KETOCONAZOLE- ketoconazole foam aerosol, foam
Ketoconazole by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Ketoconazole by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Xiromed, LLC, Xiromed Pharma Espana, S.L., Laboratorios Liconsa SAU. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KETOCONAZOLE FOAM, 2% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KETOCONAZOLE FOAM, 2%.
KETOCONAZOLE foam,
for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1981INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ketoconazole foam, 2% is indicated for topical treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in immunocompetent patients 12 years of age and older (1).
Limitations of Use
Safety and efficacy of ketoconazole foam for treatment of fungal infections have not been established.DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Foam: 2% ketoconazole in 50 g and 100 g containers (3).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed in clinical studies (incidence > 1%) were application site burning and application site reaction (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Xiromed, LLC at 844-XIROMED (844-947-6633) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Contact Sensitization
5.2 Flammable Contents
5.3 Systemic Effects
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Dermal Safety Studies
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ketoconazole foam, 2% should be applied to the affected area(s) twice daily for four weeks.
Hold the container upright, and dispense ketoconazole foam, 2% into the cap of the can or other cool surface in an amount sufficient to cover the affected area(s). Dispensing directly onto hands is not recommended, as the foam will begin to melt immediately upon contact with warm skin. Pick up small amounts of ketoconazole foam, 2% with the fingertips, and gently massage into the affected area(s) until the foam disappears. For hair-bearing areas, part the hair, so that ketoconazole foam, 2% may be applied directly to the skin (rather than on the hair).
Avoid contact with the eyes and other mucous membranes. Ketoconazole foam, 2% is not for ophthalmic, oral or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Contact Sensitization
Ketoconazole foam, 2% may result in contact sensitization, including photoallergenicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Flammable Contents
The contents of ketoconazole foam, 2% include alcohol and propane/butane, which are flammable. Avoid fire, flame and/or smoking during and immediately following application. Do not puncture and/or incinerate the containers. Do not expose containers to heat and/or store at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
5.3 Systemic Effects
Hepatitis has been seen with orally administered ketoconazole (1:10,000 reported incidence). Lowered testosterone and ACTH–induced corticosteroid serum levels have been seen with high doses of orally administered ketoconazole. These effects have not been seen with topical ketoconazole.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug, and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. The adverse reaction information from clinical trials does, however, provide a basis for identifying the adverse reactions that appear to be related to drug use and for approximating rates.
The safety data presented in Table 1 reflect exposure to ketoconazole foam, 2% in 672 subjects, 12 years and older with seborrheic dermatitis. Subjects applied ketoconazole foam, 2% or vehicle foam twice daily for 4 weeks to affected areas on the face, scalp, and/or chest. Adverse reactions occurring in > 1% of subjects are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported by > 1% Subjects in Clinical Trials Adverse
ReactionsKetoconazole foam, 2%
N = 672
n (%)Vehicle Foam
N = 497
n (%)Subjects with an
Adverse Reaction188 (28%)
122 (25%)
Application site burning
67 (10%)
49 (10%)
Application site reaction
41 (6%)
24 (5%)
Application site reactions that were reported in < 1% of subjects were dryness, erythema, irritation, paresthesia, pruritus, rash and warmth.
6.2 Dermal Safety Studies
In a photoallergenicity study, 9 of 53 subjects (17%) had reactions during the challenge period at both the irradiated and non-irradiated sites treated with ketoconazole foam, 2%. Ketoconazole foam, 2% may cause contact sensitization.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been identified during postmarketing use of ketoconazole foam, 2%:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Cheilitis
General disorders and administration site conditions: Application site pain and application site burn
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Skin burning sensation and erythemaBecause these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on ketoconazole foam, 2% use in pregnant women to identify a drug‑associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. No reproductive studies in animals have been performed with ketoconazole foam, 2%. In animal reproduction studies with pregnant mice, rats and rabbits both embryotoxic and developmental effects (structural abnormalities) were observed following oral dosing of ketoconazole during organogenesis. Assuming equivalent systemic absorption of topical and oral ketoconazole doses and an ketoconazole foam, 2% maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 8 grams (equivalent to 160 mg ketoconazole), embryotoxic effects were observed at 0.8 to 2.4 times the MRHD and developmental effects were observed at 4.8 times the MRHD [see Data].
