ALLERNAZE- triamcinolone acetonide spray, metered
AllerNaze by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
AllerNaze by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Patheon, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION:
Triamcinolone acetonide, the active ingredient of AllerNaze, is a corticosteroid with the chemical name, 9α-Fluoro-11β,16α, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3, 20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with acetone (C24 H31 FO6 ). Its structural formula is:
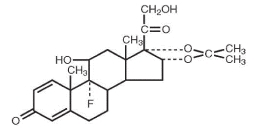
Triamcinolone acetonide, USP, is a white crystalline powder, with a molecular weight of 434.51. It is practically insoluble in water, and sparingly soluble in dehydrated alcohol, in chloroform and in methanol. It has a melting point temperature range between 292° and 294°C.
AllerNaze is a metered-dose manual spray pump in an amber polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle with 0.05% w/v triamcinolone acetonide in a solution containing citric acid, edetate disodium, polyethylene glycol 3350, propylene glycol, purified water, sodium citrate, and 0.01% benzalkonium chloride as a preservative. AllerNaze pH is 5.3.
After initial priming (three sprays) of the AllerNaze metered pump delivery system, each spray will deliver 50 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide. If the pump was not used for more than 14 days, reprime with 3 sprays or until a fine mist is observed. Each 15 mL bottle contains 7.5 mg of triamcinolone acetonide to deliver 120 metered sprays. After 120 sprays, the amount of triamcinolone acetonide delivered per spray may not be consistent and the bottle should be discarded.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Triamcinolone acetonide is a more potent derivative of triamcinolone. Triamcinolone acetonide is approximately eight times more potent than prednisone in animal models of inflammation. The clinical significance of this is unclear.
Although the precise mechanism of corticosteroid antiallergic action is unknown, corticosteroids have been shown to have a wide range of effects on multiple cell types (e.g. mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g. histamines, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, and cytokines) involved in inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption:
The pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide solution was evaluated in a single-dose study conducted in 24 patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Following a single intranasal dose of 400 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide (twice the recommended starting dose of triamcinolone acetonide solution), the mean C max of the drug was 1.12 ng/mL (SD = 0.38) with a median T max of 0.5 hours (range: 0.08 - 1.0).
A pharmacokinetic study to demonstrate dose proportionality was conducted in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. The C max and AUC of the 200 and 400 mcg doses increased less than proportionally when compared to the 100 mcg dose. Following multiple dosing (100 or 200 or 400 mcg QD for 7 days), there was no evidence of drug accumulation.
Metabolism:
In animal studies using rats and dogs, three metabolites of triamcinolone acetonide have been identified. They are 6β-hydroxytriamcinolone acetonide, 21-carboxytriamcinolone acetonide and 21-carboxy-6β-hydroxytriamcinolone acetonide. All three metabolites are expected to be substantially less active than the parent compound due to (a) the dependence of anti-inflammatory activity on the presence of a 21-hydroxyl group, (b) the decreased activity observed upon 6-hydroxylation, and (c) the markedly increased water solubility favoring rapid elimination. There appeared to be some quantitative differences in the metabolites among species. No differences were detected in metabolic pattern as a function of route of administration.
Elimination:
After a single intranasal dose of 400 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide (twice the recommended starting dose of triamcinolone acetonide solution), the mean observed elimination half-life was 2.26 hours (SD=0.77). Based upon intravenous dosing of triamcinolone acetonide phosphate ester, the half-life of triamcinolone acetonide was reported to be 88 minutes. The reported clearance was 45.2 L/hour (SD=9.1) for triamcinolone acetonide.
Special Populations
Age:
The effect of age, specifically in geriatric and pediatric patients, on the pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide has not been studied.
Gender:
Gender did not significantly influence the pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide solution.
Race:
The effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide solution has not been studied.
