METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE tablet
METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Lake Erie Medical DBA Quality Care Products LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1947WARNING: ABUSE POTENTIAL, LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, LIFE-THREATENING QT PROLONGATION, ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE, and TREATMENT FOR OPIOID ADDICTION
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
- Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP contain methadone, a Schedule II controlled substance. Monitor for signs of misuse, abuse, and addiction during Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP therapy. (5.1, 9)
- Fatal respiratory depression may occur, with highest risk at initiation and with dose increases. Instruct patients on proper administration of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP to reduce the risk. (5.2)
- QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia (torsades de pointes) have occurred during treatment with methadone. (5.3)
- Accidental ingestion of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP can result in fatal overdose of methadone, especially in children. (5.4)
- Methadone products, when used for the treatment of opioid addiction in detoxification or maintenance programs, shall be dispensed only by certified opioid treatment programs as stipulated in 42 CFR 8.12. (1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Boxed Warning 07/2012
Indications and Usage (1) 07/2012
Dosage and Administration (2) 07/2012
Contraindications (4) 07/2012
Warnings and Precautions (5) 07/2012
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP are an opioid agonist indicated for the: (1)
- Management of moderate to severe pain when a continuous, around-the-clock opioid analgesic is needed for an extended period of time,
- Detoxification treatment of opioid addiction (heroin or other morphine-like drugs), and
- Maintenance treatment of opioid addiction (heroin or other morphine-like drugs), in conjunction with appropriate social and medical services. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Management of Pain: Individualize dosing based on patient’s prior analgesic treatment experience, and titrate as needed to provide adequate analgesia and minimize adverse reactions. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3). The usual starting dose in opioid non-tolerant patients is 2.5 to 10 mg every 8 to 12 hours, slowly titrated to effect. (2.1)
- Initiation of detoxification and maintenance treatment: A single dose of 20 to 30 mg may be sufficient to suppress withdrawal syndrome. (2.4)
- Do not abruptly discontinue methadone hydrochloride in a physically dependent patient. (2.3, 5.12)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 5 mg and 10 mg. (3) (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Significant respiratory depression (4)
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma (4)
- Known or suspected paralytic ileus (4)
- Hypersensitivity to methadone (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Respiratory Depression: The peak respiratory depressant effect typically occurs later, and persists longer than the peak analgesic effect, which can contribute to iatrogenic overdose. Patients who are tolerant to other opioids may be incompletely tolerant to methadone hydrochloride. (5.2)
- May cause QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia. (5.3)
- Elderly, cachectic, and debilitated patients, and patients with chronic pulmonary disease: Monitor closely because of increased risk of respiratory depression. (5.5, 5.6)
- Interaction with CNS depressants: Consider dose reduction of one or both drugs because of additive effects. (5.7, 7.2)
- Hypotensive effect: Monitor during dose initiation and titration (5.8)
- Patients with head injury or increased intracranial pressure: Monitor for sedation and respiratory depression. Avoid use of methadone hydrochloride in patients with impaired consciousness or coma susceptible to intracranial effects of CO2 retention. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are: lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, vomiting, and sweating. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Roxane Laboratories, Inc. at 1-800-962-8364 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- CYP3A4 Inducers: Increased risk of more rapid metabolism and decreased effects of methadone. (7.1)
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Increased risk of reduced metabolism and methadone toxicity. (7.1)
- Anti-retroviral Agents: May result in increased clearance and decreased plasma levels of methadone or in certain cases, increased plasma levels and risk of toxicity. (7.1)
- Potentially Arrhythmogenic Agents: Extreme caution is necessary when any drug known to have the potential to prolong the QT interval is prescribed in conjunction with methadone. (7.3)
- Opioid antagonists, partial agonists, mixed agonist/antagonist opioid analgesics: Avoid use with methadone hydrochloride because they may reduce analgesic effect of methadone hydrochloride or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. (5.12, 7.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Nursing mothers: Methadone has been detected in human milk. Closely monitor infants of nursing women receiving methadone hydrochloride. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2013
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Initial Dosing for Management of Pain
2.2 Titration and Maintenance of Therapy for Pain
2.3 Discontinuation of Methadone Hydrochloride for Pain
2.4 Induction/Initial Dosing for Detoxification and Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Addiction
2.5 Titration and Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Dependence Detoxification
2.6 Medically Supervised Withdrawal After a Period of Maintenance Treatment for Opioid Addiction
2.7 Risk of Relapse in Patients on Methadone Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Addiction
2.8 Considerations for Management of Acute Pain During Methadone Maintenance Treatment
2.9 Dosage Adjustment During Pregnancy
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Abuse Potential
5.2 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
5.3 Life-Threatening QT Prolongation
5.4 Accidental Exposure
5.5 Elderly, Cachectic, and Debilitated Patients
5.6 Use in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease
5.7 Interactions with CNS Depressants and Illicit Drugs
5.8 Hypotensive Effect
5.9 Use in Patients with Head Injury or Increased Intracranial Pressure
5.10 Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
5.11 Use in Patients with Convulsive or Seizure Disorders
5.12 Avoidance of Withdrawal
5.13 Driving and Operating Machinery
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cytochrome P450 Interactions
7.2 CNS Depressants
7.3 Potentially Arrhythmogenic Agents
7.4 Opioid Antagonists, Mixed Agonist/Antagonists, and Partial Agonists
7.5 Antidepressants
7.6 Anticholinergics
7.7 Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
8.7 Renal Impairment
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Storage and Handling
16.2 How Supplied
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: ABUSE POTENTIAL, LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION, LIFE-THREATENING QT PROLONGATION, ACCIDENTAL EXPOSURE, and TREATMENT FOR OPIOID ADDICTION
Abuse Potential
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP contain methadone, an opioid agonist and Schedule II controlled substance with an abuse liability similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Assess each patient’s risk for opioid abuse or addiction prior to prescribing Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP. The risk for opioid abuse is increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depressive disorder). Routinely monitor all patients receiving Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP for signs of misuse, abuse, and addiction during treatment [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
Life-threatening Respiratory Depression
Respiratory depression, including fatal cases, have been reported during initiation and conversion of patients to Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP, and even when the drug has been used as recommended and not misused or abused [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Proper dosing and titration are essential and Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP should only be prescribed by healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable in the use of potent opioids for the management of chronic pain. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP or following a dose increase. The peak respiratory depressant effect of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP occurs later, and persists longer than the peak analgesic effect, especially during the initial dosing period.
Life-threatening QT Prolongation
QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia (torsades de pointes) have occurred during treatment with methadone. Most cases involve patients being treated for pain with large, multiple daily doses of methadone, although cases have been reported in patients receiving doses commonly used for maintenance treatment of opioid addiction. Closely monitor patients for changes in cardiac rhythm during initiation and titration of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP.
Accidental Exposure
Accidental ingestion of Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP, especially in children, can result in a fatal overdose of methadone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Conditions For Distribution And Use Of Methadone Products For The Treatment Of Opioid Addiction
For detoxification and maintenance of opioid dependence, methadone should be administered in accordance with the treatment standards cited in 42 CFR Section 8, including limitations on unsupervised administration [see Indications and Usage (1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP are indicated for the:
- Management of moderate to severe pain when a continuous, around-the-clock opioid analgesic is needed for an extended period of time.
- Detoxification treatment of opioid addiction (heroin or other morphine-like drugs).
- Maintenance treatment of opioid addiction (heroin or other morphine-like drugs), in conjunction with appropriate social and medical services.
