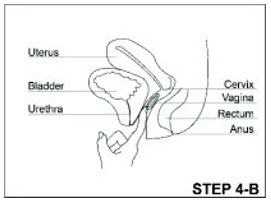
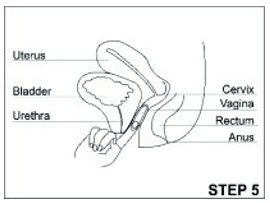
ANNOVERA- segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol ring
Annovera by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Annovera by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mayne Pharma, Sever Pharma Solutions AB, Sharp Packaging Services, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ANNOVERA safely and effectively.
See Full Prescribing Information for ANNOVERA
ANNOVERA® (segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system)
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions (5.11) 04/2022 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One ANNOVERA is inserted in the vagina. The vaginal system must remain in place continuously for 3 weeks (21 days) followed by a 1-week (7-day) vaginal system-free interval. One vaginal system provides contraception for thirteen 28-day cycles (1 year). (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ANNOVERA is a silicone elastomer vaginal system containing 103 mg segesterone acetate (SA) and 17.4 mg ethinyl estradiol (EE), which releases on average 0.15 mg/day of segesterone acetate and 0.013 mg/day of ethinyl estradiol. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases (4)
- Breast cancer (4)
- Liver tumors, acute hepatitis, or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis (4)
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding (4)
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of ANNOVERA (4)
- Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Thrombotic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems: Stop ANNOVERA if a thrombotic or thromboembolic event occurs. Stop ANNOVERA at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery. Start ANNOVERA no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery, in females who are not breastfeeding. Consider cardiovascular risk factors before initiating in all females, particularly those over 35 years. (5.1, 5.5)
- Liver Disease: Discontinue if jaundice occurs. (5.2)
- Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment: Stop ANNOVERA prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir. ANNOVERA can be restarted 2 weeks following completion of this regimen. (5.3)
- Hypertension: Do not prescribe ANNOVERA for females with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease. If used in females with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure and stop use if blood pressure rises significantly. (5.4)
- Carbohydrate and lipid metabolic effects: Monitor glucose in pre-diabetic and diabetic females taking ANNOVERA. Consider an alternate contraceptive method for females with uncontrolled dyslipidemias. (5.7)
- Headache: Evaluate significant change in headaches and discontinue ANNOVERA if indicated. (5.8)
- Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea: May cause irregular bleeding or amenorrhea. Evaluate for other causes if irregular bleeding or amenorrhea persists. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (>5%) are headache/migraine, nausea/vomiting, vulvovaginal mycotic infection/candidiasis, abdominal pain lower/upper, dysmenorrhea, vaginal discharge, urinary tract infection, breast tenderness/pain/discomfort, bleeding irregularities including metrorrhagia, diarrhea, genital pruritus. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mayne Pharma at 1-844-825-8500 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4, may decrease the effectiveness of ANNOVERA or increase breakthrough bleeding. Counsel patients to use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when enzyme inducers are used with ANNOVERA. (7.1)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 How to Use ANNOVERA
2.2 How to Start ANNOVERA
2.3 Deviations from the Recommended Regimen
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Conditions
5.2 Liver Disease
5.3 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
5.4 Hypertension
5.5 Age-Related Considerations
5.6 Gallbladder Disease
5.7 Adverse Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
5.8 Headache
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
5.10 Depression
5.11 Malignant Neoplasms
5.12 Effect on Binding Globulins
5.13 Hereditary Angioedema
5.14 Chloasma
5.15 Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
5.16 Vaginal Use
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Hormonal Contraceptives
7.2 Effects of Combined Hormonal Contraceptives on Other Drugs
7.3 Use of Vaginal Products with ANNOVERA
7.4 Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
7.5 Interference with Laboratory Tests
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
8.8 Body Mass Index (BMI)/Body Weight
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage Conditions
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combination hormonal contraceptive (CHC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in females over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, CHC should not be used by females who are over 35 years of age and smoke. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 How to Use ANNOVERA
Instruct patients that ANNOVERA should be used as directed [see How to Start ANNOVERA (2.2)]. One ANNOVERA should be placed in the vagina. For maximum contraceptive effectiveness, ANNOVERA is to remain in the vagina continuously for 21 days (3 complete weeks). It is removed for a 1-week dose-free interval, and during this time a withdrawal bleed usually occurs. The removed vaginal system should be cleaned with mild soap and warm water, patted dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel, and placed in its case during the 1-week dose- free interval. At the end of the dose-free interval, the vaginal system should be cleaned prior to being placed back in the vagina for another 21 continuous days (3 complete weeks). This pattern of ANNOVERA use made up of 3-weeks in and 1-week out is a cycle of use; one ANNOVERA vaginal system will provide contraception for 13 cycles.
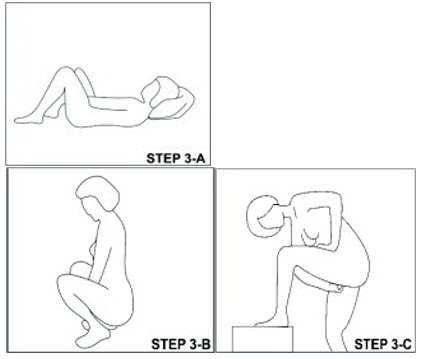
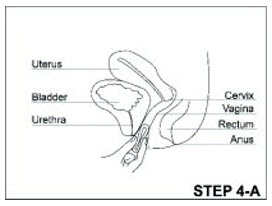
With clean hands, the user can choose an insertion position that is comfortable, such as lying down, squatting, or standing. The sides of the vaginal system are pressed together for insertion into the vagina. When properly inserted, the vaginal system should be entirely in the vagina and behind the pelvic bone. The day and time of insertion should be noted so that the vaginal system can be removed 3 weeks later on the same day and at about the same time.
ANNOVERA can be removed by hooking an index finger into the vaginal system inside the vagina and gently pulling the vaginal system.
For patient instructions regarding cleaning the vaginal system, see FDA-approved Patient Information.
2.2 How to Start ANNOVERA
IMPORTANT: Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to the first use of ANNOVERA.
No Hormonal Contraceptive Use in the Preceding Cycle and after Copper IUD Removal:
The woman should insert ANNOVERA between days 2 and 5 of her regular menstrual bleeding; no back-up contraception is needed. If menstrual cycles are irregular or if the start is more than 5 days from the last menstrual bleeding, the woman should use an additional barrier method during coitus, such as a male condom or spermicide, for the first 7 days of ANNOVERA use.
Switching from a CHC:
A woman who has been using her CHC method consistently and correctly, and who you are reasonably certain is not already pregnant, may switch from her previous CHC to ANNOVERA on any day of the CHC cycle (Day 1-28), without the need for back-up contraception, but no more than 7 hormone-free days should occur before starting ANNOVERA.
Switching from a Progestin-Only Method [Progestin-only pills (POP), Progestin Injection, Progestin Implant, Progestin Intrauterine System (IUS)]:
If a woman has no contraindications to the use of ethinyl estradiol (EE), she may elect to switch from a progestin-only method to ANNOVERA. If switching from progestin-only pills, she should begin ANNOVERA at the time she would have taken her next POP pill. If switching from an injection, she should begin ANNOVERA at the time of her next scheduled injection. If switching from an implant or an IUS, she should begin ANNOVERA at the time of implant or IUS removal. In all of these cases, the woman should use an additional barrier method during coitus, such as a male condom or spermicide, for the first 7 days of ANNOVERA use.
Use after Abortion or Miscarriage:
If a woman has no contraindications to the use of EE, ANNOVERA may be initiated for contraception within the first 5 days following a complete first trimester abortion or miscarriage without additional back-up contraception. If more than 5 days have elapsed from the first trimester abortion or miscarriage, then follow the instructions for "No Hormonal Contraceptive Use in the Preceding Cycle" and a barrier method should be used from the time of the first trimester abortion or miscarriage to the initiation of ANNOVERA.
ANNOVERA should not be started earlier than 4 weeks after a second trimester abortion or miscarriage due to the increased risk of thromboembolism [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Following Childbirth:
ANNOVERA should not be started sooner than 4 weeks postpartum and only in females who choose not to breastfeed. Prior to 4 weeks postpartum there is an increased risk of thromboembolism [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The initiation of ANNOVERA 4 weeks or more postpartum should be accompanied by an additional method of contraception during coitus, such as male condoms or spermicide, for the first 7 days if the woman has not yet had a period. Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception occurring prior to initiating ANNOVERA.
Females who are breastfeeding should not use ANNOVERA until after weaning.
2.3 Deviations from the Recommended Regimen
Contraceptive efficacy of ANNOVERA may be reduced if a woman deviates from the recommended use. ANNOVERA should remain in the vagina for a continuous period of 21 days (3 weeks); then ANNOVERA should be taken out of the vagina for 7 days. In a 28-day cycle, a deviation that involves ANNOVERA being out of the vagina for less than 7 days will not increase pregnancy risk. In a 28-day cycle, a deviation that involves ANNOVERA being out of the vagina for more than 7 days will increase pregnancy risk and back-up contraception is recommended in these instances. Deviations from the recommended regimen may result in a new vaginal system change day [See FDA- approved Patient Information].
Inadvertent Removal or Expulsion
ANNOVERA can be accidently expelled. Accidental expulsion could occur while removing a tampon, during coitus, or with straining during a bowel movement. If the vaginal system is accidentally expelled once during the 21 days of intravaginal use and is replaced within 2 hours, contraceptive efficacy should not be reduced and no back-up contraception is needed. If the vaginal system is accidently expelled, wash it with mild soap and warm water, rinse and pat dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel, and replace it as soon as possible.
