Timolol Maleate by Avera McKennan Hospital TIMOLOL MALEATE tablet
Timolol Maleate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Timolol Maleate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Avera McKennan Hospital. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
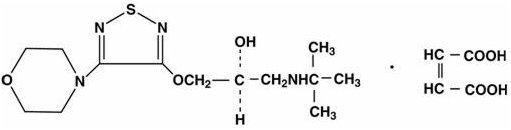
Timolol maleate is a nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent. The chemical name for timolol maleate is (S)-1-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-3-[[4-(4-morpholinyl)-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl]oxy]-2-propanol (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) salt. It possesses an asymmetric carbon atom in its structure and is provided as the levo isomer. Its molecular formula is C13H24N4O3SC4H4O4 and its structural formula is:
Timolol maleate has a molecular weight of 432.50. It is a white, odorless, crystalline powder which is soluble in water, methanol, and alcohol.
Timolol maleate is supplied as tablets containing 5 mg, 10 mg and 20 mg timolol maleate for oral administration. Inactive ingredients are: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, sodium lauryl sulfate, FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, and D&C Yellow #10 aluminum lake.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Timolol maleate is a beta1 and beta2 (nonselective) adrenergic receptor blocking agent that does not have significant intrinsic sympathomimetic, direct myocardial depressant, or local anesthetic activity.
Pharmacodynamics
Clinical pharmacology studies have confirmed the beta-adrenergic blocking activity as shown by (1) changes in resting heart rate and response of heart rate to changes in posture; (2) inhibition of isoproterenol-induced tachycardia; (3) alteration of the response to the Valsalva maneuver and amyl nitrite administration; and (4) reduction of heart rate and blood pressure changes on exercise.
Timolol decreases the positive chronotropic, positive inotropic, bronchodilator, and vasodilator responses caused by beta-adrenergic receptor agonists. The magnitude of this decreased response is proportional to the existing sympathetic tone and the concentration of timolol at receptor sites.
In normal volunteers, the reduction in heart rate response to a standard exercise was dose dependent over the test range of 0.5 to 20 mg, with a peak reduction at 2 hours of approximately 30% at higher doses.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade reduces cardiac output in both healthy subjects and patients with heart disease. In patients with severe impairment of myocardial function beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may inhibit the stimulatory effect of the sympathetic nervous system necessary to maintain adequate cardiac function.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade in the bronchi and bronchioles results in increased airway resistance from unopposed parasympathetic activity. Such an effect in patients with asthma or other bronchospastic conditions is potentially dangerous.
Clinical studies indicate that timolol maleate at a dosage of 20 to 60 mg/day reduces blood pressure without causing postural hypotension in most patients with essential hypertension. Administration of timolol to patients with hypertension results initially in a decrease in cardiac output, little immediate change in blood pressure, and an increase in calculated peripheral resistance. With continued administration of timolol, blood pressure decreases within a few days, cardiac output usually remains reduced, and peripheral resistance falls toward pretreatment levels. Plasma volume may decrease or remain unchanged during therapy with timolol. In the majority of patients with hypertension timolol also decreases plasma renin activity. Dosage adjustment to achieve optimal antihypertensive effect may require a few weeks. When therapy with timolol is discontinued, the blood pressure tends to return to pretreatment levels gradually. In most patients the antihypertensive activity of timolol is maintained with long-term therapy and is well tolerated.
The mechanism of the antihypertensive effects of beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents is not established at this time. Possible mechanisms of action include reduction in cardiac output, reduction in plasma renin activity, and a central nervous system sympatholytic action.
A Norwegian multi-center, double-blind study, which included patients 20 to 75 years of age, compared the effects of timolol maleate with placebo in 1,884 patients who had survived the acute phase of a myocardial infarction. Patients with systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg, sick sinus syndrome and contraindications to beta-blockers, including uncontrolled heart failure, second- or third-degree AV block and bradycardia (< 50 beats per minute), were excluded from the multi-center trial. Therapy with timolol, begun 7 to 28 days following infarction, was shown to reduce overall mortality; this was primarily attributable to a reduction in cardiovascular mortality. Timolol significantly reduced the incidence of sudden deaths (deaths occurring without symptoms or within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms), including those occurring within one hour, and particularly instantaneous deaths (those occurring without preceding symptoms). The protective effect of timolol was consistent regardless of age, sex or site of infarction. The effect was clearest in patients with a first infarction who were considered at a high risk of dying, defined as those with one or more of the following characteristics during the acute phase: transient left ventricular failure, cardiomegaly, newly appearing atrial fibrillation or flutter, systolic hypotension, or SGOT (ASAT) levels greater than four times the upper limit of normal. Therapy with timolol also reduced the incidence of nonfatal reinfarction. The mechanism of the protective effect of timolol is unknown.
