JOURNAVX- suzetrigine tablet, film coated
JOURNAVX by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
JOURNAVX by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use JOURNAVX safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for JOURNAVX.
JOURNAVX (suzetrigine) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JOURNAVX is a sodium channel blocker indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain, including postoperative pain, in adults. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Swallow JOURNAVX tablets whole and do not chew or crush. (2.1)
- Recommended starting JOURNAVX oral dose is 100 mg. Take the starting dose on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food. Clear liquids may be consumed during this time (e.g., water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, black coffee). (2.1)
- Starting 12 hours after the starting dose, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 12 hours. Take these doses with or without food. (2.1)
- Use JOURNAVX for the shortest duration, consistent with individual patient treatment goals. Use of JOURNAVX for the treatment of acute pain has not been studied beyond 14 days. (2.1)
- See the full prescribing information for the recommended dosage in patients with hepatic impairment (2.2), for JOURNAVX dosage modifications with concomitant use of CYP3A inhibitors (2.3), and recommendations regarding missed dose(s). (2.4)
- Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit during treatment with JOURNAVX. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 50 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Concomitant use with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Use in patients with moderate hepatic impairment may increase the risk of adverse reactions. The recommended dosage is lower in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) than those with normal hepatic function. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (greater incidence in JOURNAVX-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients) were pruritus, muscle spasms, increased creatine phosphokinase, and rash. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated at 1-877-634-8789 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated. Reduce the JOURNAVX dose when used concomitantly with moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit. (2.3, 7.1, 12.3)
- Strong and Moderate CYP3A inducers: Avoid JOURNAVX use with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. (7.1, 12.3)
- CYP3A substrates: If JOURNAVX is used concomitantly with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to loss of efficacy, refer to the Prescribing Information for the CYP3A substrates for dosing instructions. Dosage modification of the concomitant CYP3A substrates may be required when initiating or discontinuing JOURNAVX. (7.2, 12.3)
- Hormonal contraceptives: JOURNAVX-treated patients using hormonal contraceptives containing progestins other than levonorgestrel and norethindrone should use an additional nonhormonal contraceptive method or an alternative hormonal contraceptive during concomitant use and for 28 days after JOURNAVX discontinuation. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 1/2026
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Dosage Modifications for CYP3A Inhibitors
2.4 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose(s)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
5.2 Risk of Drug Interactions with Certain CYP3A Substrates
5.3 Risk of Drug Interactions with Certain Hormonal Contraceptives
5.4 Risk of Adverse Reactions in Patients with Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on JOURNAVX
7.2 Effect of JOURNAVX on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Overview of Clinical Studies
14.2 Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Full Abdominoplasty
14.3 Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Bunionectomy
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
Swallow JOURNAVX tablets whole and do not chew or crush.
The recommended starting dose of JOURNAVX is 100 mg orally. Take the starting dose on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food to avoid delay in onset of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Clear liquids may be consumed during this time (e.g., water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, black coffee).
Starting 12 hours after the initial dose, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 12 hours. Take these doses with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit during treatment with JOURNAVX [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Use JOURNAVX for the shortest duration, consistent with individual patient treatment goals. Use of JOURNAVX for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain has not been studied beyond 14 days.
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of JOURNAVX in patients with hepatic impairment is described in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended JOURNAVX Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment Degree of Hepatic Impairment (HI) Recommended Dosage Severe HI (Child-Pugh Class C) Avoid use [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. Moderate HI (Child-Pugh Class B) Dose 1: The recommended starting dose of JOURNAVX is 100 mg taken orally. Take the starting dose on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Clear liquids may be consumed during this time (e.g., water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, black coffee).
Doses 2, 3, and 4: Starting 12 hours after the initial dose, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 12 hours. Take these doses with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dose 5 and Subsequent Doses: Starting 12 hours after Dose 4, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 24 hours. Take these dose(s) with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Mild HI (Child-Pugh Class A) The recommended dosage is the same as in those with normal hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. 2.3 Dosage Modifications for CYP3A Inhibitors
JOURNAVX is contraindicated in patients taking strong CYP3A inhibitors. When JOURNAVX is administered to patients taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors reduce the JOURNAVX dose, as described below:
Dose 1: The recommended starting dose of JOURNAVX is 100 mg orally. Take the starting dose on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Clear liquids may be consumed during this time (e.g., water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, black coffee).
Doses 2, 3, and 4: Starting 12 hours after the initial dose, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 12 hours. Take these doses with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dose 5 and Subsequent Doses: Starting 12 hours after Dose 4, take 50 mg of JOURNAVX orally every 24 hours. Take these dose(s) with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit during treatment with JOURNAVX [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose(s)
For patients on the standard recommended dosing schedule [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]:
- If a dose is missed, take the missed dose as soon as possible and then take the next scheduled dose at the recommended time.
- If two or more doses are missed, take 100 mg and then take the next scheduled dose at the recommended time.