Pharmacodynamics:
A small (approximately 5 to 7 patients per treatment group), parallel trial was conducted to assess the effect of triamcinolone acetonide solution on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis. Patients with allergic rhinitis were treated for six weeks with 400 mcg, 800 mcg, or 1600 mcg total daily doses of triamcinolone acetonide solution, 10 mg oral prednisone once daily, or placebo. Adrenal response to a six-hour cosyntropin stimulation test suggests that intranasal triamcinolone acetonide solution 400 mcg/day for six weeks did not measurably affect adrenal activity. Triamcinolone acetonide solution treatment arms using doses of 800 and 1600 mcg/day demonstrated a trend toward dose-related suppression of HPA response. However, this decrease did not reach statistical significance, whereas 10 mg daily oral prednisone did.
-
CLINICAL TRIALS:
The efficacy of triamcinolone acetonide solution has been evaluated in 746 patients with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis who completed 8 controlled clinical trials.
In total, 1187 patients have been treated with triamcinolone acetonide solution in the clinical development program. Three adequate and well controlled multi-center trials involving 541 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis who received doses of triamcinolone acetonide solution ranging from 50 mcg to 400 mcg once daily were conducted. These trials evaluated the total nasal symptom scores that included stuffiness, rhinorrhea, itching, and sneezing.
The results showed that patients who received ≥ 200 mcg daily of the active drug had statistically significant relief in the total nasal symptom score compared to those receiving placebo.
In one clinical trial that examined efficacy after 2 days of 200 or 400 mcg triamcinolone acetonide solution treatment, only the 400 mcg dose showed statistically significant improvement over placebo in the nasal symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
- CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS:
The replacement of a systemic corticosteroid with a topical corticosteroid can be accompanied by signs of adrenal insufficiency and, in addition, some patients may experience symptoms of corticosteroid withdrawal, e.g., joint or muscular pain, or both, lassitude and depression. Patients previously treated for prolonged periods with systemic corticosteroids and transferred to topical corticosteroids should be carefully monitored for acute adrenal insufficiency in response to stress. In those patients who have asthma or other clinical conditions which require long-term corticosteroid treatment, too rapid a decrease in systemic corticosteroid may cause a severe exacerbation of their symptoms.
Patients who are on immunosuppressant drugs are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in children or adults on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids. In children, or adults who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. If exposed, therapy with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) as appropriate, may be indicated. If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
General:
Intranasal corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use section).
In clinical studies with triamcinolone acetonide nasal spray, the development of localized infections of the nose and pharynx with Candida albicans has rarely occurred. When such an infection develops it may require treatment with appropriate local therapy and discontinuance of treatment with AllerNaze.
AllerNaze should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculous infection of the respiratory tract or in patients with untreated fungal, bacterial, or systemic viral infections or ocular herpes simplex.
Because of the inhibitory effect of corticosteroids on wound healing, in patients who have experienced recent nasal septal ulcers, nasal surgery or trauma, a corticosteroid should be used with caution until healing has occurred. As with other nasally inhaled corticosteroids, nasal septal perforations have been reported in rare instances.
When used at excessive doses, systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal suppression may appear. If such changes occur, AllerNaze should be discontinued slowly, consistent with accepted procedures for discontinuing oral corticosteroid therapy.
Systemic Availability and HPA Axis Suppression: Triamcinolone acetonide administered intranasally as triamcinolone acetonide solution has been shown to be absorbed into the systemic circulation in humans. The bioavailability of triamcinolone acetonide when administered as a solution in triamcinolone acetonide solution is approximately 5-fold greater than when administered as a CFC aerosol suspension formulation. While triamcinolone acetonide solution administered to 5 patients with allergic rhinitis at 400 mcg/day for 42 days did not measurably affect adrenal response to a six-hour cosyntropin stimulation test, the 6-hour cosyntropin test is an insensitive assessment for subtle HPA effects of corticosteroids. Doses of 800 and of 1600 mcg/day triamcinolone acetonide solution did demonstrate a trend toward dose-related suppression of the HPA response. However, this decrease did not reach statistical significance, whereas 10 mg daily oral prednisone did. (see Clinical Pharmacology, Pharmacodynamics)
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS:
Patients being treated with AllerNaze should receive the following information and instructions:
- Patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids should be warned to avoid exposure to chickenpox or measles and, if exposed, to obtain medical advice.
