CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE AND CLIDINIUM BROMIDE capsule
Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride and Clidinium Bromide by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride and Clidinium Bromide by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cameron Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Bausch Health Companies Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
- Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
- Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required.
- Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
-
DESCRIPTION
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide combines in a single capsule formulation the antianxiety action of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and the anticholinergic/spasmolytic effects of clidinium bromide.
Each Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide capsule contains the active ingredients 5 mg chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and 2.5 mg clidinium bromide. Each capsule also contains the inactive ingredients corn starch, lactose monohydrate, talc, methylparaben, propylparaben, potassium sorbate, D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Green No. 3, titanium dioxide, and gelatin.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is a versatile, therapeutic agent of proven value for the relief of anxiety and tension. It is indicated when anxiety, tension or apprehension are significant components of the clinical profile. It is among the safer of the effective psychopharmacologic compounds.
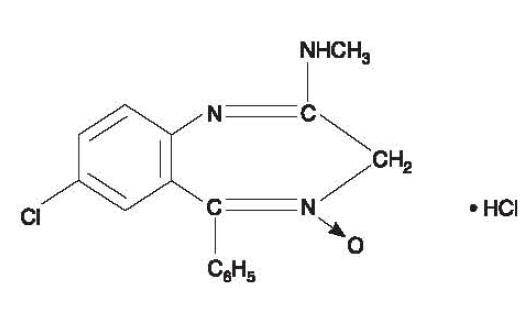
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is 7-chloro-2-methylamino-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide hydrochloride. A colorless, crystalline substance, it is soluble in water. It is unstable in solution and the powder must be protected from light. The molecular weight is 336.22. The structural formula of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is as follows:
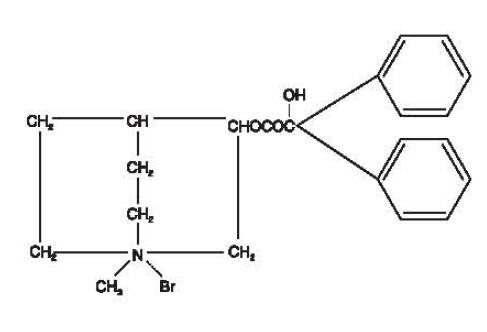
Clidinium bromide is a synthetic anticholinergic agent which has been shown in experimental and clinical studies to have a pronounced antispasmodic and antisecretory effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Structurally clidinium bromide is:
-
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride has been studied extensively in many species of animals and these studies are suggestive of action on the limbic system of the brain, which recent evidence indicates is involved in emotional responses. Hostile monkeys were made tame by oral drug doses, which did not cause sedation. Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride revealed a "taming-action with the elimination of fear and aggression". The taming effect of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride was further demonstrated in rats made vicious by lesions in the septal area of the brain. The drug dosage which effectively blocked the vicious reaction was well below the dose which caused sedation in these animals.
The oral LD50 of single doses of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, calculated according to the method of Miller and Tainter, is 720 ± 51 mg/kg as determined in mice observed over a period of 5 days following dosage.
Clidinium bromide is an effective anticholinergic agent with activity approximating that of atropine sulfate against acetylcholine-induced spasms in isolated intestinal strips. On oral administration in mice, it proved an effective antisialagogue in preventing pilocarpine-induced salivation. Spontaneous intestinal motility in both rats and dogs is reduced following oral dosing with 0.1 to 0.25 mg/kg. Potent cholinergic ganglionic blocking effects (vagal) were produced with intravenous usage in anesthetized dogs.
Oral doses of 2.5 mg/kg to dogs produced signs of nasal dryness and slight pupillary dilation. In two other species, monkeys and rabbits, doses of 5 mg/kg, po, given three times daily for 5 days did not produce apparent secretory or visual changes.
The oral LD50 of single doses of clidinium bromide is 860 ± 57 mg/kg as determined in mice observed over a period of 5 days following dosage; the calculations were made according to the method of Miller and Tainter.
Effects on Reproduction
Reproduction studies in rats fed chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, 10, 20 and 80 mg/kg daily, and bred through one or two matings showed no congenital anomalies, nor were there adverse effects on lactation of the dams or growth of the newborn. However, in another study at 100 mg/kg daily there was noted a significant decrease in the fertilization rate and a marked decrease in the viability and body weight of offspring which may be attributable to sedative activity, thus resulting in lack of interest in mating and lessened maternal nursing and care of the young. One neonate in each of the first and second matings in the rat reproduction study at the 100 mg/kg dose exhibited major skeletal defects. Further studies are in progress to determine the significance of these findings.