Limitations of Use
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP are not for use:
- As an as-needed (prn) analgesic
- For pain that is mild or not expected to persist for an extended period of time
- For acute pain
- For postoperative pain
Conditions For Distribution And Use Of Methadone Products For The Treatment Of Opioid Addiction
Code of Federal Regulations, Title 42, Sec 8
Methadone products when used for the treatment of opioid addiction in detoxification or maintenance programs, shall be dispensed only by opioid treatment programs (and agencies, practitioners or institutions by formal agreement with the program sponsor) certified by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and approved by the designated state authority. Certified treatment programs shall dispense and use methadone in oral form only and according to the treatment requirements stipulated in the Federal Opioid Treatment Standards (42 CFR 8.12). See below for important regulatory exceptions to the general requirement for certification to provide opioid agonist treatment.
Failure to abide by the requirements in these regulations may result in criminal prosecution, seizure of the drug supply, revocation of the program approval, and injunction precluding operation of the program.
Regulatory Exceptions To The General Requirement For Certification To Provide Opioid Agonist Treatment: During inpatient care, when the patient was admitted for any condition other than concurrent opioid addiction (pursuant to 21CFR 1306.07(c)), to facilitate the treatment of the primary admitting diagnosis).
During an emergency period of no longer than 3 days while definitive care for the addiction is being sought in an appropriately licensed facility (pursuant to 21CFR 1306.07(b)).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Initial Dosing for Management of Pain
Consider the following factors when selecting an initial dose of methadone hydrochloride:
- Total daily dose, potency, and prior opioid the patient has been taking previously;
- Patient’s degree of opioid experience and opioid tolerance;
- General condition and medical status of the patient;
- Concurrent medication;
- Type and severity of the patient’s pain
In addition, consider the following important factors that differentiate methadone from other opioid analgesics:
- The peak respiratory depressant effect of methadone occurs later and persists longer than its peak analgesic effect.
- A high degree of opioid tolerance does not eliminate the possibility of methadone overdose, iatrogenic or otherwise. Deaths have been reported during conversion to methadone from chronic, high-dose treatment with other opioid agonists and during initiation of methadone treatment of addiction in subjects previously abusing high doses of other opioid agonists.
- There is high interpatient variability in absorption, metabolism, and relative analgesic potency. Population-based equianalgesic conversion ratios between methadone and other opioids are not accurate when applied to individuals.
- The duration of analgesic action of methadone is 4 to 8 hours (based on single-dose studies) but the plasma elimination half-life is 8 to 59 hours.
- With repeated dosing, methadone is retained in the liver and then slowly released, prolonging the duration of potential toxicity.
- Steady-state plasma concentrations, and full analgesic effects, are not attained until 3 to 5 days after initiation of dosing.
- Methadone has a narrow therapeutic index, especially when combined with other drugs.
Methadone hydrochloride is administered at a frequency of every 8 to 12 hours.
Use of Methadone Hydrochloride as the First Opioid Analgesic: Initiate methadone hydrochloride therapy with small doses, no more than 2.5 mg to 10 mg every 8 to 12 hours. To maintain adequate analgesia, more frequent administration may be required. Monitor patients closely for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression.
Conversion from Parenteral Methadone: Use a conversion ratio of 1:2 mg for parenteral to oral methadone (e.g., 5 mg parenteral methadone to 10 mg oral methadone).
Conversion from Other Opioids: Published conversion ratios for other opioids to methadone may overestimate the dose of methadone. Deaths have occurred in opioid-tolerant patients during conversion to methadone.
Conversion ratios in many commonly used equianalgesic dosing tables are based on single-dose comparisons in patients not tolerant to the effects of opioid and do not apply in the setting of conversion of opioid tolerant patients to methadone for chronic use. In the case of a single-dose administration, the onset, duration, and potency of analgesic action of methadone are comparable to those of morphine. Incomplete cross tolerance can result in greater than expected toxicity. In addition, with repeated dosing, the potency of methadone increases due to systemic accumulation.
The conversion ratio between methadone and other opioids varies dramatically depending on baseline opioid (morphine equivalent) use as shown in the table below.
The dose conversion scheme below (Table 1) is derived from various consensus guidelines for converting chronic pain patients to methadone from morphine. Consult published conversion guidelines to determine the equivalent morphine dose for patients converting from other opioids.
Table 1: Oral Morphine to Oral Methadone Conversion for Chronic Administration Total Daily Baseline Oral
Morphine DoseEstimated Daily Oral Methadone Requirement as Percent of Total Daily Morphine Dose
< 100 mg 20% to 30% 100 to 300 mg 10% to 20% 300 to 600 mg 8% to 12% 600 mg to 1000 mg 5% to 10% > 1000 mg < 5 % Divide the total daily methadone dose derived from the table above to reflect the intended dosing schedule (i.e., for administration every 8 hours, divide total daily methadone dose by 3).
Equianalgesic methadone dosing varies not only between patients, but also within the same patient, depending on baseline morphine (or other opioid) dose. Table 1 has been included in order to illustrate this concept and to provide a recommendation for a starting point for opioid conversion.
In addition to these recommendations, take into consideration the patient’s:
- prior opioid exposure
- general medical condition
- concomitant medication
- anticipated breakthrough medication use
2.2 Titration and Maintenance of Therapy for Pain
Individually titrate methadone hydrochloride to a dose that provides adequate analgesia and minimizes adverse reactions. Continually reevaluate patients receiving methadone hydrochloride to assess the maintenance of pain control and the relative incidence of adverse reactions. During chronic therapy, especially for non-cancer-related pain (or pain associated with other terminal illnesses), periodically reassess the continued need for the use of opioid analgesics.
If the level of pain increases, attempt to identify the source of increased pain, while adjusting the methadone hydrochloride dose to decrease the level of pain. Because steady-state plasma concentrations are approximated within 24 to 36 hours, methadone hydrochloride dosage adjustments may be done every 1 to 2 days. Patients who experience breakthrough pain may require dosage adjustment or rescue medication with a small dose of an immediate-release medication.
If signs of excessive opioid-related adverse reactions are observed, the next dose may be reduced. Adjust the dose to obtain an appropriate balance between management of pain and opioid-related adverse reactions. The endpoint of titration is achievement of adequate pain relief, balanced against tolerability of opioid adverse reactions.
If a patient develops intolerable opioid related adverse reactions, the methadone dose, or dosing interval, may need to be adjusted.
2.3 Discontinuation of Methadone Hydrochloride for Pain
When a patient no longer requires therapy with methadone hydrochloride for pain, use a gradual downward titration, of the dose every two to four days, to prevent signs and symptoms of withdrawal in the physically-dependent patient. Do not abruptly discontinue methadone hydrochloride.
2.4 Induction/Initial Dosing for Detoxification and Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Addiction
For detoxification and maintenance of opioid dependence methadone should be administered in accordance with the treatment standards cited in 42 CFR Section 8.12, including limitations on unsupervised administration.
Administer the initial methadone dose under supervision, when there are no signs of sedation or intoxication, and the patient shows symptoms of withdrawal. An initial single dose of 20 to 30 mg of methadone hydrochloride will often be sufficient to suppress withdrawal symptoms. The initial dose should not exceed 30 mg.
To make same-day dosing adjustments, have the patient wait 2 to 4 hours for further evaluation, when peak levels have been reached. Provide an additional 5 to 10 mg of methadone hydrochloride if withdrawal symptoms have not been suppressed or if symptoms reappear.
The total daily dose of methadone hydrochloride on the first day of treatment should not ordinarily exceed 40 mg. Adjust the dose over the first week of treatment based on control of withdrawal symptoms at the time of expected peak activity (e.g., 2 to 4 hours after dosing). When adjusting the dose, keep in mind that methadone levels will accumulate over the first several days of dosing; deaths have occurred in early treatment due to the cumulative effects. Instruct patients that the dose will “hold” for a longer period of time as tissue stores of methadone accumulate.
Use lower initial doses for patients whose tolerance is expected to be low at treatment entry. Any patient who has not taken opioids for more than 5 days may no longer be tolerant. Do not determine initial doses based on previous treatment episodes or dollars spent per day on illicit drug use.
