WEGOVY- semaglutide injection, solution WEGOVY- semaglutide tablet
WEGOVY by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
WEGOVY by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Novo Nordisk, Novo Nordisk A/S, Catalent Belgium SA, Novo Nordisk Pharmaceutical Industries, LP. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use WEGOVY® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for WEGOVY.
WEGOVY (semaglutide) injection, for subcutaneous use
WEGOVY (semaglutide) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- In rodents, semaglutide causes thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures. It is unknown whether WEGOVY causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans as the human relevance of semaglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined. (5.1, 13.1)
- WEGOVY is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Counsel patients regarding the potential risk of MTC and symptoms of thyroid tumors. (4, 5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
WEGOVY is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist.
WEGOVY injection is indicated in combination with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity:
- to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with established CV disease and either obesity or overweight. (1)
- to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- o Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity. (1)
- o Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition. (1)
- for the treatment of noncirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis (consistent with stages F2 to F3 fibrosis) in adults. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on improvement of MASH and fibrosis [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon the verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. (1)
WEGOVY tablets are indicated in combination with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity:
- To reduce the risk of major adverse CV events (CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with established CV disease and either obesity or overweight. (1 )
- To reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in adults with obesity, or in adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition. (1 )
Limitations of Use:
- Concomitant use of WEGOVY (semaglutide) tablets or WEGOVY (semaglutide) injection with other semaglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist is not recommended. (1 )
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
In patients with diabetes, monitor blood glucose prior to starting and during WEGOVY treatment. (2.1)
WEGOVY Injection
- Administer WEGOVY injection once weekly as an adjunct to diet and increased physical activity, on the same day each week, at any time of day, with or without meals. (2.1)
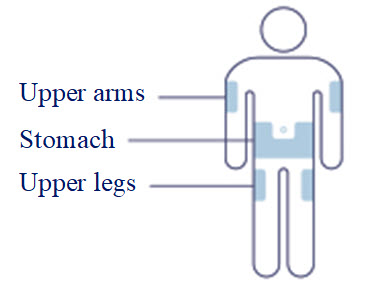
- Inject subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. (2.1)
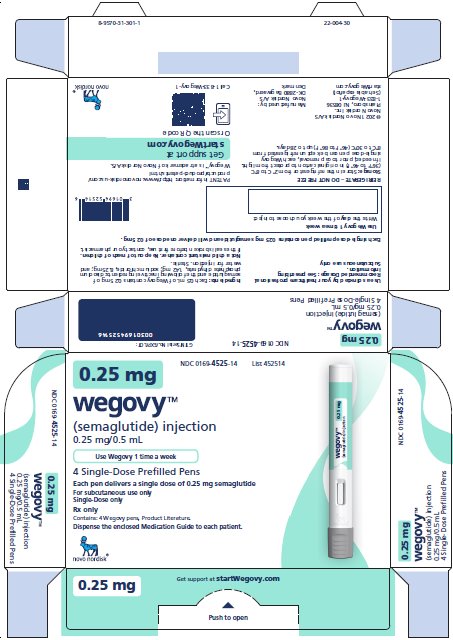
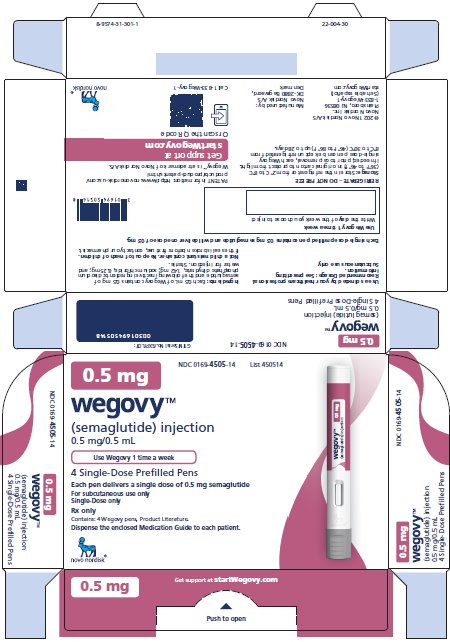
- Initiate at 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks. Then follow the dosage escalation schedule in Table 1, titrating every 4 weeks to achieve the maintenance dosage. (2.2)
- The usual recommended maintenance dosage of WEGOVY injection is 2.4 mg once weekly. Refer to the full PI for maintenance dosages based on the indication. (2.2)
WEGOVY Tablets
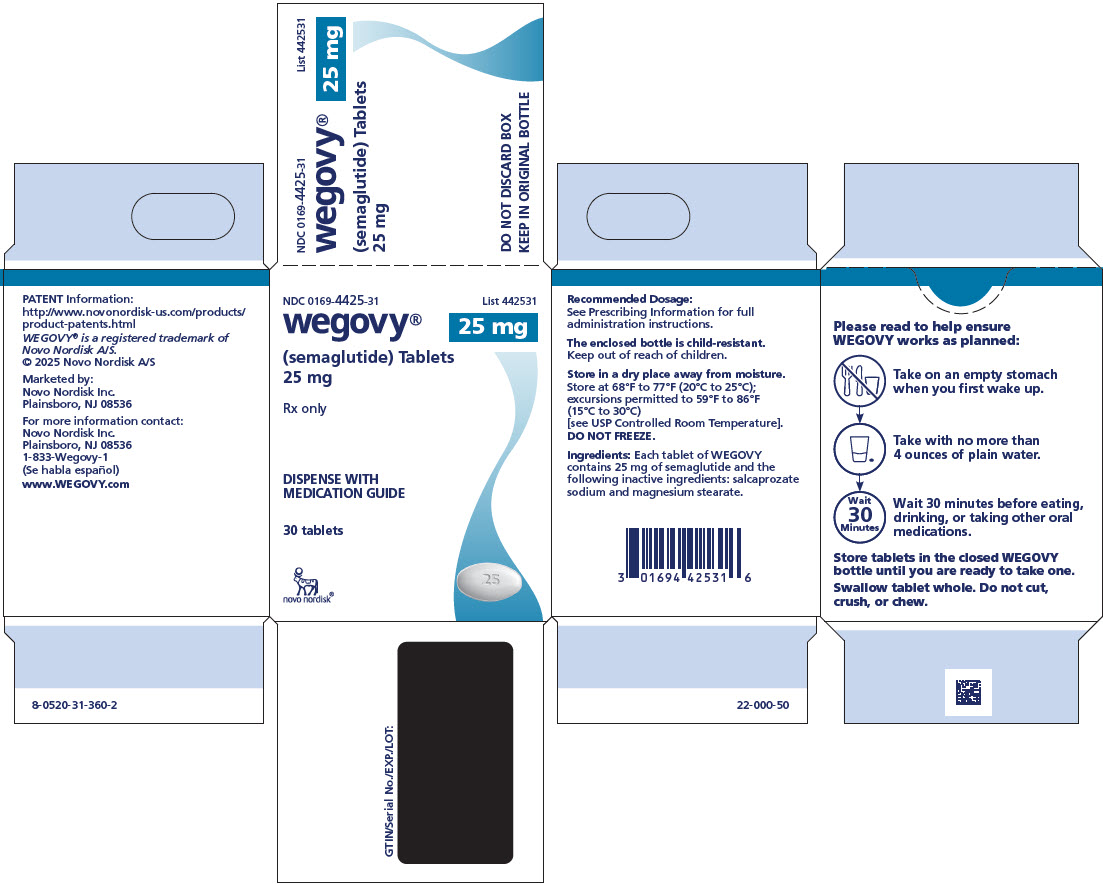
- Take WEGOVY tablets orally once-daily on an empty stomach in the morning with water (up to 4 ounces). Do not take with other liquids besides water (2.1).
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, chew or dissolve. (2.1)
- After taking WEGOVY tablet wait at least 30 minutes before eating food, drinking beverages or taking other oral medications. (2.1)
- Initiate WEGOVY tablet with a dosage of 1.5 mg once daily for 30 days. Then follow the dosage escalation schedule, titrating every 30 days to achieve the maintenance dosage. (2.2)
- The recommended maintenance dosage of WEGOVY tablets is 25 mg orally once daily for cardiovascular risk reduction and weight reduction in adults
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Acute Pancreatitis: Has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including WEGOVY. Discontinue if pancreatitis is suspected. (5.2)
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: Has occurred in clinical trials. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and clinical follow-up are indicated. (5.3)
- Hypoglycemia: Concomitant use with insulin or an insulin secretagogue may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia. Reducing the dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue may be necessary. Inform all patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. (5.4)
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion: Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions that could lead to volume depletion. (5.5)
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: Use has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe. WEGOVY is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis. (5.6)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported postmarketing. Discontinue WEGOVY if suspected and promptly seek medical advice. (5.7)
- Diabetic Retinopathy Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Has been reported in trials with semaglutide. Patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy should be monitored. (5.8)
- Heart Rate Increase: Monitor heart rate at regular intervals. (5.9)
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: Monitor for depression or suicidal thoughts. Discontinue WEGOVY if symptoms develop. (5.10)
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Has been reported in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers of any planned surgeries or procedures. (5.11)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in adults or pediatric patients aged 12 years and older are: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, headache, fatigue, dyspepsia, dizziness, abdominal distension, eructation, hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, flatulence, gastroenteritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and nasopharyngitis. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novo Nordisk Inc., at 1-833-934-6891 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
WEGOVY delays gastric emptying. May impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Consider increased clinical or laboratory monitoring when used concomitantly with other oral medications that have a narrow therapeutic index or that require clinical monitoring. (7.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. For patients receiving WEGOVY for CV risk reduction or weight reduction, discontinue WEGOVY when pregnancy is recognized. For patients with MASH, use during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. (8.1)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended during treatment with WEGOVY tablets. (8.2)
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: For patients receiving WEGOVY for CV risk reduction or weight reduction, or for MASH where the potential risk outweighs the potential benefit, discontinue WEGOVY at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy because of the long half-life of semaglutide. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 1/2026
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Monitoring and Administration Instructions
2.2 Recommended Dosage for WEGOVY Injection
2.3 Recommended Dosage of WEGOVY Tablets
2.4 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose(s)
2.5 Switching Between WEGOVY Injection and WEGOVY Tablets
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
5.2 Acute Pancreatitis
5.3 Acute Gallbladder Disease
5.4 Hypoglycemia
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
5.6 Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.8 Diabetic Retinopathy Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
5.9 Heart Rate Increase
5.10 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
5.11 Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Concomitant Use with Insulin or an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea)
7.2 Oral Medications
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial in Adult Patients with Cardiovascular Disease and Either Obesity or Overweight
14.2 Weight Reduction and Long-term Maintenance Studies in Adults with Obesity or Overweight
14.3 Weight Reduction and Long-term Maintenance Study of WEGOVY Injection in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older with Obesity
14.4 Noncirrhotic Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis with Moderate to Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Adults Treated with WEGOVY Injection
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
- In rodents, semaglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures. It is unknown whether WEGOVY causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans as human relevance of semaglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
- WEGOVY is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) [see Contraindications (4)]. Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of WEGOVY and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with WEGOVY [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
WEGOVY injection is indicated in combination with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity:
- To reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with established CV disease and either obesity or overweight.
-
To reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- o Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity.
- o Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition.
- For the treatment of noncirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), formerly known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis (consistent with stages F2 to F3 fibrosis) in adults. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on improvement of MASH and fibrosis [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon the verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
WEGOVY tablets are indicated in combination with a reduced calorie diet and increased physical activity:
- To reduce the risk of major adverse CV events (CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with established CV disease and either obesity or overweight.
- To reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in adults with obesity, or in adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition.
Limitations of Use
Concomitant use of WEGOVY (semaglutide) tablets or WEGOVY (semaglutide) injection with other semaglutide-containing products or with any other GLP-1 receptor agonist is not recommended.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Monitoring and Administration Instructions
In patients with diabetes mellitus, monitor blood glucose prior to starting WEGOVY and during WEGOVY treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Administer WEGOVY in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
WEGOVY Injection
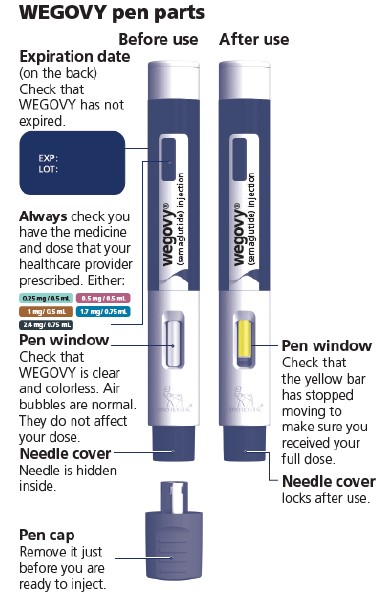
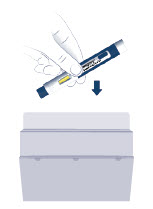
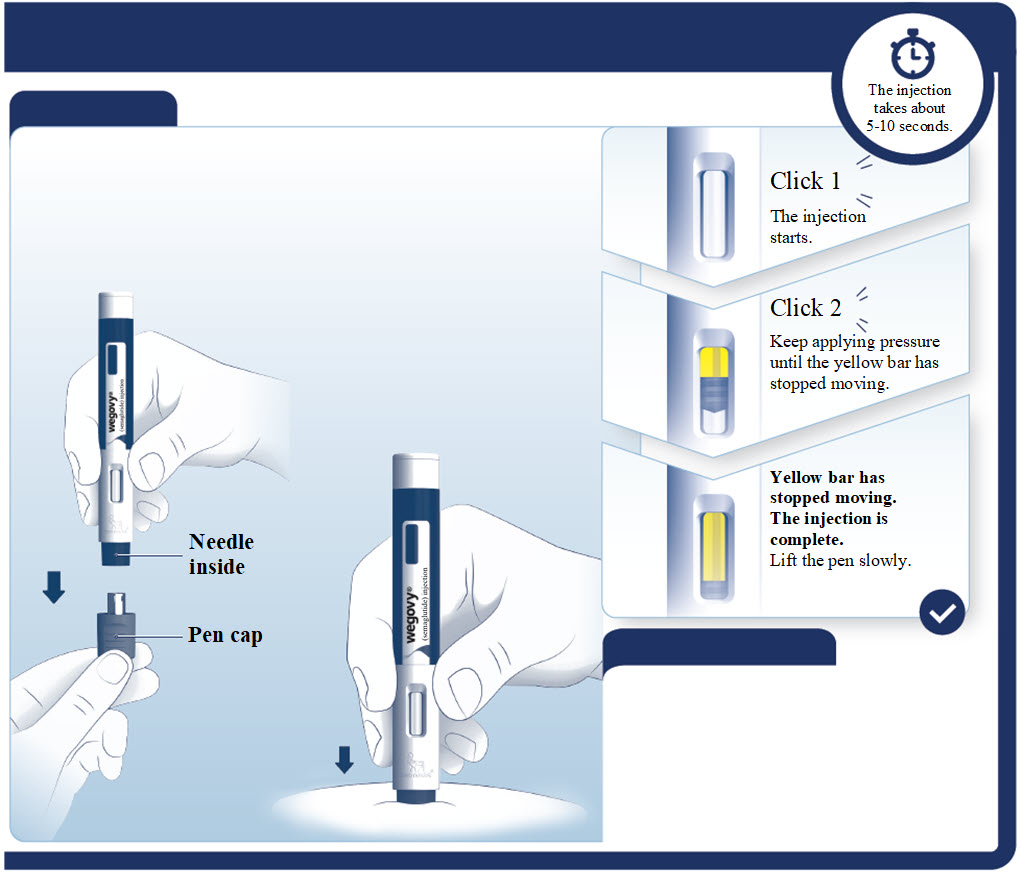
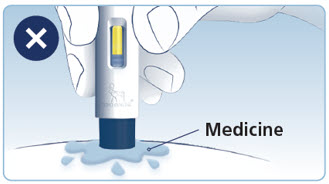
- Prior to initiation of WEGOVY injection, train patients on proper injection technique. Refer to the accompanying Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
- Visually inspect the WEGOVY injection prior to each administration. Only use if solution is clear, colorless, and contains no particles.
- Administer WEGOVY injection once weekly, on the same day each week, at any time of day, with or without meals.
- Inject WEGOVY subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. The time of day and the injection site can be changed without the need for a dosage modification.
WEGOVY Tablets
- Take one WEGOVY tablet orally once daily on an empty stomach in the morning with water (up to 4 ounces). Do not take WEGOVY tablets with other liquids besides water [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Do not take more than one tablet per day.
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not split, crush, chew or dissolve in any solution.
- After taking a WEGOVY tablet, wait at least 30 minutes before eating food, drinking beverages or taking other oral medications [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage for WEGOVY Injection
Recommended Starting Dosage and Dosage Escalation of WEGOVY Injection for All Approved Indications
- The recommended starting dosage of WEGOVY injection is 0.25 mg administered subcutaneously once weekly.
- Follow the dosage escalation in Table 1 to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- If patients do not tolerate a dose during dosage escalation, consider delaying dosage escalation for 4 weeks.
