FOTIVDA- tivozanib capsule
FOTIVDA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
FOTIVDA by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FOTIVDA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FOTIVDA.
FOTIVDA ®(tivozanib) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions ( 5.7) 8/2024 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FOTIVDA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) following two or more prior systemic therapies. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended Dose: 1.34 mg once daily with or without food for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment (28-day cycle) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. ( 2.1)
- Dose interruptions and/or dose reduction may be needed to manage adverse reactions. ( 2.2)
- For patients with moderate hepatic impairment, reduce the dose to 0.89 mg for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment (28-day cycle). ( 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 1.34 mg and 0.89 mg ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis: Control blood pressure prior to initiating FOTIVDA. Monitor for hypertension and treat as needed. For persistent hypertension despite use of anti-hypertensive medications, reduce the FOTIVDA dose. ( 5.1)
- Cardiac Failure: Monitor for signs or symptoms of cardiac failure throughout treatment with FOTIVDA. ( 5.2)
- Cardiac Ischemia and Arterial Thromboembolic Events: Closely monitor patients who are at increased risk for these events. Permanently discontinue FOTIVDA for severe arterial thromboembolic events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. ( 5.3)
- Venous Thromboembolic Events: Closely monitor patients who are at increased risk for these events. Permanently discontinue FOTIVDA for severe venous thromboembolic events. ( 5.4)
- Hemorrhagic Events: Closely monitor patients who are at risk for or who have a history of bleeding. ( 5.5)
- Proteinuria: Monitor throughout treatment with FOTIVDA. For moderate to severe proteinuria, reduce the dose or temporarily interrupt treatment with FOTIVDA. ( 5.6)
- Perforations and Fistulas: Monitor for symptoms. Discontinue FOTIVDA for severe or life-threatening gastrointestinal perforation. ( 5.7)
- Thyroid Dysfunction: Monitor before initiation and throughout treatment with FOTIVDA. ( 5.8)
- Risk of Impaired Wound Healing: Withhold FOTIVDA for at least 24 days before elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of FOTIVDA after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established. ( 5.9)
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS): Discontinue FOTIVDA if signs or symptoms of RPLS occur. ( 5.10)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. ( 5.11, 8.1, 8.3)
- Allergic Reactions to Tartrazine: The 0.89 mg capsule of FOTIVDA contains FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible patients. ( 5.12)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, hypertension, diarrhea, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, hypothyroidism, cough, and stomatitis, and the most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥5%) were sodium decreased, lipase increased, and phosphate decreased. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-833-FOTIVDA (1-833-368-4832) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Moderate Hepatic Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis
5.2 Cardiac Failure
5.3 Cardiac Ischemia and Arterial Thromboembolic Events
5.4 Venous Thromboembolic Events
5.5 Hemorrhagic Events
5.6 Proteinuria
5.7 Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula Formation
5.8 Thyroid Dysfunction
5.9 Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
5.10 Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
5.11 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
5.12 Allergic Reactions to Tartrazine (FD&C Yellow No.5)
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on FOTIVDA
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended dosage of FOTIVDA is 1.34 mg taken orally once daily for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle.
Continue treatment until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Take FOTIVDA with or without food. Swallow the FOTIVDA capsule whole with a glass of water. Do not open the capsule.
If a dose is missed, the next dose should be taken at the next scheduled time. Do nottake two doses at the same time.
2.2 Dose Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Initiate medical management for diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting prior to dose interruption or reduction.
If dose modifications are required for adverse reactions, reduce the dosage of FOTIVDA to 0.89 mg for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle.
Recommendations for dosage modifications are provided in Table 1.
Table 1. Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity * Dosage Modifications for FOTIVDA - * Grades are based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).
Hypertension
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]Grade 3 - Withhold for Grade 3 that persists despite optimal anti-hypertensive therapy.
- Resume at reduced dose when hypertension is controlled at less than or equal to Grade 2.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue.
Cardiac Failure
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Grade 3 - Withhold until improves to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at a reduced dose or discontinue depending on the severity and persistence of adverse reaction.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue.
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]Any Grade - Permanently discontinue.
Hemorrhagic Events
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]Grade 3 or 4 - Permanently discontinue.
Proteinuria
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]2 grams or greater proteinuria in 24 hours - Withhold until less than or equal to 2 grams of proteinuria per 24 hours.
- Resume at a reduced dose.
- Permanently discontinue for nephrotic syndrome.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]Any Grade - Permanently discontinue.
Other Adverse Reactions Persistent or intolerable Grade 2 or 3 adverse reaction
Grade 4 laboratory abnormality- Withhold until improves to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Resume at reduced dose.
