ELCYS- cysteine hydrochloride injection, solution
ELCYS by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ELCYS by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ELCYS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ELCYS.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1971INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ELCYS is a sulfur-containing amino acid indicated to meet the nutritional requirements of newborn infants requiring total parenteral nutrition (TPN); and of adult and pediatric patients with severe liver disease who may have impaired enzymatic processes and require TPN. It can also be added to amino acid solutions to provide a more complete profile of amino acids for protein synthesis. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) cysteine hydrochloride, USP in a 10 mL single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates: If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. (5.1)
- Vein Damage and Thrombosis: Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or more must be infused through a central catheter. (2.1, 5.2)
- Increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN): Monitor laboratory parameters and discontinue if exceeds normal postprandial limits and continues to increase. (5.3)
- Acid-Base Imbalance: Monitor laboratory parameters and supplement with electrolytes as needed. (5.4)
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Monitor liver function parameters and ammonia levels. (5.5)
- Hyperammonemia: Neurocognitive delay possible in infants; monitor blood ammonia levels. (5.6, 8.4)
- Aluminium Toxicity: Increased risk in patients with renal impairment, including preterm infants. (5.7, 8.4)
- Monitoring and Laboratory Tests: Monitor fluid and electrolytes, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, kidney and liver function, blood count and coagulation parameters throughout treatment. (5.8)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are local reactions (warm sensation, erythema, phlebitis and thrombosis at the infusion site), generalized flushing, fever and nausea (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Container
2.4 Dosing Considerations
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients and Adults
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
5.2 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
5.3 Increased Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
5.4 Acid-Base Imbalance
5.5 Hepatobiliary Disorders
5.6 Hyperammonemia
5.7 Aluminum Toxicity
5.8 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ELCYS is indicated for use as an additive to amino acid solutions to meet the nutritional requirements of newborn infants
requiring total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and of adult and pediatric patients with severe liver disease who may have
impaired enzymatic processes and require TPN. It can also be added to amino acid solutions to provide a more complete
profile of amino acids for protein synthesis.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
ELCYS is for admixing use only. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, ELCYS must be diluted
and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition (PN) solutions.
The resulting solution is for intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein. The choice of a central or peripheral
venous route should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or greater
must be infused through a central catheter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
- ELCYS is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, ELCYS must be diluted and used as anadmixture in PN solutions.
- ELCYS is to be prepared only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area). The key factor in the preparation is careful aseptic technique to avoid inadvertent touch contamination during mixing of solutions and addition of other nutrients.
- ELCYS is for addition to amino acid solutions prior to further admixing with dextrose injection using a PN container.
- Use a dedicated line for PN solutions.
- Intravenous lipid emulsions can be infused concurrently into the same vein as ELCYS containing amino acid and dextrose solutions by a Y-connector located near the infusion site; flow rates of each solution should be controlled separately by infusion pumps.
- For administration without lipid emulsion, use a 0.22 micron in-line filter.
- To prevent air embolism, use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set, avoid multiple connections, do not connect flexible containers in series, fully evacuate residual gas in the container prior to administration, do not pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off pump before the container runs dry.
- If infused with lipid emulsion, do not use administration sets and lines that contain di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP). Administration sets that contain polyvinyl chloride (PVC) components have DEHP as a plasticizer.
- Visually inspect the diluted PN solution containing ELCYS for particulate matter before admixing, after admixing, and prior to administration. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. A slight yellow color does not alter the quality and efficacy of this product.
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition (PN) Container
- Remove ELCYS vial from the carton and inspect for particulate matter.
- Transfer the required amount of ELCYS to an amino acid solution using strict aseptic techniques to avoid microbial contamination.
- The amino acid solution containing ELCYS can then be used to prepare admixtures in the PN container using strict aseptic techniques.
- Amino acids solution containing ELCYS may be mixed with dextrose injection. The following proper mixing sequence must be followed to minimize pH related problems:
- Transfer dextrose injection to the parental nutrition pooling container
- Transfer phosphate salt
- Transfer ELCYS-containing amino acid solution
- Transfer electrolytes
- Transfer trace elements
- Use gentle agitation during admixing to minimize localized concentration effects; shake containers gently after each addition.