Table 1. Recommended Starting Dosage and Dosage Escalation of WEGOVY Injection for All Approved Indications in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
Weeks
Once-weekly Subcutaneous Injection Dosage
Starting Dosage
1 through 4
0.25 mg
Dosage
Escalation5 through 8
0.5 mg
9 through 12
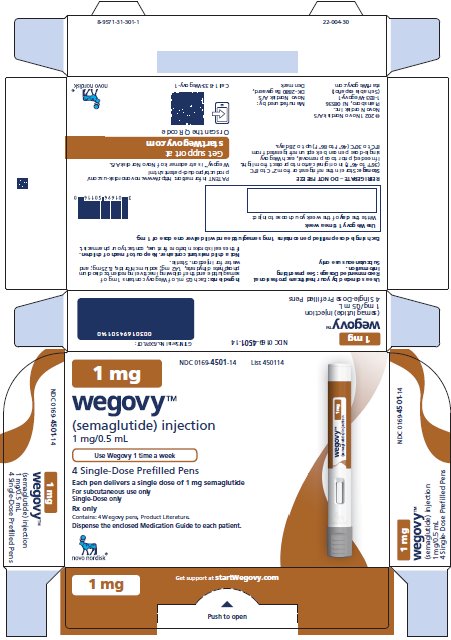
1 mg
13 through 16
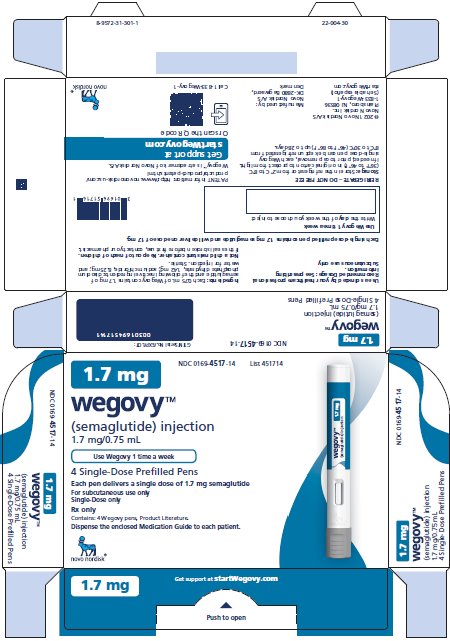
1.7 mg
Maintenance
Dosage17 and onward
See the indication below for the recommended maintenance dosage(s)
Recommended Maintenance Dosage of WEGOVY Injection for Approved Indications
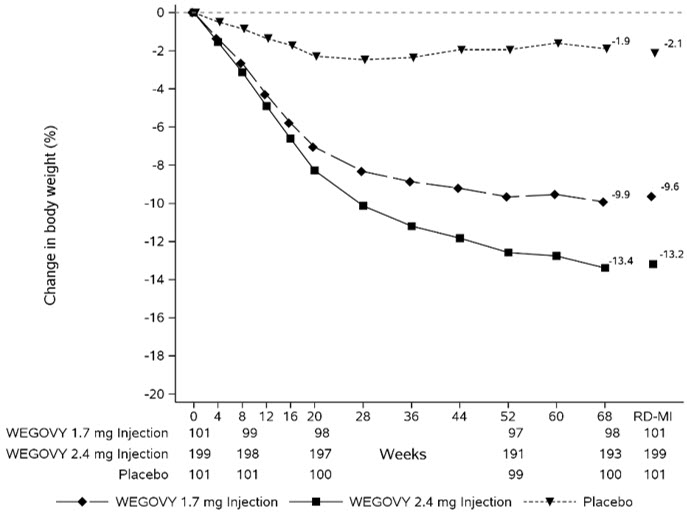
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Adults
- The maintenance dosage of WEGOVY injection for cardiovascular risk reduction in adults is either 2.4 mg (recommended) or 1.7 mg once weekly.
- Consider treatment response and tolerability when selecting the maintenance dosage [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Weight Reduction in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
The maintenance dosage of WEGOVY injection for weight reduction in adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older is either 2.4 mg (recommended) or 1.7 mg once weekly.
Consider treatment response and tolerability when selecting the maintenance dosage [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3)].
Noncirrhotic MASH with Moderate to Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Adults
The recommended maintenance dosage of WEGOVY injection for the treatment of noncirrhotic MASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis in adults is 2.4 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly. If patients do not tolerate the maintenance dosage of 2.4 mg once weekly, the dosage can be decreased to 1.7 mg once weekly. Consider reescalation to 2.4 mg once weekly [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Studies (14.4)].
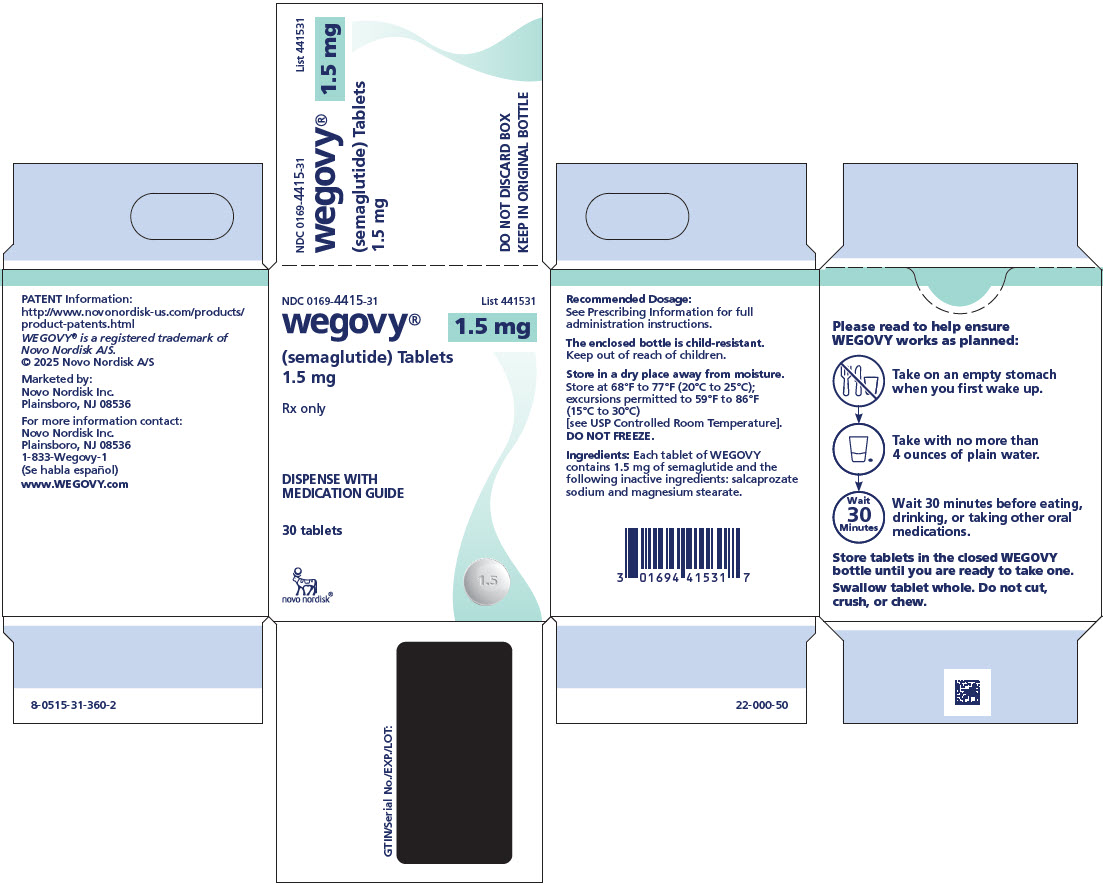
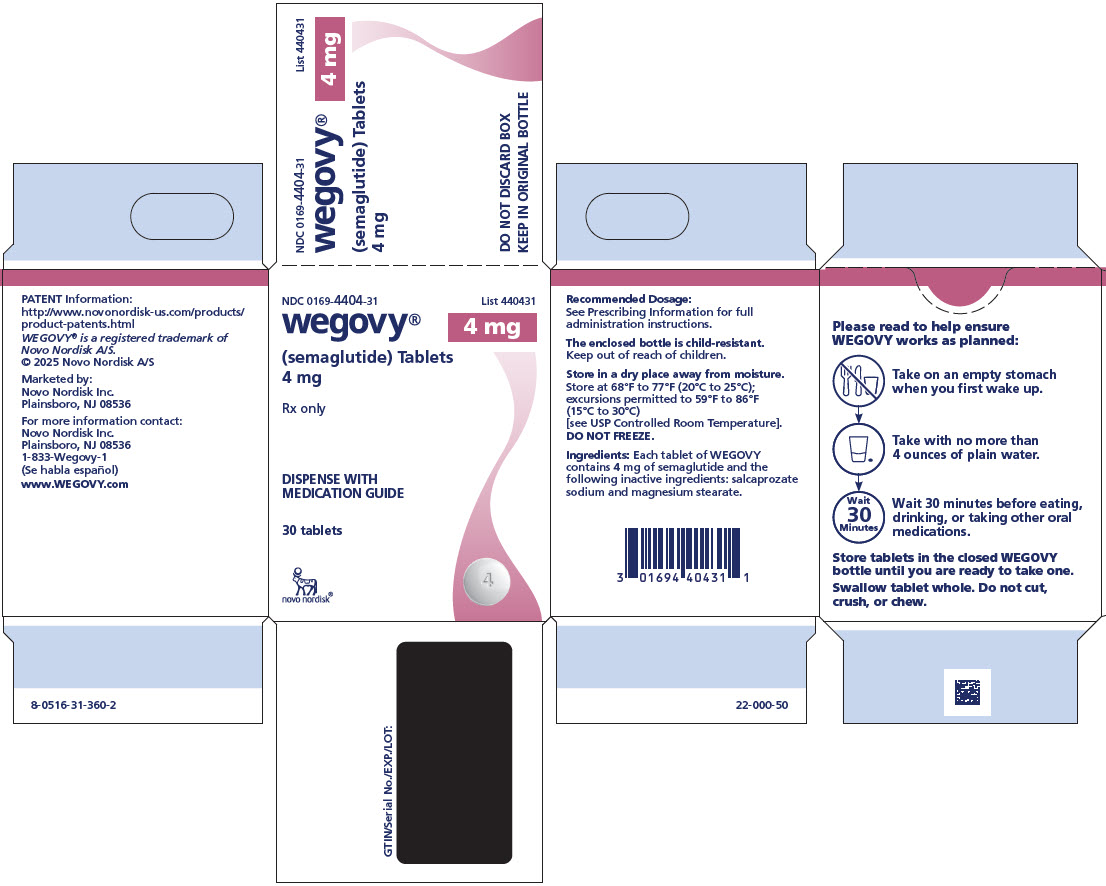
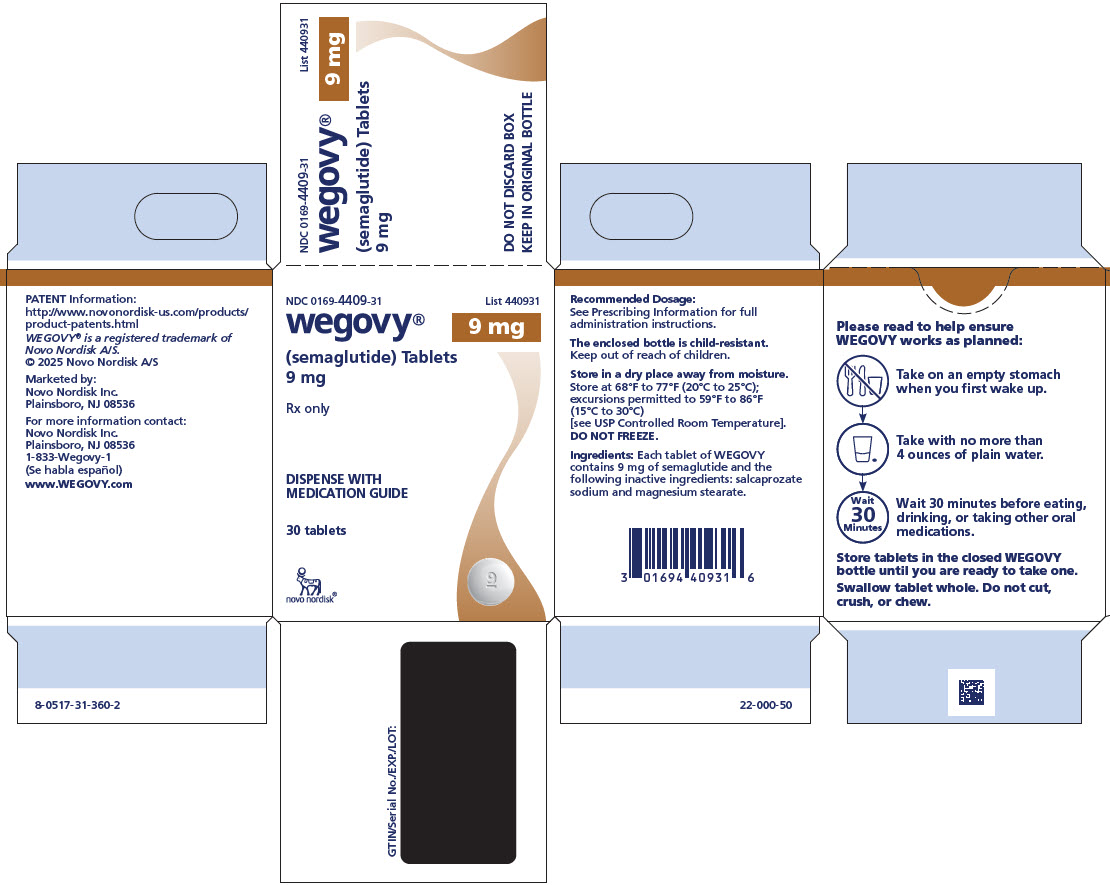
2.3 Recommended Dosage of WEGOVY Tablets
Recommended Dosage of WEGOVY Tablets for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction or Weight Reduction in Adults
- The recommended starting dosage of WEGOVY tablets is 1.5 mg taken orally once daily. Follow the dosage escalation in Table 2 to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- If patients do not tolerate a dose during dosage escalation, consider delaying dosage escalation.
- The recommended maintenance dosage of WEGOVY tablets is 25 mg orally once daily.
- If patients do not tolerate the 25 mg once daily maintenance dosage, consider switching to WEGOVY injection 1.7 mg once weekly [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
- Do not take more than one tablet per day.
Table 2. Recommended Dosage of WEGOVY Tablets for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction or Weight Reduction in Adults
Days
Once Daily Tablet
Dosage
Starting Dosage
1 through 30
1.5 mg
Dosage Escalation
31 through 60
4 mg
61 through 90
9 mg
Maintenance Dosage
91 and onward
25 mg
2.4 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose(s)
WEGOVY Injection
- If one dose of WEGOVY injection is missed and the next scheduled dose is:
- o More than 2 days away, administer WEGOVY injection as soon as possible.
- o Less than 2 days away do not administer the WEGOVY injection dose. Resume dosing on the regularly scheduled day of the week.
- If 2 or more consecutive doses of WEGOVY injection are missed, resume dosing as scheduled or, if needed, reinitiate WEGOVY injection and follow the dosage escalation schedule, which may reduce the occurrence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions associated with reinitiation of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
WEGOVY Tablets
If a dose of WEGOVY tablets is missed, skip the missed dose and take the next dose the following day.
2.5 Switching Between WEGOVY Injection and WEGOVY Tablets
Switching from WEGOVY Injection to WEGOVY Tablets
- Patients taking WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection for cardiovascular risk reduction or weight reduction in adults may switch to WEGOVY 25 mg tablets.
- One week after discontinuing WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection, initiate 25 mg of WEGOVY tablets orally once daily.
Switching from WEGOVY Tablets to WEGOVY Injection
- Patients may switch from WEGOVY 25 mg tablets to WEGOVY injection.
- The day after discontinuing WEGOVY tablets 25 mg once daily, initiate WEGOVY 2.4 mg subcutaneous injection once weekly. For patients who do not tolerate WEGOVY 25 mg tablets, consider switching to WEGOVY 1.7 mg injection.
- If additional weight reduction is needed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with WEGOVY 25 mg tablets, consider switching to WEGOVY 1.7 mg injection and follow the recommended dosage escalation for WEGOVY injection. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
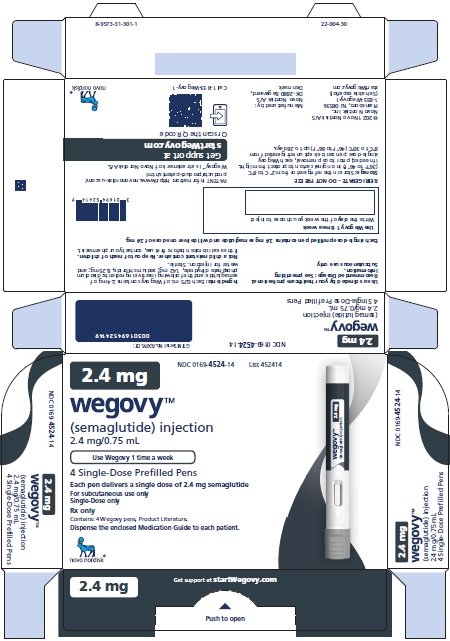
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: clear, colorless solution available in 5 prefilled, disposable, single-dose pens:
- 0.25 mg/0.5 mL
- 0.5 mg/0.5 mL
- 1 mg/0.5 mL
- 1.7 mg/0.75 mL
- 2.4 mg/0.75 mL
Tablet: white to light yellow, round shaped debossed with the strength on one side and “novo” on the other side:
- 1.5 mg
- 4 mg
- 9 mg
Tablet: white to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with the strength on one side and “novo” on the other side:
- 25 mg
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
WEGOVY is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- A personal or family history of MTC or in patients with MEN 2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- A prior serious hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide or to any of the excipients in WEGOVY injection or WEGOVY tablet. Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, have been reported with WEGOVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
In mice and rats, semaglutide caused a dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent increase in the incidence of thyroid C-cell tumors (adenomas and carcinomas) after lifetime exposure at clinically relevant plasma exposures [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. It is unknown whether WEGOVY causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including MTC, in humans, as human relevance of semaglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Cases of MTC in patients treated with liraglutide, another GLP-1 receptor agonist, have been reported in the postmarketing period; the data in these reports are insufficient to establish or exclude a causal relationship between MTC and GLP-1 receptor agonist use in humans.
WEGOVY is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with MEN 2. Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of WEGOVY and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness).
Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with WEGOVY. Such monitoring may increase the risk of unnecessary procedures, due to the low-test specificity for serum calcitonin and a high background incidence of thyroid disease. Significantly elevated serum calcitonin value may indicate MTC and patients with MTC usually have calcitonin values greater than 50 ng/L. If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated.
5.2 Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including WEGOVY [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. After initiation of WEGOVY, observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis, which may include persistent or severe abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the back), and which may or may not be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue WEGOVY and initiate appropriate management.
5.3 Acute Gallbladder Disease
Treatment with WEGOVY is associated with an increased occurrence of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. The incidence of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis was higher in WEGOVY injection-treated pediatric patients aged 12 years and older than in WEGOVY injection-treated adults. In randomized clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, cholelithiasis was reported by 1.6% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 0.7% of placebo injection-treated patients, and by 2.5% of WEGOVY tablet-treated patients and 1% of placebo tablet-treated patients. Cholecystitis was reported by 0.6% of WEGOVY injection-treated adult patients and 0.2% of placebo- treated patients. In a clinical trial in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older for weight reduction, cholelithiasis was reported by 3.8% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 0% placebo-treated patients. Cholecystitis was reported by 0.8% of WEGOVY injection-treated pediatric patients and 0% placebo-treated patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of cholelithiasis; however, the incidence of acute gallbladder disease was greater in WEGOVY-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients, even after accounting for the degree of weight loss. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated.
5.4 Hypoglycemia
WEGOVY lowers blood glucose and can cause hypoglycemia.
In a trial of WEGOVY injection in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 for weight reduction (Study 3), hypoglycemia (defined as a plasma glucose less than 54 mg/dL) was reported in more patients treated with WEGOVY versus placebo [see Adverse Reaction (6.1)]. One episode of severe hypoglycemia (requiring the assistance of another person) was reported in one WEGOVY treated patient versus no placebo-treated patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In glycemic control clinical trials, the risk of hypoglycemia was increased when semaglutide injection or tablet was used concomitantly with insulin or an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea). Patients with diabetes mellitus taking WEGOVY in combination with insulin or an insulin secretagogue may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia. The use of WEGOVY in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or in combination with insulin has not been evaluated.