Grade 4 adverse reaction - Permanently discontinue.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Moderate Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the recommended dosage of FOTIVDA to 0.89 mg capsule taken orally once daily for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle for patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.7)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis
FOTIVDA can cause severe hypertension and hypertensive crisis. Hypertension occurred in 45% of patients treated with FOTIVDA, with 22% of the events ≥ Grade 3. Median time to onset of hypertension was 2 weeks (range: 0 – 192 weeks).
Hypertensive crisis occurred in 0.8% of patients .One patient (0.1%) died due to hypertensive emergency after FOTIVDA overdose [see OVERDOSAGE (10)] .
FOTIVDA has not been studied in patients with systolic blood pressure > 150 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure > 100 mmHg.
Control blood pressure prior to treatment with FOTIVDA. Monitor blood pressure after 2 weeks and at least monthly thereafter during treatment with FOTIVDA. Treat patients with anti- hypertensive therapy when hypertension occurs during treatment with FOTIVDA.
Withhold FOTIVDA for severe hypertension despite optimal anti-hypertensive therapy. For persistent hypertension despite use of anti-hypertensive medications, reduce the FOTIVDA dose [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
Discontinue FOTIVDA if hypertension is severe and persistent despite anti-hypertensive therapy and dose reduction of FOTIVDA, or in patients who experience hypertensive crisis.
If FOTIVDA is interrupted, monitor patients receiving anti-hypertensive medications for hypotension.
5.2 Cardiac Failure
FOTIVDA can cause serious, sometimes fatal, cardiac failure. Cardiac failure in FOTIVDA- treated patients occurred in 1.6%, with 1% of events ≥ Grade 3, and 0.6% events were fatal.
FOTIVDA has not been studied in patients with symptomatic cardiac failure within the preceding 6 months before FOTIVDA treatment initiation.
Periodically monitor patients for symptoms of cardiac failure throughout treatment with FOTIVDA.
Management of cardiac failure events may require interruption, dose reduction, or permanent discontinuation of FOTIVDA therapy [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.3 Cardiac Ischemia and Arterial Thromboembolic Events
FOTIVDA can cause serious, sometimes fatal, cardiac ischemia and arterial thromboembolic events. Cardiac ischemia in FOTIVDA-treated patients occurred in 3.2%, with 1.5% of events ≥ Grade 3, and 0.4% events were fatal. Arterial thromboembolic events were reported in 2% of FOTIVDA-treated patients, including death due to ischemic stroke (0.1%).
FOTIVDA has not been studied in patients who had an arterial thrombotic event, myocardial infarction, or unstable angina within the preceding 6 months before FOTIVDA treatment initiation.
Closely monitor patients who are at risk for, or who have a history of these events (such as myocardial infarction and stroke), during treatment with FOTIVDA.
Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop any severe or life-threatening arterial thromboembolic event [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.4 Venous Thromboembolic Events
FOTIVDA can cause serious, sometimes fatal, venous thromboembolic events. Venous thromboembolic events occurred in 2.4% of patients treated with FOTIVDA, including death (0.3%).
Closely monitor patients who are at risk for, or who have a history of these events during treatment with FOTIVDA.
Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop any severe or life-threatening venous thromboembolic event [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.5 Hemorrhagic Events
FOTIVDA can cause serious, sometimes fatal, hemorrhagic events. Hemorrhagic events occurred in 11% of patients treated with FOTIVDA, including death (0.2%).
FOTIVDA has not been studied in patients with significant bleeding within the preceding 6 months before FOTIVDA treatment initiation.
Closely monitor patients who are at risk for or who have a history of bleeding during treatment with FOTIVDA.
Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop severe or life-threatening hemorrhagic events [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.6 Proteinuria
FOTIVDA can cause proteinuria. Proteinuria occurred in 8% of FOTIVDA-treated patients with 2% of events Grade 3. Of the patients who developed proteinuria, 3/81 (3.7%) had acute kidney injury either concurrently or later during treatment.
Monitor patients for proteinuria before initiation of, and periodically throughout, treatment with FOTIVDA.
For patients who develop moderate to severe proteinuria, reduce the dose or interrupt FOTIVDA treatment.
Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop nephrotic syndrome [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.7 Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula Formation
Gastrointestinal perforation including fatal cases, has been reported in patients receiving FOTIVDA. Monitor for symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation or fistula periodically throughout treatment with FOTIVDA. Permanently discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop severe or life-threatening gastrointestinal perforation.
5.8 Thyroid Dysfunction
FOTIVDA can cause thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid dysfunction events in FOTIVDA-treated patients occurred in 11%, with 0.3% Grade 3 or 4 events. Hypothyroidism was reported in 8% of patients and hyperthyroidism was reported in 1% of patients.
Monitor thyroid function before initiation of, and periodically throughout, treatment with FOTIVDA.
Treat hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism to maintain euthyroid state before and during treatment with FOTIVDA.
5.9 Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
Impaired wound healing can occur in patients who receive drugs that inhibit the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, such as FOTIVDA. Therefore, FOTIVDA has the potential to adversely affect wound healing.