During the 21 days of continuous use, if ANNOVERA is out of the vagina for more than 2 continuous hours or more than 2 cumulative hours (multiple inadvertent removals or expulsions adding up to 2 hours), then back-up contraception, such as male condoms or spermicide, should be used until the vaginal system has been in the vagina for 7 consecutive days. The use of combined hormonal contraceptives (those containing an estrogen) for emergency contraception during use of ANNOVERA is not recommended.
Prolonged Vaginal System Free Interval
If the vaginal system free interval is prolonged, consider the possibility of pregnancy and have the woman use back-up contraception, such as male condoms or spermicide, during coitus until the vaginal system has been in the vagina for 7 consecutive days. The use of combined hormonal contraceptives (those containing an estrogen) for emergency contraception during use of ANNOVERA is not recommended.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Vaginal system: Each ANNOVERA releases an approximate average 0.15 mg/day of segesterone acetate (SA) and 0.013 mg/day of ethinyl estradiol (EE) when placed in the vagina over a period of 21 days of each cycle for up to 13 cycles (total of 273 days). Each cycle of use is 28 days with 21 days in and 7 days out.
ANNOVERA (segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system) is a toroidal- shaped (ring), nonbiodegradable, flexible, opaque white, contraceptive vaginal system containing 103 mg of SA and 17.4 mg EE.
ANNOVERA is 56 mm in overall diameter and 8.4 mm in cross-sectional diameter. It contains 2 channels of approximately 3.0 mm diameter and 27 mm length into which steroid-containing cores are inserted. The cores are 3 mm in diameter with one releasing SA alone and the other releasing both SA and EE.
Each ANNOVERA is designed to be used for up to 13 cycles (1 year).
ANNOVERA is not made with natural rubber latex.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include females who are known to:
- - Smoke, if over age 35 [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have current or history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have cerebrovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- - Have uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- - Have diabetes mellitus and are over age 35, diabetes mellitus with hypertension or vascular disease, or other end-organ damage, or diabetes mellitus of >20 years duration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), (5.7)].
- - Have headaches with focal neurological symptoms, migraine headaches with aura, or are over age 35 with any migraine headaches [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
- Liver tumors, acute hepatitis, or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of ANNOVERA. Hypersensitivity reactions reported include: throat constriction, facial edema, urticaria, hives, and wheezing [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- Use of Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for alanine transaminase (ALT) elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- A high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic diseases. Examples include females who are known to:
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Conditions
Females are at increased risk for a venous thrombotic event (VTE) when using ANNOVERA. Limited data are available in females with a BMI >29.0 kg/m2 because this subpopulation was excluded from the clinical trials after VTEs were reported.
- Stop ANNOVERA if an arterial or deep venous thrombotic event occurs.
- Stop ANNOVERA if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
- Discontinue ANNOVERA during prolonged immobilization. If feasible, stop ANNOVERA at least 4 weeks before and through 2 weeks after major surgery or other surgeries known to have an elevated risk of VTE.
- Start ANNOVERA no earlier than 4 weeks after delivery in females who are not breastfeeding. The risk of postpartum VTE decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the risk of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
- Before starting ANNOVERA, evaluate any past medical history or family history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and consider whether the history suggests an inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathy. ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females with a high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases [see Contraindications (4)].
Arterial Events
CHCs increase the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. The risk is greater among older females (>35 years of age), smokers, and females with hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity.
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females over 35 years of age who smoke [see Contraindications (4)]. Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from CHC use. This risk increases with age, particularly in females over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked.
Venous Events
The use of CHCs increases the risk of VTE, such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Risk factors for VTEs include smoking, obesity, and family history of VTE, in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs [see Contraindications (4)]. While the increased risk of VTE associated with use of CHCs is well established, the rates of VTE are even greater during pregnancy, and especially during the postpartum period (see Figure 1). The rate of VTE in females using CHCs has been estimated to be 3–12 cases per 10,000 woman-years.
The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of CHC use and when restarting hormonal contraception following a break of 4 weeks or longer. The risk of VTE due to CHCs gradually disappears after use is discontinued.
Figure 1 shows the risk of developing a VTE for females who are not pregnant and do not use CHCs, for females who use CHCs, for pregnant females, and for females in the postpartum period. To put the risk of developing a VTE into perspective: If 10,000 females who are not pregnant and do not use CHCs are followed for 1 year, between 1 and 5 of these women will develop a VTE.
Figure 1: Likelihood of Developing a VTE
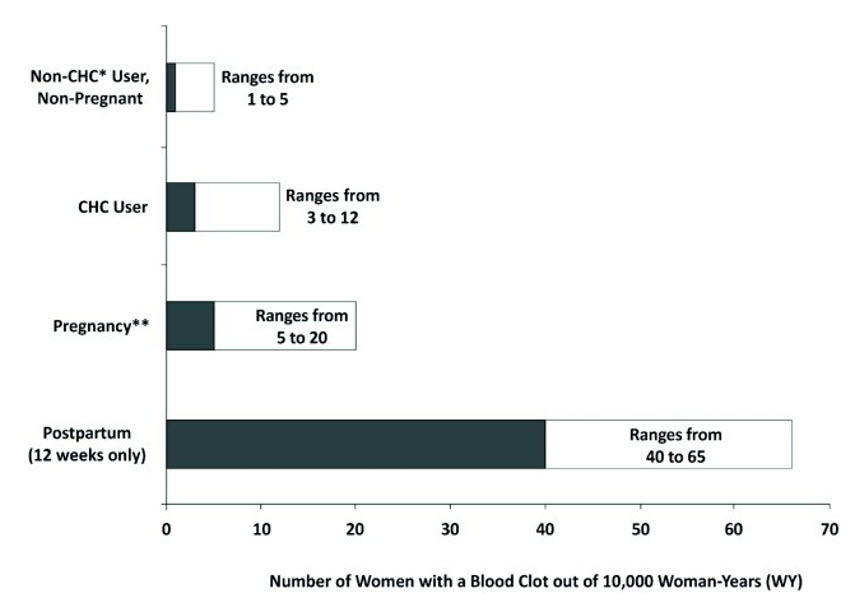
* CHC = combination hormonal contraception
** Pregnancy data based on actual duration of pregnancy in the reference studies. Based on a model assumption that pregnancy duration is 9 months, the rate is 7 to 27 per 10,000 WY.5.2 Liver Disease
Impaired Liver Function
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females with acute hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis of the liver [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue ANNOVERA if jaundice develops. Acute liver test abnormalities may necessitate the discontinuation of ANNOVERA use until the liver tests return to normal and ANNOVERA causation has been excluded.
Liver Tumors
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females with benign or malignant liver tumors [see Contraindications (4)]. Hepatic adenomas are associated with CHC use. An estimate of the attributable risk is 3.3 cases/100,000 CHC users. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long- term (>8 years) CHC users. The attributable risk of liver cancers in CHC users is less than one case per million users.
5.3 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with and without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in females using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications, such as ANNOVERA. Discontinue ANNOVERA prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir [see Contraindications (4)]. ANNOVERA can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen.
5.4 Hypertension
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Contraindications (4)]. For all females, including those with well- controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure at routine visits and stop ANNOVERA if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females using CHCs, and this increase is more likely in older females and with extended duration of use. The effect of CHCs on blood pressure may vary according to the progestin in the CHC.
5.5 Age-Related Considerations
The risk for cardiovascular disease and prevalence of risk factors for cardiovascular disease increase with age. Certain conditions, such as smoking and migraine headache without aura, that do not contraindicate CHC use in younger females, are contraindications to use in women over 35 years of age [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Consider the presence of underlying risk factors that may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease or VTE, particularly before initiating ANNOVERA for women over 35 years, such as:
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Dyslipidemia
- Obesity
5.6 Gallbladder Disease
Studies suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among CHC users. Use of CHCs may also worsen existing gallbladder disease.
A past history of CHC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent CHC use. Females with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for CHC- related cholestasis.
5.7 Adverse Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Hyperglycemia
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in diabetic females over age 35, or females who have diabetes with hypertension, nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, other vascular disease, or females with diabetes of >20 years duration [see Contraindications (4)]. ANNOVERA may decrease glucose tolerance. Carefully monitor prediabetic and diabetic females who are taking ANNOVERA.
5.8 Headache
ANNOVERA is contraindicated in females who have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or have migraine headaches with aura, and in females over age 35 years who have migraine headaches with or without aura [see Contraindications (4)].
If a woman taking ANNOVERA develops new headaches that are recurrent, persistent, or severe, evaluate the cause and discontinue ANNOVERA if indicated.
Consider discontinuation of ANNOVERA in the case of increased frequency or severity of migraine during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event) [see Contraindications (4)].
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
Bleeding and/or spotting that occurs at any time while the vaginal system is inserted is considered "unscheduled" bleeding/spotting. Bleeding/spotting that occurs during the dose-free week when the vaginal system is out is considered "scheduled" bleeding.
Unscheduled and Scheduled Bleeding and Spotting
Females using ANNOVERA may experience unscheduled (breakthrough) bleeding and spotting, especially during the first month of use. If unscheduled bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles on ANNOVERA, check for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy. If pathology and pregnancy are excluded, bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or with a change to a different CHC.
Based on subject diaries from the two clinical efficacy trials of ANNOVERA [see Clinical Trial Experience (6.1)], 5–10% of females experienced unscheduled bleeding per 28-day cycle. The average number of days with unscheduled bleeding and/or spotting, in Treatment Cycles 1 to 13 for those females who experienced unscheduled bleeding and/or spotting, was 1 day or less per cycle. A total of 41 subjects (1.7%) discontinued use due to menstrual disorders including metrorrhagia, menorrhagia, and abnormal withdrawal bleeding.
