LIDOCAINE- lidocaine hydrochloride injection, solution
Lidocaine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Lidocaine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
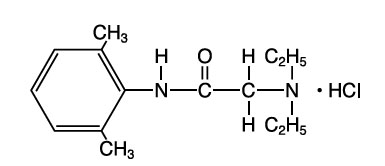
Lidocaine hydrochloride, chemical name: acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride has the following structural formula:
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP intravenous for cardiac arrhythmias, is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution prepared from lidocaine with the aid of hydrochloric acid in Water for Injection.
Each mL contains: Lidocaine HCl 20 mg; Sodium Chloride 6 mg; Water for Injection q.s. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may have been added for pH adjustment (pH 5.0 to 7.0). The container is for single use; solution contains no preservative.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Lidocaine hydrochloride exerts its antiarrhythmic effect by raising the electrical stimulation threshold of the ventricle during diastole. In usual therapeutic doses, lidocaine hydrochloride produces no change in myocardial contractility, systemic arterial pressure or in absolute refractory period.
Onset of action is rapid after an intravenous bolus with a duration of action of approximately 15 to 20 minutes.
Approximately 90% of an administered dose of lidocaine hydrochloride is metabolized in the liver. The remainder (10%) of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine. Pharmacokinetic data indicate reduced elimination of lidocaine after prolonged (24 hours) infusion with resultant prolongation of the half-life to approximately three times that seen following a single administration.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP administered intravenously is specifically indicated in the acute management of 1) ventricular arrhythmias occurring during cardiac manipulation such as cardiac surgery, and 2) life-threatening arrhythmias, particularly those which are ventricular in origin, such as those which occur during acute myocardial infarction.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is contraindicated in patients with a known history of hypersensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type. Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP should not be used in patients with STOKES-ADAMS syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or with severe degrees of sinoatrial, atrioventricular or intraventricular block.
-
WARNINGS
Constant monitoring of the electrocardiogram and blood pressure is essential in the proper administration of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP intravenously. If hypotension or excessive depression of cardiac conductivity (such as prolongation of the PR interval and QRS complex and the appearance of aggravation of arrhythmias) is seen, administration of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP should be discontinued.
Emergency resuscitative equipment and drugs must be immediately available to manage possible adverse reactions involving the cardiovascular, respiratory, or central nervous system.
Occasional acceleration of ventricular rate may occur when Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is administered to patients with atrial fibrillation.
Toxicity may be manifest as central nervous system depression (sedation) or irritability (twitching), which may progress to frank convulsions accompanied by respiratory depression and/or arrest. Early recognition of premonitory signs, assurance of adequate oxygenation and (where necessary) establishment of artificial airway with ventilatory support are essential to management of the problem. Should convulsions persist despite ventilatory support, small doses of anticonvulsant drugs may be used intravenously. Examples of such drugs include benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam, lorazepam), or an ultrashort acting barbiturate (e.g., thiopental or thiamylal). If the patient is under anesthesia, a short-acting muscle relaxant (succinylcholine) may be used. Longer acting drugs should be used only when recurrent convulsions are evidenced.
-
PRECAUTIONS
The safe use of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP requires careful ECG observation in an environment equipped and by persons trained for resuscitation.
General
Caution should be employed in the repeated use of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP in patients with severe liver or renal disease because accumulation may occur and lead to toxic phenomena since Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is metabolized mainly in the liver and excreted by the kidneys. This drug should also be used with caution in patients with hypovolemia and shock and all forms of heart block (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS).
In patients with sinus bradycardia or incomplete heart block, the administration of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP intravenously or the elimination of ventricular ectopic beats without prior acceleration in heart rate may promote more frequent and serious ventricular arrhythmias or complete heart block. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Many potent anesthetic drugs, neuromuscular blocking agents and possibly amide local anesthetics may serve as triggering agents for the fulminant hypermetabolic process termed malignant hyperthermia. Key to successful outcome of fulminant hypermetabolism is early recognition of premonitory signs, i.e., unexplained or unexpected tachycardia and increased metabolic rate as evidenced by respiratory and/or metabolic acidosis. Treatment includes administration of oxygen and discontinuation of lidocaine hydrochloride administration and where necessary administration of dantrolene sodium. For additional information on management, see prescribing information for dantrolene sodium.