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
The animal multiples of human exposure calculations are based on body surface area (BSA) comparisons of oral doses administered to animals and an ketoconazole foam, 2% maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 8 grams (equivalent to 2.67 mg ketoconazole/kg/day for a 60 kg individual or 98.8 mg ketoconazole/m2/day).
Embryofetal development studies have been conducted in mice, rats and rabbits with orally administered ketoconazole. When orally administered to mice on gestational days 6 through 18 (covering the period of organogenesis), ketoconazole was embryotoxic (25 mg/kg and higher; 0.8 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) with a high incidence of resorptions, increased number of stillbirths and delayed parturition. Delays in maturation were also observed. There was no evidence of maternal toxicity or malformations at up to 50 mg/kg (1.5 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons). No treatment related developmental effects were observed at 10 mg/kg (0.3 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
In the presence of maternal toxicity in rats, orally administered ketoconazole was both embryotoxic (40 mg/kg and higher; 2.4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons), including increased resorbed fetuses and stillbirths, and teratogenic (80 mg/kg and higher; 4.8 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons), including syndactylia, oligodactylia, waved ribs and cleft palate. Additionally, 100 mg/kg (6 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) ketoconazole orally administered on a single day during gestation (gestational days 9 through 12) was embryotoxic (increased resorptions). This same oral dose given on gestation day 12, 13, 14 or 15 induced external malformations including cleft palate, micromelia and digital anomalies (brachydactyly, ectrodactyly, syndactyly).
In pregnant rabbits orally administered ketoconazole, evidence of embryotoxicity (increased resorptions) was observed at 10 mg/kg (1.2 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) and higher and an increased incidence of skeletal abnormalities was observed at 40 mg/kg (4.8 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of ketoconazole in human milk, or the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production after topical application of ketoconazole foam, 2% to women who are breastfeeding. In animal studies ketoconazole was found in milk following oral administration. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ketoconazole foam, 2% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ketoconazole foam, 2% or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
In animal fertility studies in rats and dogs, administration of oral doses of ketoconazole between 3-day and 3-month periods resulted in infertility that was reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ketoconazole foam, 2% in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
Of the 672 subjects treated with ketoconazole foam, 2% in the clinical trials, 44 (7%) were from 12 to 17 years of age. [See Clinical Studies (14)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 672 subjects treated with ketoconazole foam, 2% in the clinical trials, 107 (16%) were 65 years and over. Clinical trials of ketoconazole foam, 2% did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Ketoconazole foam, 2% contains 2% ketoconazole USP, an antifungal agent, in a thermolabile hydroethanolic foam for topical application.
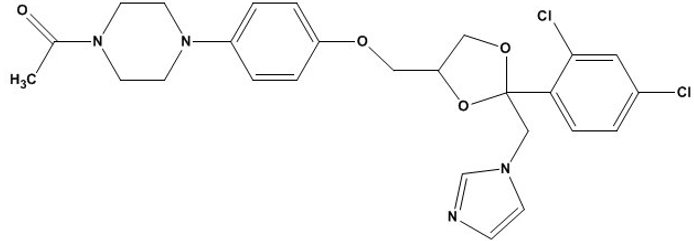
The chemical name for ketoconazole is piperazine, 1-acetyl-4-[4-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl) -2-(1H-imidazol-l-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-, cis- with the molecular formula C26H28Cl2N4O4 and a molecular weight of 531.43. The following is the chemical structure:
Ketoconazole foam, 2% contains 20 mg of ketoconazole per gram in a thermolabile hydroethanolic foam vehicle consisting of cetyl alcohol, citric acid, ethanol (denatured with tert-butyl alcohol and brucine sulfate) 58%, polysorbate 60, potassium citrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ketoconazole in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In a bioavailability study, 12 subjects with moderate to severe seborrheic dermatitis applied 3 g of ketoconazole foam, 2% twice daily for 4 weeks. Circulating plasma levels of ketoconazole were < 6 ng/mL for a majority of subjects (75%), with a maximum level of 11 ng/mL observed in one subject.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or photo-carcinogenic potential of ketoconazole foam, 2%.