Inform patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. In patients with diabetes, monitor blood glucose prior to starting WEGOVY and during WEGOVY treatment. When initiating WEGOVY, consider reducing the dose of concomitantly administered insulin or insulin secretagogue to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.5 Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, in some cases requiring hemodialysis, in patients treated with semaglutide [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. The majority of the reported events occurred in patients who experienced gastrointestinal adverse reactions leading to dehydration such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions to WEGOVY that could lead to volume depletion, especially during dosage initiation and escalation of WEGOVY.
5.6 Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Use of WEGOVY has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In clinical trials for adults for weight reduction, severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving WEGOVY than placebo. Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported in 4.1% and 0.9% of WEGOVY-injection and placebo-treated patients, respectively, and in 2% of WEGOVY tablet-treated and 0% of placebo-treated patients, respectively. Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions have also been reported postmarketing with GLP-1 receptor agonists.
WEGOVY is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis.
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema) have been reported with WEGOVY. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue use of WEGOVY, treat promptly per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. WEGOVY is contraindicated in patients with a prior serious hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide or to any of the excipients in WEGOVY [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Use caution in a patient with a history of anaphylaxis or angioedema with another GLP-1 receptor agonist because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to these reactions with WEGOVY.
5.8 Diabetic Retinopathy Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
In a 2-year trial with semaglutide 0.5 mg and 1 mg once-weekly injection in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and high CV risk, diabetic retinopathy complications (which was a 4-component adjudicated endpoint) occurred in patients treated with semaglutide injection (3%) compared to placebo (1.8%). The absolute risk increase for diabetic retinopathy complications was larger among patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy at baseline (semaglutide injection 8.2%, placebo 5.2%) than among patients without a known history of diabetic retinopathy (semaglutide injection 0.7%, placebo 0.4%).
In a trial of adult patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 for weight reduction (Study 3), diabetic retinopathy was reported by 4% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 2.7% placebo-treated patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In a glycemic control trial evaluating a dose comparable to the 9 mg dose and the 25 mg semaglutide tablet dose in patients with type 2 diabetes, a similar proportion of patients in each dose group reported diabetic retinopathy related adverse reactions during the trial; 1.3% and 1.9% of patients in the 9 mg and 25 mg semaglutide group, respectively, reported moderate-severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy events, and 0% and 0.4% reported proliferative retinopathy events, respectively.
Rapid improvement in glucose control has been associated with a temporary worsening of diabetic retinopathy. The effect of long-term glycemic control with semaglutide on diabetic retinopathy complications has not been studied. Patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy should be monitored for progression of diabetic retinopathy.
5.9 Heart Rate Increase
Treatment with WEGOVY was associated with increases in resting heart rate. Mean increases in resting heart rate of 1 to 4 beats per minute (bpm) were observed in WEGOVY injection-treated adult patients compared to placebo in clinical trials for weight reduction. More adult patients treated with WEGOVY injection compared with placebo had maximum changes from baseline at any visit of 10 to 19 bpm (41% versus 34%, respectively) and 20 bpm or more (26% versus 16%, respectively). In a clinical trial in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with normal baseline heart rate, more patients treated with WEGOVY injection compared to placebo had maximum changes in heart rate of 20 bpm or more (54% versus 39%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Findings were similar in a trial with the WEGOVY tablets.
Monitor heart rate at regular intervals consistent with usual clinical practice. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare providers of palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during WEGOVY treatment. If patients experience a sustained increase in resting heart rate, discontinue WEGOVY.
5.10 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Suicidal behavior and ideation have been reported in clinical trials with other weight management products. Monitor patients treated with WEGOVY for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue WEGOVY in patients who experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Avoid WEGOVY in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation.
5.11 Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
WEGOVY delays gastric emptying [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
Available data are insufficient to inform recommendations to mitigate the risk of pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation in patients taking WEGOVY, including whether modifying preoperative fasting recommendations or temporarily discontinuing WEGOVY could reduce the incidence of retained gastric contents. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking WEGOVY.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Risk of Thyroid C-Cell Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Acute Gallbladder Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Acute Kidney Injury due to Volume Depletion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Diabetic Retinopathy Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Heart Rate Increase [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
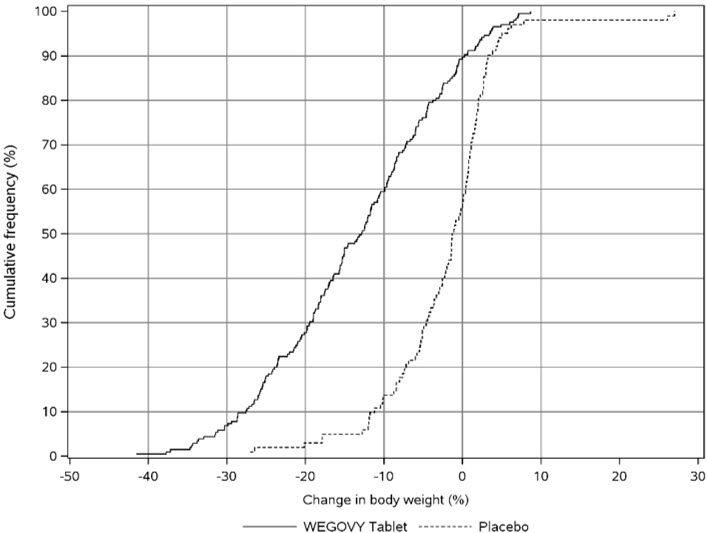
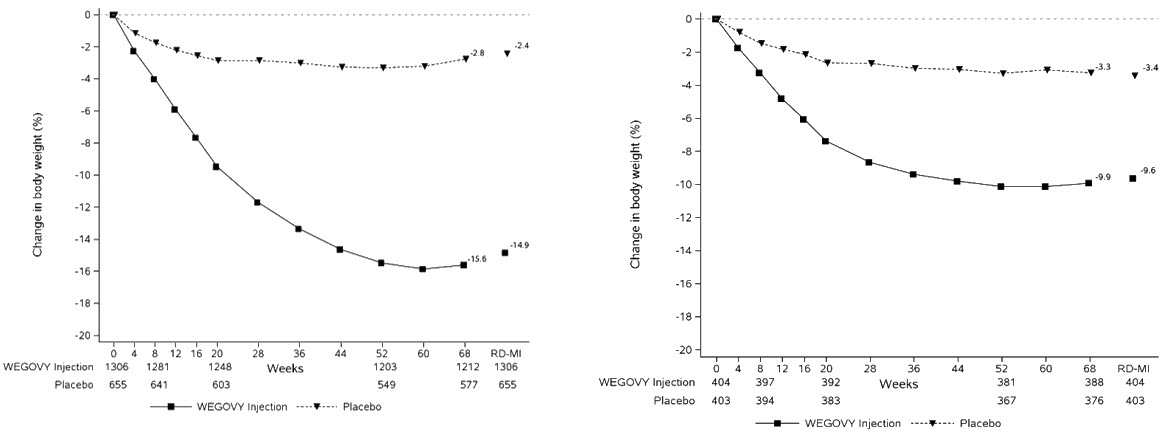
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials in Adults with Obesity or Overweight for Weight Reduction
WEGOVY 2.4 mg Subcutaneous Weekly Dosage
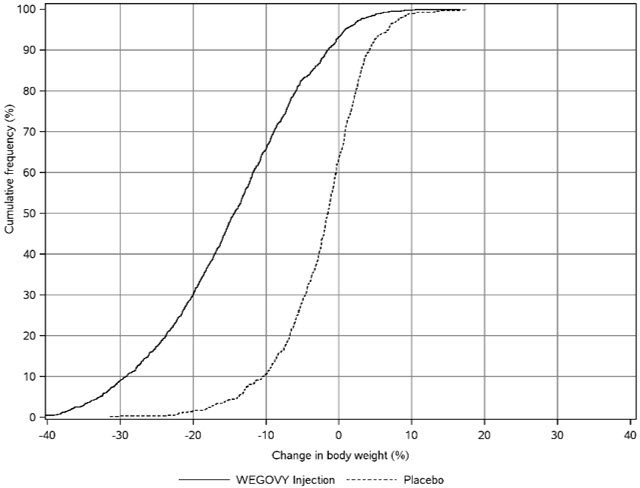
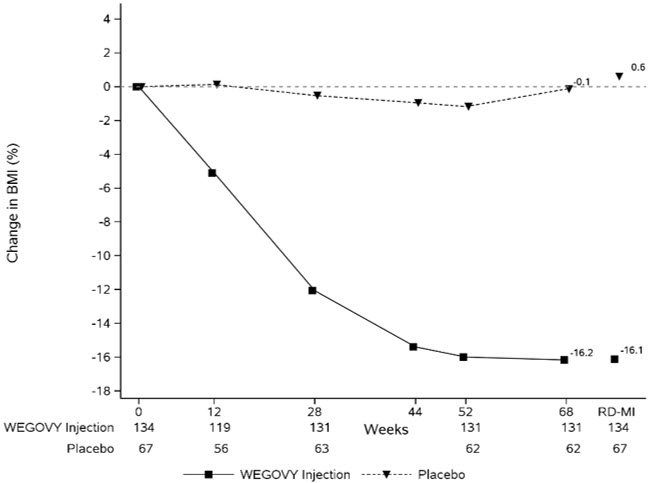
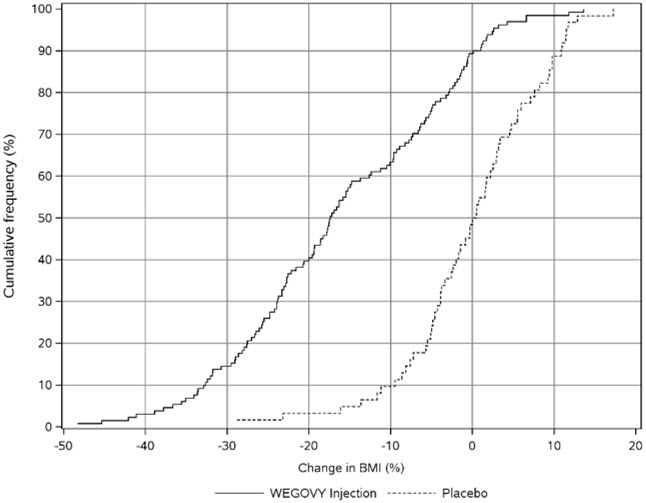
WEGOVY was evaluated for safety in 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials that included 2,116 adult patients with obesity or overweight treated with 2.4 mg WEGOVY for up to 68 weeks and a 7-week off-drug follow-up period [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Baseline characteristics included a mean age of 48 years, 71% female, 72% White, 14% Asian, 9% Black or African American, and 5% reported as other or unknown; and 85% were not Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, 13% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, and 2% reported as unknown. The baseline characteristics were 42% with hypertension, 19% with type 2 diabetes, 43% with dyslipidemia, 28% with a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2, and 4% with CV disease.
In these clinical trials, 6.8% of patients treated with 2.4 mg WEGOVY and 3.2% of patients treated with placebo permanently discontinued treatment as a result of adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation were nausea (1.8% versus 0.2%), vomiting (1.2% versus 0%), and diarrhea (0.7% versus 0.1%) for WEGOVY and placebo, respectively.
Adverse reactions reported in clinical trials in adults and greater than or equal to 2% of WEGOVY-treated patients and more frequently than in placebo-treated patients are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥2% and Greater Than Placebo) in WEGOVY Injection-treated Adults with Obesity or Overweight for Weight Reduction
Placebo
N=1,261
%WEGOVY
Injection (2.4 mg
once weekly)
N=2,116
%Nausea
16
44
Diarrhea
16
30
Vomiting
6
24
Constipation
11
24
Abdominal Paina
10
20
Headache
10
14
Fatigueb
5
11
Dyspepsia
3
9
Dizziness
4
8
Abdominal Distension
5
7
Eructation
<1
7
Hypoglycemia in T2DMc
2
6
Flatulence
4
6
Gastroenteritis
4
6
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
3
5
Gastritisd
1
4
Gastroenteritis Viral
3
4
Hair Loss
1
3
Dysesthesiae
1
2
a Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, gastrointestinal pain, abdominal tenderness, abdominal discomfort and epigastric discomfort
b Includes fatigue and asthenia
c Defined as blood glucose <54 mg/dL with or without symptoms of hypoglycemia or severe hypoglycemia (requiring the assistance of another person) in patients with type 2 diabetes not on concomitant insulin (Study 3, WEGOVY N=403, Placebo N=402). See text below for further information regarding hypoglycemia in patients with and without type 2 diabetes. T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus
d Includes chronic gastritis, gastritis, gastritis erosive, and reflux gastritis
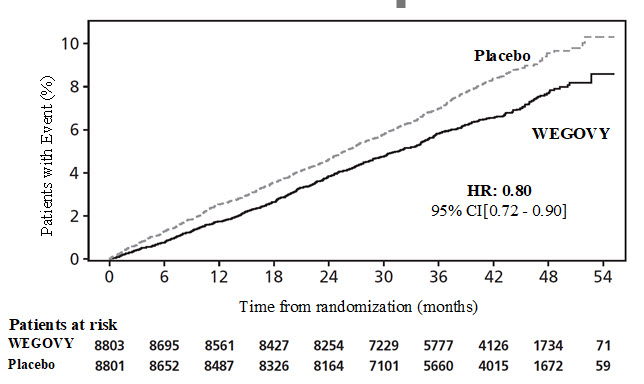
e Includes paresthesia, hyperesthesia, burning sensation, allodynia, dysesthesia, skin burning sensation, pain of skin, and sensitive skinIn a CV outcomes trial, 8,803 patients were exposed to WEGOVY injection for a median of 37.3 months and 8,801 patients were exposed to placebo for a median of 38.6 months [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Safety data collection was limited to serious adverse events (including death), adverse events leading to discontinuation, and adverse events of special interest. Sixteen percent (16%) of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 8% of placebo-treated patients, respectively, discontinued study drug due to an adverse event. Additional information from this trial is included in subsequent sections below when relevant.
WEGOVY Tablet 25 mg Oral Daily Dosage
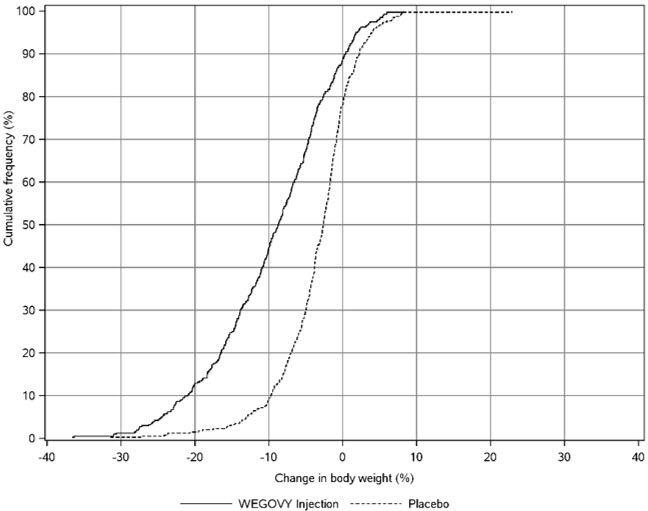
WEGOVY tablet was evaluated for safety in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that included 204 adult patients with obesity or overweight and at least one weight-related comorbidity, treated with WEGOVY tablet for up to 64 weeks and a 7-week off drug follow-up period (Study 7) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded. Baseline characteristics included a mean age of 48 years, 75.6% were female, 92.7% were White, 0.5% were Asian, 6.3% were Black or African American, and 8.3% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean baseline body weight was 106.4 kg and mean BMI was 37.5 kg/m2. The baseline characteristics were 44% with hypertension, 31% with dyslipidemia, 27% with a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2, and 1.5% with coronary artery disease.
In the clinical trial, 6.9% of patients treated with WEGOVY 25 mg tablets and 5.9% patients treated with placebo permanently discontinued treatment as a result of adverse reactions. The most common event type leading to discontinuation was gastrointestinal adverse reactions reported in 3.4% with WEGOVY tablets and 2% with placebo.
In the clinical trial with WEGOVY tablets, the types and frequency of common adverse reactions were similar to those listed in Table 3.
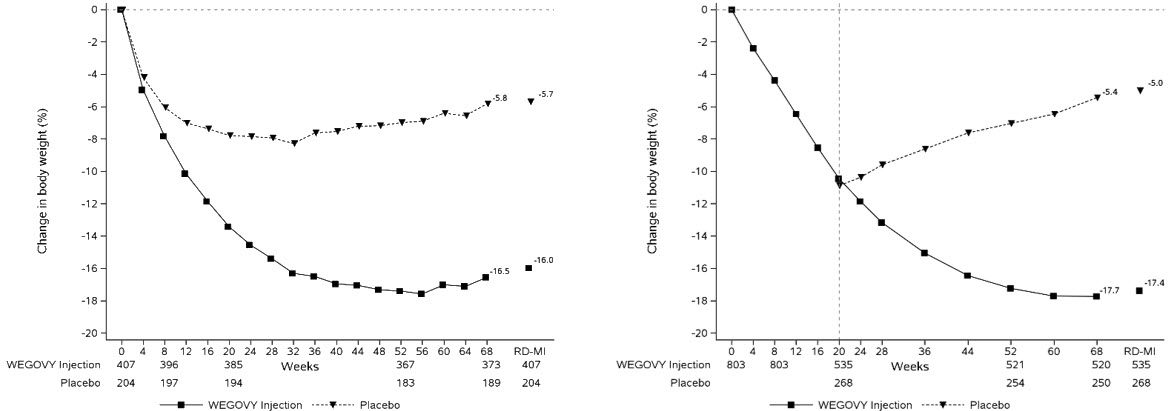
Adverse Reactions in a Clinical Trial of Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older with Obesity Treated with WEGOVY Injection for Weight Reduction
WEGOVY injection was evaluated in a 68-week, double-blind, randomized, parallel group, placebo-controlled, multi-center trial in 201 pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Baseline characteristics included a mean age of 15.4 years; 38% of patients were male; 79% were White, 8% were Black or African American, 2% were Asian, and 11% were of other or unknown race; and 11% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean baseline body weight was 107.5 kg, and mean BMI was 37 kg/m2.