Short-term Detoxification: For a brief course of stabilization followed by a period of medically supervised withdrawal, titrate the patient to a total daily dose of about 40 mg in divided doses to achieve an adequate stabilizing level. After 2 to 3 days of stabilization, gradually decrease the dose of methadone hydrochloride. Decrease the dose of methadone hydrochloride on a daily basis or at 2-day intervals, keeping the amount of methadone hydrochloride sufficient to keep withdrawal symptoms at a tolerable level. Hospitalized patients may tolerate a daily reduction of 20% of the total daily dose. Ambulatory patients may need a slower schedule.
2.5 Titration and Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Dependence Detoxification
Titrate patients in maintenance treatment to a dose that prevents opioid withdrawal symptoms for 24 hours, reduces drug hunger or craving, and blocks or attenuates the euphoric effects of self-administered opioids, ensuring that the patient is tolerant to the sedative effects of methadone. Most commonly, clinical stability is achieved at doses between 80 to 120 mg/day.
2.6 Medically Supervised Withdrawal After a Period of Maintenance Treatment for Opioid Addiction
There is considerable variability in the appropriate rate of methadone taper in patients choosing medically supervised withdrawal from methadone treatment. Dose reductions should generally be less than 10% of the established tolerance or maintenance dose, and 10 to 14-day intervals should elapse between dose reductions. Apprise patients of the high risk of relapse to illicit drug use associated with discontinuation of methadone maintenance treatment.
2.7 Risk of Relapse in Patients on Methadone Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Addiction
Abrupt opioid discontinuation can lead to development of opioid withdrawal symptoms [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)]. Opioid withdrawal symptoms have been associated with an increased risk of relapse to illicit drug use in susceptible patients.
2.8 Considerations for Management of Acute Pain During Methadone Maintenance Treatment
Patients in methadone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence who experience physical trauma, postoperative pain or other acute pain cannot be expected to derive analgesia from their existing dose of methadone. Such patients should be administered analgesics, including opioids, in doses that would otherwise be indicated for non-methadone-treated patients with similar painful conditions. When opioids are required for management of acute pain in methadone maintenance patients, somewhat higher and/or more frequent doses will often be required than would be the case for non-tolerant patients due to the opioid tolerance induced by methadone.
2.9 Dosage Adjustment During Pregnancy
Methadone clearance may be increased during pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman’s methadone dose may need to be increased or the dosing interval decreased. Methadone should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Methadone hydrochloride tablets are available in 5 mg and 10 mg dosage strengths. The 5 mg tablets are round, white and are debossed with tablet identifier “54 210” on one side and scored on the other side. The 10 mg tablets are round, white and are debossed with tablet identifier “54 142” on one side and scored on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets USP are contraindicated in patients with:
- Significant respiratory depression
- Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment
- Known or suspected paralytic ileus
- Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis) to methadone [see Adverse Reactions (6)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Abuse Potential
Methadone hydrochloride tablets contain methadone, an opioid agonist and a Schedule II controlled substance. Methadone can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit. Opioid agonists are sought by drug abusers and people with addiction disorders and are subject to criminal diversion. Consider these risks when prescribing or dispensing methadone hydrochloride in situations where there is concern about increased risks of misuse, abuse, or diversion. Concerns about abuse, addiction, and diversion should not, however, prevent the proper management of pain.
For each patient prescribed methadone hydrochloride for pain management, assess the risk for opioid abuse or addiction prior to prescribing methadone hydrochloride. The risk for opioid abuse is increased in patients with a personal or family history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction) or mental illness (e.g., major depression). Patients at increased risk may still be appropriately treated with modified-release opioid formulations; however these patients will require intensive monitoring for signs of misuse, abuse, or addiction. Routinely monitor all patients receiving opioids for signs of misuse, abuse, and addiction because these drugs carry a risk for addiction even under appropriate medical use.
Contact local state professional licensing board or state controlled substances authority for information on how to prevent and detect abuse or diversion of this product.
5.2 Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression
Respiratory depression is the primary risk of methadone hydrochloride. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Respiratory depression from opioids is manifested by a reduced urge to breathe and a decreased rate of respiration, often associated with a “sighing” pattern of breathing (deep breaths separated by abnormally long pauses). Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status [see Overdosage (10)].
While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of methadone hydrochloride, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy or following a dose increase. The peak respiratory depressant effect of methadone occurs later, and persists longer than the peak analgesic effect, especially during the initial dosing period. Closely monitor patients for respiratory depression when initiating therapy with methadone hydrochloride and following dose increases.
Instruct patients against use by individuals other than the patient for whom methadone hydrochloride was prescribed and to keep methadone hydrochloride out of the reach of children, as such inappropriate use may result in fatal respiratory depression.
To reduce the risk of respiratory depression, proper dosing and titration of methadone hydrochloride are essential [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)]. Overestimating the methadone hydrochloride dose when converting patients from another opioid product can result in fatal overdose with the first dose. Respiratory depression has also been reported with use of methadone when used as recommended and not misused or abused.
To further reduce the risk of respiratory depression, consider the following:
- Patients tolerant to other opioids may be incompletely tolerant to methadone. Incomplete cross-tolerance is of particular concern for patients tolerant to other mu-opioid agonists who are being converted to treatment with methadone, thus making determination of dosing during opioid treatment conversion complex. Deaths have been reported during conversion from chronic, high-dose treatment with other opioid agonists.
- Proper dosing and titration are essential and methadone hydrochloride should be prescribed only by healthcare professionals who are knowledgeable in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methadone, especially when converting patients from other opioids, and in the use of potent opioids for the management of chronic pain.
- Methadone hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with respiratory depression and in patients with conditions that increase the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression [see Contraindications (4)].
5.3 Life-Threatening QT Prolongation
Cases of QT interval prolongation and serious arrhythmia (torsades de pointes) have been observed during treatment with methadone. These cases appear to be more commonly associated with, but not limited to, higher dose treatment (> 200 mg/day). Most cases involve patients being treated for pain with large, multiple daily doses of methadone, although cases have been reported in patients receiving doses commonly used for maintenance treatment of opioid addiction. In most patients on the lower doses typically used for maintenance, concomitant medications and/or clinical conditions such as hypokalemia were noted as contributing factors. However, the evidence strongly suggests that methadone possesses the potential for adverse cardiac conduction effects in some patients. The effects of methadone on the QT interval have been confirmed in in vivo laboratory studies, and methadone has been shown to inhibit cardiac potassium channels in in vitro studies.
Closely monitor patients with risk factors for development of prolonged QT interval (e.g., cardiac hypertrophy, concomitant diuretic use, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia), a history of cardiac conduction abnormalities, and those taking medications affecting cardiac conduction. QT prolongation has also been reported in patients with no prior cardiac history who have received high doses of methadone.
Evaluate patients developing QT prolongation while on methadone treatment for the presence of modifiable risk factors, such as concomitant medications with cardiac effects, drugs that might cause electrolyte abnormalities, and drugs that might act as inhibitors of methadone metabolism.
Only initiate methadone hydrochloride therapy for pain in patients for whom the anticipated benefit outweighs the risk of QT prolongation and development of dysrhythmias that have been reported with high doses of methadone.
The use of methadone in patients already known to have a prolonged QT interval has not been systematically studied.
5.4 Accidental Exposure
Accidental ingestion of methadone hydrochloride, especially in children, can result in a fatal overdose of methadone. Methadone hydrochloride should be kept out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
5.5 Elderly, Cachectic, and Debilitated Patients
Respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients as they may have altered pharmacokinetics due to poor fat stores, muscle wasting, or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients. Therefore, monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating methadone hydrochloride and when methadone hydrochloride is given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.6 Use in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease
Monitor patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and patients having a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression for respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy and titrating with methadone hydrochloride, as in these patients, even usual therapeutic doses of methadone hydrochloride may decrease respiratory drive to the point of apnea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Consider the use of alternative non-opioid analgesics in these patients if possible.
