in 8 patients [8%] in the sevelamer group and 2 reactions in 2 patients [4%] on active-control). Thirteen patients (14%) in the sevelamer group and 9 patients (20%) in the active-control group discontinued, mostly for gastrointestinal adverse reactions.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of sevelamer hydrochloride or sevelamer carbonate: hypersensitivity, pruritus, rash, abdominal pain, bleeding gastrointestinal ulcers, colitis, ulceration, necrosis, fecal impaction, and uncommon cases of ileus, intestinal obstruction, and intestinal perforation. Appropriate medical management should be given to patients who develop constipation or have worsening of existing constipation to avoid severe complications.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
There are no empirical data on avoiding drug interactions between sevelamer carbonate and most concomitant oral drugs. For oral medication where a reduction in the bioavailability of that medication would have a clinically significant effect on its safety or efficacy (e.g., cyclosporine, tacrolimus, levothyroxine), consider separation of the timing of the administration of the two drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The duration of separation depends upon the absorption characteristics of the medication concomitantly administered, such as the time to reach peak systemic levels and whether the drug is an immediate-release or an extended-release product. Where possible consider monitoring clinical responses and/or blood levels of concomitant drugs that have a narrow therapeutic range.
Table 5: Sevelamer Drug Interactions
Oral drugs for which sevelamer did not alter the pharmacokinetics when administered concomitantly
Digoxin
Enalapril
Iron
Metoprolol
Warfarin
Oral drugs that have demonstrated interaction with sevelamer and are to be dosed separately from sevelamer carbonate
Dosing Recommendations
Ciprofloxacin
Take at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after sevelamer
Mycophenolate mofetil
Take at least 2 hours before sevelamer
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Sevelamer carbonate is not absorbed systemically following oral administration and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug.
Clinical Considerations
Sevelamer carbonate may decrease serum levels of fat soluble vitamins and folic acid in pregnant women [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Consider supplementation.
Data
Animal data
In pregnant rats given dietary doses of 0.5, 1.5 or 4.5 g/kg/day of sevelamer hydrochloride during organogenesis, reduced or irregular ossification of fetal bones, probably due to a reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamin D, occurred in mid and high-dose groups (human equivalent doses approximately equal to 3 to 4 times the maximum clinical trial dose of 13 g). In pregnant rabbits given oral doses of 100, 500 or 1,000 mg/kg/day of sevelamer hydrochloride by gavage during organogenesis, an increase of early resorptions occurred in the high-dose group (human equivalent dose twice the maximum clinical trial dose).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Sevelamer carbonate is not absorbed systemically by the mother following oral administration, and breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the child to sevelamer carbonate.
Clinical Considerations
Sevelamer carbonate may decrease serum levels of fat soluble vitamins and folic acid in pregnant women [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Consider supplementation.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of sevelamer carbonate in lowering serum phosphorus levels was studied in patients 6 years of age and older with CKD. In this study, sevelamer carbonate was apparently less effective in children with a low baseline serum phosphorus, which described children < 13 years of age and children not on dialysis. Given its mechanism of action, sevelamer carbonate is expected to be effective in lowering serum phosphorus levels in pediatric patients with CKD. Most adverse events that were reported as related, or possibly related, to sevelamer carbonate were gastrointestinal in nature. No new risks or safety signals were identified with the use of sevelamer carbonate in the trial.