- For automated compounding, refer to Instructions for Use of the applicable compounder.
- Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the PN container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives to the PN container, use aseptic technique.
- Inspect the final PN solution containing ELCYS to ensure that precipitates have not formed during mixing or addition on additives. Discard if any precipitates are observed.
Stability and Storage
- For single use only. Discard used container of ELCYS.
- Use of ELCYS for admixing should be limited to up to 4 hours at room temperature (25ºC/77ºF) after the container closure has been penetrated. Discard any remaining drug.
- Use PN solution containing ELCYS promptly after mixing. Any storage of the admixture should be under refrigeration and limited to a brief period of time, no longer than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Discard any remaining admixture.
- Protect PN solution from light.
2.4 Dosing Considerations
- The dosage of the final PN solution containing ELCYS must be based on the concentrations of all components in the solution and the recommended nutritional requirements [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Consult the prescribing information of all added components to determine the recommended nutritional requirements for dextrose and lipid emulsion, as applicable.
- The dosage of ELCYS should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition (ability to adequately metabolize amino acids), body weight and nutritional/fluid requirements, as well as additional energy given orally/enterally to the patient. Prior to initiating parenteral nutrition, the following patient information should be reviewed: review of all medications, gastrointestinal function and laboratory data (such as electrolytes (including magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus), glucose, urea/creatinine, liver panel, complete blood count and triglyceride level (if adding lipid emulsion).
- Prior to administration of PN solution containing ELCYS, correct severe fluid, electrolyte and acid-base disorders.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients and Adults
The recommended dosage and volume of ELCYS is shown in Table 1 and is based upon the recommended daily protein
(amino acids) requirement. For pediatric patients from birth to less than 12 years of age, the recommended dosage of
ELCYS is 22 mg/gram of amino acids. For adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, the recommended
dosage of ELCYS is 7 mg/gram of amino acids.
Table 1. Recommended Daily Dosage of ELCYS in Pediatric Patients and Adults
- Age
- Recommended Proteina Requirement
- (g AA/kg/day)1
- Recommended Dosage
- (mg ELCYS/g AA)
- Recommended Volume
- (mL ELCYS/g AA)
Preterm and term infants less than 1 month of age
- 3 to 4
- 22
- 0.44
Pediatric patients 1 month to less than 1 year of age
- 2 to 3
- 22
- 0.44
Pediatric patients 1 year to 11 years of age
- 1 to 2
- 22
- 0.44
Pediatric patients 12 years to 17 years of age
- 0.8 to 1.5
- 7
- 0.14
Adults: Stable Patients
- 0.8 to 1
- 7
- 0.14
Adults: Critically Ill Patientsb
- 1.5 to 2
- 7
- 0.14
AA = Amino Acid
a Protein is provided as amino acids (AA).
b Includes patients requiring more than 2 to 3 days in the intensive care unit with organ failure, sepsis or postoperative major surgery. Do not use in patients with
conditions that are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]
ELCYS contains 50 mg/mL of cysteine hydrochloride (equivalent to 34.5 mg/mL of cysteine). Therefore, the ELCYS
dosages in Table 1 provide:
- 15 mg cysteine/gram of amino acids for pediatric patients less than 12 years of age
- 5 mg cysteine/gram of amino acids for adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in
patients receiving PN. In some fatal cases, pulmonary embolism occurred as a result of calcium phosphate precipitates.
Precipitation following passage through an in-line filter and suspected in vivo precipitate formation has also been
reported. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the PN infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. In addition to
inspection of the solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2)], the infusion set and catheter should also
periodically be checked for precipitates.
5.2 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
ELCYS must be diluted and used as an admixture in PN solutions. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Solutions with
an osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter [see Dosage and Administration
(2.1)]. The infusion of hypertonic nutrient injections into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage,
and/or thrombosis. The primary complication of peripheral access is venous thrombophlebitis, which manifests as pain,
erythema, tenderness or a palpable cord. Remove the catheter as soon as possible, if thrombophlebitis develops.