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment or patients taking moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)], if a dose is missed, take the missed dose as soon as possible. If the next scheduled dose is within 6 hours, skip the next scheduled dose, and take the subsequent doses at the recommended time.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Concomitant use of JOURNAVX with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors
Strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors increase suzetrigine and M6-SUZ (active metabolite) exposures which may cause JOURNAVX adverse reactions. Concomitant use of JOURNAVX with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce the JOURNAVX dosage with moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Risk of Drug Interactions with Certain CYP3A Substrates
Suzetrigine is an inducer of CYP3A. If JOURNAVX is used concomitantly with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to loss of efficacy, refer to the Prescribing Information for the CYP3A substrates for dosing instructions. Dosage adjustment of the concomitant CYP3A substrates may be required when initiating or discontinuing JOURNAVX [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.3 Risk of Drug Interactions with Certain Hormonal Contraceptives
JOURNAVX-treated patients taking concomitant hormonal contraceptives containing progestins other than levonorgestrel and norethindrone should use additional nonhormonal contraceptives (such as condoms) or use alternative contraceptives (e.g., a combined oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol as the estrogen and levonorgestrel or norethindrone as the progestin, an intrauterine system) during JOURNAVX treatment and for 28 days after discontinuation of JOURNAVX [see Drug Interactions (7.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Risk of Adverse Reactions in Patients with Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate hepatic impairment have higher systemic exposures of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ (active metabolite) than those with normal hepatic function which may increase the risk of JOURNAVX related adverse reactions [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Avoid use of JOURNAVX in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). The recommended JOURNAVX dosage is lower in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) than those with normal hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety profile of JOURNAVX is primarily based on data from the pooled, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled trials in 874 adult patients with moderate to severe acute pain following full abdominoplasty (Trial 1) and bunionectomy (Trial 2) [see Clinical Studies (14)], with supportive safety data from one single arm trial in 256 adult patients with moderate to severe acute pain in a broad range of acute pain conditions (Trial 3).
In Trials 1 and 2, 874 patients received at least one dose of JOURNAVX. The proportion of patients in Trials 1 and 2 who discontinued study drug prematurely due to adverse events was:
- 0.6% in JOURNAVX-treated patients (postprocedural hematoma [0.2%], hypotension [0.2%], syncope [0.1%]),
- 0.6% in hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen (HB/APAP)-treated patients (hypotension/orthostatic hypotension [0.2%], migraine [0.1%], intra-abdominal hematoma [0.1%], nausea [0.1%], pyrexia [0.1%]), and
- 0.2% in placebo-treated patients (hypotension [0.2%], tachycardia [0.2%]).
The safety profile of JOURNAVX was also evaluated by the following subgroup analyses: age (≥ 18 to < 65 years and ≥ 65 years), sex, and race. Since most patients enrolled in the clinical trials were ≥ 18 to < 65 years of age, female, and white, there was insufficient data to detect differences in safety signals between these subgroups.
Table 2 displays adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in JOURNAVX-treated patients than placebo-treated patients in the pooled Trials 1 and 2.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥1% of JOURNAVX-Treated Patients and Greater than Rate of Placebo in Two 48-hour Trials in Moderate to Severe Acute Pain (Trials 1 and 2, Pooled) Adverse Reactions
(Preferred Term)Placebo
(N = 438)
n (%)JOURNAVX
(N = 874)
n (%)HB/APAP *
(N = 879)
n (%)- * Patients received 5 mg/325 mg of oral hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen (HB/APAP) every 6 hours.
Pruritus 7 (1.6) 18 (2.1) 30 (3.4) Muscle spasms 2 (0.5) 11 (1.3) 6 (0.7) Increased blood creatine phosphokinase 2 (0.5) 10 (1.1) 7 (0.8) Rash 2 (0.5) 10 (1.1) 6 (0.7) Nausea and Vomiting
In Trial 1, the incidence of patients who experienced either nausea or vomiting was 20% in JOURNAVX-treated patients, 33% in HB/APAP-treated patients, and 25% in placebo-treated patients. In Trial 2, the incidence of patients who experienced either nausea or vomiting was 9% in JOURNAVX-treated patients, 16% in HB/APAP-treated patients, and 12% in placebo-treated patients.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Creatine Phosphokinase Elevations: In Trials 1 and 2, 2.9% of JOURNAVX-treated patients and 1.2% of placebo-treated patients had a creatine phosphokinase (CPK) level > 3 times the upper limit of normal. The incidence of increased blood CPK was 1.1% in JOURNAVX-treated patients and 0.5% in placebo-treated patients. All reports of CPK elevations occurred in the post-surgical setting. There were no associated signs or symptoms, no serious adverse reactions, and no patients required treatment discontinuation or interruption.
Decreased Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate: In Trials 1 and 2, 2.5% of JOURNAVX-treated patients and 0.9% of placebo-treated patients had a decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of ≥ 25% but < 50%. Follow-up eGFR data for these controlled trials was not available after treatment discontinuation. Similar decreases in eGFR also occurred in Trial 3 (the open-label Phase 3 study) and appeared to resolve to baseline by the final safety follow-up visit. There was no control arm for comparison. There were no adverse reactions of eGFR decrease in JOURNAVX-treated patients.
Adverse Reactions from the Open-Label Study (Trial 3)
In an open-label study of patients with moderate to severe acute pain following a surgical procedure or nonsurgical condition [NCT05661734], a total of 256 adult patients received at least one dose of JOURNAVX. Patients received 100 mg as a first dose, then 50 mg every 12 hours and continued to receive JOURNAVX for up to 14 days or until their pain resolved. Rescue medication of 650 mg of acetaminophen and 400 mg of ibuprofen together every 6 hours was permitted as needed for pain relief. The patients' perceptions of pain control was captured by patient global assessment (PGA). The mean duration of treatment with JOURNAVX was 9.6 days. The majority of patients were female (68%), and the median age was 43 years (range: 18 to 78).
In Trial 3, a total of 222 (87%) patients received JOURNAVX for post-surgical pain; orthopedic surgery was the most common (e.g., ligament operation, arthrodesis), followed by plastic surgery (e.g., liposuction, mammoplasty), otorhinolaryngologic surgery (e.g., nasal septal operation, turbinoplasty), and general and urologic surgery (e.g., inguinal hernia repair). Thirty-four (13%) patients received JOURNAVX for non-surgical pain (e.g., arthralgias, limb pain, and sprains/strains).
