HYDROCODONE/APAP by PharmPak, Inc. HYDROCODONE/APAP
HYDROCODONE/APAP by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
HYDROCODONE/APAP by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by PharmPak, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
HYDROCODONE/APAP- hydrocodone bitartrate, tablet
PharmPak, Inc.
----------
HYDROCODONE/APAP
BOXED WARNING
Hepatotoxicity:
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product.
DESCRIPTION
Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen is supplied in tablet form for oral administration.
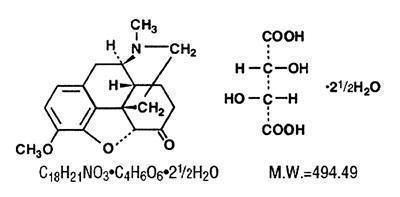
Hydrocodone bitartrate is an opioid analgesic and antitussive and occurs as fine, white crystals or as a crystalline powder. It is affected by light. The chemical name is 4,5α-Epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5). It has the following structural formula:
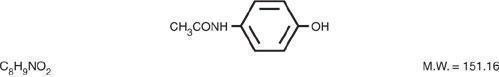
Acetaminophen, 4-hydroxyacetanilide, a slightly bitter, white, odorless, crystalline powder, is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. It has the following structured formula:
Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen USP for oral administration are available in a variety of strengths as described in the following table.

