LYNOZYFIC- linvoseltamab-gcpt injection, solution, concentrate
LYNOZYFIC by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LYNOZYFIC by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LYNOZYFIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LYNOZYFIC.
LYNOZYFIC™ (linvoseltamab-gcpt) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME and NEUROLOGIC TOXICITY, including IMMUNE EFFECTOR CELL-ASSOCIATED NEUROTOXICITY SYNDROME
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LYNOZYFIC. Initiate treatment with LYNOZYFIC step-up dosing to reduce the risk of CRS. Manage CRS, withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 5.1)
- Neurologic Toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LYNOZYFIC. Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS during treatment. Manage neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, withhold LYNOZYFIC until neurologic toxicity, including ICANS resolves and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue based on severity. (2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 5.2)
- LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program called the LYNOZYFIC Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). (5.3)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LYNOZYFIC is a bispecific B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)‑directed CD3 T-cell engager indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least four prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, and an anti‑CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s). (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Premedicate to reduce the risk of CRS and infusion-related reactions (IRR). (2.1, 2.3)
- Administer only as an intravenous infusion. (2.1, 2.6)
- Recommended Dosage (2.2):
Dosing Schedule Day Dose of LYNOZYFIC Step-Up Dosing Schedule Day 1 Step-up dose 1 5 mg Day 8 Step-up dose 2 25 mg Day 15 First treatment dose 200 mg Weekly Dosing Schedule One week after Day 15 treatment dose and once weekly from Week 4 to Week 13 for 10 treatment doses Second and subsequent treatment doses 200 mg Biweekly (Every 2 Weeks) Dosing Schedule Week 14 and every 2 weeks thereafter Subsequent treatment doses 200 mg Patients who have achieved and maintained VGPR or better at or after Week 24 and received at least 17 doses of 200 mg Every 4 Weeks Dosing Schedule At Week 24 or after and every 4 weeks thereafter Subsequent treatment doses 200 mg DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infections: Can cause serious or fatal infections. Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of infection and treat accordingly. (5.4)
- Neutropenia: Monitor complete blood cell counts at baseline and periodically during treatment. (5.5)
- Hepatotoxicity: Can cause hepatotoxicity. Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated. (5.6)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.7, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are musculoskeletal pain, cytokine release syndrome, cough, upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, fatigue, pneumonia, nausea, headache, and dyspnea. (6.1)
The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥30%) are decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased white blood cell count. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Regeneron at 1-844-467-2998 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME AND NEUROLOGIC TOXICITY, INCLUDING IMMUNE EFFECTOR CELL-ASSOCIATED NEUROTOXICITY SYNDROME
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Recommended Dosage
2.3 Recommended Pretreatment Medications
2.4 Restarting LYNOZYFIC After Dosage Delay
2.5 Management of Adverse Reactions
2.6 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome
5.3 LYNOZYFIC REMS
5.4 Infections
5.5 Neutropenia
5.6 Hepatotoxicity
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of LYNOZYFIC on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME AND NEUROLOGIC TOXICITY, INCLUDING IMMUNE EFFECTOR CELL-ASSOCIATED NEUROTOXICITY SYNDROME
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LYNOZYFIC. Initiate treatment with LYNOZYFIC step-up dosing to reduce the risk of CRS. Manage CRS, withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves, and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4, 2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), including serious or life-threatening reactions, can occur in patients receiving LYNOZYFIC. Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS during treatment. Manage neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, withhold LYNOZYFIC until neurologic toxicity, including ICANS resolves, and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4, 2.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Because of the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the LYNOZYFIC REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LYNOZYFIC is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who have received at least four prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate and durability of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trial(s).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- Administer LYNOZYFIC intravenously according to the step-up schedule to reduce the incidence and severity of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Administer only as an intravenous infusion after dilution in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
- Administer pretreatment medications [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- LYNOZYFIC should be administered by a healthcare provider with immediate access to emergency equipment and appropriate medical support to manage severe reactions such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS), infusion-related reactions (IRR), and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 and 5.2)].
- Due to the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, patients should be hospitalized for 24 hours after administration of the first step-up dose, and for 24 hours after administration of the second step-up dose.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage for LYNOZYFIC is presented in Table 1. In patients who experience CRS, ICANS, or neurologic adverse reactions, refer to Tables 3, 4, and 5, respectively, for recommendations regarding administration of the next LYNOZYFIC dose. Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The recommended dosing schedule for LYNOZYFIC is provided in Table 1. The recommended dosage of LYNOZYFIC is step-up doses of 5 mg, 25 mg, and 200 mg, followed by 200 mg weekly for 10 doses, followed by 200 mg biweekly (every 2 weeks). In patients who have achieved and maintained VGPR or better at or after Week 24 and received at least 17 doses of 200 mg, decrease the dosing frequency to 200 mg every 4 weeks.
Table 1: LYNOZYFIC Dosing Schedule Dosing Schedule Day* LYNOZYFIC Dose Duration of Infusion - * Weekly doses should be at least 5 days apart. Biweekly doses should be at least 10 days apart. Every 4-week doses should be at least 24 days apart.
- † For patients who experienced CRS with the previous dose of LYNOZYFIC, the duration of infusion should be maintained at the duration of the previous infusion; reduce the duration of infusion sequentially in subsequent doses in patients who do not experience CRS (e.g., 4 hours, 1 hour, then 30 minutes).
Step-up Dosing Schedule Day 1 Step-up dose 1 5 mg 4 hours Day 8 Step-up dose 2 25 mg Day 15 First treatment dose 200 mg Weekly Dosing Schedule One week after Day 15 treatment dose and once weekly from Week 4 to Week 13 for 10 treatment doses Second and subsequent treatment doses 200 mg 1 hour for the second treatment dose, and 30 minutes for subsequent doses† Biweekly (Every 2 Weeks) Dosing Schedule Week 14 and every 2 weeks thereafter Subsequent treatment doses 200 mg 30 minutes Patients who have achieved and maintained VGPR or better at or after Week 24 and received at least 17 doses of 200 mg Every 4 Weeks Dosing Schedule At Week 24 or after and every 4 weeks thereafter 200 mg 30 minutes 2.3 Recommended Pretreatment Medications
Administer the following pre-treatment medications before each dose of the LYNOZYFIC step-up dosing schedule, which includes step-up dose 1, step-up dose 2, and the first treatment dose, the second treatment dose, and if indicated, subsequent treatment doses (see Tables 1, 2, and 3), to reduce the risk of CRS and/or IRR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
- acetaminophen (or equivalent) 650 mg to 1,000 mg orally 30 to 60 minutes prior to infusion
- diphenhydramine (or equivalent) 25 mg orally or intravenously 30 to 60 minutes prior to infusion
- dexamethasone (or equivalent) intravenously 1 to 3 hours prior to infusion
- 40 mg dexamethasone (or equivalent) before step-up dose 1, step-up dose 2, and the first full treatment dose
- Once a treatment dose of LYNOZYFIC is tolerated without CRS and/or IRR with 40 mg dexamethasone (or equivalent), administer 10 mg dexamethasone (or equivalent) prior to the subsequent LYNOZYFIC treatment dose
Pre-treatment medications may be discontinued once a treatment dose of LYNOZYFIC is tolerated without CRS and/or IRR following pre-treatment with 10 mg dexamethasone (or equivalent), acetaminophen (or equivalent), and diphenhydramine (or equivalent) as described.