- Patients should use AllerNaze at regular intervals since its effectiveness depends on its regular use. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION)
- An improvement in some patient symptoms may be seen within the first two days of treatment, and generally, it takes one week of treatment to reach maximum benefit. Initial assessment for response should be made during this timeframe and periodically until the patient’s symptoms are stabilized.
- The patient should take the medication as directed and should not exceed the prescribed dosage. The patient should contact the physician if symptoms do not improve after three weeks, or if the condition worsens.
- Patients who experience recurrent episodes of epistaxis (nose bleeds) or nasal septum discomfort while taking this medication should contact their physician. Transient nasal irritation and/or burning or stinging may occur upon instillation with this product. Spraying triamcinolone acetonide directly into the eyes or onto the nasal septum should be avoided. For the proper use of this unit and to attain maximum improvement, the patient should read and follow the accompanying patient instructions carefully.
- The bottle should be discarded after 120 sprays following initial priming since the amount of triamcinolone acetonide delivered thereafter per spray may not be consistent. Do not transfer any remaining solution to another bottle.
CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS AND IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY:
In two-year mouse and Sprague-Dawley rat studies, triamcinolone acetonide did not increase the incidence of tumors at oral doses up to 1 and 3 mcg/kg, respectively (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose on a mcg/m2 basis).
Triamcinolone acetonide has not been found to be mutagenic in Salmonella/mammalian-microsome reverse mutation assay (Ames test) or the chromosomal aberration test in the Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells.
Triamcinolone acetonide did not impair fertility in Sprague-Dawley rats given oral doses up to 15 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose on a mcg/m2 basis).
However, triamcinolone acetonide caused increased fetal resorptions and stillbirths and decreased pup weight and survival at 5 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose on a mcg/m2 basis). These effects were not produced at 1 mcg/kg (less than the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose on a mcg/m2 basis).
PREGNANCY:
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
Triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic in rats, rabbits, and monkeys. In rats, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at inhalation doses of 20 mcg/kg and above (approximately 7/10 of the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m² basis). In rabbits, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at inhalation doses 20 mcg/kg and above (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m² basis). In monkeys, triamcinolone acetonide was teratogenic at an inhalation dose of 500 mcg/kg and above (approximately 37 times the maximum recommended daily intranasal dose in adults on a mcg/m² basis). Dose-related teratogenic effects in rats and rabbits included cleft palate, or internal hydrocephaly, or both and axial skeletal defects, whereas the effects observed in the monkey were cranial malformations.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Triamcinolone acetonide, like other corticosteroids, should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefits justify the potential risk to the fetus. Since their introduction, experience with oral corticosteroids in pharmacologic as opposed to physiologic doses suggests that rodents are more prone to teratogenic effects from corticosteroids than humans. In addition, because there is a natural increase in corticosteroid production during pregnancy, most women will require a lower exogenous corticosteroid dose and many will not need corticosteroid treatment during pregnancy.
NURSING MOTHERS:
It is not known whether triamcinolone acetonide is excreted in human breast milk. Because other corticosteroids are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when AllerNaze is administered to nursing women.
PEDIATRIC USE:
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established. Controlled clinical studies have shown that intranasal corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity in pediatric patients. This effect has been observed in the absence of laboratory evidence of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, suggesting that growth velocity is a more sensitive indicator of systemic corticosteroid exposure in pediatric patients than some commonly used tests of HPA axis function. The long-term effects of this reduction in growth velocity associated with intranasal corticosteroids, including the impact on final adult height, are unknown. The potential for "catch up" growth following discontinuation of treatment with intranasal corticosteroids has not been adequately studied. The growth of pediatric patients receiving intranasal corticosteroids, including AllerNaze, should be monitored routinely (e.g. via stadiometry). The potential growth effects of prolonged treatment should be weighed against clinical benefits obtained and the availability of safe and effective noncorticosteroid treatment alternatives. To minimize the systemic effects of intranasal corticosteroids, including AllerNaze, each patient should be titrated to the lowest dose that effectively controls his/her symptoms.