5.7 Interactions with CNS Depressants and Illicit Drugs
Hypotension, profound sedation, coma, or respiratory depression may result if methadone hydrochloride is used concomitantly with other CNS depressants (e.g., sedatives, anxiolytics, hypnotics, neuroleptics, other opioids). When considering the use of methadone hydrochloride in a patient taking a CNS depressant, assess the duration of use of the CNS depressant and the patient’s response, including the degree of tolerance that has developed to CNS depression. Additionally, consider the patient’s use, if any, of alcohol or illicit drugs that cause CNS depression. If methadone hydrochloride therapy is to be initiated in a patient taking a CNS depressant, start with a lower methadone hydrochloride dose than usual and monitor patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression and consider using a lower dose of the concomitant CNS depressant [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Deaths associated with illicit use of methadone have frequently involved concomitant benzodiazepine abuse.
5.8 Hypotensive Effect
Methadone hydrochloride may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is an increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g. phenothiazines or general anesthetics) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating or titrating the dose of methadone hydrochloride.
5.9 Use in Patients with Head Injury or Increased Intracranial Pressure
Monitor patients taking methadone hydrochloride who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors) for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with methadone hydrochloride. Methadone hydrochloride may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury.
Avoid the use of methadone hydrochloride in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
5.10 Use in Patients with Gastrointestinal Conditions
Methadone hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with paralytic ileus. Avoid the use of methadone hydrochloride in patients with other gastrointestinal obstruction.
The methadone in methadone hydrochloride may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms. Opioids may cause increases in the serum amylase.
5.11 Use in Patients with Convulsive or Seizure Disorders
The methadone in methadone hydrochloride may aggravate convulsions in patients with convulsive disorders, and may induce or aggravate seizures in some clinical settings. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control during methadone hydrochloride therapy.
5.12 Avoidance of Withdrawal
Avoid the use of partial agonists or mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (i.e., buprenorphine, pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) in patients who have received or are receiving a course of therapy with a full opioid agonist analgesic, including methadone hydrochloride. In these patients, partial agonists or mixed agonists/antagonists analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect and/or may precipitate withdrawal symptoms [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
When discontinuing methadone hydrochloride, gradually taper the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Do not abruptly discontinue methadone hydrochloride.
5.13 Driving and Operating Machinery
Methadone hydrochloride may impair the mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to the effects of methadone hydrochloride and know how they will react to the medication.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions and/or conditions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Respiratory Depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Chronic Pulmonary Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Head Injuries and Increased Intracranial Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Interactions with Other CNS Depressants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypotensive Effect [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Gastrointestinal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
The major hazards of methadone are respiratory depression and, to a lesser degree, systemic hypotension. Respiratory arrest, shock, cardiac arrest, and death have occurred.
The most frequently observed adverse reactions include lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, vomiting, and sweating. These effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory patients and in those who are not suffering severe pain. In such individuals, lower doses are advisable.
Other adverse reactions include the following:
Body as a Whole: asthenia (weakness), edema, headache
Cardiovascular: arrhythmias, bigeminal rhythms, bradycardia, cardiomyopathy, ECG abnormalities, extrasystoles, flushing, heart failure, hypotension, palpitations, phlebitis, QT interval prolongation, syncope, T-wave inversion, tachycardia, torsades de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia
Central Nervous System: agitation, confusion, disorientation, dysphoria, euphoria, insomnia, hallucinations, seizures, visual disturbances
Endocrine: hypogonadism
Gastrointestinal: abdominal pain, anorexia, biliary tract spasm, constipation, dry mouth, glossitis
Hematologic: reversible thrombocytopenia has been described in opioid addicts with chronic hepatitis
Metabolic: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, weight gain
Renal: antidiuretic effect, urinary retention or hesitancy
Reproductive: amenorrhea, reduced libido and/or potency, reduced ejaculate volume, reduced seminal vesicle and prostate secretions, decreased sperm motility, abnormalities in sperm morphology
Respiratory: pulmonary edema, respiratory depression
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: pruritus, urticaria, other skin rashes, and rarely, hemorrhagic urticaria
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in methadone hydrochloride. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention.
Maintenance on a Stabilized Dose: During prolonged administration of methadone, as in a methadone maintenance treatment program, constipation and sweating often persist and hypogonadism, decreased serum testosterone and reproductive effects are thought to be related to chronic opioid use.
Methadone Hydrochloride for the Detoxification and Maintenance Treatment of Opioid Dependence: During the induction phase of methadone maintenance treatment, patients are being withdrawn from illicit opioids and may have opioid withdrawal symptoms. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms including: lacrimation, rhinorrhea, sneezing, yawning, excessive perspiration, goose-flesh, fever, chilling alternating with flushing, restlessness, irritability, weakness, anxiety, depression, dilated pupils, tremors, tachycardia, abdominal cramps, body aches, involuntary twitching and kicking movements, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, intestinal spasms, and weight loss and consider dose adjustment as indicated.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cytochrome P450 Interactions
Methadone undergoes hepatic N-demethylation by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms, principally CYP3A4, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and CYP2D6 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Cytochrome P450 Inducers: Concurrent use of methadone hydrochloride and drugs that induce cytochrome P450 enzymes (such as rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and St. John’s Wort) may result in reduced efficacy of methadone hydrochloride and could precipitate a withdrawal syndrome. Closely monitor patients receiving methadone hydrochloride and an enzyme inducer closely for signs of withdrawal and adjust the methadone hydrochloride dose accordingly.
Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors: Coadministration of drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 (such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, clarithromycin, erythromycin, telithromycin) and/or drugs that inhibit CYP2C9 (such as sertraline and fluvoxamine) may cause decreased clearance of methadone, which could increase or prolong adverse drug effects and may cause fatal respiratory depression [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor patients closely for signs of respiratory or central nervous system depression when methadone hydrochloride is prescribed with a CYP3A4 inhibitor and reduce the dosage if necessary.
Paradoxical Effects of Antiretroviral Agents on Methadone Hydrochloride: Concurrent use of certain protease inhibitors with CYP3A4 inhibitory activity, alone and in combination, such as abacavir, amprenavir, darunavir+ritonavir, efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, telaprevir, lopinavir+ritonavir, saquinavir+ritonavir, and tipranvir+ritonavir, has resulted in increased clearance or decreased plasma levels of methadone. This may result in reduced efficacy of methadone hydrochloride and could precipitate a withdrawal syndrome. Monitor methadone-maintained patients receiving any of these anti-retroviral therapies closely for evidence of withdrawal effects and adjust the methadone dose accordingly.
Effects of Methadone Hydrochloride on Antiretroviral Agents: Didanosine and Stavudine: Experimental evidence demonstrated that methadone decreased the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) and peak levels for didanosine and stavudine, with a more significant decrease for didanosine. Methadone disposition was not substantially altered.
Zidovudine: Experimental evidence demonstrated that methadone increased the AUC of zidovudine, which could result in toxic effects.
7.2 CNS Depressants
Concurrent use of methadone hydrochloride and other central nervous system (CNS) depressants (e.g. sedatives, hypnotics, general anesthetics, antiemetics, phenothiazines, other tranquilizers, alcohol and drugs of abuse) can increase the risk of respiratory depression, hypotension, and profound sedation or coma. Monitor patients receiving CNS depressants and methadone hydrochloride for signs of respiratory depression and hypotension. When such combined therapy is contemplated, reduce the initial dose of one or both agents. Deaths have been reported when methadone has been abused in conjunction with benzodiazepines.