In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, croscarmellous sodium, crosprovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellouse, providone starch,and stearic acid
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic narcotic analgesic and antitussive with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. Most of these involve the central nervous system and smooth muscle. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opiates is not known, although it is believed to relate to the existence of opiate receptors in the central nervous system. In addition to analgesia, narcotics may produce drowsiness, changes in mood and mental clouding.
The analgesic action of acetaminophen involves peripheral influences, but the specific mechanism is as yet undetermined. Antipyretic activity is mediated through hypothalamic heat regulating centers. Acetaminophen inhibits prostaglandin synthetase. Therapeutic doses of acetaminophen have negligible effects on the cardiovascular or respiratory systems; however, toxic doses may cause circulatory failure and rapid, shallow breathing.
Pharmacokinetics:
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Hydrocodone: Following a 10 mg oral dose of hydrocodone administered to five adult male subjects, the mean peak concentration was 23.6 ± 5.2 ng/mL. Maximum serum levels were achieved at 1.3 ± 0.3 hours and the half-life was determined to be 3.8 ± 0.3 hours. Hydrocodone exhibits a complex pattern of metabolism including O-demethylation, N-demethylation and 6-ketoreduction to the corresponding 6-a- and 6-ß-hydroxymetabolites. See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed throughout most body tissues. The plasma half-life is 1.25 to 3 hours, but may be increased by liver damage and following overdosage. Elimination of acetaminophen is principally by liver metabolism (conjugation) and subsequent renal excretion of metabolites. Approximately 85% of an oral dose appears in the urine within 24 hours of administration, most as the glucuronide conjugate, with small amounts of other conjugates and unchanged drug.
See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are indicated for the relief of moderate to moderately severe pain.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
This product should not be administered to patients who have previously exhibited hypersensitivity to hydrocodone or acetaminophen.
Patients known to be hypersensitive to other opioids may exhibit cross-sensitivity to hydrocodone.
Hepatotoxicity
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product. The excessive intake of acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take another acetaminophen -containing product.
The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than 400 milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well.
Hypersensitivity/anaphylaxis
There have been post-marketing reports of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis associated with use of acetaminophen. Clinical signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria rash, pruritis, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threating anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention. Instruct patients to discontinue Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms. Do not prescribe Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP for patients with acetaminophen allergy.
Respiratory Sepression: At high doses or in sensitive patients, hydrocodone may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on the brain stem respiratory center. Hydrocodone also affects the center that controls respiratory rhythm, and may produce irregular and periodic breathing.
head Injury and Increased Intercranial Pressure: The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intercranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Acute Abdominal Conditions: The administration of narcotics may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
PRECAUTIONS
General: Special Risk Patients; As with any narcotic analgesic agent, hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostrate hypertrophy or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind.
Cough Reflex: Hydrocodone suppresses the cough reflex;as with all narcotics, caution should be exercised when hydrocodone bitertrate and acetaminophen tablets are used postoperaively and in patients with pulmonary disease.
Information for Patients/Caregivers
Do not take Hydrocodone bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP if you are allergic to any of its ingredients.
If you develope signs of allergy such as a rash or difficulty breathing stop taking Hydrocodone Bitartrate and
Acetaminophen Tablets, USP and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Do not take more than 4000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the
recommended dose.
Hydrocodone, like all narcotics, may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery; patients should be cautioned accordingly.
Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce a additive CNS depression, when taken with this combination product, and should be avoided.
Hydrocodone may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
Laboratory Tests: In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions: Patients receiving narcotics, antihistamines, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
The use of MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants with hydrocodone preparations may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions: Acetaminophen may produce false-positive test results for urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid.
Cardnogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether hydrodocone or acetaminophen have a potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy: Teretogenic Effects: Pregnancy Catagory C: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects: Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdraw signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose. There is no consensus on the best method of managing withdrawal.
Labor and Delivery: As with all narcotics, administration of this product to the mother shortly before delivery may result in some degree of respiratory depression in the newborn, especially if higher doses are used.
Nursing Mothers: Acetaminophen is excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the signaficance of its effect on nursing infants is unknown. It is not known whether hydrocodone is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from hydrocodone and acetaminophen, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use: Clinical studies of hydrocodone bitartrate 5 mg and acetaminophen 500 mg did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they responded differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. in general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Hydrocodone and the major metabolites of acetaminophen are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Thus the risk of toxic reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function due to the accumulation of the parent compound and/or metabolites in the plasma. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Hydrocodone may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets and observed closely.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions are lightheadness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, and vomiting. These effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory than in nonambulatory patients, and some of these adverse reactions may be alleviated if the patient lies down.
Other adverse reactions include:
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness, mental clouding, lethargy, impairment of mental and physical performance, anxiety, fear, dysphoria, psychic dependence, and mood changes.
Dosage should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response of the patient. However, it should be kept in mind that tolerance to hydrocodone can develop with continued use and that the incidence of untoward effects is dose related.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response of the patient. However, it should be kept in mind that tolerance to hydrocodone can develop with continued use and that the incidence of untoward effects is dose related.
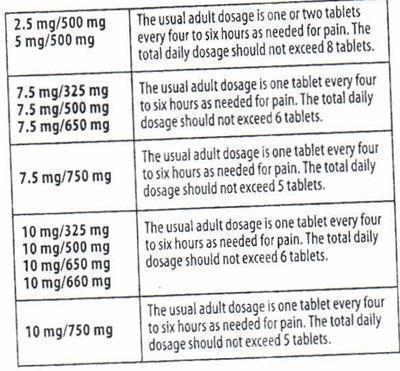
HOW SUPPLIED
Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets USP are available in the following strengths:

Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen 5/500mg Product Label
Store at 20° -25° C (68° -77° F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
HYDROCODONE/APAP
5MG/500MG TABS
5434801301
LOT G29401301C
EXP 7/31/2015
Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen
5/500mg tablets CII
For indications, dosage, precautions, etc. see package insert.
Store at controlled room temperature 20-25° C (68-77° F)
Do not use if foil wrap and seal are damaged.
For questions call: 1-800-541-6315
Mfg:
Lot# NDC#
Packaged by: Rx Only
PharmPak Qty: 1 tablet
Lot # Exp.


| HYDROCODONE/APAP
hydrocodone bitartrate, tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - PharmPak, Inc. (175493840) |
| Registrant - PharmPak, Inc. (175493840) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| PharmPak, Inc. | 175493840 | relabel(54348-013) , repack(54348-013) | |