SODIUM CHLORIDE injection
Sodium Chloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sodium Chloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Henry Schein, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION:
This preparation is designed solely for parenteral use only after addition of drugs that require dilution or must be dissolved in an aqueous vehicle prior to injection.
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9% is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. The osmolarity is 0.300 mOsmol/mL (calculated).
Each mL contains: Sodium chloride 9 mg; Water for Injection q.s. It contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer and is supplied only in single dose containers. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added for pH adjustment (pH 4.5-7.0).
Sodium chloride occurs as colorless cubic crystals or white crystalline powder and has a saline taste. Sodium chloride is freely soluble in water. It is soluble in glycerin and slightly soluble in alcohol.
The empirical formula for sodium chloride is NaCl and the molecular weight is 58.44.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Sodium chloride in water dissociates to provide sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl—) ions. These ions are normal constituents of the body fluids (principally extracellular) and are essential for maintaining electrolyte balance.
The distribution and excretion of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl—) are largely under the control of the kidney which maintains a balance between intake and output.
The small volume of fluid and amount of sodium chloride provided by Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9%, when used only as an isotonic vehicle for parenteral injection of drugs, is unlikely to exert a significant effect on fluid and electrolyte balance except possibly in neonates and very small infants.
Water is an essential constituent of all body tissues and accounts for approximately 70% of total body weight. Average normal adult daily requirement ranges from two to three liters (1 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production).
Water balance is maintained by various regulatory mechanisms. Water distribution depends primarily on the concentration of electrolytes in the body compartments and sodium (Na+) plays a major role in maintaining physiologic equilibrium.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
-
PRECAUTIONS:
Consult the manufacturer's instructions for choice of vehicle, appropriate dilution or volume for dissolving the drugs to be injected, including the route and rate of injection. Inspect reconstituted (diluted or dissolved) drugs for clarity (if soluble) and freedom from unexpected precipitation or discoloration prior to administration.
Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9%. It is also not known whether Sodium Chloride Injection containing additives can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9% containing additives should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population are based on the similarity of the clinical conditions of the pediatric and adult populations. In neonates or very small infants the volume of fluid may affect fluid and electrolyte balance.Drug Interactions
Some drugs for injection may be incompatible in a given vehicle, or when combined in the same vehicle or in a vehicle containing benzyl alcohol. Consult with pharmacist, if available.Use aseptic technique for single or multiple entry and withdrawal from all containers.
When diluting or dissolving drugs, mix thoroughly and use promptly.
Do not store reconstituted solutions of drugs for injection unless otherwise directed by the manufacturer of the solute.
Do not use unless the solution is clear and seal intact. Do not reuse single dose containers, discard unused portion.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Reactions which may occur because of this solution, added drugs or the technique of reconstitution or administration include febrile response, local tenderness, abscess, tissue necrosis or infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection and extravasation.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate countermeasures and, if possible, retrieve and save the remainder of the unused vehicle for examination.
-
OVERDOSAGE:
Use only as a diluent or solvent. This parenteral preparation is unlikely to pose a threat of carbohydrate, sodium chloride or fluid overload except possibly in neonates or very small infants. In the event these should occur, reevaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures. (See PRECAUTIONS and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
The volume of the preparation to be used for diluting or dissolving any drug for injection, is dependent on the vehicle concentration, dose and route of administration as recommended by the manufacturer.
This parenteral should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. See PRECAUTIONS.
-
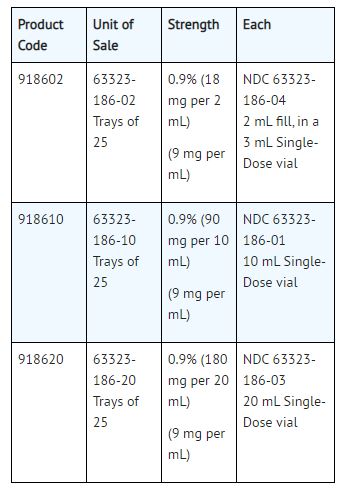
How Supplied
Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, 0.9%, preservative free, is available as follows:
Preservative Free. Discard unused portion.
Use only if solution is clear and seal intact.
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
www.fresenius-kabi.com/us
45764F
Revised: November 2020
Product repackaged by: Henry Schein, Inc., Bastian, VA 24314 From Original Manufacturer/Distributor's NDC and Unit of Sale To Henry Schein Repackaged Product NDC and Unit of Sale Total Strength/Total Volume (Concentration) per unit NDC: 63323-186-10
Unit of 25NDC: 0404-9955-10
1 10 mL Single Dose vial in a bag
(Vial bears NDC: 63323-186-01)0.9% - Sample Package Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SODIUM CHLORIDE
sodium chloride injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0404-9955(NDC:63323-186) Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) (CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) SODIUM CHLORIDE 9 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0404-9955-10 1 in 1 BAG 01/12/2022 1 10 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA088912 01/12/2022 Labeler - Henry Schein, Inc. (012430880) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Henry Schein, Inc. 830995189 relabel(0404-9955)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