Sevelamer carbonate has not been studied in pediatric patients below 6 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of sevelamer carbonate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
In CKD patients on dialysis, the maximum dose studied was 14 grams of sevelamer carbonate and 13 grams of sevelamer hydrochloride. There are no reports of overdosage with sevelamer carbonate or sevelamer hydrochloride in patients. Since sevelamer is not absorbed, the risk of systemic toxicity is low.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension is sevelamer carbonate, a polymeric amine that binds phosphate and is meant for oral administration. It was developed as a pharmaceutical alternative to sevelamer hydrochloride. Sevelamer carbonate is an anion exchange resin, with the same polymeric structure as sevelamer hydrochloride, in which carbonate replaces chloride as the counterion. While the counterions differ for the two salts, the polymer itself, the active moiety involved in phosphate-binding, is the same. Sevelamer carbonate is known chemically as poly(allylamine-co-N,N’-diallyl-1,3- diamino-2-hydroxypropane) carbonate salt. Sevelamer carbonate is hygroscopic, but insoluble in water. The structure is represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Chemical Structure of Sevelamer Carbonate
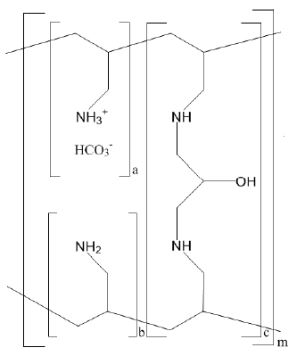
a, b = number of primary amine groups a + b = 9
c = number of cross-linking groups c = 1
m = large number to indicate extended polymer network groups
Sevelamer Carbonate Powder: Each packet of sevelamer carbonate powder contains 0.8 g or 2.4 g of sevelamer carbonate on an anhydrous basis. The inactive ingredients are: lemon flavor, microcrystalline cellulose, propylene glycol alginate, silicon dioxide, sodium chloride and sucralose.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension contains sevelamer carbonate, a non-absorbed phosphate-binding cross-linked polymer, free of metal and calcium. It contains multiple amines separated by one carbon from the polymer backbone. These amines exist in a protonated form in the intestine and interact with phosphate molecules through ionic and hydrogen bonding. By binding phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract and decreasing absorption, sevelamer carbonate lowers the phosphate concentration in the serum (serum phosphorus).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In addition to effects on serum phosphorus levels, sevelamer hydrochloride has been shown to bind bile acids in vitro and in vivo in experimental animal models. Because sevelamer binds bile acids, it may interfere with normal fat absorption and thus may reduce absorption of fat soluble vitamins such as A, D and K. In clinical trials of sevelamer hydrochloride, both the mean total and LDL cholesterol declined by 15% to 31%; the clinical significance of this finding, which was observed after 2 weeks, is unclear. Triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, and albumin did not change.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
A mass balance study using 14C-sevelamer hydrochloride, in 16 healthy male and female volunteers showed that sevelamer hydrochloride is not systemically absorbed. No absorption studies have been performed in patients with renal disease.
Drug Interactions
In vivo
Sevelamer carbonate has been studied in human drug-drug interaction studies (9.6 grams once daily with a meal) with warfarin and digoxin. Sevelamer hydrochloride, which contains the same active moiety as sevelamer carbonate, has been studied in human drug-drug interaction studies (2.4 to 2.8 grams single-dose or three times daily with meals or two times daily without meals) with ciprofloxacin, digoxin, enalapril, iron, metoprolol, mycophenolate mofetil, and warfarin.
Co-administered single-dose of 2.8 grams of sevelamer hydrochloride in fasted state decreased the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by approximately 50% in healthy subjects. Concomitant administration of sevelamer and mycophenolate mofetil in adult and pediatric patients decreased the mean MPA Cmax and AUC0-12h by 36% and 26% respectively. Sevelamer carbonate or sevelamer hydrochloride did not alter the pharmacokinetics of enalapril, digoxin, iron, metoprolol, and warfarin when co-administered.
During postmarketing experience, cases of increased thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels have been reported in patients co-administered sevelamer hydrochloride and levothyroxine. Reduction in concentrations of cyclosporine and tacrolimus leading to dose increases has also been reported in transplant patients when co-administered with sevelamer hydrochloride without any clinical consequences (for example, graft rejection). The possibility of an interaction cannot be excluded with these drugs.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Standard lifetime carcinogenicity bioassays were conducted in mice and rats. Rats were given sevelamer hydrochloride by diet at 0.3, 1, or 3 g/kg/day. There was an increased incidence of urinary bladder transitional cell papilloma in male rats of the high dose group (human equivalent dose twice the maximum clinical trial dose of 13 g). Mice received dietary administration of sevelamer hydrochloride at doses of up to 9 g/kg/day (human equivalent dose 3 times the maximum clinical trial dose). There was no increased incidence of tumors observed in mice.
In an in vitro mammalian cytogenetic test with metabolic activation, sevelamer hydrochloride caused a statistically significant increase in the number of structural chromosome aberrations. Sevelamer hydrochloride was not mutagenic in the Ames bacterial mutation assay.
Sevelamer hydrochloride did not impair the fertility of male or female rats in a dietary administration study in which the females were treated from 14 days prior to mating through gestation and the males were treated for 28 days prior to mating. The highest dose in this study was 4.5 g/kg/day (human equivalent dose 3 times the maximum clinical trial dose of 13 g).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The ability of sevelamer to control serum phosphorus in CKD patients on dialysis was predominantly determined from the effects of the hydrochloride salt to bind phosphate. Six clinical trials used sevelamer hydrochloride and three clinical trials used sevelamer carbonate. The sevelamer hydrochloride studies include one double-blind, placebo-controlled 2-week study (sevelamer N=24); two open-label, uncontrolled, 8-week studies (sevelamer N=220); and three active-controlled open-label studies with treatment durations of 8 to 52 weeks (sevelamer N=256). The sevelamer carbonate studies include one open-label, active-controlled, cross-over study with two 4-week treatment periods using sevelamer carbonate powder (N=31); and one randomized, parallel, open-label study using sevelamer carbonate powder (N=144) dosed once daily or sevelamer hydrochloride tablets (N=73) dosed three times daily for 24 weeks. Six of the active-controlled studies are described here (three sevelamer carbonate and three sevelamer hydrochloride studies).
