RHAPSIDO- remibrutinib tablet
RHAPSIDO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
RHAPSIDO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RHAPSIDO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RHAPSIDO.
RHAPSIDO® (remibrutinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 25 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of Bleeding: Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Interrupt treatment with RHAPSIDO if bleeding is observed or pre- and post-surgery. Concomitant use of antithrombotic agents with RHAPSIDO may further increase risk of bleeding. (5.1)
- Live Attenuated Vaccines: Avoid live or live-attenuated vaccines in patients receiving RHAPSIDO. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3%) were nasopharyngitis, bleeding, headache, nausea and abdominal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use with RHAPSIDO. (7.1)
- Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with RHAPSIDO. (7.1)
- P-gp Substrates: Exposure increases where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions: Monitor more frequently for adverse reactions when used concomitantly with RHAPSIDO. (7.2)
- Antithrombotic Agents: Consider the risks and benefits of concomitant use of antithrombotic agents with RHAPSIDO. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Mild, Moderate, or Severe Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use of RHAPSIDO. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Temporary Interruption of RHAPSIDO for Surgery
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Bleeding
5.2 Live Attenuated Vaccines
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on RHAPSIDO
7.2 Effect of RHAPSIDO on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage is 25 mg taken orally twice daily with or without food.
- Swallow RHAPSIDO tablet whole with water. Do not split, crush, or chew RHAPSIDO.
Missed Dose(s)
If a dose or doses of RHAPSIDO is missed, skip the missed dose, and take the next dose at its regularly scheduled time. Do not take an extra dose(s) of RHAPSIDO to make up for a missed dose(s).
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Bleeding
In placebo-controlled studies in patients with CSU, mucocutaneous-related bleeding occurred in 9% of patients who received RHAPSIDO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Interrupt treatment with RHAPSIDO if bleeding is observed and resume if the benefit is expected to outweigh the risk.
Interrupt treatment with RHAPSIDO for 3 to 7 days pre- and post-surgery or invasive procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Use of antithrombotic agents concomitantly with RHAPSIDO may further increase the risk of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Consider the benefits and risks of antithrombotic agents when used concomitantly with RHAPSIDO. Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse drug reaction (ADR) rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of RHAPSIDO was based on a pooled safety population from two identical clinical trials of 52 weeks duration, REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The pooled safety population consisted of 912 adult patients with CSU who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment and who received RHAPSIDO 25 mg orally twice daily (N=606) or placebo (N=306) for 24 weeks during the double-blind, controlled treatment period of the trial.
Adverse reactions that occurred at an incidence greater than or equal to 3% and more common than the placebo group from the pooled safety population (REMIX-1 and REMIX-2) during the 24-week blinded, placebo-controlled treatment period are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Adverse Reactions with RHAPSIDO with Incidence ≥3% and More Common than Placebo in Adult Patients with CSU (REMIX-1 and REMIX-2) a includes acute sinusitis, chronic sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, pharyngitis streptococcal, rhinitis, rhinitis allergic, and upper respiratory tract infection
b includes conjunctival bleeding, contusion, ecchymosis, epistaxis, gingival bleeding, hematoma, hematuria, hemorrhagic ovarian cyst, intermenstrual bleeding, petechiae, purpura, and urinary occult blood
c includes headache and migraine
d includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal distention, abdominal pain and abdominal pain upperAdverse Reaction RHAPSIDO
(N = 606)
n (%)Placebo
(N = 306)
n (%)Nasopharyngitisa 67 (11%) 27 (9%) Bleedingb 55 (9%) 6 (2%) Headachec 41 (7%) 19 (6%) Nausea 18 (3%) 5 (2%) Abdominal Paind 18 (3%) 6 (2%) Specific Adverse Reactions
Bleeding
In the pooled safety population (REMIX-1 and REMIX-2), bleeding occurred in 9% of patients treated with RHAPSIDO compared to 2% in the placebo group during the 24-week controlled treatment period [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Petechiae (4%) and contusion (2%) were the most commonly reported reactions in patients treated with RHAPSIDO. No severe bleeding reactions occurred. No association between bleeding reactions and low platelet counts was observed. In patients treated with RHAPSIDO, 0.5% experienced bleeding reactions that led to RHAPSIDO discontinuation, while none of these reactions occurred in the placebo group. Similar safety findings were observed through Week 52 [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on RHAPSIDO
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid use of RHAPSIDO with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Remibrutinib is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor increases remibrutinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of RHAPSIDO adverse reactions.