Timolol was studied for the prophylactic treatment of migraine headache in placebo-controlled clinical trials involving 400 patients, mostly women between the ages of 18 and 66 years. Common migraine was the most frequent diagnosis. All patients had at least two headaches per month at baseline. Approximately 50 percent of patients who received timolol had a reduction in the frequency of migraine headache of at least 50 percent, compared to a similar decrease in frequency in 30 percent of patients receiving placebo. The most common cardiovascular adverse effect was bradycardia (5%).
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Timolol maleate is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed (about 90%) following oral ingestion. Detectable plasma levels of timolol occur within one-half hour and peak plasma levels occur in about one to two hours. The drug half-life in plasma is approximately 4 hours and this is essentially unchanged in patients with moderate renal insufficiency. Timolol is partially metabolized by the liver and timolol and its metabolites are excreted by the kidney. Timolol is not extensively bound to plasma proteins; i.e., < 10% by equilibrium dialysis and approximately 60% by ultrafiltration. An in vitro hemodialysis study, using 14C timolol added to human plasma or whole blood, showed that timolol was readily dialyzed from these fluids; however, a study of patients with renal failure showed that timolol did not dialyze readily. Plasma levels following oral administration are about half those following intravenous administration indicating approximately 50% first pass metabolism. The level of beta sympathetic activity varies widely among individuals, and no simple correlation exists between the dose or plasma level of timolol maleate and its therapeutic activity. Therefore, objective clinical measurements such as reduction of heart rate and/or blood pressure should be used as guides in determining the optimal dosage for each patient.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hypertension
Timolol maleate tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. They may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, especially thiazide-type diuretics.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Timolol maleate is contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma or with a history of bronchial asthma, or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (see WARNINGS); sinus bradycardia; second- and third-degree atrioventricular block; overt cardiac failure (see WARNINGS); cardiogenic shock; hypersensitivity to this product.
-
WARNINGS
Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be essential for support of the circulation in individuals with diminished myocardial contractility, and its inhibition by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may precipitate more severe failure. Although beta-blockers should be avoided in overt congestive heart failure, they can be used, if necessary, with caution in patients with a history of failure who are well compensated, usually with digitalis and diuretics. Both digitalis and timolol maleate slow AV conduction. If cardiac failure persists, therapy with timolol maleate should be withdrawn.
In Patients Without a History of Cardiac Failure
Continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of cardiac failure, patients receiving timolol should be digitalized and/or be given a diuretic, and the response observed closely. If cardiac failure continues, despite adequate digitalization and diuretic therapy, timolol should be withdrawn.
Exacerbation of Ischemic Heart Disease Following Abrupt Withdrawal
Hypersensitivity to catecholamines has been observed in patients withdrawn from beta-blocker therapy; exacerbation of angina and, in some cases, myocardial infarction have occurred after abrupt discontinuation of such therapy. When discontinuing chronically administered timolol maleate, particularly in patients with ischemic heart disease, the dosage should be gradually reduced over a period of one to two weeks and the patient should be carefully monitored. If angina markedly worsens or acute coronary insufficiency develops, timolol maleate administration should be reinstituted promptly, at least temporarily, and other measures appropriate for the management of unstable angina should be taken. Patients should be warned against interruption or discontinuation of therapy without the physician's advice. Because coronary artery disease is common and may be unrecognized, it may be prudent not to discontinue timolol maleate therapy abruptly even in patients treated only for hypertension.