GERIATRIC USE:
Clinical studies of AllerNaze did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
In adequate, well-controlled and uncontrolled studies, 1187 patients have received triamcinolone acetonide solution. The adverse reactions summarized below, are based upon seven placebo controlled clinical trials of 2-6 weeks duration in 847 patients with seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis (504 patients received 200 mcg or 400 mcg per day of triamcinolone acetonide solution and 343 patients received vehicle placebo). Adverse events reported by 2% or more of patients (regardless of relationship to treatment) who received triamcinolone acetonide solution 200 or 400 mcg once daily and that were more common with triamcinolone acetonide solution than with placebo are displayed in the table below. Overall, the incidence and nature of adverse events with triamcinolone acetonide solution 400 mcg was comparable to that seen with triamcinolone acetonide solution 200 mcg and with vehicle placebo.
ADVERSE EVENTS REPORTED AT A FREQUENCY OF 2% OR GREATER AND MORE COMMON AMONG PATIENTS TREATED WITH TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE SOLUTION THAN PLACEBO REGARDLESS OF RELATIONSHIP TO TREATMENT ADVERSE
EVENTS200 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide once daily
n = 204400 mcg of triamcinolone acetonide once daily
n = 300Combined
(200 and 400 mcg) use of triamcinolone acetonide
n = 504Vehicle Placebo
n = 343BODY AS A WHOLE Headache 51.0% 44.3% 47.0% 41.1% Back Pain 7.8% 4.7% 6.0% 3.5% RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pharyngitis 13.7% 10.3% 11.7% 7.9% Asthma 5.4% 4.3% 4.8% 2.9% Cough Increased 2.0% 2.7% 2.4% 2.3% DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dyspepsia 4.9% 2.7% 3.6% 2.0% Nausea 2.0% 3.0% 2.6% 0.6% Vomiting 1.5% 2.7% 2.2% 1.5% SPECIAL SENSES Taste Perversion 7.8% 5.0% 6.2% 2.9% Conjunctivitis 4.4% 1.3% 2.6% 1.5% MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Myalgia 2.5% 3.3% 3.0% 2.6% Adverse events reported by 2% or more of patients who received triamcinolone acetonide solution 200 or 400 mcg once daily and that were more common with placebo than with triamcinolone acetonide solution included: application site reaction (e.g. transient nasal burning and stinging), rhinitis, dysmenorrhea, pain (unspecified) and allergic reaction.
The adverse effects related to the irritation of nasal mucous membranes (i.e. application site reaction) did not usually interfere with treatment. In the controlled and uncontrolled studies, approximately 0.3% of patients discontinued because of irritation of nasal mucous membranes.
-
OVERDOSAGE:
Like any other nasally administered corticosteroid, acute overdosing is unlikely in view of the total amount of active ingredient present. In the event that the entire contents of the bottle were administered all at once, via oral or nasal application, clinically significant adverse events would likely not result. The patient may experience some gastrointestinal upset. Chronic overdosage with any corticosteroid may result in signs or symptoms of hypercorticism (see PRECAUTIONS).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The recommended starting dose of AllerNaze for most patients is 200 mcg per day given as 2 sprays (approximately 50 mcg/spray) in each nostril once a day. The maximum dose should not exceed 400 mcg per day. If the 400 mcg dose is used, it may be given either as a once a day dosage (4 sprays in each nostril) or divided into two daily doses of two sprays/nostril twice a day.
The nasal spray pump must be primed before AllerNaze is used for the first time. To prime the pump, press down on the shoulder of the white nasal applicator using your forefinger and middle finger while supporting the base of the bottle with your thumb. Press down and release the pump until it sprays 3 times or until a fine mist is observed (see DIRECTIONS FOR USE).
Some patients may obtain relief of symptoms sooner when started on a 400 mcg per day dose of AllerNaze than with 200 mcg per day. Onset of significant relief of nasal symptoms was seen within two days after starting treatment at 400 mcg once daily. A starting dose of 400 mcg per day may be considered in patients when starting therapy with AllerNaze in cases where a faster onset of relief is desirable. Generally, maximum relief of symptoms may take several days or up to one week to occur.