Amenorrhea and Oligomenorrhea
Females who are not pregnant and use ANNOVERA may experience amenorrhea. Based on subject diary data from two clinical trials for up to 13 cycles, amenorrhea occurred in 3–5% of females per cycle using ANNOVERA and in 0.9% of females in all 13 cycles.
If scheduled bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (removed vaginal system for >2 hours during the first 21 days or does not replace after 7 days of vaginal system- free period), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and perform a pregnancy test. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule and misses 2 consecutive periods, perform a pregnancy test to rule out pregnancy.
Some females may experience amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea after stopping ANNOVERA, especially when such a condition was pre-existent.
5.10 Depression
Carefully observe females with a history of depression and discontinue ANNOVERA if depression recurs to a serious degree. Data on the association of CHCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited.
5.11 Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
Annovera is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use [see Postmarketing Experience (6.2)].
5.12 Effect on Binding Globulins
The estrogen component of ANNOVERA may raise the serum concentrations of thyroxine- binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. The dose of replacement thyroid hormone or cortisol therapy may need to be increased.
5.13 Hereditary Angioedema
In females with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of angioedema.
5.14 Chloasma
Chloasma may occur with ANNOVERA use, especially in females with a history of chloasma gravidarum. Advise females who tend to develop chloasma to avoid exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation while using ANNOVERA.
5.15 Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Cases of TSS have been reported by vaginal ring users. TSS has been associated with tampons and certain barrier contraceptives, and in some TSS cases ring users were also using tampons. Causal relationship between the use of a vaginal ring and TSS has not been established. No cases of TSS occurred in clinical trials with ANNOVERA. If a patient exhibits signs or symptoms of TSS, consider the possibility of this diagnosis, remove ANNOVERA, and initiate appropriate medical evaluation and treatment.
5.16 Vaginal Use
Some females are aware of the vaginal system on occasion during the 21 days of use or during coitus, and partners may feel the vaginal system during coitus.
There is no information on the concomitant use of ANNOVERA with diaphragms, cervical caps, and female condoms.
ANNOVERA may not be suitable for females with conditions that make the vagina more susceptible to vaginal irritation or ulceration. Vaginal and cervical erosion and/or ulceration has been reported in females using other contraceptive vaginal devices. In some cases, the ring adhered to vaginal tissue, which necessitated removal by a healthcare provider.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events and stroke [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vascular events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The clinical trials that evaluated the safety of ANNOVERA were obtained from three 13- cycle trials. One trial was conducted entirely in the U.S. (15 sites), and the other two were global studies that included 5 U.S. sites and 7 international sites (Australia, Brazil, Chile, Dominican Republic, Finland, Hungary, Sweden). All three trials were open label and enrolled healthy females, desiring contraception, 18 to 40 years of age. At about 50% enrollment, females with BMI >29 kg/m2 were excluded due to the occurrence of two VTEs in this subgroup. In total, 2,308 females contributed 21,590 cycles of exposure for safety evaluation and 999 completed 13 cycles; there were 209 subjects with BMI >29 kg/m2 who contributed 1,254 cycles of exposure with 36 subjects completing 13 cycles. The demographic profile for subjects was: mean age 26.7 years, mean BMI 24.1 (16.0- 41.5) kg/m2; 67% were from the U.S. The racial distribution was 71% Caucasian, 14% African American, 4% Asian, and 11% Other; 30% of the population was Hispanic.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 1 summarizes the most common adverse reactions reported by females using ANNOVERA. This table shows adverse reactions reported in at least 5% of subjects. In addition, 25% of subjects reported at least 1 complete expulsion during their use of ANNOVERA.
Table 1: Adverse Drug Reactions Reported by ≥ 5% of ANNOVERA-treated Subjects Adverse Reactions %
(N=2,308)Headache, including migraine 38.6 Nausea/vomiting 25.0 Vulvovaginal mycotic infection/vaginal candidiasis 14.5 Abdominal pain/lower/upper 13.3 Dysmenorrhea 12.5 Vaginal discharge 11.8 UTI/cystitis/pyelonephritis/genitourinary tract infection 10.0 Breast pain/tenderness/discomfort 9.5 Metrorrhagia/menstrual disorder 7.5 Diarrhea 7.2 Genital pruritus 5.5 Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
Among subjects using ANNOVERA for contraception, 12% discontinued from the clinical trials due to an adverse reaction. Table 2 summarizes the most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation. In addition, 1.4% of subjects discontinued ANNOVERA use due to vaginal system expulsions.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation by ≥ 1% of ANNOVERA treated Subjects Adverse Reactions %
(N=2,308)Metrorrhagia/menorrhagia 1.7 Headache, including migraine 1.3 Vaginal discharge/vulvovaginal mycotic infections 1.3 Nausea/vomiting 1.2 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 2).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 2). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 - 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.
Figure 2: Relevant Studies of Risk of Breast Cancer with Combined Oral Contraceptives
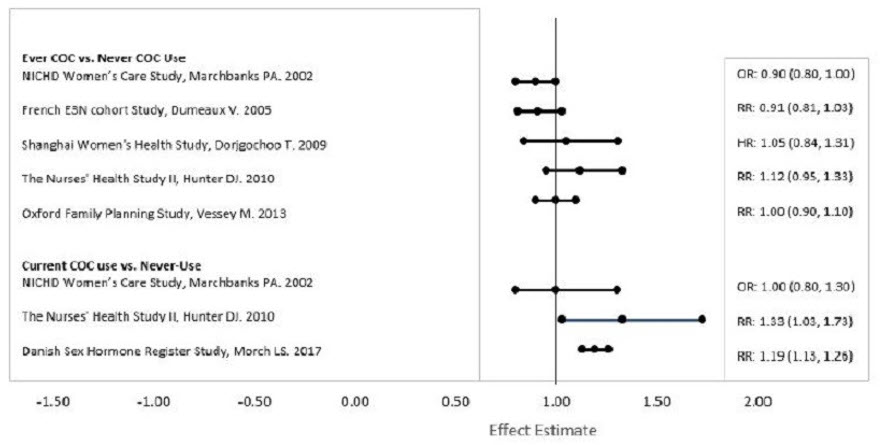
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. "ever COC" are females with current or past COC use; "never COC use" are females who never used COCs.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The sections below provide information on substances for which data on drug interactions with CHCs are available. There is little information available about the clinical effect of most drug interactions that may affect ANNOVERA. However, based on the known pharmacokinetic effects of these drugs, clinical strategies to minimize any potential adverse effect on contraceptive effectiveness or safety are suggested.
Consult the approved product labeling of all concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with ANNOVERA or the potential for metabolic enzyme or transporter system alterations.
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Hormonal Contraceptives
Substances Decreasing the Systemic Exposure of CHCs and Potentially Diminishing the Efficacy of ANNOVERA: Table 3 includes substances that demonstrated an important drug interaction with CHCs.
Table 3: Significant Drug Interactions Involving Substances That Decrease Systemic Exposure of CHCs - * Induction potency of St. John's wort may vary widely based on preparation.
Metabolic Enzyme Inducers Clinical effect - Concomitant use of CHCs with metabolic enzyme inducers may decrease the systemic concentrations of the estrogen and/or progestin component of CHCs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Decreased exposure of the estrogen and/or progestin component of CHCs may potentially diminish the effectiveness of CHCs and may lead to contraceptive failure or an increase in breakthrough bleeding.
Prevention or management - Counsel females to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method when enzyme inducers are used with CHCs.
- Continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the enzyme inducer to maintain contraceptive reliability.
Examples Aprepitant, barbiturates, bosentan, carbamazepine, efavirenz, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, rifampin, rifabutin, rufinamide, topiramate, products containing St. John's wort*, and certain protease inhibitors (see separate section on protease inhibitors below). Substances Increasing the Systemic Exposure of CHCs and Potentially Increasing Exposure to Estrogen and/or Progestin in ANNOVERA: Co- administration of atorvastatin or rosuvastatin and certain CHCs containing EE increase systemic exposure of EE by approximately 20–25%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase plasma EE concentrations, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, or ketoconazole may increase systemic exposure of the estrogen and/or progestin component of ANNOVERA.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)/ Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Protease Inhibitors and Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: Significant decreases in systemic exposure of estrogen and/or progestin have been noted when CHCs are co-administered with some HIV protease inhibitors (eg, nelfinavir, ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, (fos)amprenavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, and tipranavir/ritonavir), some HCV protease inhibitors (eg, boceprevir and telaprevir), and some non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (eg, nevirapine).
In contrast, significant increases in systemic exposure of estrogen and/or progestin have been noted when CHCs are co-administered with certain other HIV protease inhibitors (eg, indinavir and atazanavir/ritonavir) and with other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (eg, etravirine).
7.2 Effects of Combined Hormonal Contraceptives on Other Drugs
Table 4 provides significant drug interaction information for drugs co-administered with CHCs.