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid use of RHAPSIDO with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
Remibrutinib is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducer decreases remibrutinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may decrease the efficacy of RHAPSIDO.
7.2 Effect of RHAPSIDO on Other Drugs
P-gp Substrates
Monitor more frequently for adverse reactions when using RHAPSIDO with P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions (e.g., digoxin).
Remibrutinib is a P-gp inhibitor. Remibrutinib increases exposure of P-gp substrates, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to P-gp substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Antithrombotic Agents
Consider the risks and benefits of concomitant administration of antithrombotic agents with RHAPSIDO [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
No data are available on concomitant use of RHAPSIDO with anticoagulants. The concomitant use of RHAPSIDO and anticoagulants was not allowed in clinical studies. Use of the antiplatelet agents, acetyl salicylic acid at doses up to 100 mg daily or clopidogrel up to 75 mg daily, was allowed in the RHAPSIDO clinical studies.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to RHAPSIDO during pregnancy. Pregnant women exposed to RHAPSIDO and healthcare providers are encouraged to contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682.
Risk Summary
Available data on the use of RHAPSIDO during pregnancy are insufficient to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of remibrutinib to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at exposures 141-times the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 25 mg twice daily based on area under the curve (AUC) resulted in adverse developmental outcomes including external malformations. No adverse developmental effects were observed with oral administration of remibrutinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis at exposures up to 126-times the human exposure at the MRHD (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development (EFD) study in pregnant rabbits, remibrutinib was administered orally at doses of 100, 300, and 450 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Increased fetal external malformations (e.g. open/opaque eyes, small jaws, hyperflexion of forelimbs) and maternal toxicity (transiently reduced food consumption and adverse clinical signs) occurred at 300 mg/kg/day (141-times the MRHD based on AUC). The fetal findings were considered unlikely to be secondary to the maternal toxicity. The dose of 450 mg/kg/day was not tolerated by the pregnant rabbits.
In an EFD study in pregnant rats, remibrutinib was administered orally at doses of 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. Remibrutinib did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at exposures up to 126 times that at the MRHD based on AUC.
In a pre- and postnatal development (PPND) study, remibrutinib was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 to lactation day (LD) 21. Remibrutinib induced adverse effects at 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 194 times the MRHD based on body surface area [BSA]), affected maternal animals (moribundity and clinical signs of toxicity, slightly longer gestation lengths) and offspring up to LD1 (slightly higher mean number of stillborn, dead, or missing pups, and smaller mean litter size). No adverse effects at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day were noted in the surviving offspring developing into adulthood. No effects were observed at 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 58 times the MRHD based on BSA).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
No data are available regarding the presence of remibrutinib in either human or animal milk, its effects on the breastfed child, or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for RHAPSIDO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from RHAPSIDO or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RHAPSIDO have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients treated with RHAPSIDO in clinical studies for CSU, 53 (8.7%) were 65 to 85 years of age, with no patients over 85 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14)]. There were no observed differences in safety and/or effectiveness in geriatric patients compared to younger adult patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
RHAPSIDO exposure is increased in patients with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, and C) relative to patients with normal hepatic function. Avoid use of RHAPSIDO in patients with mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, and C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
RHAPSIDO (remibrutinib) is a kinase inhibitor.