Two series of reproduction experiments with clidinium bromide were carried out in rats, employing dosages of 2.5 and 10 mg/kg daily in each experiment. In the first experiment, clidinium bromide was administered for a 9-week interval prior to mating; no untoward effect on fertilization or gestation was noted. The offspring were taken by caesarean section and did not show a significant incidence of congenital anomalies when compared to control animals. In the second experiment, adult animals were given clidinium bromide for 10 days prior to and through two mating cycles. No significant effects were observed on fertility, gestation, viability of offspring or lactation, as compared to control animals, nor was there a significant incidence of congenital anomalies in the offspring derived from these experiments.
A reproduction study of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide was carried out in rats through two successive matings. Oral daily doses were administered in two concentrations: 2.5 mg/kg chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride with 1.25 mg/kg clidinium bromide or 25 mg/kg chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride with 12.5 mg/kg clidinium bromide. In the first mating, no significant differences were noted between the control or the treated groups, with the exception of a slight decrease in the number of animals surviving during lactation among those receiving the highest dosage. As with all anticholinergic drugs, an inhibiting effect on lactation may occur. In the second mating, similar results were obtained except for a slight decrease in the number of pregnant females and in the percentage of offspring surviving until weaning. No congenital anomalies were observed in both matings in either the control or treated groups. Additional animal reproduction studies are in progress.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is indicated to control emotional and somatic factors in gastrointestinal disorders. Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may also be used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer and in the treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome (irritable colon, spastic colon, mucous colitis) and acute enterocolitis.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is contraindicated in the presence of glaucoma (since the anticholinergic component may produce some degree of mydriasis) and in patients with prostatic hypertrophy and benign bladder neck obstruction. It is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and/or clidinium bromide.
-
WARNINGS
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. If a decision is made to prescribe Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide concomitantly with opioids, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use, and follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is used with opioids (see PRECAUTIONS).
As in the case of other preparations containing CNS-acting drugs, patients receiving Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide should be cautioned about possible combined effects with opioids, alcohol and other CNS depressants. For the same reason, they should be cautioned against hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle.
Usage in Pregnancy
An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of minor tranquilizers (chlordiazepoxide, diazepam and meprobamate) during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies. Because use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, their use during this period should almost always be avoided. The possibility that a woman of childbearing potential may be pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant during therapy or intend to become pregnant they should communicate with their physicians about the desirability of discontinuing the drug.
As with all anticholinergic drugs, an inhibiting effect on lactation may occur (see ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY).
-
OVERDOSAGE
Manifestations of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride overdosage include somnolence, confusion, coma and diminished reflexes. Respiration, pulse and blood pressure should be monitored, as in all cases of drug overdosage, although, in general, these effects have been minimal following chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride overdosage.
While the signs and symptoms of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide overdosage may be produced by either of its components, usually such symptoms will be overshadowed by the anticholinergic actions of clidinium bromide. The symptoms of overdosage of clidinium bromide are excessive dryness of mouth, blurring of vision, urinary hesitancy and constipation.
General supportive measures should be employed, along with immediate gastric lavage. Administer physostigmine 0.5 to 2 mg at a rate of no more than 1 mg per minute. This may be repeated in 1 to 4 mg doses if arrhythmias, convulsions or deep coma recur. Intravenous fluids should be administered and an adequate airway maintained. Hypotension may be combated by the use of levarterenol or metaraminol. Methylphenidate or caffeine and sodium benzoate may be given to combat CNS-depressive effects. Dialysis is of limited value. Should excitation occur, barbiturates should not be used. As with the management of intentional overdosage with any drug, it should be borne in mind that multiple agents may have been ingested.
