HEPARIN SODIUM injection, solution
HEPARIN SODIUM by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
HEPARIN SODIUM by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Heparin is a heterogeneous group of straight-chain anionic mucopolysaccharides, called glycosaminoglycans, having anticoagulant properties. Although others may be present, the main sugars occurring in heparin are: (1) α-L-iduronic acid 2-sulfate, (2) 2-deoxy-2-sulfamino-α-D-glucose 6-sulfate, (3) β-D-glucuronic acid, (4) 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-α-D-glucose and (5) α-L-iduronic acid. These sugars are present in decreasing amounts, usually in the order (2)> (1)> (4)> (3)> (5), and are joined by glycosidic linkages, forming polymers of varying sizes. Heparin is strongly acidic because of its content of covalently linked sulfate and carboxylic acid groups. In heparin sodium, the acidic protons of the sulfate units are partially replaced by sodium ions.
Structural formula of Heparin Sodium (representative sub-units):
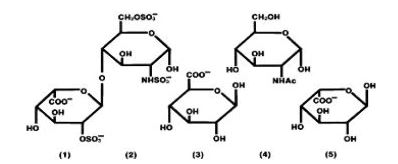
Heparin Sodium Injection, USP is a sterile solution of heparin sodium derived from porcine intestinal mucosa, standardized for anticoagulant activity. It is to be administered by intravenous or deep subcutaneous route. The potency is determined by a biological assay using a USP reference standard based on units of heparin activity per milligram.
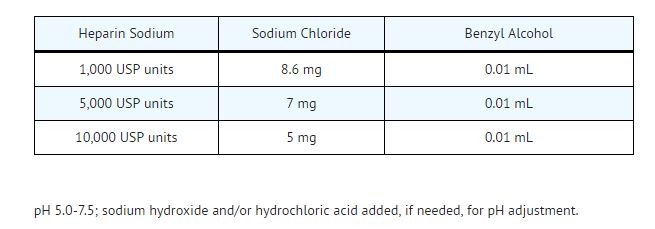
Heparin Sodium Injection, USP is available in the following concentrations per mL.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Heparin inhibits reaction that lead to the clotting of blood and the formation of fibrin clots both in vitro and in vivo. Heparin acts at multiple sites in the normal coagulation system. Small amounts of heparin in combination with antithrombin III (heparin cofactor) can inhibit thrombosis by inactivating activated Factor X and inhibiting the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. Once active thrombosis has developed, larger amounts of heparin can inhibit further coagulation by inactivating thrombin and preventing the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Heparin also prevents the formation of a stable fibrin clot by inhibiting the activation of the fibrin stabilizing factor.
Bleeding time is usually unaffected by heparin. Clotting time is prolonged by full therapeutic doses of heparin; in most cases, it is not measurably affected by low doses of heparin.
Patients over 60 years of age, following similar doses of heparin, may have higher plasma levels of heparin and longer activated partial thromboplastin times (APTTs) compared with patients under 60 years of age.
Peak plasma levels of heparin are achieved 2 to 4 hours following subcutaneous administration, although there are considerable individual variations. Loglinear plots of heparin plasma concentrations with time, for a wide range of dose levels, are linear, which suggests the absence of zero order processes. Liver and reticuloendothelial system are the sites of biotransformation. The biphasic elimination curve, a rapidly declining alpha phase (t½ =10 minutes), and after the age of 40 a slower beta phase, indicates uptake in organs. The absence of a relationship between anticoagulant half-life and concentration half-life may reflect factors such as protein binding of heparin.
Heparin does not have fibinolytic activity; therefore, it will not lyse existing clots.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Heparin Sodium Injection is indicated for:
Anticoagulant therapy in prophylaxis and treatment of venous thrombosis and its extension;
Low-dose regimen for prevention of postoperative deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients undergoing major abdominothoracic surgery or who, for other reasons, are at risk of developing thromboembolic disease (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION);
Prophylaxis and treatment of pulmonary embolism;
Atrial fibrillation with embolization;
Treatment of acute and chronic consumptive coagulopathies (disseminated intravascular coagulation);\
Prevention of clotting in arterial and cardiac surgery;
Prophylaxis and treatment of peripheral arterial embolism.