The proportion of patients who discontinued study drug prematurely was 2% due to adverse events (arrhythmia [0.4%], nausea [0.4%], somnolence [0.4%], rash [0.4%]) and 1.6% due to lack of efficacy.
The safety profile of JOURNAVX in Trial 3 was consistent with that observed in Trials 1 and 2.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on JOURNAVX
Table 3 describes drug interactions where concomitant use of another drug affects the use of JOURNAVX.
Table 3: Drug Interactions: Concomitant Use of Other Drugs that Affect the Use of JOURNAVX Strong and Moderate * CYP3A Inhibitors - * Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with JOURNAVX.
Prevention or Management Strong CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use of JOURNAVX with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Moderate CYP3A inhibitors: Reduce the JOURNAVX dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) Suzetrigine and M6-SUZ are CYP3A substrates. Strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors increase suzetrigine and M6-SUZ (active metabolite of suzetrigine) exposures [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may cause JOURNAVX adverse reactions. Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers Prevention or Management Avoid concomitant use of JOURNAVX with strong and moderate CYP3A inducers. Mechanism and Clinical Effect(s) Suzetrigine and M6-SUZ are CYP3A substrates. Concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inducers results in reduced exposures of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ, which may result in reduced JOURNAVX efficacy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 7.2 Effect of JOURNAVX on Other Drugs
CYP3A Substrates
If JOURNAVX is used concomitantly with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to loss of efficacy, refer to the Prescribing Information for the CYP3A substrates for dosing instructions. Dosage modification of the concomitant CYP3A substrates may be required when initiating or discontinuing JOURNAVX [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Suzetrigine is an inducer of CYP3A. Concomitant use with JOURNAVX may reduce the exposure of sensitive CYP3A substrates which may decrease the efficacy of these substrates. Discontinuation of JOURNAVX may increase the exposure of sensitive CYP3A substrates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Hormonal Contraceptives
JOURNAVX-treated patients using hormonal contraceptives containing progestins other than levonorgestrel and norethindrone should use additional nonhormonal contraceptives (such as condoms), or use alternative contraceptives (such as a combined oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol as the estrogen and levonorgestrel or norethindrone as the progestin, or an intrauterine system) during treatment with JOURNAVX and for 28 days after discontinuation of JOURNAVX [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
JOURNAVX did not result in clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel when used concomitantly with an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the use of JOURNAVX during pregnancy to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies in rats, effects on implantation and maintenance of pregnancy occurred at oral suzetrigine doses of ≥ 2.2-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) when administered during early embryonic development or throughout organogenesis. In a pre- and postnatal development study, reduced mean gestation length and increased postnatal pup mortality were observed at maternal rat exposures of 1.6-times the MRHD and decreased rat pup body weights were observed during the period of birth to weaning at maternal exposures of 2.2-times the MRHD. No malformations were observed when suzetrigine was administered orally to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 2.2- and 5.9-times, respectively, the MRHD. The clinical relevance of these findings is unclear.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in patients with moderate to severe acute pain is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Suzetrigine was administered orally to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 1.6-, 3.1-, and 5.9-times, respectively, the steady state MRHD exposure based on AUC). Increased post-implantation loss and lower fetal body weight were observed at 200 mg/kg/day, which is a dose that also caused maternal toxicity. No adverse embryofetal effects were observed at doses up to 100 mg/kg.
Suzetrigine was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.57-, 1.6-, and 2.2-times, respectively, the steady state MRHD exposure based on AUC). Increased post-implantation loss and lower number of live fetuses were observed at 15 mg/kg/day. No adverse embryofetal effects were observed at doses up to 10 mg/kg. Placental transfer of suzetrigine was observed in pregnant rats.
In a pre- and postnatal development study, suzetrigine was administered orally to pregnant rats at doses of 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.57-, 1.6-, and 2.2-times, respectively, the steady state MRHD exposure based on AUC) from Gestation Day 6 through Lactation Day 20. Reduced mean gestation length and increased postnatal pup mortality between birth and Postnatal Day 4 were observed at ≥ 10 mg/kg and increased incidences of fully resorbed litters, lower live newborn pups, and reductions in pup body weights were observed at 15 mg/kg. No effects on learning and memory or sexual maturation were observed at dose up to 15 mg/kg/day.
The effects on implantation, maintenance of pregnancy, reduced mean gestation length, and increased postnatal pup mortality in rats are of uncertain relevance to humans.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of suzetrigine or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Suzetrigine is present in animal milk. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for JOURNAVX and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from JOURNAVX or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Advise patients using hormonal contraceptives containing progestins other than levonorgestrel and norethindrone to use an additional nonhormonal contraceptive or to use alternative contraceptives during JOURNAVX treatment and for 28 days after discontinuation of JOURNAVX [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Infertility
In a female fertility study in rats, increased pre-implantation loss was observed at oral suzetrigine doses of ≥ 2.2-times the MRHD when administered prior to mating and through Gestation Day 7. Following discontinuation of suzetrigine for 4 weeks, the increased pre-implantation loss in rats was not observed. The finding in rats may be explained by the effect of suzetrigine on the rat progesterone receptor, which was more sensitive to suzetrigine than the human progesterone receptor based on in vitro studies. The finding in the rat study is of uncertain relevance to humans.
JOURNAVX may reversibly impact the likelihood of females of reproductive potential to become pregnant while on treatment. Patients using contraceptives should continue to use contraceptives [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of JOURNAVX has not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total 1130 patients with moderate to severe acute pain who received JOURNAVX in the Phase 3 studies [see Clinical Studies (14)], 71 patients (6.3%) were 65 years of age and older.