2.4 Restarting LYNOZYFIC After Dosage Delay
Table 2 provides recommendations for restarting therapy after a dose delay. Refer to Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5 for recommendations about management of CRS, ICANS, or other adverse reactions.
Table 2: Recommendations for Restarting Therapy with LYNOZYFIC After a Dose Delay Last Dose Administered Time since the last dose administered* Action for next dose.
(For CRS/IRR or ICANS, refer to the dose modifications in Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5.)NOTE: Administer pre-treatment medications prior to step-up dose 1, step-up dose 2, the first treatment dose, the second treatment dose, and if indicated, subsequent treatment doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. - * Consider benefit-risk of restarting LYNOZYFIC in patients who require a dose delay of more than 30 days.
5 mg 14 days or less Administer 25 mg Greater than 14 days Restart step-up dosing from 5 mg 25 mg 14 days or less Administer 200 mg Greater than 14 days and less than or equal to 28 days Restart step-up dosing from 25 mg Greater than 28 days Restart step-up dosing from 5 mg 200 mg 49 days or less Administer 200 mg Greater than 49 days Restart step-up dosing from 5 mg 2.5 Management of Adverse Reactions
Table 3 describes the management of CRS. Table 4 describes the management of ICANS. Table 5 describes the management of other adverse reactions.
Cytokine Release Syndrome
Identify CRS based on clinical presentation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Evaluate and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia, and hypotension. If CRS is suspected, withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves. CRS should be managed according to the recommendations in Table 3 and per current practice guidelines. Supportive therapy for CRS should be administered, which may include intensive care for severe or life-threatening CRS.
Table 3: Recommendations for Management of Cytokine Release Syndrome Grade* Presenting Symptoms Recommendations - * Based on American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) criteria for grading CRS (2019).
- † Attributed to CRS. Fever may not always be present concurrently with hypotension or hypoxia as it may be masked by interventions such as steroids, antipyretics, or anticytokine therapy.
- ‡ Administer pretreatment medications prior to next dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- § Follow the recommendations in Table 2 for restarting dosing.
- ¶ Low-flow oxygen defined as oxygen delivered at less than 6 L/minute: high-flow oxygen defined as oxygen delivered at greater than or equal to 6 L/minute.
- # If the last dose administered was 5 mg, administer 2.5 mg. If the last dose administered was 25 mg, restart step-up dosing from 5 mg. If the last dose administered was 200 mg, refer to Table 2 for recommendations regarding restarting therapy based on time since the last dose.
Grade 1 Fever ≥100.4ºF (38ºC)† Grade 2 Fever ≥100.4°F (38°C)† with:
Hypotension responsive to fluids and not requiring vasopressors
and/or
hypoxia requiring low-flow oxygen¶ by nasal cannula or blow-by- Withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves.
- Provide supportive care, which may include intensive care.
- When CRS resolves, resume treatment with LYNOZYFIC.‡,§
- Consider a decrease in infusion rate up to 50% (no more than 6 hours total) when resuming treatment. Increase rate on subsequent infusions if tolerated.
- Monitor patients within proximity of a healthcare facility for 24 hours following this dose, and consider hospitalization.
Grade 3 Fever ≥100.4°F (38°C)† with:
Hypotension requiring a vasopressor (with or without vasopressin)
and/or
hypoxia requiring high-flow oxygen¶ by nasal cannula, face mask, non-rebreather mask, or Venturi mask.- Withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves.
- Provide supportive care, which may include intensive care.
- When CRS resolves, resume treatment with LYNOZYFIC at reduced dose:‡, #
- Decrease infusion rate up to 50% (no more than 6 hours total).
- Hospitalize for 24 hours after the administration for this dose.
- After resuming treatment, if the administered dose is tolerated:
- Continue with the next dose of the recommended dosing regimen per Table 1.
- If the full dose is tolerated, infusion rate can be increased to the rate prior to the adverse reaction.
- Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC if Grade 3 CRS recurs with subsequent infusions.
Grade 4 Fever ≥100.4°F (38°C) † with:
Hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (excluding vasopressin)
and/or
hypoxia requiring oxygen by positive pressure (e.g., continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP), intubation, and mechanical ventilation).- Discontinue LYNOZYFIC permanently.
- CRS should be managed per Grade 3 recommendations.
Other AST/ALT greater than 5 times ULN associated with CRS Grade 3 or less - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves and AST/ALT are less than 3 times ULN if baseline was normal or 1.5 to 3 times baseline if baseline was abnormal.
- Provide supportive care, which may include intensive care, and monitor.
- No change in dose is needed in patients without CRS symptoms with transaminase levels that are trending towards baseline within 7 days.
- If values do not trend towards baseline in 7 days, decrease the dose.#
- See infusion rate information by CRS grade.
Neurologic Toxicity, including ICANS
Management recommendations for ICANS and neurologic toxicity are summarized in Table 4 and Table 5. At the first sign of suspected neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, withhold LYNOZYFIC and consider consultation with neurologist and other specialists for further evaluation and management. Rule out other causes of neurologic symptoms. Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care for severe or life-threatening ICANS. Manage per current practice guidelines.
Table 4: Recommendations for Management of ICANS Grade* Presenting Symptoms† Recommendations - * Based on American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) 2019 grading for ICANS.
- † Management is determined by the most severe event, not attributable to any other cause.
- ‡ If patient is arousable and able to perform Immune Effector Cell-Associated Encephalopathy (ICE) Assessment, assess: Orientation (oriented to year, month, city, hospital=4 points); Naming (name 3 objects, e.g., point to clock, pen, button=3 points); Following Commands (e.g., "show me 2 fingers" or "close your eyes and stick out your tongue"=1 point); Writing (ability to write a standard sentence=1 point); and Attention (count backwards from 100 by ten=1 point). If patient is unarousable and unable to perform ICE Assessment (Grade 4 ICANS)=0 points.
- § Not attributable to any other cause.
- ¶ Follow the recommendations in Table 2 for restarting dosing.
- # All references to dexamethasone administration are dexamethasone or equivalent.
- Þ If the last dose administered was 5 mg, administer 2.5 mg. If the last dose administered was 25 mg, restart step-up dosing from 5 mg. If the last dose administered was 200 mg, refer to Table 2 for recommendations regarding restarting therapy based on time since the last dose.
Grade 1 ICE‡ score 7-9,
or depressed level of consciousness§: awakens spontaneously.- Withhold until neurologic symptoms resolve or return to baseline.¶
- Provide supportive therapy. Manage per current practice guidelines.
- Consider non-sedating, anti-seizure medications for seizure prophylaxis.
Grade 2 ICE‡ score 3-6,
or depressed level of consciousness§: awakens to voice.- Withhold until neurologic symptoms resolve or return to baseline.¶
- Provide supportive therapy. Manage per current practice guidelines.
- Administer dexamethasone# 10 mg intravenously every 6 hours. Continue dexamethasone use until resolution to Grade 1 or less, then taper.
- Consider non-sedating, anti-seizure medications for seizure prophylaxis.
- Monitor patients within proximity of a healthcare facility for 24 hours following the next dose of LYNOZYFIC and consider hospitalization.
Grade 3 ICE‡ score 0-2,
or depressed level of consciousness§: awakens only to tactile stimulus,
or seizures, either:- any clinical seizure, focal or generalized, that resolves rapidly, or
- non-convulsive seizures on electroencephalogram (EEG) that resolve with intervention,
- Withhold until neurologic symptoms resolve or return to baseline.
- Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care. Manage per current practice guidelines.
- Consider neurology evaluation.
- Administer dexamethasone# 10 mg intravenously every 6 hours. Continue dexamethasone use until resolution to Grade 1 or less, then taper.
- Consider non-sedating, anti-seizure medications for seizure prophylaxis.
- Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC for recurrent Grade 3 ICANS.
- Resume treatment with LYNOZYFIC at a reduced doseÞ and hospitalize for 24 hours after the administration of the dose. After resuming treatment, if the administered dose is tolerated, continue with the next dose of the recommended dosing regimen per Table 1.
Grade 4 ICE‡ score 0,
or depressed level of consciousness§: either:- patient is unarousable or requires vigorous or repetitive tactile stimuli to arouse, or
- stupor or coma,
- life-threatening prolonged seizure (>5 minutes), or
- repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between,
- deep focal motor weakness such as hemiparesis or paraparesis,
- diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging, or
- decerebrate or decorticate posturing, or
- cranial nerve VI palsy, or
- papilledema, or
- Cushing's triad.
- Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC.
- Provide supportive therapy, which may include intensive care. Manage per current practice guidelines.
- Consider neurology evaluation.
- Administer dexamethasone# 10 mg intravenously every 6 hours. Continue dexamethasone use until resolution to Grade 1 or less, then taper.
- Consider non-sedating, anti-seizure medications for seizure prophylaxis.
Other Adverse Reactions
Management recommendations for other adverse reactions are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5: Recommendations for Management of Other Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity* Recommendations - * Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE), Version 5.0
- † If the last dose administered was 5 mg, administer 2.5 mg. If the last dose administered was 25 mg, restart step-up dosing from 5 mg. If the last dose administered was 200 mg, refer to Table 2 for recommendations regarding restarting therapy based on time since the last dose.
- ‡ Follow the recommendations in Table 2 for restarting dosing.
Infusion-Related Reactions Grade 2 - Stop infusion and treat symptoms.
- May resume treatment with the remaining infusion (total infusion time must not exceed 6 hours total) when symptoms are Grade 1 or baseline.
- Consider decreasing infusion rate by up to 50% when resuming treatment. If tolerated, infusion rate can be increased with subsequent doses.
Grade 3 - Stop infusion and treat symptoms.
- May resume when symptoms are Grade 1 or baseline.
- After resolution of the adverse event, follow the recommendations:
- Decrease the infusion rate up to 50% (no more than 6 hours total).
- Resume at reduced dose.†
- If the administered dose is tolerated, continue with the next dose of the recommended dosing regimen at the decreased infusion rate.
- Infusion rate can be increased if tolerated.
- Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC if Grade 3 IRR recurs with subsequent infusions.
Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC and treat symptoms.
Neurologic Adverse Reactions (excluding ICANS) Grade 2 - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until symptoms resolve to Grade 1 or baseline.‡
Grade 3 (First occurrence) - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until Grade 1 or baseline.‡
Grade 3 (Recurrent)
Grade 4- Permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC.
Infections Grades 2 or 3 - Withhold LYNOZYFIC in patients with active infection until the infection improves to Grade 1 or less.‡
Grade 4 - Consider permanent discontinuation of LYNOZYFIC. If treatment is not permanently discontinued, withhold subsequent treatment doses until Grade 1 or baseline.‡
Other Non-hematologic Adverse Reactions Grade 3 - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until Grade 1 or baseline.‡
Grade 4 - Consider permanent discontinuation of LYNOZYFIC.
- If LYNOZYFIC is not permanently discontinued, withhold subsequent treatment doses until Grade 1 or baseline.‡
Hematologic Adverse Reactions Platelet count less than 50,000/mcL with bleeding
OR
less than 25,000/mcL- Withhold LYNOZYFIC until 25,000/mcL or higher and no evidence of bleeding.‡
Absolute neutrophil count less than 1 × 109/L with Grade 2 or higher infection
OR
less than 0.5 × 109/L- Withhold LYNOZYFIC until 0.5 × 109/L or higher.‡
Febrile neutropenia - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until neutrophil count is greater than 1 × 109/L and fever resolves.‡
Hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL - Withhold LYNOZYFIC until hemoglobin is 8 g/dL or higher.‡
2.6 Preparation and Administration
Preparation
- Use aseptic technique to prepare LYNOZYFIC. Each vial is intended for one time use only. Do not shake.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. LYNOZYFIC is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Discard the vial if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains particulate matter.
- Determine the dose, total volume of LYNOZYFIC solution, and the number of LYNOZYFIC vials needed (see Table 6).
Dilution
- Withdraw the desired dose from the vial of LYNOZYFIC and transfer into an intravenous infusion bag [polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyolefin (PO)] of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, according to Table 6. Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake the solution.
Table 6: Dilution of LYNOZYFIC LYNOZYFIC
doseLYNOZYFIC
vial strengthVolume of LYNOZYFIC to be added to the infusion bag Size of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection Infusion Bag (PVC or PO) - * Modified dose due to adverse reaction. For instructions on when to use the modified dose refer to Table 3, Table 4, and Table 5.
2.5 mg* 5 mg/2.5 mL 1.25 mL 50 mL 5 mg 5 mg/2.5 mL 2.5 mL 50 mL or 100 mL 25 mg 5 mg/2.5 mL 12.5 mL 50 mL or 100 mL 200 mg 200 mg/10 mL 10 mL 50 mL or 100 mL Diluted LYNOZYFIC Storage
Use diluted LYNOZYFIC immediately. If not used immediately, store the solution:
- at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for no more than 8 hours from preparation to the start of the infusion.
Or - under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 48 hours from preparation to the start of the infusion.
Do not freeze.
Do not shake.
Administration
- Administer as an intravenous infusion only.
- Refer to Dosage and Administration (2.2) for infusion rates.
- Connect the prepared intravenous infusion bag containing the final LYNOZYFIC solution to intravenous tubing constructed of PVC, polyethylene (PE)-lined PVC, or polyurethane (PU).
- Use of a 0.2-micron to 5-micron polyethersulfone (PES) filter is required.
- Prime with LYNOZYFIC to the end of the intravenous tubing.
- Do not mix LYNOZYFIC with other drugs or concurrently administer other drugs through the same intravenous line.
- Upon completion of LYNOZYFIC infusion, flush the infusion line with an adequate volume of sterile 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to ensure that the entire contents of the infusion bag are administered.
- Total infusion time should include flushing of the infusion line.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
LYNOZYFIC can cause cytokine release syndrome (CRS), which can be serious or life-threatening.
In LINKER-MM1, CRS occurred in 46% (54/117) of patients who received LYNOZYFIC at the recommended dose, with Grade 1 CRS occurring in 35% (41/117) of patients, Grade 2 in 10% (12/117), and Grade 3 in 0.9% (1/117) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Thirty-eight percent (45/117) of patients had CRS following step-up dose 1, including 1 patient who experienced Grade 3 CRS; 8% (9/117) had an initial CRS event following a subsequent dose. Seventeen percent (19/113) of patients developed CRS after step-up dose 2, 10% (11/111) developed CRS after the first full 200 mg dose of LYNOZYFIC, and 3.6% (4/110) developed CRS after the second full dose. Recurrent CRS occurred in 20% (23/117) of patients. The median time to onset of CRS from the end of infusion was 11 (range: -1 to 184) hours after the most recent dose with a median duration of 15 (range: 1 to 76) hours.