Heparin may also be employed as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions, extracorporeal circulation, and dialysis procedures.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Heparin sodium should NOT be used in patients with the following conditions:
Severe thrombocytopenia;
When suitable blood coagulation testes, e.g., the whole blood clotting times, partial thromboplastin time, etc., cannot be performed at appropriate intervals (this contraindication refers to full-dose heparin; there is usually no need to monitor coagulation parameters in patients receiving low-dose heparin);
An uncontrolled active bleeding state (see WARNINGS), except when this is due to disseminated intravascular coagulation.
-
WARNINGS
Heparin is not intened for intramuscular use.
Fatal Medication ErrorsDo not use Heparin Sodium Injection as a “catheter lock flush” product. Heparin Sodium Injection is supplied in vials containing various strengths of heparin, including vials that contain a highly concentrated solution of 10,000 units in 1 mL. Fatal hemorrhages have occurred in pediatric patients due to medication errors in which 1 mL Heparin Sodium Injection vials were confused with 1 mL “catheter lock flush” vials. Carefully examine all Heparin Sodium Injection vials to confirm the correct vial choice prior to administration of the drug.
Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity
Use preservative-free Heparin Sodium Injection in neonates and infants. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse events and death in pediatric patients. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not knows. Premature and low-birth weight infants may be more likely to develop toxicity (see ADVERSE REACTIONS, Hypersensitivity).Hypersensitivity
Patients with documented hypersensitivity to heparin should be given the drug on in clearly life-threatening situations (See ADVERSE REACTIONS, Hypersensitivity).Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage can occur at virtually any site in patients receiving heparin. An unexplained fall in hematocrit, fall in blood pressure or any other unexplained symptom should lead to serious consideration of a hemorrhagic event.Heparin sodium should be used with extreme caution in disease states in which there is increased danger of hemorrhage. Some of the condition in which increased danger of hemorrhage exists are:
Cardiovascular
Subacute bacterial endocarditis severs hypertension.Surgical
During and immediately following (a) spinal tap or spinal anesthesia or (b) major surgery, especially involving the brain, spinal cord, or eye.Hematologic
Conditions associated with increased bleeding tendencies, such as hemophilia, thrombocytopenia and some vascular purpuras.Gastrointestinal
Ulcerative lesions and continuous tube drainage of the stomach or small intestine.Other
Menstruation, liver disease with impaired hemostasis.Coagulation TestingWhen heparin sodium is administered in therapeutic amounts, its dosage should be regulated by frequent blood coagulation tests. If the coagulation test is unduly prolonged or if hemorrhage occurs, heparin sodium should be promptly discontinued (see OVERDOSAGE).
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia has been reported to occur in patients receiving heparin with a reported incidence of up to 30%. Platelet counts should be obtained at baseline and periodically during heparin administration. Mild thrombocytopenia (count greater than 100,000/mm3) may remain stable or reverse even if heparin is continued. However, thrombocytopenia of any degree should be monitored closely. If the count falls below 100,000/mm3 or if recurrent thrombosis develops (see Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) With or Without Thrombosis), the heparin product should be discontinued and, if necessary, an alternative anticoagulant administered.Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) (With or Without Thrombosis)
HIT is a serious immune-mediated reaction resulting from irreversible aggregation of platelets. HIT may progress to the development of venous and arterial thrombosis, a condition referred to as HIT with thrombosis. Thrombotic events may also be the initial presentation for HIT. Theses serious thromboembolic events may also be the initial presentation for HIT. Theses serious thromboembolic events include deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, cerebral vein thrombosis, limp ischemia, stroke, myocardial infarction, mesenteric thrombosis, renal arterial thrombosis, renal arterial thrombosis, skin necrosis, gangrene of the extremities that may lead to amputation, and fatal outcomes.Once HIT (with or without thrombosis) is diagnosed or strongly suspected, all heparin sodium sources (including heparin flushes) should be discontinued and an alternate anticoagulant used. Future use of heparin sodium, especially within 3 to 6 months following the diagnosis of HIT (with or without thrombosis), and while patients test positive for HIT antibodies, should be avoided.
