Penicillin V Potassium by Pharmasource Meds LLC
Penicillin V Potassium by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Penicillin V Potassium by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Pharmasource Meds LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM- penicillin v potassium tablet, film coated
Pharmasource Meds LLC
----------
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of penicillin V potassium and other antibacterial drugs, penicillin V potassium should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
Penicillin V is the phenoxymethyl analog of penicillin G. Penicillin V potassium is the potassium salt of penicillin V.
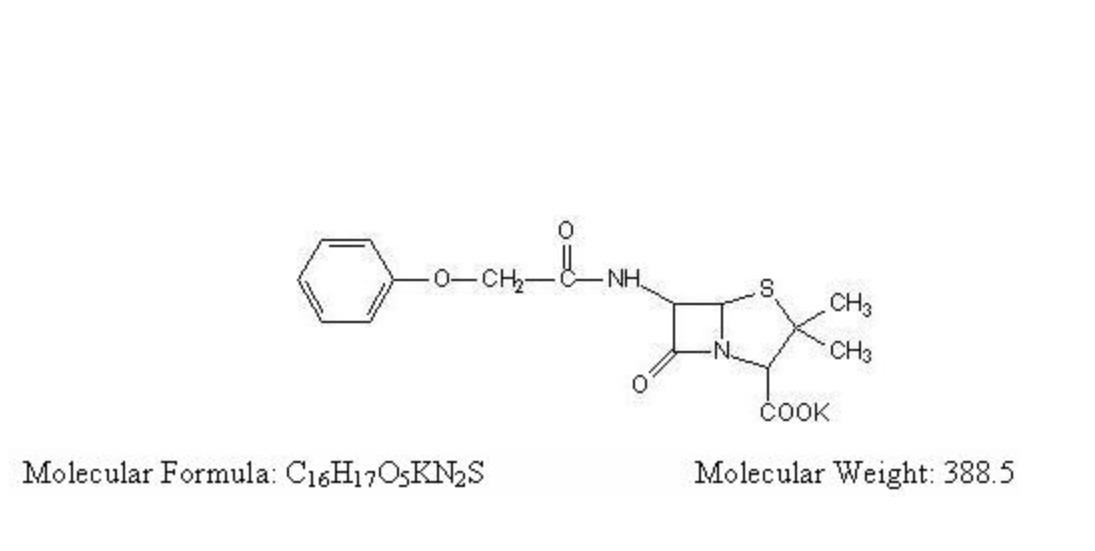
Penicillin V potassium tablets, for oral administration, contain 250 mg (400,000 units) or 500 mg (800,000 units). The 250 mg tablet is equivalent to 250 mg (400,000 units) penicillin V and the 500 mg tablet is equivalent to 500 mg (800,000 units) penicillin V. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
Penicillin V exerts a bactericidal action against penicillin-sensitive microorganisms during the stage of active multiplication. It acts through the inhibition of biosynthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide. It is not active against the penicillinase-producing bacteria, which include many strains of staphylococci. The drug exerts high in vitro activity against staphylococci (except penicillinase-producing strains), streptococci (groups A, C, G, H, L and M), and pneumococci. Other organisms sensitive in vitro to penicillin V are Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Bacillus anthracis, Clostridia, Actinomyces bovis, Streptobacillus moniliformis, Listeria monocytogenes, Leptospira, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Treponema pallidum is extremely sensitive.
The potassium salt of penicillin V has the distinct advantage over penicillin G in resistance to inactivation by gastric acid. It may be given with meals; however, blood levels are slightly higher when the drug is given on an empty stomach. Average blood levels are two to five times higher than the levels following the same dose of oral penicillin G and also show much less individual variation.
Once absorbed, penicillin V is about 80% bound to serum protein. Tissue levels are highest in the kidneys, with lesser amounts in the liver, skin, and intestines. Small amounts are found in all other body tissues and the cerebrospinal fluid. The drug is excreted as rapidly as it is absorbed in individuals with normal kidney function; however, recovery of the drug from the urine indicates that only about 25% of the dose given is absorbed. In neonates, young infants, and individuals with impaired kidney function, excretion is considerably delayed.
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of penicillin V potassium and other antibacterial drugs, penicillin V potassium should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Penicillin V potassium tablets are indicated in the treatment of mild to moderately severe infections due to penicillin G-sensitive microorganisms. Therapy should be guided by bacteriologic studies (including sensitivity tests) and by clinical response.
NOTE: Severe pneumonia, empyema, bacteremia, pericarditis, meningitis, and arthritis should not be treated with penicillin V during the acute stage. Indicated surgical procedures should be performed.
The following infections will usually respond to adequate dosage of penicillin V.
Streptococcal Infections (without bacteremia)
Mild-to-moderate infections of the upper respiratory tract, scarlet fever, and mild erysipelas.
NOTE: Streptococci in groups A, C, G, H, L, and M are very sensitive to penicillin. Other groups, including group D (enterococcus), are resistant.
Pneumococcal Infections
Mild to moderately severe infections of the respiratory tract.
Staphylococcal infections– penicillin G-sensitive
Mild infections of the skin and soft tissues.
NOTE: Reports indicate an increasing number of strains of staphylococci resistant to penicillin G, emphasizing the need for culture and sensitivity studies in treating suspected staphylococcal infections.
Fusospirochetosis (Vincent’s gingivitis and pharyngitis)
Mild to moderately severe infections of the oropharynx usually respond to therapy with oral penicillin.
NOTE: Necessary dental care should be accomplished in infections involving the gum tissue.
Medical conditions in which oral penicillin therapy is indicated as prophylaxis: For the prevention of recurrence following rheumatic fever and/or chorea: Prophylaxis with oral penicillin on a continuing basis has proven effective in preventing recurrence of these conditions.