Clinical signs and symptoms of CRS included, but were not limited to pyrexia, chills, hypoxia, tachycardia, and hypotension.
Administer pretreatment medications and initiate therapy according to LYNOZYFIC step-up dosing to reduce the incidence and severity of CRS [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of CRS after infusion. Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur.
At the first sign of CRS, immediately evaluate patients for hospitalization, manage per current practice guidelines, and administer supportive care; withhold LYNOZYFIC until CRS resolves and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Infusion Related Reactions
Infusion-related reactions (IRR) may be clinically indistinguishable from manifestations of CRS. In the patients who were treated with the recommended step-up dosing regimen and pretreatment medications [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)], the rate of IRR was 9% [11/117 including Grade 2 IRR (4.3%) and Grade 3 IRR (1.7%)]. For IRR, interrupt or slow the rate of infusion or permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC based on severity of reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5.2 Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome
LYNOZYFIC can cause serious or life-threatening neurologic toxicity, including immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In LINKER-MM1, neurologic toxicity occurred in 54% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 neurologic toxicity occurring in 8%, at the recommended dose [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Neurologic toxicities included ICANS, depressed level of consciousness, encephalopathy, and toxic encephalopathy.
ICANS occurred in 8% of patients who received LYNOZYFIC with the recommended dosing regimen, including Grade 3 events in 2.6%. Most patients experienced ICANS following step-up dose 1 (5%). Two patients (1.8%) experienced initial ICANS following step-up dose 2 and one patient developed the first occurrence of ICANS following a subsequent full dose of LYNOZYFIC. Recurrent ICANS occurred in one patient. The median time to onset of ICANS was 1 (range: 1 to 4) day after the most recent dose with a median duration of 2 (range: 1 to 11) days. The onset of ICANS can be concurrent with CRS, following resolution of CRS, or in the absence of CRS.
The most common clinical signs and symptoms of ICANS are confusion, depressed level of consciousness, and lethargy. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicity during treatment. At the first sign of neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, immediately evaluate the patient; provide supportive therapy and consider further management per current practice guidelines. Withhold LYNOZYFIC until ICANS resolves and modify the next dose or permanently discontinue LYNOZYFIC based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention should signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicity occur at any time.
Due to the potential for neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, patients receiving LYNOZYFIC are at risk of confusion and depressed consciousness. Advise patients to refrain from driving, or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery, for 48 hours after completion of each of the step-up doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] and in the event of new onset of any neurological symptoms, until symptoms resolve.
LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5.3 LYNOZYFIC REMS
LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the LYNOZYFIC REMS because of the risks of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Notable requirements of the LYNOZYFIC REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the program by enrolling and completing training.
- Prescribers must counsel patients receiving LYNOZYFIC about the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, and provide patients with LYNOZYFIC Patient Wallet Card.
- Pharmacies and healthcare settings that dispense LYNOZYFIC must be certified with the LYNOZYFIC REMS program and must verify prescribers are certified through the LYNOZYFIC REMS program.
- Wholesalers and distributors must only distribute LYNOZYFIC to certified pharmacies or healthcare settings.
Further information about the LYNOZYFIC REMS program is available at lynozyficREMS.com or by telephone at 1-855-212-6391.
5.4 Infections
LYNOZYFIC can cause serious, life-threatening, or fatal infections.
In patients who received LYNOZYFIC at the recommended dose in LINKER-MM1, serious infections, including opportunistic infections, occurred in 42% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 infections in 38% and fatal infections in 4% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The most common serious infection reported (≥10%) were pneumonia and sepsis. Two cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurred in patients receiving LYNOZYFIC.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection and immunoglobulin levels prior to and during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and treat appropriately. Administer prophylactic antimicrobials, antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, vaccines, and subcutaneous or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) according to guidelines, including prophylaxis for PJP and herpesviruses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Withhold LYNOZYFIC or consider permanent discontinuation of LYNOZYFIC based on severity of the infection [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.5 Neutropenia
LYNOZYFIC can cause neutropenia and febrile neutropenia.
In patients who received LYNOZYFIC at the recommended dose in LINKER-MM1, decreased neutrophil count occurred in 62% of patients with Grade 3 or 4 decreased neutrophil count in 47%. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 8% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor complete blood cell counts at baseline and periodically during treatment and provide supportive care per local guidelines. Monitor patients with neutropenia for signs of infection. Withhold LYNOZYFIC based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.6 Hepatotoxicity
LYNOZYFIC can cause hepatotoxicity.
In LINKER-MM1, elevated ALT occurred in 46% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 ALT elevation occurring in 6%; elevated AST occurred in 61% of patients, with Grade 3 or 4 AST elevation occurring in 10% of patients who received the recommended dose. Grade 3 or 4 total bilirubin elevations occurred in 1.7% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Liver enzyme elevation can occur with or without concurrent CRS.
Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated. Withhold LYNOZYFIC or consider permanent discontinuation of LYNOZYFIC based on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, LYNOZYFIC may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma
The safety of LYNOZYFIC was evaluated in LINKER-MM1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients (n=117) received LYNOZYFIC as step-up doses of 5 mg on Day 1 and 25 mg on Day 8, and the first treatment dose of 200 mg on Day 15. Patients then received 200 mg intravenously once weekly from Week 4 to Week 13, followed by 200 mg every 2 weeks from Week 14. In the Phase 2 portion of the study, patients who achieved and maintained VGPR or better at or after Week 24 and received at least 17 doses of 200 mg were able to receive every 4-week dosing. The median duration of treatment was 47 weeks (range 1, 151); 55% of patients were exposed for 9 months or longer and 36% were exposed for 1 year or longer.
The median age of patients who received LYNOZYFIC was 70 years (range: 37 to 91 years); 55% were male; 71% were White, 17% were Black or African American, and 9% were Asian.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 74% of patients who received LYNOZYFIC. Serious adverse reactions that occurred in >5% of patients included cytokine release syndrome (27%), pneumonia (13%), COVID-19 (7%), and acute kidney injury (5%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 7% of patients, and included sepsis (3.4%), chronic kidney disease (0.9%), pneumonia (0.9%), tumor lysis syndrome (0.9%), and encephalopathy (0.9%).
Permanent discontinuation of LYNOZYFIC due to adverse reactions occurred in 16% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation that occurred in at least 2 patients included sepsis, pneumonia, and encephalopathy.
Dosage interruptions or delays of LYNOZYFIC due to adverse reactions occurred in 74% of patients. Adverse reactions which required a dosage interruption or delay in >10% of patients included neutropenia (29%), upper respiratory tract infection (18%), pneumonia (15%), and COVID-19 infection (11%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were musculoskeletal pain, cytokine release syndrome, cough, upper respiratory tract infection, diarrhea, fatigue, pneumonia, nausea, headache, and dyspnea. The most common Grade 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥30%) were decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased white blood cell count.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions in LINKER-MM1.
Table 7: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma Who Received LYNOZYFIC in LINKER-MM1 Adverse Reaction LYNOZYFIC
(N=117)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)- * Includes other related terms.
- † Only Grade 3 adverse reactions occurred.
- ‡ Pneumonia includes atypical pneumonia, COVID-19 pneumonia, PJP, pneumonia, pneumonia cytomegaloviral, pneumonia fungal, pneumonia influenzal, and pneumonia viral.
- § Includes fatal outcome.
