ETOPOPHOS- etoposide phosphate injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
ETOPOPHOS by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ETOPOPHOS by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by E.R. Squibb & Sons, L.L.C.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ETOPOPHOS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ETOPOPHOS.
ETOPOPHOS® (etoposide phosphate) for injection,
for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1983INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Refractory testicular tumors: 50 to 100 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours on days 1 through 5, or 100 mg/m2 administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours on days 1, 3, and 5. (2.1)
- Small cell lung cancer: 35 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours for 4 days or 50 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours for 5 days. (2.2)
- Do not give by bolus injection. (2.4)
- Renal impairment: Reduce the recommended dose to 75% in patients with creatinine clearance 15 to 50 mL/min. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Myelosuppression: Obtain complete blood counts prior to each cycle and more frequently as clinically indicated. (5.1)
- Secondary leukemias: Can occur with long-term use. (5.2)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis may occur. (5.3)
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: ETOPOPHOS can cause fetal harm. Advise females of potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception during treatment with ETOPOPHOS and for 6 months after final dose. Advise males to use effective contraception for 4 months, after the last dose of ETOPOPHOS. (5.4, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reaction is neutropenia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-800-721-5072 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Warfarin: Co-administration can result in elevated international normalized ratio (INR). Measure INR frequently. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Do not breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE1.1 Refractory Testicular Tumors
1.2 Small Cell Lung Cancer
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Refractory Testicular Tumors
2.2 Small Cell Lung Cancer
2.3 Dosage Modification
2.4 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
5.2 Secondary Leukemias
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Refractory Testicular Tumors
The recommended dose of ETOPOPHOS is:
- 50 to 100 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours on days 1 through 5 of each 21-day (or 28-day cycle), or
- 100 mg/m2 administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours on days 1, 3, and 5 of each 21-day (or 28-day cycle).
2.2 Small Cell Lung Cancer
The recommended dose of ETOPOPHOS is:
35 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours for 4 days, or
50 mg/m2 per day administered intravenously over 5 minutes to 3.5 hours for 5 days.2.3 Dosage Modification
In patients with a creatinine clearance (CLcr) 15-50 mL/min, administer 75% of the recommended dose.
Data are not available in patients with CLcr less than 15 mL/min. Consider further dose reduction in these patients.2.4 Preparation and Administration
Preparation
- Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection, USP; 5% Dextrose Injection, USP; 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP; Bacteriostatic Water for Injection with Benzyl Alcohol; or Bacteriostatic Sodium Chloride for Injection with Benzyl Alcohol, using the quantity of diluent shown below:
Vial Strength
Volume of Diluent
Final Concentration
100 mg
5 mL
20 mg/mL
10 mL
10 mg/mL
- Following reconstitution, ETOPOPHOS can be further diluted to concentrations as low as 0.1 mg/mL with either 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Inspect parenteral drug products visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
Storage
After reconstitution, store under the following conditions:- Refrigerated 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) for 7 days;
- Room temperature at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) for 24 hours following reconstitution with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP;
- Room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) for 48 hours following reconstitution with Bacteriostatic Water for Injection with benzyl alcohol or Bacteriostatic Sodium Chloride for Injection with benzyl alcohol.
Reconstituted ETOPOPHOS solutions further diluted as directed can be stored under refrigeration 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) or at room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) for 24 hours.
Administration
DO NOT GIVE ETOPOPHOS BY BOLUS INTRAVENOUS INJECTION. ETOPOPHOS solutions may be administered at infusion rates up to 3.5 hours. Extravasation of ETOPOPHOS may result in swelling, pain, cellulitis, and necrosis including skin necrosis.ETOPOPHOS is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1 To minimize the risk of dermal exposure, use of gloves is recommended. If dermal contact occurs, immediately and thoroughly wash areas of skin contact with soap and water and flush mucosa with water.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 114 mg etoposide phosphate (equivalent to 100 mg etoposide), white to off-white, lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution [see Description (11)].
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ETOPOPHOS is contraindicated in patients with a history of a severe hypersensitivity reaction to etoposide products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myelosuppression
ETOPOPHOS causes myelosuppression that results in thrombocytopenia and neutropenia. Fatal infections and bleeding have occurred. Obtain complete blood counts prior to each cycle of ETOPOPHOS and more frequently as clinically indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
ETOPOPHOS can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, urticaria, pruritus, and anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, immediately interrupt ETOPOPHOS and institute supportive management. Permanently discontinue ETOPOPHOS in patients who experience a severe hypersensitivity reaction.5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action, ETOPOPHOS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ETOPOPHOS and for at least 6 months after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception for 4 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Secondary leukemias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates, observed in the clinical trials of a drug, cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
ETOPOPHOS has been used as a single agent in clinical studies involving 206 patients with a variety of malignancies (including one non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma) and in combination with cisplatin in 60 patients with small cell lung cancer. The most common adverse reaction was neutropenia.