Immune-mediated HIT is diagnosed based on clinical findings supplemented by laboratory tests confirming the presence of antibodies to heparin sodium, or platelet activation induced by heparin sodium. A drop in platelet count greater than 50% from baseline is considered indicative of HIT. Platelet counts begin to fall 5 to 10 days after exposure to heparin sodium in heparin sodium-naïve individuals, and reach a threshold by days 7 to 14. In contrast, “rapid onset” HIT can occur very quickly (within 24 hours following heparin sodium initiation), especially in patients with a recent exposure to heparin sodium (i.e., previous 3 months). Thrombosis development shortly after documenting thrombocytopenia is a characteristic found in almost half of all patients with HIT.
Thrombocytopenia of any degree should be monitored closely. If the platelet count falls below 100,000/mm3 or if recurrent thrombosis develops, the heparin product should be promptly discontinued and alternative anticoagulants considered if patients require continued anticoagulation.
Delayed Onset of HIT (With or Without Thrombosis)Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia (with or without thrombosis) can occur up to several weeks after the discontinuation of heparin therapy. Patients presenting with thrombocytopenia or thrombosis after discontinuation of heparin sodium should be evaluated for HIT (with or without thrombosis).
Use in NeonatesThis product contains the preservative benzyl alcohol and is not recommended foruse in neonates. There have been reports of fatal ‘gasping syndrome’ in neonates (children less than one month of age) following the administration of intravenous solutions containing the preservative benzyl alcohol. Symptoms include a striking onset of gasping respiration, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse.
Carefully examine all Heparin Sodium Injection vials to confirm choice of the correct strength prior to administration of the drug. Pediatric patients, including neonates, have died as a result of medication errors in which Heparin Sodium Injection vials have been confused with ‘catheter lock flush” vials (see WARNINGS, Fatal Medication Errors).
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Thrombocytopenia, Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) (With or Without Thrombosis) and Delayed Onset of HIT (With or Without Thrombosis.)
See WARNINGSHeparin Resistance
Increased resistance to heparin is frequently encountered in fever, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, infections with thrombosing tendencies, myocardial infarction, cancer and in postsurgical patients.Increased Risk to Older Patients, Especially Women
A higher incidence of bleeding has been reported iin patients, particularly women, over 60 years of age.Laboratory TestsPeriodic platelet counts, hematocrits, and tests for occult blood in stool are recommended during the entire course of heparin therapy, regardless of the route of administration (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Drug InteractionsOral Anticoagulants
Heparin sodium may prolong the one-stage prothrombin time. Therefore, when heparin sodium is given with dicumarol or warfarin sodium, a period of at least 5 hours after the last intravenous dose or 24 hours after the last subcutaneous dose should elapse before blood is drawn, if a valid prothrombin time is to be obtained.Platelet Inhibitors
Drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid, dextran, phenlbutazone, ibuprofen, indomethacin, dipyidamole, hydroxychloroquine and others that interfere with platelet-aggregation reaction (the main hemostatic defense of heparinized patients) may induce bleeding and should be used with caution in patients receiving heparin sodium.Other Interactions
Digitalis, tetracyclines, nicotine or antihistamines may partially counteract the anticoagulant action of heparin sodium. Intravenous nitroglycerin administered to heparinized patients may result in a decrease of the partial thromboplastin time with subsequent rebound effect upon discontinuation of nitroglycerin. Careful monitoring of partial thromboplastin time and adjustment of heparin dosage are recommended during coadministration of heparin and intravenous nitroglycerin.Drug/Laboratory Tests InteractionsHyperaminotransferasemia
Significant elevations of aminotransferase (SGOT[S-AST] and SGPT[S-ALT]) levels have occurred in high percentage of patients (and healthy subjects) who have received heparin. Since aminotravsferase determinations are important in the differential diagnosis of myocardial infarction, liver disease and pulmonary emboli, increases that might be caused by drugs (like heparin) should be interpreted with caution.Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityNo long-term studies in animals have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential of heparin. Also, no reproductions studies in animals have been performed concerning mutagenesis or impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies on heparin use in pregnant women. In published reports, heparin exposure during pregnancy did not show evidence of an increased risk of adverse maternal or fetal outcomes in humans. Heparin sodium does not cross the placenta based on human and animal studies. Adminsitration of heparin to pregnant animals at doses higher than the miximum human daily does based on body weight resulted in increased resorptions. Use heparin sodium during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.If available, preservative-free Heparin Sodium Injection is recommended when heparin therapy is needed during pregnancy. There are no known adverse outcomes associated with fetal exposure to the preservative benzyl alcohol through maternal drug administration; however, the preservative e benzyl alcohol can cause serious adverse events and death when administered intravenously to neonates and infants (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).