Withhold FOTIVDA for at least 24 days prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of FOTIVDA after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established.
5.10 Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS), a syndrome of subcortical vasogenic edema diagnosed by MRI, can occur with FOTIVDA. Perform an evaluation for RPLS in any patient presenting with seizures, headaches, visual disturbances, confusion, or altered mental function.
Discontinue FOTIVDA in patients who develop RPLS [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)] .
5.11 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, FOTIVDA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In embryo-fetal developmental studies, oral administration of tivozanib to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis caused maternal toxicity, fetal malformations and embryo-fetal death at doses below the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis.
Advise pregnant woman of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1), (8.3)and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.1)].
5.12 Allergic Reactions to Tartrazine (FD&C Yellow No.5)
FOTIVDA 0.89 mg capsule contains FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) as an imprint ink which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible patients. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Cardiac Failure [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
- Cardiac Ischemia and Arterial Thromboembolic Events [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)]
- Venous Thromboembolic Events [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)]
- Hemorrhagic Events [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)]
- Proteinuria [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.6)]
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula Formation [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)]
- Thyroid Dysfunction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.8)]
- Risk of Impaired Wound Healing [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)]
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS) [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.10)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to FOTIVDA administered at 1.34 mg orally once daily with or without food for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle in 1008 patients with advanced RCC in TIVO-3 and five other monotherapy studies. Among 1008 patients who received FOTIVDA, 52% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 34% were exposed for greater than one year.
Relapsed or Refractory Advanced RCC Following Two or More Prior Systemic Therapies
The safety of FOTIVDA was evaluated in TIVO-3, a randomized, open-label trial in 350 patients with relapsed or refractory advanced RCC who received 2 or 3 prior systemic treatments [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14)] . Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive FOTIVDA 1.34 mg orally once daily for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle, or to receive sorafenib 400 mg orally twice a day continuously until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Among patients who received FOTIVDA, 53% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 31% were exposed for greater than one year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients who received FOTIVDA. Serious adverse reactions in > 2% of patients included bleeding (3.5%), venous thromboembolism (3.5%), arterial thromboembolism (2.9%), acute kidney injury (2.3%), and hepatobiliary disorders (2.3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 8% of patients who received FOTIVDA, including pneumonia (1.7%), hepatobiliary disorders (1.2%), respiratory failure (1.2%), myocardial infarction (0.6%), cerebrovascular accident (0.6%), and subdural hematoma (0.6%).
Permanent discontinuation of FOTIVDA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 21% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of FOTIVDA in > 2 patients included hepatobiliary disorders, fatigue, and pneumonia.
Dosage interruptions of FOTIVDA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 48% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in > 5% of patients included fatigue, hypertension, decreased appetite, and nausea.
Dose reductions of FOTIVDA due to an adverse reaction occurred in 24% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in > 3% of patients included fatigue, diarrhea, and decreased appetite.
The most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, hypertension, diarrhea, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, hypothyroidism, cough, and stomatitis, and the most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 5%) were sodium decreased, lipase increased, and phosphate decreased.
Table 2summarizes the adverse reactions in TIVO-3.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions (≥ 15%) in Patients Who Received FOTIVDA in TIVO-3 Adverse Reaction FOTIVDA (n = 173) Sorafenib (n = 170) All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)- * Includes fatigue and asthenia
- † Includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, hypertensive crisis
- ‡ Includes hematuria, epistaxis, hemoptysis, hematoma, rectal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage, contusion, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematochezia, intraocular hematoma, melena, metrorrhagia, pulmonary hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, gingival bleeding, hematemesis, hemorrhage intracranial, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, splinter hemorrhages
- § Includes diarrhea and frequent bowel movements
- ¶ Includes hypothyroidism, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased, tri-iodothyronine decreased, tri-iodothyronine free decreased
- # Includes dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis contact, drug eruption, eczema, eczema nummular, erythema, erythema multiforme, photosensitivity reaction, pruritus, psoriasis, rash, rash erythematous, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash morbilliform, rash pruritic, seborrheic dermatitis, skin exfoliation, skin irritation, skin lesion, swelling face, toxic skin eruption, urticaria
Any 99 67 100 72 General Fatigue * 67 13 48 12 Vascular Hypertension † 44 24 31 17 Bleeding ‡ 17 3 12 1 Gastrointestinal Diarrhea § 43 2 54 11 Nausea 30 0 18 4 Stomatitis 21 2 23 2 Vomiting 18 1 17 2 Metabolism and nutrition Decreased appetite 39 5 30 4 Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal Dysphonia 27 1 9 0 Cough 22 0 15 1 Dyspnea 15 3 11 1 Endocrine Hypothyroidism ¶ 24 1 11 0 Musculoskeletal Back pain 19 2 16 2 Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash # 18 1 52 15 Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome 16 1 41 17 Investigations Weight decreased 17 3 22 3 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 15% of patients who received FOTIVDA included proteinuria, venous thromboembolism, arterial thromboembolism, hyperthyroidism, hepatobiliary disorders, osteonecrosis, cardiac failure, and delirium.