Table 4 shows adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 3% of WEGOVY injection-treated pediatric patients and more frequently than in the placebo group from a study in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions (≥3% and Greater than Placebo) in WEGOVY Injection-treated Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older with Obesity for Weight Reduction
Placebo
N=67
%WEGOVY
Injection (2.4 mg
once weekly)
N=133
%Nausea
18
42
Vomiting
10
36
Diarrhea
19
22
Headache
16
17
Abdominal Pain
6
15
Nasopharyngitis
10
12
Dizziness
3
8
Gastroenteritis
3
7
Constipation
2
6
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
2
4
Sinusitis
2
4
Urinary tract infection
2
4
Ligament sprain
2
4
Anxiety
2
4
Hair Loss
0
4
Cholelithiasis
0
4
Eructation
0
4
Influenza
0
3
Rash
0
3
Urticaria
0
3
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials in Adults with MASH Treated with WEGOVY Injection
The safety of WEGOVY injection was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Study 9) that included 1,195 adult patients with MASH, including 800 patients who were exposed to WEGOVY for a median of 95.3 weeks and 395 patients who were exposed to placebo for a median of 83.1 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
The most commonly reported adverse reactions were consistent with the other approved WEGOVY indications (see Table 3). There is limited information in patients with MASH and a BMI <25 kg/m2. Additional information from the MASH trial is included in subsequent sections when notable. Unless indicated, the incidence of the adverse reactions in MASH patients was similar to other approved indications.
Other Adverse Reactions in Adults and/or Pediatric Patients Treated with WEGOVY Injection or WEGOVY Tablets
Acute Gallbladder Disease
In WEGOVY clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, cholelithiasis was reported by 1.6% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 0.7% of placebo-treated patients and by 2.5% of WEGOVY tablet-treated patients and 1% of placebo tablet-treated patients. Cholecystitis was reported by 0.6% of WEGOVY injection-treated adult patients and 0.2% of placebo-treated patients. In a clinical trial in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older for weight reduction [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], cholelithiasis was reported by 3.8% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 0% placebo-treated patients. Cholecystitis was reported by 0.8% of WEGOVY injection-treated pediatric patients and 0% placebo-treated patients.
Hypoglycemia
Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
In a trial of adult patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 for weight reduction, clinically significant hypoglycemia (defined as a plasma glucose less than 54 mg/dL) was reported in 6.2% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients versus 2.5% of placebo-treated patients. A higher rate of clinically significant hypoglycemic episodes was reported with WEGOVY injection (semaglutide 2.4 mg) versus semaglutide 1 mg injection (10.7 vs. 7.2 episodes per 100 patient years of exposure, respectively); the rate in the placebo-treated group was 3.2 episodes per 100 patient years of exposure. In addition, one episode of severe hypoglycemia requiring intravenous glucose was reported in a WEGOVY injection-treated patient versus none in placebo-treated patients. The risk of hypoglycemia was increased when WEGOVY was used with a sulfonylurea.
In a glycemic control trial evaluating a dose comparable to the 9 mg dose and the 25 mg semaglutide tablet dose in patients with type 2 diabetes not on insulin, clinically significant hypoglycemia was reported in similar proportions of subjects in both treatment groups.
Patients without Type 2 Diabetes
Episodes of hypoglycemia have been reported with GLP-1 receptor agonists in adult patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus. In WEGOVY clinical trials in adult patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus for weight reduction, there was no systematic capturing or reporting of hypoglycemia.
In a CV outcomes trial in adult patients without type 2 diabetes, 3 episodes of serious hypoglycemia were reported in WEGOVY injection-treated patients versus 1 episode in placebo. Patients with a history of bariatric surgery (a risk factor for hypoglycemia) had more events of serious hypoglycemia while taking WEGOVY injection (2.3%, 2/87) than placebo (0%, 0/97).
Retinal Disorders in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
In a trial of adult patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 for weight reduction, retinal disorders were reported by 6.9% of patients treated with WEGOVY injection (semaglutide 2.4 mg), 6.2% of patients treated with semaglutide 1 mg, and 4.2% of patients treated with placebo. The majority of events were reported as diabetic retinopathy (4%, 2.7%, and 2.7%, respectively) and non-proliferative retinopathy (0.7%, 0%, and 0%, respectively).
In a glycemic control trial evaluating the 9 mg and 25 mg semaglutide tablet doses in patients with type 2 diabetes, a similar proportion of patients in each dose group reported diabetic retinopathy related adverse reactions during the trial; 1.3% and 1.9% of patients in the 9 mg and 25 mg semaglutide group, respectively, reported moderate-severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy events, and 0% and 0.4% reported proliferative retinopathy events, respectively.
In a 2-year trial with semaglutide 0.5 mg and 1 mg once-weekly injection in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk, diabetic retinopathy complications (which was a 4-component adjudicated endpoint) occurred in patients treated with semaglutide injection (3%) compared to placebo (1.8%). The absolute risk increase for diabetic retinopathy complications was larger among patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy at baseline (semaglutide injection 8.2%, placebo 5.2%) than among patients without a known history of diabetic retinopathy (semaglutide injection 0.7%, placebo 0.4%).
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, 73% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 47% of patients receiving placebo reported gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including severe reactions that were reported more frequently among patients receiving WEGOVY injection (4.1%) than placebo (0.9%). The most frequently reported reactions were nausea (44% vs. 16%), vomiting (25% vs. 6%), and diarrhea (30% vs. 16%). Other reactions that occurred at a higher incidence among WEGOVY injection-treated adult patients included dyspepsia, abdominal pain, abdominal distension, eructation, flatulence, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, hemorrhoids, and hiccups. These reactions were most frequently reported during dosage escalation.
Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported in 2% of WEGOVY tablet-treated and 0% of placebo-treated patients, respectively.
In the pediatric clinical trial for weight reduction, 62% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 42% of placebo-treated patients reported gastrointestinal adverse reactions. The most frequently reported reactions were nausea (42% vs. 18%), vomiting (36% vs. 10%), and diarrhea (22% vs. 19%). Other gastrointestinal-related reactions that occurred at a higher incidence than placebo among WEGOVY injection-treated pediatric patients included abdominal pain, constipation, eructation, gastroesophageal reflux disease, dyspepsia, and flatulence.
Permanent discontinuation of treatment as a result of a gastrointestinal adverse reaction occurred in 4.3% of WEGOVY injection-treated adult patients versus 0.7% of placebo-treated patients. In a pediatric clinical trial for weight reduction, 2.3% of patients treated with WEGOVY injection versus 1.5% of patients who received placebo discontinued treatment as a result of gastrointestinal adverse reactions.
Other Adverse Reactions in Adults and/or Pediatric Patients Treated with WEGOVY Injection
The below adverse reactions are applicable for both WEGOVY injection and WEGOVY tablets and include descriptions of WEGOVY injection clinical trial data, where relevant. The safety and effectiveness of WEGOVY tablets have not been established in pediatric patients or patients with MASH.
Acute Pancreatitis
In WEGOVY clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, acute pancreatitis was confirmed by adjudication in 4 WEGOVY-treated patients (0.2 cases per 100 patient years) and 1 in placebo-treated patients (less than 0.1 cases per 100 patient years). One additional case of acute pancreatitis was confirmed in a patient treated with WEGOVY in another clinical trial.
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury occurred in clinical trials for weight reduction in 7 adult patients (0.4 cases per 100 patient years) receiving WEGOVY versus 4 patients (0.2 cases per 100 patient years of exposure) receiving placebo. Some of these adverse reactions occurred in association with gastrointestinal adverse reactions or dehydration. In addition, 2 patients treated with WEGOVY had acute kidney injury with dehydration in other clinical trials. The risk of renal adverse reactions with WEGOVY was increased in adult patients with a history of renal impairment (trials included 65 patients with a history of moderate or severe renal impairment at baseline), and occurred more frequently during dose titration.
Increase in Heart Rate
Mean increases in resting heart rate of 1 to 4 beats per minute (bpm) were observed with routine clinical monitoring in WEGOVY-treated adult patients compared to placebo in clinical trials for weight reduction. In weight reduction trials in which adult patients were randomized prior to dose-escalation, more patients treated with WEGOVY, compared with placebo, had maximum changes from baseline at any visit of 10 to 19 bpm (41% versus 34%, respectively) and 20 bpm or more (26% versus 16%, respectively). In a clinical trial for weight reduction in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with normal baseline heart rate, more patients treated with WEGOVY compared to placebo had maximum changes in heart rate of 20 bpm or more (54% versus 39%).
Hypotension and Syncope
Adverse reactions related to hypotension (hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and decreased blood pressure) were reported in 1.3% of WEGOVY-treated adult patients versus 0.4% of placebo-treated patients and syncope was reported in 0.8% of WEGOVY-treated patients versus 0.2% of placebo-treated patients in clinical trials for weight reduction. Some reactions were related to gastrointestinal adverse reactions and volume loss associated with WEGOVY. Hypotension and orthostatic hypotension were more frequently seen in patients on concomitant antihypertensive therapy. In a clinical trial in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older for weight reduction, hypotension was reported in 2.3% of WEGOVY-treated patients versus 0% in placebo-treated patients.
Appendicitis
Appendicitis (including perforated appendicitis) occurred in 10 (0.5%) WEGOVY-treated adult patients and 2 (0.2%) patients receiving placebo in clinical trials for weight reduction.
Injection Site Reactions
In clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, 1.4% of WEGOVY-treated patients and 1% of patients receiving placebo experienced injection site reactions (including injection site pruritus, erythema, inflammation, induration, and irritation).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema) have been reported with WEGOVY.
In a pediatric clinical trial for weight reduction, rash was reported in 3% of WEGOVY-treated patients and 0% of placebo-treated patients, and urticaria was reported in 3% of WEGOVY-treated patients and 0% of placebo-treated patients.
In adult clinical trials for weight reduction, allergic reactions occurred in 16% (8/50) of WEGOVY-treated patients with anti-semaglutide antibodies and in 7% (114/1659) of WEGOVY-treated patients who did not develop anti-semaglutide antibodies [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.6)].
Fractures
In the CV outcomes trial in adults, more fractures of the hip and pelvis were reported on WEGOVY than on placebo in female patients: 1% (24/2,448) vs. 0.2% (5/2,424), and in patients ages 75 years and older: 2.4% (17/703) vs. 0.6% (4/663), respectively.
In a clinical trial in adults with MASH, fractures occurred in 4.4% of WEGOVY-treated patients (2.6 cases per 100 patient years) compared to 3.3% of placebo-treated patients (2 cases per 100 patient years). Fractures were reported in both males and females with a median age of 61 years (range, 44 to 75).
Urolithiasis
In a CV outcomes trial, 1.2% of WEGOVY-treated patients and 0.8% of patients receiving placebo reported urolithiasis, including serious reactions that were reported more frequently among patients receiving WEGOVY (0.6%) than placebo (0.4%).
Dysgeusia
In clinical trials in adults for weight reduction, 1.7% of WEGOVY-treated patients and 0.5% of placebo-treated patients reported dysgeusia.
Other Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients Treated with WEGOVY Tablets for Weight Reduction
Dysesthesia
In a clinical trial with WEGOVY tablets, 4.9% of WEGOVY-treated patients and no placebo-treated patients reported dysesthesia adverse reactions, with preferred terms including sensitive skin, hyperesthesia, paresthesia, allodynia, and skin burning sensation.
Laboratory Abnormalities in Adults and/or Pediatric Patients Treated with WEGOVY Injection
The below laboratory abnormalities are applicable for both WEGOVY injection and WEGOVY tablets and include descriptions of WEGOVY injection clinical trial data, where relevant. The safety and effectiveness of WEGOVY tablets have not been established in pediatric patients or patients with MASH.
Amylase and Lipase
Adult and pediatric patients treated with WEGOVY had a mean increase from baseline in amylase of 15% to 16% and lipase of 39% in clinical trials for weight reduction. These changes were not observed in the placebo group.
In a clinical trial in adults with MASH, increases in lipase greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in 4.7% (35/750) of WEGOVY-treated patients compared with 1.3% (5/374) of placebo-treated patients. The clinical significance of elevations in lipase or amylase with WEGOVY is unknown in the absence of other signs and symptoms of pancreatitis.
Liver Tests
In a pediatric clinical trial for weight reduction, increases in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) greater than or equal to 5 times the ULN were observed in 4 (3%) WEGOVY-treated patients compared with 0% of placebo-treated patients. In some patients, increases in ALT and AST were associated with other confounding factors (such as gallstones). In the CV outcomes trial in adults, increases in total bilirubin greater than or equal to 3 times the ULN were observed in 0.3% (30/8,585) of WEGOVY-treated patients versus 0.2% (14/8,579) of placebo-treated patients.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of semaglutide, the active ingredient of WEGOVY. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: acute pancreatitis and necrotizing pancreatitis, sometimes resulting in death; ileus, intestinal obstruction, severe constipation including fecal impaction
Hypersensitivity: anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria
Pulmonary: Pulmonary aspiration has occurred in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation
Renal and Urinary Disorders: acute kidney injury
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Concomitant Use with Insulin or an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea)
WEGOVY lowers blood glucose and can cause hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when WEGOVY is used concomitantly with insulin or insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylureas). The addition of WEGOVY in patients treated with insulin has not been evaluated.
When initiating WEGOVY, consider reducing the dose of concomitantly administered insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
7.2 Oral Medications
WEGOVY causes a delay of gastric emptying and thereby has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. In clinical pharmacology trials with semaglutide 1 mg once weekly injection, semaglutide did not affect the absorption of orally administered medications [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In a drug interaction study with the semaglutide tablet, levothyroxine exposure was increased 33% (90% CI: 1.25-1.42). Monitor the effects of oral medications concomitantly administered with WEGOVY. Consider increased clinical or laboratory monitoring for medications that have a narrow therapeutic index or that require clinical monitoring.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to semaglutide during pregnancy. Pregnant women exposed to WEGOVY and healthcare providers are encouraged to contact Novo Nordisk at 1-877-390-2760 or www.wegovypregnancyregistry.com.
Risk Summary
Based on animal reproduction studies, there may be potential risks to the fetus from exposure to semaglutide during pregnancy. Available pharmacovigilance data and data from clinical trials with WEGOVY use in pregnant patients are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Weight loss offers no benefit to a pregnant patient and may cause fetal harm. When a pregnancy is recognized, advise the pregnant patient of the risk to a fetus, and discontinue WEGOVY (see Clinical Considerations).
There may be risks to the mother and fetus related to underlying MASH with advanced liver fibrosis (see Clinical Considerations). Whether semaglutide treatment during pregnancy reduces these risks is unknown. WEGOVY for the treatment of MASH should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In pregnant rats administered semaglutide during organogenesis, embryofetal mortality, structural abnormalities and alterations to growth occurred at maternal exposures below the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on AUC. In rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys administered semaglutide during organogenesis, early pregnancy losses and structural abnormalities were observed at below the MRHD (rabbit) and greater than or equal to 2-fold the MRHD (monkey). These findings coincided with a marked maternal body weight loss in both animal species (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Appropriate weight gain based on pre-pregnancy weight is currently recommended for all pregnant patients, including those who already have overweight or obesity, because of the obligatory weight gain that occurs in maternal tissues during pregnancy.
There may be risks to the mother and fetus related to MASH with advanced liver fibrosis, such as increased risks of gestational diabetes, hypertensive complications, preterm birth, and postpartum hemorrhage. The effect of semaglutide on these risks is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined fertility and embryofetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03, and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.04-, 0.1-, and 0.4-fold the MRHD) were administered to males for 4 weeks prior to and throughout mating and to females for 2 weeks prior to mating, and throughout organogenesis to Gestation Day 17. In parental animals, pharmacologically mediated reductions in body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. In the offspring, reduced growth and fetuses with visceral (heart blood vessels) and skeletal (cranial bones, vertebra, ribs) abnormalities were observed at the human exposure.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rabbits, subcutaneous doses of 0.001, 0.0025, or 0.0075 mg/kg/day (0.01-, 0.1-, and 0.9-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis from Gestation Day 6 to 19. Pharmacologically mediated reductions in maternal body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. Early pregnancy losses and increased incidences of minor visceral (kidney, liver) and skeletal (sternebra) fetal abnormalities were observed at greater than or equal to 0.0025 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (0.4-, 2-, and 6-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis, from Gestation Day 16 to 50. Pharmacologically mediated, marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with the occurrence of sporadic abnormalities (vertebra, sternebra, ribs) at greater than or equal to 0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (greater than or equal to 2 times human exposure).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (0.2-, 1-, and 3-fold the MRHD) were administered from Gestation Day 16 to 140. Pharmacologically mediated marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with an increase in early pregnancy losses and led to delivery of slightly smaller offspring at greater than or equal to 0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (greater than or equal to 1-time human exposure).
Salcaprozate sodium (SNAC), an absorption enhancer in WEGOVY tablets, crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in rats. In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant Sprague Dawley rats, SNAC was administered orally at 1,000 mg/kg/day (exposure levels were not measured) on Gestation Day 7 through lactation Day 20. An increase in gestation length, an increase in the number of stillbirths and a decrease in pup viability were observed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
WEGOVY Oral Tablets
Data from a clinical lactation study with semaglutide oral tablet formulation reported semaglutide concentrations below the lower limit of quantification in human milk. However, SNAC and/or its metabolites are present in human milk. Since the activity of enzymes involved in SNAC clearance may be lower in infants compared to adults, higher SNAC plasma levels may occur in neonates and infants. Because of the unknown potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant due to the possible accumulation of SNAC, and because there are alternative formulations of semaglutide that do not contain SNAC that can be used during lactation, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with WEGOVY tablets.
WEGOVY Subcutaneous Injection
There are no data on the presence of subcutaneously administered semaglutide or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. WEGOVY subcutaneous injection does not contain the SNAC metabolites.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for WEGOVY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from WEGOVY or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Because of the potential for fetal harm, discontinue WEGOVY in patients at least 2 months before they plan to become pregnant to account for the long half-life of semaglutide [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of WEGOVY injection in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity have been established. Use of WEGOVY injection for this indication is supported by a 68-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 201 pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with a BMI corresponding to ≥95th percentile for age and sex [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] and from trials in adult patients with obesity [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Use of the 1.7 mg once weekly maintenance dosage of WEGOVY injection in pediatric patients is also supported by additional exposure-efficacy and safety analyses in pooled adult and pediatric patients.
Adverse reactions with WEGOVY-injection treatment in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older were generally similar to those reported in adults. Pediatric patients aged 12 years and older treated with WEGOVY injection had greater incidences of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hypotension, rash, and urticaria compared to adults treated with WEGOVY [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Although there was an increased frequency of hypoglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes with obesity or overweight treated with WEGOVY injection, there are insufficient data to determine if the risk of hypoglycemia is higher in WEGOVY-treated pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes with obesity. Inform pediatric patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. In pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with type 2 diabetes, monitor blood glucose prior to starting WEGOVY injection and during treatment. When initiating WEGOVY injection in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with type 2 diabetes, consider reducing the dosage of concomitantly administered insulin secretagogue (such as sulfonylureas) or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
The safety and effectiveness of WEGOVY injection have not been established in pediatric patients:
- to reduce the risk of major adverse CV events. Clinical trials for this indication are highly impracticable because of the low prevalence of the condition in pediatric patients.