14.2 Cross-Over Study of Sevelamer Carbonate Powder and Sevelamer Hydrochloride Tablets
Stage 5 CKD patients on hemodialysis were entered into a four-week sevelamer hydrochloride run-in period and 31 patients received, in random order, sevelamer carbonate powder and sevelamer hydrochloride tablets for four weeks each with no intervening washout. Study dose during the cross-over period was determined based on the sevelamer hydrochloride dose during the run-in period on a gram-per-gram basis. The phosphorus levels at the end of each of the two cross-over periods were similar. Average actual daily dose was 6 g/day divided among meals for sevelamer carbonate powder and 6.4 g/day divided among meals for sevelamer hydrochloride tablets.
14.3 Clinical Study of Sevelamer Carbonate Powder and Tablets in Pediatric Patients
A clinical study with sevelamer carbonate was conducted in 101 patients 6 to 18 years of age with chronic kidney disease. This study included a washout period for patients on a phosphate-binder, a 2-week, double-blind, fixed-dose period (FDP) in which patients were randomized to sevelamer carbonate (n=50) or placebo (n=51), and a 26-week, open-label, sevelamer carbonate dose titration period (DTP). Most patients were 13 to 18 years of age (73%) and had a BSA ≥ 1.2 m2 (84%). Approximately 78% of patients were CKD patients on dialysis.
Sevelamer carbonate significantly reduced serum phosphorus through Week 2 (primary endpoint) by an LS Mean difference of -0.90 (SE 0.27) mg/dL compared to placebo (p = 0.001). A similar treatment response was observed in patients who received sevelamer carbonate during the 6-month open-label DTP. Approximately 30% of subjects reached their target serum phosphorus. The median prescribed daily dose was approximately 7.0 g per day during the titration period.
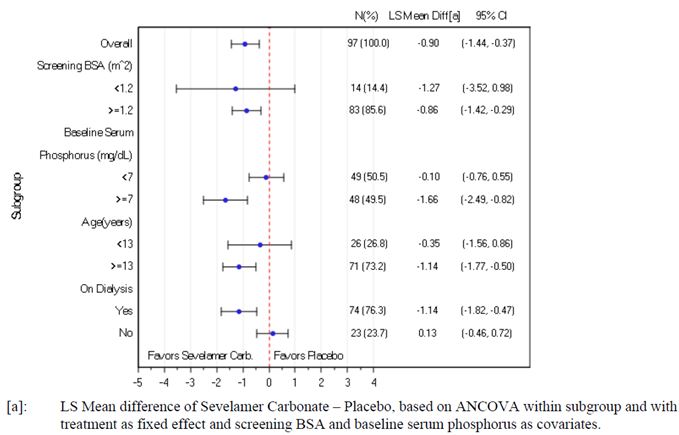
The results of the primary efficacy endpoint were consistent by BSA subgroup. In contrast, a treatment effect was not observed in subjects with a baseline serum phosphorus below 7 mg/dL, many of whom were the subjects 6 to < 13 years of age or the subjects not on dialysis (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Change in Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) from Baseline to Week 2 by Subgroup
14.4 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control, Cross-Over Study in Hemodialysis Patients
Eighty-four CKD patients on hemodialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus > 6.0 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate binder washout period were randomized in a cross-over design to receive in random order sevelamer hydrochloride and active-control for eight weeks each. Treatment periods were separated by a two-week phosphate binder washout period. Patients started on treatment three times per day with meals. Over each eight-week treatment period, at three separate time points the dose of sevelamer hydrochloride could be titrated up to control serum phosphorus, the dose of active-control could also be altered to attain phosphorus control. Both treatments significantly decreased mean serum phosphorus by about 2 mg/dL (Table 6).