Table 4: Significant Drug Interaction Information for Drugs Co-Administered with CHCs Lamotrigine Clinical effect Concomitant use of CHCs with lamotrigine may significantly decrease systemic exposure of lamotrigine due to induction of lamotrigine glucuronidation. Prevention or management Dose adjustment for lamotrigine may be necessary. Consult the approved product labeling for lamotrigine. Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy or Corticosteroid Replacement Therapy Clinical effect Concomitant use of CHCs with thyroid hormone replacement therapy or corticosteroid replacement therapy may increase systemic exposure of thyroid-binding and cortisol-binding globulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. Prevention or management The dose of replacement thyroid hormone or cortisol therapy may need to be increased. Consult the approved product labeling for the therapy in use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. Other Drugs Clinical effect Concomitant use of CHCs may decrease systemic exposure of acetaminophen, morphine, salicylic acid, and temazepam. Concomitant use with ethinyl estradiol-containing CHCs may increase systemic exposure of other drugs (eg, cyclosporine, prednisolone, theophylline, tizanidine, and voriconazole). Prevention or management The dosage of drugs that can be affected by this interaction may need to be increased or decreased. Consult the approved product labeling for the concomitantly used drug. 7.3 Use of Vaginal Products with ANNOVERA
In a drug-drug interaction study with ANNOVERA and the concurrent use of three different formulations of vaginal miconazole, the use of water-based vaginal miconazole cream resulted in no change in exposure to EE or SA from the vaginal system. However, the use of either the 1- day or the 3-day oil-based miconazole suppository was associated with an overall increase in exposure up to 67% for EE and 32% for SA. Considering the potential long-term effect on vaginal system performance, concurrent use of oil-based vaginal suppositories should not occur with ANNOVERA use. If there is a need to treat a vaginal condition, water-based vaginal cream or oral therapy may be used concurrently with the vaginal system [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Lubricants: Water-based vaginal lubricants have no effect on ANNOVERA; however, oil- based (including silicone-based) vaginal lubricants will alter the vaginal system and/or exposure to EE and SA and should not be used.
ANNOVERA use is compatible with male condoms made with natural rubber latex, polyisoprene, and polyurethane.
The effect of tampon use on the systemic exposure of SA and EE from ANNOVERA has not been studied.
7.4 Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer ANNOVERA with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to CHCs before conception or during early pregnancy.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Discontinue ANNOVERA if pregnancy occurs, because there is no reason to use CHCs during pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Contraceptive hormones and/or metabolites are present in human milk. CHCs can reduce milk production in breastfeeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breastfeeding is well established. Advise the nursing female to use another method of contraception until she discontinues breastfeeding [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Data
Human Data
No studies have been conducted of the use of ANNOVERA in breastfeeding females. Two studies have been conducted in breastfeeding females of segesterone acetate implants delivering lower levels of segesterone acetate than ANNOVERA. Maternal serum levels of up to 141 pg/mL were associated with infant exposure of up to 7 pg/mL. No safety signals in feeding, growth, and development were observed in the infants between the segesterone acetate implant group and the control group.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of ANNOVERA have been established in women of reproductive age. Efficacy is expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents under the age of 18 as for users 18 years and older. Use of ANNOVERA before menarche is not indicated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
ANNOVERA has not been studied in females who have reached menopause and is not indicated in this population.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the disposition of ANNOVERA. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with hepatic impairment. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate the discontinuation of CHC use until markers of liver function return to normal and CHC causation has been excluded [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No studies were conducted in subjects with renal impairment; ANNOVERA is not recommended in patients with renal impairment.
8.8 Body Mass Index (BMI)/Body Weight
The safety and efficacy of ANNOVERA in females with a BMI >29 kg/m2 have not been adequately evaluated because this subpopulation was excluded from the clinical trials after 2 VTEs occurred in females with a BMI > 29 kg/m2 [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)]. Higher body weight is associated with lower systemic exposure of SA and EE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ANNOVERA (segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system) is a toroidal- shaped (ring), nonbiodegradable, flexible, opaque white vaginal system containing two active components, a progestin, segesterone acetate, and an estrogen, ethinyl estradiol. When placed in the vagina, each ANNOVERA releases an approximate average 0.15 mg/day of segesterone acetate and 0.013 mg/day of ethinyl estradiol over the 21 days in-use period of each cycle for up to 13 cycles (total of 273 days). Each cycle is 28 days, with 21 days in and 7 days out.
The inactive ingredients are dibutyltin dilaurate, silicone elastomers, silicone medical adhesive, and titanium dioxide. The elastomers are all methyl siloxane-based polymers.
The vaginal system body has an overall diameter of 56 mm and a cross-sectional diameter of 8.4 mm. It contains two channels of approximately 3.0 mm diameter and 27 mm length into which steroid-containing cores are inserted. Each ANNOVERA contains 103 mg of SA distributed throughout both cores and 17.4 mg of EE distributed throughout only one core. The core containing 40% SA and 12% EE of its mass is 3 mm in diameter and 18 mm in length. The core containing 50% SA of its mass is 3 mm in diameter and 11 mm in length. Contact between the cores and the vaginal system body is fixed by coating the channels with silicone medical adhesive before introducing the cores. After insertion of the cores, the channels are sealed with the silicone medical adhesive.
The structural formulas, and properties for the active components are shown below:
STRUCTURAL FORMULAS:
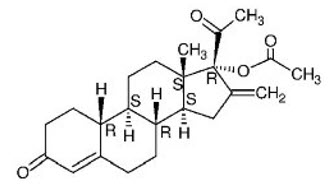
Segesterone Acetate (SA)
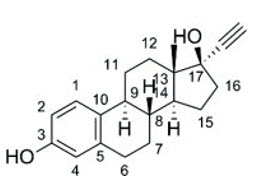
Ethinyl Estradiol (EE)
PROPERTIES:
Established Name: Segesterone Acetate
Chemical Name: 16-methylene-17α-acetoxy-19-nor-pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
Molecular Formula: C23H30O4
Molecular Weight: 370.5
Physical Form: White, or yellowish white powder
Solubility: Slightly soluble in n-hexane, soluble in ethyl acetate and methanol, freely soluble in acetone (USP classification)
Melting Point: 173°C–177°CEstablished Name: Ethinyl Estradiol
Chemical Name: 19-Nor-17α -pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol
Molecular Formula: C20H24O2
Molecular Weight: 296.4
Physical Form: White to slightly yellowish-white crystalline powder
Solubility: Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, it dissolves in alkaline solution
Melting Point: 181°C–185°CThe steroids diffuse out of the vaginal system with release rates that vary over time. Based on in vitro data, the daily release rates of SA and EE are higher during each initial 24–48 hours of use achieving a somewhat lower steady-state with continued use over the subsequent days in each cycle. The vaginal system is designed to be used for 13 cycles (1 year) on a 21/7 days in/out schedule. The total in-use time with the 21/7 days in/out schedule over 13 cycles is 273 days. Based on the residual amount of drug in vaginal systems used in clinical trials over 13 cycles, a total of 41.3 mg of SA and 3.4 mg of EE are released over this period. This translates to an approximate average daily dose of 0.15 mg of segesterone acetate and 0.013 mg of ethinyl estradiol with higher release rate expected at the beginning of dosing and a lower release rate toward the end.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CHCs lower the risk of becoming pregnant primarily by suppressing ovulation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of SA on the QTc interval was evaluated in a Phase 1 randomized, placebo and positive controlled, double-blind, single-dose, three-period, crossover thorough QTc study in 44 healthy adult female subjects. At the single intravenous bolus dose which produces 4.5-fold the therapeutic serum concentrations of SA achieved with ANNOVERA, SA did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of ANNOVERA were determined in 39 women who used ANNOVERA for up to 13 cycles. Following vaginal administration, SA and EE were absorbed into systemic circulation with median tmax of about 2 hours in Cycle 1, Cycle 3, and Cycle 13. Concentrations of both components declined after tmax and became more constant after 96 hours post-dose. Over subsequent cycles of use, the peak serum concentrations of SA and EE declined. Serum concentration-time profiles of SA and EE for Cycles 1, 3, and 13 of ANNOVERA use are provided in Figure 2 and Figure 3 with PK parameters summarized in Table 5 and Table 6.
Figure 3: Mean SA and EE Serum Concentrations Delivered by ANNOVERA Over 21 Days of Dosing for Cycles 1, 3, and 13
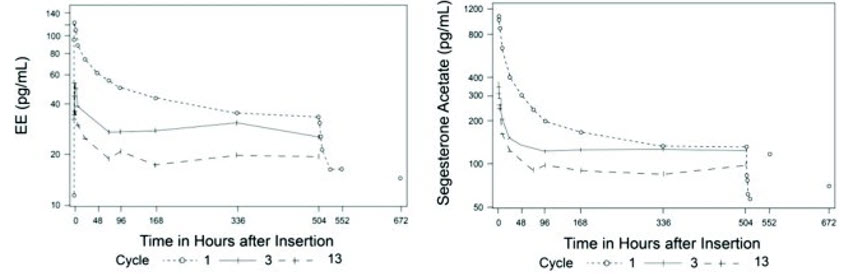
Figure 4: Mean SA and EE Serum Concentrations Delivered by ANNOVERA Over the First 48 Hours of Dosing for Cycles 1, 3, and 13
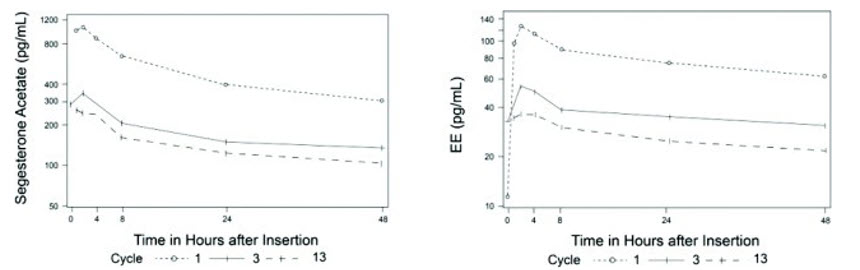
Table 5: Mean (SD) PK Parameters for SA following ANNOVERA Administration Cycle AUC0-21 day
(ng*hr/mL)AUC0-1 day
(ng*hr/mL)Cmax
(pg/mL)Cavg
(pg/mL)1 96.2 (16.9) 15 (3.2) 1,147 (315) 191 (34) 3 65.9 (14.8) 5 (1.6) 363 (133) 131 (29) 13 47.2 (10.1) 3.9 (1.4) 294 (116) 94 (20) Table 6: Mean (SD) PK Parameters for EE following ANNOVERA Administration Cycle AUC0-21 day
(ng*hr/mL)AUC0-1 day
(ng*hr/mL)Cmax (pg/mL) Cavg
(pg/mL)1 22.2 (9.8) 2.1 (0.7) 129 (39) 44 (19) 3 14.7 (4.7) 0.9 (0.4) 60 (32) 29 (9) 13 9.6 (4.1) 0.7 (0.3) 39 (16) 19 (8) Distribution
The volume of distribution of SA is 19.6 L/kg. SA is approximately 95% bound to human serum proteins and has negligible binding affinity for sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). EE is highly protein bound but not specifically bound to serum albumin (98.5%) and induces an increase in the serum concentrations of SHBG.