Its empirical formula (remibrutinib) is C27H27F2N5O3. The chemical name for remibrutinib is N-(3-{6-Amino-5-[2-(N-methylprop-2-enamido)ethoxy]pyrimidin-4-yl}-5-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-2-fluorobenzamide. Its molecular weight is approximately 507.54 g/mol. The chemical structure of remibrutinib is:
Remibrutinib is white to pale yellow powder, and it is practically insoluble in water.
RHAPSIDO is supplied as film-coated tablets for oral administration, with each film-coated tablet containing 25 mg of remibrutinib. The tablet core inactive ingredients are copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablet coating inactive ingredients are polyethylene glycol 4000, polyvinyl alcohol, red iron oxide (E172), talc, titanium dioxide (E171), and yellow iron oxide (E172).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Remibrutinib is an oral, small molecule kinase inhibitor that inhibits Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). BTK is an intracellular protein expressed in mast cells, basophils, B cells, macrophages, and thrombocytes. BTK is involved in intracellular signaling via Fc epsilon receptor-1 (FcεR1), Fc gamma receptors (FcγR), and the B cell antigen receptor (BCR). Remibrutinib also inhibits the BTK-related kinases tec protein tyrosine kinase (TEC) and BMX non-receptor tyrosine kinase (BMX).
Remibrutinib inhibits mast cell and basophil degranulation, including release of histamine and other proinflammatory mediators, mediated by pathogenic IgE or IgG directed against the FcεR1 or IgE.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response
Within the range from 0.2 to 4 times the daily recommended dose, a flat dose-response relationship was observed for the weekly urticaria activity score (UAS7) at Week 4.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At concentrations approximately 9 times the mean steady state peak plasma concentrations provided by the recommended dose, clinically significant QTc prolongation was not observed.
Effects on Blood Pressure
The effect of remibrutinib treatment on blood pressure was assessed in CSU patients using a 24-hour blood pressure measurement by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) at steady state (Week 4) compared to baseline in a multi-center, open-label study (A2305). The study enrolled 144 patients with CSU inadequately controlled by H1 antihistamines, who were administered remibrutinib 25 mg twice daily. Remibrutinib 25 mg twice daily was not associated with clinically significant changes in blood pressure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following administration of remibrutinib 25 mg twice daily, the mean (standard deviation) Cmax is 57 (27) ng/mL and AUClast is 193 (136) ng*h/mL at steady state. Remibrutinib Cmax and AUC increase in a dose-proportional manner between 0.4 to 4 times the recommended dosage. Following administration of multiple doses of 25 mg twice daily, Cmax increases 1.6-fold and AUC0-4 increases 2.7-fold.
No clinically significant differences in remibrutinib pharmacokinetics were observed between healthy subjects and patients with CSU.
Absorption
Remibrutinib median (min, max) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 1 hour (0, 4 hours) at steady state.
Effect of food
No clinically significant differences in remibrutinib pharmacokinetics were observed following administration of a high-fat meal (1000 calories, 50% fat).
Distribution
Remibrutinib blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.813 in vitro. Plasma protein binding is 95.4% and is not concentration-dependent in vitro. The estimated remibrutinib steady state apparent (oral) volume of distribution is 1238 L.
Elimination
Remibrutinib estimated elimination half-life is 1 to 2 hours with an apparent (oral) clearance of 160 L/hr.
Metabolism
Remibrutinib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4.