- to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in those less than 12 years of age.
- for the treatment of noncirrhotic MASH.
The safety and effectiveness of WEGOVY tablets have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the WEGOVY injection clinical trials for weight reduction and long-term maintenance, 233 (9%) WEGOVY injection-treated patients were aged 65 to less than 75 years and 23 (1%) WEGOVY injection-treated patients were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. In a WEGOVY tablets clinical trial for weight reduction and long-term maintenance, 16 (8%) WEGOVY tablets-treated patients were aged 65 to less than 75 years and 5 (2%) WEGOVY tablet-treated patients were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In a CV outcomes trial, 2,656 (30%) WEGOVY injection-treated patients were aged 65 to 75 years and 703 (8%) WEGOVY injection-treated patients were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. No overall difference in the effectiveness was observed between patients aged 65 years and older and younger adult patients. In the CV outcomes trial, patients aged 75 years and older reported more hip and pelvis fractures in the WEGOVY injection-treated patients than placebo-treated patients. Patients aged 75 years and older (WEGOVY injection-treated and placebo-treated) reported more serious adverse reactions overall compared to younger adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the clinical trial in patients with MASH, of the 534 patients randomized to WEGOVY injection, 138 (26%) were aged 65 years and older and 13 (2%) were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of WEGOVY injection have been observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients with MASH.
8.6 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
WEGOVY tablets have not been studied for weight reduction in adults with type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Administration of WEGOVY injection resulted in less weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight compared to those without type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
In patients without type 2 diabetes, the average semaglutide blood concentrations following administration of WEGOVY 25 mg tablets once daily or WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection once weekly were similar. In patients with type 2 diabetes, the average semaglutide blood concentrations following administration of WEGOVY 25 mg tablets once daily were lower than the average semaglutide blood concentrations following use of WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection once weekly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The lower semaglutide blood concentrations after administration of WEGOVY tablets in patients with type 2 diabetes may be associated with reductions in absolute bioavailability.
Given the differences in average semaglutide blood concentrations after administration of WEGOVY tablets and WEGOVY injection, and the higher variability in semaglutide blood concentrations after administration of WEGOVY tablets in all patient populations, some patients with type 2 diabetes taking WEGOVY tablets may experience subtherapeutic semaglutide blood concentrations. In patients with type 2 diabetes with an inadequate response to WEGOVY tablets, consider alternative therapies, including switching to WEGOVY injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses have been reported with other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Effects have included severe nausea, severe vomiting, and severe hypoglycemia. In the event of overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patient’s clinical signs and symptoms. In the event of an overdose of WEGOVY, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations. A prolonged period of observation and treatment for these symptoms may be necessary, taking into account the long half-life of WEGOVY of approximately 1 week.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
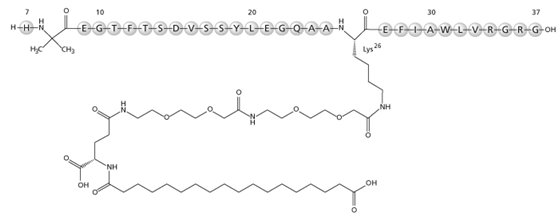
WEGOVY contains semaglutide, a human GLP-1 receptor agonist (or GLP-1 analog). The peptide backbone is produced by yeast fermentation. The main protraction mechanism of semaglutide is albumin binding, facilitated by modification of position 26 lysine with a hydrophilic spacer and a C18 fatty di-acid. Furthermore, semaglutide is modified in position 8 to provide stabilization against degradation by the enzyme dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4). A minor modification was made in position 34 to ensure the attachment of only one fatty di-acid. The molecular formula is C187H291N45O59 and the molecular weight is 4113.58 g/mol.
- Figure 1. Structural Formula of Semaglutide
WEGOVY injection is a sterile, aqueous, clear, colorless solution. Each 0.5 mL single-dose pen contains a solution of WEGOVY containing 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg or 1 mg of semaglutide; and each 0.75 mL single-dose pen contains a solution of WEGOVY containing 1.7 or 2.4 mg of semaglutide. Each 1 mL of WEGOVY contains the following inactive ingredients: disodium phosphate dihydrate, 1.42 mg; sodium chloride, 8.25 mg; and water for injection. WEGOVY has a pH of approximately 7.4. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH.
WEGOVY tablets include semaglutide as a white to almost white hygroscopic powder. Each tablet of WEGOVY contains 1.5 mg, 4 mg, 9 mg or 25 mg of semaglutide and the following inactive ingredients: Salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) and magnesium stearate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analogue with 94% sequence homology to human GLP-1. Semaglutide acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist that selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor, the target for native GLP-1.
GLP-1 is a physiological regulator of appetite and caloric intake, and the GLP-1 receptor is present in several areas of the brain involved in appetite regulation. Animal studies show that semaglutide distributed to and activated neurons in brain regions involved in regulation of food intake.
The exact mechanism of semaglutide in CV risk reduction in adults has not been established.
For treatment of MASH in humans, the precise mechanism of action of semaglutide is not fully understood and may involve multiple pathways mediated by weight loss and other factors. In a mouse model of diet-induced MASH, treatment with semaglutide resulted in histological improvements in steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in liver compared to baseline, which was associated with body weight loss, intermittent periods of reduced food intake, and improvements in relevant biomarkers. The relationship between the pathophysiology of MASH in animal models and humans has not been fully established.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Semaglutide lowers body weight with greater fat mass loss than lean mass loss. Semaglutide decreases calorie intake. The effects are likely mediated by affecting appetite.
Semaglutide stimulates insulin secretion and reduces glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. These effects can lead to a reduction of blood glucose.
Gastric Emptying
Semaglutide delays gastric emptying.
Cardiac Electrophysiology (QTc)
The effect of semaglutide on cardiac repolarization was tested in a thorough QTc trial. Semaglutide did not prolong QTc intervals at subcutaneous doses up to 1.5 mg at steady state.
Noninvasive Liver Disease Markers
Semaglutide decreases liver fat content measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Proton Density Fat Fraction (MRI-PDFF), liver stiffness assessed by transient elastography (TE), Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score, and the levels of the pro-peptide of type III collagen biomarker (Pro-C3). The clinical relevance of these changes is yet to be confirmed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
WEGOVY Injection
Absolute bioavailability of semaglutide is 89% following subcutaneous administration. Maximum concentration of semaglutide is reached 1 to 3 days post dose.
Similar exposure was achieved with subcutaneous administration of semaglutide in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
The average semaglutide steady state concentration following subcutaneous administration of WEGOVY 2.4 mg once weekly was approximately 75 nmol/L in patients with obesity or overweight (BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2). The steady state exposure concentrations increased proportionally with doses up to 2.4 mg once weekly.
WEGOVY Tablets
WEGOVY tablets are co-formulated with SNAC which facilitates the absorption of semaglutide after oral WEGOVY tablet administration. The absorption of semaglutide predominantly occurs in the stomach.
Absolute bioavailability of semaglutide is estimated to be approximately 1% to 2% following oral tablet administration. Maximum concentration of semaglutide is reached 1 hour post dose.
The average semaglutide steady state concentration following 25 mg tablet oral administration was approximately 77 nmol/L in patients with obesity or overweight (BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2). The steady-state concentrations increased approximately proportionally with doses up to 25 mg once daily.
In patients with overweight or obesity without type 2 diabetes, semaglutide concentrations following once-daily administration of oral WEGOVY 25 mg tablet are predicted to be comparable to WEGOVY 2.4 mg once-weekly injection, with higher variability in semaglutide concentrations compared to subcutaneous administration (90% of patients had average concentrations between 27 and 186 nmol/L with WEGOVY 25 mg tablet versus 51 and 110 nmol/L with WEGOVY 2.4 mg once-weekly injection).
Effect of Volume and Timing of Water Consumption: Single doses of oral semaglutide tablet were administered with 50 mL or 240 mL of water after an 8-hour overnight fast and a continued fast of 4 hours post-dose in healthy subjects. Semaglutide absorption [i.e., area under the curve (AUC) and peak concentrations (Cmax)] was higher following dosing with 50 mL water compared to that of 240 mL water.
For 10 days, healthy subjects received once daily doses of oral semaglutide with 50 mL or 120 mL of water under fasting conditions with post-dose fasting period of 15, 30, 60, or 120 minutes. In this study, semaglutide absorption (i.e., AUC and Cmax) was higher after a longer post-dose fasting period. There were no clinically significant differences in semaglutide absorption with administration of 50 mL or 120 mL of water.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of semaglutide following subcutaneous administration in patients with obesity or overweight is approximately 12.5 L. Semaglutide is extensively bound to plasma albumin (greater than 99%) which results in decreased renal clearance and protection from degradation.
Elimination
The apparent clearance of semaglutide in patients with overweight or obesity is approximately 0.05 L/h. With an elimination half-life of approximately 1 week, semaglutide will be present in the circulation for about 5 to 7 weeks after the last injectable dose of 2.4 mg or oral dose of 25 mg.
Metabolism
The primary route of elimination for semaglutide is metabolism following proteolytic cleavage of the peptide backbone and sequential beta-oxidation of the fatty acid sidechain.
Excretion
The primary excretion routes of semaglutide-related material are via the urine and feces. Approximately 3% of the dose is excreted in the urine as intact semaglutide.
Specific Populations
Age, Sex, Race, Ethnicity, Body Weight, and Other Intrinsic Factors
No clinically significant differences in semaglutide pharmacokinetics were observed based on age (<65 years, 65-74, ≥75 years old), sex, race (White, Asian, or Black or African American), ethnicity, body weight, upper GI disease (i.e. chronic gastritis and/or gastroesophageal reflux disease), renal impairment [estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥30 to <90 mL/minute], or mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A-C) or fibrosis stage (F2 or F3 in patients with MASH).
There is no difference observed in the exposure of semaglutide following subcutaneous administration of WEGOVY between patients with MASH and patients with overweight or obesity.
Patients with Type 2 Diabetes:
The average semaglutide steady state concentration following subcutaneous administration of WEGOVY 2.4 mg once weekly was approximately 68 nmol/L in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight (BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2). The average semaglutide steady state concentration following 25 mg oral administration was approximately 44 nmol/L in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity or overweight (BMI greater than or equal to 25 kg/m2) with higher variability in semaglutide concentrations compared to subcutaneous administration (90% of patients had average concentrations between 11 nmol/L and 134 nmol/L with WEGOVY 25 mg tablet versus 47 nmol/L and 99 nmol/L with WEGOVY 2.4 mg once-weekly injection) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Drug Interactions Studies
Subcutaneous Injection
The delay of gastric emptying with semaglutide may influence the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Oral Tablets
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches: The delay of gastric emptying with semaglutide may influence the absorption of concomitantly administered oral drugs [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Trials were conducted to study the potential effect of semaglutide on the absorption of oral drugs taken with semaglutide tablets administered orally at steady-state exposure.
Levothyroxine: Total thyroxine (i.e., adjusted for endogenous levels) AUC of was increased by 33% following administration of a single dose of levothyroxine 600 mcg concomitantly administered with oral semaglutide. Maximum exposure (Cmax) was unchanged.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in semaglutide pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with omeprazole. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of the following drugs were observed when used concomitantly with semaglutide: lisinopril, S-warfarin, R-warfarin, metformin, digoxin, ethinyl estradiol, levonorgestrel, furosemide or rosuvastatin.
In Vitro Studies: Semaglutide has very low potential to inhibit or induce CYP enzymes, and to inhibit drug transporters.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of semaglutide or of other semaglutide products.
During the 68-week treatment periods in Studies 2 and 3 in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], 50/1709 (3%) of WEGOVY injection-treated patients developed anti-semaglutide antibodies (referred to as anti-drug-antibodies or ADA). Of these 50 WEGOVY injection-treated patients, 28 patients (2% of the total WEGOVY injection-treated study population) developed antibodies that cross-reacted with native GLP-1. In adults with MASH treated with WEGOVY for 72 weeks in Study 9 [see Clinical Studies (14.4)], 3/763 (0.4%) of patients developed ADA which were also cross-reactive to native GLP-1. No identified clinically significant effect of ADA on pharmacokinetics for WEGOVY injection was observed. There is insufficient evidence to characterize the effects of ADA on pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of semaglutide products.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, subcutaneous doses of 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg/day (2-, 8-, and 22-fold the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of WEGOVY subcutaneous injection 2.4 mg/week, or WEGOVY oral tablet 25 mg daily based on AUC) were administered to the males, and 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg/day (0.6-, 2-, and 5-fold MRHD) were administered to the females. A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas and a numerical increase in C-cell carcinomas were observed in males and females at all dose levels (greater than or equal to 0.6 times human exposure).
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Sprague Dawley rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.0025, 0.01, 0.025 and 0.1 mg/kg/day were administered (below quantification, 0.2-, 0.4-, and 2-fold the exposure at the MRHD). A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas was observed in males and females at all dose levels, and a statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell carcinomas was observed in males at greater than or equal to 0.01 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
Human relevance of thyroid C-cell tumors in rats is unknown and could not be determined by clinical studies or nonclinical studies [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Semaglutide was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a standard battery of genotoxicity tests (bacterial mutagenicity [Ames] human lymphocyte chromosome aberration, rat bone marrow micronucleus).
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.04-, 0.1-, and 0.4-fold the MRHD) were administered to male and female rats. Males were dosed for 4 weeks prior to mating, and females were dosed for 2 weeks prior to mating and throughout organogenesis until Gestation Day 17. No effects were observed on male fertility. In females, an increase in estrus-cycle length was observed at all dose levels, together with a small reduction in numbers of corpora lutea at greater than or equal to 0.03 mg/kg/day. These effects were likely an adaptive response secondary to the pharmacological effect of semaglutide on food consumption and body weight.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
The WEGOVY tablet contains SNAC as an absorption enhancer. An increase in lactate levels and a decrease in glucose levels in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were observed in mechanistic studies with SNAC in rats. Small but statistically significant increases in lactate levels (up to 2-fold) were observed in a few animals at approximately the clinical exposure. At higher exposures these findings were associated with moderate to marked adverse clinical signs (lethargy, abnormal respiration, ataxia, and reduced activity, body tone and reflexes) and marked decreases in plasma and CSF glucose levels. These findings are consistent with inhibition of cellular respiration and lead to mortality at SNAC concentrations >100-times the clinical Cmax.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial in Adult Patients with Cardiovascular Disease and Either Obesity or Overweight
Overview of Clinical Trial
Study 1 (NCT03574597) was a multi-national, multi-center, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial to determine the effect of WEGOVY injection relative to placebo on major adverse CV events (MACE) when added to current standard of care, which included management of CV risk factors and individualized healthy lifestyle counseling (including diet and physical activity) in adults with established CV disease and either obesity or overweight. The primary endpoint, MACE, was the time to first occurrence of a three-part composite outcome which included CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke. During the 16-week dose escalation period, patients were titrated to WEGOVY 2.4 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly or placebo. Patients who could not tolerate the recommended escalation dosage, could stay at a lower dose level.
All patients were 45 years or older, with an initial BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater and established CV disease (prior myocardial infarction, prior stroke, or peripheral arterial disease). Patients with a history of type 1 or type 2 diabetes were excluded. Concomitant CV therapies could be adjusted, at the discretion of the investigator, to ensure participants were treated according to the current standard of care for patients with established CV disease.
In this trial, 17,604 patients were randomized to WEGOVY injection or placebo. At baseline, the mean age was 62 years (range 45-93), 72% were male, 84% were White, 4% were Black or African American, and 8% were Asian, and 10% were Hispanic or Latino. Mean baseline body weight was 97 kg and mean BMI was 33 kg/m2. At baseline, prior myocardial infarction was reported in 76% of randomized individuals, prior stroke in 23%, and peripheral arterial disease in 9%. Heart failure was reported in 24% of patients. At baseline, CV disease and risk factors were managed with lipid-lowering therapy (90%), platelet aggregation inhibitors (86%), angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (74%), and beta blockers (70%). A total of 10% had moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73m2) and 0.4% had severe renal impairment eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2.
Results
In total, 96.9% of patients completed the trial, and vital status was available for 99.4% of patients. The median follow-up duration was 41.8 months. A total of 31% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 27% of placebo-treated patients permanently discontinued study drug. Of those patients on treatment at 1 year, 76% were on the 2.4 mg dose, 8% were on the 1.7 mg dose, and 16% were on lower doses. Of those patients on treatment at 2 years, 77% were on the 2.4 mg dose, 7% were on the 1.7 mg dose, and 17% were on lower doses.
For the primary analysis, a Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for superiority. Type 1 error was controlled across multiple tests.
WEGOVY injection significantly reduced the risk for first occurrence of MACE. The estimated hazard ratio (95% CI) was 0.80 (0.72, 0.90) (see Figure 2 and Table 5).
Figure 2. Cumulative Incidence Function: Time to First Occurrence of MACE in Study 1 with WEGOVY Injection
Data from the in-trial period. Cumulative incidence estimates are based on time from randomization to first EAC-confirmed cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke with non-CV death modeled as competing risk using the Aalen-Johansen estimator. Patients without events of interest were censored at the end of their in-trial observation period. Time from randomization to first cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke was analyzed using a Cox proportional hazards model with treatment as categorical fixed factor. The hazard ratio and confidence interval are adjusted for the group sequential design using the likelihood ratio ordering.
HR: Hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CV: cardiovascular
The treatment effect for the primary composite endpoint, its components, and other relevant endpoints in Study 1 are shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Treatment Effect for MACE and Other Events in Study 1 with WEGOVY Injection
Patients with events
n (%)Placebo
N=8,801WEGOVY Injection
N=8,803Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)Primary composite endpoint
Composite of CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke1
701 (8%)
569 (6.5%)
0.8 (0.72; 0.9)*2
Key secondary endpoints
CV death3
262 (3%)
223 (2.5%)
0.85 (0.71; 1.01)
All-cause death4
458 (5.2%)
375 (4.3%)
0.81 (0.71; 0.93)
Other endpoints
Fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction5
334 (3.8%)
243 (2.8%)
0.72 (0.61; 0.85)
Fatal or non-fatal stroke5
178 (2%)
160 (1.8%)
0.89 (0.72; 1.11)
Hospitalization for heart failure or urgent heart failure visits5,6
122 (1.4%)
97 (1.1%)
0.79 (0.60; 1.03)
* p-value <0.001, one-sided p-value
1 Primary endpoint
2 Adjusted for group sequential design using the likelihood ratio ordering.
3 CV death was the first confirmatory secondary endpoint in the testing hierarchy and superiority was not confirmed.
4 Confirmatory secondary endpoint. Not statistically significant based on the prespecified testing hierarchy.
5 Not included in the prespecified testing hierarchy for controlling type-I error.
6 Effect on heart failure has not been established.
NOTE: Time to first event was analyzed in a Cox proportional hazards model with treatment as factor. For patients with multiple events, only the first event contributed to the composite endpoint.