- ¶ Encephalopathy includes agitation, amnesia, cognitive disorder, confusional state, delirium, depressed level of consciousness, encephalopathy (including hyperammonemic and toxic encephalopathy), irritability, lethargy, memory impairment, mental status changes, somnolence, and excludes ICANS.
- # Rash includes dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis contact, drug eruption, erythema, rash, rash erythematous, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, and stasis dermatitis.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Musculoskeletal pain* 53 3.4† Immune system disorders Cytokine release syndrome 46 0.9† Hypogammaglobulinemia 13 0.9† Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Cough* 39 0 Dyspnea* 21 0.9† Nasal congestion 16 0 Infections and infestations Upper respiratory tract infection* 35 6† Pneumonia‡,§ 28 21 COVID-19 17 5 Urinary tract infections* 16 8† Sepsis 10 6 Gastrointestinal disorders Diarrhea 35 1.7† Nausea 23 0 Vomiting 19 0 Constipation 17 0 General disorders and administration site conditions Fatigue* 34 0 Edema* 19 0.9† Pyrexia 17 0 Nervous system disorders Headache* 22 0.9† Encephalopathy§,¶ 18 3.4 Sensory Neuropathy* 13 0.9 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased appetite 15 0.9† Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash# 15 1.7† Psychiatric disorders Insomnia 13 0 Vascular disorders Hypertension 10 4.3† Clinically significant adverse reactions that occurred in <10% of patients treated with LYNOZYFIC included IRR, motor dysfunction, febrile neutropenia, ICANS, CMV infection, and PML.
Table 8 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in LINKER-MM1.
Table 8: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥5% for Grade 3 or 4) That Worsened from Baseline in Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with LYNOZYFIC in LINKER-MM1 Laboratory Abnormality* LYNOZYFIC
(N=117)†All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)- * Laboratory tests were graded according to NCI-CTCAE (National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events) Version 5.0.
- † The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 106 to 117 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
Hematology Lymphocyte count decreased 97 92 Hemoglobin decreased 72 42 Platelet count decreased 64 19 White blood cell count decreased 63 31 Neutrophil count decreased 62 47 Chemistry Aspartate aminotransferase increased 61 10 Phosphorus decreased 55 24 Creatinine increased 47 7 Alanine aminotransferase increased 46 6 -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of LYNOZYFIC on Other Drugs
Certain CYP substrates
Monitor for toxicity unless otherwise recommended in the Prescribing Information of certain CYP substrates where minimal changes in the concentration may lead to serious adverse reactions when used concomitantly with LYNOZYFIC.
Linvoseltamab-gcpt causes the release of cytokines [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] that may suppress cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme activity. Concomitant use with LYNOZYFIC increases CYP substrate exposure which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates. Increased CYP substrate exposure is more likely to occur from initiation of the LYNOZYFIC step-up dosing schedule up to 14 days after the first 200 mg dose, and during and after CRS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on the mechanism of action, LYNOZYFIC may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on the use of LYNOZYFIC in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug associated risk. No animal reproductive or developmental toxicity studies have been conducted with LYNOZYFIC.
Linvoseltamab-gcpt causes T-cell activation and cytokine release; immune activation may compromise pregnancy maintenance. In addition, based on the finding of B-cell depletion in non-pregnant animals, linvoseltamab-gcpt can cause B-cell lymphocytopenia in infants exposed to linvoseltamab-gcpt in-utero. Human immunoglobulin (IgG) is known to cross the placenta after the first trimester of pregnancy; therefore, linvoseltamab-gcpt has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to the fetus.
LYNOZYFIC is associated with hypogammaglobulinemia, therefore, assessment of immunoglobulin levels in newborns of mothers treated with LYNOZYFIC should be considered.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of linvoseltamab-gcpt in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
LYNOZYFIC may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LYNOZYFIC have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 117 patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma who received LYNOZYFIC, 42 (36%) of patients were 65 to 74 years of age and 31 (26%) were 75 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14)]. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed in patients 65 years of age and older, including patients 75 years of age and older, when compared with younger patients.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Linvoseltamab-gcpt, a bispecific B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed CD3 T-cell engager, is a recombinant human immunoglobulin (Ig)G4 antibody. Linvoseltamab-gcpt is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell suspension culture. The molecular weight of linvoseltamab-gcpt is approximately 146 kDa.
LYNOZYFIC (linvoseltamab-gcpt) injection for intravenous use is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution with a pH 6.0.
Each LYNOZYFIC 5 mg/2.5 mL vial contains 5 mg of linvoseltamab-gcpt. Each mL contains 2 mg of linvoseltamab-gcpt, histidine (0.7 mg), L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (1.1 mg), polysorbate 80 (1 mg), sucrose (100 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
Each LYNOZYFIC 200 mg/10 mL vial contains 200 mg of linvoseltamab-gcpt. Each mL contains 20 mg of linvoseltamab-gcpt, histidine (0.7 mg), L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (1.1 mg), polysorbate 80 (1 mg), sucrose (100 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Linvoseltamab-gcpt is a bispecific T-cell engaging antibody that binds to the CD3 receptor expressed on the surface of T-cells and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) expressed on the surface of multiple myeloma cells and some healthy B-lineage cells.
In vitro, linvoseltamab-gcpt activated T-cells, caused the release of various proinflammatory cytokines, and resulted in the lysis of multiple myeloma cells. Linvoseltamab-gcpt had anti-tumor activity in mouse models of multiple myeloma.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The 200 mg once weekly dosing regimen was associated with better objective response rate and complete response rate when compared to the 50 mg once weekly (0.25 times the recommended dosage) dosing regimen in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
Linvoseltamab-gcpt exposure-response relationships have not been fully characterized.
Effect on Circulating Cytokines
Transient elevation of circulating cytokines (IL-2, IL-6, and IFN-γ) was primarily observed during the step-up dose regimen and the first full 200 mg dose. The highest elevation of cytokines was generally observed 4 hours after each infusion and generally returned to baseline prior to the next dose. Limited cytokine release was observed following subsequent doses.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters were evaluated at the recommended dosage in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and are presented as geometric mean (CV%) unless otherwise specified.
Linvoseltamab-gcpt PK exposures following use of the recommended dosing schedule are presented in Table 9. Linvoseltamab-gcpt Ctrough increased more than proportionally over a dose range of 96 mg to 800 mg (0.48 to 4 times the recommended full dose). Linvoseltamab-gcpt maximum concentration (127 mg/L [51%]) is achieved after the first dose of the every-2-weeks dosing regimen (i.e., the 12th dose of 200 mg).
Table 9: Geometric Mean (CV%) Exposure Following the Recommended Dosage for Linvoseltamab-gcpt Dosing Period Cmax (mg/L) Ctrough (mg/L) Cavg (mg /L) - * Steady state values are approximated at Week 28.
First 200 mg weekly dose 52.7 (37.2) 15.5 (64.8) 27.4 (34.2) End of 200 mg weekly dosing (11th dose of 200 mg) 124 (50.4) 61.8 (123) 84.6 (74.6) End of 200 mg every 2 weeks dosing (16th dose of 200 mg) 97.9 (52.7) 30.2 (213) 51.9 (95.3) Steady state* with 200 mg every 4 weeks dosing 64.8 (45.1) 6.3 (362) 20.5 (84.6) Elimination
Linvoseltamab-gcpt clearance is 0.68 L/day (52.2%) at baseline and 0.43 L/day (83.8%) at steady state.