Although no controlled clinical efficacy studies have been conducted, penicillin V has been suggested by the American Heart Association and the American Dental Association for use as an oral regimen for prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis in patients who have congenital heart disease or rheumatic or other acquired valvular heart disease when they undergo dental procedures and surgical procedures of the upper respiratory tract1. Oral penicillin should not be used in those patients at particularly high risk for endocarditis (e.g., those with prosthetic heart valves or surgically constructed systemic pulmonary shunts). Penicillin V should not be used as adjunctive prophylaxis for genitourinary instrumentation or surgery, lower-intestinal tract surgery, sigmoidoscopy, and childbirth. Since it may happen that alpha hemolytic streptococci relatively resistant to penicillin may be found when patients are receiving continuous oral penicillin for secondary prevention of rheumatic fever, prophylactic agents other than penicillin may be chosen for these patients and prescribed in addition to their continuous rheumatic fever prophylactic regimen.
NOTE: When selecting antibiotics for the prevention of bacterial endocarditis, the physician or dentist should read the full joint statement of the American Heart Association and the American Dental Association 1.
SERIOUS AND OCCASIONALLY FATAL HYPERSENSITIVITY (anaphylactic) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS ON PENICILLIN THERAPY. THESE REACTIONS ARE MORE LIKELY TO OCCUR IN INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY AND/OR A HISTORY OF SENSITIVITY TO MULTIPLE ALLERGENS. THERE HAVE BEEN REPORTS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY WHO HAVE EXPERIENCED SEVERE REACTIONS WHEN TREATED WITH CEPHALOSPORINS. BEFORE INITIATING THERAPY WITH PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM TABLETS, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE CONCERNING PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO PENICILLINS, CEPHALOSPORINS, OR OTHER ALLERGENS. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION OCCURS, PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM TABLETS SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AND APPROPRIATE THERAPY INSTITUTED.
SERIOUS ANAPHYLACTIC REACTIONS REQUIRE IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE. OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS STEROIDS, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, INCLUDING INTUBATION, SHOULD ALSO BE ADMINISTERED AS INDICATED.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including penicillin V potassium tablets, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Penicillin should be used with caution in individuals with histories of significant allergies and/or asthma.
Prescribing penicillin V potassium in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
The oral route of administration should not be relied upon in patients with severe illness, or with nausea, vomiting, gastric dilatation, cardiospasm, or intestinal hypermotility. Occasionally patients will not absorb therapeutic amounts of orally administered penicillin.
In streptococcal infections, therapy must be sufficient to eliminate the organism (10-day minimum); otherwise the sequelae of streptococcal disease may occur. Cultures should be taken following completion of treatment to determine whether streptococci have been eradicated.
Prolonged use of antibiotics may promote the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. Should superinfection occur, appropriate measures should be taken.
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including penicillin V potassium should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When penicillin V potassium is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by penicillin V potassium or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Although the incidence of reactions to oral penicillins has been reported with much less frequency than following parenteral therapy, it should be remembered that all degrees of hypersensitivity, including fatal anaphylaxis, have been reported with oral penicillin.
The most common reactions to oral penicillin are nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and black hairy tongue. The hypersensitivity reactions reported are skin eruptions (maculopapular to exfoliative dermatitis), urticaria and other serum-sickness like reactions, laryngeal edema, and anaphylaxis.
Fever and eosinophilia may frequently be the only reaction observed. Hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neuropathy, and nephropathy are infrequent reactions and usually associated with high doses of parenteral penicillin.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Rising Health, LLC at 1-833-395-6928 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
The dosage of Penicillin V should be determined according to the sensitivity of the causative microorganisms and the severity of infection, and adjusted to the clinical response of the patient.
The usual dosage recommendations for adults and children 12 years and over are as follows:
Streptococcal Infections
Mild to moderately severe - of the upper respiratory tract and including scarlet fever and erysipelas: 125 to 250 mg (200,000 to 400,000 units) every 6 to 8 hours for 10 days.
Pneumococcal Infections
Mild to moderately severe - of the respiratory tract, including otitis media: 250 to 500 mg (400,000 to 800,000 units) every 6 hours until the patient has been afebrile for at least 2 days.
Staphylococcal Infections
Mild infections of skin and soft tissue (culture and sensitive tests should be performed): 250 to 500 mg (400,000 to 800,000 units) every 6 to 8 hours.
Fusospirochetosis (Vincent’s infection) of the oropharynx. Mild to moderately severe infections: 250 to 500 mg (400,000 to 800,000 units) every 6 to 8 hours.
For the prevention of recurrence following rheumatic fever and/or chorea: 125 mg to 250 mg (200,000 to 400,000 units) twice daily on a continuing basis.
For prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis1 in patients with congenital heart disease or rheumatic or other acquired valvular heart disease when undergoing dental procedures or surgical procedures of the upper respiratory tract: 2 gram of penicillin V (1 gram for children under 60 lbs.) 1 hour before the procedure, and then, 1 gram (500 mg for children under 60 lbs.) 6 hours later.
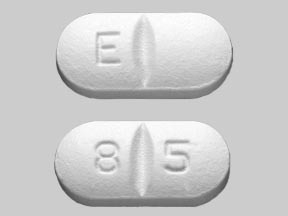
Penicillin V Potassium Tablets USP, 500 mg (800,000 units) are white to off-white, capsule shaped, film-coated tablets, debossed with 'E' and a break line on one side and '8' and '5' separated with a break line on the other side.
Bottles of 20 NDC: 82982-0120-20
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight container, as defined in the USP.
Keep tightly closed.
Keep out of reach of children.
| PENICILLIN V POTASSIUM
penicillin v potassium tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pharmasource Meds LLC (118772692) |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