Table 3summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in TIVO-3.
Table 3. Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) That Worsened from Baseline in Patients with Advanced RCC Who Received FOTIVDA Laboratory Abnormality FOTIVDA *(n = 173) Sorafenib *(n = 170) All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4 (%) - * The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 139 to 171 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Hematology Lymphocytes decreased 25 5 42 6 Hemoglobin increased 19 0 8 0 Platelets decreased 19 0 18 1 Hemoglobin decreased 16 1 27 4 Chemistry Creatinine increased 50 0 37 1 Glucose increased 50 3 40 0 Phosphate decreased 38 5 63 31 Sodium decreased 36 9 30 11 Lipase increased 32 9 36 10 ALT increased 30 4 29 2 Alkaline phosphatase increased 30 4 32 2 AST increased 28 1 31 2 Potassium increased 26 3 23 0 Magnesium decreased 26 0 23 1 Amylase increased 23 2 28 3 Calcium increased 15 2 7 2 Bilirubin increased 11 3 11 0 Coagulation Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged 26 1 18 0 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of FOTIVDA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Gastrointestinal perforation and pancreatitis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on FOTIVDA
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Concomitant use of FOTIVDA with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases tivozanib exposure [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)], which may reduce FOTIVDA anti-tumor activity.
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers with FOTIVDA.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action, FOTIVDA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.1)] . There are no available data on FOTIVDA use in pregnant woman to inform the drug-associated risk. In embryo-fetal developmental studies, oral administration of tivozanib to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis caused maternal toxicity, fetal malformations and embryo- fetal death at doses below the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis [see DATA] . Advise pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically-recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20% respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental study in pregnant rats, daily oral administration of tivozanib at doses ≥ 0.03 mg/kg/day (0.2 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis) during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity, increases in early and late resorptions, and an increase in fetal external malformations (body edema, short/kinked tail), and skeletal developmental delays.
In an embryo-fetal developmental study in pregnant rabbits, daily oral administration of tivozanib at 1 mg/kg/day (14.5 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis) during the period of organogenesis resulted in fetal malformations including ventricular septal defects and major vessel anomalies. No maternal toxicity was reported at doses up to 1 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tivozanib in human milk, or the effects of tivozanib on the breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
FOTIVDA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1)] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with FOTIVDA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1)] .
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose [see NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY (13.1)] .
Infertility
Females and Males
Based on findings in animal studies, FOTIVDA can impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [see NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY (13.1)] .
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of FOTIVDA in pediatric patients have not been established.
Animal Data
Juvenile animal studies have not been conducted with tivozanib.
In a 13-week repeat-dose study, oral administration of tivozanib to young and growing cynomolgus monkeys resulted in growth plate hypertrophy, absence of active corpora lutea, and no maturing follicles at doses ≥ 0.3 mg/kg/day (4.4 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis). In a 13-week repeat-dose study in rats, teeth abnormalities (thin, brittle teeth, tooth loss, malocclusions) and growth plate hypertrophy were observed following oral administration of tivozanib at doses ≥ 0.1 mg/kg/day (0.7 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1008 patients with advanced RCC treated with FOTIVDA, 29% were ≥ 65 years of age and 4% were ≥ 75 of age. No overall differences in safety were observed between patients ≥ 65 versus < 65 years of age.
Of the 175 patients with advanced RCC following two or more prior systemic therapies randomized to FOTIVDA, 44% were ≥ 65 years of age and 9% were ≥ 75 of age. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between patients ≥ 65 versus < 65 years of age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage modification is recommended for patients with mild to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 15-89 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The recommended dosage for patients with end-stage renal disease has not been established [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)] .
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the dosage when administering FOTIVDA in patients with moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 to 3 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.3)] . No dosage modification is recommended for patients with mild (total bilirubin less than or equal to ULN with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment. The recommended dosage of FOTIVDA in patients with severe (total bilirubin greater than 3 to 10 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment has not been established [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)] .
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with FOTIVDA can cause severe hypertension and hypertensive crisis that may result in death [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)] .
During clinical studies, three patients inadvertently received doses ≥ 2.68 mg (≥ 2 times the recommended dose) of FOTIVDA. One patient who received two daily doses of 8.9 mg of FOTIVDA experienced hypertensive crisis with severe hypertensive retinopathy; a second patient who received three doses of 1.34 mg in one day experienced fatal uncontrolled hypertension; and a third patient who received two doses of 1.34 mg FOTIVDA in one day experienced persistent hypertension lasting over 5 days.
There is no specific treatment or antidote for FOTIVDA overdose.