Withdrawal symptoms of the barbiturate type have occurred after the discontinuation of benzodiazepines (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
-
PRECAUTIONS
In debilitated patients, it is recommended that the dosage be limited to the smallest effective amount to preclude the development of ataxia, oversedation or confusion (not more than 2 Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide capsules per day initially, to be increased gradually as needed and tolerated). In general, the concomitant administration of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide and other psychotropic agents is not recommended. If such combination therapy seems indicated, careful consideration should be given to the pharmacology of the agents to be employed — particularly when the known potentiating compounds such as the MAO inhibitors and phenothiazines are to be used. The usual precautions in treating patients with impaired renal or hepatic function should be observed.
Paradoxical reactions to chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, e.g., excitement, stimulation and acute rage, have been reported in psychiatric patients and should be watched for during Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide therapy. The usual precautions are indicated when chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is used in the treatment of anxiety states where there is any evidence of impending depression; it should be borne in mind that suicidal tendencies may be present and protective measures may be necessary. Although clinical studies have not established a cause and effect relationship, physicians should be aware that variable effects on blood coagulation have been reported very rarely in patients receiving oral anticoagulants and chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride.
Information for Patients
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is used with opioids or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, and not to use these concomitantly unless supervised by a healthcare provider (see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
To assure the safe and effective use of benzodiazepines, patients should be informed that, since benzodiazepines may produce psychological and physical dependence, it is advisable that they consult with their physician before either increasing the dose or abruptly discontinuing this drug.
Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Limit dosage and duration of concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids, and follow patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
Geriatric Use
Geriatric subjects may be particularly prone to experiencing drowsiness, ataxia and confusion while receiving Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide. These effects can usually be avoided with proper dosage adjustment, although they have occasionally been observed even at the lower dosage ranges. Dosing in geriatric subjects should be initiated cautiously (no more than 2 capsules per day) and increased gradually if needed and tolerated (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is contraindicated in the presence of glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy and benign bladder neck obstruction (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
No side effects or manifestations not seen with either compound alone have been reported with the administration of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide. However, since Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide contains chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide, the possibility of untoward effects which may be seen with either of these two compounds cannot be excluded.
When chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride has been used alone the necessity of discontinuing therapy because of undesirable effects has been rare. Drowsiness, ataxia and confusion have been reported in some patients — particularly the elderly and debilitated. While these effects can be avoided in almost all instances by proper dosage adjustment, they have occasionally been observed at the lower dosage ranges. In a few instances syncope has been reported.
Other adverse reactions reported during therapy with chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride include isolated instances of skin eruptions, edema, minor menstrual irregularities, nausea and constipation, extrapyramidal symptoms, as well as increased and decreased libido. Such side effects have been infrequent and are generally controlled with reduction of dosage. Changes in EEG patterns (low-voltage fast activity) have been observed in patients during and after chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride treatment.
Blood dyscrasias, including agranulocytosis, jaundice and hepatic dysfunction have occasionally been reported during therapy with chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride. When chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride treatment is protracted, periodic blood counts and liver function tests are advisable.
Adverse effects reported with use of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide are those typical of anticholinergic agents, i.e., dryness of the mouth, blurring of vision, urinary hesitancy and constipation. Constipation has occurred most often when Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide therapy has been combined with other spasmolytic agents and/or a low residue diet.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Withdrawal symptoms, similar in character to those noted with barbiturates and alcohol (convulsions, tremor, abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting and sweating), have occurred following abrupt discontinuance of chlordiazepoxide. The more severe withdrawal symptoms have usually been limited to those patients who had received excessive doses over an extended period of time. Generally milder withdrawal symptoms (e.g., dysphoria and insomnia) have been reported following abrupt discontinuance of benzodiazepines taken continuously at therapeutic levels for several months. Consequently, after extended therapy, abrupt discontinuation should generally be avoided and a gradual dosage tapering schedule followed. Addiction-prone individuals (such as drug addicts or alcoholics) should be under careful surveillance when receiving chlordiazepoxide or other psychotropic agents because of the predisposition of such patients to habituation and dependence.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Because of the varied individual responses to tranquilizers and anticholinergics, the optimum dosage of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide varies with the diagnosis and response of the individual patient. The dosage, therefore, should be individualized for maximum beneficial effects. The usual maintenance dose is 1 or 2 capsules, 3 or 4 times a day administered before meals and at bedtime.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is available in light green opaque capsules, each containing 5 mg chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and 2.5 mg clidinium bromide, in bottles of 100 (NDC: 42494-409-01), with LIBRAX® ICN imprinted on the body of the capsule.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F).