7.3 Potentially Arrhythmogenic Agents
Monitor patients closely for cardiac conduction changes when any drug known to have the potential to prolong the QT interval is prescribed in conjunction with methadone. Pharmacodynamic interactions may occur with concomitant use of methadone and potentially arrhythmogenic agents such as class I and III antiarrhythmics, some neuroleptics and tricyclic antidepressants, and calcium channel blockers.
Similarly, monitor patients closely when prescribing methadone concomitantly with drugs capable of inducing electrolyte disturbances (hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia) that may prolong the QT interval, including diuretics, laxatives, and, in rare cases, mineralocorticoid hormones.
7.4 Opioid Antagonists, Mixed Agonist/Antagonists, and Partial Agonists
As with other mu-agonists, patients maintained on methadone may experience withdrawal symptoms when given opioid antagonists, mixed agonist/antagonists, and partial agonists. Examples of such agents are naloxone, naltrexone, pentazocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol, and buprenorphine.
7.5 Antidepressants
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors: Therapeutic doses of meperidine have precipitated severe reactions in patients concurrently receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors or those who have received such agents within 14 days. Similar reactions thus far have not been reported with methadone. However, if the use of methadone is necessary in such patients, a sensitivity test should be performed in which repeated small, incremental doses of methadone are administered over the course of several hours while the patient’s condition and vital signs are carefully observed.
Desipramine: Blood levels of desipramine have increased with concurrent methadone administration.
7.6 Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics or other drugs with anticholinergic activity when used concurrently with opioids may result in increased risk of urinary retention and/or severe constipation, which may lead to paralytic ileus. Monitor patients for signs of urinary retention or reduced gastric motility when methadone hydrochloride is used concurrently with anticholinergic drugs.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: There are no adequate and well controlled studies of methadone use in pregnant women. Methadone has been shown to be teratogenic in the hamster at doses 2 times the human daily oral dose (120 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis) and in mice at doses equivalent to the human daily oral dose (120 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis). Increased neonatal mortality and significant differences in behavioral tests have been reported in the offspring of male rodents that were treated with methadone prior to mating when compared to control animals. Methadone has been detected in human amniotic fluid and cord plasma at concentrations proportional to maternal plasma and in newborn urine at lower concentrations than corresponding maternal urine. Methadone should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Dosage Adjustment during Pregnancy: The disposition of oral methadone has been studied in approximately 30 pregnant patients in 2nd and 3rd trimesters. Total body clearance of methadone was increased in pregnant patients compared to the same patients postpartum or to non-pregnant opioid-dependent women. The terminal half-life of methadone is decreased during 2nd and 3rd trimesters. The decrease in plasma half-life and increased clearance of methadone resulting in lower methadone trough levels during pregnancy can lead to withdrawal symptoms in some pregnant patients. The dosage may need to be increased or the dosing interval decreased in pregnant patients receiving methadone to achieve therapeutic effect [see Dosage and Administration (2.9)].
Effects on the Neonate: Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery may be physically dependent. Onset of withdrawal symptoms in infants is usually in the first days after birth. Monitor newborn for withdrawal signs and symptoms including: irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyper-active reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the neonatal withdrawal syndrome does not always correlate with the maternal dose or the duration of maternal exposure. The duration of the withdrawal signs may vary from a few days to weeks or even months. There is no consensus on the appropriate management of infant withdrawal [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Human Data: Reported studies have generally compared the benefit of methadone to the risk of untreated addiction to illicit drugs; the relevance of these findings to pain patients prescribed methadone during pregnancy is unclear. Pregnant women involved in methadone maintenance programs have been reported to have significantly improved prenatal care leading to significantly reduced incidence of obstetric and fetal complications and neonatal morbidity and mortality when compared to women using illicit drugs. Several factors, including maternal use of illicit drugs, nutrition, infection and psychosocial circumstances, complicate the interpretation of investigations of the children of women who take methadone during pregnancy. Information is limited regarding dose and duration of methadone use during pregnancy, and most maternal exposure appears to occur after the first trimester of pregnancy.
A review of published data on experiences with methadone use during pregnancy by the Teratogen Information System (TERIS) concluded that maternal use of methadone during pregnancy as part of a supervised, therapeutic regimen is unlikely to pose a substantial teratogenic risk (quantity and quality of data assessed as “limited to fair”). However, the data are insufficient to state that there is no risk (TERIS, last reviewed October, 2002). A retrospective case series of 101 pregnant, opioid-dependent women who underwent inpatient opioid detoxification with methadone did not demonstrate any increased risk of miscarriage in the 2nd trimester or premature delivery in the 3rd trimester. Recent studies suggest an increased risk of premature delivery in opioid-dependent women exposed to methadone during pregnancy, although the presence of confounding factors makes it difficult to determine a causal relationship. Several studies have suggested that infants born to narcotic-addicted women treated with methadone during all or part of pregnancy have been found to have decreased fetal growth with reduced birth weight, length, and/or head circumference compared to controls. This growth deficit does not appear to persist into later childhood. Children prenatally exposed to methadone have been reported to demonstrate mild but persistent deficits in performance on psychometric and behavioral tests. In addition, several studies suggest that children born to opioid-dependent women exposed to methadone during pregnancy may have an increased risk of visual development anomalies; however, a causal relationship has not been assigned.
There are conflicting reports on whether Sudden Infant Death Syndrome occurs with an increased incidence in infants born to women treated with methadone during pregnancy. Abnormal fetal non-stress tests have been reported to occur more frequently when the test is performed 1 to 2 hours after a maintenance dose of methadone in late pregnancy compared to controls.
Animal Data: Methadone did not produce teratogenic effects in rat or rabbit models. Methadone produced teratogenic effects following large doses, in the guinea pig, hamster and mouse. One published study in pregnant hamsters indicated that a single subcutaneous dose of methadone ranging from 31 to 185 mg/kg (the 31 mg/kg dose is approximately 2 times a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis) on day 8 of gestation resulted in a decrease in the number of fetuses per litter and an increase in the percentage of fetuses exhibiting congenital malformations described as exencephaly, cranioschisis, and “various other lesions.” The majority of the doses tested also resulted in maternal death. In another study, a single subcutaneous dose of 22 to 24 mg/kg methadone (estimated exposure was approximately equivalent to a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis) administered on day 9 of gestation in mice also produced exencephaly in 11% of the embryos. However, no effects were reported in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 40 mg/kg (estimated exposure was approximately 3 and 6 times, respectively, a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis) administered during days 6 to 15 and 6 to 18, respectively.
Published animal data have reported increased neonatal mortality in the offspring of male rodents that were treated with methadone prior to mating. In these studies, the female rodents were not treated with methadone, indicating paternally-mediated developmental toxicity. Specifically, methadone administered to the male rat prior to mating with methadone-naïve females resulted in decreased weight gain in progeny after weaning. The male progeny demonstrated reduced thymus weights, whereas the female progeny demonstrated increased adrenal weights. Behavioral testing of these male and female progeny revealed significant differences in behavioral tests compared to control animals, suggesting that paternal methadone exposure can produce physiological and behavioral changes in progeny in this model. Other animal studies have reported that perinatal exposure to opioids including methadone alters neuronal development and behavior in the offspring. Perinatal methadone exposure in rats has been linked to alterations in learning ability, motor activity, thermal regulation, nociceptive responses and sensitivity to drugs.
Additional animal data demonstrates evidence for neurochemical changes in the brains of methadone-treated offspring, including changes to the cholinergic, dopaminergic, noradrenergic and serotonergic systems. Studies demonstrated that methadone treatment of male rats for 21 to 32 days prior to mating with methadone-naïve females did not produce any adverse effects, suggesting that prolonged methadone treatment of the male rat resulted in tolerance to the developmental toxicities noted in the progeny. Mechanistic studies in this rat model suggest that the developmental effects of “paternal” methadone on the progeny appear to be due to decreased testosterone production. These animal data mirror the reported clinical findings of decreased testosterone levels in human males on methadone maintenance therapy for opioid addiction and in males receiving chronic intraspinal opioids.