In a published study conducted in rats and rabbits, p[regnant animals received heparin intravenously during organogenesis at a dose of 10,000 units/kg/day, approximately 10 times the maximum human daily dose based on body weight. The number of early resorptions increased in both species. There was no evidence of teratogenic effects.
Nursing Mothers
If available, preservative-free Heparin Sodium Injection is recommended when heparin therapy is needed during lactation. Due to its large molecular weight, heparin is not likely to be excreted in human milk, and any heparin in milk would not be orally absorbed by a nursing infant. Exercise caution when administering Heparin Sodium Injection to a nursing mother. (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).Pediatric Use
There are no adequate and well controlled studies on heparin use in pediatric patients. Pediatric dosing recommendations are based on clinical experience (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Pediatric Use).Carefully examine all Heparin Sodium Injection vials to confirm choice of the correct strength prior to administration of the drug. Pediatric patients, including neonates, have dies as a result of medication errors in which Heparin Sodium Injection vials have been confused with “catheter lock flush” vials (see WARNINGS, Fatal Medication Errors).
Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity
Use preservative-free Heparin Sodium Injection in neonates and infants. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse events and death in pediatric patients. The “gasping syndrome” (characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, gasping respirations, and high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites found in the blood and urine.) has been associated with benzyl alcohol dosages <99 mg/kg/day in neonates and low-birth weight infants. Additional symptoms may include gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse.Although normal therapeutic doses of this product deliver amounts of benzyl alcohol that are substantially lower than those reported in association with the “gasping syndrome”, the minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity may occur is not known. Premature and low-birth weight infants may be more likely to develop toxicity. Practitioners administering this and other medications contain benzyl alcohol should consider the combine daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources.
Geriatric UseA higher incidence of bleeding has been reported in patients over 60 years of age, especially women (see PRECAUTIONS, General). Clinical studies indicate that lower doses of heparin may be indicated in these patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage is the chief complication that may result from heparin therapy (see WARNINGS). As overly prolonged clotting time or minor bleeding during therapy can usually be controlled by withdrawing the drug (see OVERDOSAGE). It should be appreciated that gastrointestinal or urinary tract bleeding during anticoagulant therapy may indicate the presence of an underlying occult lesion. Bleeding can occur at any site but certain specific hemorrhagic complications may be difficult to detect:- Adrenal hemorrhage, with resultant acute adrenal insufficiency, has occurred during anticoagulant therapy. Therefore, such treatment should be discontinued in patients who develop signs and symptoms of acute adrenal hemorrhage and insufficiency. Initiation of corrective therapy should not depend on laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis, since any delay in an acute situation may result in the patient's death.
- Ovarian (corpus luteum) hemorrhage developed in a number of women of reproductive age receiving short- or long-term anticoagulant therapy. This complication, if unrecognized, may be fatal.
- Retroperitoneal hemorrhage.
Thrombocytopenia, Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) (With or Without Thrombosis) and Delayed Onset of HIT (With or Without Thrombosis).