Table 6: Mean Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) at Baseline and Endpoint
Sevelamer
Hydrochloride
(N=81)
Active
Control
(N=83)
Baseline at End of Washout
8.4
8.0
Endpoint
6.4
5.9
Change from Baseline at Endpoint
-2.0*
-2.1*
(95% Confidence Interval)
(-2.5, -1.5)
(-2.6, -1.7)
*p<0.0001, within treatment group comparison
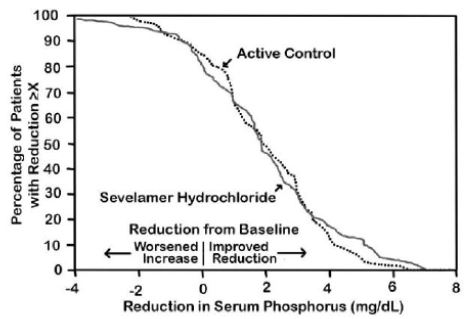
The distribution of responses is shown in Figure 3. The distributions are similar for sevelamer hydrochloride and active control. The median response is a reduction of about 2 mg/dL in both groups. About 50% of subjects have reductions between 1 and 3 mg/dL.
Figure 3: Percentage of Patients (Y-axis) Attaining a Phosphorus Reduction from Baseline (mg/dL) at Least as Great as the Value of the X-axis
Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 4.9 g (range of 0 to 12.6 g).
14.5 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control in Hemodialysis Patients
Two hundred CKD patients on hemodialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus > 5.5 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate-binder washout period were randomized to receive sevelamer hydrochloride 800 mg tablets (N=99) or an active-control (N=101). At week 52, using last observation carried forward, sevelamer and active-control both significantly decreased mean serum phosphorus (Table 7).
Table 7: Mean Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) and Ion Product at Baseline and Change from Baseline to End of Treatment
Sevelamer Hydrochloride
(N=94)
Active-Control
(N=98)
Phosphorus
Baseline
7.5
7.3
Change from Baseline at Endpoint
-2.1
-1.8
Ca × Phosphorus Ion Product
Baseline
70.5
68.4
Change from Baseline at Endpoint
-19.4
-14.2
Sixty-one percent of sevelamer hydrochloride patients and 73% of the control patients completed the full 52 weeks of treatment.
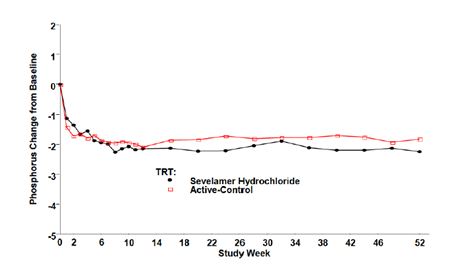
Figure 4, a plot of the phosphorus change from baseline for the completers, illustrates the durability of response for patients who are able to remain on treatment.
Figure 4: Mean Phosphorus Change from Baseline for Patients who Completed 52 Weeks of Treatment
Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 6.5 g (range of 0.8 to 13 g).
14.6 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients
One hundred and forty-three patients on peritoneal dialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus > 5.5 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate binder washout period were randomized to receive sevelamer hydrochloride (N=97) or active-control (N=46) open label for 12 weeks. Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 5.9 g (range 0.8 to 14.3 g). Thirteen patients (14%) in the sevelamer group and 9 patients (20%) in the active-control group discontinued, mostly for gastrointestinal adverse reactions. There were statistically significant changes in serum phosphorus (p < 0.001) for sevelamer hydrochloride (-1.6 mg/dL from baseline of 7.5 mg/dL), similar to the active-control.
14.7 Once-Daily versus Three-Times-Per-Day Dosing
Stage 5 CKD patients on hemodialysis with a serum phosphate level of > 5.5 mg/dL after washout from baseline therapies were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive either sevelamer carbonate powder once daily (N=144) or sevelamer hydrochloride as a tablet with the dose divided three times per day (N=73) for 24 weeks. The initial dose for the two groups was 4.8 g/day. At the end of the study, the total daily dose was 6.2 g/day of sevelamer carbonate powder once daily and 6.7 g/day of sevelamer hydrochloride tablets three times per day. A greater percentage of subjects on the once-daily dose than three-times-per-day regimen discontinued therapy prematurely, 35% versus 15%. The reasons for discontinuation were largely driven by adverse events and withdrawal of consent in the once-daily dosing regimen. Serum phosphate levels and calcium-phosphate product were better controlled on the three-times-per-day regimen than on the once-daily regimen. Mean serum phosphorus decreased 2.0 mg/dL for sevelamer carbonate powder once daily and 2.9 mg/dL for sevelamer hydrochloride tablets three times per day.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension is supplied as opaque, foil lined, heat sealed, packets containing 0.8 g or 2.4 g of sevelamer carbonate on an anhydrous basis.