Other Important Adverse Reactions
Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Nausea and vomiting are the major gastrointestinal toxicities. The severity of nausea and vomiting is generally mild to moderate, with treatment discontinuation required in 1% of patients. Nausea and vomiting are managed with standard antiemetic therapy.Other Toxicities
Other clinically important adverse reactions in clinical trials were:
Gastrointestinal: abdominal pain, constipation, dysphagia
General: fever
Ocular: transient cortical blindness, optic neuritis
Respiratory: interstitial pneumonitis/pulmonary fibrosis
Skin: pigmentation, radiation recall dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Neurologic: seizure, aftertaste
Hepatobiliary disorder: hepatotoxicity6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ETOPOPHOS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Extravasation
Extravasation, resulting in local soft tissue toxicity. Extravasation of ETOPOPHOS can result in swelling, pain, cellulitis, and necrosis, including skin necrosis.Acute Renal Failure
Reversible cases of acute renal failure have been reported with administration of high dose (2220 mg/m2) ETOPOPHOS with total body irradiation used for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The ETOPOPHOS formulation contains dextran 40, which has been associated with acute renal failure when administered in high doses.
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal data and its mechanism of action, ETOPOPHOS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Etoposide, the active moiety of etoposide phosphate is teratogenic in mice and rats (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential hazard to a fetus.
Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid becoming pregnant.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.Data
Animal Data
In rats, an intravenous etoposide dose of 0.4 mg/kg/day (about 0.05 times of the 50 mg/m2 human dose based on body surface area [BSA]) during organogenesis caused maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and teratogenicity (skeletal abnormalities, exencephaly, encephalocele, and anophthalmia); higher doses of 1.2 and 3.6 mg/kg/day (about 0.14 and 0.5 times the 50 mg/m2 human dose based on BSA) resulted in 90% and 100% embryonic resorptions. In mice, a single etoposide dose of 1.0 mg/kg (approximately 0.06 times the 50 mg/m2 human dose based on BSA) administered intraperitoneally on days 6, 7, or 8 of gestation caused embryotoxicity, cranial abnormalities, and major skeletal malformations. An intraperitoneal dose of 1.5 mg/kg (about 0.1 times the 50 mg/m2 human based on BSA) on day 7 of gestation caused an increase in the incidence of intrauterine death and fetal malformations and a significant decrease in the average fetal body weight [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].8.2 Lactation
There is no information regarding the presence of etoposide in human milk or its effects on breastfed infant milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ETOPOPHOS, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ETOPOPHOS.8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ETOPOPHOS and for 6 months after the final dose.
Males
ETOPOPHOS may damage spermatozoa and testicular tissue, resulting in possible genetic fetal abnormalities. Males with female sexual partners of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment with ETOPOPHOS and for 4 months after the final dose.Infertility
Females
In females of reproductive potential, ETOPOPHOS may cause infertility and result in amenorrhea. Premature menopause can occur with ETOPOPHOS. Recovery of menses and ovulation is related to age at treatment.
Males
In male patients, ETOPOPHOS may result in oligospermia, azoospermia, and permanent loss of fertility. Sperm counts have been reported to return to normal levels in some men, and in some cases, have occurred several years after the end of therapy [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of etoposide did not include sufficient numbers (n=71) of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ETOPOPHOS (etoposide phosphate) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. The chemical name for etoposide phosphate is: 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin 9-[4,6-O-(R)-ethylidene-β-D-glucopyranoside], 4' (dihydrogen phosphate).
Etoposide phosphate has the following structure: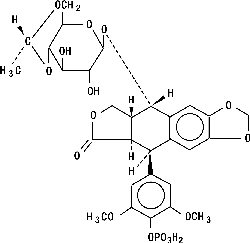
Etoposide phosphate is a phosphate ester of etoposide, a semi-synthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin. ETOPOPHOS is available for intravenous infusion as a sterile lyophilized powder in single-dose vials for reconstitution containing 114 mg etoposide phosphate, equivalent to 100 mg etoposide, 32.7 mg sodium citrate USP, and 300 mg dextran 40.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Etoposide phosphate is a prodrug that is converted to its active moiety, etoposide, by dephosphorylation. Etoposide causes the induction of DNA strand breaks by an interaction with DNA-topoisomerase II or the formation of free radicals, leading to cell cycle arrest, primarily at the G2 stage of the cell cycle, and cell death.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following intravenous administration of 90, 100, and 110 mg/m2 dose of ETOPOPHOS over 60 minutes, mean nadir values (expressed as percent decrease from baseline) for granulocytes, hemoglobin, and thrombocytes were 81.0 ± 16.5%, 21.4 ± 9.9%, and 44.1 ± 20.7%, respectively.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following intravenous administration of an etoposide formulation, the area under the concentration time curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) values increased linearly and etoposide did not accumulate in the plasma following daily administration for 4 to 5 days.