Table 6. Mean Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters at Week 104 in Study 11,2
PLACEBO
WEGOVY Injection
Baseline
Change from Baseline
(LSMean)Baseline
Change from Baseline
(LSMean)Difference from Placebo
(LSMean)Body Weight (kg)
96.8
-0.93
96.5
-9.43
-8.53
Waist Circumference (cm)
111.4
-1
111.3
-7.6
-6.5
Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)
131
-0.5
131
-3.8
-3.3
Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)
79
-0.5
79
-1
-0.5
Heart Rate
69
0.7
69
3.8
3.1
HbA1c (%)
5.8
0
5.8
-0.3
-0.3
Baseline
% Change from Baseline
(LSMean)Baseline
% Change from Baseline
(LSMean)Relative difference from placebo (%)
(LSMean)Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)4
156
-1.9
155.5
-4.6
-2.8
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)4
78.5
-3.1
78.5
-5.3
-2.2
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)4
44.2
0.6
44.1
4.9
4.2
Triglycerides (mg/dL)4
139.5
-3.2
138.6
-18.3
-15.6
1 Parameters listed in the table were not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
2 Responses were analyzed using an ANCOVA with treatment as fixed factor and baseline value as covariate. Before analysis, missing data were multiple imputed. The imputation model (linear regression) was done separately for each treatment arm and included baseline value as a covariate and was fitted to all subjects with a measurement regardless of treatment status at Week 104.
3 For body weight the ‘change from baseline’ and ‘difference to placebo’ the unit is percentage change from baseline.
4 Baseline value is the geometric mean.
The reduction of MACE with WEGOVY injection was not impacted by age, sex, race, ethnicity, BMI at baseline, or level of renal function impairment.
14.2 Weight Reduction and Long-term Maintenance Studies in Adults with Obesity or Overweight
Overview of Clinical Studies in Adults
The efficacy of WEGOVY once weekly subcutaneous injection for weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity were studied in three 68-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials; one 68-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo withdrawal trial; one 68-week, randomized, double-blind trial that investigated 2 different doses of WEGOVY injection versus placebo. In Studies 2 (NCT#03548935), 3 (NCT#03552757), and 4 (NCT#03611582), WEGOVY or matching placebo was escalated to 2.4 mg subcutaneous injection weekly during a 16-week period followed by 52 weeks on maintenance dose. In Study 5 (NCT#03548987), WEGOVY injection was escalated during a 20-week run-in period, and patients who reached a WEGOVY 2.4 mg subcutaneous injection weekly dosage after the run-in period were randomized to either continued treatment with WEGOVY injection or placebo for 48 weeks. In Study 6 (NCT#03811574), WEGOVY injection was escalated to 1.7 mg or 2.4 mg subcutaneous weekly dosages or placebo over 12 to 16 weeks followed by 52 weeks on either maintenance dose.
The efficacy of WEGOVY 25 mg oral once daily tablet for weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity was evaluated in a 64-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [Study 7 (NCT#05564117)]. WEGOVY tablet or matching placebo was escalated to a 25 mg tablet once daily during a 12-week period followed by 52-week maintenance period.
In Studies 2, 3, 5 and 7, all patients received instruction for a reduced-calorie diet (approximately 500 kcal/day deficit) and increased physical activity counseling (recommended to a minimum of 150 min/week) that began with the first dose of study medication or placebo and continued throughout the trial. In Study 4, patients received an initial 8-week low-calorie diet (total energy intake 1,000 to 1,200 kcal/day) followed by 60 weeks of a reduced-calorie diet (1200 to 1800 kcal/day) and increased physical activity (100 mins/week with gradual increase to 200 mins/week).
Study 2 was a 68-week trial that enrolled 1,961 patients with obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2) or with overweight (BMI 27 to 29.9 kg/m2) and at least one weight-related comorbid condition, such as treated or untreated dyslipidemia or hypertension; patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded. Patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either WEGOVY injection or placebo. At baseline, mean age was 46 years (range 18 to 86), 74% were female, 75% were White, 13% were Asian and 6% were Black or African American. A total of 12% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean baseline body weight was 105.3 kg and mean BMI was 37.9 kg/m2.
Study 3 was a 68-week trial that enrolled 807 patients with type 2 diabetes and BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2. Patients included in the trial had HbA1c 7-10% and were treated with either: diet and exercise alone or 1 to 3 oral anti‑diabetic drugs (metformin, sulfonylurea, glitazone or sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor). Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either WEGOVY injection or placebo. At baseline, the mean age was 55 years (range 19 to 84), 51% were female, 62% were White, 26% were Asian and 8% were Black or African American. A total of 13% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean baseline body weight was 99.8 kg and mean BMI was 35.7 kg/m2.
Study 4 was a 68-week trial that enrolled 611 patients with obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2) or with overweight (BMI 27 to 29.9 kg/m2) and at least one weight-related comorbid condition such as treated or untreated dyslipidemia or hypertension; patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded. The patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive either WEGOVY injection or placebo. At baseline, the mean age was 46 years, 81% were female, 76% were White, 19% were Black or African American and 2% were Asian. A total of 20% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean baseline body weight was 105.8 kg and mean BMI was 38 kg/m2.
Study 5 was a 68-week trial that enrolled 902 patients with obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2) or with overweight (BMI 27 to 29.9 kg/m2) and at least one weight-related comorbid condition such as treated or untreated dyslipidemia or hypertension; patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded. Mean body weight at baseline for the 902 patients was 106.8 kg and mean BMI was 38.3 kg/m². All patients received WEGOVY injection during the run-in period of 20 weeks that included 16 weeks of dose escalation. Trial product was permanently discontinued before randomization in 99 of 902 patients (11%); the most common reason was adverse reactions (n=48, 5.3%); 803 patients reached WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection and were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either continue on WEGOVY injection or receive placebo. Among the 803 randomized patients, the mean age was 46 years, 79% were female, 84% were White, 13% were Black or African American, and 2% Asian. A total of 8% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean body weight at randomization (Week 20) was 96.1 kg and mean BMI at randomization (Week 20) was 34.4 kg/m2.
Study 6 was a 68-week trial that enrolled 401 East-Asian patients (Japan and South Korea) with BMI greater than or equal to 35 kg/m2 and at least one weight-related comorbid condition or with BMI 27 to 34.9 kg/m2 and at least two weight-related comorbid conditions. The patients were randomized 2:1:1 to receive subcutaneous injection of WEGOVY 2.4 mg, WEGOVY 1.7 mg, or placebo. At baseline, the mean age was 51 years, 63% were male, and all patients were Asian. Mean baseline body weight was 87.5 kg and mean BMI was 31.9 kg/m2. At baseline, 24.7% of patients had type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Study 7 was a 64-week trial that enrolled 307 patients with obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2) or with overweight (BMI 27-29.9 kg/m2) and at least one weight-related comorbid condition, such as treated or untreated dyslipidemia or hypertension; patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded. Patients were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either WEGOVY 25 mg tablet or placebo. At baseline, mean age was 48 years, 79% were women, 92% were White, 1% were Asian and 7% were Black or African American. A total of 7.8% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean baseline body weight was 106 kg and mean BMI was 38 kg/m2.
Results
In Studies 2, 3, and 4, 16% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 19% of the placebo-treated patients discontinued therapy. In these studies, 6.8% of WEGOVY injection-treated patients and 3.2% of placebo-treated patients discontinued their treatment due to an adverse reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In Study 5, the proportions of patients who discontinued study drug were 5.8% and 11.6% for WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively. In Study 6, the proportions of patients who discontinued study drug were 7.9%, 6.5%, and 3% for WEGOVY 1.7 mg injection, WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection, and placebo, respectively. In Study 7, the proportions of patients who discontinued study drug were 18% and 25.5% for WEGOVY 25 mg tablet and placebo, respectively. Adverse reactions led to treatment discontinuation in 6.8% of patients treated with WEGOVY 25 mg tablet and 5.9% patients receiving placebo.
For Studies 2, 3 and 4, the primary efficacy parameters were mean percent change in body weight and the percentages of patients achieving greater than or equal to 5% weight loss from baseline to Week 68.
After 68 weeks, treatment with WEGOVY injection resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared with placebo. Greater proportions of patients treated with WEGOVY injection achieved 5%, 10% and 15% weight loss than those treated with placebo as shown in Table 7.
- Table 7. Changes in Body Weight at Week 68 in Studies 2, 3, and 4 with WEGOVY Injection
Study 2
(Obesity or overweight with comorbidity)Study 3
(Type 2 diabetes with obesity or overweight)Study 4
(Obesity or overweight with comorbidity undergoing intensive lifestyle therapy)Intention-to-Treat1 PLACEBO
N=655WEGOVY Injection
N=1,306PLACEBO
N=403WEGOVY Injection
N=404PLACEBO
N=204WEGOVY Injection
N=407Body Weight
- Baseline mean (kg)
105.2
105.4
100.5
99.9
103.7
106.9
- % change from baseline (LSMean)
-2.4
-14.9
-3.4
-9.6
-5.7
-16
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
-12.4
(‑13.3; ‑11.6)*-6.2
(-7.3; -5.2)*-10.3
(-11.8; -8.7)*% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 5% body weight
31.1
83.5
30.2
67.4
47.8
84.8
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
52.4
(48.1; 56.7)*
37.2 (30.7; 43.8)*
37
(28.9; 45.2)*% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 10% body weight
12
66.1
10.2
44.5
27.1
73
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
54.1
(50.4; 57.9)*
34.3 (28.4; 40.2)*
45.9
(38; 53.7)*
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 15% body weight
4.8
47.9
4.3
25.1
13.2
53.4
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
43.1
(39.8; 46.3)*
20.7
(15.7; 25.8)*
40.2 (33.1; 47.3)*
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 20% body weight2
1.7
30.2
2.3
12.8
3.5
33.9
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)2
28.6
(25,8; 31.3)10.6
(6.4; 14.7)
30.4
(24.8; 36.1)
LSMean = least squares mean; CI = confidence interval
1 The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. In Study 2, at Week 68, the body weight was missing for 7.2% and 11.9% of patients randomized to WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively. In Study 3, at Week 68, the body weight was missing for 4% and 6.7% of patients randomized to WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively. In Study 4, at Week 68, the body weight was missing for 8.4% and 7.4% of patients randomized to WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively. Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI).
2 Not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
* p<0.0001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority.
For Study 5, the primary efficacy parameter was mean percent change in body weight from randomization (Week 20) to Week 68.
From randomization (week 20) to Week 68, treatment with WEGOVY injection resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared with placebo (Table 8). Because patients who discontinued WEGOVY injection during titration and those who did not reach the 2.4 mg weekly dose were not eligible for the randomized-treatment period, the results may not reflect the experience of patients in the general population who are first starting WEGOVY injection.
Table 8. Changes in Body Weight at Week 68 in Study 5 (Obesity or Overweight with Comorbidity After 20-week Run-in) with WEGOVY Injection
WEGOVY Injection
N=8031
Body Weight (only randomized patients)
- Mean at Week 0 (kg)
107.2
PLACEBO
N=268
WEGOVY Injection
N=535
Body Weight
- Mean at Week 20 (SD) (kg)
95.4 (22.7)
96.5 (22.5)
- % change from Week 20 at Week 68 (LSMean)
6.9
-7.9
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
-14.8 (-16; -13.5)*
LSMean = least squares mean; CI = confidence interval
1 902 patients were enrolled at Week 0 with a mean baseline body weight of 106.8 kg. The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At Week 68, the body weight was missing for 2.8% and 6.7% of patients randomized to WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively. Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI).
* p<0.001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority, controlled for multiplicity.
For Study 6, the primary efficacy parameters were mean percent change in body weight and the percentage of patients achieving greater than or equal to 5% weight loss from baseline to Week 68.
After 68 weeks, treatment with WEGOVY 1.7 mg and 2.4 mg injection resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared with placebo. Greater proportions of patients treated with WEGOVY injection achieved 5%, 10%, and 15% weight loss than those treated with placebo as shown in Table 9.
Table 9. Changes in Body Weight at Week 68 in Study 6 in East-Asian Patients (WEGOVY 1.7 mg) with WEGOVY Injection
Study 6 (BMI ≥35 kg/m2 with at least one comorbidity or
BMI 27-34.9 kg/m2 with at least two comorbidities)
Intention-to-treat1
PLACEBO
N=101
WEGOVY 1.7 mg Injection
N=101
WEGOVY 2.4 mg Injection
N=199
Body Weight
- Baseline mean (kg)
90.2
86.1
86.9
- % change from baseline (LSMean)
-2.1
-9.6
-13.2
- % difference from placebo
- (LSMean) (95% CI)
-7.5
(-9.6; -5.4)*
-11.1
(-12.9; -9.2)*
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 5% body weight
19.4
72.8
84
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
53.3
(41; 65.6)*
64.5
(54.8; 74.3)*
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 10% body weight
4.5
39.1
59.9
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
34.5
(23.9; 45.1)*
55.4
(47.3; 63.6)*
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 15% body weight
2.6
20.8
38.2
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)
18.2
(9.8; 26.7)*
35.6
(27.9; 43.3)*
LSMean = least squares mean; CI = confidence interval
1 The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. At baseline, 24.7% of patients had type 2 diabetes mellitus. At Week 68, the body weight was missing for 3%, 3%, and 1% of patients randomized to WEGOVY 1.7 mg injection, WEGOVY 2.4 mg injection, and placebo, respectively. Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI).
* p<0.0001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority.
For Study 7, the primary efficacy parameters were mean percent change in body weight and the percentages of patients achieving greater than or equal to 5% weight loss from baseline to Week 64.
After 64 weeks, treatment with WEGOVY tablets resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared with placebo. Greater proportions of patients treated with WEGOVY tablets achieved 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% weight loss than those treated with placebo as shown in Table 10.
Table 10. Changes in Body Weight at Week 64 in Study 7 with WEGOVY Tablet
Study 7 (Obesity or overweight with comorbidity) Intention-to-Treat1 PLACEBO
N = 102WEGOVY Tablet
N = 205Body Weight
- Baseline mean (kg)
104.8
106.4
- % change from baseline (LSMean)3
-2.4
-13.6
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)3
-11.2 [-13.6; -8.8]2
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 5% body weight3
31.3
76.3
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)3
45.1 [33.8; 56.3]2
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 10% body weight
14.4
59.8
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)3
45.3 [35.5; 55.2]2
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 15% body weight3
5.5
47.0
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)3
41.5 [33.2; 49.8]2
% of Patients losing greater than or equal to 20% body weight3
3.1
27.9
- % difference from placebo (LSMean) (95% CI)3
24.8 [17.7; 31.9]2
LSMean = least squares mean; CI = confidence interval
1 The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. In Study 7, at Week 64, the body weight was missing for 6.3% and 11.8% of patients randomized to WEGOVY tablets and placebo, respectively.
2 p<0.0001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority.
3 Model based estimates are based on an analysis of covariance (or logistic regression for the 5%, 10%, 15% or 20% achievement endpoints) including treatment as a factor and baseline value as a covariate. Missing data were multiple imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI). The imputation model was a linear regression of the endpoint with gender as factor and baseline value of the endpoint, timing and the value of last available observation – on study (LAO-OS) of the endpoint as covariates, imputed by treatment status. For the 5%, 10%, 15% or 20% achievement endpoints, the missing body weight measurements were imputed before performing the logistic regression analyses.
RD-MI: Retrieved Drop-outs Multiple Imputation
A reduction in body weight was observed with WEGOVY irrespective of age, sex, race, ethnicity, BMI at baseline, body weight (kg) at baseline, and level of renal function impairment.
The cumulative frequency distributions of change in body weight are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 for Studies 2, 3 and 7. One way to interpret this figure is to select a change in body weight of interest on the horizontal axis and note the corresponding proportions of patients (vertical axis) in each treatment group who achieved at least that degree of weight loss. For example, note that the vertical line arising from ‑10% in Study 2 intersects the WEGOVY injection and placebo curves at approximately 66%, and 12%, respectively, which correspond to the values shown in Table 8.
Figure 3. Change in Body Weight (%) from Baseline to Week 68 (Study 2) with WEGOVY Injection
Observed data from in-trial period including imputed data for missing observations (RD-MI).
Figure 4. Change in Body Weight (%) from Baseline to Week 68 (Study 3) with WEGOVY Injection
Observed data from in-trial period including imputed data for missing observations (RD-MI).
Figure 5. Change in Body Weight (%) from Baseline to Week 64 (Study 7) with WEGOVY Tablets
Observed data from in-trial period including imputed data for missing observations (RD-MI). The missing observation was the patient-level average from the 1,000 imputed datasets.
The time courses of weight loss with WEGOVY injection and placebo from baseline through Week 68 are depicted in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Figure 6. Change from Baseline (%) in Body Weight (Study 2 on Left and Study 3 on Right) with WEGOVY Injection
Observed values for patients completing each scheduled visit, and estimates with multiple imputations from retrieved dropouts (RD-MI).
Figure 7. Change from Baseline (%) in Body Weight (Study 4 on Left and Study 5a on Right) with WEGOVY Injection
Observed values for patients completing each scheduled visit, and estimates with multiple imputations from retrieved dropouts (RD-MI).
a Change from Week 0 was not a primary endpoint in Study 5. Dotted line indicates time of randomization. Randomized patients (shown) do not include 99 patients that discontinued during the 20-week run-in period.
Figure 8. Change in Body Weight (%) from Baseline to Week 68 (Study 6 in East-Asian Patients) with WEGOVY Injection
Observed values for patients completing each scheduled visit and estimates with multiple imputations from retrieved dropouts (RD-MI). At baseline, 24.7% of patients had type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Effect of WEGOVY Injection on Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Adults
Changes in waist circumference and cardiometabolic parameters with WEGOVY injection are shown in Table 11 for Studies 2, 3, and 4; in Table 12 for Study 5; and in Table 13 for Study 6.