Linvoseltamab-gcpt clearance decreases over time because its elimination is mediated by two parallel processes: a linear, non-saturable catabolic process and a nonlinear, saturable target-mediated pathway. Patients who discontinue linvoseltamab-gcpt are expected to have a 97% reduction from Cmax at a median (5th to 95th percentile) time of 77.7 (18 to 154) days after last dose.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of linvoseltamab-gcpt were observed based on age (37 to 91 years), weight (44 to 172 kg), sex, race (White, Asian, or Black), ethnicity (Hispanic/Latino or not Hispanic/Latino), mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CrCL] 30 to 89 mL/min, by Cockcroft-Gault [C-G] equation), or mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin less than or equal to upper limit of normal [ULN] with AST greater than ULN or total bilirubin greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN with any AST).
The effect of severe renal impairment (CrCL 15 to 29 mL/min), end-stage renal disease (CrCL less than 15 mL/min), and moderate to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin greater than 1.5 times ULN with any AST) on the pharmacokinetics of linvoseltamab-gcpt is unknown.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the study described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of linvoseltamab-gcpt.
During treatment in LINKER-MM1 (evaluated through 30 months) [see Clinical Studies (14)], 1% (2/192) of LYNOZYFIC-treated patients developed anti-linvoseltamab-gcpt antibodies. Because of the low occurrence of anti-drug antibodies, the effect of these antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and/or effectiveness of linvoseltamab products is unknown.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma
The efficacy of LYNOZYFIC was evaluated in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma in an open-label, multi-center, multi-cohort study: LINKER-MM1 (NCT03761108). The study included patients who had previously received at least 3 prior therapies, including a proteasome inhibitor (PI), an immunomodulatory agent (IMiD), and an anti-CD38 antibody. The study included patients with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score of 0 or 1 and adequate baseline hematologic (absolute neutrophil count > 1 × 109/L, platelet count > 50 × 109/L, hemoglobin level >8 g/dL), renal (CrCL > 30 mL/min), and hepatic (AST and ALT ≤ 2.5 × ULN, total bilirubin ≤ 1.5 × ULN, alkaline phosphatase ≤ 2.5 × ULN) function.
The study excluded patients with known multiple myeloma brain lesions or meningeal involvement, history of a neurodegenerative condition, history of seizure within 12 months prior to study enrollment, active infection, a history of an allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplantation within 12 weeks, prior BCMA-directed bispecific antibody therapy, prior bispecific T-cell engaging therapy, or prior BCMA CAR-T cell therapy.
Patients received a step-up dose of 5 mg on Day 1, 25 mg on Day 8, and the first treatment dose of 200 mg on Day 15 of LYNOZYFIC by intravenous infusion. Then, patients received 200 mg of LYNOZYFIC weekly from Week 4 to Week 13, followed by 200 mg every other week thereafter. After at least 24 weeks, the Phase 2 patients who achieved a very good partial response (VGPR) or greater received 200 mg of LYNOZYFIC every 4 weeks. Patients were treated until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The efficacy population included 80 patients who had received at least four prior lines of therapy. The median age was 71 (range: 37 to 83) years with 30% of patients 75 years or older; 64% were male and 36% were female; 69% were White, 14% were Black or African American, 13% were Asian, and 2.5% were Hispanic/Latino.
The International Staging System (ISS) at study entry was Stage I in 39%, Stage II in 36%, and Stage III in 19%. High-risk cytogenetics (presence of del(17p), t(4;14) and t(14;16)) were present in 40% of patients. Eighteen percent of patients had extramedullary disease at baseline.
The median number of prior lines of therapy was 5 (range: 4 to 13); 83% of patients were refractory to the last line of therapy. Sixty-five percent of patients received prior stem cell transplantation. Seventy-nine percent of patients were triple-class refractory (refractory to a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody). Thirteen percent of patients were previously treated with a BCMA antibody-drug conjugate.
Efficacy was established based on objective response rate (ORR) as determined by blinded independent review committee (IRC), as measured using the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) criteria (see Table 10). The median time to first response was 0.95 months (range: 0.5 to 6 months). With a median follow-up of 11.3 months among responders, the estimated duration of response (DOR) rate was 89% (95% CI: 77, 95) at 9 months and 72% (95% CI: 54, 84) at 12 months.
Table 10: Efficacy Results for LINKER-MM1 Efficacy Endpoints LYNOZYFIC
N=80CI=confidence interval; NE=not estimable - * Based on Kaplan-Meier estimation.
Objective Response Rate (ORR) % (n) 70% (56) (95% CI) (59,80) Complete response (CR) or better, % (n) 45% (36) (95% CI) (34,57) Stringent complete response (sCR), % (n) 39% (31) Complete response (CR), % (n) 6% (5) Very good partial response (VGPR) % (n) 19% (15) Partial response (PR), % (n) 6% (5) Duration of Response (DOR)* Median, months (95% CI) NR (12, NE) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LYNOZYFIC (linvoseltamab-gcpt) injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution in a single-dose vial. It is supplied as provided in Table 11.
Table 11: Packaging Configurations Carton contents NDC One 5 mg/2.5 mL (2 mg/mL) single-dose vial 61755-054-01 One 200 mg/10 mL (20 mg/mL) single-dose vial 61755-056-01 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
Advise patients that they should be hospitalized for 24 hours after administration of the first and second step-up doses of LYNOZYFIC [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Inform patients of the risk of CRS, and discuss the signs and symptoms associated with CRS, including fever, chills, hypoxia, tachycardia, and hypotension. Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur at any time [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Neurologic Toxicity, including Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with neurologic toxicity, including ICANS, including confusion, depressed level of consciousness, and lethargy. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicity. Advise patients to refrain from driving, or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery, for 48 hours after completion of each of the step-up doses or if they experience new onset of neurologic toxicity symptoms until the symptoms resolve [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
LYNOZYFIC REMS
LYNOZYFIC is available only through a restricted program called the LYNOZYFIC REMS. Inform patients that they will be given a Patient Wallet Card that they should carry with them at all times and show to all of their healthcare providers. This card describes symptoms of CRS and neurologic toxicity, including ICANS which, if experienced, should prompt the patient to seek immediate medical attention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Infections
Advise patients of the risk of serious infections. Instruct patients to immediately report infection-related signs or symptoms of infection (e.g., fever, chills, weakness) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Neutropenia
Discuss the signs and symptoms associated with neutropenia and febrile neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that liver enzymes elevations may occur and that they should report symptoms that may indicate liver toxicity, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine, or jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
LYNOZYFIC™ (lin-oh-ZI-fik)
(linvoseltamab-gcpt)
injection, for intravenous useThis Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: July 2025 What is the most important information I should know about LYNOZYFIC?
LYNOZYFIC may cause serious or life-threatening side effects, including:- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) and infusion related reactions (IRR). CRS is common during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and can also be serious or life-threatening. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of CRS or IRR, including:
- fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher
- chills or shaking
- trouble breathing
- fast heartbeat
- dizziness or light-headedness
- Neurologic problems. LYNOZYFIC can cause neurologic problems that can be serious or life-threatening. Tell your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of neurologic problems, including:
- headache
- agitation, trouble staying awake, confusion or disorientation, seeing or hearing things that are not real (hallucinations)
- trouble speaking, writing, thinking, remembering things, paying attention, or understanding things
- problems walking, muscle weakness, shaking (tremors), loss of balance, or muscle spasms
- numbness and tingling (feeling like "pins and needles")
- burning, throbbing, or stabbing pain
- changes in your handwriting
- seizures
Due to the risk of CRS and neurologic problems, you will receive LYNOZYFIC on a "step-up dosing schedule" and should be hospitalized for 24 hours after the first and second "step-up" doses. - During the "step-up dosing schedule":
- For your first dose, you will receive a smaller "step-up" dose of LYNOZYFIC on Day 1 of your treatment.