After symptoms have been brought under control, patients should be titrated to the minimum effective dose to reduce the possibility of adverse effects.
If relief of symptoms is not achieved after 14-21 days of AllerNaze therapy given in an adequate dose, AllerNaze should be discontinued and alternative diagnosis and therapies considered.
AllerNaze is not recommended for use in persons under 12 years of age since its safety and effectiveness have not been established in this age group.
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Each 15 mL bottle of AllerNaze (NDC: 27437-143-01) contains 7.5 mg (0.50 mg/mL) of triamcinolone acetonide, USP and is fitted with a meter pump with white nasal applicator, teal blue dust cover and teal blue locking clip sealed in a foil pouch. The unit delivers 120 metered actuations and comes with a patient's instructions for use leaflet. The bottle should be discarded when the labeled number of actuations has been reached even though the bottle is not completely empty.
Keep out of reach of children.
Store at controlled room temperature: 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). Protect from freezing.
Use AllerNaze within 2 months after opening of the protective foil pouch or before expiration date, whichever comes first.
Rx only
Lupin Pharma
Baltimore, MD 21202
Tel: 1-800-399-2561
www.lupinpharmaceuticals.comAllerNazeTM [AL-er-nāz]
(triamcinolone acetonide, USP)
Nasal Spray
-
PATIENT’S INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT
These instructions provide a summary of important information about AllerNaze. Please read it carefully before use. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any additional questions.
What is AllerNaze?
AllerNaze is a prescription medicine called a corticosteroid used to treat seasonal and year-round allergies in adults and children age 12 and older. When AllerNaze is sprayed in your nose, this medicine helps lessen the symptoms of sneezing, runny nose, and nasal itching associated with nasal allergies.
Do not use AllerNaze if you
1. are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
2. are breast feeding.
3. have had a reaction to triamcinolone acetonide or to any other nasal spray.
How do I use AllerNaze?
- Use AllerNaze on a regular schedule exactly as prescribed by your doctor
- Do not use more AllerNaze or take it more often than your doctor tells you. It usually takes several days to one week of regular use to feel the medicine working.
- Protect your eyes from the spray.
- If your symptoms do not improve, or if they become worse, contact your doctor.
- Do not stop taking AllerNaze without contacting your doctor.
- AllerNaze does not relieve the red and itchy eye symptoms that some people have with allergic rhinitis. Ask your doctor for advice on treatment.
- Tell your doctor if you have irritation, burning or stinging inside your nose that does not go away when using AllerNaze.
- You may have nosebleeds after using AllerNaze. If so, contact your doctor right away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Patient Instructions for Use
Read these instructions carefully before use. The following instructions tell you how to prepare your AllerNaze spray pump so that it is ready for your use.
Open the foil pouch and remove the pump unit. See Figure A for a picture of the spray pump, the cap, and the safety clip.
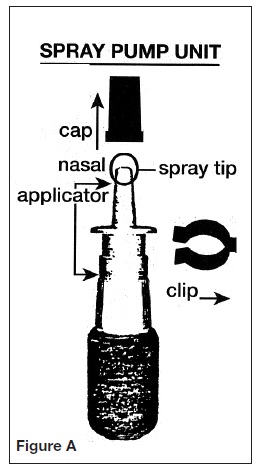
Priming the Pump:
The pump needs to be primed before using it for the first time and then again if you have not used the spray for 2 weeks. You will prime the pump the same way each time.
1. Remove the blue plastic cap and the blue safety clip from the nasal applicator of the spray pump unit. See Figure B.
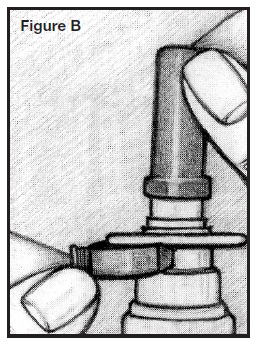
2. Prime the pump by holding the bottle with your thumb on the bottom and your index and middle fingers on top, on either side of the white nasal applicator. See Figure C.

3. Point the bottle up and away from your eyes. Press down on either side of the white nasal applicator using your forefinger and middle finger, while supporting the base of the bottle with your thumb.