See WARNINGSLocal IrritationLocal irritation, erythema, mild pain, hematoma or ulceration may follow deep subcutaneous (intrafat) injection of heparin sodium. These complications are much more common after intramuscular use, and such use is not recommended.
HypersensitivityGeneralized hypersensitivity reactions have been reported, with chills, fever and urticaria as the most usual manifestations, and asthma, rhinitis, lacrimation, headache, nausea and vomiting, and anaphylactoid reactions, including shock, occurring more rarely. Itching and burning, especially on the plantar side of the feet, may occur. (See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Certain episodes of painful, ischemic and cyanosed limbs have in the past been attributed to allergic vasospastic reactions. Whether these are in fact identical to the thrombocytopenia-associated complications remains to be determined.
Miscellaneous
Osteoporosis following long-term administration of high doses of heparin, cutaneous necrosis after systemic administration, suppression of aldosterone synthesis, delayed transient alopecia, priapism, and rebound hyperlipemia on discontinuation of heparin sodium have also been reported.Significant elevations of aminotransferase (SGOT [S-AST] and SGPT [S-ALT]) levels have occurred in a high percentage of patients (and healthy subjects) who have received heparin.
-
OVERDOSAGE
SymptomsBleeding is the chief sign of heparin overdosage. Nosebleeds, blood in urine or tarry stools may be noted as the first sign of bleeding. Easy bruising or petechial formations may precede frank bleeding.
TreatmentNeutralization of heparin effect.
When clinical circumstances (bleeding) require reversal of heparinization, protamine sulfate (1% solution) by slow infusion will neutralize heparin sodium. No more than 50 mg should be administered, very slowly, in any 10-minute period. Each mj of protamine sulfate neutralizes approximately 100 USP of heparin units. The amount of protamine required decreases over time as heparin is metabolized. Although the metabolism of heparin is complex, it may, for the purpose of choosing a protamine dose, be assumed to have a half-life of about ½ hour after intravenous injection.
Administration of protamine sulfate can cause severe hypotensive and anaphylactoid reactions. Because fatal reactions often resembling anaphylaxis have been reported, the drug should be given only when resuscitation techniques and treatment of anaphylactoid shock are readily available.
For additional information consult the labeling of Protamine Sulfate Injection, USP products.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution ad container permits.
Slight discoloration does not alter potency.Confirm the choice of the correct Heparin Sodium Injection vial prior to administration of the drug to a patient (see WARNINGS, Fatal Medication Errors). The 1 mL vial must not be confused with a “catheter lock flush” vial or other 1 mL vial of appropriate strength. Confirm that you have selected the correct medication and strength prior to administration of the drug.
When heparin is added to an infusion solution for continuous intravenous administration, the container should be inverted at least six times to ensure adequate mixing and prevent pooling of the heparin in solution.
Heparin sodium is not effective by oral administration and should be given by intermittent intravenous injection, intravenous infusion, or deep subcutaneous (intrafat, i.e., above the iliac crest or abdominal fat layer) injection. The intramuscular route of administration should be avoided because of the frequent occurrence of hematoma at the injection site.
The dosage of heparin sodium should be adjusted according to the patient's coagulation test results. When heparin is given by continuous intravenous infusion, the coagulation time should be determined approximately every 4 hours in the early stages of treatment. When the drug is administered intermittently by intravenous injection, coagulation tests should be performed before each injection during the early stages of treatment and at appropriate intervals thereafter. Dosage is considered adequate when the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) is 1.5 to 2 times normal or when the whole blood clotting time is elevated approximately 2.5 to 3 times the control value. After deep subcutaneous (intrafat) injections, tests for adequacy of dosage are best performed on samples drawn 4 to 6 hours after the injection.
Periodic platelet counts, hematocrits and tests for occult blood in stool are recommended during the entire course of heparin therapy, regardless of the route of administration.