Excretion
Following IV administration of 14C remibrutinib to healthy subjects, 70% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces (0% as unchanged remibrutinib), and 30% was recovered in urine (2.9% as unchanged remibrutinib).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of remibrutinib were observed based on age (range: 18 to 80 years), sex (63.5% females and 36.5% males), race/ethnicity (59.3% Non-Asian [White, Black, and Others], 8.8% Mainland Chinese, 12.2% Japanese, and 19.7% other Asian), body weight (range: 39 to 162 kg), and mild (eGFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m2, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault), moderate (eGFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73 m2) or severe (eGFR 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of remibrutinib were evaluated in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh Class A), moderate (Child-Pugh Class B), and severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment following administration of 25 mg twice daily. Relative to patients with normal hepatic function, remibrutinib AUC increased 2.33-fold and Cmax increased 1.85-fold in patients with mild hepatic impairment, AUC increased 2.3-fold and Cmax increased 1.65-fold in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, and AUC increased 3.49-fold and Cmax increased 1.99-fold in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Special Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Remibrutinib Cmax increased by 3.3-fold and AUC increased by 4.3-fold following concomitant administration with ritonavir (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) 100 mg twice daily for 4 days [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Remibrutinib Cmax increased by 1.24-fold and AUC increased by 1.3-fold when co-administered with grapefruit juice.
Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Remibrutinib Cmax is predicted to increase by approximately 1.9-fold and AUC is predicted to increase by approximately 2.3-fold following concomitant administration with erythromycin (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) 500 mg four times a day for 7 days [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Remibrutinib Cmax decreased by 74% and AUC decreased by approximately 77% following concomitant administration with carbamazepine (a strong CYP3A4 inducer) 300 mg twice daily for 14 days [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Remibrutinib Cmax is predicted to decrease by approximately 60% and AUC is predicted to decrease by approximately 64% following concomitant administration with efavirenz (a moderate CYP3A4 inducer) 600 mg once daily for 14 days [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
P-gp Substrates: Co-administration of remibrutinib at four times the recommended dosage with a single dose of 0.25 mg digoxin (a P-gp substrate) increased digoxin Cmax by 2.1-fold and AUC by 1.4-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
BCRP Substrates: Co-administration of remibrutinib at four times the recommended dosage with a single dose of 10 mg rosuvastatin (a BCRP and OATP1B substrate) increased rosuvastatin Cmax by 1.6-fold and AUC by 1.7-fold.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of the following drugs were observed when used concomitantly with remibrutinib: oral midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate), oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel (CYP3A4 substrate), tolbutamide (CYP2C9 substrate), caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate), and coproporphyrin I (an endogenous OATP1B substrate).
In Vitro Studies
CYP450 Enzymes: Remibrutinib is a CYP3A4 substrate. Remibrutinib inhibits CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4/5. Remibrutinib induces CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9 and CYP3A4/5.
Transporter Systems: In vitro, remibrutinib is a P-gp substrate. Remibrutinib inhibits P-gp, BCRP, BSEP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1, OCT2 and MATE1.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Remibrutinib did not show evidence of carcinogenic potential in a 6-month rasH2 mouse study at oral doses up to 1500 mg/kg/day and a 2-year rat carcinogenicity study at oral doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times and 98 times than MRHD of 25 mg twice daily based on AUC for males and females, respectively).
Remibrutinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in an in vitro micronucleus assay in human peripheral lymphocytes or in an in vivo blood reticulocyte micronucleus assay in rats.
In a fertility study in rats, remibrutinib did not impact fertility in female or male rats up to the maximum achievable exposures of 79 and 15 times higher than MRHD of 25 mg twice daily based on AUC.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of RHAPSIDO for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) in adult patients who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment was evaluated in two identical, 52-week, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (REMIX-1 [NCT05030311] and REMIX-2 [NCT05032157]).
REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 enrolled a total of 925 adult patients, diagnosed with CSU inadequately controlled despite treatment with H1 antihistamines, as defined by the presence of itch and hives for ≥6 consecutive weeks. All patients were required to have a weekly urticaria activity score (UAS7) ≥16 (range 0-42), a weekly itch severity score (ISS7) ≥6 (range 0-21) and a weekly hives severity score (HSS7) ≥6 (range 0-21) for 7 days prior to randomization. Patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive either RHAPSIDO 25 mg or placebo, respectively, orally twice daily for 24 weeks during the double-blind treatment period and subsequently continued in a 28-week open-label treatment period, during which all patients received RHAPSIDO 25 mg twice daily. While REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 clinical trials included an open-label period, efficacy is based on results from 912 patients treated during the controlled period of 24 weeks.