Metabolism
In vitro data show that both SA and EE are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 isoenzyme. In human serum, two oxidative metabolites (5α-dihydro- and 17α- hydroxy-5α-dihydro metabolites) constitute 50% of exposure relative to SA. Both metabolites are not considered as active metabolites with EC50 to progesterone receptor 10-fold higher than that of SA. EE is primarily metabolized by aromatic hydroxylation, but a wide variety of hydroxylated and methylated metabolites are formed. These are present as free metabolites and as sulfate and glucuronide conjugates. The hydroxylated EE metabolites have weak estrogenic activity.
Excretion
The mean (SD) half-life of SA is 4.5 (3.4) hours. EE is known to be excreted in the urine and feces as glucuronide and sulfate conjugates, and it undergoes enterohepatic recirculation. The mean (SD) half-life of EE is 15.1 (7.5) hours.
Specific Populations
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Higher body weight associates with lower systemic exposure of SA and EE. In a PK study conducted in 18 females with BMI <25 (16.89–24.34) kg/m2 and 21 females with BMI >25 (25.15–37.46) kg/m2, up to 16% and 33% decreases in the systemic exposure (AUC0- 21day) of SA and EE, respectively, were observed between the two BMI groups.
Interaction with Vaginal Medications
A clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) study was conducted to evaluate the effect of vaginal antimycotic medication (miconazole nitrate) on the PK of SA and EE in 29 females using ANNOVERA. The results showed that a single-dose vaginal administration of 1,200 mg miconazole suppository on Day 8 of ANNOVERA use increased the systemic exposure of EE (AUCDay8-21) by approximately 67%. A similar trend was observed with SA with AUCDay8-9, AUCDay8-10, and AUCDay8-21 increasing by approximately 30%, 32%, and 19%, respectively. When 200 mg miconazole vaginal suppositories were administered on Day 8, Day 9, and Day 10 of ANNOVERA use, EE AUCDay8-11 and AUCDay8-21 were increased by 9% and 42%, respectively. SA AUCDay8-11 and AUCDay8- 21 were increased by 28% and 27%, respectively. Water-based vaginal miconazole cream had no effect on ANNOVERA [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
The in vitro studies suggest that SA is unlikely to inhibit or induce CYP enzymes at the therapeutic dose.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats with subdermal implants releasing 40, 100, and 200 mcg segesterone acetate per day (approximately 17–86 times the daily dose of segesterone acetate in females using ANNOVERA, based on body surface area), no drug-related increase in tumor incidence was observed. In a 2-year intravaginal carcinogenicity study in mice, segesterone acetate gel produced an increased incidence of adenocarcinoma and lobular hyperplasia in the breast at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day, approximately 10 times the systemic exposure of segesterone acetate per day in females using ANNOVERA, based on AUC. A dose of 10 mg/kg/day in the mouse, approximately 3 times the systemic exposure of segesterone acetate per day based on AUC, did not result in carcinogenic findings.
Long-term continuous administration of natural and synthetic estrogens in certain animal species increases the frequency of carcinomas of the breast, uterus, cervix, vagina, testis, and liver.
Mutagenesis
Segesterone acetate was neither mutagenic nor clastogenic in the Ames/Salmonella reverse mutation assay, the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells, or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
A return to fertility study was conducted with segesterone acetate in rats, using subdermal implants releasing a dose approximately 25 times the anticipated daily vaginal human dose (based on body surface area). Three months of treatment with segesterone acetate suppressed fertility, but 7 weeks after cessation of treatment, there were no adverse effects on ovulation or resulting litter parameters.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of ANNOVERA was evaluated in two 1-year multicenter trials enrolling 2,265 females, age 18–40 years, who were healthy and sexually active with regular menstrual cycles. The trials were conducted in the U.S., Dominican Republic, Brazil, Chile, Finland, Hungary, Sweden, and Australia, with 67.1% of females from the U.S. The racial/ethnic distribution was Caucasian (71.2%), African-American (14.1%), Asian (3.5%), other/multiple races (11.2%); 28.7% of the study population was Hispanic. The mean age was 26.7 years and the mean (range) BMI was 24.1 (16.0, 41.5) kg/m2. At approximately 50% enrollment, women with BMI >29.0 kg/m2 were no longer enrolled in the two trials and all women with a BMI >29.0 kg/m2 were discontinued from the trials.
Based on pooled data from the two trials, 2,111 females ≤35 years of age completed 17,427 evaluable 28-day cycles (cycles in which no back-up contraception was used). The pooled pregnancy rate, evaluated by the Pearl Index (PI), was 2.98 (95% Confidence Interval [2.13, 4.06]) per 100 woman-years of ANNOVERA use.
Return to fertility was assessed in 290 of the subjects in the two trials who either desired pregnancy or switched to a nonhormonal method after the trials, and all 290 subjects reported a return to fertility during the 6-month follow-up period (defined as a return of menses or pregnancy).
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1. Dinger, J, Mohner S, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular risk associated with the use of an etonogestrel- containing vaginal ring. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2013; 122(4): 800-808.
- 2. Sidney, S, Cheetham TC, Connell FA, Oullet-Hellstrom R, Graham DJ, Davis D,, Recent combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk of thromboembolism and other cardiovascular events in new users. Contraception 2013; 87: 93–100.
- 3. Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk of cardiovascular endpoints. Sidney, S. (primary author) http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM277384.pdf, accessed 04- April-2019.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
ANNOVERA (segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system) is a toroidal- shaped (ring), nonbiodegradable, flexible, opaque white vaginal system. The vaginal system body has an overall diameter of 56 mm and a cross-sectional diameter of 8.4 mm. When placed inside the vagina, each ANNOVERA releases an approximate average 0.15 mg/day of segesterone acetate and 0.013 mg/day of ethinyl estradiol over 21-day in-use period of each cycle for up to 13 cycles (total 273 days). Each cycle is 28 days, with 21 days in and 7 days out.
Each ANNOVERA is individually packaged in an aluminum pouch. The pouch consists of a laminate from outside to inside of polyester, aluminum foil, and polyethylene.
First insertion of ANNOVERA must be prior to the date of expiration. Discard one year after first insertions.
A black compact case is provided with the drug product for storage of ANNOVERA by patients during each 7-day vaginal system-out interval.
The vaginal system should be placed in the compact case after 13 cycles of use and discarded via a drug take-back option if one is available. If a take-back option is unavailable, then discard in the waste receptacle out of reach of children and pets. The vaginal system should NOT be flushed down the toilet. See www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for more information about disposal of medicines.
Each box contains 1 ANNOVERA vaginal system in a pouch and 1 storage case.
NDC: 68308-752-01
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Cigarette Smoking
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from CHC use, and females who are over 35 years old and smoke should not use ANNOVERA [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Venous Thromboembolism
Increased risk of VTE compared to nonusers of CHCs is greatest after initially starting a CHC or restarting (following a 4-week or greater dose-free interval) the same or a different CHC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Sexually Transmitted Infections
ANNOVERA does not protect against HIV-infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections. ANNOVERA is compatible with male condoms made with natural rubber latex, polyisoprene, and polyurethane.
Use During Pregnancy
ANNOVERA is not to be used during pregnancy; instruct the patient to remove ANNOVERA if pregnancy is confirmed during treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
ANNOVERA Dosing and Instructions
Advise the woman on proper use of ANNOVERA and what to do if she does not comply with the labeled timing of insertion and removal. The efficacy of ANNOVERA is greatest when ANNOVERA is kept in the vagina continuously for the scheduled 21 consecutive days. Removal of ANNOVERA even briefly during the scheduled 21 days of use can reduce efficacy.
ANNOVERA should be washed with mild soap and water and rinsed and patted dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel prior to each insertion and at each removal. Prior to initial use, the storage case should be labeled with the discard date to avoid using the product beyond 13 cycles [see Dosage and Administration (2) and FDA-approved Patient Information].
Place the completely used ANNOVERA in the case provided and discard via a drug take- back option if one is available. If a take-back option is unavailable, then discard in the waste receptacle out of reach of children and pets. The vaginal system should NOT be flushed down the toilet. See www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for more information about disposal of medicines. [see How Supplied (16.1)].