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (e.g., CHRONIC BRONCHITIS, EMPHYSEMA) OF MILD OR MODERATE SEVERITY, BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASE OR A HISTORY OF BRONCHOSPASTIC DISEASE (OTHER THAN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA OR A HISTORY OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA, IN WHICH ‘TIMOLOL MALEATE’ IS CONTRAINDICATED, see CONTRAINDICATIONS), SHOULD IN GENERAL NOT RECEIVE BETA-BLOCKERS, INCLUDING ‘TIMOLOL’. However, if timolol is necessary in such patients, then the drug should be administered with caution since it may block bronchodilation produced by endogenous and exogenous catecholamine stimulation of beta2 receptors.
Major Surgery
The necessity or desirability of withdrawal of beta-blocking therapy prior to major surgery is controversial. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade impairs the ability of the heart to respond to beta-adrenergically mediated reflex stimuli. This may augment the risk of general anesthesia in surgical procedures. Some patients receiving beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents have been subject to protracted severe hypotension during anesthesia. Difficulty in restarting and maintaining the heartbeat has also been reported. For these reasons, in patients undergoing elective surgery, some authorities recommend gradual withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents.
If necessary during surgery, the effects of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may be reversed by sufficient doses of such agonists as isoproterenol, dopamine, dobutamine or norepinephrine (see OVERDOSAGE).
Diabetes Mellitus
Timolol should be administered with caution in patients subject to spontaneous hypoglycemia or to diabetic patients (especially those with labile diabetes) who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Impaired Hepatic or Renal Function
Since timolol is partially metabolized in the liver and excreted mainly by the kidneys, dosage reductions may be necessary when hepatic and/or renal insufficiency is present.
Dosing in the Presence of Marked Renal Failure
Although the pharmacokinetics of timolol are not greatly altered by renal impairment, marked hypotensive responses have been seen in patients with marked renal impairment undergoing dialysis after 20 mg doses. Dosing in such patients should therefore be especially cautious.
Muscle Weakness
Beta-adrenergic blockade has been reported to potentiate muscle weakness consistent with certain myasthenic symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and generalized weakness). Timolol has been reported rarely to increase muscle weakness in some patients with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms.
Cerebrovascular Insufficiency
Because of potential effects of beta-adrenergic blocking agents relative to blood pressure and pulse, these agents should be used with caution in patients with cerebrovascular insufficiency. If signs or symptoms suggesting reduced cerebral blood flow are observed, consideration should be given to discontinuing these agents.
Drug Interactions
Catecholamine-Depleting Drugs
Close observation of the patient is recommended when timolol is administered to patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs such as reserpine, because of possible additive effects and the production of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia, which may produce vertigo, syncope, or postural hypotension.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Blunting of the antihypertensive effect of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs has been reported. When using these agents concomitantly, patients should be observed carefully to confirm that the desired therapeutic effect has been obtained.
Calcium Antagonists
Literature reports suggest that oral calcium antagonists may be used in combination with beta-adrenergic blocking agents when heart function is normal, but should be avoided in patients with impaired cardiac function. Hypotension, AV conduction disturbances, and left ventricular failure have been reported in some patients receiving beta-adrenergic blocking agents when an oral calcium antagonist was added to the treatment regimen. Hypotension was more likely to occur if the calcium antagonist were a dihydropyridine derivative, e.g., nifedipine, while left ventricular failure and AV conduction disturbances were more likely to occur with either verapamil or diltiazem.
Intravenous calcium antagonists should be used with caution in patients receiving beta-adrenergic blocking agents.
Digitalis and Either Diltiazem or Verapamil
The concomitant use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents with digitalis and either diltiazem or verapamil may have additive effects in prolonging AV conduction time.
Quinidine
Potentiated systemic beta-blockade (e.g., decreased heart rate) has been reported during combined treatment with quinidine and timolol, possibly because quinidine inhibits the metabolism of timolol via the P-450 enzyme, CYP2D6.
Clonidine
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may exacerbate the rebound hypertension which can follow the withdrawal of clonidine. If the two drugs are coadministered, the beta-adrenergic blocking agent should be withdrawn several days before the gradual withdrawal of clonidine. If replacing clonidine by beta-blocker therapy, the introduction of beta-adrenergic blocking agents should be delayed for several days after clonidine administration has stopped.