Demographics and baseline characteristics in REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 are provided in Table 2.
Table 2 Baseline Demographic and Disease Characteristics of Adult Patients with CSU in REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 CSU: chronic spontaneous urticaria, UAS7: weekly urticaria activity score, HSS7: weekly hive severity score, ISS7 score: weekly itch severity score REMIX-1
(N=462)REMIX-2
(N=450)Age 18-65 years, n (%) 419 (91) 416 (92) >65 years, n (%) 43 (9) 34 (8) Mean age, years 45 42 Sex, n (%) Female 313 (68) 294 (65) Race, n (%) White or Caucasian 270 (58) 234 (52) Black or African American 15 (3) 10 (2) Asian 139 (30) 201 (45) Ethnicity, n (%) Hispanic/Latino 116 (25) 21 (5) Disease characteristics UAS7 ≥28, n (%) 298 (65) 269 (60) Mean HSS7 score 16 16 Mean ISS7 score 15 14 Previous experience of Angioedema, n (%) 240 (52) 208 (46) Previous exposure to anti-IgE biologics, n (%) 147 (32) 138 (31) The reported mean duration of CSU at enrollment across treatment groups was 6.6 and 5.2 years in REMIX-1 and REMIX-2, respectively, with 39% and 29% of the patients having a duration of CSU > 5 years.
The co-primary endpoints were absolute change from baseline in ISS7 and HSS7 at Week 12. The ISS7 (range 0 to 21) was defined as the sum of the daily itch severity scores (range 0 to 3) recorded over a 7-day period. The HSS7 (range 0 to 21) was defined as the sum of the daily hive severity scores (range 0 to 3) recorded over a 7-day period. The key secondary endpoint was absolute change from baseline in UAS7 at Week 12. The UAS7 (range 0 to 42) was a composite of the ISS7 and HSS7.
Secondary endpoints included proportion of patients who achieved UAS7 ≤6 at Weeks 2 and 12, and the proportion of patients who achieved complete absence of itch and hives (UAS7 = 0) at Week 12. In both REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 studies, the co-primary and all secondary endpoints showed statistically significant improvement in itch and hives symptoms in patients treated with RHAPSIDO compared to patients treated with placebo. Results are presented in Table 3.
Table 3 Efficacy Results of Adult Patients with CSU in REMIX-1 and REMIX-2 at Week 12a LS Mean: Least squares mean, SE: standard error, CFB: change from baseline, CI: confidence interval
a Multiple imputation techniques were implemented for missing data.REMIX-1 REMIX-2 RHAPSIDO
(N = 309)Placebo
(N = 153)RHAPSIDO
(N = 297)Placebo
(N = 153)Change from Baseline in ISS7 at Week 12 LS mean (SE) CFB -9.52 (0.34) -6.89 (0.47) -8.95 (0.34) -5.72 (0.45) Difference in LS mean (SE) vs placebo -2.63 (0.54) -3.23 (0.55) 95% CI for difference -3.70, -1.56 -4.29, -2.16 Change from Baseline in HSS7 at Week 12 LS mean (SE) CFB -10.47 (0.40) -6.86 (0.55) -10.47 (0.39) -6.00 (0.53) Difference in LS mean (SE) vs placebo -3.61 (0.64) -4.47 (0.64) 95% CI for difference -4.85, -2.36 -5.71, -3.23 Change from Baseline in UAS7 at Week 12 LS mean (SE) CFB -20.02 (0.72) -13.79 (0.98) -19.41 (0.70) -11.73 (0.95) Difference in LS mean (SE) vs placebo -6.22 (1.14) -7.68 (1.14) 95% CI for difference -8.45, -4.00 -9.91, -5.46 Proportion of Patients with UAS7 ≤6 at Week 2 n (%) 104 (33.7) 5 (3.3) 89 (30.0) 9 (5.9) Treatment difference 30.20 24.55 (95% CI) 24.30, 36.10 18.31, 30.80 Proportion of Patients with UAS7 ≤6 at Week 12 n (%) 154 (49.8) 38 (24.8) 139 (46.8) 30 (19.6) Treatment difference 25.44 27.61 (95% CI) 16.48, 34.39 19.14, 36.08 Proportion of Patients with UAS7 = 0 at Week 12 n (%) 96 (31.1) 16 (10.5) 83 (27.9) 10 (6.5) Treatment difference 20.55 21.60 (95% CI) 13.35, 27.75 15.10, 28.10 Figure 1 shows the effect of RHAPSIDO over time up to Week 24 in REMIX-2 patients treated with RHAPSIDO. The results were similar in REMIX-1.