They are available as follows:
0.8 g:
0.8 Grams Packet: NDC: 0115-1365-30
Carton of 90 Packets: NDC: 0115-1365-29
2.4 g:
2.4 Grams Packet: NDC: 0115-1366-30
Carton of 90 Packets: NDC: 0115-1366-29
Storage:
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients to take sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension with meals and adhere to their prescribed diets.
For patients using an oral medication where a reduction in the bioavailability of that medication would have a clinically significant effect on its safety or efficacy, advise the patient to take the oral medication at least one hour before or three hours after sevelamer carbonate for oral suspension.
For sevelamer carbonate powder, brief the patient on preparation of the powder in water.
Advise patients to report new onset or worsening of existing constipation or bloody stools promptly to their physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Ahmedabad 382220, INDIADistributed by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807Rev. 12-2020-00
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
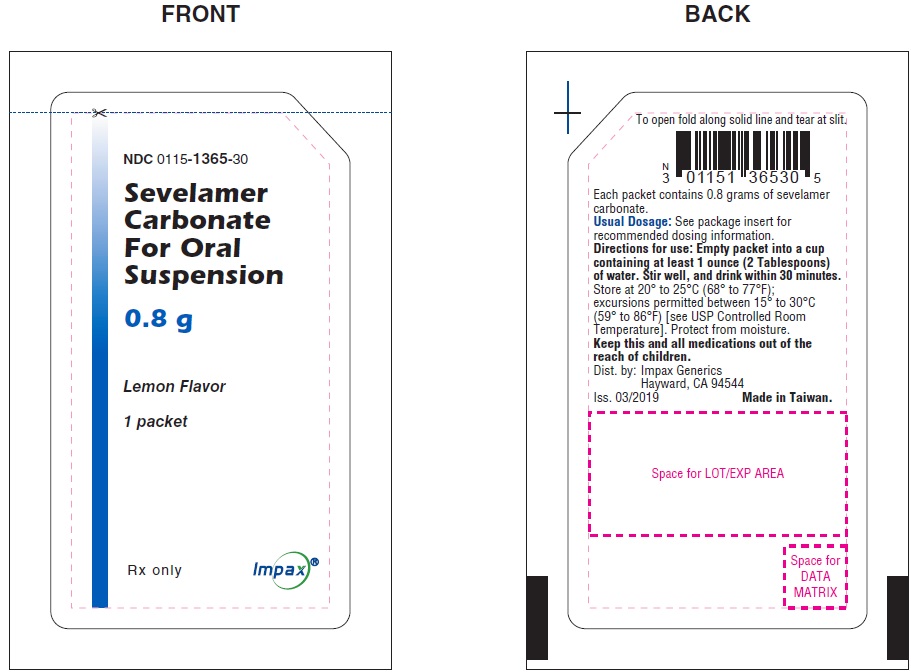
NDC: 0115-1365-30
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension, 0.8 g
Rx only
Packet Label
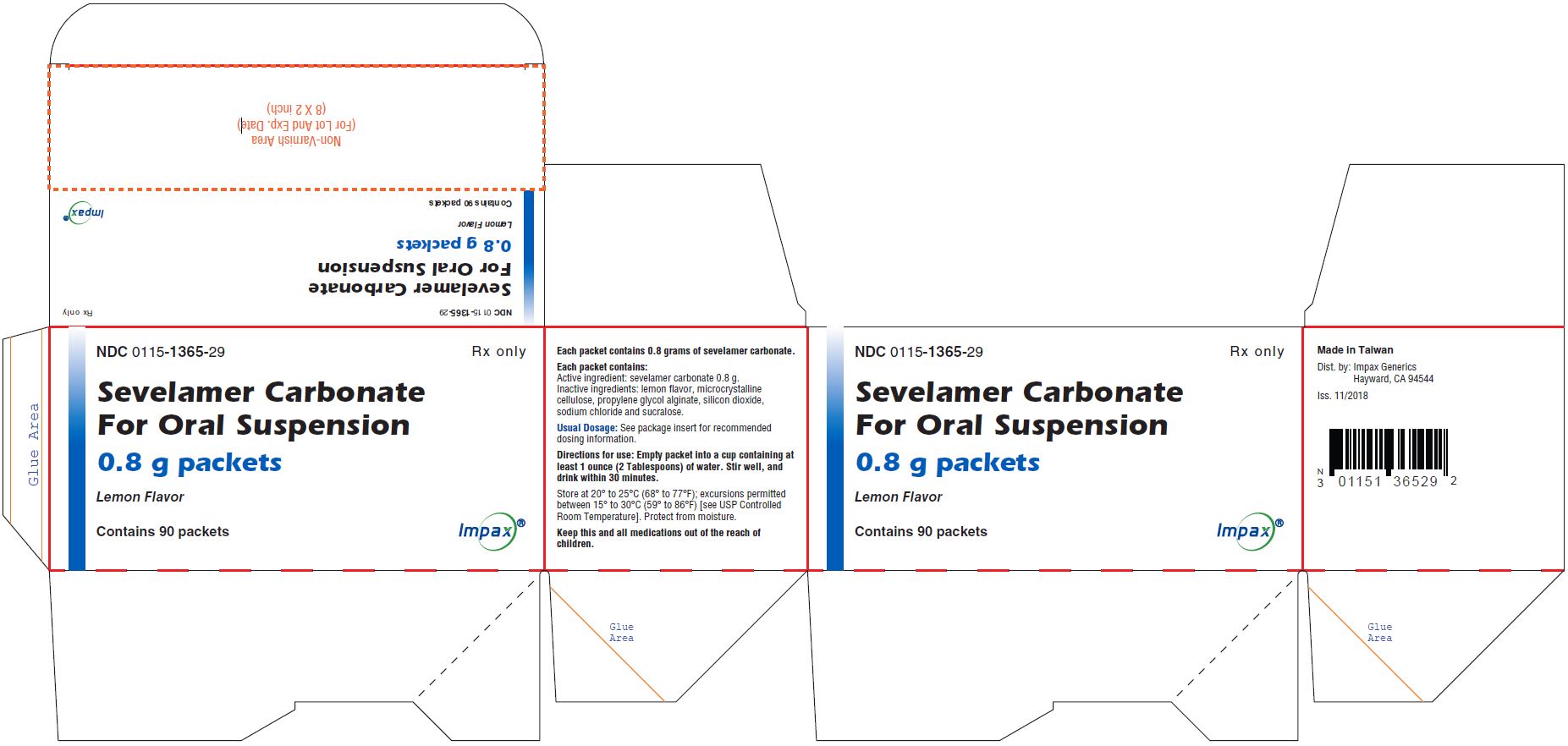
NDC: 0115-1365-29
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension, 0.8 g
Rx only
Carton Label
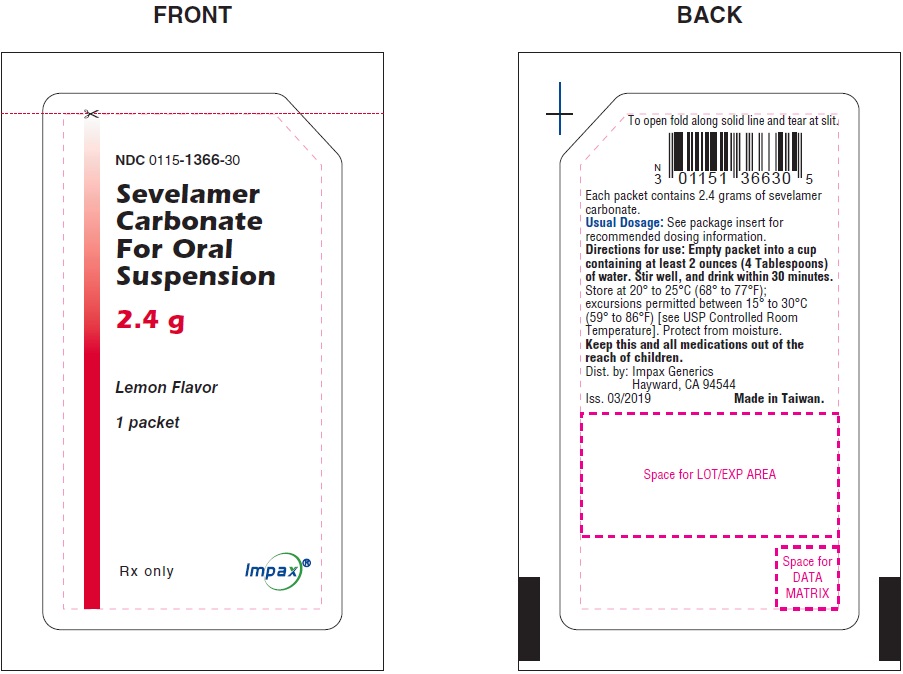
NDC: 0115-1366-30
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension, 2.4 g
Rx only
Packet Label
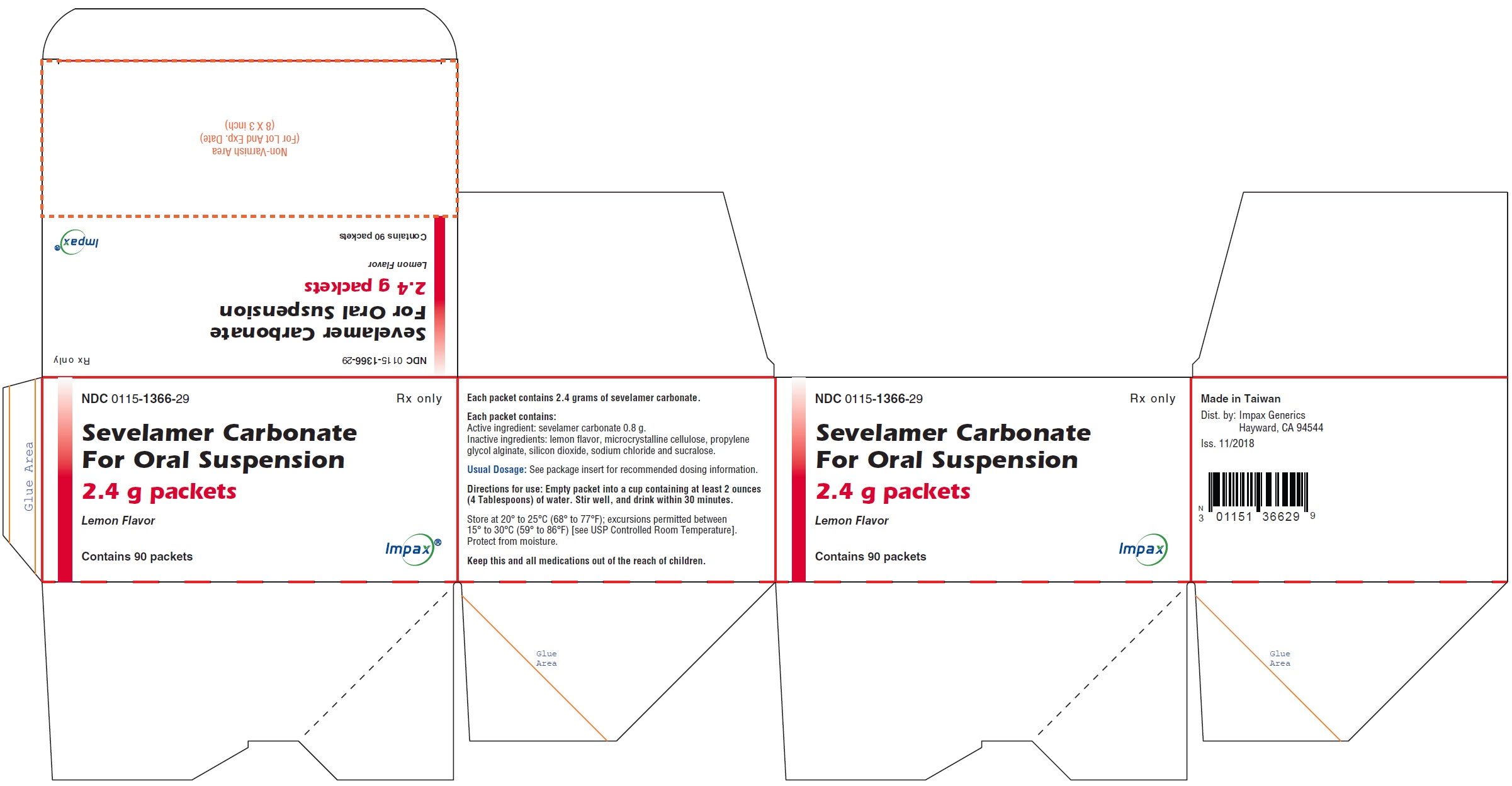

NDC: 0115-1366-29
Sevelamer Carbonate for Oral Suspension, 2.4 g
Rx only
Carton Label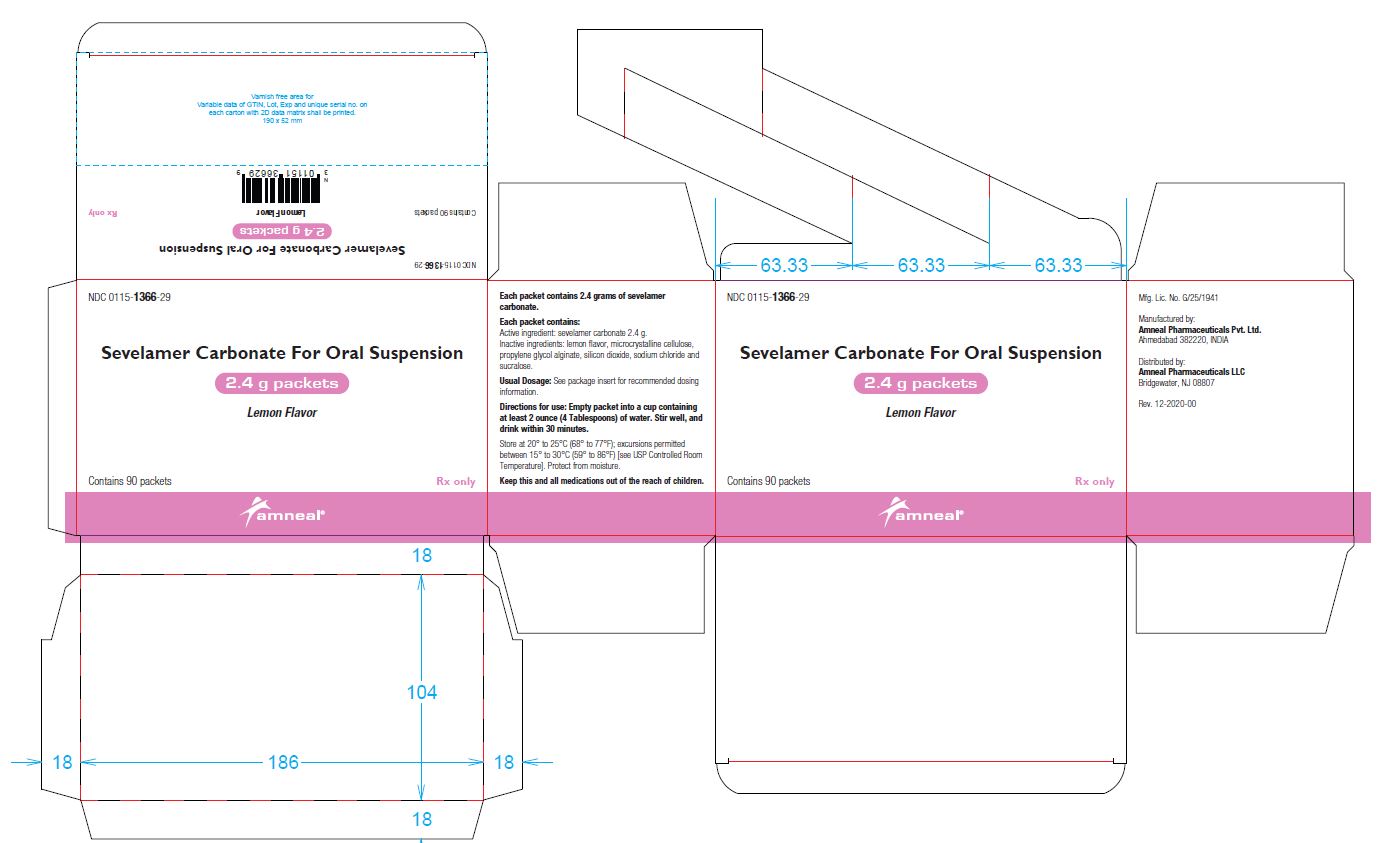