Drug Interaction
The effect of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP for the management of cardiac arrhythmias is potentiated with the simultaneous or prior administration of propranolol.
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP should be used with caution in patients with digitalis toxicity accompanied by atrioventricular block. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Drug interaction was studied with several beta-blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, nadolol, and pindolol). Pretreatment with propranolol, metoprolol and nadolol increased the serum concentration of lidocaine. Pretreatment with pindolol did not affect the serum concentration of lidocaine.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential or the effect on fertility have not been conducted.
Pregnancy Category B
Reproductive studies have been performed in the rat at doses up to 5 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP. There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
The effects of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP solution on the mother and the fetus, when used in the management of cardiac arrhythmias during labor and delivery, are not known. Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP readily crosses the placental barrier.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children have not been established by controlled clinical studies. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most adverse reactions accompanying administration of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP result from systemic toxicity affecting primarily the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system.
Systemic reactions of the following types have been reported:
1. Central Nervous System
Light-headedness; drowsiness; dizziness; apprehension; euphoria; tinnitus; blurred vision or double vision; vomiting; sensations of heat; cold or numbness; twitching; tremors; convulsions; unconsciousness; respiratory depression and arrest.
2. Cardiovascular System
Hypotension; cardiovascular collapse; and bradycardia which may lead to cardiac arrest. Continuous monitoring of blood pressure and the electrocardiogram are essential to prevent these events.
3. Allergic reactions may occur but are infrequent. There have been no reports of cross-sensitivity between lidocaine hydrochloride and procainamide or between lidocaine and quinidine.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Management of Adverse Reactions—
- In the case of severe reaction, discontinue the use of Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP.
- Institute emergency resuscitative procedures and administer the emergency drugs necessary to manage the severe reaction. For severe convulsions, small increments of diazepam or an ultra short-acting barbiturate (thiopental or thiamylal); or if those are not available a short-acting barbiturate (pentobarbital or secobarbital); or if the patient is under anesthesia, a short-acting muscle relaxant (succinylcholine) may be given intravenously. Muscle relaxants and intravenous medications should only be used by those familiar with their use. Patency of the airway and adequacy of ventilation must be assured. (See WARNINGS.)
- Should circulatory depression occur, vasopressors, such as ephedrine, or meta raminol may be used. Should cardiac arrest occur, immediate initiation of standard CPR procedures should commence.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult
For Direct Injection–The usual dose is 50 to 100 mg administered intravenously under ECG monitoring. This dose may be administered at the rate of approximately 25 to 50 mg/min. Sufficient time should be allowed to enable a slow circulation to carry the drug to the site of action. If the initial injection of 50 to 100 mg does not produce a desired response, a second dose may be repeated after 5 minutes.
NO MORE THAN 200 TO 300 MG OF LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP SHOULD BE ADMINISTERED DURING A ONE HOUR PERIOD.
This product is for DIRECT INJECTION ONLY. For continuous infusion protocol, see prescribing information for lidocaine hydrochloride, USP for infusion solution.
Pediatric
Although controlled clinical studies to establish pediatric dosing schedules have not been conducted, the American Heart Association’s Standards and Guidelines recommends a bolus dose of 1 mg/kg followed by an infusion rate of 30 mcg/kg/min.
This product is for DIRECT INJECTION ONLY. For continuous infusion protocol, see prescribing information for lidocaine hydrochloride, USP for infusion solution.
Sterilization, Storage and Technical Procedures
It is recommended that chemical disinfection be accomplished by wiping the vial thoroughly with cotton or gauze that has been moistened with either 91% isopropyl alcohol or 70% ethyl alcohol, just prior to use. Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LIDOCAINE
lidocaine hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63323-208 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: V13007Z41A) (LIDOCAINE - UNII:98PI200987) LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE ANHYDROUS 20 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 6 mg in 1 mL HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63323-208-05 25 in 1 TRAY 09/05/2000 1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA017584 09/05/2000 Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC 840771732 manufacture(63323-208)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