Clinical studies of JOURNAVX did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. However, based on population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients with ages ranging from 18 to 75 years, age does not have a clinically relevant impact on suzetrigine exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
JOURNAVX has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Avoid use of JOURNAVX in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. The recommended JOURNAVX dosage is lower in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)] than those with normal hepatic function. The recommended dosage in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) is the same as those with normal hepatic function.
Patients with moderate hepatic impairment had greater suzetrigine and M6-SUZ (the active metabolite) exposure than those with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of suzetrigine adverse reactions.
8.7 Renal Impairment
JOURNAVX has not been studied in patients with renal impairment of eGFR < 15 mL/min. Avoid use of JOURNAVX in patients with renal impairment of eGFR < 15 mL/min [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The recommended dosage in patients with eGFR > 15 mL/min is the same as those with normal kidney function.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidote is available for overdose with JOURNAVX. Treatment of overdose consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdose management recommendations.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient in JOURNAVX (suzetrigine) tablets is suzetrigine, a sodium channel blocker, which has the following chemical name:
- 4-[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-3-(3,4-difluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dimethyl-5-(trifluoromethyl)oxolane-2-amido]pyridine-2-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C21H20F5N3O4.
Suzetrigine's molecular weight is 473.39 g/mol. Suzetrigine has the following structural formula:
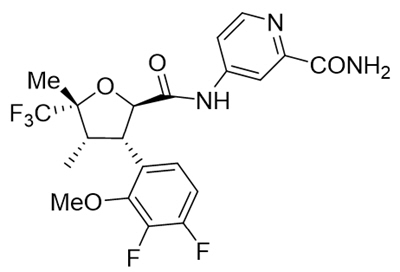
Suzetrigine is a white to off-white solid and is practically insoluble in water.
JOURNAVX is available as a blue, film-coated tablet for oral administration containing 50 mg of suzetrigine and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film coat contains FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Suzetrigine is a selective blocker of the NaV1.8 voltage-gated sodium channel, compared to other known voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV1.1 through 1.9). NaV1.8 is expressed in peripheral sensory neurons including dorsal root ganglion neurons, where its role is to transmit pain signals (action potentials). By selectively inhibiting NaV1.8 channels, suzetrigine inhibits transmission of pain signals to the spinal cord and brain. M6-SUZ, a major active metabolite, is a less potent inhibitor of NaV1.8 than suzetrigine by 3.7-fold.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic parameters for suzetrigine and its major active metabolite, M6-SUZ, are shown in Table 4.
Table 4: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Suzetrigine and M6-SUZ Suzetrigine M6-SUZ (Active Metabolite) * AUC: area under the concentration versus time curve; CV: coefficient of variation; Cmax: maximum observed concentration; Tmax: time of maximum concentration; NA: not applicable - * Based on an in vitro electrophysiology assay in human dorsal root ganglion neurons, M6-SUZ is a less potent inhibitor of NaV1.8 than suzetrigine by 3.7-fold.
- † Based on simulations of a dose of 50 mg every 12 hours (q12h).
- ‡ Suzetrigine and M6-SUZ do not partition preferentially into human red blood cells.
General Information Steady State AUC0-24h (CV%), µg*h/mL 11.5 (25.6%) 34.7 (25.6%) Steady State Cmax (CV%), µg/mL 0.62 (27.7%) 1.5 (24.5%) Time to 90% Steady State, days 3 5 Mean (CV%) Accumulation Ratio † 3.4 (30.2%) 4.5 (30.6%) Absorption Median Tmax (range), hours 3.0 hours (1.50, 5.03) 10.0 hours (4.0, 48.1) Distribution ‡ Mean (CV%) Apparent Volume of Distribution, L 495 (25.0%) NA Protein Binding 99% 96% Elimination Mean (CV%) Effective Half-Life, hours † 23.6 (36.2%) 33.0 (34.9%) Steady State Mean (CV%) Apparent Oral Clearance, L/hours 13.9 (37.5%) NA Metabolism Primary Pathway CYP3A CYP3A Excretion Primary Pathway - Feces: 49.9% (9.1% SUZ and rest as metabolites)
- Urine: 44.0% (primarily as metabolites)
Effect of Food
Administration of 100 mg of JOURNAVX (the first dose) with a high-fat meal (800 to 1000 calories, 50% derived from fat), a moderate-fat meal (600 calories, 30% derived from fat), and a low-fat meal (up to 500 calories with no more than 25% derived from fat) resulted in decreased initial concentrations of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ in comparison to a fasted state. The median Tmax of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ in the fasted state was 3 hours and 8 to 10 hours, respectively. When administered in the fed state (high-fat meal or moderate-fat meal) the median Tmax of suzetrigine was delayed to 5 hours and the median Tmax of M6-SUZ was delayed to 24 hours. The Cmax and AUC of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ were not affected by any of the meal conditions, including a high-fat meal consumed one hour after JOURNAVX administration.