In oral carcinogenicity studies in mice (18-months) and rats (24-months) at dose levels of 5, 20 and 80 mg/kg/day ketoconazole was not carcinogenic. The high dose in these studies was approximately 2.4 to 4.8 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons. In a bacterial reverse mutation assay, ketoconazole did not express any mutagenic potential. In three in vivo assays (sister chromatid exchange in humans, dominant lethal and micronucleus tests in mice), ketoconazole did not exhibit any genotoxic potential.
In animal fertility studies, oral ketoconazole impaired both male and female fertility in rats in a dose and duration dependent manner. In females, oral doses up to 40 mg/kg (2.4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) had no effect on fertility, while doses of 75 mg/kg (4.5 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) and higher decreased the pregnancy rate and number of implantation sites. In male rats, oral dosing at 200 mg/kg/day (12 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) for three days decreased fertility and 400 mg/kg/day (24 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) for three days resulted in a complete loss of fertility. When administered for longer durations (up to 3 months), decreased fertility in male rats was observed at doses as low as 24 mg/kg/day (1.4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons). In male beagle dogs, an oral dose of 25 mg/kg/day ketoconazole for up to 4 weeks (5.2 times the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) resulted in decreased sperm motility, decreased sperm count, increased abnormal sperm and atrophy of the testes. These effects were reversed subsequent to withdrawal of treatment.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of ketoconazole foam, 2% were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial in subjects 12 years and older with mild to severe seborrheic dermatitis. In the trial, 427 subjects received ketoconazole foam, 2% and 420 subjects received vehicle foam. Subjects applied ketoconazole foam, 2% or vehicle foam twice daily for 4 weeks to affected areas on the face, scalp, and/or chest. The overall disease severity in terms of erythema, scaling, and induration was assessed at Baseline and week 4 on a 5-point Investigator’s Static Global Assessment (ISGA) scale.
Treatment success was defined as achieving a Week 4 (end of treatment) ISGA score of 0 (clear) or 1 (majority of lesions have individual scores for scaling, erythema, and induration that averages 1 [minimal or faint]) and at least two grades of improvement from baseline. The results are presented in Table 2. The database was not large enough to assess whether there were differences in effects in age, gender, or race subgroups.
Table 2: Efficacy Results Number of Subjects
Ketoconazole foam, 2%
N = 427
n (%)Vehicle Foam
N = 420
n (%)Subjects Achieving
Treatment Success
239 (56%)
176 (42%) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ketoconazole foam, 2% contains 20 mg of ketoconazole, USP per gram. The thermolabile hydroethanolic foam is available as follows:
NDC: 70700-160-19
50 g aluminum canNDC: 70700-160-20
100 g aluminum canStore at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Do not store under refrigerated conditions.Contents are flammable. Do not expose containers to heat and/or store at temperatures above 49°C (120°F). Do not store in direct sunlight.
Contents under pressure. Do not puncture and/or incinerate container.
Keep out of reach of children.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Package Insert).
Instruct patients on a proper use of ketoconazole foam, 2%
- Avoid fire, flame and/or smoking during and immediately following application.
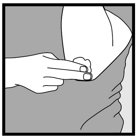
- Do not apply ketoconazole foam, 2% directly to hands. Dispense onto a cool surface, and apply to the affected areas using the fingertips.
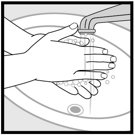
- Wash their hands after application
- Ketoconazole foam, 2% may cause skin irritation (application site burning and/or reactions)
- Instruct a patient to contact a health care provider if the area of application shows signs of increased irritation and report any signs of adverse reactions.
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
Ketoconazole (kee” toe kon’ a zole)
Foam, 2%Important Information: Ketoconazole foam, 2% is for use on the skin only. Do not use ketoconazole foam, 2% in your eyes, mouth or vagina.
What is ketoconazole foam, 2%?
Ketoconazole foam, 2% is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat seborrheic dermatitis in people 12 years of age and older with a normal immune system.
It is not known if ketoconazole foam, 2% is safe and effective when used to treat fungal infections.
It is not known if ketoconazole foam, 2% is safe and effective in children less than 12 years of age.
Before using ketoconazole foam, 2%, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ketoconazole foam, 2% will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ketoconazole foam, 2% passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with ketoconazole foam, 2%.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use ketoconazole foam, 2%?
- Use ketoconazole foam, 2% exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.See the detailed “Instructions for Use” at the end of this leaflet for directions about how to apply ketoconazole foam, 2% the right way.