Figure 1 Mean Change from Baseline in Weekly Itch Severity Score (ISS7) and Hive Severity Score (HSS7) up to Week 24 in REMIX-2 (Observed Data)
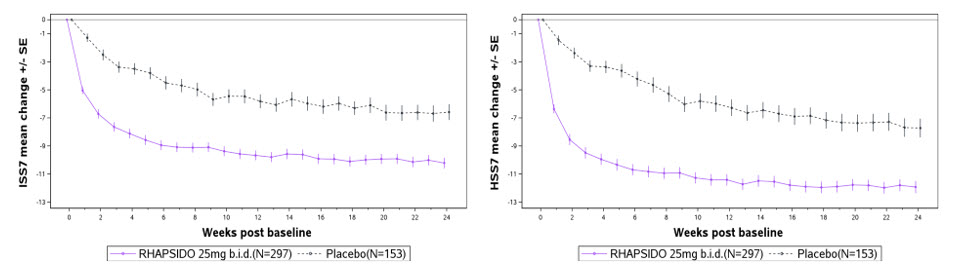
Improvements in ISS7 and HSS7 at Week 12 were consistent regardless of patients’ baseline total IgE level.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
RHAPSIDO tablets are supplied as described in Table 4:
Table 4 RHAPSIDO Tablets and Package Configuration Strength Tablet Description Package Configuration NDC 25 mg light yellow, round, curved, unscored, film-coated tablet, debossed with “LV” on one side and Novartis logo on the other side. Tablet diameter is 7 mm. 40 mL HDPE bottle containing 60 tablets with 2 gm silica gel and a child-resistant closure 0078-1483-20 Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense and store in the original container in order to protect from moisture.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Administration Instructions:
Inform patients to take RHAPSIDO with or without food. Advise patients not to split, crush, or chew the tablet and to swallow the tablet whole with water [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Risk of Bleeding:
Inform patients that bleeding can occur with the use of RHAPSIDO, and to report any signs and symptoms to their healthcare practitioner. Inform patients that RHAPSIDO should be interrupted for 3 to 7 days for any surgical procedures. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare practitioner if they use RHAPSIDO with antithrombotic agents due to the potential increased risk of bleeding [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Live Attenuated Vaccines:
Instruct patients to inform the healthcare practitioner that they are taking RHAPSIDO prior to any potential vaccinations. Advise patients that the vaccines containing live virus (live and live-attenuated) should not be given during treatment with RHAPSIDO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pregnancy:
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to RHAPSIDO during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
One Health Plaza
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936© Novartis
T2025-55
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 9/2025 Patient Information
RHAPSIDO® (RAP-si-doe)
(remibrutinib)
tablets, for oral useWhat is RHAPSIDO?
RHAPSIDO is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who continue to have symptoms that are not controlled with antihistamine treatment.
RHAPSIDO should not be used to treat any other forms of hives (urticaria).