5.3 Increased Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Intravenous infusion of amino acids may induce a rise in blood urea nitrogen (BUN), especially in patients with impaired
hepatic or renal function. Appropriate laboratory tests should be performed periodically and infusion discontinued if BUN
levels exceed normal postprandial limits and continue to rise. It should be noted that a modest rise in BUN normally
occurs as a result of increased protein intake.
Administration of amino acid solutions in the presence of impaired renal function may augment an increasing BUN, as
does any protein dietary component.
5.4 Acid-Base Imbalance
Administration of ELCYS may result in metabolic acidosis in preterm infants.
Administration of amino acid solutions to a patient with hepatic impairment may result in serum amino acid imbalances,
metabolic alkalosis, prerenal azotemia, hyperammonemia, stupor and coma.
Frequent clinical evaluation and laboratory determinations are necessary for proper monitoring of acid-base balance
during parenteral nutrition therapy. Significant deviations from normal concentrations may require the use of additional
electrolyte supplements.
5.5 Hepatobiliary Disorders
Hepatobiliary disorders are known to develop in some patients without preexisting liver disease who receive PN,
including cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholestasis, hepatic steatosis, fibrosis and cirrhosis, possibly leading to hepatic
failure. The etiology of these disorders is thought to be multifactorial and may differ between patients.
Monitor liver function parameters and ammonia levels. Patients developing signs of hepatobiliary disorders should be
assessed early by a clinician knowledgeable in liver diseases in order to identify possible causative and contributory
factors, and possible therapeutic and prophylactic interventions.
5.6 Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia is of special significance in infants, as it can result in neurocognitive delays. Therefore, it is essential
that blood ammonia levels be measured frequently in infants.
Instances of asymptomatic hyperammonemia have been reported in patients without overt liver dysfunction. The
mechanisms of this reaction are not clearly defined but may involve genetic defects and immature or subclinically
impaired liver function [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.7 Aluminum Toxicity
ELCYS contains aluminum that may be toxic.
Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration in patients with renal impairment. Preterm
infants are particularly at risk for aluminum toxicity because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts
of calcium and phosphate solutions, which also contain aluminum.
Patients with renal impairment, including preterm infants, who receive greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day of parenteral
aluminum can accumulate aluminum to levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading
may occur at even lower rates of administration.
Exposure to aluminum from ELCYS is not more than 0.21 mcg/kg/day when preterm and term infants less than 1 month
of age are administered the recommended maximum dosage of ELCYS (15 mg cysteine/g of amino acids and 4 g of
amino acids/kg/day) [see Table 1, Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. When prescribing ELCYS for use in PN containing
other small volume parenteral products, the total daily patient exposure to aluminum from the admixture should be
considered and maintained at no more than 5 mcg/kg/day [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.8 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
Monitor fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count and
coagulation parameters throughout treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased BUN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Acid-base imbalance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hyperammonemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Adverse reactions with the use of cysteine hydrochloride injection were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Local infusion site reactions, including a warm sensation, erythema, phlebitis and thrombosis at the infusion site
- Generalized flushing, fever and nausea
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Appropriate administration of ELCYS is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or
fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with cysteine hydrochloride.
The estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All
pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the
estimated background risk of major birth defect and miscarriage in the clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15
to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data available on the effects of cysteine hydrochloride on infants, either directly or through breastmilk, do not suggest a
significant risk of adverse events from exposure. Although there are no data on the presence of cysteine hydrochloride in
human or animal milk or the effects on milk production, appropriate administration of ELCYS is not expected to cause
harm to a breastfed infant. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the
mother’s clinical need for ELCYS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ELCYS or from the
underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
ELCYS is approved for use in pediatric patients, from birth to 17 years of age, for use as an additive to amino acid
solutions to meet the nutritional requirements of newborn infants, including preterm infants, requiring total parenteral
nutrition (TPN) and pediatric patients with severe liver disease who may have impaired enzymatic processes and require
TPN. The safety profile for ELCYS use in pediatric patients includes risks of acid-base imbalance and hyperammonemia.