Additional data have been published indicating that methadone treatment of male rats (once a day for three consecutive days) increased embryolethality and neonatal mortality. Examination of uterine contents of methadone-naïve female mice bred to methadone-treated mice indicated that methadone treatment produced an increase in the rate of preimplantation deaths in all post-meiotic states.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Methadone hydrochloride is not for use in women during and immediately prior to labor, where shorter acting analgesics or other analgesic techniques are more appropriate [see Indications and Usage (1)]. Opioid analgesics may prolong labor by temporarily reducing the strength, duration and frequency of uterine contractions. However, these effects are not consistent and may be offset by an increased rate of cervical dilatation, which tends to shorten labor.
Opioids with mixed agonist-antagonist properties should not be used for pain control during labor in patients chronically treated with methadone as they may precipitate acute withdrawal [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Opioids cross the placenta and may produce respiratory depression and psycho-physiologic effects in neonates. Closely observe neonates whose mothers received opioid analgesics during labor for signs of respiratory depression. An opioid antagonist, such as naloxone, should be available for reversal of opioid-induced respiratory depression in the neonate.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Methadone is secreted into human milk. At maternal oral doses of 10 to 80 mg/day, methadone concentrations from 50 to 570 mcg/L in milk have been reported, which, in the majority of samples, were lower than maternal serum drug concentrations at steady state. Peak methadone levels in milk occur approximately 4 to 5 hours after an oral dose. Based on an average milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day, an infant would consume approximately 17.4 mcg/kg/day which is approximately 2 to 3% of the oral maternal dose. Methadone has been detected in very low plasma concentrations in some infants whose mothers were taking methadone. Cases of sedation and respiratory depression in infants exposed to methadone through breast milk have been reported. Caution should be exercised when methadone is administered to a nursing woman.
Advise women who are being treated with methadone and who are breastfeeding or express a desire to breastfeed of the presence of methadone in human milk. Instruct breastfeeding mothers how to identify respiratory depression and sedation in their babies and when it may be necessary to contact their healthcare provider or seek immediate medical care. Breastfed infants of mothers using methadone should be weaned gradually to prevent development of withdrawal symptoms in the infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety, effectiveness, and pharmacokinetics of methadone in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of methadone did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently compared to younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, start elderly patients at the low end of the dosing range, taking into account the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in geriatric patients. Closely monitor elderly patients for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression.
8.6 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Chronic maternal use of methadone during pregnancy can affect the fetus with subsequent withdrawal signs. Neonatal withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea and failure to gain weight. The onset, duration and severity of neonatal withdrawal syndrome vary based on the drug used, duration of use, the dose of last maternal use, and rate of elimination drug by the newborn. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening and should be treated according to protocols developed by neonatology experts.
8.7 Renal Impairment
Methadone pharmacokinetics have not been extensively evaluated in patients with renal insufficiency. Since unmetabolized methadone and its metabolites are excreted in urine to a variable degree, start these patients on lower doses and with longer dosing intervals and titrate slowly while carefully monitoring for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression.
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
Methadone has not been extensively evaluated in patients with hepatic insufficiency. Methadone is metabolized by hepatic pathways; therefore, patients with liver impairment may be at risk of increased systemic exposure to methadone after multiple dosing. Start these patients on lower doses and titrate slowly while carefully monitoring for signs of respiratory and central nervous system depression.
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Methadone is a mu-agonist opioid with an abuse liability similar to other opioid agonists and is a Schedule II controlled substance. Methadone and other opioids used in analgesia have the potential for being abused and are subject to criminal diversion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
9.2 Abuse
All patients treated with opioids for pain management require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, since use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use.
Drug abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of an over-the-counter or prescription drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological or physiological effects. Drug abuse includes, but is not limited to the following examples: the use of a prescription or over-the counter drug to get “high”, or the use of steroids for performance enhancement and muscle build up.
Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and include: a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes a physical withdrawal.
“Drug-seeking” behavior is very common in addicts and drug abusers. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing or referral, repeated claims of lost prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating physician(s). “Doctor shopping” (visiting multiple prescribers) to obtain additional prescriptions is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction. Preoccupation with achieving adequate pain relief can be appropriate behavior in a patient with poor pain control.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Physicians should be aware that addiction may not be accompanied by concurrent tolerance and symptoms of physical dependence in all addicts. In addition, abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction.
Methadone hydrochloride, like other opioids, can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels of distribution. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests as required by state law, is strongly advised.
Abuse of methadone hydrochloride poses a risk of overdose and death. This risk is increased with concurrent abuse of methadone with alcohol and other substances. Methadone is for oral use only and must not be injected. Parenteral drug abuse is commonly associated with transmission of infectious diseases such as hepatitis and HIV.
Proper assessment and selection of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids may also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.6)].
9.3 Dependence
Both tolerance and physical dependence can develop during chronic opioid therapy.
Tolerance is the need for increasing doses of opioids to maintain a defined effect such as analgesia (in the absence of disease progression or other external factors). Tolerance may occur to both the desired and undesired effects of drugs, and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Physical dependence results in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Withdrawal also may be precipitated through the administration of drugs with opioid antagonist activity, e.g., naloxone, or mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics (pentazocine, butorphanol, buprenorphine, nalbuphine). Physical dependence may not occur to a clinically significant degree until after several days to weeks of continued opioid usage.
Methadone hydrochloride should not be abruptly discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. If methadone hydrochloride is abruptly discontinued in a physically dependent patient, an abstinence syndrome may occur. Some or all of the following can characterize this syndrome: restlessness, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, yawning, perspiration, chills, myalgia, and mydriasis. Other signs and symptoms also may develop, including irritability, anxiety, backache, joint pain, weakness, abdominal cramps, insomnia, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, or increased blood pressure, respiratory rate, or heart rate.
Infants born to mothers physically dependent on opioids will also be physically dependent and may exhibit respiratory difficulties and withdrawal symptoms [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.6)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Symptoms: Acute overdosage of methadone is manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, maximally constricted pupils, skeletal-muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes, bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, particularly by the intravenous route, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, and death may occur.
Treatment of Overdose: In case of overdose, priorities are the re-establishment of a patent and protected airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation if needed. Employ other supportive measures (including oxygen, vasopressors) in the management of circulatory shock and pulmonary edema as indicated. Cardiac arrest or arrhythmias will require advanced life support techniques.
The opioid antagonists, such as naloxone, are specific antidotes to respiratory depression resulting from opioid overdose. Opioid antagonists should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to methadone overdose. Such agents should be administered cautiously to patients who are known, or suspected to be, physically dependent on methadone hydrochloride. In such cases, an abrupt or complete reversal of opioid effects may precipitate an acute withdrawal syndrome.
Because the duration of reversal would be expected to be less than the duration of action of methadone in methadone hydrochloride, carefully monitor the patient until spontaneous respiration is reliably re-established. If the response to opioid antagonists is suboptimal or not sustained, additional antagonist should be given as directed in the product’s prescribing information.
In an individual physically dependent on opioids, administration of an opioid receptor antagonist may precipitate an acute withdrawal. The severity of the withdrawal produced will depend on the degree of physical dependence and the dose of the antagonist administered. If a decision is made to treat serious respiratory depression in the physically dependent patient, administration of the antagonist should be begun with care and by titration with smaller than usual doses of the antagonist.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Methadone hydrochloride is chemically described as 6-(dimethylamino)-4,4-diphenyl-3-hepatanone hydrochloride. Methadone hydrochloride is a white, crystalline material that is water-soluble. Its molecular formula is C21H27NO HCl and it has a molecular weight of 345.91. Methadone hydrochloride has a melting point of 235°C, and a pKa of 8.25 in water at 20°C. Its octanol/water partition coefficient at pH 7.4 is 117. A solution (1:100) in water has a pH between 4.5 and 6.5.