Risk of Anaphylactic Reaction
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reaction to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic challenge with such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2 year study of timolol maleate in rats, there was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of adrenal pheochromocytomas in male rats administered 300 mg/kg/day (250 times1 the maximum recommended human dose). Similar differences were not observed in rats administered doses equivalent to approximately 20 or 80 times1 the maximum recommended human dose.
In a lifetime study in mice, there were statistically significant increases in the incidence of benign and malignant pulmonary tumors, benign uterine polyps and mammary adenocarcinoma in female mice at 500 mg/kg/day (approximately 400 times1 the maximum recommended human dose), but not at a 5 or 50 mg/kg/day. In a subsequent study in female mice, in which postmortem examinations were limited to uterus and lungs, a statistically significant increase in the incidence of pulmonary tumors was again observed at 500 mg/kg/day.
The increased occurrence of mammary adenocarcinoma was associated with elevations in serum prolactin that occurred in female mice administered timolol maleate at 500 mg/kg/day, but not at doses of 5 or 50 mg/kg/day. An increased incidence of mammary adenocarcinomas in rodents has been associated with administration of several other therapeutic agents which elevate serum prolactin, but no correlation between serum prolactin levels and mammary tumors has been established in man. Furthermore, in adult human female subjects who received oral dosages of up to 60 mg of timolol maleate, the maximum recommended daily human oral dosage, there were no clinically meaningful changes in serum prolactin.
Timolol maleate was devoid of mutagenic potential when elevated in vivo (mouse) in the micronucleus test and cytogenetic assay (doses up to 800 mg/kg) and in vitro in a neoplastic cell transformation assay (up to 100 mcg/mL). In Ames tests the highest concentrations of timolol employed, 5,000 or 10,000 mcg/plate, were associated with statistically significant elevations of revertants observed with tester strain TA100 (in seven replicate assays), but not in three additional strains. In the assays with tester strain TA100, no consistent dose-response relationship was observed, nor did the ratio of test to control revertants reach 2. A ratio of 2 is usually considered the criterion for a positive Ames test.
Reproduction and fertility studies in rats showed no adverse effect on male or female fertility at doses up to 125 times1 the maximum recommended human dose.
- 1 Based on patient weight of 50 kg.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Teratogenicity studies with timolol in mice, rats and rabbits at doses up to 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 40 times1 the maximum recommended daily human dose) showed no evidence of fetal malformations. Although delayed fetal ossification was observed at this dose in rats, there were no adverse effects on postnatal development of offspring. Doses of 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 830 times1 the maximum recommended daily human dose) were maternotoxic in mice and resulted in an increased number of fetal resorptions. Increased fetal resorptions were also seen in rabbits at doses of approximately 40 times1 the maximum recommended daily human dose, in this case without apparent maternotoxicity. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Timolol should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Timolol maleate has been detected in human milk.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from timolol in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of timolol for the treatment of hypertension or migraine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
In a clinical study of timolol in patients who had survived the acute phase of a myocardial infarction, approximately 350 patients (37%) were 65 to 75 years of age. Safety and efficacy were not different between these patients and younger patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacodynamics).
Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. (See PRECAUTIONS: Impaired Hepatic or Renal Function and Dosing in the Presence of Marked Renal Failure.)
The results from 5 single- and/or multiple-dose PK studies comparing the impact of age on the PK of hydrochlorothiazide, when given in combination with other antihypertensive drugs, were consistent. They indicated a mean median increase in Cmax and AUC of 38% and 99% respectively, in elderly relative to younger subjects.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Timolol maleate tablets are usually well tolerated in properly selected patients. Most adverse effects have been mild and transient.