Administration of the second JOURNAVX dose of 50 mg with or without regard to meals is predicted to not affect the systemic exposures of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ were observed based on age (18-75 years), sex, body weight (44-126 kg), race, and renal impairment (eGFR ≥ 15 mL/min by CKD-EPI equation with adjustment for the body surface area). The effect of renal impairment with eGFR < 15 mL/min on suzetrigine and M6-SUZ pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A), no clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ were observed. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), at steady state, suzetrigine AUC0-12h increased by 1.5-fold (90% CI: 1.1-2.1) and Cmax increased by 1.3-fold (90% CI: 1.0-1.7) and M6-SUZ AUC0-12h and Cmax both increased by 1.2-fold (AUC 90% CI: 0.83-1.6; Cmax 90% CI: 0.84-1.6). The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on suzetrigine and M6-SUZ pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Concomitant administration of itraconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) with a single dose of JOURNAVX increased the geometric mean (90% CI) AUC0-inf of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ by 4.8-fold (4.3-5.4) and 4.4-fold (3.6-5.4), respectively, while the geometric mean (90% CI) Cmax of suzetrigine increased by 1.5-fold (1.3-1.6) and Cmax of M6-SUZ decreased by 32% (24-39%) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Concomitant administration of fluconazole (a moderate CYP3A inhibitor) with JOURNAVX with the recommended dosage modification [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] is predicted to increase the geometric mean (90% CI) AUCtau of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ by 1.5-fold (1.4-1.5) and 1.2-fold (1.2-1.3), respectively, while the geometric mean (90% CI) Cmax of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ is predicted to increase by 1.4-fold (1.4-1.5) and 1.1-fold (1.1-1.2), respectively, when compared to the regular recommended dosage in the absence of fluconazole [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Concomitant administration of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) at steady state with a single dose of JOURNAVX decreased the geometric mean (90% CI) AUC0-inf of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ by 93% (91-94%) and 85% (83-86%), respectively, while the geometric mean (90% CI) Cmax of suzetrigine decreased by 80% (75-83%) and the Cmax of M6-SUZ increased by 1.3-fold (1.1-1.5) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Moderate CYP3A Inducers: Concomitant administration of efavirenz (moderate CYP3A inducer) with a single dose of JOURNAVX is predicted to decrease the geometric mean (90% CI) AUC0-t of suzetrigine and M6-SUZ by 63% (61-65%) and 60% (58-62%), respectively, while the geometric mean (90% CI) Cmax of suzetrigine is predicted to decrease by 29% (27-32%) and M6-SUZ is predicted to increase by 1.3-fold (1.3-1.4), respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Sensitive CYP3A Substrates: JOURNAVX administered 50 mg every 12 hours, at steady state decreased the geometric mean (90% CI) AUC0-inf of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) by 48% (43-53%) and Cmax by 37% (27-45%) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) Enzymes: Suzetrigine inhibits CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, but is not expected to result in clinically significant drug interactions. Suzetrigine does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2D6, and CYP3A enzymes, and M6-SUZ does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A enzymes. Suzetrigine induces CYP3A and to a lesser extent CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. Suzetrigine does not induce CYP1A2.
Transporter Systems: Suzetrigine and M6-SUZ are not substrates of BCRP, OATP1B1 or OATP1B3. Suzetrigine is not a P-gp substrate, but M6-SUZ is a P-gp substrate. Suzetrigine inhibits OATP1B1, OATP1B3 and OAT3 but is not expected to result in clinically significant drug interactions. Suzetrigine does not inhibit BCRP, OAT1, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2/K transporters. M6-SUZ inhibits OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, and OAT3 but is not expected to result in clinically significant drug interactions. M6-SUZ does not inhibit P-gp, BCRP, OCT2, MATE1 and MATE2/K transporters.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term animal studies have not been completed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of suzetrigine.
Mutagenesis
Suzetrigine was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test), or clastogenic in the in vitro micronucleus assay with a human TK6 lymphoblastoid cell line, or in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In a female fertility study, female rats were treated orally with suzetrigine at 5, 10, and 15 mg/kg/day for a minimum of 14 days prior to mating, throughout mating, and through Gestation Day 7. These doses are approximately 0.57, 1.6, and 2.2-times the steady state MRHD exposure based on AUC. Increased pre-implantation loss was observed at 15 mg/kg (approximately 2.2-times the MRHD based on AUC). The finding in rats may be explained by the effect of suzetrigine on the rat progesterone receptor, which was more sensitive to suzetrigine than the human progesterone receptor based on in vitro studies. Following 4-week withdrawal of treatment, there were no effects on female fertility and early embryonic development. The finding in the rat study is of uncertain relevance to humans.
In a male fertility study, male rats were treated orally with suzetrigine at 200, 600, and 1000 mg/kg/day for a minimum of 28 days prior to mating and through mating. These doses are 3.6, 9.7, and 13.8-times the steady state MRHD exposure based on AUC, respectively. Suzetrigine had no effects on sperm parameters (motility, concentration, or morphology), reproductive performance or uterine parameters (number of implants, viable implants, pre-implantation loss, early resorptions, and post-implantation loss) at any dose.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Overview of Clinical Studies
The efficacy of JOURNAVX in the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults was established in two randomized, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled trials of acute pain, one following full abdominoplasty (Trial 1) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] and the other following bunionectomy (Trial 2) [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. In each trial, pain intensity was measured using a patient-reported 11-point numeric pain rating scale (NPRS), ranging from 0 to 10, where zero corresponds to no pain and 10 corresponds to the worst pain imaginable.
Patients were eligible for study participation if they had moderate to severe pain on the verbal categorical rating system (VRS) and a pain score of ≥ 4 on the NPRS, within 4 hours of the abdominoplasty completion (Trial 1) or during the 9-hour period after discontinuation of regional anesthesia following bunionectomy (Trial 2). Once eligible, patients were randomized to receive oral JOURNAVX, placebo, or hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen (HB/APAP) for a duration of 48 hours. For the JOURNAVX treatment regimen, patients received an initial loading dose of 100 mg JOURNAVX, followed by 50 mg every 12 hours. For the HB/APAP-control regimen, patients received 5 mg/325 mg every 6 hours. For both studies, 400 mg of ibuprofen every 6 hours, as needed for pain relief, was permitted as a rescue medication.