It has the following structural formula:
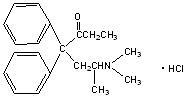
Each Methadone Hydrochloride Tablet USP contains 5 or 10 mg of methadone hydrochloride, USP and the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and starch.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Methadone hydrochloride is a mu-agonist; a synthetic opioid analgesic with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of morphine, the most prominent of which involves the central nervous system and organs composed of smooth muscle. The principal therapeutic uses for methadone are for analgesia and for detoxification or maintenance in opioid addiction. The methadone withdrawal syndrome, although qualitatively similar to that of morphine, differs in that the onset is slower, the course is more prolonged, and the symptoms are less severe.
Some data also indicate that methadone acts as an antagonist at the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. The contribution of NMDA receptor antagonism to methadone’s efficacy is unknown. Other NMDA receptor antagonists have been shown to produce neurotoxic effects in animals.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Following oral administration the bioavailability of methadone ranges between 36 to 100% and peak plasma concentrations are achieved between 1 to 7.5 hours. Dose proportionality of methadone pharmacokinetics is not known. However, after administration of daily oral doses ranging from 10 to 225 mg, the steady-state plasma concentrations ranged between 65 to 630 ng/mL and the peak concentrations ranged between 124 to 1255 ng/mL. Effect of food on the bioavailability of methadone has not been evaluated.
Distribution: Methadone is a lipophilic drug and the steady-state volume of distribution ranges between 1.0 to 8.0 L/kg. In plasma, methadone is predominantly bound to α1-acid glycoprotein (85% to 90%). Methadone is secreted in saliva, breast milk, amniotic fluid and umbilical cord plasma.
Metabolism: Methadone is primarily metabolized by N-demethylation to an inactive metabolite, 2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidene (EDDP). Cytochrome P450 enzymes, primarily CYP3A4, CYP2B6, and CYP2C19 and to a lesser extent CYP2C9 and CYP2D6, are responsible for conversion of methadone to EDDP and other inactive metabolites, which are excreted mainly in the urine. Methadone appears to be a substrate for P-glycoprotein but its pharmacokinetics do not appear to be significantly altered in case of P-glycoprotein polymorphism or inhibition.
Excretion: The elimination of methadone is mediated by extensive biotransformation, followed by renal and fecal excretion. Published reports indicate that after multiple dose administration the apparent plasma clearance of methadone ranged between 1.4 and 126 L/h, and the terminal half-life (T1/2) was highly variable and ranged between 8 to 59 hours in different studies. Methadone is a basic (pKa=9.2) compound and the pH of the urinary tract can alter its disposition in plasma. Also, since methadone is lipophilic, it has been known to persist in the liver and other tissues. The slow release from the liver and other tissues may prolong the duration of methadone action despite low plasma concentrations.
Drug Interactions: Cytochrome P450 Interactions: Methadone undergoes hepatic N-demethylation by cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms, principally CYP3A4, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and CYP2D6. Coadministration of methadone with CYP inducers may result in more rapid metabolism and potential for decreased effects of methadone, whereas administration with CYP inhibitors may reduce metabolism and potentiate methadone’s effects. Although antiretroviral drugs such as efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, lopinavir+ritonavir combination are known to inhibit some CYPs, they are shown to reduce the plasma levels of methadone, possibly due to CYP induction activity [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Therefore, drugs administered concomitantly with methadone should be evaluated for interaction potential; clinicians are advised to evaluate individual response to drug therapy.
Cytochrome P450 Inducers: The following drug interactions were reported following coadministration of methadone with known inducers of cytochrome P450 enzymes:
Rifampin: In patients well-stabilized on methadone, concomitant administration of rifampin resulted in a marked reduction in serum methadone levels and a concurrent appearance of withdrawal symptoms.
Phenytoin: In a pharmacokinetic study with patients on methadone maintenance therapy, phenytoin administration (250 mg twice daily initially for 1 day followed by 300 mg daily for 3 to 4 days) resulted in an approximately 50% reduction in methadone exposure and withdrawal symptoms occurred concurrently. Upon discontinuation of phenytoin, the incidence of withdrawal symptoms decreased and methadone exposure increased to a level comparable to that prior to phenytoin administration.
St. John’s Wort, Phenobarbital, Carbamazepine: Administration of methadone with other CYP3A4 inducers may result in withdrawal symptoms.
Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors: Since the metabolism of methadone is mediated primarily by CYP3A4 isozyme, coadministration of drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 activity may cause decreased clearance of methadone.
Voriconazole: Repeat dose administration of oral voriconazole (400 mg every 12 hours for 1 day, then 200 mg every 12 hours for 4 days) increased the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and AUC of (R)-methadone by 31% and 47%, respectively, in subjects receiving a methadone maintenance dose (30 to 100 mg daily. The Cmax and AUC of (S)-methadone increased by 65% and 103%, respectively. Increased plasma concentrations of methadone have been associated with toxicity including QT prolongation. Frequent monitoring for adverse events and toxicity related to methadone is recommended during coadministration. Dose reduction of methadone may be needed [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Antiretroviral drugs: Although antiretroviral drugs such as efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, telaprevir, lopinavir+ritonavir combination are known to inhibit some CYPs, they are shown to reduce the plasma levels of methadone, possibly due to CYP induction activity.
Abacavir, amprenavir, darunavir+ritonavir, efavirenz, nelfinavir, nevirapine, ritonavir, telaprevir, lopinavir+ritonavir, saquinavir+ritonavir, tipranvir+ritonavir combination: Coadministration of these anti-retroviral agents resulted in increased clearance or decreased plasma levels of methadone [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Didanosine and Stavudine: Methadone decreased the AUC and peak levels for didanosine and stavudine, with a more significant decrease for didanosine. Methadone disposition was not substantially altered [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Zidovudine: Methadone increased the AUC of zidovudine which could result in toxic effects [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: The results of carcinogenicity assessment in B6C2F1 mice and Fischer 344 rats following dietary administration of two doses of methadone HCl have been published. Mice consumed 15 mg/kg/day or 60 mg/kg/day methadone for two years. These doses were approximately 0.6 and 2.5 times a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day on a body surface area basis (mg/m2). There was a significant increase in pituitary adenomas in female mice treated with 15 mg/kg/day but not with 60 mg/kg/day. Under the conditions of the assay, there was no clear evidence for a treatment-related increase in the incidence of neoplasms in male rats. Due to decreased food consumption in males at the high dose, male rats consumed 16 mg/kg/day and 28 mg/kg/day of methadone for two years. These doses were approximately 1.3 and 2.3 times a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day, based on body surface area comparison. In contrast, female rats consumed 46 mg/kg/day or 88 mg/kg/day for two years. These doses were approximately 3.7 and 7.1 times a human daily oral dose of 120 mg/day, based on body surface area comparison. Under the conditions of the assay, there was no clear evidence for a treatment-related increase in the incidence of neoplasms in either male or female rats.
Mutagenesis: There are several published reports on the potential genetic toxicity of methadone. Methadone tested positive in the in vivo mouse dominant lethal assay and the in vivo mammalian spermatogonial chromosome aberration test. Additionally, methadone tested positive in the E. coli DNA repair system and Neurospora crassa and mouse lymphoma forward mutation assays. In contrast, methadone tested negative in tests for chromosome breakage and disjunction and sex-linked recessive lethal gene mutations in germ cells of Drosophila using feeding and injection procedures.