In a multi-center (12 week) clinical trial comparing timolol maleate and placebo in hypertensive patients, the following adverse reactions were reported spontaneously and considered to be causally related to timolol maleate:
Timolol Maleate
(n=176)
%Placebo
(n=168)
%BODY AS A WHOLE
fatigue/tiredness
3.4
0.6
headache
1.7
1.8
chest pain
0.6
0
asthenia
0.6
0
CARDIOVASCULAR
bradycardia
9.1
0
arrhythmia
1.1
0.6
syncope
0.6
0
edema
0.6
1.2
DIGESTIVE
dyspepsia
0.6
0.6
nausea
0.6
0
SKIN
pruritus
1.1
0
NERVOUS SYSTEM
dizziness
2.3
1.2
vertigo
0.6
0
paresthesia
0.6
0
PSYCHIATRIC
decreased libido
0.6
0
RESPIRATORY
dyspnea
1.7
0.6
bronchial spasm
0.6
0
rales
0.6
0
SPECIAL SENSES
eye irritation
1.1
0.6
tinnitus
0.6
0
These data are representative of the incidence of adverse effects that may be observed in properly selected patients treated with timolol maleate, i.e., excluding patients with bronchospastic disease, congestive heart failure or other contraindications to beta-blocker therapy.
In patients with migraine the incidence of bradycardia was 5 percent.
In a coronary artery disease population studied in the Norwegian multi-center trial (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY), the frequency of the principal adverse reactions and the frequency with which these resulted in discontinuation of therapy in the timolol and placebo groups were:
Adverse Reaction* Withdrawal† Timolol
(n=945)
%Placebo
(n=939)
%Timolol
(n=945)
%Placebo
(n=939)
%- * When an adverse reaction recurred in a patient, it is listed only once.
- † Only principal reason for withdrawal in each patient is listed. These adverse reactions can also occur in patients treated for hypertension.
Asthenia or Fatigue
5
1
<1
<1
Heart Rate < 40 beats/minute
5
<1
4
<1
Cardiac Failure-Nonfatal
8
7
3
2
Hypotension
3
2
3
1
Pulmonary Edema-Nonfatal
2
<1
<1
<1
Claudication
3
3
1
<1
AV Block 2nd or 3rd Degree
<1
<1
<1
<1
Sinoatrial Block
<1
<1
<1
<1
Cold Hands and Feet
8
<1
<1
0
Nausea or Digestive Disorders
8
6
1
<1
Dizziness
6
4
1
0
Bronchial Obstruction
2
<1
1
<1
The following additional adverse effects have been reported in clinical experience with the drug: Body as a Whole: anaphylaxis, extremity pain, decreased exercise tolerance, weight loss, fever; Cardiovascular: cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, cerebral vascular accident, worsening of angina pectoris, worsening of arterial insufficiency, Raynaud's phenomenon, palpitations, vasodilatation; Digestive: gastrointestinal pain, hepatomegaly, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia; Hematologic: nonthrombocytopenic purpura; Endocrine: hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia; Skin: rash, skin irritation, increased pigmentation, sweating, alopecia; Musculoskeletal: arthralgia; Nervous System: local weakness, increase in signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis; Psychiatric: depression, nightmares, somnolence, insomnia, nervousness, diminished concentration, hallucinations; Respiratory: cough; Special Senses: visual disturbances, diplopia, ptosis, dry eyes; Urogenital: impotence, urination difficulties.
There have been reports of retroperitoneal fibrosis in patients receiving timolol maleate and in patients receiving other beta-adrenergic blocking agents. A causal relationship between this condition and therapy with beta-adrenergic blocking agents has not been established.
Potential Adverse Effects
In addition, a variety of adverse effects not observed in clinical trials with timolol maleate, but reported with other beta-adrenergic blocking agents, should be considered potential adverse effects of timolol. Nervous System: Reversible mental depression progressing to catatonia; an acute reversible syndrome characterized by disorientation for time and place, short-term memory loss, emotional lability, slightly clouded sensorium, and decreased performance on neuropsychometrics; Cardiovascular: Intensification of AV block (see CONTRAINDICATIONS); Digestive: Mesenteric arterial thrombosis, ischemic colitis; Hematologic: Agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenic purpura; Allergic: Erythematous rash, fever combined with aching and sore throat, laryngospasm with respiratory distress; Miscellaneous: Peyronie's disease.
There have been reports of a syndrome comprising psoriasiform skin rash, conjunctivitis sicca, otitis, and sclerosing serositis attributed to the beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent, practolol. This syndrome has not been reported with timolol.