It is not known if RHAPSIDO is safe and effective in children.Before taking RHAPSIDO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have had a recent surgery or plan to have surgery. Your healthcare provider may tell you to stop taking RHAPSIDO for at least 3 to 7 days before and after any planned medical or surgical procedures.
- have bleeding problems or are taking a blood thinner medicine.
- have liver problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if RHAPSIDO will harm your unborn baby.
Pregnancy Exposure Registry: If you become pregnant during treatment with RHAPSIDO, talk to your healthcare provider about registering in the pregnancy exposure registry for RHAPSIDO. You or your healthcare provider can enroll in this registry by calling 1-888-669-6682. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of RHAPSIDO during pregnancy. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if RHAPSIDO passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide the best way to feed your baby while taking RHAPSIDO.
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive an immunization (vaccine). Talk to your healthcare provider about receiving any immunizations before taking RHAPSIDO. You should not receive live or live-attenuated vaccines during treatment with RHAPSIDO.
How should I take RHAPSIDO? - Take RHAPSIDO exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking RHAPSIDO unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Take 1 RHAPSIDO tablet 2 times a day.
- RHAPSIDO can be taken with or without food.
- Swallow RHAPSIDO tablet whole with water. Do not split, crush, or chew the tablets.
- If you miss a dose of RHAPSIDO, skip the missed dose, and take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take an extra dose of RHAPSIDO to make up for a missed dose.
- If you take too much RHAPSIDO, call your healthcare provider or Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are possible side effects of RHAPSIDO?
RHAPSIDO may cause serious side effects, including:
Risk of bleeding. Bleeding may happen while being treated with RHAPSIDO. Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of bleeding and may stop your treatment if bleeding happens. Your risk of bleeding may increase if you are also taking a blood thinner medicine. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any signs or symptoms of bleeding, such as:- bruising, or red or purple skin marks
- pink or brown urine
- headache, dizziness, confusion, or feeling weak
- red or black stools that look like tar
These are not all the possible side effects of RHAPSIDO.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store RHAPSIDO? - Store RHAPSIDO at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store RHAPSIDO in the original container to protect from moisture.
General information about the safe and effective use of RHAPSIDO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use RHAPSIDO for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give RHAPSIDO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about RHAPSIDO that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in RHAPSIDO? - Active Ingredient: remibrutinib
- Inactive Ingredients: copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablet coating is composed of polyethylene glycol 4000, polyvinyl alcohol, red iron oxide (E172), talc, titanium dioxide (E171), and yellow iron oxide (E172).
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, One Health Plaza, East Hanover, NJ 07936
For more information, go to www.RHAPSIDO.com or call 1-888-669-6682.© Novartis
T2025-56
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 0078-1483-20
Rhapsido®
(remibrutinib) tablets
25 mg per tablet
Swallow tablets whole with water.
Do not split, crush, or chew tablets.
Rx only
60 tablets
NOVARTIS

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
RHAPSIDO
remibrutinib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0078-1483 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength REMIBRUTINIB (UNII: I7MVZ8HDNU) (REMIBRUTINIB - UNII:I7MVZ8HDNU) REMIBRUTINIB 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength COPOVIDONE K25-31 (UNII: D9C330MD8B) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) SODIUM STEARYL FUMARATE (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 4000 (UNII: 4R4HFI6D95) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW (light yellow) Score no score Shape ROUND (curved) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code LV;IMPRINT Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0078-1483-20 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/30/2025 2 NDC: 0078-1483-92 2 in 1 CARTON 09/30/2025 2 NDC: 0078-1483-93 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218436 09/30/2025 Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023)
Trademark Results [RHAPSIDO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 RHAPSIDO 98828714 not registered Live/Pending |
Novartis AG 2024-10-30 |
 RHAPSIDO 86650479 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Novartis AG 2015-06-03 |
 RHAPSIDO 85533214 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Novartis AG 2012-02-03 |
 RHAPSIDO 79247188 not registered Live/Pending |
Novartis AG 2018-09-26 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.