In cases of suspected overdose, withhold FOTIVDA, closely monitor patients for hypertension and hypertensive crisis and other potential adverse reactions. Immediately manage signs or symptoms of hypertension and provide other supportive care as clinically indicated.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Tivozanib is a kinase inhibitor. Tivozanib hydrochloride, the active ingredient, has the chemical name 1-{2-chloro-4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]phenyl}-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea hydrochloride hydrate. The molecular formula is C 22H 19ClN 4O 5∙ HCl ∙ H 2O and the molecular weight is 509.34 Daltons. The chemical structure is:
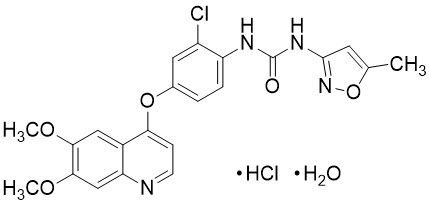
Tivozanib hydrochloride is a white to light brown crystalline powder that is practically insoluble in water (0.09 mg/mL).
FOTIVDA 1.34 mg capsule contains 1.5 mg of tivozanib hydrochloride (equivalent to 1.34 mg tivozanib) with inactive ingredients: mannitol and magnesium stearate. Capsule composition: gelatin, titanium dioxide, FDA yellow iron oxide, and Blue SB-6018 (ink).
FOTIVDA 0.89 mg capsule contains 1.0 mg of tivozanib hydrochloride (equivalent to 0.89 mg tivozanib) with inactive ingredients: mannitol and magnesium stearate. Capsule composition: gelatin, titanium dioxide, FDA yellow iron oxide, FD&C Blue #2, Blue SB-6018 (ink) and Yellow SB-3017 (ink). The Yellow SB-3017 ink contains FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tivozanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. In vitro cellular kinase assays demonstrated that tivozanib inhibits phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-1, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and inhibits other kinases including c-kit and PDGFR β at clinically relevant concentrations. In tumor xenograft models in mice and rats, tivozanib inhibited angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and tumor growth of various tumor cell types including human renal cell carcinoma.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of tivozanib were evaluated in patients with solid tumors administered 1.34 mg once daily unless otherwise specified. Steady-state tivozanib AUC and C maxincreased in a dose-proportional manner over the dose range of 0.89 to 1.78 mg once daily (0.67 to 1.3 times the recommended dose).
Steady-state was reached by 14 days and the accumulation ratio after administration of 1.34 mg once daily was approximately 6- to 7- fold. Mean steady-state tivozanib [coefficient of variation (CV%)] C maxwas 86.9 (44.7%) ng/mL and AUC 0-24hwas 1510 (46.1%) ng*h/mL.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of tivozanib is 123 L.
Protein binding of tivozanib is ≥ 99%, primarily to albumin in vitro and is independent of concentration. The mean blood-to-plasma concentration ratios ranged from 0.495 to 0.615 in healthy subjects.
Elimination
The apparent clearance (CL/F) of tivozanib is 0.75 L/h and the half-life is 111 hours.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of tivozanib were observed based on age (18 years to 88 years), sex, race (93% Caucasian, 3% African American, 2% Asian, 2% others), body weight (39 kg to 158 kg), mild to severe renal impairment (CLcr 15-89 mL/min as estimated by Cockcroft-Gault) or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin less than or equal to ULN with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST). The effect of end-stage renal disease or severe hepatic impairment on tivozanib pharmacokinetics is unknown [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.6)and (8.7)] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, tivozanib AUC tauincreased by 1% in patients with mild (total bilirubin less than or equal to ULN with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment. Compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, tivozanib AUC tauincreased by 62% in patients with moderate (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 to 3 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment. The effect of severe (total bilirubin greater than 3 to 10 times ULN with any AST) hepatic impairment on tivozanib pharmacokinetics has not been studied [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.3)and USE IN SPECIFIC POPLATIONS (8.7)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: Tivozanib does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations. Tivozanib does not induce CYP1A, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP3A at clinically relevant concentrations.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with tivozanib.
Tivozanib was not mutagenic in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in an in vitro cytogenetic assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells or in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
In animal studies assessing mating and fertility parameters, oral doses ≥ 0.03 mg/kg/day (0.2 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis) in rats were associated with increased epididymis and testis weights, and doses ≥ 0.3 mg/kg/day (2 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis) reduced mating and produced infertility. An increase in embryo lethality was noted at doses ≥ 0.1 mg/kg/day (0.7 times the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/m 2basis).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of FOTIVDA was evaluated in TIVO-3 (NCT02627963), a randomized (1:1), open- label, multicenter trial of FOTIVDA versus sorafenib in patients with relapsed or refractory advanced RCC who received 2 or 3 prior systemic treatments including at least one VEGFR kinase inhibitor other than sorafenib or tivozanib. Patients were randomized to receive FOTIVDA 1.34 mg orally once daily for 21 days on treatment followed by 7 days off treatment for a 28-day cycle, or to receive sorafenib 400 mg orally twice a day continuously, until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Randomization was stratified by prior therapy [two kinase inhibitors (KIs), a KI plus an immune checkpoint inhibitor, or a KI plus other systemic agents] and by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) prognostic score. Patients were excluded if they had more than 3 prior treatments or Central Nervous System metastases. The main efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS) assessed by a blinded independent radiology review committee. Other efficacy endpoints were objective response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS).