- For your second dose, you will receive a larger "step-up" dose of LYNOZYFIC, which is usually given on Day 8 of your treatment.
- For your third dose, you will receive the first treatment dose of LYNOZYFIC, which is usually given on Day 15 of your treatment.
- Your healthcare provider may repeat one or both of the "step-up" doses depending on side effects or if your treatment is delayed.
- Before the "step-up" doses and the first two treatment doses of LYNOZYFIC, you will receive medicines to help reduce your risk of CRS and IRR. Your healthcare provider will decide if you need to receive medicine to help reduce your risk of side effects with future doses.
- See "How will I receive LYNOZYFIC?" for more information about how you will receive LYNOZYFIC.
- LYNOZYFIC is available only through the LYNOZYFIC Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) due to the risk of side effects of CRS and neurologic problems. You will receive a Patient Wallet Card from your healthcare provider. Carry the LYNOZYFIC Patient Wallet Card with you at all times and show it to all of your healthcare providers. The LYNOZYFIC Patient Wallet Card lists signs and symptoms of CRS and neurologic problems. Get medical help right away if you develop any of the signs and symptoms listed on the LYNOZYFIC Patient Wallet Card. You may need to be treated in a hospital.
If you have any questions about LYNOZYFIC, ask your healthcare provider.
See "What are the possible side effects of LYNOZYFIC?" below for more information about side effects.What is LYNOZYFIC?
LYNOZYFIC is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with multiple myeloma who:- have already received at least 4 treatment regimens, including a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody to treat their multiple myeloma, and
- their cancer has come back or did not respond to prior treatment.
Before receiving LYNOZYFIC, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have an infection.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. LYNOZYFIC may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think that you may be pregnant during treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
- You should use an effective form of birth control (contraception) during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after your last dose of LYNOZYFIC.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known whether LYNOZYFIC passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and for 3 months after your last dose of LYNOZYFIC.
- LYNOZYFIC will be given to you by your healthcare provider by infusion through a needle placed in a vein (intravenous infusion).
- See "What is the most important information I should know about LYNOZYFIC?" for more information about how you will receive LYNOZYFIC.
- After the "step-up dosing schedule", the treatment dose of LYNOZYFIC is usually given 1 time each week for 11 doses, and then 1 time every other week for 5 doses. After these doses and based on how your disease responds, your healthcare provider will decide if you are able to receive LYNOZYFIC less often (every 4 weeks) or will continue to have every other week treatment.
- Your healthcare provider will decide how long you will receive treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
- If you miss any appointments, call your healthcare provider as soon as possible to reschedule your appointment. It is important for you to be monitored closely for side effects during treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
What should I avoid while receiving LYNOZYFIC?
Do not drive, or operate heavy or potentially dangerous machinery, or do other dangerous activities for 48 hours after completing each of your "step-up" doses or at any time during treatment with LYNOZYFIC if you develop new neurologic symptoms, until the symptoms go away.
See "What is the most important information I should know about LYNOZYFIC?" for more information about signs and symptoms of neurologic problems.What are the possible side effects of LYNOZYFIC?
LYNOZYFIC may cause serious side effects, including:- See "What is the most important information I should know about LYNOZYFIC?"
-
Infections. LYNOZYFIC can cause bacterial, viral, or fungal infections that are serious, life-threatening, or that may lead to death. Upper respiratory tract infections and pneumonia are common during treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
- Your healthcare provider will monitor you for signs and symptoms of infection before and during treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
- Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicines for you to help prevent infections and treat you as needed if you develop an infection during treatment with LYNOZYFIC.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop any signs or symptoms of infection during treatment with LYNOZYFIC, including:
-
- fever of 100.4 °F (38 °C) or higher
- chills
- cough
- shortness of breath
-
- chest pain
- sore throat
- pain during urination
- feeling weak or generally unwell
- Decreased white blood cell counts. Decreased white blood cell counts are common during treatment with LYNOZYFIC and can also be severe. Fever can happen with low white blood cell counts and may be a sign that you have an infection. Your healthcare provider will check your blood cell counts before you start treatment and during treatment with LYNOZYFIC, and will treat you as needed.
- Liver problems. LYNOZYFIC can cause increased liver enzymes and bilirubin in your blood. These increases can happen with or without you also having CRS. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check your liver before starting and during treatment with LYNOZYFIC. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop any of the following signs or symptoms of liver problems:
- tiredness
- loss of appetite
- pain in your right upper stomach-area (abdomen)
- dark urine
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes
The most common side effects of LYNOZYFIC include: - muscle and bone pain
- cough
- diarrhea
- tiredness or weakness
- nausea
- headache
- shortness of breath
The most common severe abnormal blood test results with LYNOZYFIC include: low white blood cell counts and low red blood cell counts.
These are not all of the possible side effects of LYNOZYFIC.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about safe and effective use of LYNOZYFIC
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about LYNOZYFIC that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in LYNOZYFIC?
Active ingredient: linvoseltamab-gcpt
Inactive ingredients: histidine, L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80, sucrose, and Water for Injection.Manufactured by: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, NY 10591 U.S. License No. 1760
For more information about LYNOZYFIC, go to www.LYNOZYFIC.com or call 1-844-746-4363.