Acid-base imbalance, including metabolic acidosis, may occur with ELCYS administration in preterm infants. Frequent
clinical and laboratory assessments are necessary to monitor and manage fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and
acid-base balance during parenteral nutrition therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hyperammonemia is of special significance in infants (birth to two years of age). This reaction appears to be related to a
deficiency of the urea cycle amino acids of genetic or product origin. It is essential that blood ammonia be measured
frequently in infants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged PN treatment with ELCYS may be at higher risk
of aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies with ELCYS have not been performed to determine whether patients aged 65 and over respond differently
from younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Monitor patients with impaired renal function receiving PN solutions containing the recommended dosage of ELCYS with
frequent clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to assess renal function, including serum electrolytes and fluid balance
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Monitor patients with impaired liver function receiving PN solutions containing the recommended dosage of ELCYS with
frequent clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to assess liver function, such as bilirubin and liver function parameters
[see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ELCYS (cysteine hydrochloride injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous use. Each 10 mL of ELCYS
contains 500 mg of cysteine hydrochloride, USP (equivalent to 345 mg of cysteine) in water for injection. Sodium
hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid are used as needed to adjust the pH. The pH range is 1.0 to 2.5.
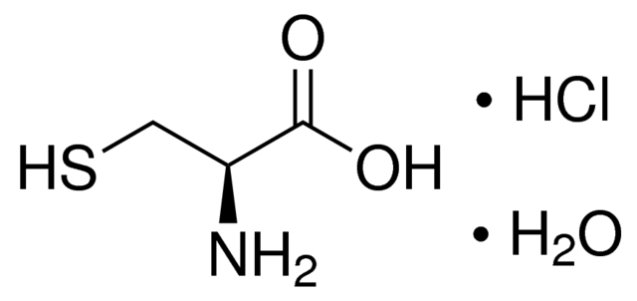
The active ingredient is cysteine hydrochloride. Cysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid. The chemical name of
cysteine hydrochloride is L-cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate and is chemically designated as C3H7NO2S HCI H2O
having a molecular weight of 175.63. Cysteine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder soluble in water. Cysteine
aqueous solution is prone to oxidation when exposed to air, and when mixed with amino acids solutions, cysteine may
convert to insoluble cystine which leads to precipitation over time. It has the following structural formula:
ELCYS contains no more than 120 mcg/L of aluminum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous cysteine is synthesized from methionine by the enzyme, cystathionase, via the trans-sulfuration pathway, and
serves as a precursor substrate for both glutathione and taurine. ELCYS provides cysteine to the systemic circulation of
patients who require PN and cannot synthesize adequate quantities of cysteine due to insufficient or deficient
cystathionase activity.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ELCYS is supplied as follows:
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) of cysteine hydrochloride, USP is a clear, colorless, sterile and nonpyrogenic solution in 10
mL single-dose vials (51754-1007-1), packaged as 10 per carton (NDC: 51754-1007-3)
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Avoid excessive heat. Protect from
freezing. If accidentally frozen, discard the vial.
For storage of admixed solution see Dosage and Administration (2.3).
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients, caregivers, or home healthcare providers of the following risks of ELCYS:
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Increased BUN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Acid base imbalance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hyperammonemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Monitoring and laboratory tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
Manufactured and Distributed by:
Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC
Lenoir, NC 28645
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-Vial Label
Rx Only NDC: 51754-1007-1
ELCYS
(Cysteine Hydrochloride
Injection), USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must Be Diluted
For Intravenous Use Only After Dilution
10 mL Single Dose Sterile Vial-
Discard Unused Portion
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL-Carton Label
NDC: 51754-1007-3 Rx Only
ELCYS
(Cysteine Hydrochloride Injection), USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must Be Diluted. For Intravenous Use Only.
10 x 10 mL Single Dose SterileVials-
Discard Unused Portion
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ELCYS
cysteine hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51754-1007 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CYSTEINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: ZT934N0X4W) (CYSTEINE - UNII:K848JZ4886) CYSTEINE 10 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51754-1007-1 10 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/28/2019 2 NDC: 51754-1007-3 100 mL in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/28/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA210660 05/28/2019 Labeler - Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC (831274399) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Exela Pharma Sciences, LLC 831274399 MANUFACTURE(51754-1007) , PACK(51754-1007) , LABEL(51754-1007)
Trademark Results [ELCYS]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ELCYS 88350906 5899186 Live/Registered |
Exela Holdings, Inc. 2019-03-21 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.