The median age was 63 years (range: 30 to 90 years), 73% were male, 95% were Caucasian, ECOG performance status was 0 in 48% and 1 in 49% of patients (respectively), and 98% of patients had clear cell or clear cell component histology. Prior therapy included two KIs (45%), a KI plus an immune checkpoint inhibitor (26%), and a KI plus another systemic agent (29%). At the time of study entry, 20% of patients had favorable, 61% intermediate, and 19% poor IMDC prognoses.
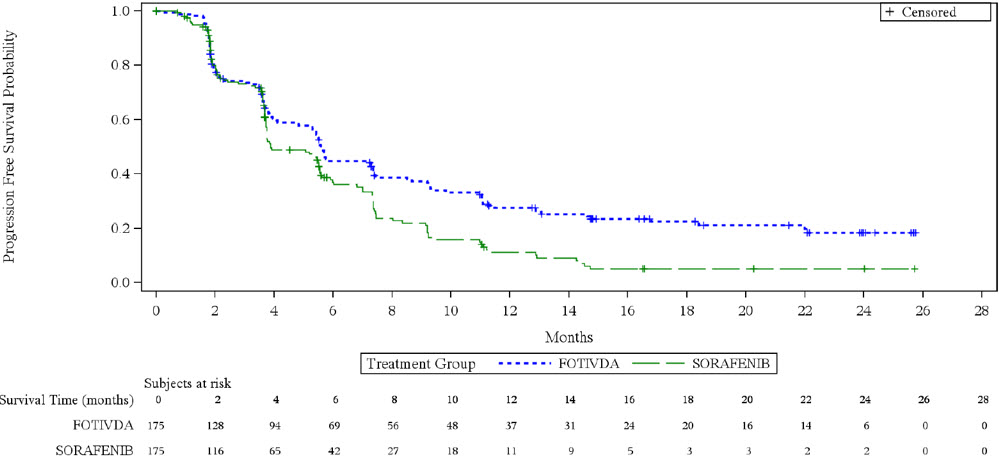
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 4and Figure 1.
Table 4. Efficacy Results in TIVO-3 (ITT) Endpoint FOTIVDA
N= 175Sorafenib
N= 175CI: Confidence interval; HR: Hazard ratio (FOTIVDA/sorafenib); NE: not estimable. - * Assessed by blinded independent radiology review committee according to RECIST v1.1.
- † Based on the Cox proportional hazards model stratified by IMDC prognostic score and prior therapy.
- ‡ Based on the log-rank test stratified by IMDC prognostic score and prior therapy.
Progression Free Survival (PFS)* Events, n (%) 123 (70) 123 (70) Progressive Disease 103 (59) 109 (62) Death 20 (11) 14 (8) Median (95% CI), months 5.6 (4.8, 7.3) 3.9 (3.7, 5.6) HR (95% CI) † 0.73 (0.56, 0.95) P-value ‡ 0.016 Overall Survival Deaths, n (%) 125 (71) 126 (72) Median (95% CI), months 16.4
(13.4, 21.9)19.2
(14.9, 24.2)HR (95% CI) † 0.97 (0.75, 1.24) Objective Response Rate % (95% CI)* 18
(12, 24)8
(4, 13)Median duration of response in months (95% CI) NE
(9.8, NE)5.7
(5.6, NE)Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Plot of PFS in TIVO-3
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
FOTIVDA (tivozanib) capsules, for oral use are supplied as follows:
Capsule Strength Opaque Capsule Color Capsule Markings Pack Size NDC Code Tivozanib 1.34 mg (equivalent to 1.5 mg tivozanib hydrochloride) Bright yellow cap and body "TIVZ" imprinted with dark blue ink on cap; "SD" imprinted with dark blue ink on body Bottle of 21 NDC: 45629-134-01 Tivozanib 0.89 mg (equivalent to 1.0 mg tivozanib hydrochloride) Dark blue cap and bright yellow body "TIVZ" imprinted with yellow ink on cap; "LD" imprinted with dark blue ink on body Bottle of 21 NDC: 45629-089-01 Tivozanib 1.34 mg (equivalent to 1.5 mg tivozanib hydrochloride) Bright yellow cap and body "TIVZ" imprinted with dark blue ink on cap; "SD" imprinted with dark blue ink on body Bottle of 21 in a Carton NDC: 45629-134-02 Tivozanib 0.89 mg (equivalent to 1.0 mg tivozanib hydrochloride) Dark blue cap and bright yellow body "TIVZ" imprinted with yellow ink on cap; "LD" imprinted with dark blue ink on body Bottle of 21 in a Carton NDC: 45629-089-02 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling [see PATIENT INFORMATION] .
Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis
Inform patients that hypertension or hypertensive crisis may occur during FOTIVDA treatment. Advise patients to undergo routine blood pressure monitoring and to contact their healthcare provider if blood pressure is elevated. Advise patients that if they experience signs or symptoms of hypertension to immediately contact their healthcare provider [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
Cardiac Failure
Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of cardiac failure [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)].
Cardiac Ischemia and Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Inform patients that arterial thromboembolic events (including fatal outcomes) may occur during FOTIVDA treatment. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if new onset of chest discomfort, sudden weakness, or other events suggestive of a thrombotic event occurs [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3)].
Venous Thromboembolic Events
Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of dyspnea or localized limb edema [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.4)].
Hemorrhagic Events
Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider to seek immediate medical attention for signs or symptoms of unusual bleeding or hemorrhage [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.5)] .
Perforations and Fistulas
Inform patients that gastrointestinal perforations or fistulas may develop during FOTIVDA treatment. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience persistent or severe abdominal pain [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)] .
Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
Inform patients that FOTIVDA may impair wound healing. Advise patients that temporary interruption of FOTIVDA is recommended prior to elective surgery. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider before any planned surgeries, including dental surgery [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1)and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)] .
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Inform patients that RPLS may occur during FOTIVDA treatment. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider in the event of seizures, headaches, visual disturbances, confusion or difficulty thinking [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.10)].
Overdosage
Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately if they inadvertently take too much FOTIVDA [see OVERDOSAGE (10)] .
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.10)and USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose.
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1)and (8.3)and NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with FOTIVDA and for one month after the last dose [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise males and females of reproductive potential that FOTIVDA can impair fertility [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.3)] .
Allergic Reactions to Tartrazine (FD&C Yellow No.5)
FOTIVDA 0.89 mg capsule contains FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) as an imprint ink which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible patients. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.12)] .
Other Common Events
Advise patients that other adverse reactions with FOTIVDA treatment may include diarrhea, vomiting, dysphonia (hoarseness of voice), fatigue, asthenia and stomatitis (sores in the mouth), and cough [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
Important Administration Information
Instruct patient if a dose of FOTIVDA is missed, the next dose should be taken at the regularly scheduled time. Do not take two doses in the same day [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.1)] .
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, vitamins, or dietary and herbal supplements [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 08/2024 PATIENT INFORMATION
FOTIVDA ®(fo-TIV-dah)
(tivozanib)
capsulesWhat is FOTIVDA?
FOTIVDA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with advanced kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma or RCC) that has been treated with 2 or more prior medicines and has come back or did not respond to treatment.
It is not known if FOTIVDA is safe and effective in children.Before taking FOTIVDA, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you: - have high blood pressure.
- have a history of heart failure.
- have a history of blood clots in your veins or arteries (types of blood vessels), including stroke, heart attack, or change in vision.
- have bleeding problems.
- have thyroid problems.
- have liver problems.
- have an unhealed wound.
- plan to have surgery or have had recent surgery, including dental surgery. You should stop taking FOTIVDA at least 24 days before planned surgery. See " What are the possible side effects of FOTIVDA?"
- are allergic to FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) or aspirin.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. FOTIVDA can harm your unborn baby.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with FOTIVDA.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 month after your last dose of FOTIVDA. Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that may be right for you during this time.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you might be pregnant during treatment with FOTIVDA.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 1 month after your last dose of FOTIVDA.
- If your female partner becomes pregnant during your treatment with FOTIVDA, tell your healthcare provider right away.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if FOTIVDA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 1 month after your last dose of FOTIVDA.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take FOTIVDA? - Take FOTIVDA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take FOTIVDA 1 time each day for 21 days on treatment, followed by 7 days off treatment. This is 1 cycle of treatment. You will repeat this cycle for as long as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- FOTIVDA can be taken with or without food.
- Swallow the FOTIVDA capsule whole with a glass of water. Do not open the capsule.
- If you miss a dose of FOTIVDA, take your next dose at your next scheduled time. Do nottake 2 doses in the same day.
- If you take too much FOTIVDA, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of FOTIVDA?