Keep out of reach of children.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in USP/NF.
Distributed by:
Cameron Pharmaceuticals
Louisville, KY 40245 USAManufactured by: Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
Steinbach, MB R5G 1Z7 Canada
Librax is a trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
or its affiliates.©Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
9542102
20001848
Revised: 04/2017 -
Medication Guide
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide
capsulesWhat is the most important information I should know about Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
- Do not stop taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide suddenly can cause serious side effects.
-
Taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide with opioid medicines, alcohol, or other central nervous system depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, breathing problems (respiratory depression), coma and death.
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide affects you.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other drugs that may make you sleepy or dizzy while taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide without first talking to your healthcare provider. When taken with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness, Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may make your sleepiness or dizziness much worse.
-
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide can cause abuse and dependence.
- Do not stop taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide all of a sudden. Stopping Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide suddenly can cause seizures, shaking, stomach and muscle cramps, vomiting and sweating.
- Physical dependence is not the same as drug addiction. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about the differences between physical dependence and drug addiction.
What is Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
-
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is a prescription medicine that is used with other therapies for the treatment of:
- stomach (peptic) ulcers
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- inflammation of the colon called acute enterocolitis
- Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide contains the medicines chlordiazepoxide HCl and clidinium bromide.
- Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may harm others. Tell your healthcare provider if you have abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or street drugs.
- It is not known if Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide is safe and effective in children.
Do not take Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide if you:
- have glaucoma
- have an enlarged prostate
- have a blockage of your bladder that causes problems with urination
- are allergic to chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride or clidinium bromide
Before you take Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have eye problems
- have problems urinating or emptying your bladder
- have coordination problems
- have kidney or liver problems
- have a history of depression, mental illness, or suicidal thoughts
- have a history of drug or alcohol abuse or addiction
- have bleeding problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may harm your unborn baby. Avoid taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide during the first trimester of pregnancy. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant during treatment with Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may pass through your breast milk and may harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide. Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may decrease the amount of breast milk your body makes.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide or the other medicines work.
Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you:
- take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medicine or an anti-psychotic medicine called phenothiazine.
How should I take Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
- Take Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide if needed. Do not change your dose of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide or suddenly stop taking Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide without talking with your healthcare provider.
- If you take too much Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide may cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information I should know about Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?"
The most common side effects of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide include:
- dry mouth
- nausea
- skin problems
- blurred vision
- constipation
- swelling
- irregular menstrual (periods) cycles
- increased and decreased desire for sex (libido)
- problems starting to urinate
- drowsiness, coordination problems, and confusion may happen, especially in people who are elderly or weak
These are not all the possible side effects of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
- Store Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide at room temperature 77°F (25°C).
- Keep Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Chlordiazepoxide HCl/Clidinium Bromide?
Active ingredient: chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide
Inactive ingredients: corn starch, lactose and talc. Gelatin capsule shells may contain methylparaben, propylparaben, and potassium sorbate, with the following dye systems: D&C Yellow No. 10 and FD&C Green No. 3.
Distributed by: Cameron Pharmaceuticals
Louisville, KY 40245 USAManufactured by: Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
Steinbach, MB R5G 1Z7 CanadaLibrax is a trademark of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. or its affiliates.
©Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
For more information, go to www.valeant.com or contact Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC at 1-800-321-4576.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 04/2017
9542102 20001848
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 Capsule Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE HYDROCHLORIDE AND CLIDINIUM BROMIDE
chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 42494-409 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIV Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride (UNII: MFM6K1XWDK) (Chlordiazepoxide - UNII:6RZ6XEZ3CR) Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride 5 mg Clidinium Bromide (UNII: 91ZQW5JF1Z) (CLIDINIUM - UNII:BO76JF850N) Clidinium Bromide 2.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Starch, Corn (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) POTASSIUM SORBATE (UNII: 1VPU26JZZ4) D&C Yellow No. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C Green No. 3 (UNII: 3P3ONR6O1S) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Product Characteristics Color GREEN (light green opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code LIBRAX;ICN Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 42494-409-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/01/1966 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA authorized generic NDA012750 09/01/1966 Labeler - Cameron Pharmaceuticals, LLC (078371442) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. 253292734 MANUFACTURE(42494-409)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.