Table 11. Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters at Week 68 in Studies 2, 3 and 4 with WEGOVY Injection
Study 2
(Obesity or overweight with comorbidity)Study 3
(Type 2 diabetes with obesity or overweight)Study 4
(Obesity or overweight with comorbidity undergoing intensive lifestyle therapy)Intention-to-Treat PLACEBO
N=655WEGOVY Injection
N=1,306PLACEBO
N=403WEGOVY Injection
N=404PLACEBO
N=204WEGOVY Injection
N=407Waist Circumference (cm)
- Baseline
- Changes from baseline (LSMean1)
- Difference from placebo (LSMean)
114.8
-4.1
114.6
-13.5
-9.4
115.5
-4.5
114.5
-9.4
-4.9
111.8
-6.3
113.6
-14.6
-8.3
Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)
- Baseline
- Changes from baseline (LSMean1)
- Difference from placebo (LSMean)
127
-1.1
126
-6.2
-5.1
130
-0.5
130
-3.9
-3.4
124
-1.6
124
-5.6
-3.9
Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)2
- Baseline
- Changes from baseline (LSMean1)
- Difference from placebo (LSMean)
80
-0.4
80
-2.8
-2.4
80
-0.9
80
-1.6
-0.7
81
-0.8
80
-3
-2.2
Heart Rate2,3
- Baseline
- Changes from baseline (LSMean1)
- Difference from placebo (LSMean)
72
-0.7
72
3.5
4.3
76
-0.2
75
2.5
2.7
71
2.1
71
3.1
1
HbA1c (%)2
- Baseline
- Changes from baseline (LSMean1)
- Difference from placebo (LSMean)
5.7
-0.2
5.7
-0.4
-0.3
8.1
-0.4
8.1
-1.6
-1.2
5.8
-0.3
5.7
-0.5
-0.2
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
- Baseline
- Percent Change from baseline (LSMean1)
- Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
192.1
0.1
189.6
-3.3
-3.3
170.8
-0.5
170.8
-1.4
-0.9
188.7
2.1
185.4
-3.9
-5.8
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
- Baseline
- Percent Change from baseline (LSMean1)
- Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
112.5
1.3
110.3
-2.5
-3.8
90.1
0.1
90.1
0.5
0.4
111.8
2.6
107.7
-4.7
-7.1
HDL (mg/dL)2,4
- Baseline
- Percent Change from baseline (LSMean1)
- Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
49.5
1.4
49.4
5.2
3.8
43.8
4.1
44.7
6.9
2.7
50.9
5
51.6
6.5
1.5
Triglycerides (mg/dL)2,4
- Baseline
- Percent Change from baseline (LSMean1)
- Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
127.9
-7.3
126.2
-21.9
-15.8
159.5
-9.4
154.9
-22
-13.9
110.9
-6.5
107.9
-22.5
-17
Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI)
1 Model based estimates based on an analysis of covariance model including treatment (and stratification factors for Study 3 only) as a factor and baseline value as a covariate
2 Not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing (except HbA1c for Study 3)
3 Model based estimates based on a mixed model for repeated measures including treatment (and stratification factors for Study 3 only) as a factor and baseline values as a covariate
4 Baseline value is the geometric mean
Table 12. Mean Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Study 5 (Obesity or Overweight with Comorbidity After 20-week Run-in)1 with WEGOVY Injection
PLACEBO
N=268
WEGOVY Injection
N=535
Randomization
(Week 20)
Change from
Randomization
(Week 20) to
Week 68
(LSMean1)
Randomization
(Week 20)
Change from
Randomization
(Week 20) to
Week 68
(LSMean1)
Difference
from placebo
(LSMean)
Waist Circumference (cm)
104.7
3.3
105.5
-6.4
-9.7
Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)
121
4.4
121
0.5
-3.9
Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)2
78
0.9
78
0.3
-0.5
Heart Rate2,3
76
-5.3
76
-2
3.3
HbA1c (%)2
5.4
0.1
5.4
-0.1
-0.2
Randomization
(Week 20)
% Change
from
Randomization
(Week 20)
(LSMean1)
Randomization
(Week 20)
% Change
from
Randomization
(Week 20)
(LSMean1)
Relative
difference from
placebo
(LSMean)
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
175.1
11.4
175.9
4.9
-5.8
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
109.1
7.6
108.7
1.1
-6.1
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
43.6
17.8
44.5
18.2
0.3
Triglycerides (mg/dL)2,4
95.3
14.8
98.1
-5.6
-17.8
Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI).
1 Model based estimates based on an analysis of covariance model including treatment as a factor and baseline value as a covariate.
2 Not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
3 Model based estimates based on a mixed model for repeated measures including treatment as a factor and baseline values as a covariate.
4 Baseline value is the geometric mean.
Table 13. Mean Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters at Week 68 in Study 6 in East-Asian Patients with WEGOVY Injection
Study 6 (BMI ≥35 kg/m2 with at least one comorbidity or BMI 27
to 34.9 kg/m2 with at least two comorbidities)
Intention-to-treat
PLACEBO
N=101
WEGOVY 1.7 mg
Injection
N=101
WEGOVY 2.4 mg
Injection
N=199
Waist circumference (cm)
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
103.8
-1.8
101.4
-7.7
-5.9
103.8
-11
-9.3
Systolic blood pressure (mmHg)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
133
-5.3
135
-10.8
-5.4
133
-10.8
-5.5
Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
86
-2.2
85
-4.6
-2.4
83
-5.3
-3.1
Heart Rate2, 3
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
73
2.4
73
4.4
2
73
6.3
3.9
HbA1c (%)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
6.4
0
6.4
-0.9
-0.9
6.4
-0.9
-0.9
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
203.1
0.8
203.3
-6.6
-7.3
197.2
-8.7
-9.4
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
123.3
-3.8
120.1
-10.1
-6.5
116.5
-14.6
-11.2
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,4
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
48.7
5.9
50.2
6.7
0.7
50.8
9.2
3.1
Triglyceride (mg/dL)2,4
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
134.2
5.5
138.8
-19.5
-23.7
127.1
-21.2
-25.3
Missing data were imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI). At baseline, 24.7% of patients had type 2 diabetes mellitus.
1 Model based estimates based on an analysis of covariance model including treatment and type 2 diabetes status as factors and baseline value as a covariate.
2 Not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
3 Model based estimates based on a mixed model for repeated measures including treatment and type 2 diabetes status as factors and baseline values as a covariate.
4 Baseline value is the geometric mean.
Table 14. Mean Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Study 7 with WEGOVY Tablet (Obesity or Overweight with Comorbidity)
Study 7 (Obesity or overweight with comorbidity)
Intention-to-treat
PLACEBO
N=102
WEGOVY tablets 25 mg
N=205
Waist circumference (cm)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
113.6
-2.8
114
-12.2
-9.4
Systolic blood pressure (mmHg)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
131
-5.4
131
-7.0
-1.6
Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
83
-1.8
83
-2.8
-1.0
Heart Rate2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
74
2.4
72
2.7
0.4
HbA1c (%)2
Baseline
Change from baseline (LSMean1)
Difference from placebo (LSMean)
5.7
-0.1
5.7
-0.3
-0.2
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,3
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
190.5
-2.2
191.4
-3.3
-1.2
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,3
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
114.2
0.2
111.1
-2.9
-3.1
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,3
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
50.1
-1.1
49.6
3.3
4.5
Triglyceride (mg/dL)2,3
Baseline
Percent change from baseline (LSMean1)
Relative difference from placebo (LSMean)
117.5
-9.1
115.9
-18.1
-9.9
1 Model based estimates are based on an analysis of covariance including treatment as a factor and baseline value as a covariate. Missing data were multiple imputed from retrieved subjects of the same randomized treatment arm (RD-MI). The imputation model was a linear regression of the endpoint with gender as factor and baseline value of the endpoint, timing and the value of last available observation – on study (LAO-OS) of the endpoint as covariates, imputed by treatment status.
RD-MI: Retrieved Drop-outs Multiple Imputation
2 Not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
3 Baseline value is the geometric mean.
14.3 Weight Reduction and Long-term Maintenance Study of WEGOVY Injection in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older with Obesity
Overview of Clinical Trial in Pediatric Patients
WEGOVY injection was evaluated to reduce excess body weight in pediatric patients aged 12 years of age and older with obesity in a 68-week, double-blind, randomized, parallel group, placebo-controlled, multi-center trial in 201 pubertal pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with BMI corresponding to ≥95th percentile standardized for age and sex (Study 8) (NCT#04102189). After a 12-week lifestyle run-in period (including dietary recommendations and physical activity counseling), patients were randomized 2:1 to WEGOVY injection once weekly or placebo once weekly. WEGOVY injection or matching placebo was escalated to 2.4 mg or maximally tolerated dose during a 16-week period followed by 52 weeks on maintenance dose. Of WEGOVY injection-treated patients who completed the trial, 86.7% were on the 2.4 mg dosage at the end of the trial; for 5% of patients, 1.7 mg was the maximum tolerated dosage.
The mean age was 15 years; 38% of patients were male; 79% were White, 8% were Black or African American, 2% were Asian, and 11% were of other or unknown race; and 11% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean baseline body weight was 108 kg, and mean BMI was 37 kg/m2.
Results
The proportions of patients who discontinued study drug were 10% for the WEGOVY injection-treated group and 10% for the placebo-treated group.
The primary endpoint was percent change in BMI from baseline to Week 68. After 68 weeks, treatment with WEGOVY injection resulted in a statistically significant reduction in percent BMI compared with placebo. Greater proportions of patients treated with WEGOVY injection achieved ≥5% reduction in baseline BMI than those treated with placebo as shown in Table 15.
Table 15. Changes in Weight and BMI at Week 68 in Pediatric Patients with Obesity Aged 12 Years and Older in Study 8 with WEGOVY Injection
Intention-to-Treata PLACEBO
N=67WEGOVY Injection
N=134BMI
- Baseline mean (kg/m2)
35.7
37.7
- % change from baseline in BMI (LSMean)
0.6
-16.1
- % difference from placebo
- (LSMean) (95% CI)
-16.7
(-20.3; -13.2)*
% of Patients with greater than or equal to 5% reduction in baseline BMIb
19.7
77.1
- % difference from placebo (LSMean)
57.4
% of Patients with greater than or equal to 10% reduction in baseline BMIb
7.7
65.1
- % difference from placebo (LSMean)
57.5
% of Patients with greater than or equal to 15% reduction in baseline BMIb
4
57.8
- % difference from placebo (LSMean)
53.9
Body Weightb
- Baseline mean (kg)
102.6
109.9
- % change from baseline (LSMean)a
2.7
-14.7
- % difference from placebo (LSMean)
-17.4
LSMean = least squares mean; CI = confidence interval
a The intention-to-treat population includes all randomized patients. Missing data were imputed using available data according to value and timing of last available observation on treatment and endpoint’s baseline value from retrieved subjects (RD-MI). At week 68, the BMI was missing for 2.2% and 7.5% of patients randomized to WEGOVY injection and placebo, respectively.
b Parameters not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
* p<0.0001 (unadjusted 2-sided) for superiority.
The time course of change in BMI with WEGOVY injection and placebo from baseline through Week 68 is depicted in Figure 9. The cumulative frequency distribution of change in BMI is shown in Figure 10.
Figure 9. Change from Baseline (%) in BMI in Pediatric Patients with Obesity Aged 12 Years and Older in Study 8 with WEGOVY Injection
Observed values for patients completing each scheduled visit, and estimates with multiple imputations from retrieved dropouts (RD-MI).
Figure 10. Change in BMI (%) from Baseline to Week 68 in Pediatric Patients with Obesity Aged 12 Years and Older in Study 8 with WEGOVY Injection
Observed data from in-trial period including imputed data for missing observations (RD-MI).
Effect of WEGOVY Injection on Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Pediatric Patients with Obesity Aged 12 Years and Older
Changes in waist circumference and cardiometabolic parameters with WEGOVY injection are shown in Table 16 for the study in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older.
Table 16. Mean Changes in Anthropometry and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Pediatric Patients with Obesity Aged 12 Years and Older in Study 8 with WEGOVY Injection
PLACEBO
N=67
WEGOVY Injection
N=134
Baseline
Change from
Baseline
(LSMean)
Baseline
Change from
Baseline
(LSMean)
Difference
from placebo
(LSMean)
Waist Circumference (cm)2
107.3
-0.6
111.9
-12.7
-12.1
Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)2
120
-0.8
120
-2.7
-1.9
Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg)2
73
-0.8
73
-1.4
-0.6
Heart Rate3
76
-2.3
79
1.2
3.5
HbA1c (%)2,4
5.4
-0.1
5.5
-0.4
-0.2
Baseline
% Change
from Baseline
(LSMean)
Baseline
% Change
from Baseline
(LSMean)
Relative
difference from
placebo
(LSMean)
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,5
160.1
-1.3
159.4
-8.3
-7.1
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,5
91.7
-3.6
89.8
-9.9
-6.6
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)2,5
43.3
3.2
43.7
8
4.7
Triglycerides (mg/dL)2,5
108
2.6
111.3
-28.4
-30.2
1 Parameters listed in the table were not included in the pre-specified hierarchical testing.
2 Missing data were imputed using available data according to value and timing of last available observation on treatment and endpoint’s baseline value from retrieved subjects (RD-MI). Model based estimates based on an analysis of covariance model including treatment and stratification groups (gender, Tanner stage group) and the interaction between stratification groups as factors and baseline value as a covariate.
3 Model based estimates based on a mixed model for repeated measures including treatment as a factor and baseline value as a covariate all nested within visit.
4 For patients without type 2 diabetes at randomization (N=129 for WEGOVY injection-treated patients and N=64 for placebo-treated patients).
5 Baseline value is the geometric mean.
14.4 Noncirrhotic Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis with Moderate to Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Adults Treated with WEGOVY Injection
Overview of Clinical Trial
The efficacy of WEGOVY injection was evaluated based on an efficacy analysis at Week 72 in Study 9 (NCT#04822181), a 240-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Enrolled patients had a baseline or recent liver biopsy showing clinically significant MASLD (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease), defined as MASH with fibrosis stage 2 or 3 and a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Activity Score (NAS) ≥4 with a score of 1 or more in steatosis, lobular inflammation, and hepatocyte ballooning. Efficacy determination was based on the effect of WEGOVY injection on resolution of steatohepatitis without worsening of liver fibrosis and on at least one stage improvement in liver fibrosis without worsening of steatohepatitis, on post-baseline liver biopsies collected at 72 weeks.
The Week 72 analysis included 800 F2 and F3 (at eligibility) patients randomized 1:2 to receive placebo (n=266) or WEGOVY once weekly (n=534), in addition to standard of care for cardiometabolic comorbidities and healthy lifestyle counseling. WEGOVY injection or matching placebo was escalated to 2.4 mg once weekly during the initial 16 weeks of the treatment period. Dose escalation could be prolonged or patients could remain at a lower dose if 2.4 mg once weekly was not tolerable.
Demographic and baseline characteristics were balanced between treatment and placebo groups. Overall, the median (Q1 to Q3) age of patients at baseline was 57 (49 to 65) years, 57% were female, 18% were Hispanic, 68% were White, 27% were Asian, and 0.6% were Black or African American. Median (Q1 to Q3) body mass index (BMI) was 34 (30 to 38) kg/m2 and median (Q1 to Q3) body weight was 93 (79 to 110) kg. Baseline characteristics are presented in Table 17.
Table 17. Baseline Characteristics in Adults Patients with Noncirrhotic MASH with Stage 2 to Stage 3 Fibrosis in Study 9
Characteristic
Overall (N=800)
Fibrosis stage, n (%)
F2
F3
250 (31)
550 (69)
Body Mass Index (BMI, kg/m2), n (%)a
<25
25-30
30-35
≥35
53 (7)
164 (21)
252 (32)
330 (41)
Lean MASH, n (%)b
22 (3)
Type 2 Diabetes, n (%)
447 (56)
Hypertension, n (%)
503 (63)
Dyslipidemia, n (%)
198 (25)
Statin use, n (%)
300 (38)
Fibrosis Index Based on 4 Factors (FIB-4), Median (Q1, Q3)a
1.6 (1.1, 2.3)
Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF), Median (Q1, Q3)
9.9 (9.3, 10.5)
a Less than 5% missingness in the variable is omitted.
b Lean MASH defined as BMI <25 kg/m2 for non-Asian patients and BMI <23 kg/m2 for Asian patients.
Among the 79% of the patients with vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) at baseline, median (Q1 to Q3) VCTE was 10.9 (8.6 to 15.5) kPa, which may not be representative of the entire study population. The 21% of patients with missing VCTE at baseline had higher percentages of being female and having baseline diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
Results
Table 18 presents the Week 72 histopathology primary endpoint results comparing WEGOVY injection with placebo on
1) the estimated percentage of patients with resolution of steatohepatitis and no worsening of liver fibrosis and
2) the estimated percentage of patients with at least one stage improvement in liver fibrosis and no worsening of steatohepatitis. The secondary endpoint results of the estimated percentage of patients with resolution of steatohepatitis and improvement in liver fibrosis at Week 72 are also presented. Two pathologists independently read the liver biopsies for each patient; a third pathologist performed adjudication if consensus could not be reached between the two pathologists. WEGOVY injection demonstrated improvement on these histopathology endpoints at Week 72 compared to placebo.Table 18. Efficacy Results at Week 72 in Adult Patients with Noncirrhotic MASH with Stage 2 or
Stage 3 Fibrosis in Study 9 of WEGOVY Injection
Placebo
N=266
WEGOVY Injection
N=534
Resolution of steatohepatitis and no worsening of liver fibrosis
Response Rate (%)
34
63
Difference in response rate vs. placebo (95% CI)
29 (21, 36)*
Improvement in liver fibrosis and no worsening of steatohepatitis
Response Rate (%)
22
37
Difference in response rate vs. placebo (95% CI)
14 (8, 21)*
Resolution of steatohepatitis and improvement in liver fibrosis
Response Rate (%)
16
33
Difference in response rate vs. placebo (95% CI)
17 (10, 23)*
* Results were statistically significant.
Endpoints were evaluated according to the MASH Clinical Research Network (CRN). Resolution of steatohepatitis is defined as a score of 0 to 1 for lobular inflammation, 0 for ballooning, and any value for steatosis. No worsening of steatohepatitis is defined as no increase from baseline in score for ballooning, lobular inflammation, or steatosis.
Estimated using pooled Mantel-Haenszel (MH) estimates stratified by baseline type 2 diabetes status (presence or absence) and baseline fibrosis stage (F2 or F3) with missing data handled by reference-based multiple imputation and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) calculated using Rubin’s rule to pool Sato’s estimate of standard errors across the imputed datasets.
Another secondary endpoint was the percent change in body weight from baseline to Week 72. Patients treated with WEGOVY injection (mean baseline body weight 95.4 kg) achieved an average of 10.5% weight loss from baseline at Week 72, and patients treated with placebo (mean baseline weight 97.6 kg) achieved an average of 2% weight loss from baseline at Week 72; treatment with WEGOVY injection resulted in an average of 8.5% greater weight loss from baseline compared to placebo (95% CI: 7.4% to 9.5%).