Use with Vaginal Products
Water-based vaginal lubricants have no effect on the vaginal system; however, oil-based (including silicone-based) vaginal lubricants will alter the vaginal system and/or exposure to EE and SA and should not be used [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Need for Additional Contraception
Use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when:
-
Enzyme inducers are used with CHCs [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
ANNOVERA has been out for more than 2 hours cumulative during the 21 days of continuous use or the vaginal system-free interval exceeds 7 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Postpartum females who have not yet had a period should use an additional method of contraception until ANNOVERA has been in place for 7 consecutive days [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Lactation
ANNOVERA may reduce breast milk production. This is less likely to occur if breastfeeding is well established. Females who are breastfeeding should not use ANNOVERA until after weaning [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Amenorrhea and Possible Symptoms of Pregnancy
Amenorrhea may occur. Consider pregnancy in the event of amenorrhea and rule out pregnancy if amenorrhea is associated with symptoms of pregnancy, such as morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Fertility Following Discontinuation of ANNOVERA
Resumption of fertility after discontinuation of ANNOVERA is expected. All women followed for return of fertility experienced a return of fertility by 6 months after discontinuing ANNOVERA [see Clinical Studies (14)].
-
Enzyme inducers are used with CHCs [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
ANNOVERA® (ann-o-VER-ah)
(segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system)Read this Patient Information carefully before you decide if ANNOVERA is right for you. This information does not take the place of talking with your gynecologist or other healthcare provider who specializes in women's health. If you have any questions about ANNOVERA, ask your healthcare provider. You should also learn about other birth control methods to choose the one that is best for you. What is the most important information I should know about ANNOVERA?
-
Do not use ANNOVERA if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old.
Smoking increases your risk of serious heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) side effects from hormonal birth control methods, including death from heart attack, blood clots, or stroke. This risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes you smoke.
ANNOVERA does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). What is ANNOVERA?
ANNOVERA is a hormone-releasing system used by females who are able to become pregnant to prevent pregnancy. You insert ANNOVERA into your vagina. ANNOVERA is in the shape of a ring that is reusable for 1 year. The vaginal system is made of silicone and contains two female hormones that are slowly released into your vagina and then enter your blood. One hormone is an estrogen called ethinyl estradiol. The other hormone is a progestin called segesterone acetate.How well does ANNOVERA work for contraception?
Your chance of getting pregnant depends on how well you follow the directions for using the vaginal system. The more carefully you follow the directions, the less chance you have of getting pregnant.
Based on the results of two clinical studies that lasted 12 months, about 2 to 4 women out of 100 women may get pregnant during the first year they use ANNOVERA. ANNOVERA was designed to be reused for 1 year. Replace ANNOVERA at the end of 1 year if you choose to continue using ANNOVERA. There is not enough hormone left in the vaginal system to provide you effective birth control after 1 year of use.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in how well they work to prevent pregnancy. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box at the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
ANNOVERA, a vaginal system with hormones, is in the second box from the top of the chart.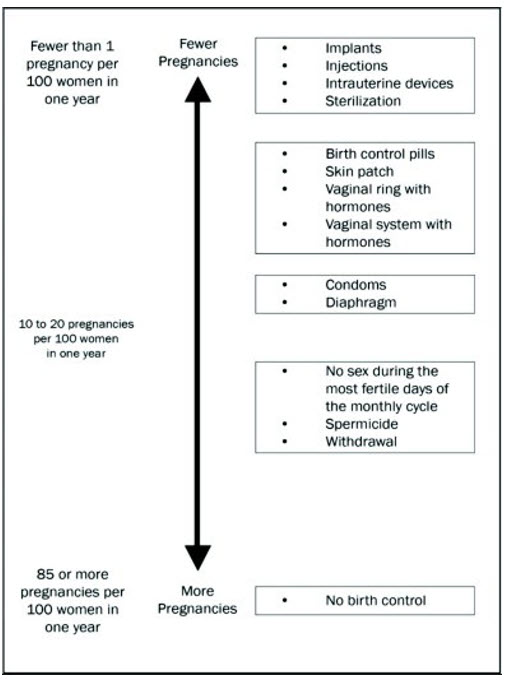
Who should not use ANNOVERA?
Do not use ANNOVERA if you:- smoke and are over 35 years old.
- have or have had a blood clot in your arms, legs, lungs, or eyes.
- have had a stroke.
- have reduced blood flow to your brain (cerebrovascular disease).
- have reduced blood flow or blockage in 1 or more of the arteries that supply blood to your heart (coronary artery disease).
- have had a heart attack.
- have heart rhythm or heart valve problems that increase your risk of having blood clots, such as an infection of the inner lining of the heart and heart valves or a type of irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation.
- have a problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal.
- have high blood pressure that is not controlled with medicine or have high blood pressure with blood vessel damage.
- have diabetes and are over 35 years old; have diabetes with high blood pressure or problems with your kidneys, blood vessels, eyes, or nerves; or have had diabetes for longer than 20 years.
- have headaches with changes in vision, numbness or weakness, have migraine headaches with aura, or are over age 35 years old and have any type of migraine headaches.
- have liver disease or liver tumors.
- have or have had breast cancer or any cancer that is sensitive to the female hormones estrogen or progesterone.
- have unexplained vaginal bleeding.
- are allergic to segesterone acetate, ethinyl estradiol, or any of the ingredients in ANNOVERA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in ANNOVERA.
- take any Hepatitis C drug combination medicine containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the blood.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using ANNOVERA?
Before you use ANNOVERA tell your healthcare provider if you:- have any of the conditions listed above.
- smoke.
- are pregnant or think you are pregnant.
- recently had a baby, miscarriage, or abortion.
- have breast problems such as an abnormal mammogram or breast x-ray, breast nodules, fibrocystic breast disease, or a family history of breast cancer.
- have any medical condition, especially migraine headaches, depression, seizures, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol or triglycerides, gallbladder disease, liver disease, heart disease, or kidney disease.
- have a family history of blood clots or stroke.
- have yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
- have a condition that makes your vagina become irritated easily.
- have a history of toxic shock syndrome.
- had gallbladder problems when you were pregnant.
- are scheduled for surgery. The hormones in ANNOVERA may increase your risk of blood clots after surgery. You should stop using ANNOVERA at least 4 weeks before you have surgery and not restart until at least 2 weeks after your surgery.
- are scheduled for any laboratory tests. Certain blood tests may be affected by hormonal birth control methods.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. You should not use ANNOVERA if you are breastfeeding. The hormones in ANNOVERA may decrease your milk production. The hormones in ANNOVERA pass into your breast milk. Talk with your healthcare provider about the best birth control method for you while breastfeeding.
- anti-seizure medicines
- medicine used to treat fungal infections
- combinations of HIV medicines
- Hepatitis C (HCV) medicines
- non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors medicine to
- treat tuberculosis
- medicine to treat high blood pressure in the vessels of the lung medicine to
- treat chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
- St. John's wort
Do not use any vaginal products such as oil-based suppositories, oil-based creams, or oil-based gels while the vaginal system is in your vagina. Do not use any vaginal lubricants that have silicone or oil in them. Water-based lubricants are ok to use. Be sure to read the ingredients on the label carefully before you buy a vaginal lubricant.
Some medicines and grapefruit juice may increase the level of ethinyl estradiol in your blood if used together, including:- the pain reliever acetaminophen
- ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- types of medicines used to treat fungal infections
- HIV medicines
- non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors medicines to
- lower cholesterol
Females who take thyroid hormone replacement medicine or corticosteroid replacement medicine may need increased doses of their thyroid hormone or cortisol medicines.
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you take any of the medicines listed above.
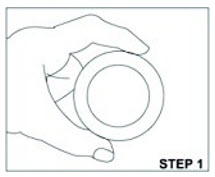
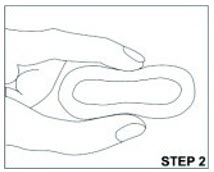
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you start taking a new medicine.How should I use ANNOVERA? - Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information that comes with ANNOVERA for information about the right way to insert, remove, clean, store, and dispose of (throw away) ANNOVERA.
- Use ANNOVERA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
After you insert ANNOVERA for the first time, you will remove it at the end of week 3 and leave it out for 7 days. You will reinsert ANNOVERA at the end of week 4 of each 4- week cycle. You will repeat this pattern with ANNOVERA for up to 13 cycles. Scheduled insertions and removals of ANNOVERA should be at about the same time of the day and the same day of the week for each monthly cycle.- The day of the week when you first insert ANNOVERA (referred to as "Day 1") is your vaginal system change day.
- For each cycle, you put the vaginal system into your vagina and let it stay there 3 weeks (21 full days). Remember to keep the vaginal system in for the whole 3 weeks (21 full days).
- You take the vaginal system out on your vaginal system change day (Day 22) and let it stay out for 1 week (7 full days). Note that your vaginal system should be cleaned with warm water and mild soap, dried with a clean cloth towel or paper towel, and stored in the case provided, away from children, pets, and extreme temperatures. (See the Instructions for Use.)
- Then you start over again for another 4 weeks. You may not be bleeding when you put the vaginal system in.
- Always put the vaginal system in or take it out on your vaginal system change day at about the same time of day. For example, if you put your vaginal system in on Monday at 9:00 in the morning, always take it out or put it back in on Monday at about 9:00 in the morning.
- You do not have to take the vaginal system out when you have sex. If you decide to remove it, remember to reinsert it within 2 hours after removing it or you may not be protected from pregnancy. However, if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina for more than 2 hours at one time or if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina at different times that add up to more than a total of 2 hours over the first 21 days of your cycle, you will need to use another method of birth control (such as male condoms or spermicide) until ANNOVERA has been in your vagina for 7 days in a row.
Schedule Cycle 1 Put vaginal system in →
(vaginal system change day)Day 1 Weeks 1, 2, and 3
Days 1-21Take vaginal system out→
(vaginal system change day)Day 22 Week 4
Days 22-28Cycle 2
(repeat for Cycles 3-13)Put vaginal system in→
(vaginal system change day)Day 1 Weeks 1, 2, and 3
Days 1-21Take vaginal system out→
(vaginal system change day)Day 22 Week 4
Days 22-28- Repeat the 4-week cycle for all 13 cycles of the use of the vaginal system.