DistributionFollowing administration of an injectable etoposide formulation, the mean volume of distribution of etoposide at steady state was 18 to 29 liters.
Etoposide enters the CSF poorly.
In vitro, etoposide is 97% bound to human plasma proteins, primarily albumin.
EliminationThe terminal elimination half-life of etoposide ranges from 4 to 11 hours. Total body clearance values range from 33 to 48 mL/min.
Metabolism
Following intravenous administration of ETOPOPHOS, etoposide phosphate is completely converted to etoposide in plasma. Etoposide is metabolized by opening of the lactone ring, O-demethylation, and conjugation (i.e., glucuronidation and sulfation). O-demethylation occurs through the CYP450 3A4 isoenzyme pathway to produce the active catechol metabolite.
ExcretionAt 120 hours after intravenous administration of radiolabeled etoposide formulation, the mean recovery of radioactivity in the urine was 56% of the dose, 45% of which was excreted as etoposide and 8% or less as metabolites. Fecal recovery of radioactivity was 44% of the dose.
Specific Populations
Following intravenous administration of etoposide in adults, the total body clearance of etoposide was correlated with creatinine clearance, serum albumin concentration, and non-renal clearance. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of etoposide were observed based on age and sex.
Drug Interaction Studies
Cisplatin: Co-administration of cisplatin may increase exposure to etoposide.
Highly protein-bound drugs: Phenylbutazone, sodium salicylate, and aspirin displaced protein-bound etoposide in vitro.
Select antiepileptic medications: Co-administration with antiepileptic medications including phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and valproic acid may increase etoposide clearance.
Etoposide may be a substrate of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporter system based upon in vitro studies. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
ETOPOPHOS was non-mutagenic in an in vitro Ames microbial mutagenicity assay; however, ETOPOPHOS is rapidly and completely converted to etoposide in vivo. Therefore, as etoposide is mutagenic in the Ames assay, ETOPOPHOS is considered mutagenic in vivo.
In rats, oral dosing of ETOPOPHOS for 5 consecutive days at doses greater than or equal to 86 mg/kg/day (about 10 times the 50 mg/m2 human dose based on BSA) resulted in irreversible testicular atrophy. Irreversible testicular atrophy was also present in rats treated with ETOPOPHOS intravenously for 30 days at 5.11 mg/kg/day (about 0.5 times the 50 mg/m2 human dose based on BSA).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1 was a multicenter trial in patients, with previously untreated, small cell lung cancer, randomized (1:1) to receive either etoposide phosphate (80 mg/m2/day) plus cisplatin (20 mg/m2/day) for 5 days, or etoposide (80 mg/m2/day) plus cisplatin (20 mg/m2/day). The major efficacy outcome measure was objective response rate (ORR).
Among the 121 patients enrolled, the median age was 64 years, 65% of patients were male, 89% were White, and ECOG performance score was 0 to 2.
Study 1 demonstrated an overall response rate of 61% (95% confidence interval [CI] 47, 73) for patients treated with etoposide phosphate plus cisplatin, and 58% (95% CI: 45, 71) for those receiving etoposide plus cisplatin. - 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied/Storage
ETOPOPHOS is supplied as a single-dose vial containing etoposide phosphate equivalent to 100 mg etoposide as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution, individually packaged in a carton:
NDC: 0015-3404-20
Store unopened vials at 2° to 8°C (36°-46°F). Keep vial in outer carton to protect from light.Handling
ETOPOPHOS is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Myelosuppression
- Advise patients that periodic monitoring of their blood counts is required. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for new onset of bleeding, fever, or symptoms of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and 6 months after treatment with ETOPOPHOS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Advise males with female sexual partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with ETOPOPHOS and for at least 4 months after the final dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Manufactured for:
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Distributed by:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
1252629A7 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
---------------------------------------------
ETOPOPHOS 100 mg for Injection Representative PackagingSee How Supplied section for a complete list of available packages of ETOPOPHOS.
NDC: 0015-3404-20
Single-Dose Vial
ETOPOPHOS®(etoposide phosphate) for Injection
For IV use
Etoposide phosphate equivalent to
100 mg etoposide
Rx only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ETOPOPHOS
etoposide phosphate injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0015-3404 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength etoposide phosphate (UNII: 528XYJ8L1N) (etoposide - UNII:6PLQ3CP4P3) etoposide 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) 32.7 mg dextran 40 (UNII: K3R6ZDH4DU) 300 mg Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0015-3404-20 1 in 1 CARTON 06/01/2009 04/30/2021 1 1 in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA020457 06/01/2009 04/30/2021 Labeler - E.R. Squibb & Sons, L.L.C. (968242821)
Trademark Results [ETOPOPHOS]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ETOPOPHOS 74179774 1757537 Live/Registered |
CHEPLAPHARM ARZNEIMITTEL GMBH 1991-06-25 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.