Converting to Oral Anticoagulant
When an oral anticoagulant of the coumarin or similar type is to be begun in patients already receiving heparin sodium, baseline and subsequent tests of prothrombin activity must be determined at a time when heparin activity is too low to affect the prothrombin time. This is about 5 hours after the last intravenous bolus and 24 hours after the last subcutaneous dose. If continuous IV heparin infusion is used, prothrombin time can usually be measured at any time.In converting from heparin to an oral anticoagulant, the dose of the oral anticoagulant should be the usual initial amount and thereafter prothrombin time should be determined at the usual intervals. To ensure continuous anticoagulation it is advisable to continue full heparin therapy for several days after the prothrombin time has reached the therapeutic range. Heparin therapy may then be discontinued without tapering.
Therapeutic Anticoagulant Effect With Full-Dose Heparin
Although dosage must be adjusted for the individual patient according to the results of suitable laboratory tests, the following dosage schedule may be used as guidelines: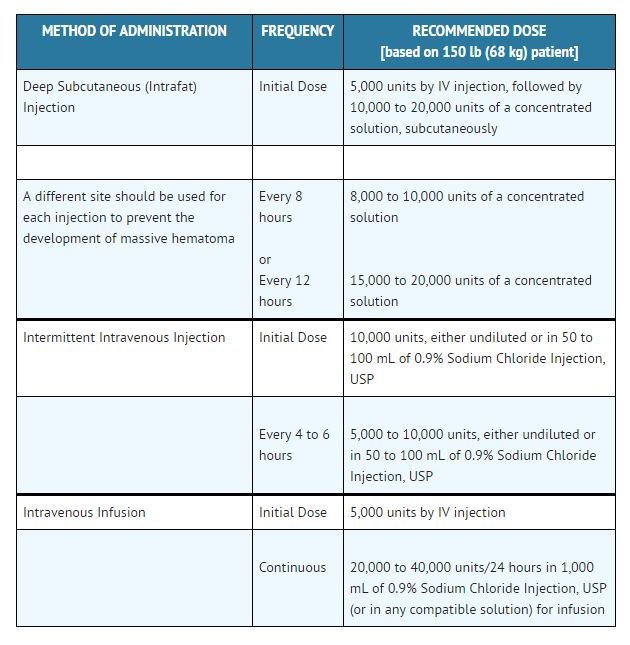
Pediatric Use
Use preservative-free Heparin Sodium Injection in neonates and infants (see WARNINGS, Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity and PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).There are no adequate and well controlled studies on heparin used in pediatric patients. Pediatric dosing reconditions are based on clinical experience. In general, the following dosage schedule may be used as a guideline in pediatric patients:
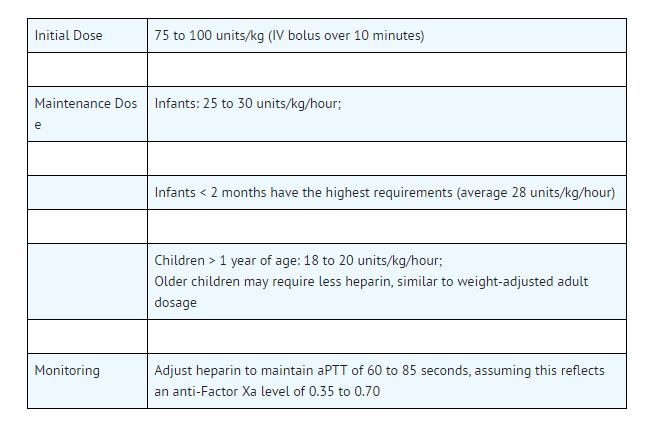
Geriatric Use
Patients over 60 years of age may require lower doses of heparin.Surgery of the Heart and Blood Vessels
Patients undergoing total body perfusion for open-heart surgery should receive an initial dose of not less than 150 unit of heparin sodium per kilogram of body weight. Frequently, a dose of 300 units per kilogram is used for procedures estimated to last less than 60 minutes, or 400 units per kilogram for those estimated to last longer than 60 minutes.Low-Dose Prophylaxis of Postoperative ThromboembolismA number of well-controlled clinical trials have demonstrated that low-dose heparin prophylaxis, given just prior to and after surgery, will reduce the incidence of postoperative deep vein thrombosis in the legs (as measured by the I-125 fibrinogen technique and venography) and of clinical pulmonary embolism. The most widely used dosage has been 5,000 units 2 hours before surgery and 5,000 units every 8 to 12 hours thereafter for 7 days or until the patient is fully ambulatory, whichever is longer. The heparin is given by deep subcutaneous injection in the arm or abdomen with a fine needle (25 to 26 gauge) to minimize tissue trauma. A concentrated solution of heparin sodium is recommended. Such prophylaxis should be reserved for patients