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SEVELAMER CARBONATE
sevelamer carbonate powder, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0115-1365 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEVELAMER CARBONATE (UNII: 9YCX42I8IU) (SEVELAMER - UNII:941N5DUU5C) SEVELAMER CARBONATE 800 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LEMON (UNII: 24RS0A988O) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE 102 (UNII: PNR0YF693Y) PROPYLENE GLYCOL ALGINATE (UNII: 26CD3J2R0C) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) Product Characteristics Color white (white to off-white powder) Score Shape Size Flavor LEMON Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0115-1365-29 90 in 1 CARTON 11/20/2020 1 NDC: 0115-1365-30 1 in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA211316 11/20/2020 SEVELAMER CARBONATE
sevelamer carbonate powder, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0115-1366 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEVELAMER CARBONATE (UNII: 9YCX42I8IU) (SEVELAMER - UNII:941N5DUU5C) SEVELAMER CARBONATE 2400 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LEMON (UNII: 24RS0A988O) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE 102 (UNII: PNR0YF693Y) PROPYLENE GLYCOL ALGINATE (UNII: 26CD3J2R0C) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) Product Characteristics Color white (white to off-white powder) Score Shape Size Flavor LEMON Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0115-1366-29 90 in 1 CARTON 11/20/2020 1 NDC: 0115-1366-30 1 in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA211316 11/20/2020 Labeler - Amneal Pharmaceuticals of New York LLC (123797875)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.