14.2 Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Full Abdominoplasty
Trial 1 [NCT05558410] evaluated the efficacy of JOURNAVX over 48 hours in 1,118 adult patients with moderate to severe acute pain following a full abdominoplasty procedure (JOURNAVX n = 447, placebo n = 223, and hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen (HB/APAP) n = 448). The majority of patients were female (98%), and the mean age was 42 years (range: 18 to 69). The study population consisted of 70% White participants, 27% Black or African American participants, 1% Asian participants, 0.8% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander participants, 0.5% American Indian or Alaska Native participants, and 0.9% Other or Multiracial participants, among which 34% identified as Hispanic or Latino. The mean pain score at baseline was 7.4 (range: 4 to 10). All baseline characteristics, including NPRS, VRS, and BMI were generally balanced across treatment arms.
In Trial 1, 89% of patients in the JOURNAVX group completed the treatment period (compared to 75% of patients in the placebo group and 85% of patients in the HB/APAP group), and 9% of patients in the JOURNAVX group discontinued due to lack of efficacy (compared to 22% of patients in the placebo group and 13% of patients in the HB/APAP group).
Efficacy was evaluated by the time-weighted sum of the pain intensity difference from 0 to 48 hours (SPID48) in the JOURNAVX group compared to the placebo group and then to the HB/APAP group. Treatment with JOURNAVX demonstrated statistically significant superior reduction in pain compared to treatment with placebo (see Table 5).
In an exploratory analysis, the time-weighted sum of the pain intensity difference from 0 to 24 hours (SPID24) reported using the least square mean was 48.0 for the JOURNAVX group and 24.2 for the placebo group. The mean pain intensities over time are depicted for the JOURNAVX, placebo, and HB/APAP groups in Figure 1.
Table 5: SPID48 Results in Adults with Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Full Abdominoplasty (Trial 1) Efficacy Measure JOURNAVX
N = 447Placebo
N = 223HB/APAP *
N = 448LS: Least Squares; CI: Confidence Interval - * HB/APAP = hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen
- † A larger value of LS mean indicates better efficacy measured by SPID48.
LS mean † 118.4 70.1 111.8 LS Mean Difference vs placebo (95% CI)
P value48.4 (33.6, 63.1)
< 0.0001- - LS Mean Difference vs HB/APAP (95% CI) 6.6 (-5.4, 18.7) - - Figure 1: Mean Pain Intensity Over Time in Adults with Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Full Abdominoplasty (Trial 1)
Note: Pre-rescue pain scores were carried forward for 6 hours following the use of rescue medication.
HB/APAP = hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen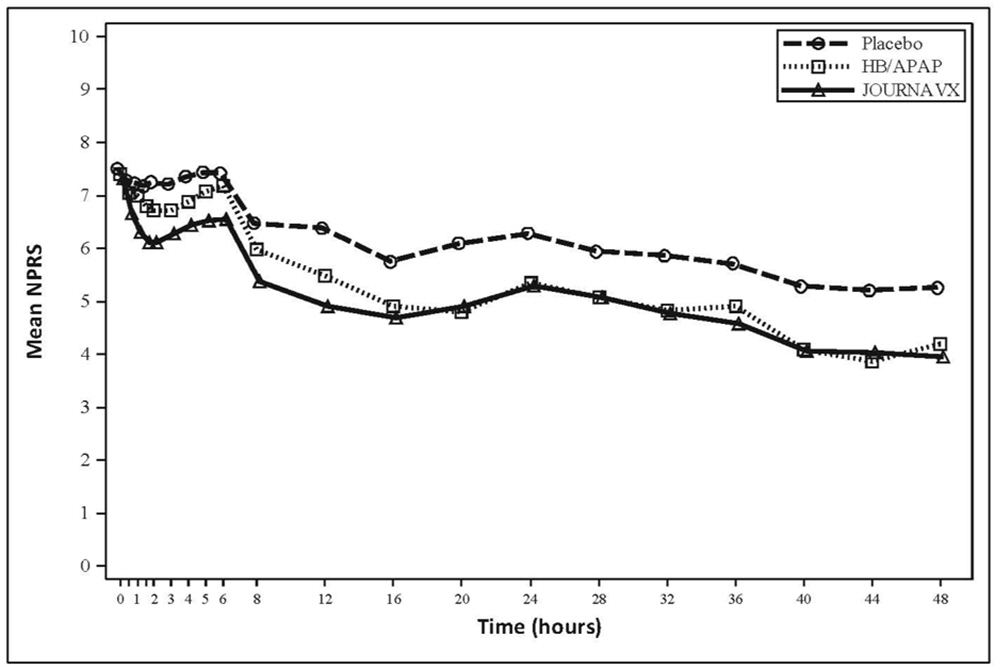
Time to Onset of Pain Relief
The median time to meaningful pain relief (defined as a ≥ 2-point reduction in NPRS) was 119 minutes for patients in the JOURNAVX group and 480 minutes for patients in the placebo group. The median time to onset of perceptible pain relief (defined as a ≥ 1-point reduction in NPRS) for patients in the JOURNAVX group was 34 minutes.
14.3 Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Bunionectomy
Trial 2 [NCT05553366] evaluated the efficacy of JOURNAVX over 48 hours in 1,073 adult patients with moderate to severe acute pain following bunionectomy (JOURNAVX n = 426, placebo n = 216, and HB/APAP n = 431). The majority of patients were female (85%), and the mean age was 48 years (range: 18 to 75). The study population consisted of 71% White participants, 24% Black or African American participants, 2% Asian participants, 0.2% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander participants, 1% American Indian or Alaska Native participants, and 1% Other or Multiracial participants, and 0.3% with race missing, among which 34% identified as Hispanic or Latino. The mean pain score at baseline was 6.8 (range: 4 to 10). All baseline characteristics, including NPRS, VRS, and BMI were generally balanced across treatment arms.