over the age of 40 who are undergoing major surgery. Patients with bleeding disorders and those having neurosurgery, spinal anesthesia, eye surgery or potentially sanguineous operations should be excluded, as should patients receiving oral anticoagulants or platelet-active drugs (see WARNINGS). The value of such prophylaxis in hip surgery has not been established. The possibility of increased bleeding during surgery or postoperatively should be borne in mind. If such bleeding occurs, discontinuance of heparin and neutralization with protamine sulfate are advisable. If clinical evidence of thromboembolism develops despite low-dose prophylaxis, full therapeutic doses of anticoagulants should be given unless contraindicated. All patients should be screened prior to heparinization to rule out bleeding disorders, and monitoring should be performed with appropriate coagulation tests just prior to surgery. Coagulation test values should be normal or only slightly elevated. There is usually no need for daily monitoring of the effect of low-dose heparin in patients with normal coagulation parameters.
Extracorporeal Dialysis
Follow equipment manufacturers’ operating directions carefully.Blood Transfusion
Addition of 400 to 600 USP units per 100 mL of whole blood is usually employed to prevent coagulation. Usually, 7,500 USP units of heparin sodium are added to 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP (or 75,000 USP units per 1,000 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP) and mixed; from this sterile solution, 6 to 8 mL are added per 100 mL of whole blood.Laboratory Samples
Addition of 70 to 150 unites of heparin sodium per 10 to 20 mL sample of whole blood is usually employed to prevent coagulation of the sample. Leukocyte counts should be performed on heparinized blood within 2 hours after addition of the heparin. Heparinized blood should not be used for isoagglutinin, complement, or erythrocyte fragility tests or platelet counts. -
HOW SUPPLIED
Heparin Sodium Injection, USP, is available as follows:
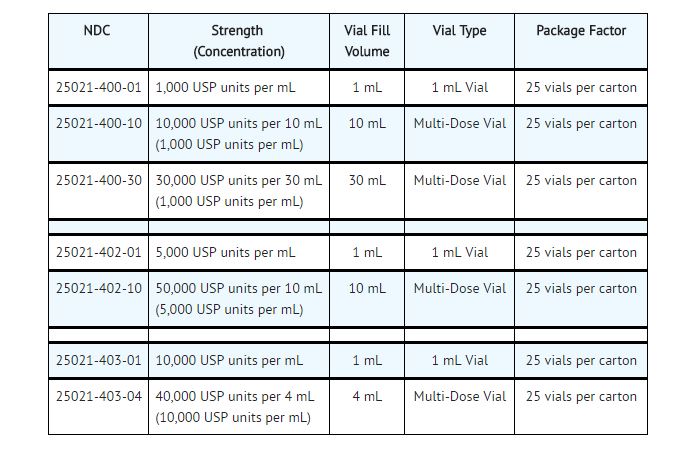
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage Conditions
Store at 20°to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sagent Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-625-1618 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
- REFERENCES
- SAMPLE PACKAGE LABEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HEPARIN SODIUM
heparin sodium injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 52584-400(NDC:25021-400) Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Heparin Sodium (UNII: ZZ45AB24CA) (Heparin - UNII:T2410KM04A) Heparin 1000 [USP'U] in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 52584-400-01 1 in 1 BAG 09/13/2011 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA090808 09/13/2011 Labeler - General Injectables & Vaccines, Inc (108250663)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