Clinical Laboratory Test Findings
Clinically important changes in standard laboratory parameters were rarely associated with the administration of timolol. Slight increases in blood urea nitrogen, serum potassium, uric acid, and triglycerides, and slight decreases in hemoglobin, hematocrit and HDL cholesterol occurred, but were not progressive or associated with clinical manifestations. Increases in liver function tests have been reported.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage has been reported with timolol maleate tablets. A 30 year old female ingested 650 mg of timolol maleate (maximum recommended daily dose - 60 mg) and experienced second- and third-degree heart block. She recovered without treatment but approximately 2 months later developed irregular heart beat, hypertension, dizziness, tinnitus, faintness, increased pulse rate and borderline first degree heart block.
The oral LD50 of the drug is 1190 and 900 mg/kg in female mice and female rats, respectively.
An in vitro hemodialysis study, using 14C timolol added to human plasma or whole blood, showed that timolol was readily dialyzed from these fluids; however, a study of patients with renal failure showed that timolol did not dialyze readily.
The most common signs and symptoms to be expected with overdosage with a beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent are symptomatic bradycardia, hypotension, bronchospasm, and acute cardiac failure. Therapy with timolol should be discontinued and the patient observed closely. The following additional therapeutic measures should be considered:
- (1) Gastric lavage.
- (2) Symptomatic bradycardia: Use atropine sulfate intravenously in a dosage of 0.25 mg to 2 mg to induce vagal blockade. If bradycardia persists, intravenous isoproterenol hydrochloride should be administered cautiously. In refractory cases the use of a transvenous cardiac pacemaker may be considered.
- (3) Hypotension: Use sympathomimetic pressor drug therapy, such as dopamine, dobutamine or norepinephrine. In refractory cases the use of glucagon hydrochloride has been reported to be useful.
- (4) Bronchospasm: Use isoproterenol hydrochloride. Additional therapy with aminophylline may be considered.
- (5) Acute cardiac failure: Conventional therapy with digitalis, diuretics, and oxygen should be instituted immediately. In refractory cases the use of intravenous aminophylline is suggested. This may be followed if necessary by glucagon hydrochloride which has been reported to be useful.
- (6) Heart block (second- or third-degree): Use isoproterenol hydrochloride or a transvenous cardiac pacemaker.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hypertension
The usual initial dosage of timolol maleate is 10 mg twice a day, whether used alone or added to diuretic therapy. Dosage may be increased or decreased depending on heart rate and blood pressure response. The usual total maintenance dosage is 20 to 40 mg per day. Increases in dosage to a maximum of 60 mg per day divided into two doses may be necessary. There should be an interval of at least 7 days between increases in dosages.
Timolol maleate tablets may be used with a thiazide diuretic or with other antihypertensive agents. Patients should be observed carefully during initiation of such concomitant therapy.
Myocardial Infarction
The recommended dosage for long-term prophylactic use in patients who have survived the acute phase of a myocardial infarction is 10 mg given twice daily (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Migraine
The usual initial dosage of timolol maleate is 10 mg twice a day. During maintenance therapy the 20 mg daily dosage may be administered as a single dose. Total daily dosage may be increased to a maximum of 30 mg, given in divided doses, or decreased to 10 mg once per day, depending on clinical response and tolerability. If a satisfactory response is not obtained after 6 to 8 weeks use of the maximum daily dosage, therapy with timolol should be discontinued.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Timolol Maleate Tablets, USP are available containing 5 mg, 10 mg and 20 mg of timolol maleate, USP.
The 5 mg tablets are green, unscored, flat-faced round tablets debossed with M over 55 on one side of the tablet and blank on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-0055-01
bottles of 100 tabletsNDC 69189-0496-1 single dose pack with 1 tablet as repackaged by Avera McKennan Hospital
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP for Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Keep container tightly closed.
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505REVISED AUGUST 2006
TIM:R15
- Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TIMOLOL MALEATE
timolol maleate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69189-0496(NDC:0378-0055) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TIMOLOL MALEATE (UNII: P8Y54F701R) (TIMOLOL ANHYDROUS - UNII:5JKY92S7BR) TIMOLOL ANHYDROUS 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) Product Characteristics Color GREEN Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code M;55 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69189-0496-1 1 in 1 DOSE PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/27/2016 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA072668 01/27/2016 Labeler - Avera McKennan Hospital (068647668) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Avera McKennan Hospital 068647668 relabel(69189-0496) , repack(69189-0496)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.