- Do not use the vaginal system for more than 13 cycles (1 year). At the end of the 13 cycles, take the vaginal system out of your vagina. Place the used vaginal system in the case that comes with ANNOVERA and dispose of it (throw away) at a drug take-back location, if available. If a drug take-back location is not available, dispose of it in the trash out of reach of children and pets. Do not flush ANNOVERA down the toilet.
- If you want to continue using ANNOVERA after 13 cycles, you will need to receive a new prescription from your healthcare provider for a new vaginal system.
- If you start using ANNOVERA 4 or more weeks after having a baby and you have not had a menstrual period yet, you should use another method of birth control until you have used ANNOVERA for 7 days in a row.
What happens if I am off schedule using the vaginal system?
It is very important to follow the schedule every cycle and remove and insert ANNOVERA on your vaginal system-in and vaginal system-out days at about the same time. If you take the vaginal system out too soon or put it back in too late, your chance of getting pregnant is higher.
If you are more than 1 or 2 days off schedule for vaginal system insertion you will need to use new vaginal system-in and vaginal system-out days for the remaining cycles of use. You will also need to use back-up contraception, such as condoms or spermicide, for the first 7 days of the new schedule if you have sexual intercourse.If you put the vaginal system back in: Then: Too early, after it had been out for only 5 or 6 days. Keep the vaginal system in for at least 3 weeks (21 days). You may keep it in up to your normal vaginal system-out day. Too late, after it had been out for more than 7 days. Put the vaginal system back in right away. You will now have a new vaginal system-in day. You must use condoms or spermicide as back-up contraception for the next 7 days when you have sexual intercourse. If you took the vaginal system out: Then: Too early, after it had been in for only 19 or 20 days. Leave the vaginal system out for 1 week. Put it back in after the week is over, as you would normally do. You may then keep it in up to your normal vaginal system-out day, 22 or 23 days after you put the vaginal system in. Too late, after it had been in for 22 or 23 days. Remove the vaginal system as soon as you realize this. Then reinsert the vaginal system 7 days later. During the 21 days of continuous use, if ANNOVERA is out of the vagina for more than 2 continuous hours or more than 2 cumulative hours (multiple inadvertent removals or expulsions adding up to 2 hours), then back-up contraception such as male condoms or spermicide should be used until the vaginal system has been in the vagina for 7 consecutive days. What if I miss my menstrual period or if I think I am pregnant?
It is possible that you are pregnant if you miss your scheduled period (no bleeding on the 7 days that the vaginal system is out). Tell your healthcare provider right away that you have missed your period. Also, tell your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. It is important that your healthcare provider check you to find out if you are pregnant. You may need a pregnancy test to determine if you are pregnant. Do not remove the vaginal system until you are certain you are pregnant. Stop using ANNOVERA if your healthcare provider tells you that you are pregnant.What are the possible side effects of ANNOVERA? ANNOVERA can cause serious side effects, including:
See: "What is the most important information I should know about ANNOVERA?"-
blood clots. Like pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives increase the risk of serious blood clots, especially in women who have other risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, or age greater than 35. This increased risk is highest when you first start taking hormonal contraceptives and when you restart the same or different hormonal contraceptive after not using it for 4 weeks or more.
-
It is possible to die or be permanently disabled from a problem caused by a blood clot, such as a heart attack or a stroke. Some examples of serious blood clots are blood clots in the:
- legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- eyes (loss of eyesight)
- heart (heart attack)
- brain (stroke)
-
Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical care right away if you have:
- leg pain that does not go away
- sudden shortness of breath
- sudden changes in vision or blindness
- severe pain or pressure in your chest
- a sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches
- weakness or numbness in an arm or leg
- trouble speaking
-
It is possible to die or be permanently disabled from a problem caused by a blood clot, such as a heart attack or a stroke. Some examples of serious blood clots are blood clots in the:
- toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Some symptoms of TSS are the same as flu symptoms, but they can become serious very quickly. Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical care right away if you have he following symptoms:
- sudden high fever
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- fainting or feeling faint when standing up
- a sunburn-like rash
- muscle aches
- dizziness
- liver problems, including liver tumors. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice).
- high blood pressure
- gallbladder problems or worsening of a gallbladder problem you already have. You may have an increased risk of gallbladder problems with the use of ANNOVERA if you had gallbladder problems when you were pregnant.
- changes in the sugar and fat (cholesterol and triglycerides) levels in your blood.
- headache. Tell your healthcare provider if you have new headaches that keep coming back, that do not go away, or are severe. Also tell your healthcare provider if your migraine headaches happen more often or are more severe than normal.
- irregular or unusual vaginal bleeding and spotting between your menstrual periods, especially during the first month of using ANNOVERA, or the absence of menstrual periods (amenorrhea).
- depression.
- possible cancer in your cervix.
- swelling of your skin especially around your mouth, eyes, and in your throat (angioedema). Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical care right away if you have a swollen face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat as this may lead to difficulty swallowing or breathing. Your risk of having angioedema is higher if you have a history of angioedema.
- dark patches of skin on your forehead, cheeks, upper lip, and chin (chloasma). Your risk of getting chloasma with the use of ANNOVERA is higher if you had chloasma during pregnancy. Women who tend to get chloasma should avoid spending a long time in sunlight, tanning booths, and under sunlamps while using ANNOVERA. Use sunscreen if you have to be in the sunlight.
- headache, including migraine
- nausea/vomiting
- vaginal yeast infection (candidiasis)
- lower/upper abdomen pain
- painful periods
- vaginal discharge
- urinary tract infection
- breast pain/tenderness
- irregular vaginal bleeding
- diarrhea
- genital itching
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to Mayne Pharma at 1-844-825-8500.
No serious problems have been reported from a hormonal contraceptive overdose.Does hormonal birth control cause cancer?
It is not known if hormonal birth control causes breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Women who use hormonal contraceptives may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons such as having more sexual partners.What should I know about my period when taking ANNOVERA?
When you take ANNOVERA you should expect to have regular 28-day cycles. Each period is likely to last about 5 days. You may have bleeding or spotting between your scheduled periods especially during the first cycle. This bleeding or spotting tends to decrease after the first cycle. Do not stop taking ANNOVERA because of this bleeding or spotting. If the spotting continues for more than 7 consecutive days or if the bleeding is unusually heavy, call your healthcare provider.
Tell your healthcare provider if you do not have your period.What if I want to become pregnant?
You may stop using ANNOVERA whenever you wish. Consider a visit with your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking ANNOVERA.General information about the safe and effective use of ANNOVERA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ANNOVERA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ANNOVERA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ANNOVERA that is written for health professionals.What if I have other questions?
If you have concerns or questions, ask your healthcare provider.What are the ingredients in ANNOVERA?
Active ingredients: segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol.
Inactive ingredients: dibutyltin dilaurate, silicone elastomers, silicone medical adhesive, and titanium dioxide. -
Do not use ANNOVERA if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old.
-
Instructions for Use
ANNOVERA® (ann-o-VER-ah)
(segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol vaginal system)
Read this Instructions for Use carefully before you decide if ANNOVERA is right for you. This information does not take the place of talking with your gynecologist or other healthcare provider who specializes in women's health. If you have any questions about ANNOVERA, ask your healthcare provider. You should also learn about other birth control methods to choose the one that is best for you.
How should I start using ANNOVERA?
If you are not currently using hormonal birth control, start using ANNOVERA between Days 2 and 5 of your menstrual period.
- If your menstrual periods are not regular or if you start using ANNOVERA more than 5 days from when you started your menstrual period, you should use a barrier method of birth control, such as a male condom or spermicide during sexual intercourse for the first 7 days you use ANNOVERA.
If you are changing from a birth control pill or patch or monthly disposable contraceptive vaginal ring to ANNOVERA:
- If you have been using your birth control method correctly and are certain that you are not pregnant, you can change to ANNOVERA any day of your birth control cycle. Do not start ANNOVERA any later than the day you would start your next birth control pill, apply your next patch or insert your next monthly disposable contraceptive vaginal ring.
If you are changing from a progestin-only birth control method, such as a minipill, injection, implant or intrauterine system (IUS):
- You may switch from a minipill on any day. Start using ANNOVERA on the day that you would have taken your next minipill.
- You should switch from an injectable and start using ANNOVERA on the day when your next injection would be due.
- You should switch from an implant or the IUS and start using ANNOVERA at the time the implant or IUS is removed.
If you are changing from a minipill, injection, implant, or an intrauterine system to ANNOVERA, you should use a barrier method of birth control, such as a male condom or spermicide, during sexual intercourse for the first 7 days you use ANNOVERA.
If you start using ANNOVERA after an abortion or miscarriage:
-
Following a first trimester abortion or miscarriage: You may start ANNOVERA within 5 days following a first trimester abortion or miscarriage (the first 12 weeks of pregnancy). You do not need to use an additional birth control method.
- If you do not start ANNOVERA within 5 days after a first trimester abortion or miscarriage, use a non-hormonal birth control method, such as male condoms or spermicide, while you wait for your menstrual period to start. Start using ANNOVERA between days 2 and 5 of your menstrual period.
- If you start using ANNOVERA more than 5 days from when you started your menstrual period, you should use a barrier method of birth control, such as a male condom or spermicide during sexual intercourse for the first 7 days you use ANNOVERA.
- Following a second trimester abortion or miscarriage: You may start using ANNOVERA no sooner than 4 weeks (28 days) after a second trimester abortion (after the first 12 weeks of pregnancy).