FOTIVDA may cause serious side effects, including:- High blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure is common with FOTIVDA and may sometimes be severe.FOTIVDA may also cause a sudden, severe increase in your blood pressure (hypertensive crisis) that can lead to death. Your healthcare provider should check your blood pressure after 2 weeks and at least monthly during treatment with FOTIVDA. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine to treat your high blood pressure if you develop blood pressure problems. You should check your blood pressure regularly during treatment with FOTIVDA and tell your healthcare provider if you have increased blood pressure. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms:
- confusion
- headaches
- dizziness
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- Heart failure.FOTIVDA can cause heart failure which can be serious, and sometimes lead to death. Your healthcare provider should check you for symptoms of heart failure regularly during treatment with FOTIVDA. Call your healthcare provider right away if you get symptoms of heart problems, such as shortness of breath or swelling of your ankles.
- Heart attack and blood clots in your veins or arteries.FOTIVDA can cause blood clots which can be serious, and sometimes lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- new chest pain or pressure
- numbness or weakness on one side of your body
- pain in your arms, back, neck or jaw
- trouble talking
- shortness of breath
- sudden severe headache
- vision changes
- swelling in the arms or legs
- Bleeding problems.FOTIVDA can cause bleeding which can be serious, and sometimes lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms:
- unusual bleeding from the gums
- red or black stools (looks like tar)
- menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
- bruises that happen without a known cause or get larger
- headaches, feeling dizzy or weak
- bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- coughing up blood or blood clots
- pink or brown urine
- vomiting blood or your vomit looks like "coffee grounds"
- unexpected pain, swelling, or joint pain
- Protein in your urine.Your healthcare provider should check your urine for protein before and during your treatment with FOTIVDA.
- Tear (perforation) in your stomach or intestines or an abnormal connection between two or more body parts (fistula).Get medical help right away if you experience tenderness or pain in your stomach-area (abdomen) that is severe and does not go away.
- Thyroid gland problems.Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your thyroid gland function before and during your treatment with FOTIVDA. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine if you develop thyroid gland problems.
-
Risk of wound healing problems.Wounds may not heal properly during FOTIVDA treatment. Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have surgery before starting or during treatment with FOTIVDA, including dental surgery.
- You should stop taking FOTIVDA at least 24 days before planned surgery.
- Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking FOTIVDA again after surgery.
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS).A condition called reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) can happen during treatment with FOTIVDA. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get:
- headaches
- seizures
- confusion
- blindness or change in vision
- difficulty thinking
- Allergic reactions to tartrazine (FD&C Yellow No.5).FOTIVDA 0.89 mg capsules contain a dye called FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions, including bronchial asthma, in certain people. This allergic reaction is most often seen in people who also have an allergy to aspirin.
The most common side effects of FOTIVDA include: - tiredness
- diarrhea
- decreased appetite
- nausea
- hoarseness
- low levels of thyroid hormones
- cough
- mouth sores
- decreased levels of salt (sodium) and phosphate in the blood
- increased levels of lipase in the blood (a blood test done to check your pancreas)
Other side effects include vomiting and weakness or lack of energy.
FOTIVDA may cause fertility problems in males and females, which may affect your ability to have a child. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with FOTIVDA if you have certain side effects.
These are not all of the possible side effects of FOTIVDA.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store FOTIVDA? - Store FOTIVDA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
General information about the safe and effective use of FOTIVDA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use FOTIVDA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FOTIVDA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about FOTIVDA that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in FOTIVDA?
Active ingredient:tivozanib hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients:mannitol and magnesium stearate. The capsule contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, FDA yellow iron oxide, and Blue SB-6018 (ink). The 0.89 mg capsule also contains FD&C Blue #2 and Yellow SB-3017 (ink). The Yellow SB-3017 ink contains FD&C Yellow No.5 (tartrazine).
Manufactured for:
AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc., an LG Chem Company
Boston, MA 02210
Manufactured by: Catalent CTS, Inc. Kansas City, MO 64137
For more information go to www.fotivda.com or call 1-833-FOTIVDA (1-833-368-4832).
For patent information: www.aveooncology.com/patents
©2024 AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.89 mg Capsule Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1.34 mg Capsule Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FOTIVDA
tivozanib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 45629-089 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TIVOZANIB HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 8A9H4VK35Z) (TIVOZANIB - UNII:172030934T) TIVOZANIB 0.89 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color blue (Dark Blue) , yellow (Bright Yellow) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code TIVZ;LD Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 45629-089-01 1 in 1 BAG 03/10/2021 1 21 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 45629-089-02 1 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2025 2 21 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212904 03/10/2021 FOTIVDA
tivozanib capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 45629-134 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TIVOZANIB HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 8A9H4VK35Z) (TIVOZANIB - UNII:172030934T) TIVOZANIB 1.34 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color yellow (Bright Yellow) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code TIZV;SD Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 45629-134-01 1 in 1 BAG 03/10/2021 1 21 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 45629-134-02 1 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2025 2 21 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212904 03/10/2021 Labeler - AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (111045360)
Trademark Results [FOTIVDA]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FOTIVDA 86580973 4984746 Live/Registered |
AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2015-03-30 |
 FOTIVDA 85430468 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2011-09-23 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