4. Press down and release the pump several times until you get 3 sprays or until a fine mist is seen. A fine mist can only be made by a rapid and firm pumping action. See Figure C.
Using the spray correctly:
1. Gently blow your nose to clear it before using the medication.
2. Remove the blue plastic cap and the blue safety clip from the nasal applicator. See Figure D.
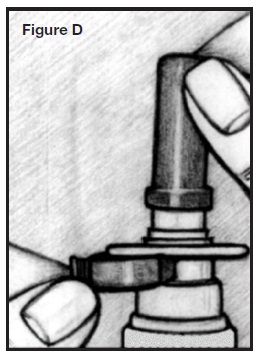
3. Prime the pump. See Figures A, B, and C in the “Priming the Pump” section.
4. Tilt your head backward slightly. Breathe out slowly.
5. Use a finger on your other hand to close your nostril on the side not receiving the medication. See Figure E.

6. Insert spray tip into one nostril, as shown in the illustration. Do not insert too far back. Do not spray AllerNaze directly onto the nasal tissue inside your nose; aim the spray to the back of your nose. See Figure F.
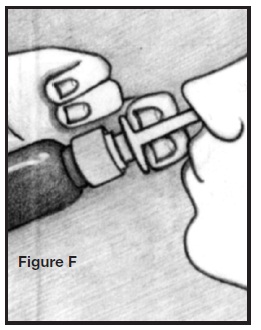
7. Breathe in through the nostril and while breathing in press the applicator once to release the spray. You will need to press firmly and rapidly. Breathe out through your mouth.
8. If the doctor has prescribed 2 sprays on each side, repeat Step 7 (above) in the same nostril and then switch to use the nasal spray in the other nostril.
9. Do not blow your nose for 15 minutes.
10. After use, wipe the spray bottle applicator off with a tissue and put the cap and safety clip back on to the bottle.
If your nasal passages are severely swollen, your doctor may recommend a decongestant nasal spray or nose drops for 3 or 4 days before using AllerNaze.
CLEANING the nasal applicator:
If the nasal applicator becomes blocked, and does not spray, remove it and allow it to soak in warm water for 10-15 minutes. Then rinse the applicator with clean warm water, allow it to air dry and put it back on the bottle. Do not try to unblock the applicator by inserting a pin or other sharp object. This could change the amount of medicine you spray and cause an overdose.
STORING and discarding AllerNaze:
- Store between 68º to 77º F (20º to 25º C).
- Do not freeze.
- Use AllerNaze within 2 months after opening the protective foil pouch or before the expiration date on the box or label, whichever comes first.
- After using 120 sprays of AllerNaze throw the bottle away – the dose may not be accurate.
Information about nasal symptoms of allergies (allergic rhinitis):
Allergic rhinitis is a condition that causes swelling and increased watery fluid in the nose and nasal passages. This can result in sneezing, runny nose, itching, and difficulty in breathing through the nose.
This response is caused by an allergy to pollen that comes from many types of plants including trees, grasses, and weeds. Allergic responses of this type may also be caused by mold spores, house dust mites, animal dander, and other substances.
Lupin Pharma
Baltimore, MD 21202
Tel: 1-800-399-2561
www.lupinpharmaceuticals.com 2000002549 - PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ALLERNAZE
triamcinolone acetonide spray, meteredProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 27437-143 Route of Administration NASAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE (UNII: F446C597KA) (TRIAMCINOLONE - UNII:1ZK20VI6TY) TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 27437-143-01 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE, SPRAY Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020120 02/01/2011 Labeler - Lupin Pharmaceuticals (965791259) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon, Inc. 243790024 MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS, LABEL, PACK Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon, Inc. 259484350 ANALYSIS
Trademark Results [AllerNaze]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ALLERNAZE 86721277 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Lupin Atlantis Holdings S.A. 2015-08-11 |
 ALLERNAZE 85551246 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Lupin Atlantis Holdings S.A. 2012-02-23 |
 ALLERNAZE 77546760 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
LUPIN HOLDINGS B.V. 2008-08-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