In Trial 2, 87% of patients in the JOURNAVX group completed the treatment period (compared to 82% of patients in the placebo group and 90% of patients in the HB/APAP group), and 12% of patients in the JOURNAVX group discontinued due to lack of efficacy (compared to 16% of patients in the placebo group and 8% of patients in the HB/APAP group).
Efficacy was evaluated by the time-weighted sum of the pain intensity difference from 0 to 48 hours (SPID48) in the JOURNAVX group compared to the placebo group and then to the HB/APAP group. Treatment with JOURNAVX demonstrated statistically significant superior reduction in pain compared to treatment with placebo (see Table 6).
In an exploratory analysis, the time-weighted sum of the pain intensity difference from 0 to 24 hours (SPID24) reported using the least square mean was 30.6 in the JOURNAVX group and 19.8 in the placebo group. The mean pain intensities over time are depicted for the JOURNAVX, placebo, and HB/APAP groups in Figure 2.
Table 6: SPID48 Results in Adults with Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Bunionectomy (Trial 2) Efficacy Measure JOURNAVX
N = 426Placebo
N = 216HB/APAP *
N = 431LS: Least Squares; CI: Confidence Interval - * HB/APAP = hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen
- † A larger value of LS mean indicates better efficacy measured by SPID48.
LS mean † 99.9 70.6 120.1 LS Mean Difference vs placebo (95% CI)
P value29.3 (14.0, 44.6)
0.0002- - LS Mean Difference vs HB/APAP (95% CI) -20.2
(-32.7, -7.7)- - Figure 2: Mean Pain Intensity Over Time in Adults with Moderate to Severe Acute Pain Following Bunionectomy (Trial 2)
Note: Pre-rescue pain scores were carried forward for 6 hours following the use of rescue medication.
HB/APAP = hydrocodone bitartrate/acetaminophen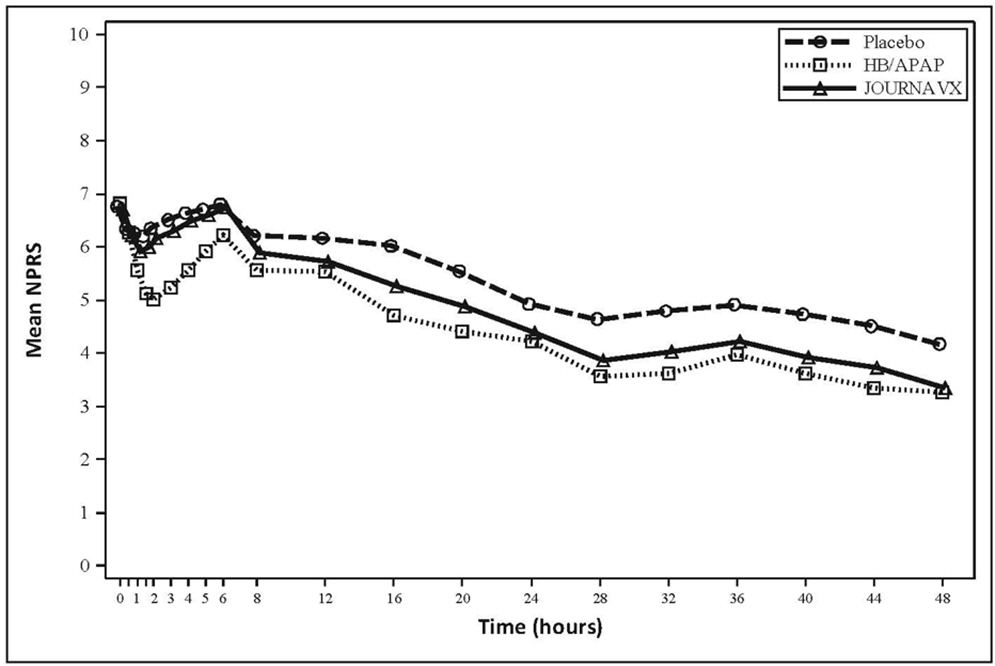
Time to Onset of Pain Relief
The median time to meaningful pain relief (defined as ≥ 2-point reduction in NPRS) was 240 minutes for patients in the JOURNAVX group and 480 minutes in the placebo group. The median time to onset of perceptible pain relief (defined as a ≥ 1-point reduction in NPRS) for patients in the JOURNAVX group was 60 minutes.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
JOURNAVX (suzetrigine) tablets are supplied as blue, film-coated, oblong tablets containing 50 mg of suzetrigine. Each tablet is debossed with the characters "VX50" on one side and plain on the other, and is packaged as follows:
- 30-count bottle NDC: 51167-548-30
- 100-count bottle NDC: 51167-548-31
- 100-count Hospital Unit Dose Carton (10 blister cards, each containing 10 tablets) NDC: 51167-548-34
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Drug Interactions
Ask patients to tell you all the medications they are taking, including any herbal supplements or vitamins [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
When used concomitantly with hormonal contraceptives containing a progestin other than levonorgestrel or norethindrone, advise patients to use an additional nonhormonal contraceptive (such as condoms) or use alternative contraceptives during JOURNAVX treatment and for 28 days after discontinuation of JOURNAVX [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Females of Reproductive Potential
Advise females of reproductive potential that JOURNAVX may reversibly impact the likelihood to become pregnant while on treatment. Patients using contraceptives should continue to use contraceptives [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Inquire and/or assess whether patients have hepatic impairment.
Administration Instructions
Advise patients to take the starting dose of JOURNAVX on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food to avoid delay in onset of action. Clear liquids may be consumed (such as water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, or black coffee) during this time. Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit during treatment with JOURNAVX [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
Subsequent doses of JOURNAVX can be taken with or without food.