Fertility: Published animal studies show that methadone treatment of males can alter reproductive function. Methadone produces a significant regression of sex accessory organs and testes of male mice and rats.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Storage and Handling
Methadone hydrochloride tablets contain methadone which is a controlled substance. Like fentanyl, morphine, oxycodone, hydromorphone, and oxymorphone, methadone is controlled under Schedule II of the Federal Controlled Substances Act. Methadone hydrochloride may be targeted for theft and diversion by criminals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
16.2 How Supplied
Methadone Hydrochloride Tablets, USP
5 mg Tablets: round, white tablets debossed with tablet identifier 54 210 on one side and scored on the other side.
NDC: 0054-4570-25: Bottles of 100 tablets.
NDC: 0054-8553-24: Unit dose, 25 tablets per card (reverse numbered), 4 cards per shipper.
10 mg Tablets: round, white tablet debossed with tablet identifier 54 142 on one side and scored on the other side.
NDC: 0054-4571-25: Bottles of 100 tablets.
NDC: 0054-8554-24: Unit dose, 25 tablets per card (reverse numbered), 4 cards per shipper.
DEA order form required.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
Abuse Potential: Inform patients that methadone hydrochloride contains methadone, a Schedule II controlled substance that is subject to abuse. Instruct patients not to share methadone hydrochloride with others and to take steps to protect methadone hydrochloride from theft or misuse.
Life-threatening Respiratory Depression: Discuss the risk of respiratory depression with patients, explaining that the risk is greatest when starting methadone hydrochloride or when the dose is increased. Advise patients how to recognize respiratory depression and to seek medical attention if they are experiencing breathing difficulties.
Symptoms of Arrhythmia: Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms suggestive of an arrhythmia (such as palpitations, near syncope, or syncope) when taking methadone.
Accidental Exposure: Instruct patients to take steps to store methadone hydrochloride securely. Accidental exposure, especially in children, may result in serious harm or death. Advise patients to dispose of unused methadone hydrochloride by flushing the tablets down the toilet.
Risks from Concomitant Use of Alcohol and other CNS Depressants: Inform patients that the concomitant use of alcohol with methadone hydrochloride can increase the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression. Instruct patients not to consume alcoholic beverages, as well as prescription and over-the-counter drug products that contain alcohol, during treatment with methadone hydrochloride.
Inform patients that potentially serious additive effects may occur if methadone hydrochloride is used with other CNS depressants, and not to use such drugs unless supervised by a health care provider.
Important Administration Instructions: Instruct patients how to properly take methadone hydrochloride, including the following:
Using methadone hydrochloride exactly as prescribed to reduce the risk of life-threatening adverse reactions (e.g., respiratory depression)
Not discontinuing methadone hydrochloride without first discussing the need for a tapering regimen with the prescriber
Hypotension: Inform patients that methadone hydrochloride may cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope. Instruct patients how to recognize symptoms of low blood pressure and how to reduce the risk of serious consequences should hypotension occur (e.g., sit or lie down, carefully rise from a sitting or lying position).
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery: Inform patients that methadone hydrochloride may impair the ability to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating heavy machinery. Advise patients not to perform such tasks until they know how they will react to the medication.
Constipation: Advise patients of the potential for severe constipation, including management instructions and when to seek medical attention.
Anaphylaxis: Inform patients that anaphylaxis has been reported with ingredients contained in methadone hydrochloride. Advise patients how to recognize such a reaction and when to seek medical attention.
Pregnancy: Advise female patients that methadone hydrochloride can cause fetal harm and to inform the prescriber if they are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Breastfeeding: Instruct nursing mothers using methadone hydrochloride to watch for signs of methadone toxicity in their infants, which include increased sleepiness (more than usual), difficulty breastfeeding, breathing difficulties, or limpness. Instruct nursing mothers to talk to the baby’s healthcare provider immediately if they notice these signs. If they cannot reach the healthcare provider right away, instruct them to take the baby to the emergency room or call 911 (or local emergency services).
Roxane Laboratories, Inc.
Columbus, Ohio 43216
4077442//06
© RLI, 2012
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE Tablets USP, CII
Methadone hydrochloride is:
- A strong prescription pain medicine that contains methadone, an opioid (narcotic) that is used to treat moderate to severe around-the-clock pain.
- Used to manage drug addiction.
Important information about methadone hydrochloride:
- Get emergency help right away if you take too much methadone hydrochloride (overdose). Methadone hydrochloride overdose can cause life threatening breathing problems that can lead to death.
- Never give anyone else your methadone hydrochloride. They could die from taking it. Store methadone hydrochloride away from children and in a safe place to prevent stealing or abuse. Selling or giving away methadone hydrochloride is against the law.
Do not take methadone hydrochloride if you have:
- Severe asthma, trouble breathing, or other lung problems.
- A bowel blockage or have narrowing of the stomach or intestines.
Before taking methadone hydrochloride, tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of:
- head injury, seizures
- heart, liver, kidney, thyroid problems
- problems urinating
- pancreas or gallbladder problems
- abuse of street or prescription drugs, alcohol addiction, or mental health problems.
Tell your healthcare provider if you are:
- pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Methadone hydrochloride may harm your unborn baby.
- breastfeeding. Methadone hydrochloride passes into breast milk and may harm your baby.
- taking prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements.
When taking methadone hydrochloride:
- Do not change your dose. Take methadone hydrochloride exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Do not take more than your prescribed dose in 24 hours. If you take methadone hydrochloride for pain and miss a dose, take methadone hydrochloride as soon as possible and then take your next dose 8 or 12 hours later as directed by your healthcare provider. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule.
- If you take methadone hydrochloride for opioid addiction, take your next dose the following day as scheduled. Do not take extra doses. Taking more than the prescribed dose may cause you to overdose because methadone hydrochloride builds up in your body over time.
- Call your healthcare provider if the dose you are taking does not control your pain.
- Do not stop taking methadone hydrochloride without talking to your healthcare provider.
- After you stop taking methadone hydrochloride, flush any unused tablets down the toilet.
While taking methadone hydrochloride Do Not:
- Drive or operate heavy machinery, until you know how methadone hydrochloride affects you. Methadone hydrochloride can make you sleepy, dizzy, or lightheaded.
- Drink alcohol or use prescription or over-the-counter medicines that contain alcohol.
The possible side effects of methadone hydrochloride are:
- constipation, nausea, sleepiness, vomiting, tiredness, headache, dizziness. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of these symptoms and they are severe.
Get emergency medical help if you have:
- trouble breathing, shortness of breath, fast heartbeat, chest pain, swelling of your face, tongue or throat, extreme drowsiness, or you are feeling faint.
These are not all the possible side effects of methadone hydrochloride. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. For more information go to fda.report.
Manufactured by: Roxane Laboratories, Inc., Columbus, Ohio 43216, www.Roxane.com, or call 1-800-962-8364
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. FDA. Issue: July 2012
4077442//06
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE
methadone hydrochloride tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 35356-835(NDC:0054-4570) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 229809935B) (METHADONE - UNII:UC6VBE7V1Z) METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code 54;210 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 35356-835-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 2 NDC: 35356-835-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 3 NDC: 35356-835-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 10/11/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA006134 01/01/2008 METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE
methadone hydrochloride tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 35356-834(NDC:0054-4571) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 229809935B) (METHADONE - UNII:UC6VBE7V1Z) METHADONE HYDROCHLORIDE 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 54;142 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 35356-834-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 2 NDC: 35356-834-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 12/31/2014 3 NDC: 35356-834-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 4 NDC: 35356-834-01 120 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/01/2008 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA006134 01/01/2008 Labeler - Lake Erie Medical DBA Quality Care Products LLC (831276758) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Lake Erie Medical DBA Quality Care Products LLC 831276758 repack(35356-835, 35356-834)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