If you are starting ANNOVERA after childbirth:
- You may start using ANNOVERA no sooner than 4 weeks (28 days) after having a baby if you are not breastfeeding.
- If you have not gotten your menstrual period after childbirth, you should talk to your healthcare provider. You may need a pregnancy test to make sure you are not pregnant before you start using ANNOVERA.
- Use another birth control method, such as a male condom or spermicide, during sexual intercourse for the first 7 days you use ANNOVERA if you have not yet had a period.
If you are breastfeeding, you should not use ANNOVERA. Use other birth control methods until you are no longer breastfeeding.
How do I use ANNOVERA?
Step 1. Open the package and remove ANNOVERA. - Wash your hands with mild soap and water. Dry them well.
- Take ANNOVERA out of its package (See Figure, Step 1).
- Wash ANNOVERA with mild soap and water, rinse and pat dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel.
Step 2. Prepare to insert ANNOVERA. - Hold ANNOVERA between your thumb and first (index) finger.
- Press the sides of ANNOVERA together to make it narrow (See Figure, Step 2).
Step 3. Choose a position for insertion of ANNOVERA. - Choose the position that is comfortable for you. For example, lying down, squatting, or standing with 1 leg up (See Figures, Steps 3-A, 3-B, 3-C).
Step 4. Insert ANNOVERA into your vagina. - Gently insert the folded ANNOVERA into your vagina (See Figure, Step 4-A).
- Push ANNOVERA further up into your vagina using your index finger.
- Push it in as far as you can. It sometimes helps to push down with the muscles in your vagina while you are inserting ANNOVERA.
- When you insert ANNOVERA, it may be in different positions in your vagina, but ANNOVERA does not have to be in an exact position for it to work.
- Mark your vaginal system "in day" on your calendar.
Note: - If you feel the ANNOVERA in your vagina or if it feels uncomfortable, you may not have pushed the ANNOVERA into your vagina far enough. Use your index finger to gently push ANNOVERA as far as you can into your vagina (See Figure, Step 4- B). There is no danger of ANNOVERA being pushed too far up in the vagina or getting lost.
- You should not feel ANNOVERA after you have placed it into your vagina.
- Some women and their partners may be aware of ANNOVERA in the vagina during sexual intercourse.
Step 5. How do I remove ANNOVERA? - Wash and dry your hands.
- Choose the position that is most comfortable for you (See Step 3).
- Put your index finger into your vagina and hook it through ANNOVERA. Gently pull downward and forward to remove ANNOVERA and pull it out (See Figure, Step 5). It sometimes helps to push down with the muscles in your vagina while you are removing ANNOVERA.
- Wash the ANNOVERA vaginal system with mild soap and lukewarm water, pat it dry, and store in the case provided.
- Mark your vaginal system "out day" on your calendar.
What else should I know about ANNOVERA?
- The day of the week when you first insert ANNOVERA (called "Day 1") is your vaginal system change day. This is described further in the Patient Information section entitled "How should I use ANNOVERA?"
- For each cycle, you put the vaginal system into your vagina and let it stay there 3 weeks (21 full days). Remember to keep the vaginal system in for the whole 3 weeks (21 full days).
- You take the vaginal system out on your vaginal system change day (Day 22) and let it stay out for 1 week (7 full days). Note that your vaginal system should be stored in the case provided, away from children, pets, and extreme temperatures.
- Then you start over again for another 4 weeks. You may not be bleeding when you put the vaginal system in.
- Always put the vaginal system in or take it out on your vaginal system change day at about the same time of day. For example, if you put your vaginal system in on Monday at 9:00 in the morning, always take it out or put it back in on Monday at about 9:00 in the morning.
- You do not have to take the vaginal system out when you have sex. If you decide to remove it, remember to reinsert it within 2 hours after removing it or you may not be protected from pregnancy. However, if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina for more than 2 hours at one time or if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina at different times that add up to more than a total of 2 hours over the first 21 days of your cycle, you will need to use another method of birth control until ANNOVERA has been in your vagina for 7 days in a row, such as male condoms or spermicides.
- Repeat the 4-week cycle for all 13 cycles of the use of the vaginal system.
- Do not use the vaginal system for more than 13 cycles (1 year). When you take the vaginal system out of your vagina at the end of the 13 cycles, dispose of it. See "How should I dispose of (throw away) ANNOVERA?" below.
- If you want to continue using ANNOVERA after 13 cycles, you will need to get a new prescription from your healthcare provider to obtain a new vaginal system.
- Do not to use any vaginal products such as oil-based suppositories, oil-based creams, or oil-based gels while the vaginal system is in your vagina. Do not use any vaginal lubricants that have silicone or oil in them. Water-based lubricants are ok to use. Be sure to read the ingredients on the labels carefully before you buy a vaginal lubricant.
- First insertion of ANNOVERA must be prior to the date of expiration. Discard one year after first insertion. See "How should I dispose of (throw away) ANNOVERA?" below.
- Do not take any medicines unless your healthcare provider says it is ok to take them.
Tell your healthcare provider when you start a new medicine.
How do I clean ANNOVERA?
- After removing ANNOVERA from your vagina, wash it with mild soap and warm water, rinse, and pat it dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel before you store it. Only use mild soap and warm water to clean.
- Wash ANNOVERA with mild soap and warm water and pat it dry before you put it back into your vagina.
- Store ANNOVERA in the case provided.
How should I store ANNOVERA?
- Store ANNOVERA in the supplied case at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Protect ANNOVERA from direct sunlight.
- Do not refrigerate or freeze ANNOVERA.
- Avoid storing ANNOVERA in extreme heat.
- Keep ANNOVERA and all medicines out of the reach of children and pets.
How should I dispose of (throw away) ANNOVERA?
- After 13 cycles of use, place ANNOVERA in the case that comes with it.
- Dispose of ANNOVERA at a drug take-back location, if available. If a drug take-back location is not available, dispose of ANNOVERA in the trash, out of the reach of children and pets.
- Do not throw away ANNOVERA in the toilet.
- See www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for more information about disposal of medicines.
When does ANNOVERA become effective?
ANNOVERA becomes effective on the day it is inserted (Day 1), if it is inserted between Days 2 and 5 of your menstrual period. If ANNOVERA is inserted more than 5 days from when you start your menstrual period, you should use a barrier method of birth control, such as a male condom or spermicide, during sexual intercourse for the first 7 days you use ANNOVERA.
Will ANNOVERA interfere during sexual intercourse?
- If ANNOVERA is placed as high as possible in your vagina, it will not interfere with sexual intercourse.
Can I take ANNOVERA out during the first 3 weeks of my cycle?
- You should leave ANNOVERA in the entire 21 days (3 weeks).
- If ANNOVERA comes out or if you remove it, put it back in as soon as possible. If you put ANNOVERA back into your vagina before 2 hours has passed, you do not need to use another method of birth control. However, if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina for more than 2 hours at one time or if ANNOVERA is out of your vagina at different times that add up to more than a total of 2 hours over the first 21 days of your cycle, you will need to use another method of birth control until ANNOVERA has been in your vagina for 7 days in a row, such as male condoms or spermicides.
What should I do if ANNOVERA comes out of my vagina?
ANNOVERA can slip or accidentally come out of your vagina (expelled), for example, during sexual intercourse, bowel movements, or use of tampons.
- If ANNOVERA slips out of your vagina, wash ANNOVERA with mild soap and warm water, rinse and pat dry with a clean cloth towel or paper towel and put it back in your vagina right away or within 2 hours. See "Can I take ANNOVERA out during the first 3 weeks of my cycle?" in the section above.
- ANNOVERA can move around and become visible at the opening of your vagina. If this happens follow "Step 4" above for directions on how to push ANNOVERA back to its right position.
What if I lose ANNOVERA?
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you lose ANNOVERA. You should use a back-up method of birth control such as a male condom or spermicide for preventing pregnancy until you get a new ANNOVERA.
If you have other questions call your healthcare provider.
For information, call Mayne Pharma at 1-844- 825-8500
Distributed by:
Mayne Pharma
Raleigh, NC 27609ANNOVERA is a registered trademark of Population Council and licensed under license.
The Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised 08/2024
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Ring Pouch Carton
NDC: 68308-752-01
Rx onlyAnnovera®
(segesterone acetate and
ethinyl estradiol vaginal system)
Delivers 0.15 mg/0.013 mg per dayThis product is intended to prevent pregnancy.
It does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS)
and other sexually transmitted diseases.Keep out of reach of children and pets
For Vaginal Use
CONTAINS 1 VAGINAL SYSTEMmayne pharma
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ANNOVERA
segesterone acetate and ethinyl estradiol ringProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68308-752 Route of Administration VAGINAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength segesterone acetate (UNII: 9AMX4Q13CC) (segesterone - UNII:09Q5UV3747) segesterone acetate 103 mg ethinyl estradiol (UNII: 423D2T571U) (ethinyl estradiol - UNII:423D2T571U) ethinyl estradiol 17.4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) dibutyltin dilaurate (UNII: L4061GMT90) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68308-752-01 1 in 1 CARTON 08/16/2024 1 30 in 1 POUCH; Type 4: Device Coated/Impregnated/Otherwise Combined with Drug Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA209627 08/16/2024 Labeler - Mayne Pharma (867220261) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sever Pharma Solutions AB 508638848 ANALYSIS(68308-752) , MANUFACTURE(68308-752) , PACK(68308-752) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sharp Packaging Services, LLC 002346625 PACK(68308-752) , LABEL(68308-752)
Trademark Results [Annovera]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ANNOVERA 87849469 not registered Live/Pending |
The Population Council, Inc. 2018-03-26 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.