Patients should be instructed to swallow JOURNAVX tablets whole (do not chew or crush).
Inform patients about what to do in the event they miss a dose of JOURNAVX [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
PATIENT INFORMATION
JOURNAVX (jor na vix)
(suzetrigine)
tablets, for oral useThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 01/2026 What is JOURNAVX?
JOURNAVX is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with moderate to severe short-term (acute) pain, including postoperative pain.
It is not known if JOURNAVX is safe and effective in children.Do not take JOURNAVX if you take certain medicines that are strong inhibitors of an enzyme called CYP3A.
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.Before taking JOURNAVX, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have liver problems. People with liver problems may have an increased risk of getting side effects from taking JOURNAVX.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if JOURNAVX will harm your unborn baby. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take JOURNAVX while you are pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. It is not known if JOURNAVX passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take JOURNAVX while you are breastfeeding.
Taking JOURNAVX with certain other medicines may affect the way JOURNAVX and the other medicines work and may increase your risk of side effects. See "Do not take JOURNAVX". Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:- hormonal birth control (contraceptives) containing progestins other than levonorgestrel or norethindrone. If you take one of these contraceptives (progestins other than levonorgestrel or norethindrone), they may not work as well during treatment with JOURNAVX. You should also use nonhormonal contraceptives such as condoms or use other forms of hormonal birth control during treatment with JOURNAVX and for 28 days after you stop taking JOURNAVX.
- medicines that are substrates of the CYP3A enzyme since they may become less effective during treatment with JOURNAVX. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust the dose of your medicine when starting or stopping JOURNAVX.
How should I take JOURNAVX? - Take JOURNAVX by mouth exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Swallow JOURNAVX tablets whole. Do not chew or crush the tablets.
- For your first dose of JOURNAVX:
- Take 2 JOURNAVX tablets on an empty stomach.
- Take your first dose of JOURNAVX at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after food. During this time, you may drink clear liquids, such as water, apple juice, vegetable broth, tea, or black coffee.
-
After your first dose of JOURNAVX:
- Take 1 JOURNAVX tablet 12 hours later, with or without food.
- Continue to take 1 JOURNAVX tablet every 12 hours as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Take JOURNAVX for the shortest time needed.
- If you have liver problems or take certain other medicines, your dosing schedule may be different.
- If you miss a dose of JOURNAVX and do not have liver problems or take certain other medicines:
- Take the missed dose as soon as possible, then take your next scheduled dose at your recommended time.
- If you miss 2 or more doses of JOURNAVX, take 2 JOURNAVX tablets, then take your next scheduled dose at your recommended time.
- If you miss a dose of JOURNAVX and you have liver problems or are taking moderate inhibitors of an enzyme called CYP3A:
- Take the missed dose as soon as possible.
- If you took the missed dose and your next scheduled dose is within 6 hours, skip that dose and take your next scheduled dose at your recommended time.
- If you are not sure about your dosing, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- If you take too much JOURNAVX, call your healthcare provider or Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking JOURNAVX? - Do not take food or drink containing grapefruit during treatment with JOURNAVX.
What are possible side effects of JOURNAVX?
The most common side effects of JOURNAVX include:- itching
- muscle spasms
- increased blood level of creatine phosphokinase
- rash
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of JOURNAVX.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store JOURNAVX?
Store JOURNAVX at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep JOURNAVX and all medicines out of the reach of children.General information about the safe and effective use of JOURNAVX.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use JOURNAVX for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give JOURNAVX to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about JOURNAVX that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in JOURNAVX?
Active ingredient: suzetrigine
Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablet film coat contains FD&C Blue #2 aluminum lake, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Manufactured for: Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated; 50 Northern Avenue, Boston, MA 02210
JOURNAVX, VERTEX and associated logos are registered trademarks of Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated.
©2026 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
For more information, go to www.JOURNAVX.com or call 1-877-634-8789. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Bottle Label
Rx Only
NDC: 51167-548-30
JOURNAVX™
(suzetrigine) tablets50 mg
Contains: 30 tablets
For Oral UseRecommended Dosage:
See Prescribing Information.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Bottle Label - NDC: 51167-548-31
Rx Only
NDC: 51167-548-31
JOURNAVX™
(suzetrigine) tablets50 mg
Contains: 100 tablets
For Oral UseRecommended Dosage:
See Prescribing Information.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Blister Pack Carton
For institutional use only
NDC: 51167-548-34
Rx OnlyJOURNAVX™
(suzetrigine) tablets50 mg
100 tablets
UNIT DOSE

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 50 mg Tablet Blister Pack Carton - Professional Sample
PROFESSIONAL SAMPLE - NOT FOR SALE
NDC: 51167-548-25
Rx OnlyJOURNAVX™
(suzetrigine) tablets50 mg per tablet
For Oral Use
Contains:
5 blister wallets
with 5 tablets each
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
JOURNAVX
suzetrigine tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51167-548 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Suzetrigine (UNII: LOG73M21H5) (Suzetrigine - UNII:LOG73M21H5) Suzetrigine 50 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYPROMELLOSE ACETATE SUCCINATE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: A7ZHS2RJ34) Microcrystalline cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) Titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score no score Shape OVAL (Oblong) Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code VX50 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51167-548-34 10 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2025 1 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 51167-548-25 5 in 1 CARTON 01/30/2025 2 NDC: 51167-548-05 5 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 51167-548-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/30/2025 4 NDC: 51167-548-31 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/30/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219209 01/30/2025 Labeler - Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated (602478257)
Trademark Results [JOURNAVX]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 JOURNAVX 98107706 not registered Live/Pending |
Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated 2023-07-28 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.