LYNOZYFIC is a trademark of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
© 2025 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
All rights reserved. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg / 2.5 mL Vial Carton
NDC: 61755-054-01
Rx onlyLYNOZYFIC™
(linvoseltamab-gcpt)
Injection5 mg / 2.5 mL (2 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion after Dilution
Single-Dose Vial. Discard unused portion.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.One 2.5 mL Vial
REGENERON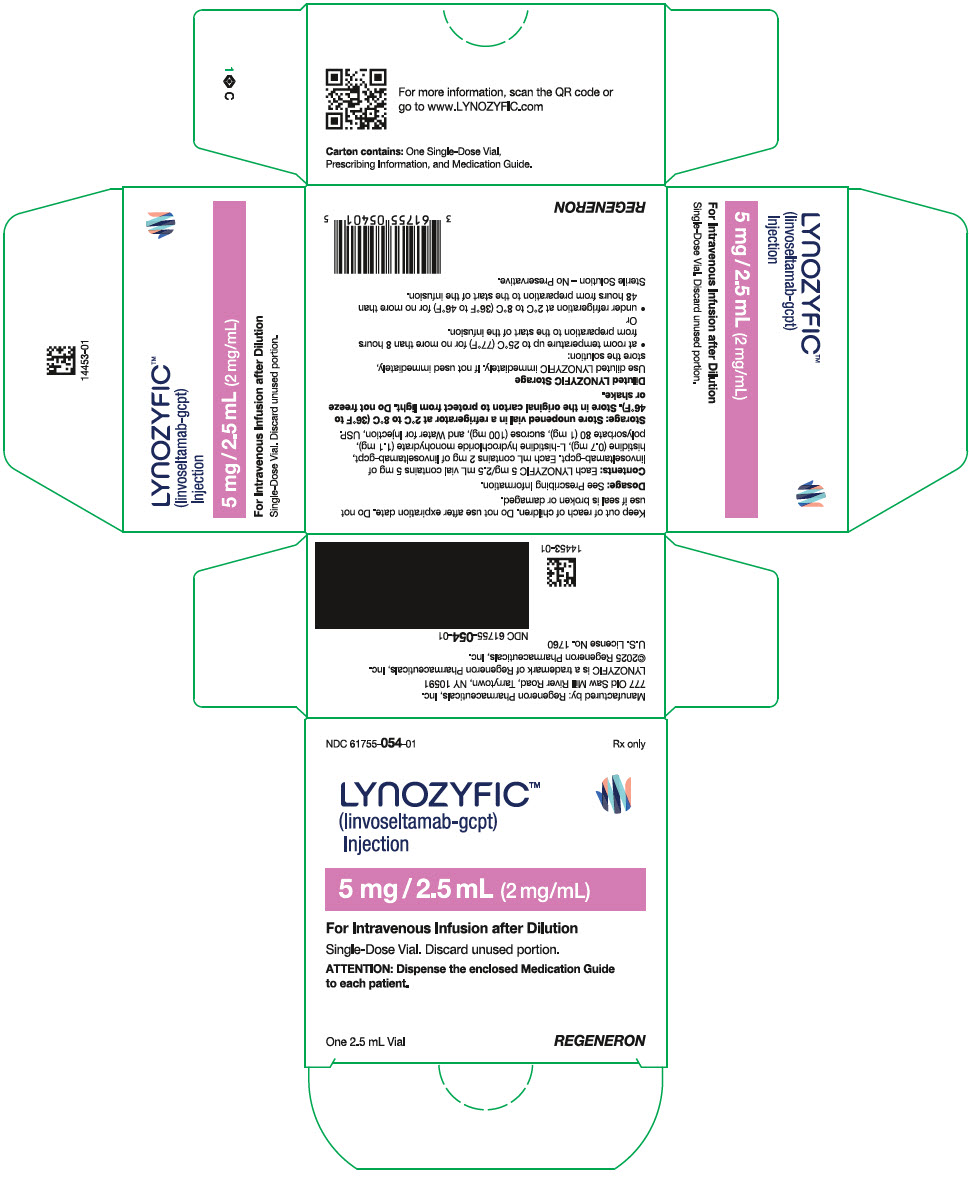
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mg / 10 mL Vial Carton
NDC: 61755-056-01
Rx onlyLYNOZYFIC™
(linvoseltamab-gcpt)
Injection200 mg / 10 mL (20 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion after Dilution
Single-Dose Vial. Discard unused portion.
ATTENTION: Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.One 10 mL Vial
REGENERON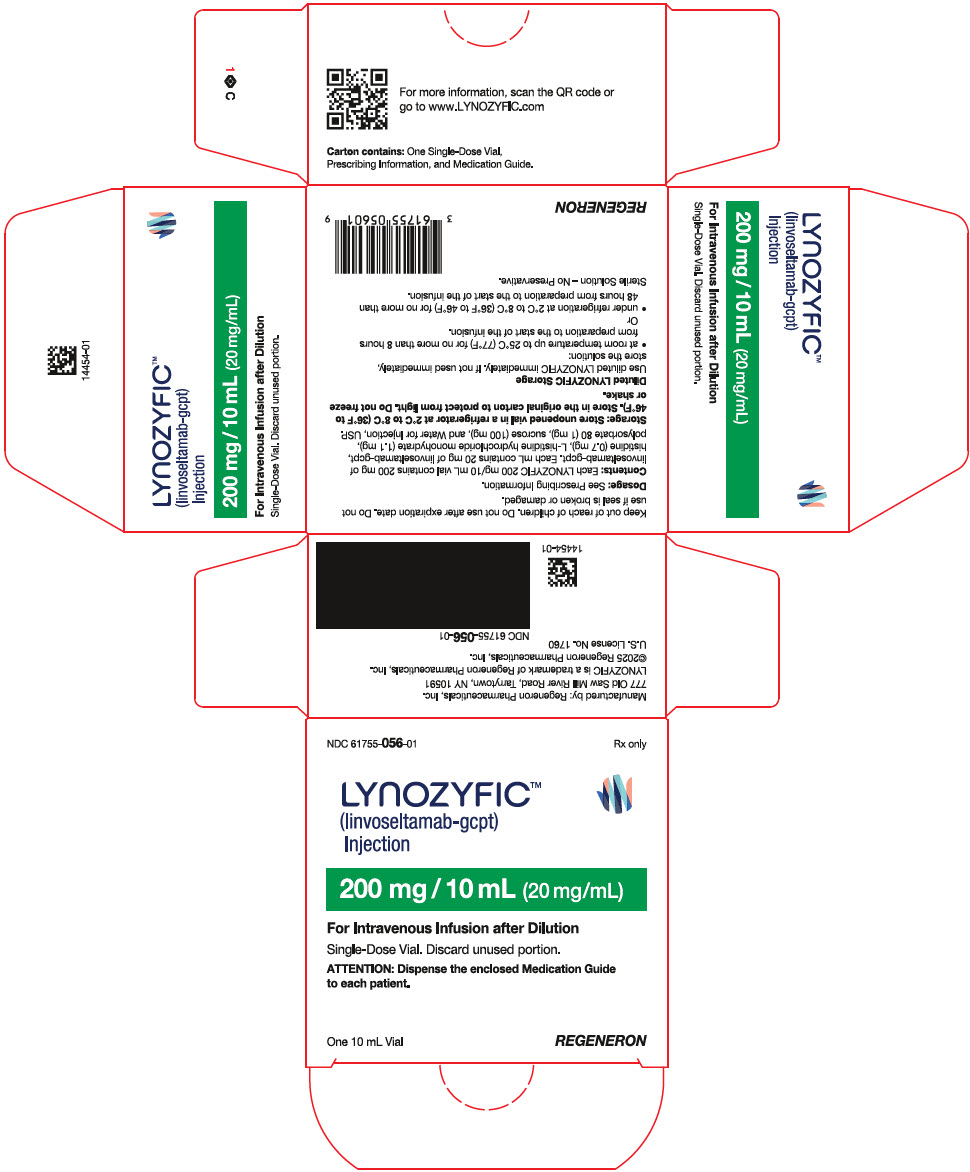
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LYNOZYFIC
linvoseltamab-gcpt injection, solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 61755-054 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LINVOSELTAMAB (UNII: M3CPC50MZS) (LINVOSELTAMAB - UNII:M3CPC50MZS) LINVOSELTAMAB 5 mg in 2.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) HISTIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: X573657P6P) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 61755-054-01 1 in 1 CARTON 07/02/2025 1 NDC: 61755-054-00 2.5 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761400 07/02/2025 LYNOZYFIC
linvoseltamab-gcpt injection, solution, concentrateProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 61755-056 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LINVOSELTAMAB (UNII: M3CPC50MZS) (LINVOSELTAMAB - UNII:M3CPC50MZS) LINVOSELTAMAB 200 mg in 10 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HISTIDINE (UNII: 4QD397987E) HISTIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: X573657P6P) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 61755-056-01 1 in 1 CARTON 07/02/2025 1 NDC: 61755-056-00 10 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761400 07/02/2025 Labeler - Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (194873139) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 945589711 API MANUFACTURE(61755-054, 61755-056) , ANALYSIS(61755-054, 61755-056)
Trademark Results [LYNOZYFIC]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 LYNOZYFIC 97771269 not registered Live/Pending |
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2023-01-27 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.