Starting at Week 12 and through Week 72, there was a trend of greater reductions from baseline in average ALT and AST in the WEGOVY injection group as compared to the placebo group.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
WEGOVY Injection
How Supplied
WEGOVY injection is a clear, colorless solution in a prefilled, disposable, single-dose pen-injector with an integrated needle. It is supplied in cartons containing 4 pen-injectors in the following packaging configurations:
Total Strength per Total Volume
NDC
0.25 mg/0.5 mL
0169-4525-14
0.5 mg/0.5 mL
0169-4505-14
1 mg/0.5 mL
0169-4501-14
1.7 mg/0.75 mL
0169-4517-14
2.4 mg/0.75 mL
0169-4524-14
Recommended Storage
Store the WEGOVY single-dose pen in the refrigerator from 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). If needed, prior to cap removal, the pen can be kept from 8°C to 30°C (46°F to 86°F) up to 28 days. Do not freeze. Protect WEGOVY from light. WEGOVY must be kept in the original carton until time of administration. Discard the WEGOVY pen after use.
WEGOVY Tablets
How Supplied
WEGOVY tablets are available as:
Tablet
strength
Description
Package
Configuration
NDC Number
1.5 mg
White to light yellow, round shaped debossed with “1.5” on one side and “novo” on the other side
Bottle of 30 tablets
0169-4415-31
4 mg
White to light yellow, round shaped debossed with “4” on one side and “novo” on the other side
Bottle of 30 tablets
0169-4404-31
9 mg
White to light yellow, round shaped debossed with “9” on one side and “novo” on the other side
Bottle of 30 tablets
0169-4409-31
25 mg
White to light yellow, oval shaped debossed with “25” on one side and “novo” on the other side
Bottle of 30 tablets
0169-4425-31
Recommended Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store and dispense WEGOVY tablets in the original bottle. Store WEGOVY tablet in the original bottle until use to protect tablets from moisture. Store WEGOVY tablets in a dry place away from moisture.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors
Inform patients that semaglutide causes thyroid C-cell tumors in rodents and that the human relevance of this finding has not been determined. Counsel patients to report symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a lump in the neck, hoarseness, dysphagia, or dyspnea) to their physician [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Acute Pancreatitis
Inform patients of the potential risk for acute pancreatitis and its symptoms: severe abdominal pain that sometimes radiates to the back, and which may or may not be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Instruct patients to discontinue WEGOVY promptly and contact their physician if pancreatitis is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Acute Gallbladder Disease
Inform patients of the risk of acute gallbladder disease. Advise patients that substantial or rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallbladder disease, but that gallbladder disease may also occur in the absence of substantial or rapid weight loss. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider for appropriate clinical follow-up if gallbladder disease is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypoglycemia
Inform patients of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate patients on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia. Advise patients with diabetes mellitus on glycemic lowering therapy that they may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia when using WEGOVY and to report signs and/or symptoms of hypoglycemia to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
Inform patients of the potential risk of acute kidney injury due to dehydration associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions. Advise patients to take precautions to avoid fluid depletion. Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury and instruct them to promptly report any of these signs or symptoms or persistent (or extended) nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Inform patients of the potential risk of severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if they have severe or persistent gastrointestinal symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during postmarketing use of semaglutide, the active ingredient in WEGOVY. Advise patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions and instruct them to stop taking WEGOVY and seek medical advice promptly if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Inform patients with type 2 diabetes to contact their physician if changes in vision are experienced during treatment with WEGOVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Heart Rate Increase
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare providers of palpitations or feelings of a racing heartbeat while at rest during WEGOVY treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Advise patients to report emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Inform patients that if they experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors, they should stop taking WEGOVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
Inform patients that WEGOVY may cause their stomach to empty more slowly which may lead to complications with anesthesia or deep sedation during planned surgeries or procedures. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking WEGOVY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Pregnancy
WEGOVY may cause fetal harm. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise patients who are exposed to WEGOVY during pregnancy to contact Novo Nordisk at 1-877-390-2760 or www.wegovypregnancyregistry.com [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Missed Doses
Inform patients if a dose of WEGOVY injection is missed and the next scheduled dose is more than 2 days away (48 hours), administer WEGOVY injection as soon as possible. If one dose is missed and the next scheduled dose is less than 2 days away (48 hours), do not administer the dose. Inform patients to resume their regular once-weekly dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Inform patients if a dose of WEGOVY tablets is missed, skip the missed dose and take the next dose the following day [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with WEGOVY tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Marketed by: Novo Nordisk Inc., Plainsboro, NJ 08536
For additional information about WEGOVY contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
1-833-934-6891
WEGOVY® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Patent Information: http://www.novonordisk-us.com/products/product-patents.html
© 2025 Novo Nordisk
-
Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE
WEGOVY® (wee-GOH-vee)
(semaglutide)
injection, for subcutaneous use
WEGOVY® (wee-GOH-vee)
(semaglutide)
tablets, for oral use
Read this Medication Guide and Instructions for Use before you start using WEGOVY and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about WEGOVY?
WEGOVY may cause serious side effects, including:
- Possible thyroid tumors, including cancer. Tell your healthcare provider if you get a lump or swelling in your neck, hoarseness, trouble swallowing, or shortness of breath. These may be symptoms of thyroid cancer. In studies with rodents, WEGOVY and other medicines that work like WEGOVY caused thyroid tumors, including thyroid cancer. It is not known if WEGOVY will cause thyroid tumors or a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in people.
- Do not use WEGOVY if you or any of your family have ever had a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), or if you have an endocrine system condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
What is WEGOVY?
- WEGOVY injection is a prescription medicine used with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to:
- o reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events such as death, heart attack, or stroke in adults with known heart disease and with either obesity or overweight).
- o help adults and children aged 12 years and older with obesity, or some adults with excess weight (overweight) who also have weight-related medical problems to lose weight and keep the weight off.
- o treat adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with moderate to advanced liver scarring (fibrosis), but not with cirrhosis of the liver.
-
WEGOVY tablets are a prescription medicine used with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to:
- o reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events such as death, heart attack, or stroke in adults with known heart disease and with either obesity or overweight.
- o help adults with obesity, or some adults with excess weight (overweight) who also have weight-related medical problems to lose weight and keep the weight off.
- WEGOVY contains semaglutide and should not be used with other semaglutide-containing products or other GLP-1 receptor agonist medicines.
- It is not known if WEGOVY injection is safe and effective:
- o to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events (death, heart attack, or stroke) in people under 18 years.
- o to help children under 12 years of age lose weight and keep the weight off.
- o for the treatment of MASH in people under 18 years of age.
- It is not known if WEGOVY tablets are safe and effective for use in people under 18 years of age.
Do not use WEGOVY if:
- you or any of your family have ever had a type of thyroid cancer called MTC or if you have an endocrine system condition called MEN 2.
- you have had a serious allergic reaction to semaglutide or any of the ingredients in WEGOVY injection or WEGOVY tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in WEGOVY injection and WEGOVY tablets. See “What are the possible side effects of WEGOVY?” for symptoms of a serious allergic reaction.
Before using WEGOVY, tell your healthcare provider if you have any other medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had problems with your pancreas or kidneys.
- have type 2 diabetes and a history of diabetic retinopathy.
- have or have had depression or suicidal thoughts, or mental health issues.
- are scheduled to have surgery or other procedures that use anesthesia or deep sleepiness (deep sedation).
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. WEGOVY may harm your unborn baby. You should stop using WEGOVY 2 months before you plan to become pregnant.
- o Pregnancy Exposure Registry: There is a pregnancy exposure registry for women who use WEGOVY during pregnancy. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this registry or you may contact Novo Nordisk at 1-877-390-2760 or www.wegovypregnancyregistry.com.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with WEGOVY tablets. It is not known if WEGOVY when received through an injection passes into your breast milk. You should talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while using WEGOVY.
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. WEGOVY may affect the way some medicines work and some medicines may affect the way WEGOVY works. Tell your healthcare provider if you are taking other medicines to treat diabetes, including sulfonylureas or insulin. WEGOVY slows stomach emptying and can affect medicines that need to pass through the stomach quickly.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use WEGOVY?
- Use WEGOVY exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Use WEGOVY with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
- If you take too much WEGOVY, you may have severe nausea, severe vomiting and severe low blood sugar. Call your healthcare provider or Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. Advice is also available online at poisonhelp.org.
WEGOVY Injection
- Read the Instructions for Use that comes with WEGOVY.
- Your healthcare provider should show you how to use WEGOVY before you use it for the first time.
- WEGOVY is injected under the skin (subcutaneously) of your stomach (abdomen), thigh, or upper arm. Do not inject WEGOVY into a muscle (intramuscularly) or vein (intravenously).
- Change (rotate) your injection site with each injection. Do not use the same site for each injection.
- Use WEGOVY 1 time each week, on the same day each week, at any time of the day.
- If you need to change the day of the week, you may do so as long as your last dose of WEGOVY was given 2 or more days before.
- If you miss a dose of WEGOVY and the next scheduled dose is more than 2 days away (48 hours), take the missed dose as soon as possible. If you miss a dose of WEGOVY and the next schedule dose is less than 2 days away (48 hours), do not administer the dose. Take your next dose on the regularly scheduled day.
- If you miss doses of WEGOVY for 2 or more weeks, take your next dose on the regularly scheduled day or call your healthcare provider to talk about how to restart your treatment.
- You can take WEGOVY with or without food.
WEGOVY Tablets
- Take 1 WEGOVY tablet by mouth on an empty stomach in the morning with water (no more than 4 ounces). Do not take WEGOVY tablets with any other liquids besides water.
- Do not split, crush, chew or dissolve WEGOVY tablets. Swallow WEGOVY tablets whole.
- Do not take more than 1 WEGOVY tablet each day.
- After 30 minutes, you can eat, drink, or take other oral medicines.
- If you miss a dose of WEGOVY, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule for the next dose.
What are the possible side effects of WEGOVY?
WEGOVY may cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about WEGOVY?”
- inflammation of your pancreas (pancreatitis). Stop using WEGOVY and call your healthcare provider right away if you have severe pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that will not go away, with or without nausea or vomiting. Sometimes you may feel the pain from your abdomen to your back.
- gallbladder problems. WEGOVY may cause gallbladder problems including gallstones. Some gallbladder problems need surgery. Call your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms:
- o pain in your upper stomach (abdomen)
- o yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
- o fever
- o clay-colored stools
- increased risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in patients with type 2 diabetes, especially those who also take medicines to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus such as an insulin or a sulfonylureas. Low blood sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes who receive WEGOVY can be both a serious and common side effect. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to recognize and treat low blood sugar. You should check your blood sugar before you start taking WEGOVY and while you take WEGOVY. Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include:
- o dizziness or light-headedness
- o sweating
- o shakiness
- o blurred vision
- o slurred speech
- o weakness
- o anxiety
- o hunger
- o headache
- o irritability or mood changes
- o confusion or drowsiness
- o fast heartbeat
- o feeling jittery
- dehydration leading to kidney problems. Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting may cause a loss of fluids (dehydration) which may cause kidney problems. It is important for you to drink fluids to help reduce your chance of dehydration. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea that does not go away.
- severe stomach problems. Stomach problems, sometimes severe, have been reported in people who use WEGOVY. Tell your healthcare provider if you have stomach problems that are severe or will not go away.
- serious allergic reactions. Stop using WEGOVY and get medical help right away, if you have any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction including:
- o swelling of your face, lips, tongue or throat
- o severe rash or itching
- o very rapid heartbeat
- o problems breathing or swallowing
- o fainting or feeling dizzy
- change in vision in people with type 2 diabetes. Tell your healthcare provider if you have changes in vision during treatment with WEGOVY.
- increased heart rate. WEGOVY can increase your heart rate while you are at rest. Your healthcare provider should check your heart rate while you take WEGOVY. Tell your healthcare provider if you feel your heart racing or pounding in your chest and it lasts for several minutes.
- depression or thoughts of suicide. You should pay attention to any mental changes, especially sudden changes in your mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any mental changes that are new, worse, or worry you.
- food or liquid getting into the lungs during surgery or other procedures that use anesthesia or deep sleepiness (deep sedation). WEGOVY may increase the chance of food getting into your lungs during surgery or other procedures. Tell all your healthcare providers that you are taking WEGOVY before you are scheduled to have surgery or other procedures.
- The most common side effects of WEGOVY in adults or children aged 12 years and older may include:
- nausea
- stomach (abdomen) pain
- dizziness
- gas
- diarrhea
- headache
- feeling bloated
- stomach flu
- vomiting
- tiredness (fatigue)
- belching
- heartburn
- constipation
- upset stomach
- low blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes
- runny nose or sore throat
Talk to your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of WEGOVY.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800‑FDA‑1088.
How should I store WEGOVY?
WEGOVY Injection
- Store the WEGOVY pen in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- If needed, before removing the pen cap, WEGOVY can be stored from 46°F to 86°F (8°C to 30°C) in the original carton for up to 28 days.
- Keep WEGOVY in the original carton to protect it from light.
- Do not freeze.
- Throw away the pen if WEGOVY has been frozen, has been exposed to light or temperatures above 86°F (30°C), or has been out of the refrigerator for 28 days or longer.
WEGOVY Tablets
- Store WEGOVY tablets at room temperature between 68°F and 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store tablets in the original closed WEGOVY bottle until you are ready to take one. Do not store in any other container.
- Store in a dry place away from moisture.
Keep WEGOVY and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of WEGOVY.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use WEGOVY for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give WEGOVY to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about WEGOVY that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in WEGOVY?
Active Ingredient: semaglutide
Inactive Ingredients in WEGOVY injection: disodium phosphate dihydrate, 1.42 mg; sodium chloride, 8.25 mg; water for injection; and hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH.
Inactive Ingredients in WEGOVY tablets: salcaprozate sodium (SNAC) and magnesium stearate
Marketed by: Novo Nordisk Inc., Plainsboro, NJ 08536
WEGOVY® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Patent Information: http://novonordisk-us.com/products/product-patents.html
© 2025 Novo Nordisk
For more information, go to startWegovy.com or call 1-833-Wegovy-1.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 1/2026
-
Instructions for Use
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 0.25 mg Injection
NDC 0169-4525-14 List 452514
0.25 mg
wegovy®
(semaglutide) injection
0.25 mg/0.5 mL
Use Wegovy 1 time a week
4 Single-Dose Prefilled Pens
Each pen delivers a single dose of 0.25 mg semaglutide
For subcutaneous use only
Single-Dose only
Rx only
Contains: 4 Wegovy pens, Product Literature.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 0.5 mg Injection
NDC 0169-4505-14 List 450514
0.5 mg
wegovy®
(semaglutide) injection
0.5 mg/0.5 mL
Use Wegovy 1 time a week
4 Single-Dose Prefilled Pens
Each pen delivers a single dose of 0.5 mg semaglutide
For subcutaneous use only
Single-Dose only
Rx only
Contains: 4 Wegovy pens, Product Literature.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 1 mg Injection
NDC 0169-4501-14 List 450114
1 mg
wegovy®
(semaglutide) injection
1 mg/0.5 mL
Use Wegovy 1 time a week
4 Single-Dose Prefilled Pens
Each pen delivers a single dose of 1 mg semaglutide
For subcutaneous use only
Single-Dose only
Rx only
Contains: 4 Wegovy pens, Product Literature.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 1.7 mg Injection
NDC 0169-4517-14 List 451714
1.7 mg
wegovy®
(semaglutide) injection
1.7 mg/0.75 mL
Use Wegovy 1 time a week
4 Single-Dose Prefilled Pens
Each pen delivers a single dose of 1.7 mg semaglutide
For subcutaneous use only
Single-Dose only
Rx only
Contains: 4 Wegovy pens, Product Literature.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 2.4 mg Injection
NDC 0169-4524-14 List 452414
2.4 mg
wegovy®
(semaglutide) injection
2.4 mg/0.75 mL
Use Wegovy 1 time a week
4 Single-Dose Prefilled Pens
Each pen delivers a single dose of 2.4 mg semaglutide
For subcutaneous use only
Single-Dose only
Rx only
Contains: 4 Wegovy pens, Product Literature.
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 1.5 mg Tablets
- NDC: 0169-4415-31 LIST 441531
- wegovy® 1.5 mg
(semaglutide) Tablets
1.5 mg
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
30 tablets
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 4 mg Tablets
- NDC: 0169-4404-31 LIST 440431
- wegovy® 4 mg
(semaglutide) Tablets
4 mg
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
30 tablets
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 9 mg Tablets
- NDC: 0169-4409-31 LIST 440931
- wegovy® 9 mg
(semaglutide) Tablets
9 mg
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
30 tablets
-
Package/Label Display Panel – 25 mg Tablets
- NDC: 0169-4425-31 LIST 442531
- wegovy® 25 mg
(semaglutide) Tablets
25 mg
Rx only
DISPENSE WITH MEDICATION GUIDE
30 tablets
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
WEGOVY
semaglutide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4525 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 0.25 mg in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4525-14 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 1 NDC: 0169-4525-01 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC: 0169-4525-94 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 2 NDC: 0169-4525-90 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215256 06/05/2021 WEGOVY
semaglutide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4505 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 0.5 mg in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4505-14 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 1 NDC: 0169-4505-01 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215256 06/05/2021 WEGOVY
semaglutide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4501 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 1.0 mg in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4501-14 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 1 NDC: 0169-4501-01 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215256 06/05/2021 WEGOVY
semaglutide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4517 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 1.7 mg in 0.75 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4517-14 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 1 NDC: 0169-4517-01 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215256 06/05/2021 WEGOVY
semaglutide injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4524 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 2.4 mg in 0.75 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4524-14 4 in 1 CARTON 06/05/2021 1 NDC: 0169-4524-01 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, PLASTIC; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215256 06/05/2021 WEGOVY
semaglutide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4415 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 1.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SALCAPROZATE SODIUM (UNII: 1YTW0422YU) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Light Yellow) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code 1;5;novo Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4415-31 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/06/2026 2 NDC: 0169-4415-92 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/06/2026 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218316 01/06/2026 WEGOVY
semaglutide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4404 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SALCAPROZATE SODIUM (UNII: 1YTW0422YU) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Light Yellow) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code 4;novo Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4404-31 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/06/2026 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218316 01/06/2026 WEGOVY
semaglutide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4409 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 9 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SALCAPROZATE SODIUM (UNII: 1YTW0422YU) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Light Yellow) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code 9;novo Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4409-31 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/06/2026 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218316 01/06/2026 WEGOVY
semaglutide tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0169-4425 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SEMAGLUTIDE (UNII: 53AXN4NNHX) (SEMAGLUTIDE - UNII:53AXN4NNHX) SEMAGLUTIDE 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SALCAPROZATE SODIUM (UNII: 1YTW0422YU) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (Light Yellow) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 12mm Flavor Imprint Code 25;novo Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0169-4425-31 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/06/2026 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA218316 01/06/2026 Labeler - Novo Nordisk (622920320)
Trademark Results [WEGOVY]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 WEGOVY 79324913 not registered Live/Pending |
Novo Nordisk A/S 2021-08-17 |
 WEGOVY 79303393 not registered Live/Pending |
Novo Nordisk A/S 2020-10-29 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.