- Apply ketoconazole foam, 2% to the affected skin area(s) 2 times each day for 4 weeks. You should apply enough ketoconazole foam, 2% to cover the entire affected area(s).
- Talk to your healthcare provider if your skin does not improve after 4 weeks of treatment with ketoconazole foam, 2%.
- Dispense ketoconazole foam, 2% directly into the cap. Do not dispense ketoconazole foam, 2% directly onto your hands, because the foam will begin to melt on contact with warm skin.
- Wash your hands after applying ketoconazole foam, 2%.
What should I avoid while using ketoconazole foam, 2%?
- Ketoconazole foam, 2% is flammable. Avoid fire, flames, or smoking during and right after you apply ketoconazole foam, 2% to your skin.
- Avoid getting ketoconazole foam, 2% in or near your eyes, mouth, lips or vagina. If you get ketoconazole foam, 2% on your lips or in your eyes, mouth or vagina, rinse well with water.
What are the possible side effects of ketoconazole foam, 2%?
Ketoconazole foam, 2% may cause serious side effects, including:
- Skin irritation at the application area(s), including skin reactions caused by exposure to light. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop skin irritation during treatment with ketoconazole foam, 2%.
The most common side effects of ketoconazole foam, 2% include, burning, dryness, redness, irritation, numbness, itching, rash and warmth at the application site.
These are not all of the possible side effects of ketoconazole foam, 2%.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ketoconazole foam, 2%?
- Store ketoconazole foam, 2% at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not store the ketoconazole foam, 2% can in the refrigerator or freezer.
- Keep ketoconazole foam, 2% away from heat. Never throw the ketoconazole foam, 2% can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
- Do not store ketoconazole foam, 2% at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
- Do not break through (puncture) the ketoconazole foam, 2% can.
Keep ketoconazole foam, 2% and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of ketoconazole foam, 2%.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ketoconazole foam, 2% for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ketoconazole foam, 2% to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ketoconazole foam, 2% that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in ketoconazole foam, 2%?
Active ingredient: ketoconazole
Inactive ingredients: cetyl alcohol, citric acid, ethanol (denatured with tert-butyl alcohol and brucine sulfate) 58%, polysorbate 60, potassium citrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant
Manufactured for:
Xiromed, LLC.
Florham Park, NJ 07932
Manufactured by:
Laboratorios Liconsa SAU
Azuqueca de Henares, Guadalajara, 19200, SpainFor more information, call Xiromed, LLC at 844-XIROMED (844-947-6633) or visit www.XIROMED.com.
This Patient Information leaflet has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 04/2020
Instructions for Use
Ketoconazole (kee” toe kon’ a zole)
Foam, 2%Important Information: Ketoconazole foam, 2% is for use on the skin only. Do not use ketoconazole foam, 2% in your eyes, mouth or vagina.
How should I store ketoconazole foam, 2%?
- Store ketoconazole foam, 2% at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not store the ketoconazole foam, 2% can in the refrigerator or freezer.
- Keep ketoconazole foam, 2% away from heat. Never throw the can into a fire, even if the can is empty.
- Do not store ketoconazole foam, 2% at temperatures above 120°F (49°C).
- Do not break through (puncture) the ketoconazole foam, 2% can.
Keep ketoconazole foam, 2% and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
01/2021
Manufactured for:
Xiromed, LLC.
Florham Park, NJ 07932Manufactured by:
Laboratorios Liconsa SAU
Azuqueca de Henares, Guadalajara, 19200, SpainPI160-00
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
KETOCONAZOLE
ketoconazole foam aerosol, foamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70700-160 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength KETOCONAZOLE (UNII: R9400W927I) (KETOCONAZOLE - UNII:R9400W927I) KETOCONAZOLE 20 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CETYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 936JST6JCN) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) POLYSORBATE 60 (UNII: CAL22UVI4M) POTASSIUM CITRATE (UNII: EE90ONI6FF) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) STEARYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 2KR89I4H1Y) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70700-160-19 50 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2021 2 NDC: 70700-160-20 100 g in 1 CAN; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/21/2021 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA213601 05/21/2021 Labeler - Xiromed, LLC (080228637) Registrant - Xiromed Pharma Espana, S.L. (468835741) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Laboratorios Liconsa SAU 471409309 manufacture(70700-160)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.